Proline-Rich Protein Tyrosine Kinase 2 in Inflammation and Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biological Functions of Pyk2
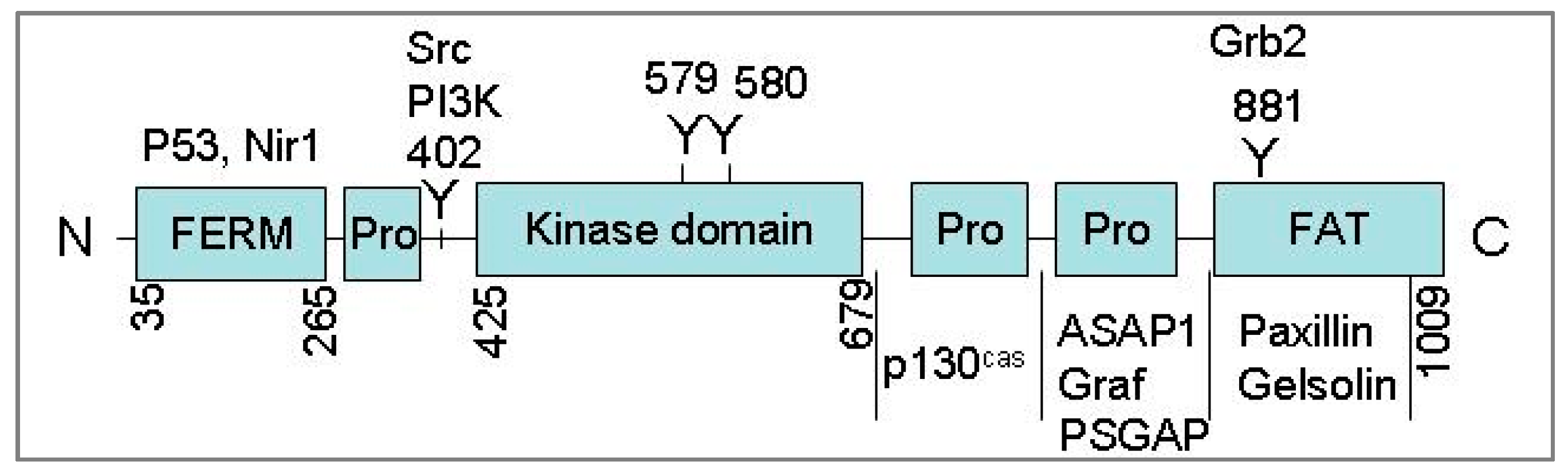
2.1. Cloning and Characterization of Pyk2
2.2. Cellular Functions of Pyk2
2.3. Pathological Functions of Pyk2
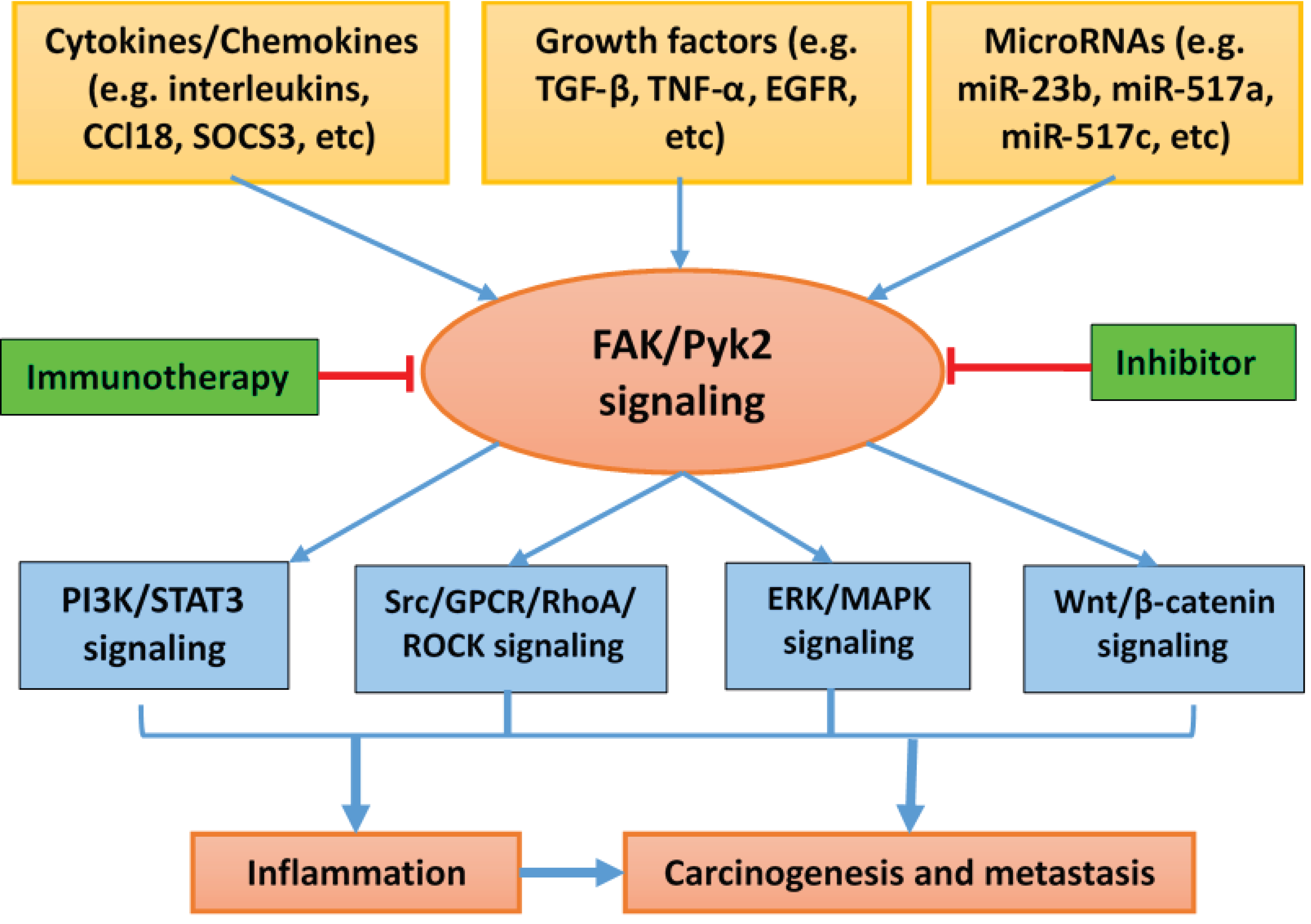
3. Signaling Mechanisms by Which Pyk2 Regulates Inflammation
3.1. Pyk2 in Integrin Mediated Migration
3.2. Pyk2 for Cytokine Secretion
3.3. Pyk2 for Cell Survival
4. Pyk2 and Cancers
4.1. Pyk2 and Lung Cancer
4.2. Pyk2 and Breast Cancer
4.3. Pyk2 and Gastrointestinal Cancer
4.4. Pyk2 and Liver Cancer
4.5. Pyk2 and Other Cancers
4.6. Pyk2 in Cancer Therapy
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FAK | focal adhesion kinase |
| Pyk2 | proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 |
| CSF-1 | colony-stimulating factor-1 |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| SOCS3 | suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 |
| CCL18 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
| MaCSCs | mammary cancer stem cells |
| GSK3β | glycogen synthase kinase 3β |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
References
- Hauck, C.R.; Klingbeil, C.K.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Focal adhesion kinase functions as a receptor-proximal signaling component required for directed cell migration. Immunol. Res. 2000, 21, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.T.; Martin, K.H.; Slack, J.K.; Taylor, J.M.; Weed, S.A. Focal adhesion kinase: A regulator of focal adhesion dynamics and cell movement. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5606–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, D.; Furuta, Y.; Kanazawa, S.; Takeda, N.; Sobue, K.; Nakatsuji, N.; Nomura, S.; Fujimoto, J.; Okada, M.; Yamamoto, T. Reduced cell motility and enhanced focal adhesion contact formation in cells from FAK-deficient mice. Nature 1995, 377, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuortes, M.; Jin, W.W.; Nathan, C. Beta 2 integrin-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin in human neutrophils treated with tumor necrosis factor. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Abraham, R.T.; Okada, S.; Kita, H. Ligation of the β2 integrin triggers activation and degranulation of human eosinophils. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1998, 18, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraham, H.; Park, S.Y.; Schinkmann, K.; Avraham, S. RAFTK/Pyk2-mediated cellular signalling. Cell Signal. 2000, 12, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okigaki, M.; Davis, C.; Falasca, M.; Harroch, S.; Felsenfeld, D.P.; Sheetz, M.P.; Schlessinger, J. Pyk2 regulates multiple signaling events crucial for macrophage morphology and migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10740–10745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinamard, R.; Okigaki, M.; Schlessinger, J.; Ravetch, J.V. Absence of marginal zone B cells in Pyk-2-deficient mice defines their role in the humoral response. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lev, S.; Moreno, H.; Martinez, R.; Canoll, P.; Peles, E.; Musacchio, J.M.; Plowman, G.D.; Rudy, B.; Schlessinger, J. Protein tyrosine kinase Pyk2 involved in Ca2+-induced regulation of ion channel and map kinase functions. Nature 1995, 376, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Nagura, K.; Ishino, M.; Tobioka, H.; Kotani, K.; Sasaki, T. Cloning and characterization of cell adhesion kinase beta, a novel protein-tyrosine kinase of the focal adhesion kinase subfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 21206–21219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraham, S.; London, R.; Fu, Y.; Ota, S.; Hiregowdara, D.; Li, J.; Jiang, S.; Pasztor, L.M.; White, R.A.; Groopman, J.E.; et al. Identification and characterization of a novel related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase (RAFTK) from megakaryocytes and brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 27742–27751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.C.; Macklem, M.; Parsons, J.T. Expression and characterization of splice variants of Pyk2, a focal adhesion kinase-related protein. J. Cell. Sci. 1998, 111 Pt 14, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dikic, I.; Dikic, I.; Schlessinger, J. Identification of a new Pyk2 isoform implicated in chemokine and antigen receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14301–14308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Richardson, A.; Parsons, T. A mechanism for regulation of the adhesion-associated proteintyrosine kinase pp125FAK. Nature 1996, 380, 538–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.C.; Hao, J. Control and prevention of myocardial fibrosis using Pyk2-related non-kinase. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 18284–18292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paone, C.; Rodrigues, N.; Ittner, E.; Santos, C.; Buntru, A.; Hauck, C.R. The tyrosine kinase Pyk2 contributes to complement-mediated phagocytosis in murine macrophages. J. Innate Immun. 2016, 8, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Li, Z.N.; Fang, Q.G.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.L.; Sun, C.F.; Liu, F.Y. The role of Pyk2 in the CCR7-mediated regulation of metastasis and viability in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cells in vivo and in vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 3280–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panera, N.; Crudele, A.; Romito, I.; Gnani, D.; Alisi, A. Focal adhesion kinase: Insight into molecular roles and functions in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Sengbusch, A.; Gassmann, P.; Fisch, K.M.; Enns, A.; Nicolson, G.L.; Haier, J. Focal adhesion kinase regulates metastatic adhesion of carcinoma cells within liver sinusoids. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Colarusso, P.; Zhang, H.; Stevens, K.M.; Patel, K.D. FRNK negatively regulates IL-4-mediated inflammation. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Xin, X.; Xin, H.; Shen, X.; Zhu, Y.Z. Hydrogen sulfide recruits macrophage migration by integrin beta1-Src-FAK/Pyk2-rac pathway in myocardial infarction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, K.A.; Pixley, F.J.; Thomas, K.S.; Vicente-Manzanares, M.; Ray, B.J.; Horwitz, A.F.; Parsons, J.T.; Beggs, H.E.; Stanley, E.R.; Bouton, A.H. Regulation of lamellipodial persistence, adhesion turnover, and motility in macrophages by focal adhesion kinase. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, K.J.; Bliska, J.B.; Bouton, A.H. Distinct mechanisms of integrin binding by yersinia pseudotuberculosis adhesins determine the phagocytic response of host macrophages. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1474–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, K.W.; Lin, K.B.; Dang-Lawson, M.; Guzman-Perez, A.; Aspnes, G.E.; Buckbinder, L.; Gold, M.R. Small molecule inhibitors of the Pyk2 and FAK kinases modulate chemoattractant-induced migration, adhesion and Akt activation in follicular and marginal zone B cells. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 275, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beinke, S.; Phee, H.; Clingan, J.M.; Schlessinger, J.; Matloubian, M.; Weiss, A. Proline-rich tyrosine kinase-2 is critical for CD8 T-cell short-lived effector fate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16234–16239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.M.; Ostergaard, H.L. Pyk2 controls integrin-dependent CTL migration through regulation of de-adhesion. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamen, L.A.; Schlessinger, J.; Lowell, C.A. Pyk2 is required for neutrophil degranulation and host defense responses to bacterial infection. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Boetticher, E.; Wang, L.; Duan, Y.; Learoyd, J.; Leff, A.R. Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 regulates spreading and migration of eosinophils after β2-integrin adhesion. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posritong, S.; Hong, J.M.; Eleniste, P.P.; McIntyre, P.W.; Wu, J.L.; Himes, E.R.; Patel, V.; Kacena, M.A.; Bruzzaniti, A. Pyk2 deficiency potentiates osteoblast differentiation and mineralizing activity in response to estrogen or raloxifene. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Hooker, R.A.; Nguyen, K.; Gerard-O’Riley, R.; Waning, D.L.; Chitteti, B.R.; Meijome, T.E.; Chua, H.L.; Plett, A.P.; Orschell, C.M.; et al. Pyk2 regulates megakaryocyte-induced increases in osteoblast number and bone formation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckbinder, L.; Crawford, D.T.; Qi, H.; Ke, H.Z.; Olson, L.M.; Long, K.R.; Bonnette, P.C.; Baumann, A.P.; Hambor, J.E.; Grasser, W.A., 3rd; et al. Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 regulates osteoprogenitor cells and bone formation, and offers an anabolic treatment approach for osteoporosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10619–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Henn, H.; Destaing, O.; Sims, N.A.; Aoki, K.; Alles, N.; Neff, L.; Sanjay, A.; Bruzzaniti, A.; De Camilli, P.; Baron, R.; et al. Defective microtubule-dependent podosome organization in osteoclasts leads to increased bone density in Pyk2−/− mice. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, L.T.; Lakkakorpi, P.T.; Nakamura, I.; Machwate, M.; Nagy, R.M.; Rodan, G.A. Pyk2 in osteoclasts is an adhesion kinase, localized in the sealing zone, activated by ligation of alpha(v)beta3 integrin, and phosphorylated by src kinase. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 102, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allingham, M.J.; van Buul, J.D.; Burridge, K. Icam-1-mediated, Src- and Pyk2-dependent vascular endothelial cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation is required for leukocyte transendothelial migration. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4053–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girault, J.A.; Costa, A.; Derkinderen, P.; Studler, J.M.; Toutant, M. Fak and Pyk2/cakbeta in the nervous system: A link between neuronal activity, plasticity and survival? Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.C.; Mei, L. Roles of fak family kinases in nervous system. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, s676–s682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Learoyd, J.; Meliton, A.Y.; Clay, B.S.; Leff, A.R.; Zhu, X. Inhibition of Pyk2 blocks airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 42, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Learoyd, J.; Meliton, A.Y.; Leff, A.R.; Zhu, X. Inhibition of Pyk2 blocks lung inflammation and injury in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, I.C.; OuYang, C.N.; Yuan, S.N.; Li, H.P.; Chen, J.T.; Shieh, H.R.; Chen, Y.J.; Ojcius, D.M.; Chu, C.L.; Yu, J.S.; et al. Pyk2 activates the NLRP3 inflammasome by directly phosphorylating Asc and contributes to inflammasome-dependent peritonitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas, C.; Kumar, S.; Franklin, B.S.; Dierkes, T.; Brinkschulte, R.; Tejera, D.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Schwartz, S.; Santarelli, F.; Kummer, M.P.; et al. Microglia-derived Asc specks cross-seed amyloid-beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2017, 552, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giralt, A.; Brito, V.; Chevy, Q.; Simonnet, C.; Otsu, Y.; Cifuentes-Diaz, C.; de Pins, B.; Coura, R.; Alberch, J.; Gines, S.; et al. Pyk2 modulates hippocampal excitatory synapses and contributes to cognitive deficits in a huntington’s disease model. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakkakorpi, P.T.; Bett, A.J.; Lipfert, L.; Rodan, G.A.; Duong le, T. Pyk2 autophosphorylation, but not kinase activity, is necessary for adhesion-induced association with c-Src, osteoclast spreading, and bone resorption. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11502–11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, K.W.; Dang-Lawson, M.; Lee, R.L.; Vong, D.; Bulic, A.; Buckbinder, L.; Gold, M.R. B cell receptor-induced phosphorylation of Pyk2 and focal adhesion kinase involves integrins and the rap gtpases and is required for B cell spreading. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22865–22877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cioccio, V.; Strippoli, R.; Bizzarri, C.; Troiani, G.; Cervellera, M.N.; Gloaguen, I.; Colagrande, A.; Cattozzo, E.M.; Pagliei, S.; Santoni, A.; et al. Key role of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 in interleukin-8 (Cxcl8/IL-8)-mediated human neutrophil chemotaxis. Immunology 2004, 111, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Learoyd, J.; Duan, Y.; Leff, A.R.; Zhu, X. Hematopoietic Pyk2 regulates migration of differentiated hl-60 cells. J. Inflamm. (Lond.) 2010, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, M.D. Cellular functions of FAK kinases: Insight into molecular mechanisms and novel functions. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvak, V.; Tian, D.; Shaul, Y.D.; Lev, S. Targeting of Pyk2 to focal adhesions as a cellular mechanism for convergence between integrins and G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32736–32746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab, M.; Lu, Y.; Kohler, K.; Smith, X.; Strebhardt, K.; Rudd, C.E. Lfa-1 activates focal adhesion kinases FAK1/PYK2 to generate LAT-GRB2-SKAP1 complexes that terminate T-cell conjugate formation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.; Lim, S.T.; Tomar, A.; Gardel, M.; Bernard-Trifilo, J.A.; Chen, X.L.; Uryu, S.A.; Canete-Soler, R.; Zhai, J.; Lin, H.; et al. Pyk2 and FAK connections to p190rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor regulate rhoa activity, focal adhesion formation, and cell motility. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.R.; Du, Q.S.; Huang, Y.Z.; Ao, S.Z.; Mei, L.; Xiong, W.C. Regulation of cdc42 gtpase by proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 interacting with psgap, a novel pleckstrin homology and src homology 3 domain containing rhogap protein. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valimaki, E.; Miettinen, J.J.; Lietzen, N.; Matikainen, S.; Nyman, T.A. Monosodium urate activates Src/Pyk2/PI3 kinase and cathepsin dependent unconventional protein secretion from human primary macrophages. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostergaard, H.L.; Lysechko, T.L. Focal adhesion kinase-related protein tyrosine kinase Pyk2 in T-cell activation and function. Immunol. Res. 2005, 31, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.T.; Miller, N.L.; Nam, J.O.; Chen, X.L.; Lim, Y.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Pyk2 inhibition of p53 as an adaptive and intrinsic mechanism facilitating cell proliferation and survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, B.H.; Zhang, M.Q.; Xu, L.H.; Hu, L.J.; Wang, H.B.; Zhao, W.F.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X. Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 and its phosphorylated form py881 are novel prognostic markers for non-small-cell lung cancer progression and patients’ overall survival. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Qiu, X.; Gu, Y.; Wang, E. Up-regulation of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2008, 62, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelle, S.; Grosse, R.; Buech, T.; Chubanov, V.; Gudermann, T. Essential role of Pyk2 and Src kinase activation in neuropeptide-induced proliferation of small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, D.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, X.; Wang, E. Socs3 inhibiting migration of a549 cells correlates with Pyk2 signaling in vitro. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, E.; Qiu, X. Socs3 expression is inversely correlated with Pyk2 in non-small cell lung cancer and exogenous socs3 inhibits proliferation and invasion of a549 cells. Pathology 2012, 44, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behmoaram, E.; Bijian, K.; Jie, S.; Xu, Y.; Darnel, A.; Bismar, T.A.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A. Focal adhesion kinase-related proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 and focal adhesion kinase are co-overexpressed in early-stage and invasive erbb-2-positive breast cancer and cooperate for breast cancer cell tumorigenesis and invasiveness. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selitrennik, M.; Lev, S. Pyk2 integrates growth factor and cytokine receptors signaling and potentiates breast cancer invasion via a positive feedback loop. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22214–22226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Cui, X.Y.; Wu, W.; Yu, F.Y.; Yao, H.R.; Liu, Q.; Song, E.W.; Chen, J.Q. Pyk2 and Src mediate signaling to CCL18-induced breast cancer metastasis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yin, C.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Liu, N.; Sun, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; et al. Nir1 promotes invasion of breast cancer cells by binding to chemokine (C–C motif) ligand 18 through the Pi3k/Akt/Gsk3β/snail signalling pathway. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3900–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, M.K.; Schiemann, B.J.; Parvani, J.G.; Lee, Y.H.; Kang, Y.; Schiemann, W.P. Tgf-beta stimulates Pyk2 expression as part of an epithelial-mesenchymal transition program required for metastatic outgrowth of breast cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Guan, J.L. Compensatory function of Pyk2 protein in the promotion of focal adhesion kinase (FAK)-null mammary cancer stem cell tumorigenicity and metastatic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 18573–18582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Chen, G.; Kuan, S.F.; Zhang, D.H.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hu, J. Fak/Pyk2 promotes the wnt/beta-catenin pathway and intestinal tumorigenesis by phosphorylating gsk3beta. eLife 2015, 4, e10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narendra Talabattula, V.A.; Morgan, P.; Frech, M.J.; Uhrmacher, A.M.; Herchenroder, O.; Putzer, B.M.; Rolfs, A.; Luo, J. Non-canonical pathway induced by wnt3a regulates beta-catenin via Pyk2 in differentiating human neural progenitor cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 491, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.K.; Ng, K.T.; Sun, B.S.; Ho, J.W.; Lee, T.K.; Ng, I.; Poon, R.T.; Lo, C.M.; Liu, C.L.; Man, K.; et al. The significance of proline-rich tyrosine kinase2 (pyk2) on hepatocellular carcinoma progression and recurrence. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.K.; Man, K.; Ng, K.T.; Ho, J.W.; Lim, Z.X.; Cheng, Q.; Lo, C.M.; Poon, R.T.; Fan, S.T. Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (pyk2) promotes proliferation and invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through c-Src/ERK activation. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J.; Qian, Y.W.; Ren, Y.B.; Su, B.; Luo, T.; Dai, R.Y.; Huang, L.; Yan, J.J.; et al. High expression of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 is associated with poor survival of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt pathway. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20 (Suppl. 3), S312–S323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Liu, J.; Long, J.; Fu, J.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y. Microrna-23b suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting Pyk2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.F.; Xu, X.; Huang, J.; Fei, Q.L.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.D.; Han, Z.G. Down-regulation of mir-517a and mir-517c promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting Pyk2. Cancer Lett. 2013, 329, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Tran, N.L.; Menashi, E.; Rohl, C.; Kloss, J.; Bay, R.C.; Berens, M.E.; Loftus, J.C. The tyrosine kinase Pyk2 promotes migration and invasion of glioma cells. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, J.C.; Yang, Z.; Tran, N.L.; Kloss, J.; Viso, C.; Berens, M.E.; Lipinski, C.A. The Pyk2 ferm domain as a target to inhibit glioma migration. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, J.C.; Ross, J.T.; Paquette, K.M.; Paulino, V.M.; Nasser, S.; Yang, Z.; Kloss, J.; Kim, S.; Berens, M.E.; Tran, N.L. Mirna expression profiling in migrating glioblastoma cells: Regulation of cell migration and invasion by mir-23b via targeting of Pyk2. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guessous, F.; Yang, Y.; Johnson, E.; Marcinkiewicz, L.; Smith, M.; Zhang, Y.; Kofman, A.; Schiff, D.; Christensen, J.; Abounader, R. Cooperation between c-met and focal adhesion kinase family members in medulloblastoma and implications for therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Moschetta, M.; Huynh, D.; Tai, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Mishima, Y.; Ring, J.E.; Tam, W.F.; Xu, Q.; et al. Pyk2 promotes tumor progression in multiple myeloma. Blood 2014, 124, 2675–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meads, M.B.; Fang, B.; Mathews, L.; Gemmer, J.; Nong, L.; Rosado-Lopez, I.; Nguyen, T.; Ring, J.E.; Matsui, W.; MacLeod, A.R.; et al. Targeting Pyk2 mediates microenvironment-specific cell death in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2723–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, E.; Duan, W.; Bai, S.; Safdar, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, C. Chemokine receptor 7 promotes tumor migration and invasiveness via the rhoa/rock pathway in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lane, D.; Matte, I.; Laplante, C.; Garde-Granger, P.; Carignan, A.; Bessette, P.; Rancourt, C.; Piche, A. Ccl18 from ascites promotes ovarian cancer cell migration through proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 signaling. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meirson, T.; Samson, A.O.; Gil-Henn, H. An in silico high-throughput screen identifies potential selective inhibitors for the non-receptor tyrosine kinase Pyk2. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 1535–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Loftus, J.C. Targeting Pyk2 for therapeutic intervention. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Keir, S.T.; Song, L.; Wickman, S.; Jackson, D.; Ohmori, O.; Bigner, D.D.; Friedman, H.S.; Rich, J.N. A novel low-molecular weight inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase, TAE226, inhibits glioma growth. Mol. Carcinog. 2007, 46, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, J.; Lin, Y.G.; Merritt, W.M.; Spannuth, W.A.; Nick, A.M.; Honda, T.; Kamat, A.A.; Han, L.Y.; Kim, T.J.; Lu, C.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor TAE226 in ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10976–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, W.G.; Ung, E.; Whalen, P.; Cooper, B.; Hulford, C.; Autry, C.; Richter, D.; Emerson, E.; Lin, J.; Kath, J.; et al. Antitumor activity and pharmacology of a selective focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, pf-562,271. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperandio, O.; Miteva, M.A.; Segers, K.; Nicolaes, G.A.; Villoutreix, B.O. Screening outside the catalytic site: Inhibition of macromolecular inter-actions through structure-based virtual ligand screening experiments. Open Biochem. J. 2008, 2, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wells, J.A.; McClendon, C.L. Reaching for high-hanging fruit in drug discovery at protein-protein interfaces. Nature 2007, 450, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Tran, N.L.; Dooley, A.; Pang, Y.P.; Rohl, C.; Kloss, J.; Yang, Z.; McDonough, W.; Craig, D.; Berens, M.E.; et al. Critical role of the ferm domain in Pyk2 stimulated glioma cell migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Hegde, S.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Zhu, Y.; Herndon, J.M.; Meyer, M.A.; Nywening, T.M.; Hawkins, W.G.; Shapiro, I.M.; Weaver, D.T.; et al. Targeting focal adhesion kinase renders pancreatic cancers responsive to checkpoint immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Fukuoka, K.; Takeda, M.; Iwasa, T.; Yoshida, T.; Horobin, J.; Keegan, M.; Vaickus, L.; Chavan, A.; Padval, M.; et al. A first-in-asian phase 1 study to evaluate safety, pharmacokinetics and clinical activity of VS-6063, a focal adhesion kinase (FAK) inhibitor in japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Shao, D.; Jia, Y.; He, K.; Li, K.; Chen, L. Chemotherapy induces ovarian cancer cell repopulation through the caspase 3-mediated arachidonic acid metabolic pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 5817–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanteti, R.; Mirzapoiazova, T.; Riehm, J.J.; Dhanasingh, I.; Mambetsariev, B.; Wang, J.; Kulkarni, P.; Kaushik, G.; Seshacharyulu, P.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; et al. Focal adhesion kinase a potential therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer and malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Bao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, W. Proline-Rich Protein Tyrosine Kinase 2 in Inflammation and Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10050139
Zhu X, Bao Y, Guo Y, Yang W. Proline-Rich Protein Tyrosine Kinase 2 in Inflammation and Cancer. Cancers. 2018; 10(5):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10050139
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiangdong, Yonghua Bao, Yongchen Guo, and Wancai Yang. 2018. "Proline-Rich Protein Tyrosine Kinase 2 in Inflammation and Cancer" Cancers 10, no. 5: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10050139
APA StyleZhu, X., Bao, Y., Guo, Y., & Yang, W. (2018). Proline-Rich Protein Tyrosine Kinase 2 in Inflammation and Cancer. Cancers, 10(5), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10050139





