Elevated Polyamines in Saliva of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
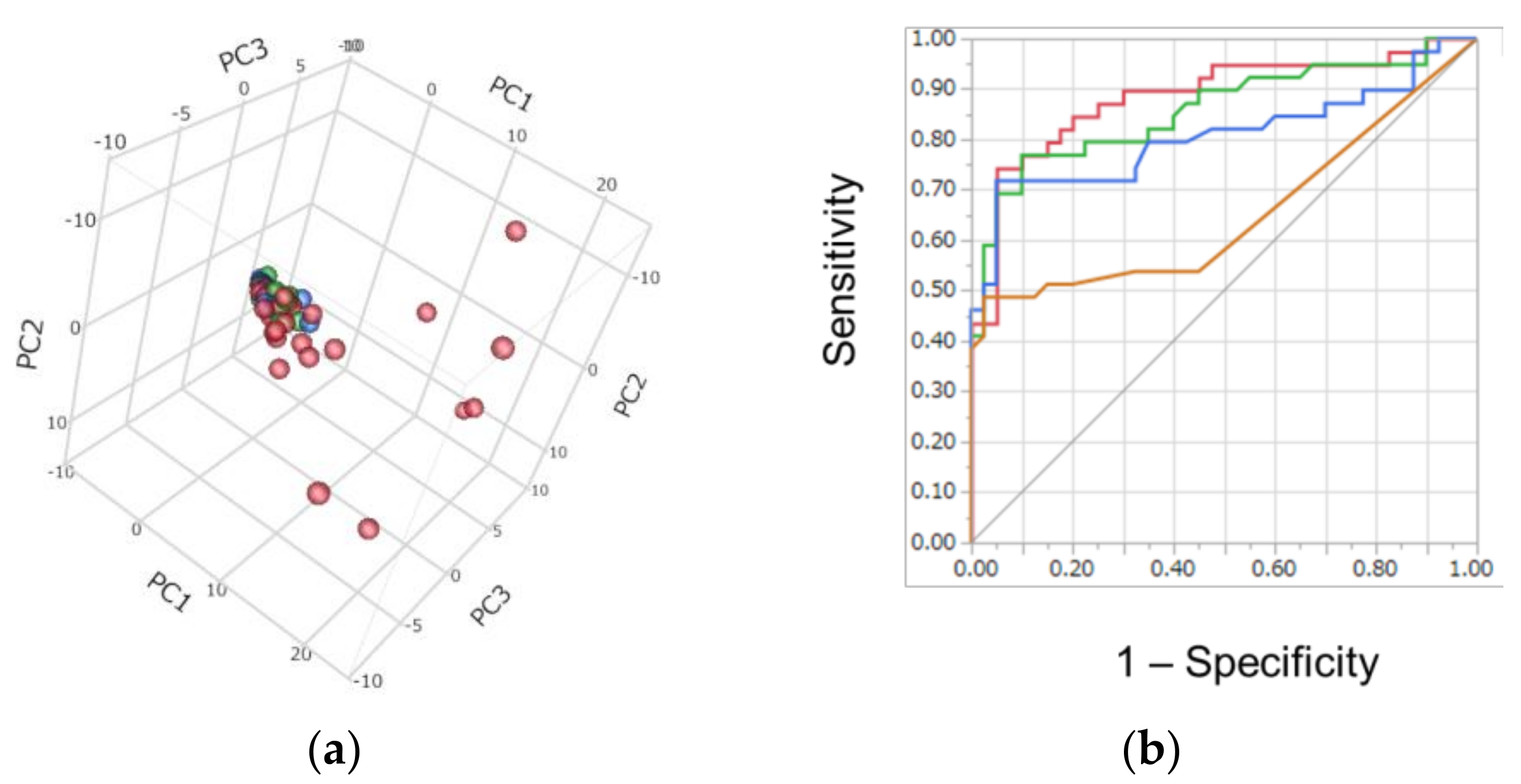
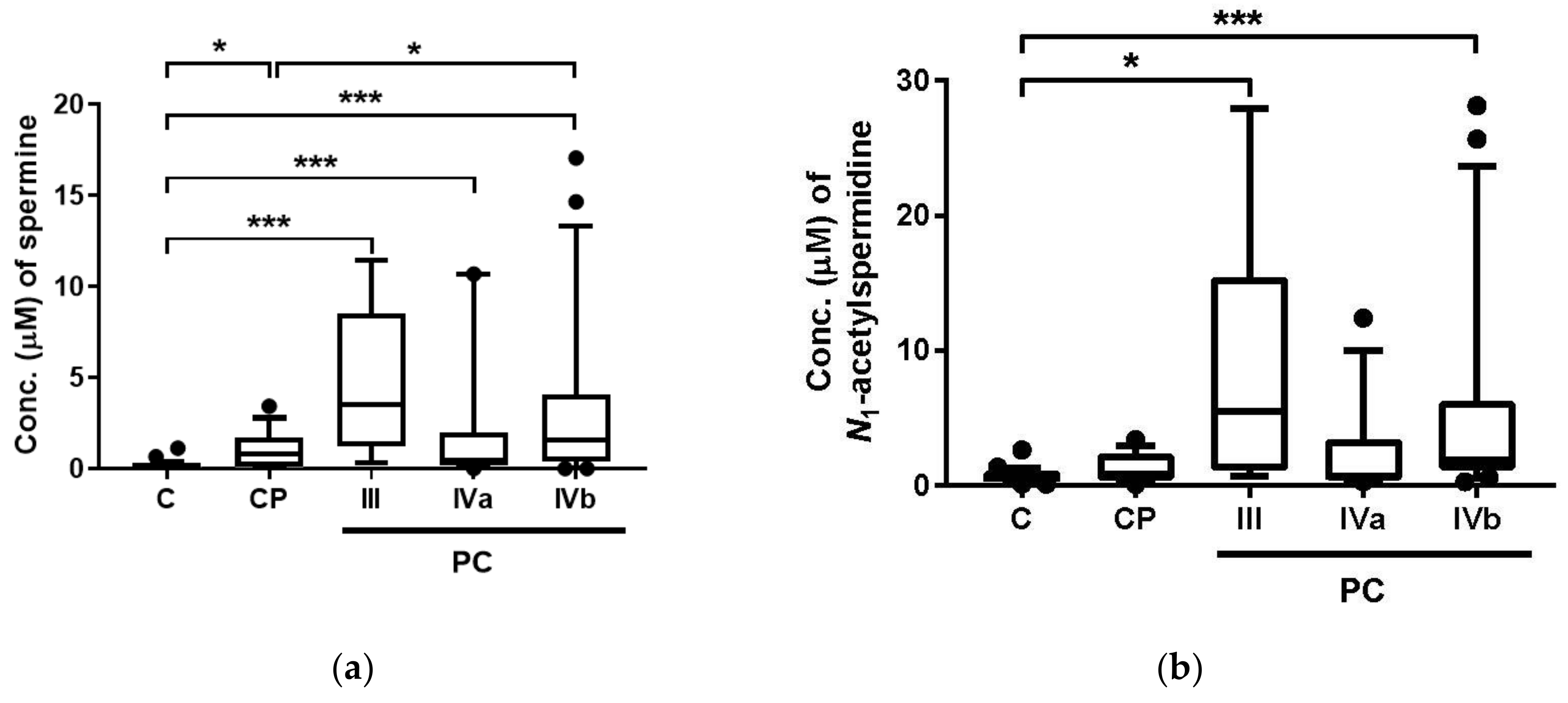
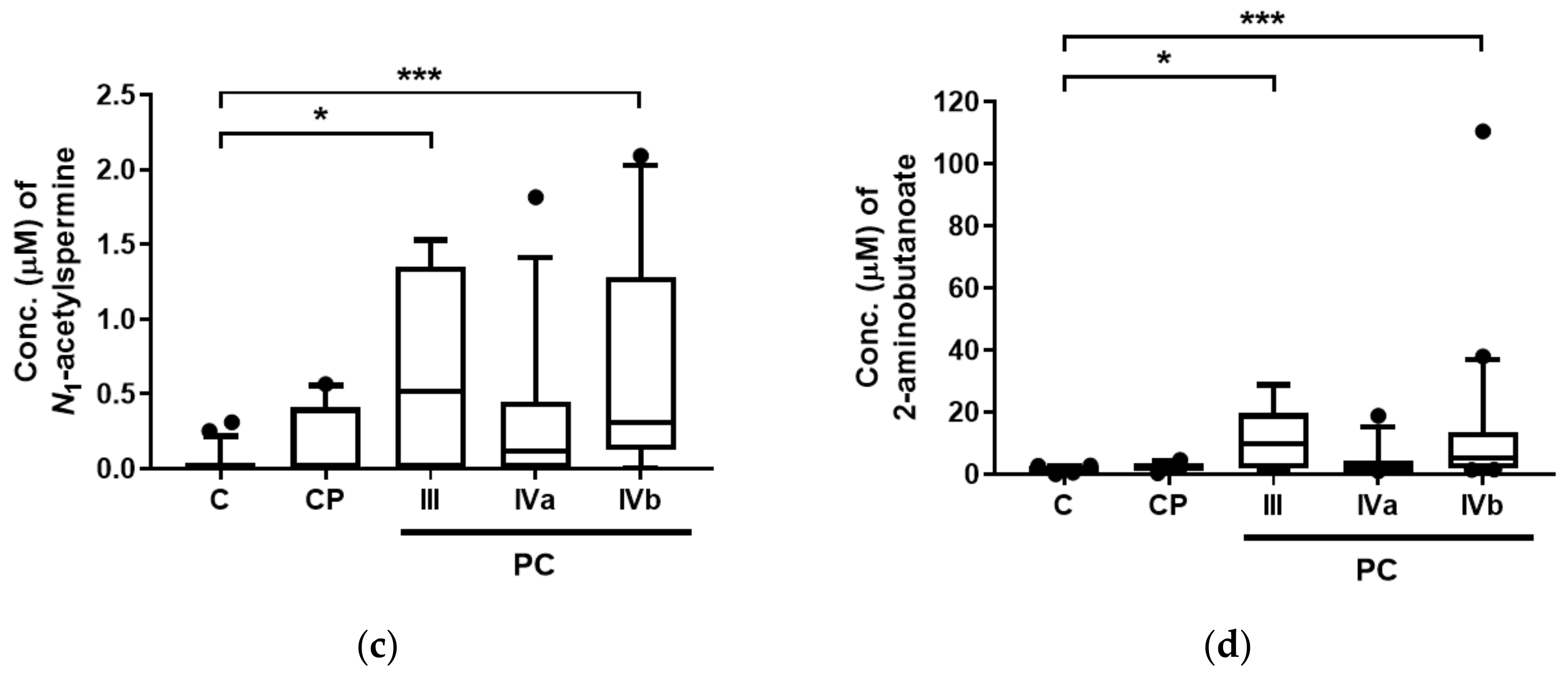
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Individual Selection
4.2. Protocols for Saliva Collection and Sample Preparation
4.3. Measurement Conditions and Processing of Raw Data
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Hao, Y.; Xu, J.; Murray, T.; Thun, M.J. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2008, 58, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosty, C.; Goggins, M. Early detection of pancreatic carcinoma. Hematol./Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 16, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, M.I.; Hruban, R.H.; Fishman, E.K.; Kamel, I.R.; Schulick, R.; Zhang, Z.; Topazian, M.; Takahashi, N.; Fletcher, J.; Petersen, G.; et al. Frequent detection of pancreatic lesions in asymptomatic high-risk individuals. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 796–804, quiz e714-795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadatos-Pastos, D.; Thillai, K.; Rabbie, R.; Ross, P.; Sarker, D. Folfirinox—A new paradigm in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2014, 14, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiriyama, S.; Hayakawa, T.; Kondo, T.; Shibata, T.; Kitagawa, M.; Ono, H.; Sakai, Y. Usefulness of a new tumor marker, span-1, for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Cancer 1990, 65, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Liu, C.; Guo, M.; Cheng, H.; Lu, Y.; Jin, K.; Liu, L.; Long, J.; Xu, J.; Lu, R.; et al. Potential biomarkers in lewis negative patients with pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, K.; Kawamoto, H.; Hirao, K.; Sakakihara, I.; Yamamoto, N.; Noma, Y.; Fujii, M.; Kato, H.; Ogawa, T.; Ishida, E.; et al. Monitoring of CA19-9 and SPAN-1 can facilitate the earlier confirmation of progressing pancreatic cancer during chemotherapy. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerner, E.W.; Meyskens, F.L., Jr. Polyamines and cancer: Old molecules, new understanding. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabala-Letona, A.; Arruabarrena-Aristorena, A.; Martin-Martin, N.; Fernandez-Ruiz, S.; Sutherland, J.D.; Clasquin, M.; Tomas-Cortazar, J.; Jimenez, J.; Torres, I.; Quang, P.; et al. Mtorc1-dependent amd1 regulation sustains polyamine metabolism in prostate cancer. Nature 2017, 547, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.K.; Libby, P.R.; Bergeron, R.J.; Porter, C.W. Modulation of polyamine biosynthesis and transport by oncogene transfection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 157, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Lee, C.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Liu, G.Y.; Hung, H.C. Multifaceted interactions and regulation between antizyme and its interacting proteins cyclin d1, ornithine decarboxylase and antizyme inhibitor. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23917–23929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phanstiel, O. An overview of polyamine metabolism in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2017. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Bradshaw, A.D.; Gera, S.; Dewan, M.Z.; Xu, R. The tgf-beta/smad4 signaling pathway in pancreatic carcinogenesis and its clinical significance. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejure, F.R.; Eilers, M. Myc and tumor metabolism: Chicken and egg. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 3409–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, Q.; Ma, R.; Lin, X.; Xu, H.; Bi, K. Determination of polyamine metabolome in plasma and urine by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method: Application to identify potential markers for human hepatic cancer. Anal. Chim. Act. 2013, 791, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemi, R.J.; Roine, A.N.; Hakkinen, M.R.; Kumpulainen, P.S.; Keinanen, T.A.; Vepsalainen, J.J.; Lehtimaki, T.; Oksala, N.K.; Maenpaa, J.U. Urinary polyamines as biomarkers for ovarian cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2017, 27, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, E. A metabolomics-based biomarker signature discriminates pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis. Gut 2018, 67, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, K.Y.; Wu, H.J.; Menon, S.S.; Fallah, Y.; Zhong, X.; Rizk, N.; Unger, K.; Mapstone, M.; Fiandaca, M.S.; Federoff, H.J.; et al. Metabolomic biomarkers of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68899–68915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoi, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Umeda, J.; Sofuni, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Tsuji, S.; Tanaka, R.; Tonozuka, R.; Honjo, M.; Moriyasu, F.; et al. Serum metabolomic profiles for human pancreatic cancer discrimination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Zhong, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Serum metabolomics differentiating pancreatic cancer from new-onset diabetes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29116–29124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, A.; Heuchel, R.; Forshed, J.; Lehtio, J.; Lohr, M.; Nordstrom, A. Discrimination of pancreatic cancer and pancreatitis by LC-MS metabolomics. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayerle, J.; Kalthoff, H.; Reszka, R.; Kamlage, B.; Peter, E.; Schniewind, B.; Gonzalez Maldonado, S.; Pilarsky, C.; Heidecke, C.D.; Schatz, P.; et al. Metabolic biomarker signature to differentiate pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from chronic pancreatitis. Gut 2018, 67, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumas, J.; Kvederaviciute, K.; Petrulionis, M.; Kurlinkus, B.; Rimkus, A.; Sakalauskaite, G.; Cicenas, J.; Sileikis, A. Metabolomics in pancreatic cancer biomarkers research. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Zhan, B.; Feng, J.; Hu, W.; Lin, X.; Bai, J.; Huang, H. Non-invasively predicting differentiation of pancreatic cancer through comparative serum metabonomic profiling. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Xu, J.W.; Cheng, Y.G.; Gao, J.Y.; Hu, S.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhan, H.X. Early detection of pancreatic cancer: Where are we now and where are we going? Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herreros-Villanueva, M.; Bujanda, L. Non-invasive biomarkers in pancreatic cancer diagnosis: What we need versus what we have. Ann. Trans. Med. 2016, 4, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, P.J.; Fletcher, E.M.; Gibbons, S.M.; Bouvet, M.; Doran, K.S.; Kelley, S.T. Characterization of the salivary microbiome in patients with pancreatic cancer. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Wong, D.T.; Hirayama, A.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M. Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Liu, R.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y.; Bi, K.; Li, Q. Quantification of free polyamines and their metabolites in biofluids and liver tissue by uhplc-ms/ms: Application to identify the potential biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6891–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, T.H.; Chan, C.F.; Chan, W.L.; Chiu, K.F.; Wong, W.T.; Ng, C.F.; Wong, K.L. Urinary polyamines: A pilot study on their roles as prostate cancer detection biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Liu, R.; He, B.; Bi, C.W.; Bi, K.; Li, Q. Polyamine metabolites profiling for characterization of lung and liver cancer using an LC-tandem MS method with multiple statistical data mining strategies: Discovering potential cancer biomarkers in human plasma and urine. Molecules 2016, 21, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loser, C.; Folsch, U.R.; Paprotny, C.; Creutzfeldt, W. Polyamine concentrations in pancreatic tissue, serum, and urine of patients with pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 1990, 5, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Shimizu, I.; Toyama, T.; Yoshimoto, N.; Endo, Y.; Inoue, K.; Todoroki, K.; Min, J.Z.; Mizuno, H.; et al. Diagnostic approach to breast cancer patients based on target metabolomics in saliva by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Act. 2016, 452, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsui, H.; Mochizuki, T.; Inoue, K.; Toyama, T.; Yoshimoto, N.; Endo, Y.; Todoroki, K.; Min, J.Z.; Toyo’oka, T. High-throughput LC-MS/MS based simultaneous determination of polyamines including n-acetylated forms in human saliva and the diagnostic approach to breast cancer patients. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11835–11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Kawakami, M.; Robert, M.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M. Bioinformatics tools for mass spectroscopy-based metabolomic data processing and analysis. Curr. Bioinform. 2012, 7, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Saruta, J.; Matsuki, C.; To, M.; Onuma, H.; Kaneko, M.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M.; Tsukinoki, K. Physiological and environmental parameters associated with mass spectrometry-based salivary metabolomic profiles. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, K. The mechanisms by which polyamines accelerate tumor spread. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, P.; Wang, X.; Duan, Y. Investigation and identification of potential biomarkers in human saliva for the early diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 427, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Kitabatake, K.; Sugano, A.; Nakamura, M.; Kaneko, M.; Ota, S.; Hiwatari, K.; Enomoto, A.; Soga, T.; et al. Identification of salivary metabolomic biomarkers for oral cancer screening. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuma, N.; Saita, M.; Hoshi, N.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Kimoto, K. Effect of masticatory stimulation on the quantity and quality of saliva and the salivary metabolomic profile. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Kitabatake, K.; Tu, M.; Sugano, A.; Yamamori, I.; Iba, A.; Yusa, K.; Kaneko, M.; Ota, S.; et al. Effect of timing of collection of salivary metabolomic biomarkers on oral cancer detection. Amino Acid 2017, 49, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storey, J.D.; Tibshirani, R. Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9440–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Pal, C.J. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
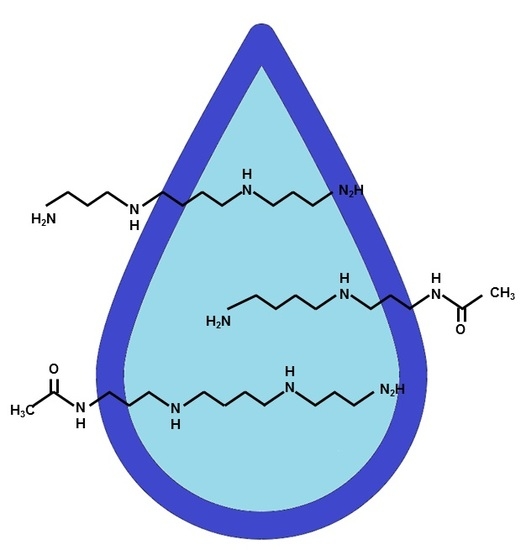
| Parameters | C | CP | PC | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 26 | 14 | 39 | - | |
| Age 1 | 50.8 ± 16.4 | 51.1 ± 12.4 | 66.1 ± 9.86 | <0.0001 | *** |
| Sex (F/M) 2 | 13/13 | 3/11 | 18/21 | 0.189 | |
| Markers | Unit Odds Ratio 1 | Coefficients 1,2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| alanine | 0.990 (0.980–1.00) | −0.0103 (−0.0203–−0.0003) | 0.043 * |
| N1-acetylspermidine | 2.92 (1.35–6.31) | 1.07 (0.30–1.84) | 0.0065 *** |
| 2-oxobutyrate | 1.15 (1.02–1.29) | 0.14 (0.02–0.25) | 0.019 * |
| 2-hydroxybutyrate | 1.46 (1.07–1.99) | 0.38 (0.07–0.69) | 0.017 * |
| (Intercept) | - | −2.21 (−3.21–−1.21) | <0.0001 *** |
| Marker 1 | CP 2 (n = 14) | PC 3 | p-Value 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| III (n = 6) | IVa (n = 12) | IVb (n = 21) | |||
| CEA | 3.46 ± 3.27 | 2.75 ± 1.46 | 7.25 ± 4.18 | 43.8 ± 101 | 0.0196 * |
| >5.0 ng/mL | 3 (21.4) | 0 (0.00) | 9 (75.0) | 10 (47.6) | |
| #MV 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| CA19-9 | 19.9 ± 21.3 | 2.90 × 102 ± 6.26 × 102 | 7.43 × 102 ± 9.98 × 102 | 6.25 × 103 ± 1.77 × 104 | 0.0016 *** |
| >37 U/mL | 2 (14.3) | 3 (50.0) | 12 (100.0) | 16 (76.2) | |
| #MV 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| DUPAN2 | 74.0 ± 86.7 | 6.17 × 102 ± 7.67 × 102 | 5.28 × 102 ± 6.52 × 102 | 9.98 × 102 ± 6.52 × 102 | 0.0008 *** |
| >150 U/mL | 2 (16.7) | 4 (66.7) | 6 (50.0) | 18 (90.0) | |
| #MV 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| SPAN1 | 16.2 ± 17.1 | 89.0 ± 1.58 × 102 | 3.63 × 102 ± 4.83 × 102 | 3.25 × 103 ± 8.44 × 103 | <0.0001 *** |
| >30 U/mL | 2 (18.2) | 3 (50.0) | 10 (83.3) | 19 (95.0) | |
| #MV 5 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| MLR | 0.334 ± 0.266 | 0.800 ± 0.299 | 0.633 ± 0.363 | 0.786 ± 0.268 | 0.002 *** |
| > 0.5533 | 2 (14.3) | 5 (83.3) | 7 (58.3) | 16 (76.2) | |
| #MV 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asai, Y.; Itoi, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Sofuni, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Tanaka, R.; Tonozuka, R.; Honjo, M.; Mukai, S.; Fujita, M.; et al. Elevated Polyamines in Saliva of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10020043
Asai Y, Itoi T, Sugimoto M, Sofuni A, Tsuchiya T, Tanaka R, Tonozuka R, Honjo M, Mukai S, Fujita M, et al. Elevated Polyamines in Saliva of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2018; 10(2):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10020043
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsai, Yasutsugu, Takao Itoi, Masahiro Sugimoto, Atsushi Sofuni, Takayoshi Tsuchiya, Reina Tanaka, Ryosuke Tonozuka, Mitsuyoshi Honjo, Shuntaro Mukai, Mitsuru Fujita, and et al. 2018. "Elevated Polyamines in Saliva of Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 10, no. 2: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10020043
APA StyleAsai, Y., Itoi, T., Sugimoto, M., Sofuni, A., Tsuchiya, T., Tanaka, R., Tonozuka, R., Honjo, M., Mukai, S., Fujita, M., Yamamoto, K., Matsunami, Y., Kurosawa, T., Nagakawa, Y., Kaneko, M., Ota, S., Kawachi, S., Shimazu, M., Soga, T., ... Sunamura, M. (2018). Elevated Polyamines in Saliva of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 10(2), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10020043