Photopatternable Magnetic Hollowbots by Nd-Fe-B Nanocomposite for Potential Targeted Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
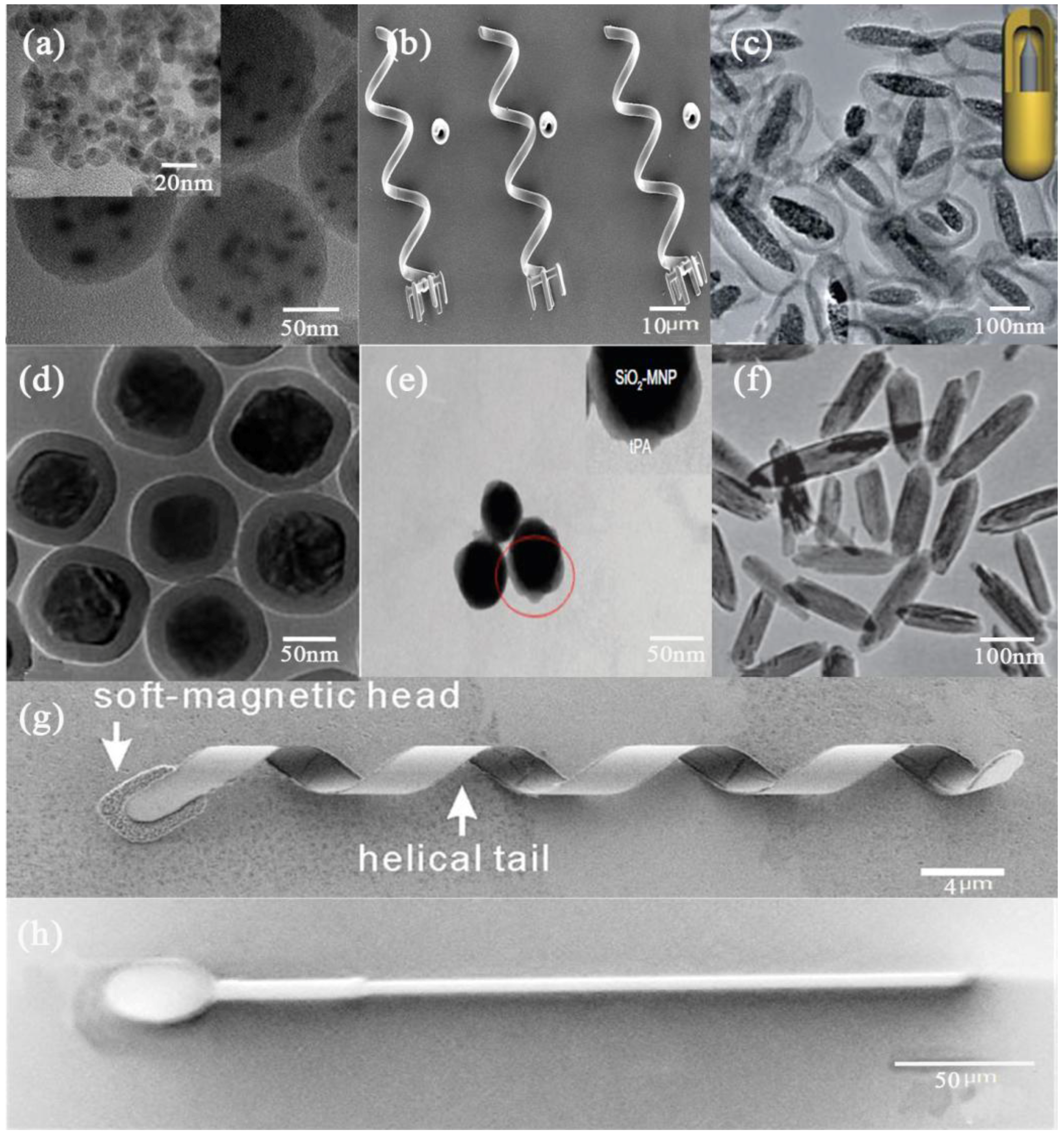
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
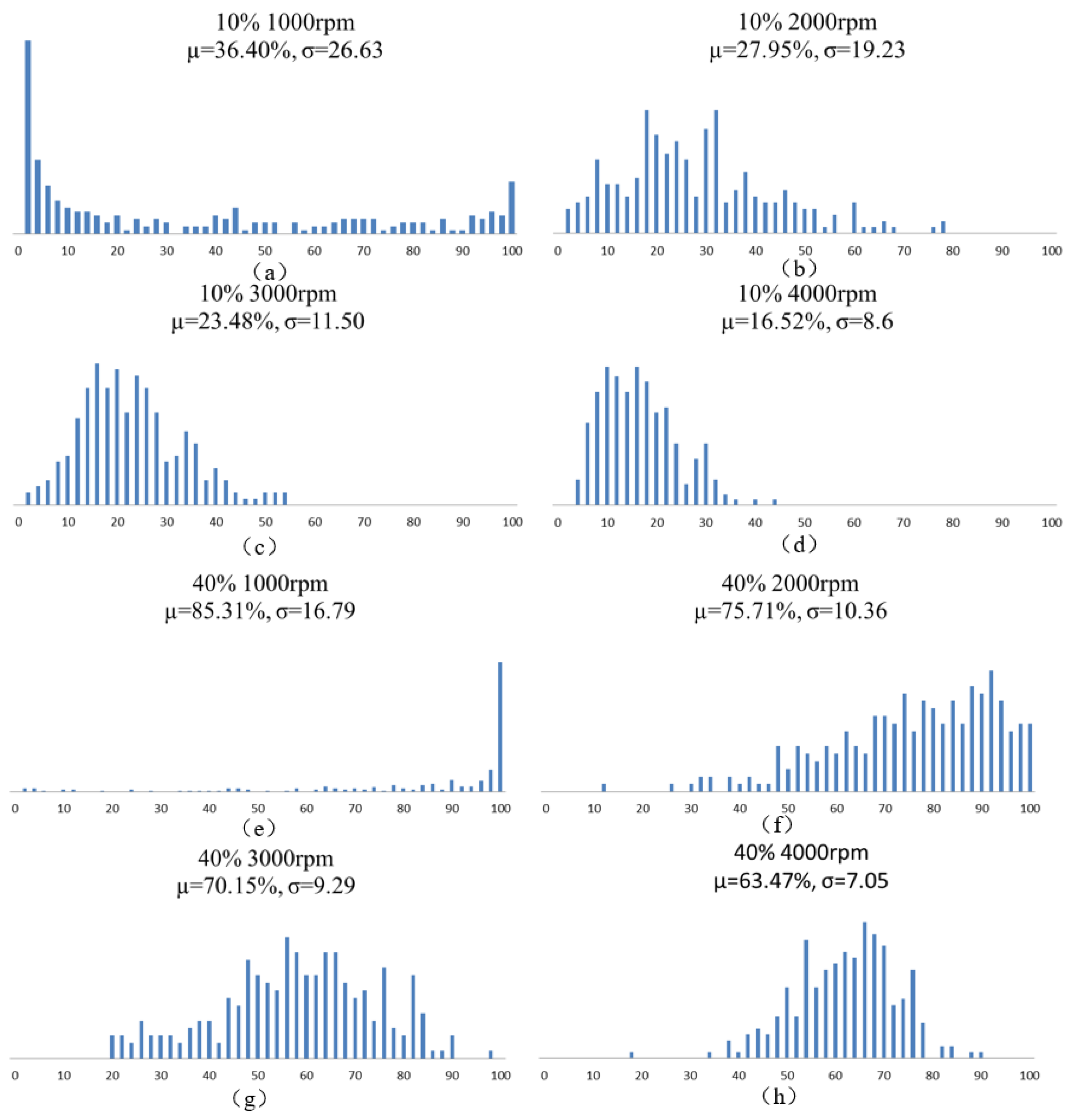
2.1. Magnetic Composite Preparation
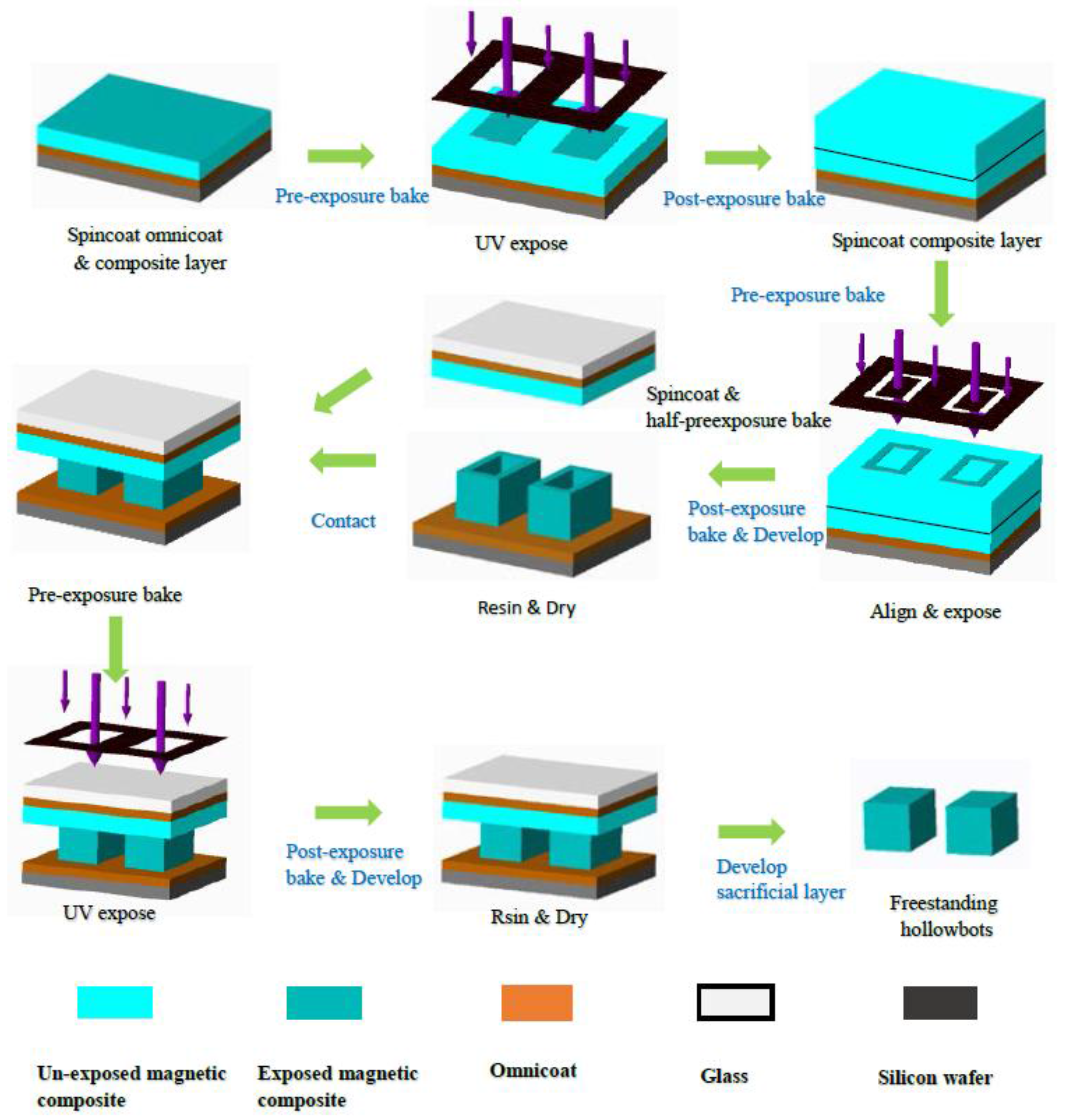
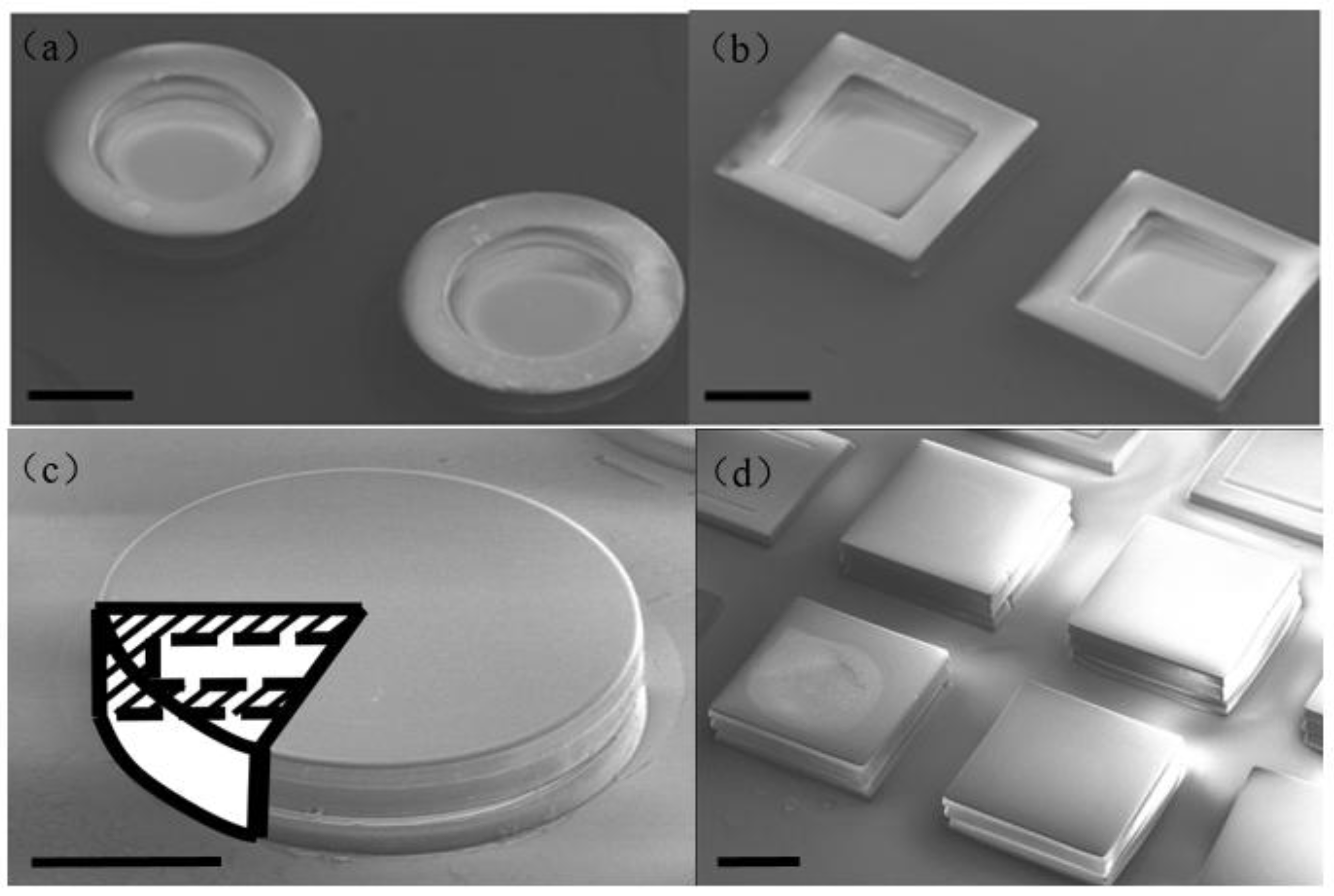
2.2. Hollowbots Fabrication
3. Characterization
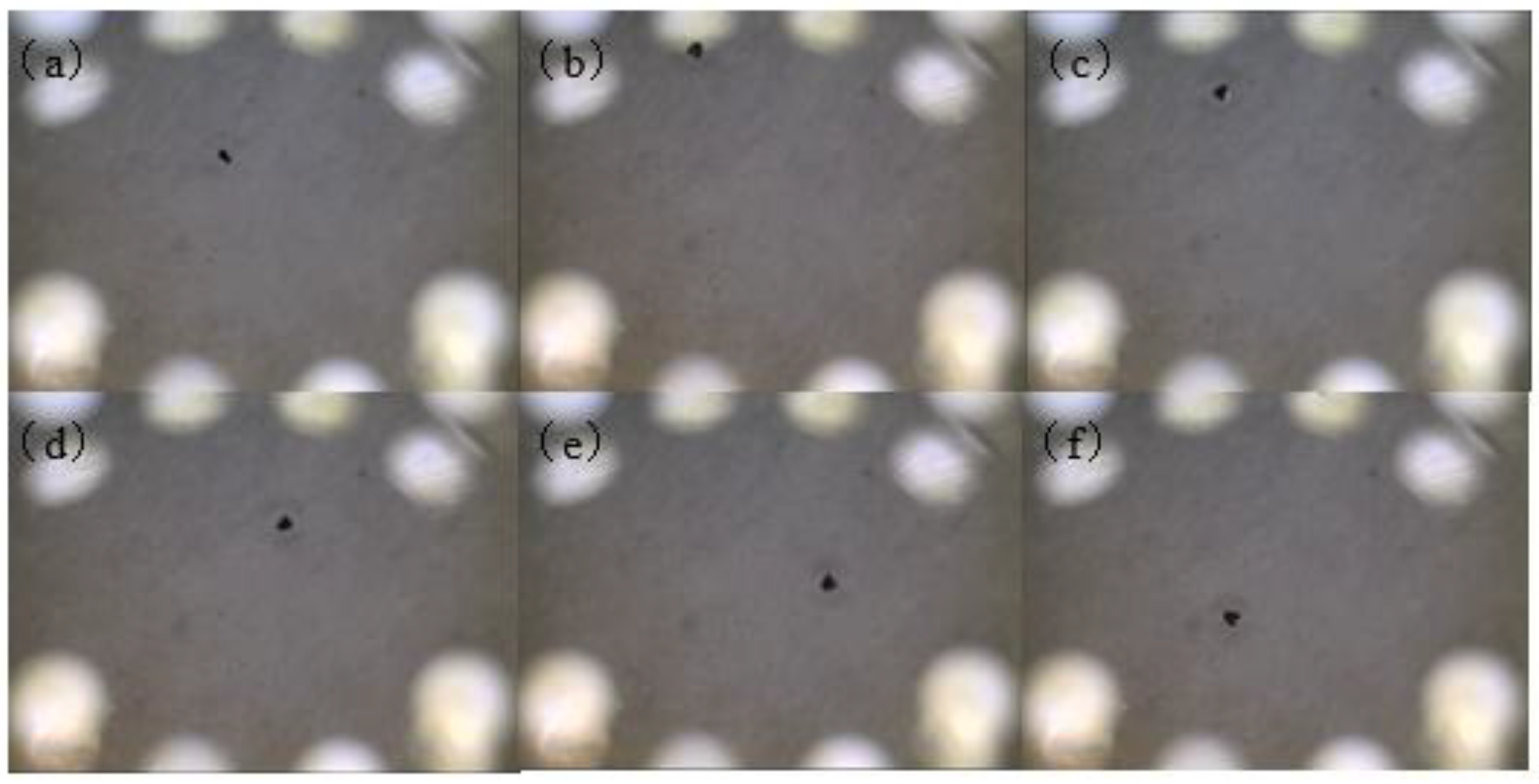
4. Actuation
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Drug delivery systems: Entering the mainstream. Science 2004, 303, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talelli, M.; Barz, M.; Rijcken, C.J.; Kiessling, F.; Hennink, W.E.; Lammers, T. Core-crosslinked polymeric micelles: Principles, preparation, biomedical applications and clinical translation. Nano Today 2015, 10, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminade, A.-M.; Turrin, C.-O. Dendrimers for drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4055–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kadasala, N.R.; Abouelmagd, S.A.; Castanares, M.A.; Collins, D.S.; Wei, A.; Yeo, Y. Polymer–iron oxide composite nanoparticles for epr-independent drug delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 101, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, K.J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Linehan, A.R.; Yang, D.; Behrens, A.M.; Rose, S.; Tochka, Z.L.; Tzeng, S.Y.; Norman, J.J.; Anselmo, A.C.; et al. Fabrication of fillable microparticles and other complex 3d microstructures. Science 2017, 357, 1138–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traverso, G.; Schoellhammer, C.M.; Schroeder, A.; Maa, R.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Polat, B.E.; Anderson, D.G.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Microneedles for drug delivery via the gastrointestinal tract. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, V.; Kang, W.S.; Robbins, T.A.; Spencer, A.J.; Kim, E.S.; McKenna, M.J.; Kujawa, S.G.; Fiering, J.; Pararas, E.E.; Mescher, M.J.; et al. Microfabricated reciprocating micropump for intracochlear drug delivery with integrated drug/fluid storage and electronically controlled dosing. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tottori, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, F.; Krawczyk, K.K.; Franco-Obregón, A.; Nelson, B.J. Magnetic helical micromachines: Fabrication, controlled swimming, and cargo transport. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.-M.; Gao, F.-Y.; Yin, T.; Zhang, H.-X.; Ma, M.; Yang, Y.-J.; Yue, F. Crgd-functionalized polymeric magnetic nanoparticles as a dual-drug delivery system for safe targeted cancer therapy. Pharm. Res. 2013, 70, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Shi, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based nano drug delivery systems: Synthesis, controlled drug release and delivery, pharmacokinetics and biocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5845–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, S.; Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, H. Biocompatibility, mr imaging and targeted drug delivery of a rattle-type magnetic mesoporous silica nanosphere system conjugated with peg and cancer-cell-specific ligands. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Yang, P.-C.; Ma, Y.-H.; Tu, S.-J.; Lu, Y.-J. Targeted delivery of tissue plasminogen activator by binding to silica-coated magnetic nanoparticle. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Cui, X.; Ruan, M.; He, Q.; Bu, W. A hollow-core, magnetic, and mesoporous double-shell nanostructure: In situ decomposition/reduction synthesis, bioimaging, and drug-delivery properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 1850–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Abbott, J.J.; Dong, L.; Kratochvil, B.E.; Bell, D.; Nelson, B.J. Artificial bacterial flagella: Fabrication and magnetic control. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 064107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.S.; Dijkslag, H.C.; Abelmann, L.; Misra, S. Magnetosperm: A microrobot that navigates using weak magnetic fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 223701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, W.S.N. Microrobots and micromechanical systems. Sens. Actuator 1989, 19, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugat, O.; Delamare, J.; Reyne, G. Magnetic micro-actuators and systems (magmas). IEEE Trans. Magn. 2003, 39, 3607–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steager, E.B.; Selman Sakar, M.; Magee, C.; Kennedy, M.; Cowley, A.; Kumar, V. Automated biomanipulation of single cells using magnetic microrobots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Kershaw, J.; Wang, L. Fabrication and wireless micromanipulation of magnetic biocompatible microrobots using microencapsulation for microrobotics and microfluidics applications. J. Microencapsul. 2016, 33, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Xu, W.; Syed, A.A.; Chau, Y.; Chen, L.; Chew, B.; Yassine, O.; Wu, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Design and fabrication of magnetically functionalized flexible micropillar arrays for rapid and controllable microfluidic mixing. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2125–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, M.M.; Yunas, J.; Pawinanto, R.E.; Majlis, B.Y.; Bais, B. Pdms based electromagnetic actuator membrane with embedded magnetic particles in polymer composite. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 245, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, M.P.; Abbott, J.J.; Kratochvil, B.E.; Borer, R.; Sengul, A.; Nelson, B.J. Octomag: An electromagnetic system for 5-dof wireless micromanipulation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2010, 26, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzipirpiridis, G.; Ergeneman, O.; Pokki, J.; Ullrich, F.; Fusco, S.; Ortega, J.A.; Sivaraman, K.M.; Nelson, B.J.; Pané, S. Electroforming of implantable tubular magnetic microrobots for wireless ophthalmologic applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basumatary, H.; Chelvane, J.A.; Rao, D.S.; Kamat, S.; Ranjan, R. Effect of sputtering parameters on the structure, microstructure and magnetic properties of tb-fe films. Thin Solid Films 2015, 583, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.H.; Yang, K.C.; Park, J.W.; Yun, D.H.; Kim, K.N.; Yeom, G.Y. Etching of magnetic tunnel junction materials using reactive ion beam. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 11823–11830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Jauhari, D. Double-ion imprinted polymer@ magnetic nanoparticles modified screen printed carbon electrode for simultaneous analysis of cerium and gadolinium ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 875, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Fabrication of Magnetic Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Microstructures for Microfluidics and Microrobotics Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, G.; Wang, L. Photopatternable Magnetic Hollowbots by Nd-Fe-B Nanocomposite for Potential Targeted Drug Delivery Applications. Micromachines 2018, 9, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9040182
Li H, Chen J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhao G, Wang L. Photopatternable Magnetic Hollowbots by Nd-Fe-B Nanocomposite for Potential Targeted Drug Delivery Applications. Micromachines. 2018; 9(4):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9040182
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hui, Jing Chen, Jinjie Zhang, Jingyong Zhang, Guoru Zhao, and Lei Wang. 2018. "Photopatternable Magnetic Hollowbots by Nd-Fe-B Nanocomposite for Potential Targeted Drug Delivery Applications" Micromachines 9, no. 4: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9040182
APA StyleLi, H., Chen, J., Zhang, J., Zhang, J., Zhao, G., & Wang, L. (2018). Photopatternable Magnetic Hollowbots by Nd-Fe-B Nanocomposite for Potential Targeted Drug Delivery Applications. Micromachines, 9(4), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9040182





