Microfabrication of Micropore Array for Cell Separation and Cell Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
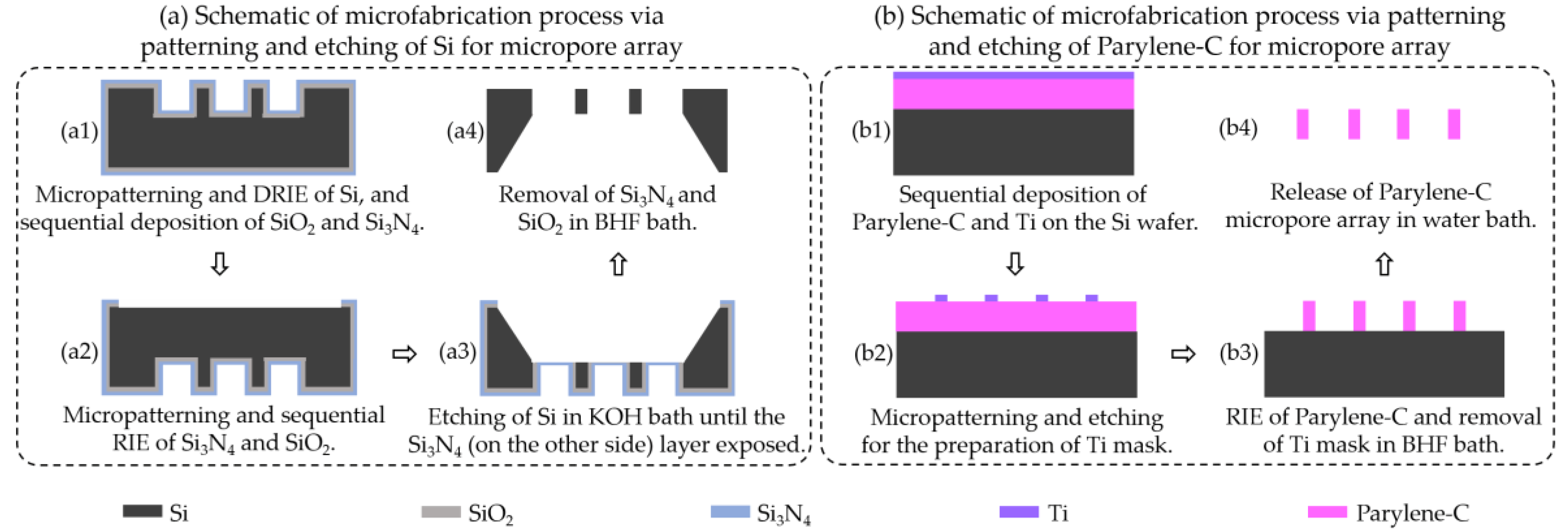
2.1. Micropatterning and Etching of Silicon for Micropore Array Preparation
2.2. Micropatterning and Etching of Parylene-C for Micropore Array Preparation
2.3. Parylene-C Molding with PDMS Micropillar Array as the Template for Micropore Array Preparation
2.4. Parylene-C Molding with Silicon Micropillar Array as the Template for Micropore Array Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
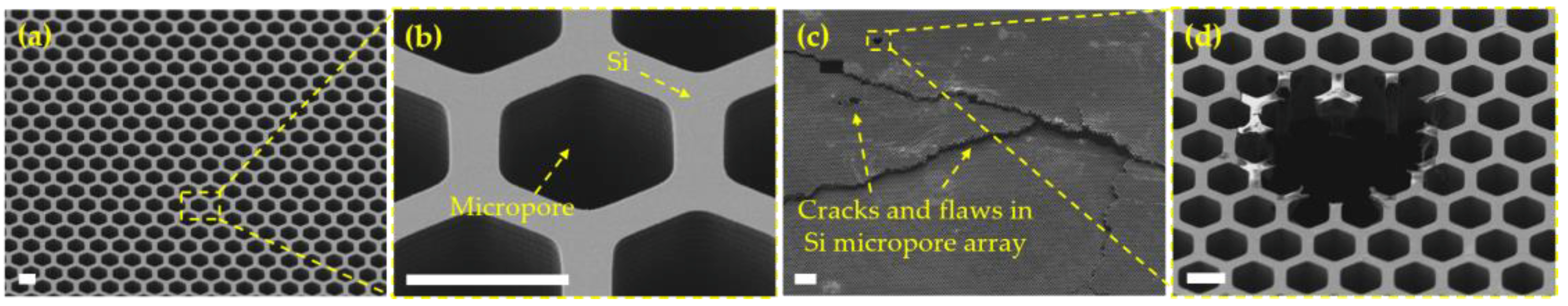
3.1. Micropore Arrays Obtained from Micropatterning and Etching of Silicon
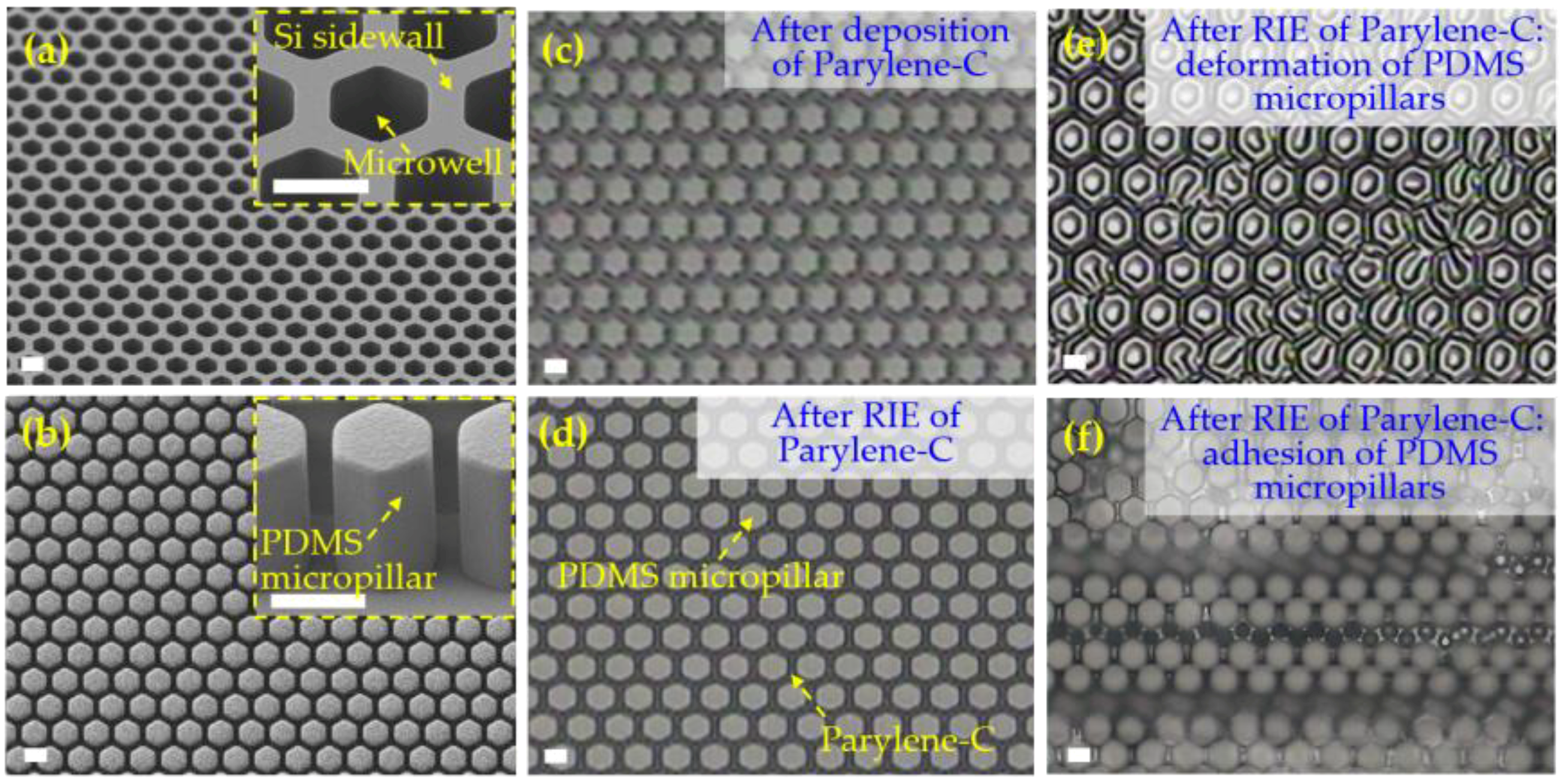
3.2. Micropore Arrays Obtained from Micropatterning and Etching of Parylene-C
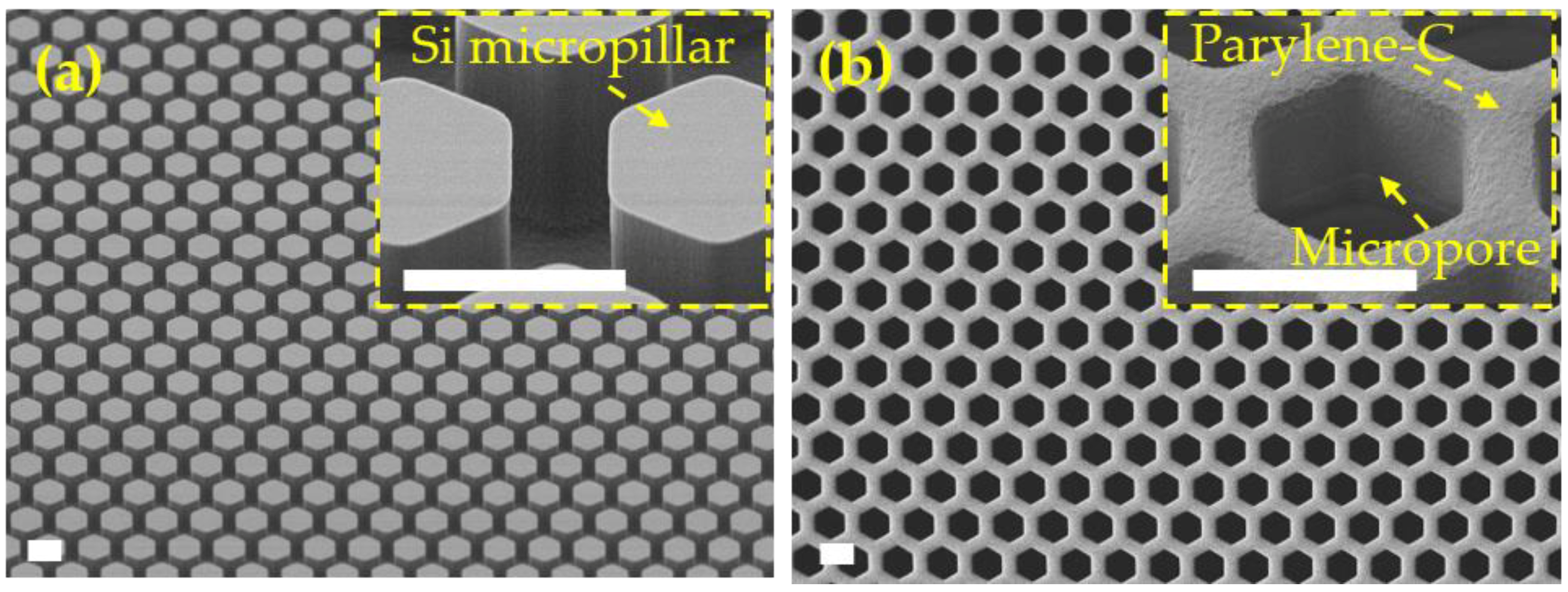
3.3. Micropore Arrays Obtained from Parylene-C Molding with PDMS Template
3.4. Micropore Arrays Obtained from Parylene-C Molding with Silicon Template
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arya, S.K.; Lim, B.; Rahman, A.R.A. Enrichment, detection and clinical significance of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1995–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.S.; Duffy, S.P.; Simon, P.; Ma, H. Microfluidic Separation of Circulating Tumor Cells Based on Size and Deformability. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1634, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Wu, L.; Tay, A.K.P.; Han, J. Large-volume microfluidic cell sorting for biomedical applications. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 17, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, C.W., IV; Ohiri, K.A.; Szott, L.M.; López, G.P. Translating microfluidics: Cell separation technologies and their barriers to commercialization. Cytometry Part B-Clin. Cytometry 2017, 92, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, R.L.; Price, P.B.; Symes, E.M.; Miller, D.S. Fission-track ages and track-annealing behavior of some micas. Science 1964, 143, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, R.L.; Alter, H.W.; Furman, S.C.; Price, P.B.; Walker, R.M. Particle track etching. Science 1972, 178, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolfus, C.; Piton, N.; Toure, E.; Sabourin, J.C. Circulating tumor cell isolation: The assets of filtration methods with polycarbonate track-etched filters. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 27, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desitter, I.; Guerrouahen, B.S.; Benali-Furet, N.; Wechsler, J.; Jänne, P.A.; Kuang, Y.; Yanagita, M.; Wang, L.; Berkowitz, J.A.; Distel, R.J.; et al. A new device for rapid isolation by size and characterization of rare circulating tumor cells. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Wit, S.; Van Dalum, G.; Lenferink, A.T.; Tibbe, A.G.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Groen, H.J.; Van Rijn, C.J.; Terstappen, L.W. The detection of EpCAM+ and EpCAM− circulating tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.L.; Zhu, P.; Makarova, O.V.; Martin, S.S.; Charpentier, M.; Chumsri, S.; Li, S.; Amstutz, P.; Tang, C.M. The systematic study of circulating tumor cell isolation using lithographic microfilters. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4334–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.L.; Stefansson, S.; Haudenschild, C.; Martin, S.S.; Charpentier, M.; Chumsri, S.; Cristofanilli, M.; Tang, C.M.; Alpaugh, R.K. Cytometric characterization of circulating tumor cells captured by microfiltration and their correlation to the CellSearch® CTC test. Cytometry Part A 2015, 87, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.L.; Alpaugh, R.K.; Martin, S.S.; Charpentier, M.; Chumsri, S.; Cristofanilli, M.; Adams, D.K.; Makarova, O.V.; Zhu, P.; Li, S.; et al. Precision microfilters as an all in one system for multiplex analysis of circulating tumor cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 6405–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.T.; Doh, I.; Cho, Y.H. Tapered-slit membrane filters for high-throughput viable circulating tumor cell isolation. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, M.; Arakaki, A.; Takahashi, M.; Mori, T.; Takeyama, H.; Matsunaga, T. High-density microcavity array for cell detection: Single-cell analysis of hematopoietic stem cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5308–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, M.; Hayata, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Arakaki, A.; Yoshino, T.; Tanaka, T.; Matsunaga, T. Size-selective microcavity array for rapid and efficient detection of circulating tumor cells. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6629–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Cayre, Y.E.; Chen, Y. Microfluidic device with integrated microfilter of conical-shaped holes for high efficiency and high purity capture of circulating tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Jia, C.; Yang, J.; Li, G.; Mao, H.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J. A microfluidic chip integrated with a high-density PDMS-based microfiltration membrane for rapid isolation and detection of circulating tumor cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harouaka, R.A.; Zhou, M.D.; Yeh, Y.T.; Khan, W.J.; Das, A.; Liu, X.; Christ, C.C.; Dicker, D.T.; Baney, T.S.; Kaifi, J.T.; et al. Flexible micro spring array device for high-throughput enrichment of viable circulating tumor cells. Clin. Chem. 2014, 60, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Lu, B.; Tai, Y.C.; Goldkorn, A. A cancer detection platform which measures telomerase activity from live circulating tumor cells captured on a microfilter. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6420–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Lin, H.; Liu, J.Q.; Balic, M.; Datar, R.; Cote, R.J.; Tai, Y.C. Membrane microfilter device for selective capture, electrolysis and genomic analysis of human circulating tumor cells. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1162, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Lin, H.K.; Lu, B.; Williams, A.; Datar, R.; Cote, R.J.; Tai, Y.C. 3D microfilter device for viable circulating tumor cell (CTC) enrichment from blood. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusa, A.; Toneri, M.; Masuda, T.; Ito, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Okochi, M.; Kondo, N.; Iwata, H.; Yatabe, Y.; Ichinosawa, Y.; et al. Development of a new rapid isolation device for circulating tumor cells (CTCs) using 3D palladium filter and its application for genetic analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Dai, W.; Li, H.; Wang, W. 2.5-Dimensional Parylene C micropore array with a large area and a high porosity for high-throughput particle and cell separation. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2018, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, W.; Yang, F.; Li, H. Filtration membrane with ultra-high porosity and pore size controllability fabricated by parylene c molding technique for targeted cell separation from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on TRANSDUCERS, Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Anchorage, AK, USA, 21–25 June 2015; pp. 1767–1769. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, E.; Li, P.Y.; Tai, Y.C. Plasma removal of Parylene C. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortigoza-Diaz, J.; Scholten, K.; Larson, C.; Cobo, A.; Hudson, T.; Yoo, J.; Baldwin, A.; Weltman Hirschberg, A.; Meng, E. Techniques and Considerations in the Microfabrication of Parylene C Microelectromechanical Systems. Micromachines 2018, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, W. SF6 Optimized O2 Plasma Etching of Parylene C. Micromachines 2018, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.S.; Tai, Y.C. Micromachined high-aspect-ratio parylene spring and its application to low-frequency accelerometers. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.C.; Chen, C.W. Fabrication suspended high-aspect-ratio parylene structures for large displacement requirements. Int. J. Autom. Smart Technol. 2014, 4, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ref. No. | Material | Fabrication Strategy | Area | Porosity 1 | Edge-to-Edge Space |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | Polycarbonate | Track-etching technique | 1 cm2 | N/A | N/A (Randomly distributed) |
| 9 | Silicon | Photolithography-based micropatterning, and DRIE and KOH etching | 0.64 cm2 | 10% | 9 μm |
| 10−12 | SU-8 | Photolithography-based micropatterning | 0.64 cm2 | <12.5% | 13 μm |
| 13 | SU-8 | Photolithography-based micropatterning | 1 cm2 | 6.2%/11% | N/A |
| 14 | PET | Photolithography-based micropatterning and laser drilling | 4 cm2 | 0.008% | 58 μm |
| 15 | Ni | Photolithography-based micropatterning and electroforming | 1 cm2 | 0.64% | 51 μm |
| 16 | PEGDA | Micropatterning and UV-assisted molding | 0.81 cm2 | 3.25−5.88% | 22−24.5 μm |
| 17 | PDMS | Modified soft lithography | 2.25 cm2 | 20% | 14.2−18.1 μm |
| 18 | Parylene-C | Photolithography-based micropatterning and oxygen plasma etching | 0.5 cm2 | N/A | N/A |
| 19 | Parylene-C | 0.36 cm2 | 18% | N/A | |
| 20 | Parylene-C | 1 cm2 | <5.6% | 10/12 μm | |
| 21 | Parylene-C | 1 cm2 | <6.96% | 11/12 μm | |
| 22 | Palladium | Photolithography-based micropatterning and electroforming | 1 cm2 | 5.02% | 4/26 μm |
| Process | Size Precision/Controllability | Realization of High Porosity | Process Robustness | Realization of Large Area | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micropatterning and etching of silicon | High | Yes | Poor | Difficult | Low |
| Micropatterning and etching of Parylene-C | Low | No | Poor | Achievable | Low |
| Parylene-C molding with PDMS template | Low | No | Poor | N/A | Low |
| Parylene-C molding with silicon template | High | Yes | Strong | Easily achievable | High |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Microfabrication of Micropore Array for Cell Separation and Cell Assay. Micromachines 2018, 9, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9120620
Liu Y, Xu H, Zhang L, Wang W. Microfabrication of Micropore Array for Cell Separation and Cell Assay. Micromachines. 2018; 9(12):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9120620
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yaoping, Han Xu, Lingqian Zhang, and Wei Wang. 2018. "Microfabrication of Micropore Array for Cell Separation and Cell Assay" Micromachines 9, no. 12: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9120620
APA StyleLiu, Y., Xu, H., Zhang, L., & Wang, W. (2018). Microfabrication of Micropore Array for Cell Separation and Cell Assay. Micromachines, 9(12), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9120620





