A Spherical Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Enhanced Water Wave Energy Harvesting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Characterization
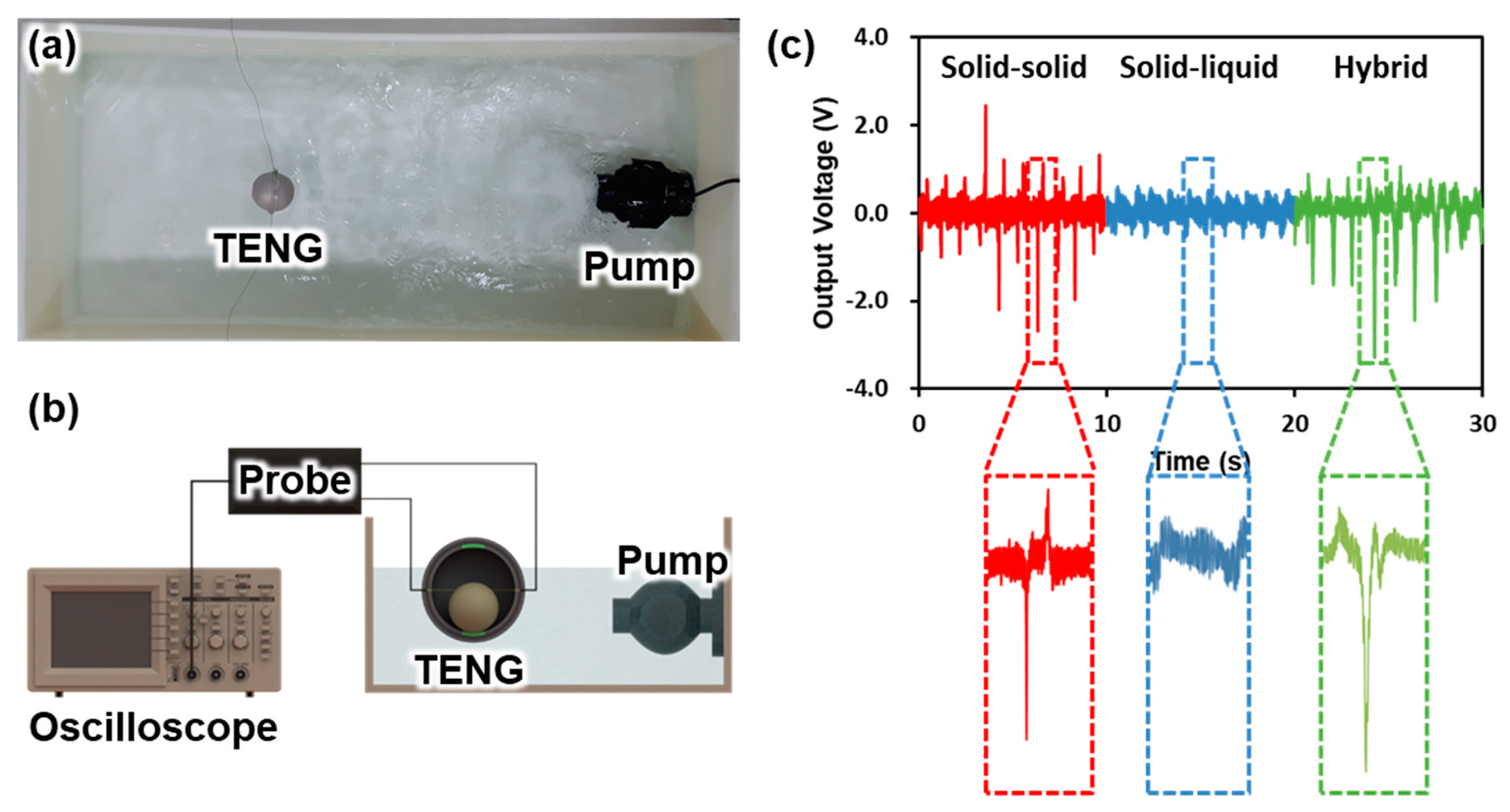
2.3. Electrical Output Measurement of the Spherical Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerator (SH-TENG)
3. Results and Discussion
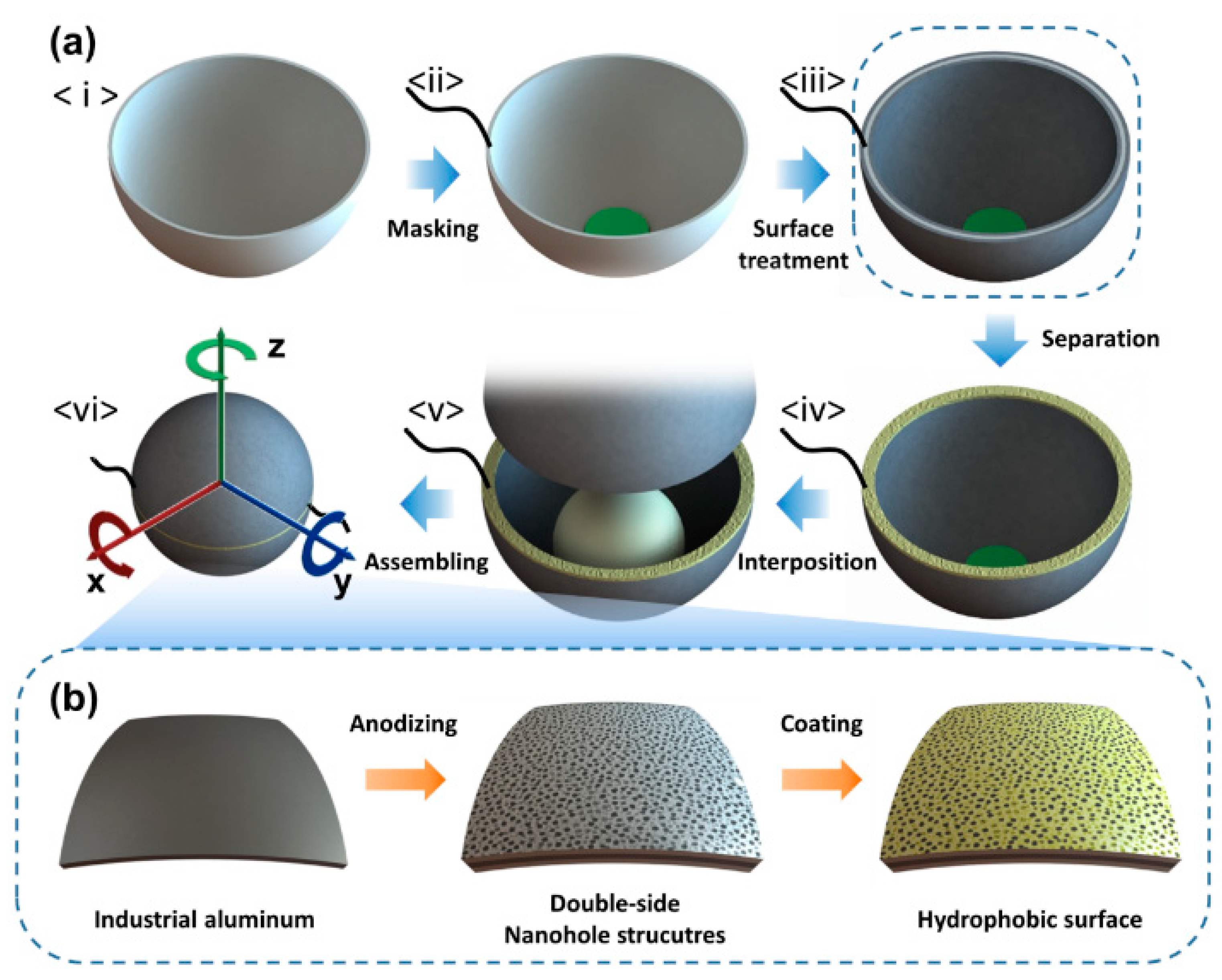
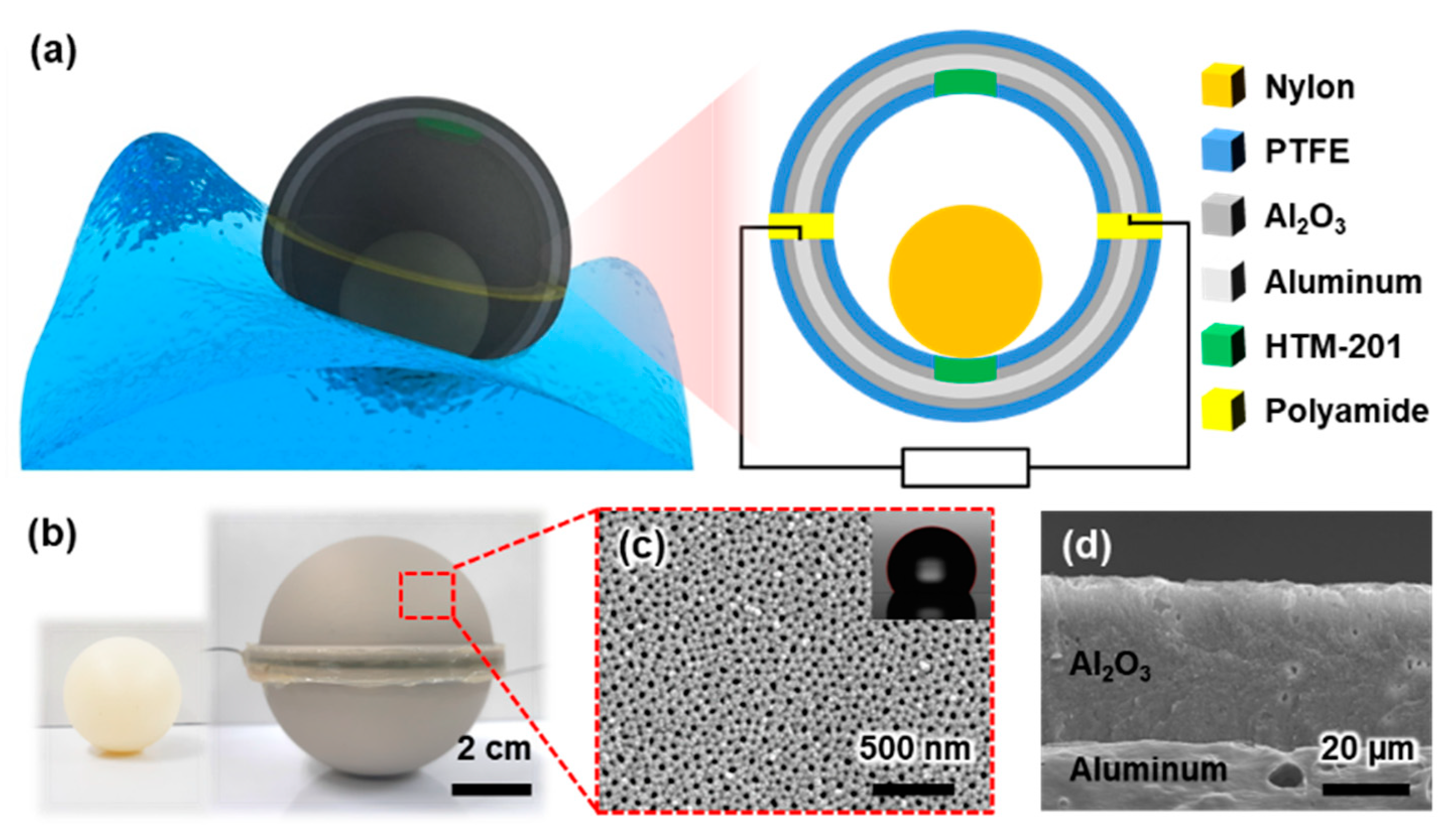
3.1. Design and Features of the SH-TENG
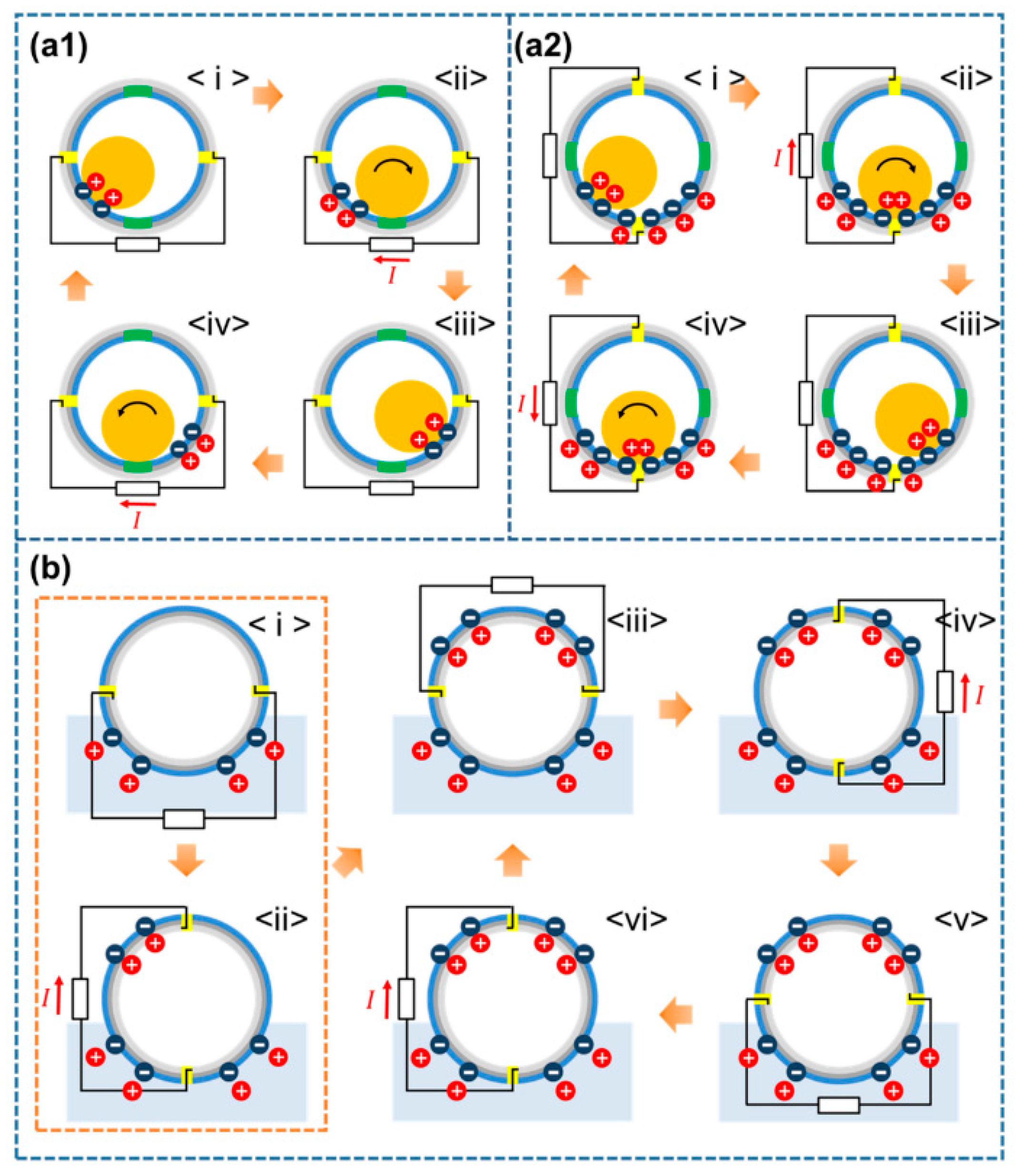
3.2. Operating Principle
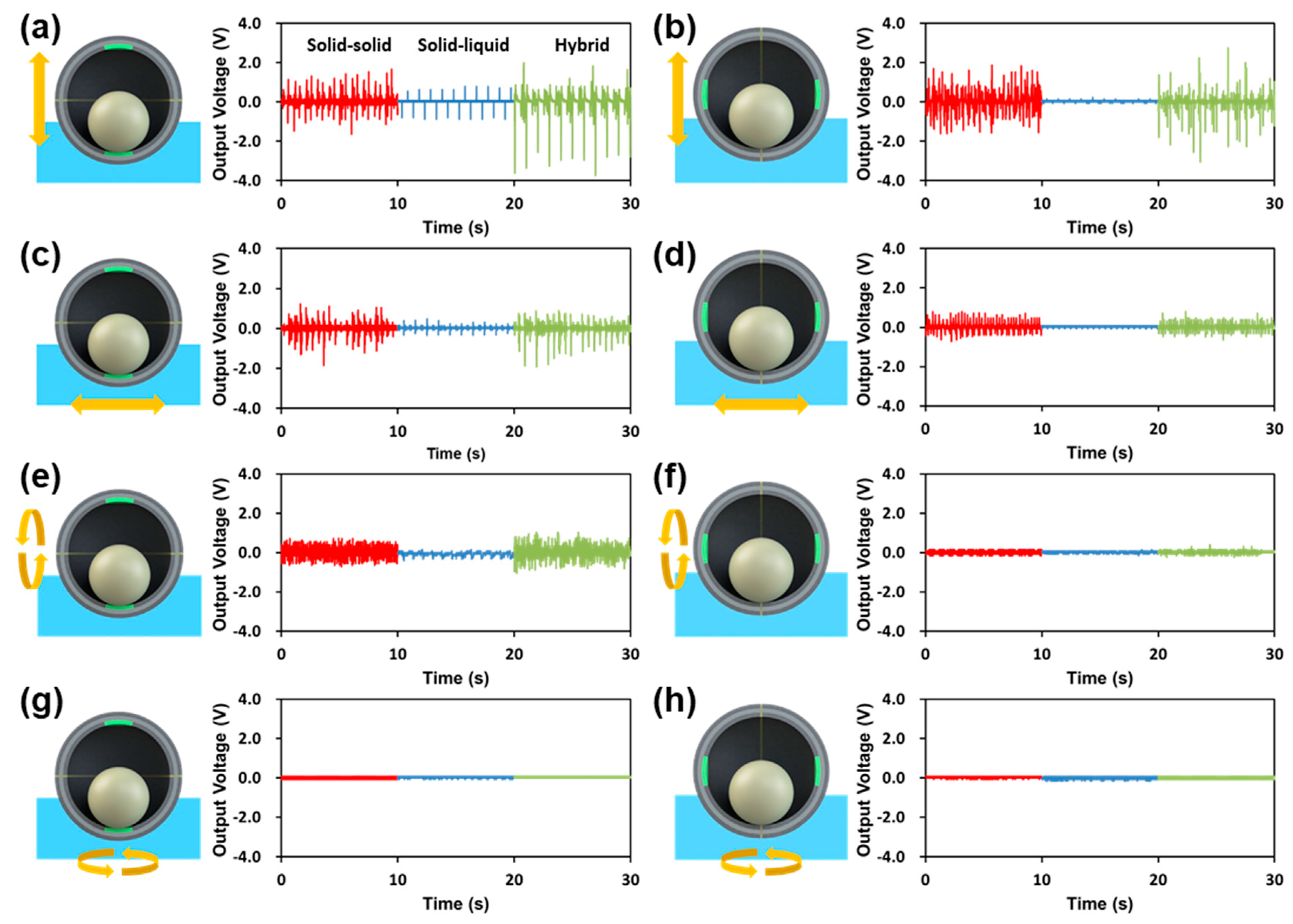
3.3. Electrical Output of SH-TENG during 6 Degrees of Freedom (DoF) Motion
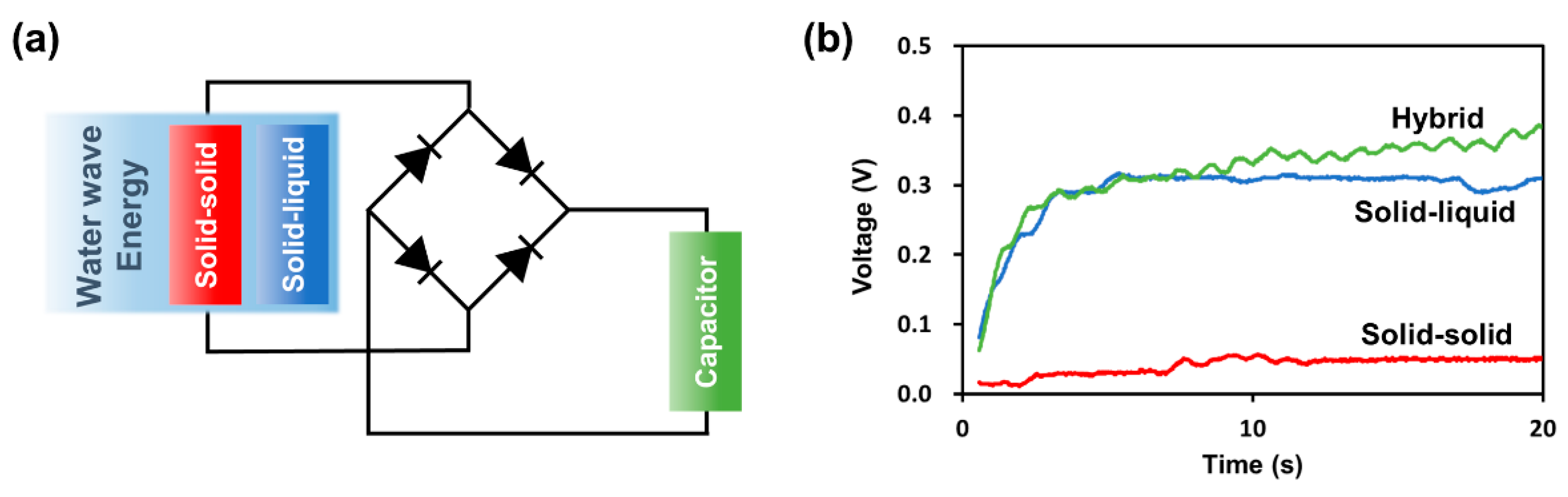
3.4. Electrical Output of SH-TENG for Water Wave Motion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schiermeier, Q.; Tollefson, J.; Scully, T.; Witze, A.; Morton, O. Electricity without Carbon. Nature 2008, 454, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, J.A. US renewable energy consumption. Clean. Techn. Environ. Policy 2007, 9, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clery, D. Renewable energy. U.K. ponders world’s biggest tidal power scheme. Science 2008, 320, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, M.-L.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Ray Liu, K.J. Advances in Energy Harvesting Communications: Past, Present, and Future Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1384–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Kempa, T.J.; Lieber, C.M. Single nanowire photovoltaics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zou, H.; Liu, R.; Tao, C.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.L. Micro-cable structured textile for simultaneously harvesting solar and mechanical energy. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Pan, C. Progress in nanogenerators for portable electronics. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.L. Direct-Current Nanogenerator Driven by Ultrasonic Waves. Science 2007, 316, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Guo, W.; Yang, J.; Du, J.; Fan, X.; Tao, C. A Wearable All-Solid Photovoltaic Textile. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Awais, Q.; Yang, J. Broadband and three-dimensional vibration energy harvesting by a non-linear magnetoelectric generator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 253903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, Z.L. Piezoelectric Nanogenerators Based on Zinc Oxide Nanowire Arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellabban, O.; Abu-Rub, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Renewable energy resources: Current status, future prospects and their enabling technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 748–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Guo, H.; Zi, Y.; Yeh, M.H.; Wang, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Hu, C.; Zhu, L.; et al. Harvesting Broad Frequency Band Blue Energy by a Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6526–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, E. Energy: To Catch a Wave. Nature 2007, 450, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scruggs, J.; Jacob, P. Engineering. Harvesting Ocean Wave Energy. Science 2009, 323, 1176–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forristall, G.Z. Measurements of a saturated range in ocean wave spectra. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouws, E.; Günther, H.; Rosenthal, W.; Vincent, C.L. Similarity of the wind wave spectrum in finite depth water: 1. Spectral form. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 1985, 90, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffoli, A.; Bitner-Gregersen, E.M. Types of Ocean Surface Waves, Wave Classification. Enc. Mari. Offshore Eng. 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On Maxwell’s displacement current for energy and sensors: The origin of nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology and self-powered sensors-principles, problems and perspectives. Faraday Discuss. 2014, 176, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, Y.; Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Yeh, M.H.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Low-Frequency (<5 Hz) Irregular Mechanical Energy: A Possible Killer Application of Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4797–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Nanoscale triboelectric-effect-enabled energy conversion for sustainably powering portable electronics. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6339–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Sliding-triboelectric nanogenerators based on in-plane charge-separation mechanism. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2226–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Quantitative Measurements of Vibration Amplitude Using a Contact-Mode Freestanding Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12004–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding triboelectric-layer-based nanogenerators for harvesting energy from a moving object or human motion in contact and non-contact modes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, J. Large-Scale and Washable Smart Textiles Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator Arrays for Self-Powered Sleeping Monitoring. Adv. Func. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L. Progress in triboelectric nanogenerators as a new energy technology and self-powered sensors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2250–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Reviving Vibration Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensing by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Joule 2017, 1, 480–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, W.; Jing, Q.; Bai, P.; Yang, Y.; Hou, T.C.; Wang, Z.L. Harmonic-resonator-based triboelectric nanogenerator as a sustainable power source and a self-powered active vibration sensor. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6094–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Deng, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Safety Helmet Based on Hybridized Nanogenerator for Emergency. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7874–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, J.; Bai, P.; Su, Y.; Jing, Q.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Energy from the Natural Vibration of Human Walking. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11317–11324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Power-generating shoe insole based on triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered consumer electronics. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.-C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.-J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator built inside shoe insole for harvesting walking energy. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, K.; Wei, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Enabled Body Sensor Network for Self-Powered Human Heart-Rate Monitoring. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8830–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Lin, Z.-H.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.L. Integrated Multilayered Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Biomechanical Energy from Human Motions. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3713–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W.; Bai, P.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Broadband Vibrational Energy Harvesting Based on a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, J.; Jing, Q.; Bai, P.; Yang, W.; Qi, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Personalized Keystroke Dynamics for Self-Powered Human-Machine Interfacing. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, L.; Pradel, K.C.; Fan, X.; Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Yeh, M.-H.; Yu, C.; et al. High-efficiency ramie fiber degumming and self-powered degumming wastewater treatment using triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2016, 22, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Kuang, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Wang, A.C.; Ding, W.; Lai, Y.-C.; Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Lin, Z.; et al. Shape Memory Polymers for Body Motion Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Mechanosensing. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.H.; Cheng, G.; Lin, L.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.L. Water-solid surface contact electrification and its use for harvesting liquid-wave energy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12777–12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.H.; Cheng, G.; Lee, S.; Pradel, K.C.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting water drop energy by a sequential contact-electrification and electrostatic-induction process. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4690–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Built on Suspended 3D Spiral Structure as Vibration and Positioning Sensor and Wave Energy Harvester. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10424–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Zi, Y.; Jing, Q.; Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Pradel, K.C.; Niu, S.; et al. Networks of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Harvesting Water Wave Energy: A Potential Approach toward Blue Energy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Q.; Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Xie, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, R.P.S.; Wang, Z.L. Case-Encapsulated Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Energy from Reciprocating Sliding Motion. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3836–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L.; Su, Y.; Wen, Z.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.L. Automatic Mode Transition Enabled Robust Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 12334–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Long, L.; Jing, Q.; Lin, Z.-H.; Niu, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on a Hybridized Mechanism for Harvesting Wind Energy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7119–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Lin, Z.-H.; Du, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Simultaneously Harvesting Electrostatic and Mechanical Energies from Flowing Water by a Hybridized Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, J.; Adams, K.; Lee, S.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Vibration Energy in Full Space and as Self-Powered Acceleration Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, S.; Yin, Y.; Yi, F.; You, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Fully Enclosed Rolling Spherical Structure for Harvesting Low-Frequency Water Wave Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, M.L.; Han, J.W.; Jeon, S.B.; Meyyappan, M.; Choi, Y.K. Floating Oscillator-Embedded Triboelectric Generator for Versatile Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Saadatnia, Z.; Hassan, I.; Zi, Y.; Xi, Y.; He, X.; Zu, J.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Wireless Sensor Node Enabled by a Duck-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Water Wave Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhu, G.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Bai, P.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Hybrid triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting water wave energy and as a self-powered distress signal emitter. Nano Energy 2014, 9, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, G.; Wu, W.; Pradel, K.C.; Wang, Z.L. Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Water Energy and as a Self-Powered Ethanol Nanosensor. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6440–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Lee, C. Self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator buoy ball for applications ranging from environment monitoring to water wave energy farm. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Gu, L.; Lei, Y.; Liu, J.; Qin, Y.; Ma, X.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Dynamic Behavior of the Triboelectric Charges and Structural Optimization of the Friction Layer for a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6131–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooding, D.M.; Kaufman, G.K. Tribocharging and the Triboelectric Series. Encycl. Inorg. Bioinorg. Chem. 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Hwang, W. Theoretical study of micro/nano roughness effect on water-solid triboelectrification with experimental approach. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Investigation and Structural Optimization of Single-Electrode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.S.; Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theory of freestanding triboelectric-layer-based nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.; Lee, J.-w.; Kim, K.; Yoo, D.; Kim, D.S.; Hwang, W.; Song, I.; Sim, J.-Y. A Spherical Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Enhanced Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Micromachines 2018, 9, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110598
Lee K, Lee J-w, Kim K, Yoo D, Kim DS, Hwang W, Song I, Sim J-Y. A Spherical Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Enhanced Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Micromachines. 2018; 9(11):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110598
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kwangseok, Jeong-won Lee, Kihwan Kim, Donghyeon Yoo, Dong Sung Kim, Woonbong Hwang, Insang Song, and Jae-Yoon Sim. 2018. "A Spherical Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Enhanced Water Wave Energy Harvesting" Micromachines 9, no. 11: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110598
APA StyleLee, K., Lee, J.-w., Kim, K., Yoo, D., Kim, D. S., Hwang, W., Song, I., & Sim, J.-Y. (2018). A Spherical Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Enhanced Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Micromachines, 9(11), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110598




