A Bi-Directional Out-of-Plane Actuator by Electrostatic Force
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structure and Operation Principle
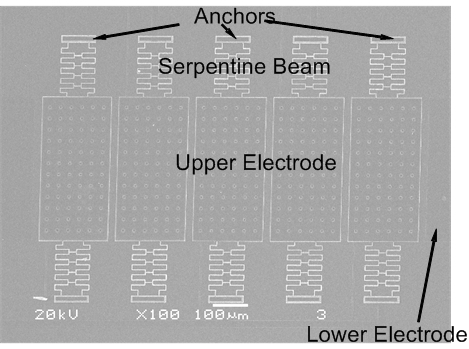
2.1. Structure of a Novel Bi-Directional Out-of-Plane Actuator
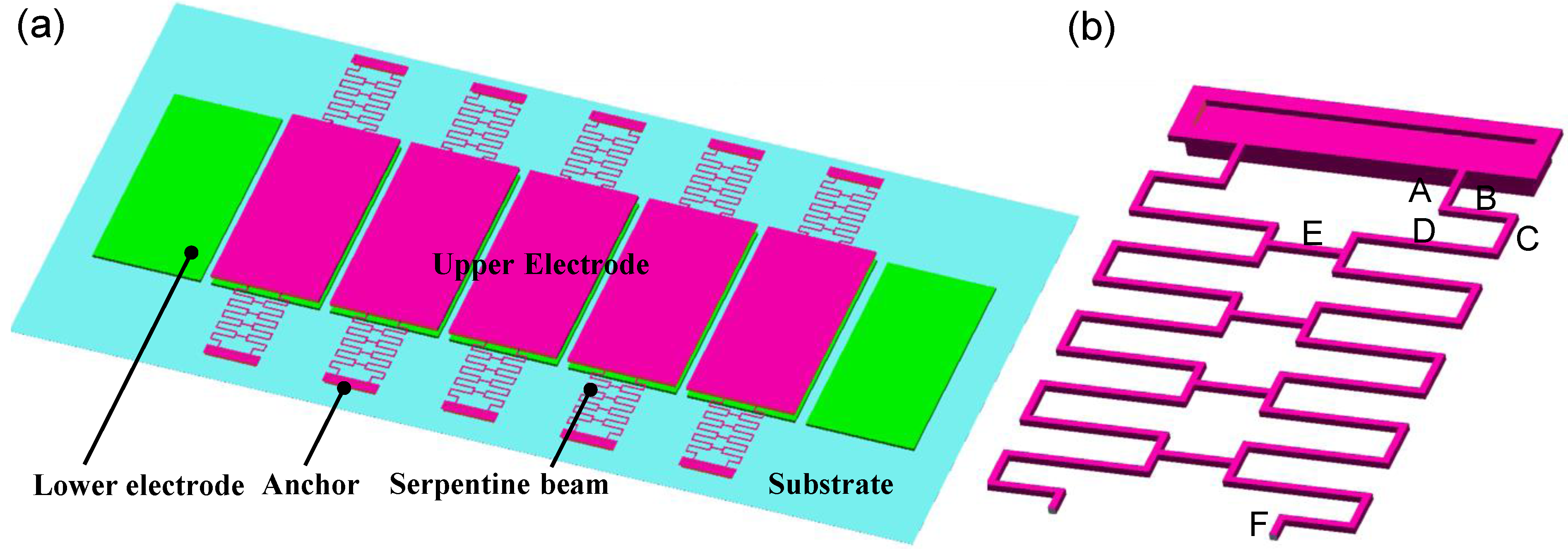
2.2. Operation Principle
2.2.1. Electrostatic Repulsive Mode
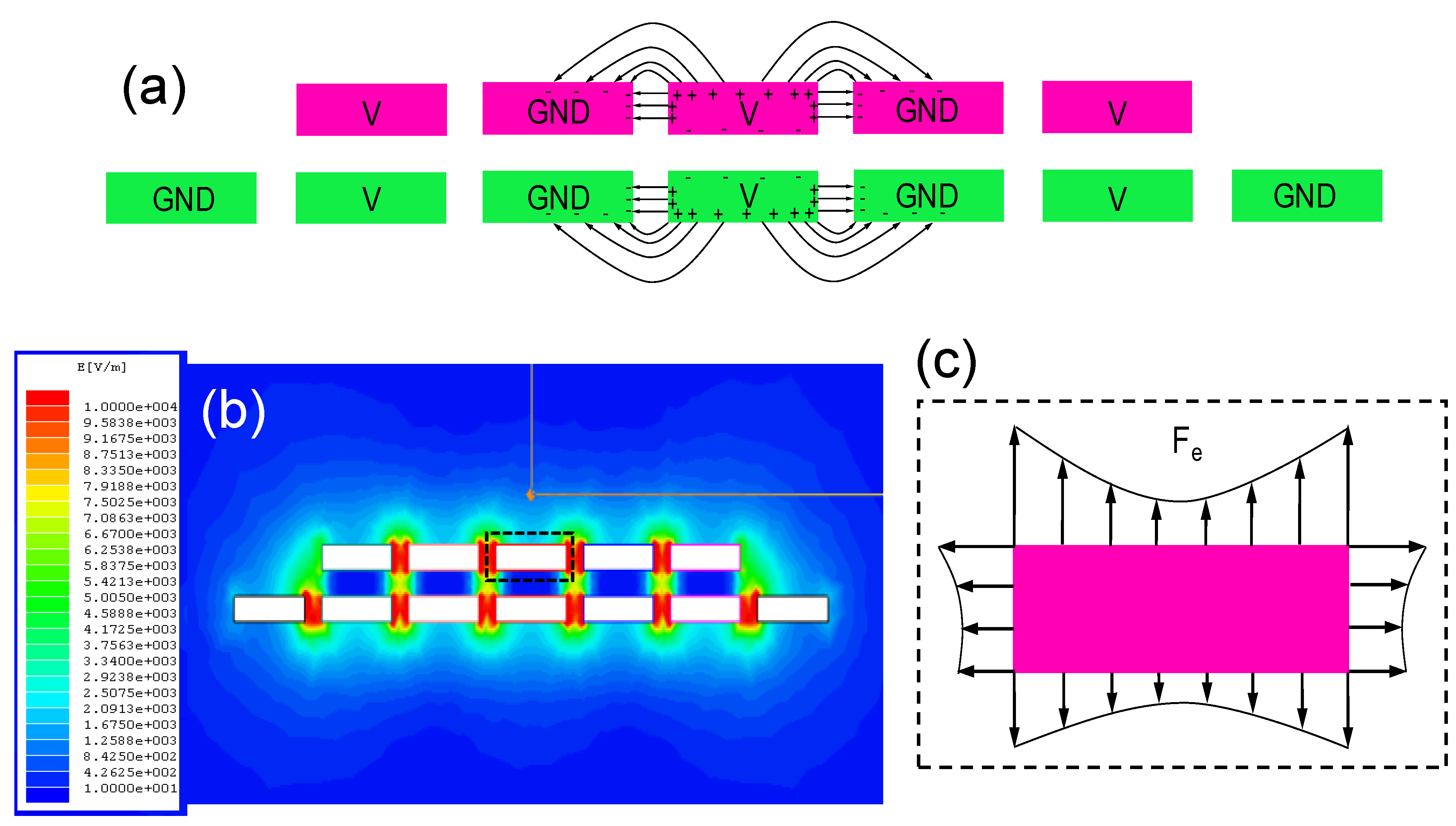
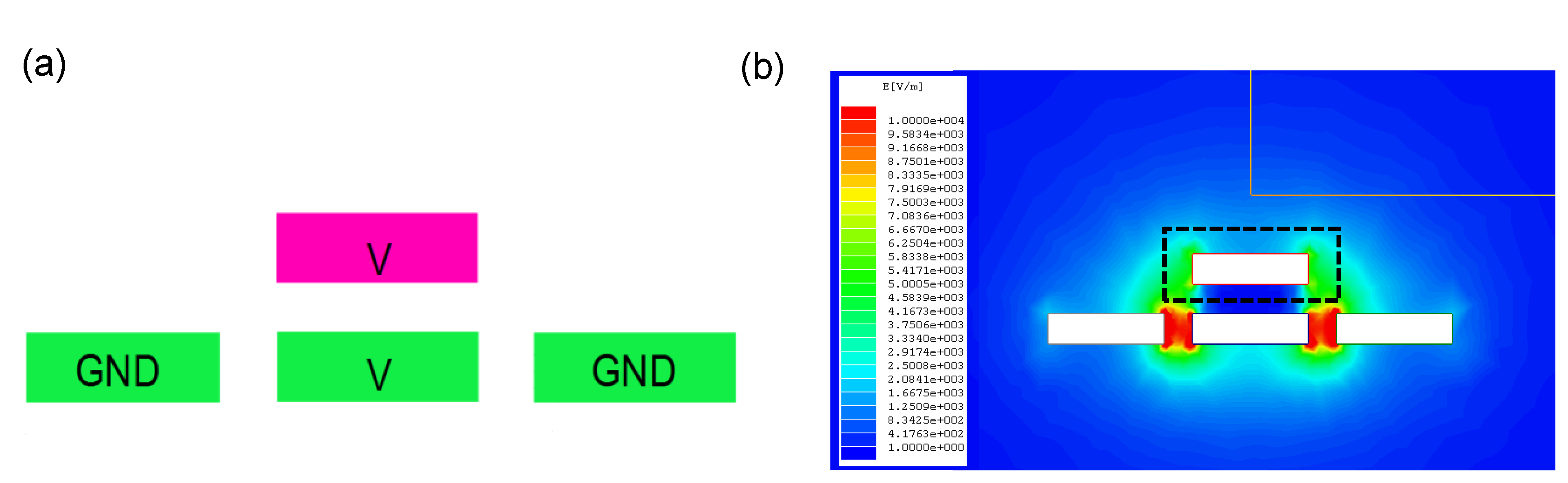
2.2.2. Electrostatic Attractive Mode
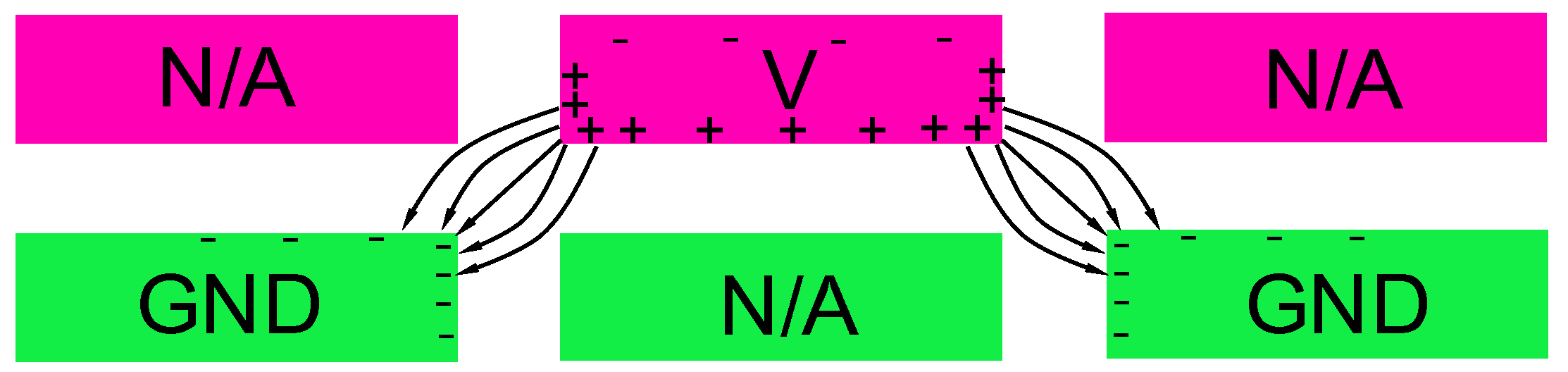
3. Characteristics of the Actuator
3.1. The Length of Electrodes
3.2. The Width of Electrodes
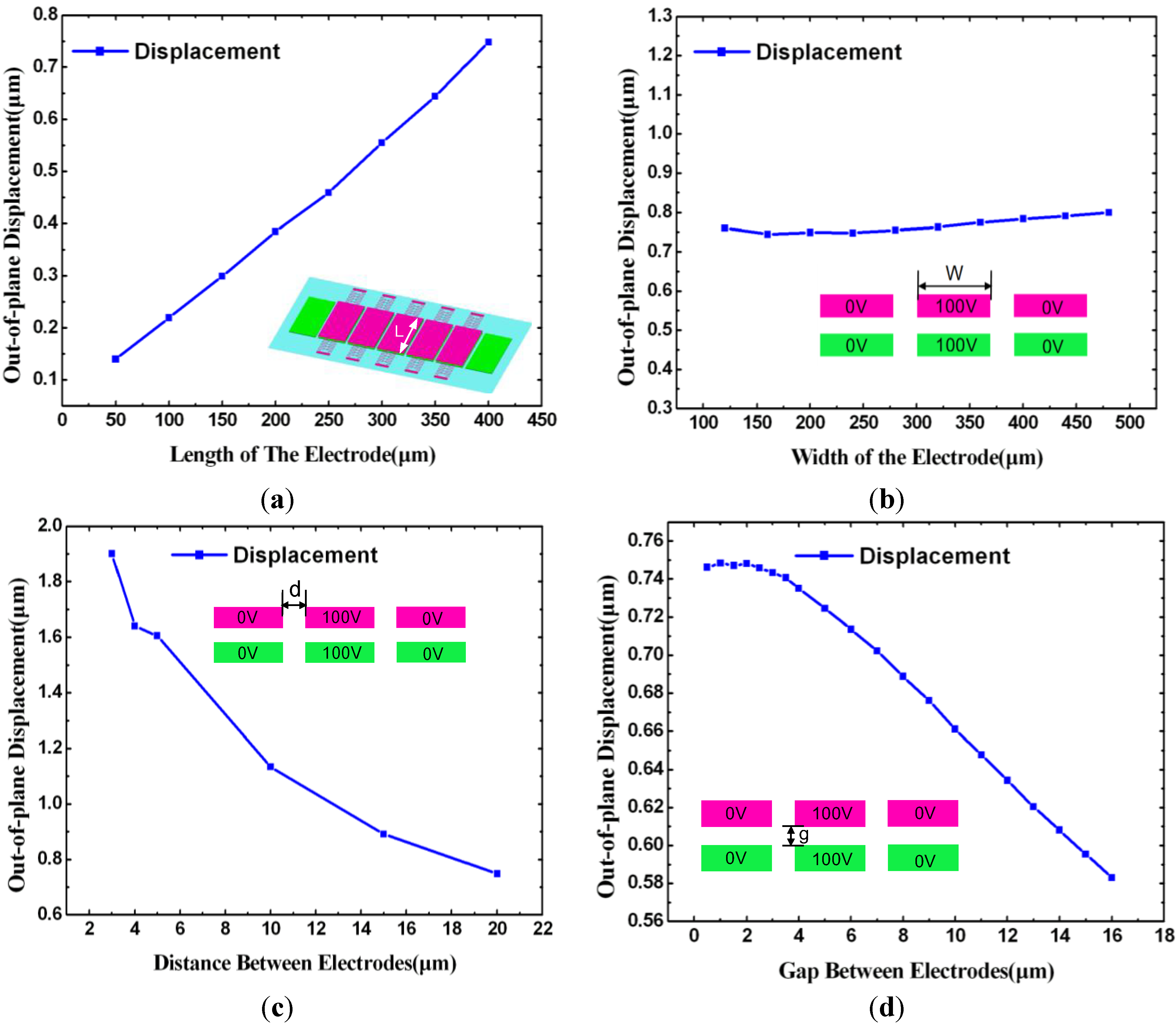
3.3. The Distance between Electrodes
3.4. Gap between Upper and Lower Electrodes
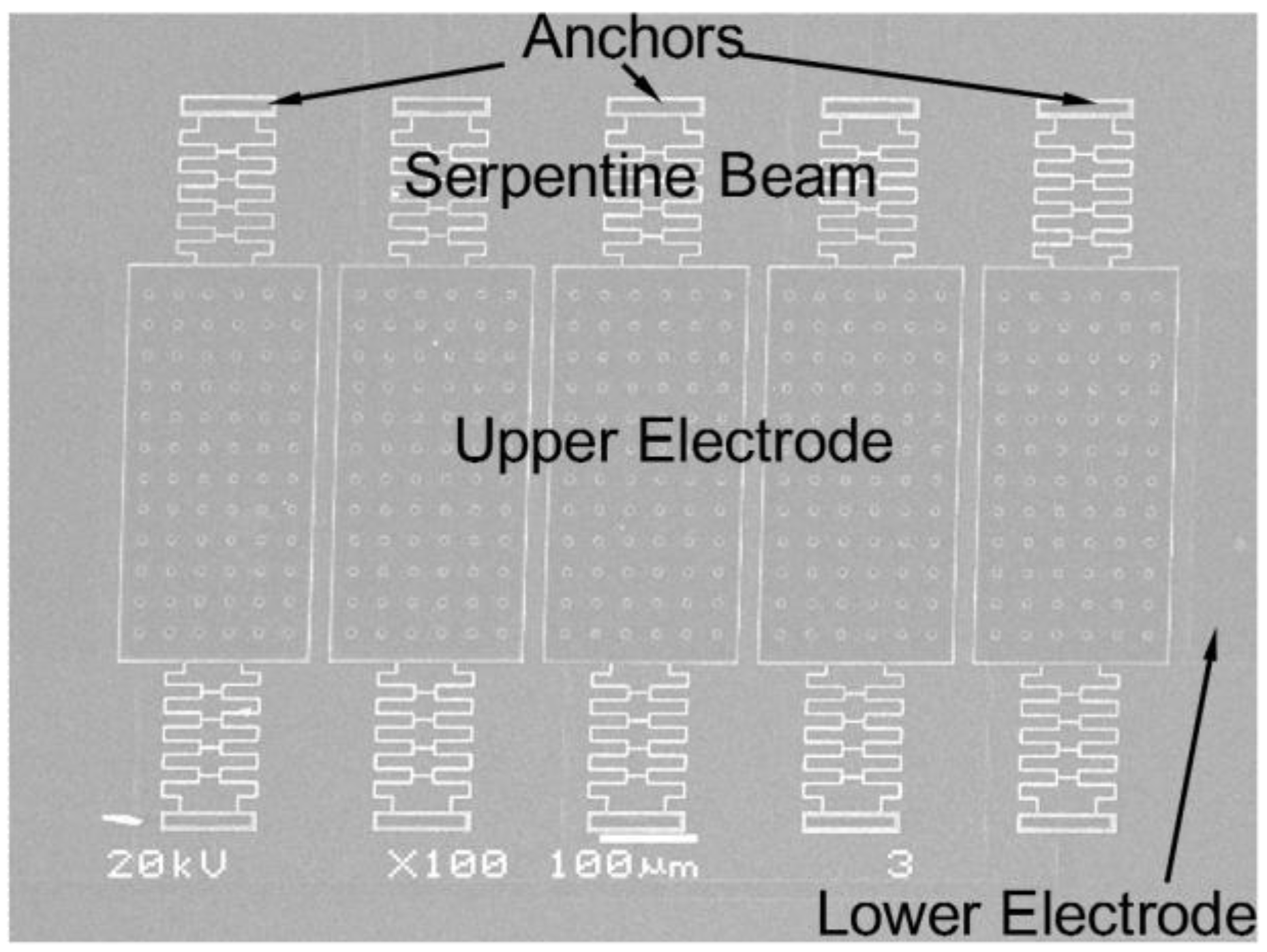
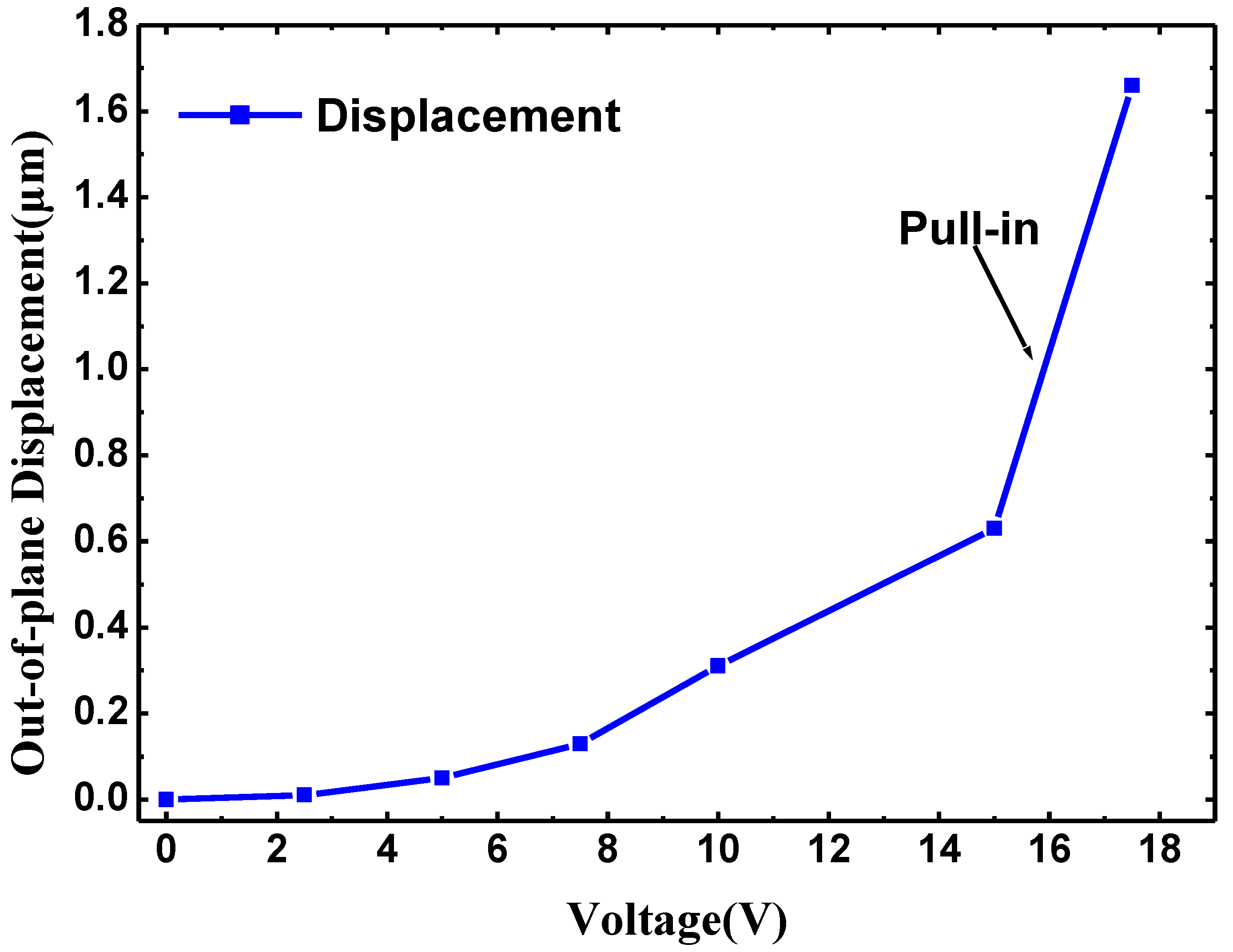
4. Fabrication and Test
| Description | Symbol | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Length of electrode | L | 400 |
| Width of electrode | w | 200 |
| Gap between electrodes | g | 2 |
| Distance between electrodes | d | 20 |
| Serpentine beam segment | A | 14 |
| Serpentine beam segment | B | 19 |
| Serpentine beam segment | C | 16 |
| Serpentine beam segment | D | 38 |
| Serpentine beam segment | E | 20 |
| Serpentine beam segment | F | 12 |



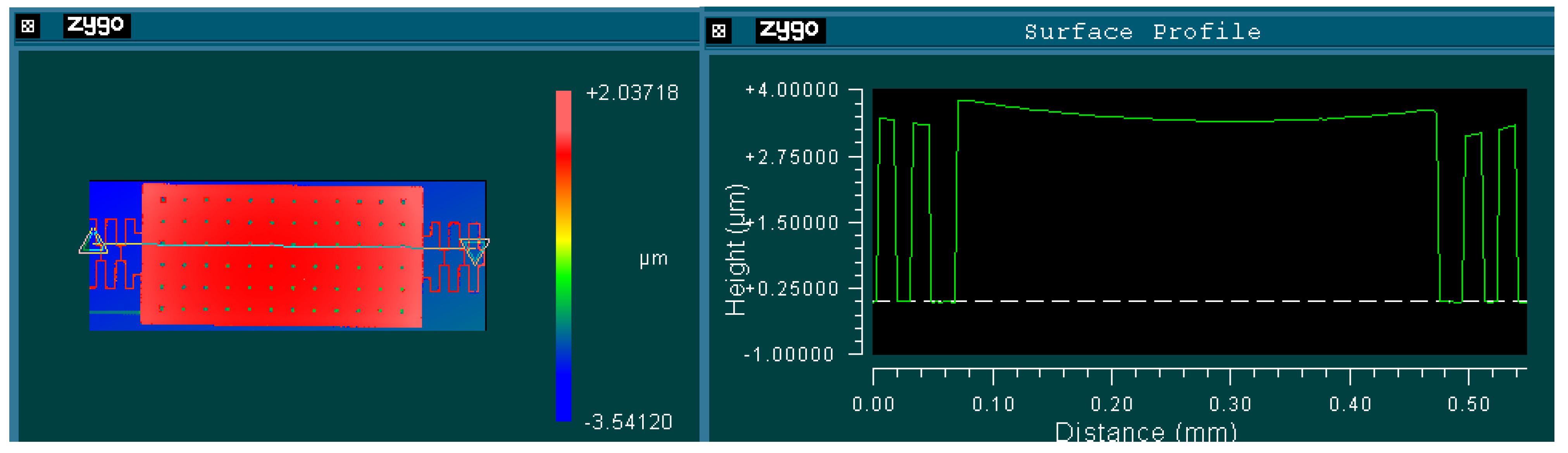
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horenstein, M.N.; Pappas, S.; Fishov, A.; Bifano, T.G. Electrostatic micromirrors for subaperturing in an adaptive optics system. J. Electrostat. 2002, 54, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hah, D.; Huang, S.-Y.; Tsai, J.-C.; Toshiyoshi, H.; Wu, M.C. Low-voltage, large-scan angle mems analog micromirror arrays with hidden vertical comb-drive actuators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2004, 13, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.B.; Bifano, T.G.; Cornelissen, S.; Bierden, P.; Levine, B.M.; Cook, T. Design and development of a 331-segment tip–tilt–piston mirror array for space-based adaptive optics. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 138, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, E.; Olivier, S.; Solgaard, O. Large-stroke self-aligned vertical comb drive actuators for adaptive optics applications. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Su, B.; Harsh, K.F.; Gupta, K.; Bright, V.; Lee, Y. Design and Modeling of RF MEMS Tunable Capacitors using Electro-thermal Actuators. In Proceedings of Microwave Symposium Digest, 1999 IEEE MTT-S International, Anaheim, CA, USA, 13–19 June 1999; pp. 1507–1510.
- Rebeiz, G.M.; Muldavin, J.B. RF MEMS switches and switch circuits. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2001, 2, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakri-Kassem, M.; Mansour, R.R. Two movable-plate nitride-loaded MEMS variable capacitor. IEEE T. Microw. Theory 2004, 52, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Mrad, R.B. A Novel MEMS Tunable Capacitor. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on MEMS, NANO and Smart Systems, Banff, Alberta, Canada, 25–27 August 2004; pp. 618–622.
- Ji, C.-H.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Yee, Y.; Bu, J.-U. An electrostatic scanning micromirror with diaphragm mirror plate and diamond-shaped reinforcement frame. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugat, O.; Basrour, S.; Divoux, C.; Mounaix, P.; Reyne, G. Deformable magnetic mirror for adaptive optics: Technological aspects. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 89, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-H.; Li, B.-Q.; Feng, Y.; Chu, J.-R. Design, fabrication and characterization of a bulk-pzt-actuated MEMS deformable mirror. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atre, A. Analysis of out-of-plane thermal microactuators. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.W. Adaptive Optics for Astronomical Telescopes; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Yao, J.; Qiu, C.; Ren, H. A MEMS micromirror driven by electrostatic force. J. Electrost. 2010, 68, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, S.; Bierden, P.; Bifano, T. A 4096 element continuous facesheet mems deformable mirror for high-contrast imaging. J. Micro/Nanolith. MEMS MOEMS 2009, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-t.; Brown, R.A.; Mathews, S.; Farmer, K. Extending the Travel Range of Electrostatic Micro-Mirrors Using Insulator Coated Electrodes. In Proceedings of 2000 IEEE/LEOS International Conference on Optical MEMS, Sheraton Kauai, HI, USA, 21–24 August 2000; pp. 151–152.
- Helmbrecht, M.A.; He, M.; Juneau, T.; Hart, M.; Doble, N. Segmented MEMS deformable-mirror for wavefront correction. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagel, D.J.; Cowan, W.D.; Spahn, O.B.; Grossetete, G.D.; Griñe, A.J.; Shaw, M.J.; Resnick, P.J.; Jokiel, B., Jr. Large-stroke MEMS deformable mirrors for adaptive optics. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deladi, S.; Krijnen, G.; Elwenspoek, M. Parallel-beams/lever electrothermal out-of-plane actuator. Microsyst. Technol. 2004, 10, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-C.; Wu, M.C. Design, fabrication, and characterization of a high fill-factor, large scan-angle, two-axis scanner array driven by a leverage mechanism. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Tao, F.; Wang, W.; Yao, J. An out-of-plane electrostatic actuator based on the lever principle. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 045019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Ni, Z.G.; Chen, J.M.; Gong, A.L.; Yao, J. A micro spatial light modulator based on leverage principle. Key Eng. Mat. 2011, 483, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.B.; Cho, Y.-H. Laterally driven electrostatic repulsive-force microactuators using asymmetric field distribution. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2001, 10, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Ben Mrad, R. Design, modeling, and demonstration of a MEMS repulsive-force out-of-plane electrostatic micro actuator. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Hu, F.; Cai, D.; Jiang, W. Design and analysis of repulsive electrostatic driven MEMS actuators. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Hu, F; Qiu, C.; Yao, J. Design and analysis of a novel out-of-plane actuator. (in Chinese). J. Micronanoelectron. Technol. 2009, 46, 546–550. [Google Scholar]
- IntelliSense. Available online: http://www.intellisense.com (accessed on 1 November 2013).
- MUMPs. Available online: http://www.memscap.com/en_mumps.html (accessed on 1 November 2013).
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, H.; Wang, W.; Tao, F.; Yao, J. A Bi-Directional Out-of-Plane Actuator by Electrostatic Force. Micromachines 2013, 4, 431-443. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi4040431
Ren H, Wang W, Tao F, Yao J. A Bi-Directional Out-of-Plane Actuator by Electrostatic Force. Micromachines. 2013; 4(4):431-443. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi4040431
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Hao, Weimin Wang, Fenggang Tao, and Jun Yao. 2013. "A Bi-Directional Out-of-Plane Actuator by Electrostatic Force" Micromachines 4, no. 4: 431-443. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi4040431
APA StyleRen, H., Wang, W., Tao, F., & Yao, J. (2013). A Bi-Directional Out-of-Plane Actuator by Electrostatic Force. Micromachines, 4(4), 431-443. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi4040431