Design of an Afocal Telescope System Integrated with Digital Imaging for Enhanced Optical Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design Methodology
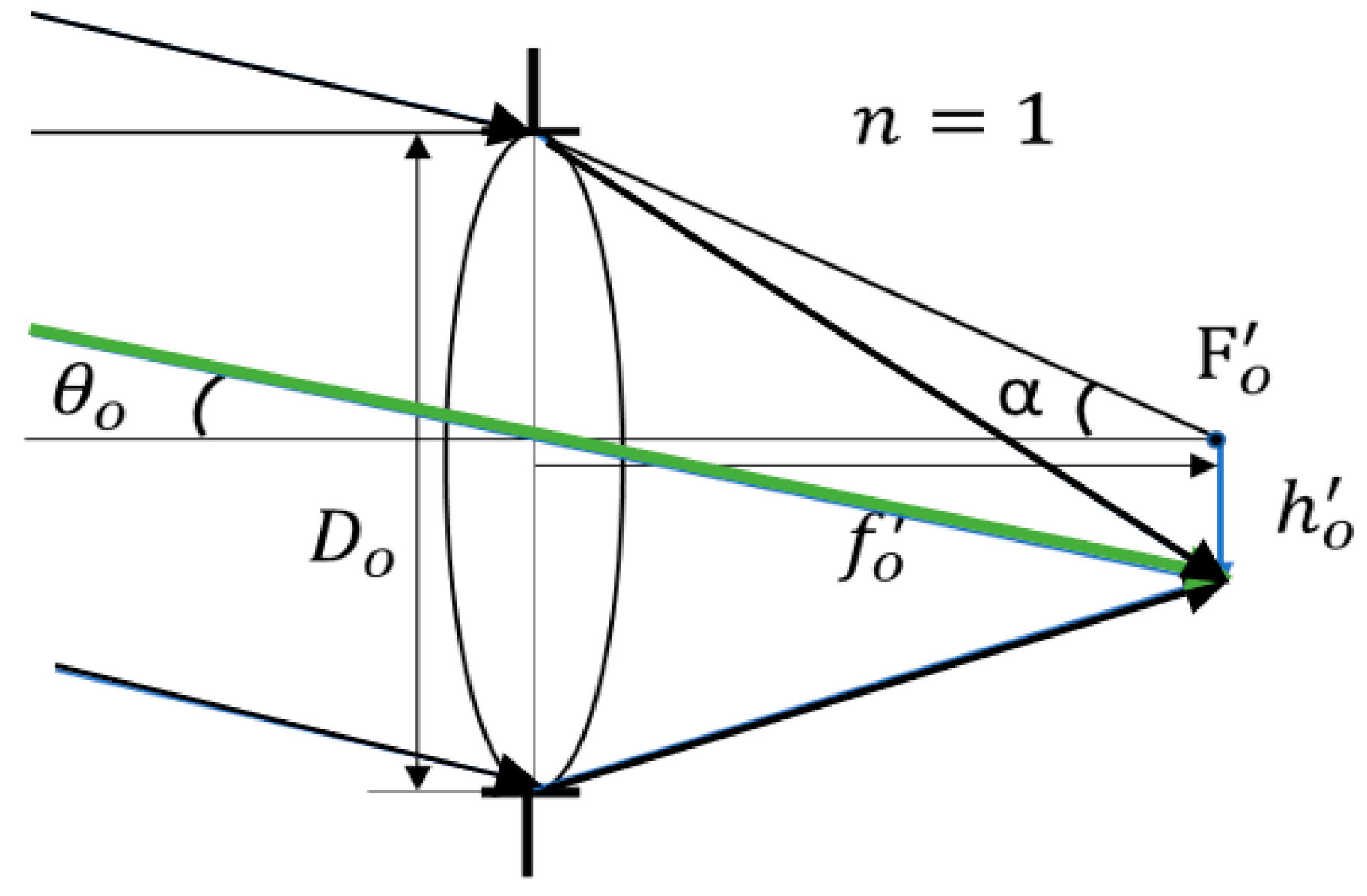
2.1. Objective Lens Design
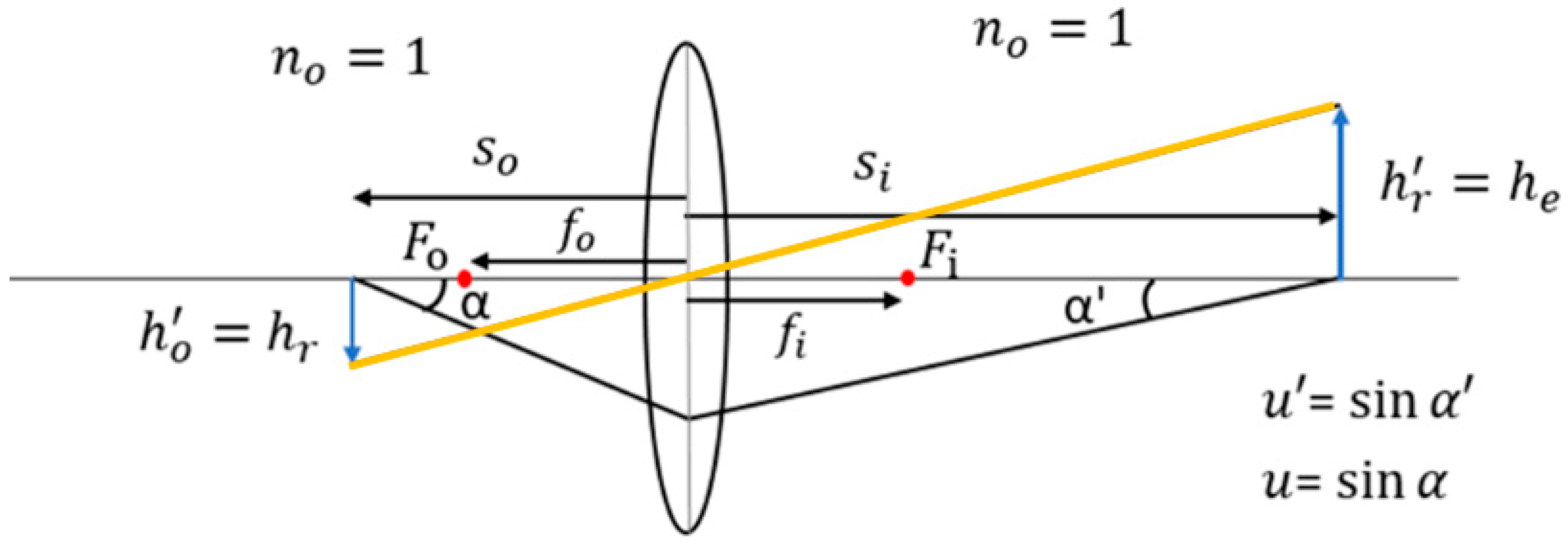
2.2. Erecting Lens Design
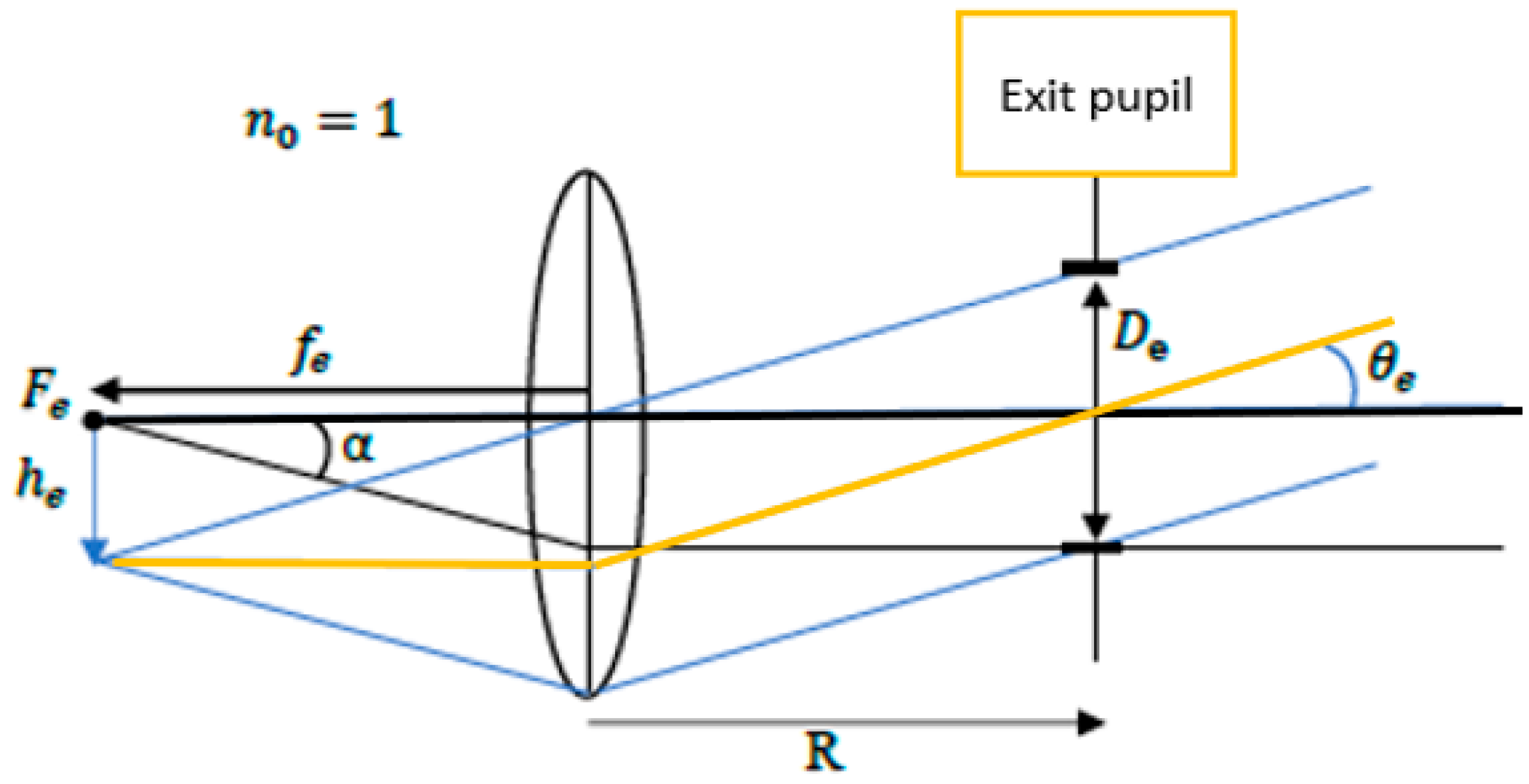
2.3. Eyepiece Lens Design
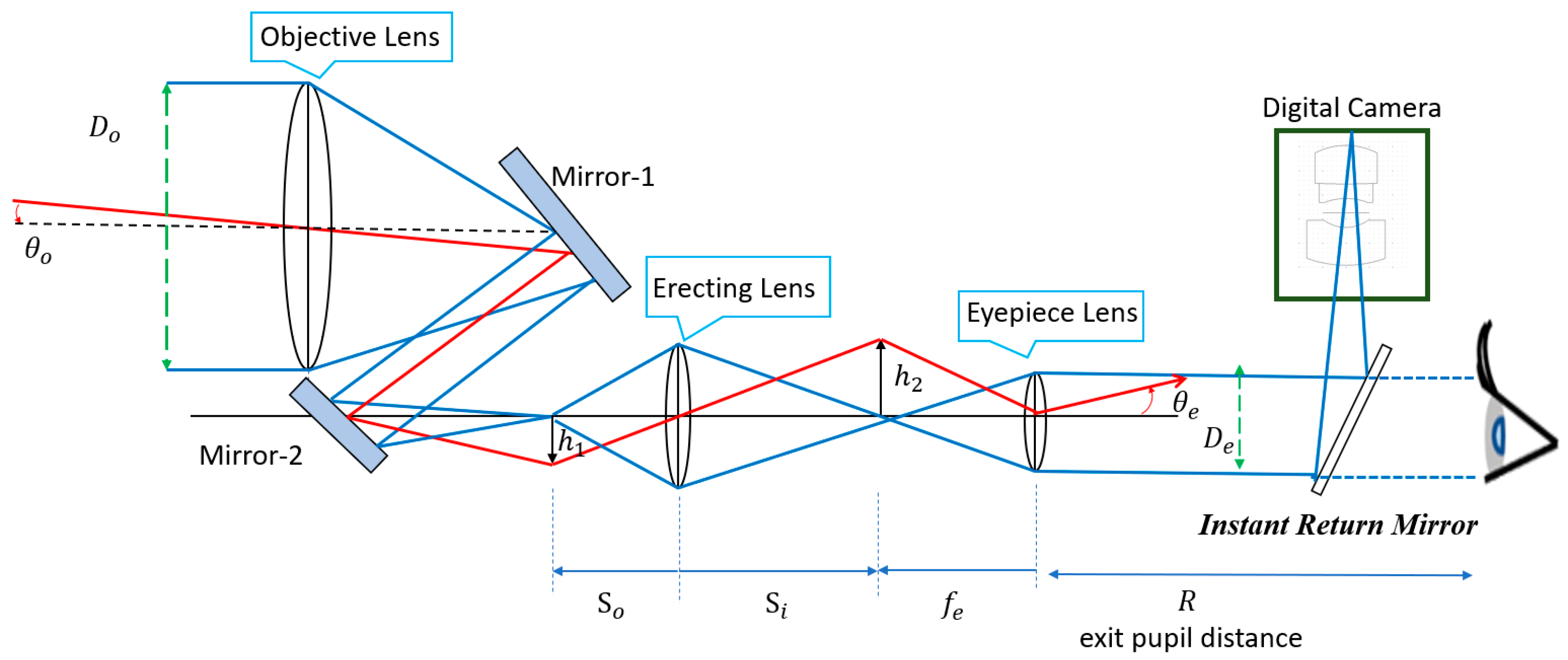
2.4. Optical Design of the Digital-Imaging Afocal Telescope System
2.5. Digital Camera System
3. Optical Design Results
3.1. Objective Lens Design
3.2. Erecting Lens Design
3.3. Eyepiece Lens Design
3.4. Digital Camera System
4. Optical System Quality and Analysis of the Digital-Imaging Afocal Telescope System
4.1. Afocal Telescope System
4.2. Design Results of the Digital-Imaging Afocal Telescope System
5. Conclusions
- I.
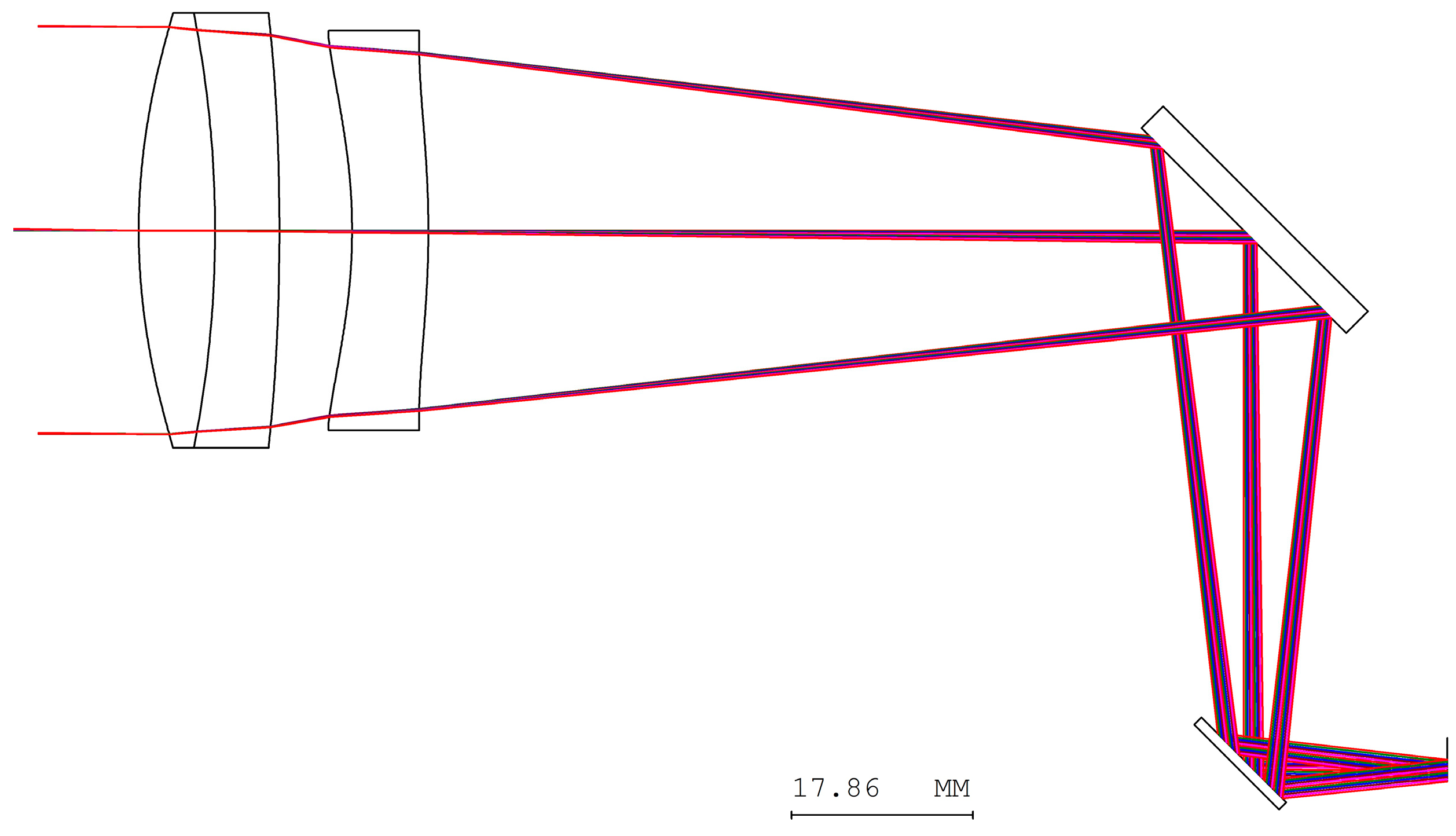
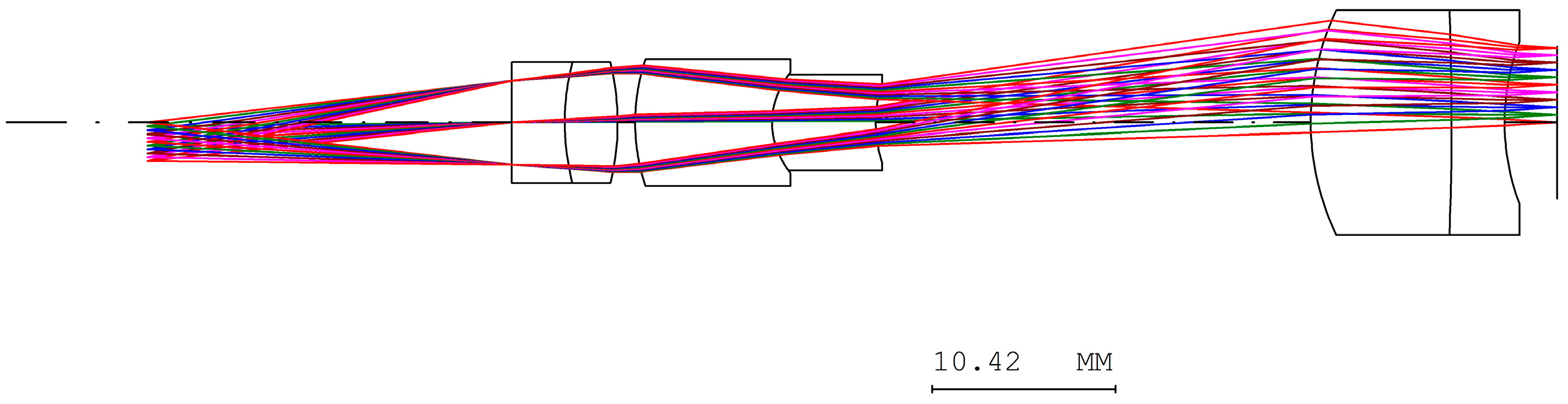
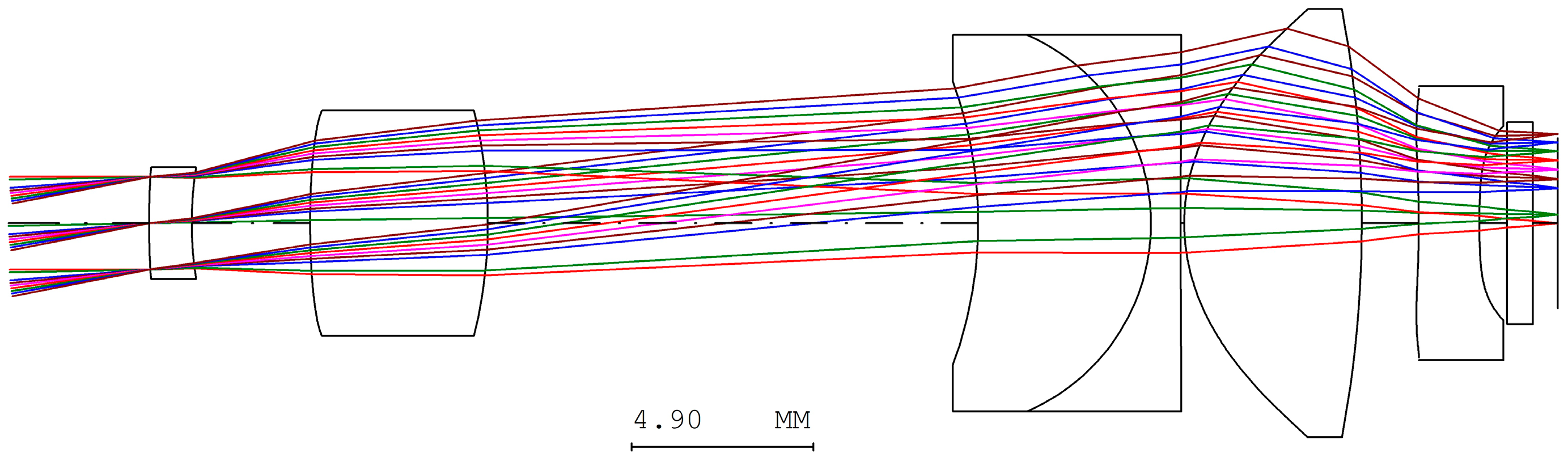
- The objective lens system has an effective focal length of 170 mm and a back focal length of 152.2 mm. The optical axis is defined along the z-axis. To reduce the overall length of the objective system along the z-axis, two mirrors are introduced within the objective lens system. The separation between the two mirrors is 52 mm, which shortens the back focal length along the z-axis to 100.2 mm. As a result, the overall length of the telescope system is significantly reduced, preventing an excessively long structure, as illustrated in Figure 22.
- II.
- A movable mirror tilted at 45° is placed between the telescope and the digital camera. This mirror enables dual operating modes: direct visual observation by the human eye and digital image capture by the camera. By switching the mirror position, the system can selectively provide real-time visual observation or digital image recording.
- III.
- In the proposed optical design, the aperture stop of the digital camera lens must be located at the front of the lens or on its first optical surface, such that the aperture coincides with the entrance pupil. Moreover, the aperture position must coincide with the exit pupil of the telescope, namely the eye-relief location. This position corresponds to the optimal viewing point for the human eye, where the observed image is both brightest and sharpest. In addition, the entrance pupil diameter and the incident half-field angle of the digital camera lens must match the exit pupil size and exit angle of the telescope to ensure efficient optical coupling.
- IV.
- The image data captured by the digital camera can be transmitted to augmented reality (AR) glasses. In the past two years, we have published three related papers on AR glasses design [27,28,29]. Since AR glasses are capable of displaying digital camera images, the integration of the proposed optical system with AR glasses offers substantial commercial and entertainment potential. This system is well suited for visual observation applications such as bird watching, whale watching, and large-scale sporting events. Furthermore, it minimizes visual fatigue caused by prolonged observation through the eyepiece, thereby enhancing user comfort and operational convenience.
- V.
- The telescope system consists of three optical subsystems: the objective lens, erecting lens, and eyepiece lens systems. These subsystems were independently designed and subsequently integrated to form the complete telescope system. Although the resulting system satisfies the afocal condition, residual aberrations remain. While these aberrations have negligible impact on human visual observation, they can slightly degrade the optical performance of the digital telescope system when combined with an independently designed digital camera. Therefore, with the telescope parameters fixed—along with the aperture position, aperture size, and focal length of the camera lens—the camera lens parameters were further optimized to compensate for the residual aberrations of the telescope, thereby improving the overall optical performance of the digital telescope system.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malacara, D.; Malacara, Z. Visual Systems, Visual Telescopes, and Afocal System. In Handbook of Optical Design, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ćatović, A.; Jašarević, D. Review of design parameters and optical characteristics of the main types of amateur telescopes. Orig. Res. 2025, 6, 49–90. [Google Scholar]
- Klevtsov, Y.A. Optical systems of wide-angle telescopes for monitoring celestial objects. J. Opt. Technol. 2017, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greivenkamp, J.E. Optical Design and Instrumentation: Keplerian Telescope; University of Arizona: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Galan, M.; Strojnik, M.; Wang, Y. Design method for compact, achromatic, highperformance, solid catadioptric system (SoCatS), from visible to IR. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahromi, O. A new optical adjustment mechanism for riflescopes. Proc. SPIE 2021, 12078, 120781D. [Google Scholar]
- Jahromi, O.S. Telescopic Gun Sight with Rotating Optical Adjustment Mechanism. US Patent No. 9,164,269, 20 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jahromi, O.S. Telescopic Gun Sight with Tilting Optical Adjustment Mechanism. US Patent No. 2016/0018188 A1, 21 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.; Milster, T. Molding Error and Its Compensation in Multi-Order Diffractive Lens Segmented Telescope Assembly. In OSA Optical Design and Fabrication; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; p. OTu5B.3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, W.; Gong, D.; Li, H. Design of a zoom telescope optical system with a large aperture, long focal length, and wide field of view via a catadioptric switching solution. J. Opt. Technol. 2021, 1, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.C.; Zhang, C.; Rolland, P.J. Exit pupil quality analysis and optimization in freeform afocal telescope systems. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 24691–24701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.; Fan, X.; Zhao, H.; Pang, Z.; Xie, X.; Xu, L. Optical design of a 5× zoom afocal telescope with deformable mirrors. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 34622–34638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defense Supply Agency, Optical Design, MIL-HDBK-141. Military Standardization Handbook; Defense Supply Agency: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1981; Chapters 4. [Google Scholar]
- Helden, A.V. The beginnings, from Lipperhey to Huygens and Cassini. Exp. Astron. 2009, 25, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, E.N.; Va, R. Telescopic Sight for Day/Night Viewing. United States Patent, US005084780A, 28 January 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, V.N. Optical Imaging and Aberration; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1998; Chapters 3. [Google Scholar]
- Khatsevich, T.N. Stabilization of the exit pupil in an optical zoom sight with variable magnification. J. Opt. Technol. 2017, 84, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, V.N. Afocal System in Optical Imaging and Aberration; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1998; Chapters 6. [Google Scholar]
- Borissova, D. Night Vision Weapon Sight. In Night Vision Devices Modeling and Optimal Design; Bugarian Academy of Sciences: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2015; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Malacara, D.; Malacara, Z. Astronomical Telescopes. In Handbook of Lens Design; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Chapter 14. [Google Scholar]
- Velzel, C. A Course in Lens Design. In Optical Sciences; Lotsch, H.K.V., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Chapter 2.4; Volume 183. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, V.N. Fundamentals of Geometrical Optics; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE): Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Chapter 6.5 Telescope; p. 255. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, F.A.; White, H.E. Fundamentals of Optics, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: London, UK, 1957; Chapter 3.8 “Magnification”. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.J. Basic Optical Devices. In Modern Optical Engineering, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: London, UK, 2000; Chapter 9. [Google Scholar]
- Synopsys, CODE V Documentation Library, Version 2024.03, Diffraction Analysis Reference Manuals & Tolerance Reference. Available online: https://www.keysight.com/us/en/products/software/optical-solutions-software/optical-design-solutions/codev.html (accessed on 23 December 2025).
- OMNIVISION for products by Sensor Specification-OV5695. Available online: https://www.ovt.com/press-releases/omnivisions-high-performance-ov5675-and-ov5695-bring-5-megapixel-selfies-to-next-generation-smartphones-and-tablets/ (accessed on 23 December 2025).
- Sun, W.S.; Su, Y.L.; Hsu, Y.S.; Tien, C.L.; Cheng, N.J.; Sun, C.C. Compact Design of a 50° Field of View Collimating Lens for Lightguide-Based Augment Reality Glass. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.S.; Hsu, Y.S.; Su, Y.L.; Huang, G.W.; Lin, W.K.; Su, W.C.; Lin, S.H.; Lee, T.X.; Yu, Y.W.; Sun, C.C. Design of a 65-degree Collimating lens for Lightguide-based AR Glasses. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 24861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.S.; Hsu, Y.S.; Tien, C.L.; Lin, W.K.; Su, Y.L.; Yu, J.Y.; Zhou, S.K.; Liang, Y.Y.; Tsai, W.P.; Sun, C.; et al. Design and Manufacture of 30-degree Projection lens for Augmented Reality Waveguide. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
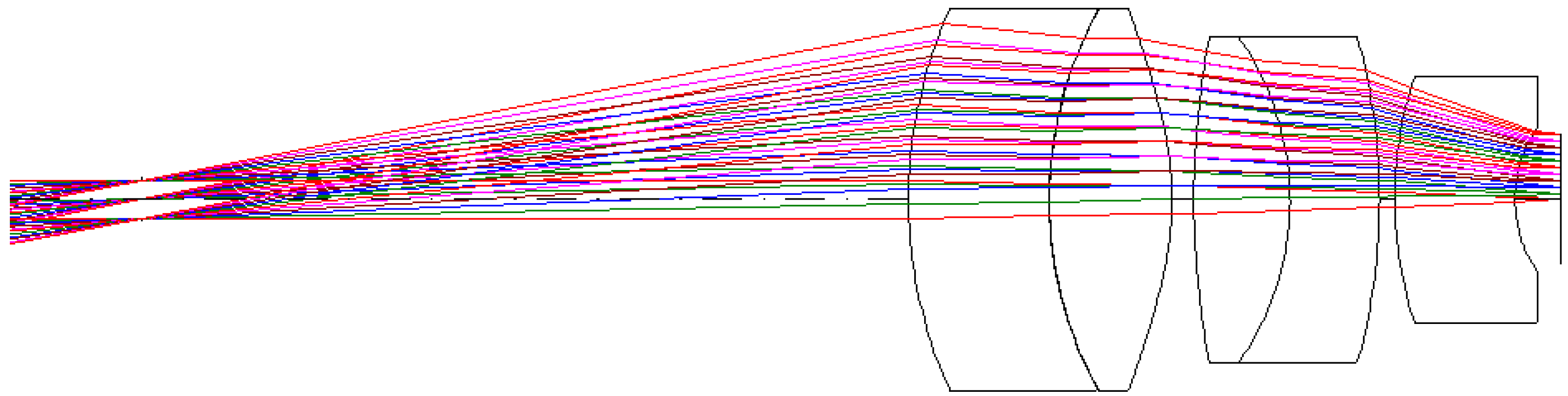
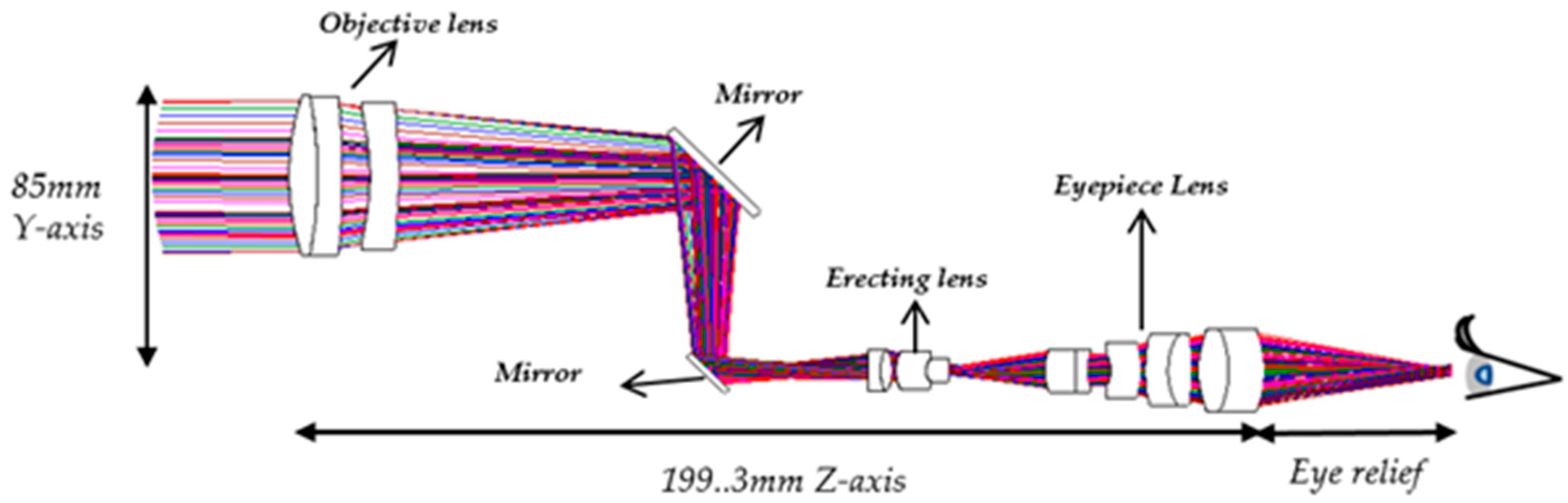
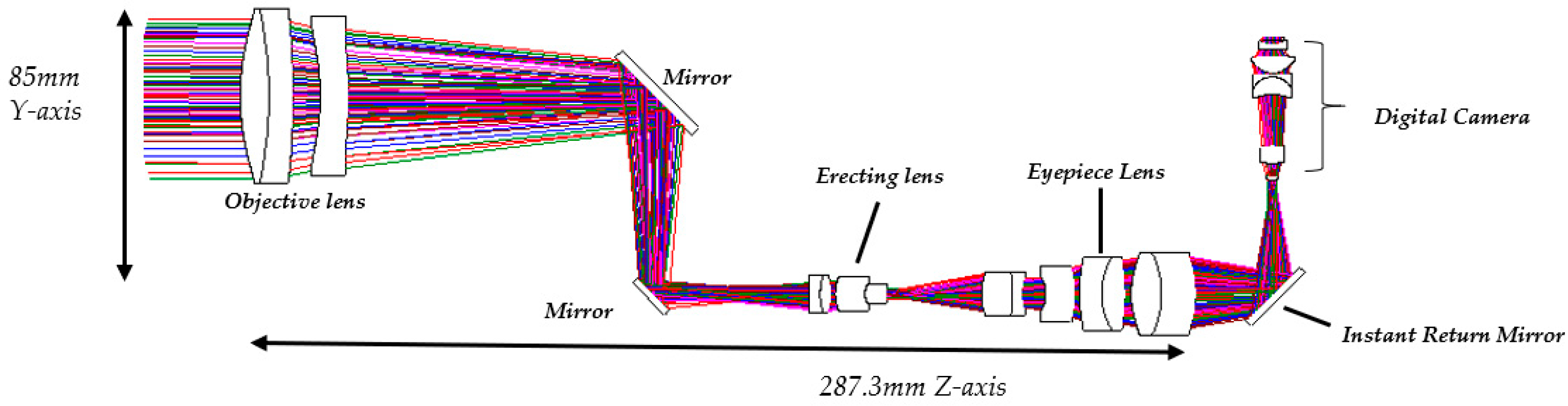
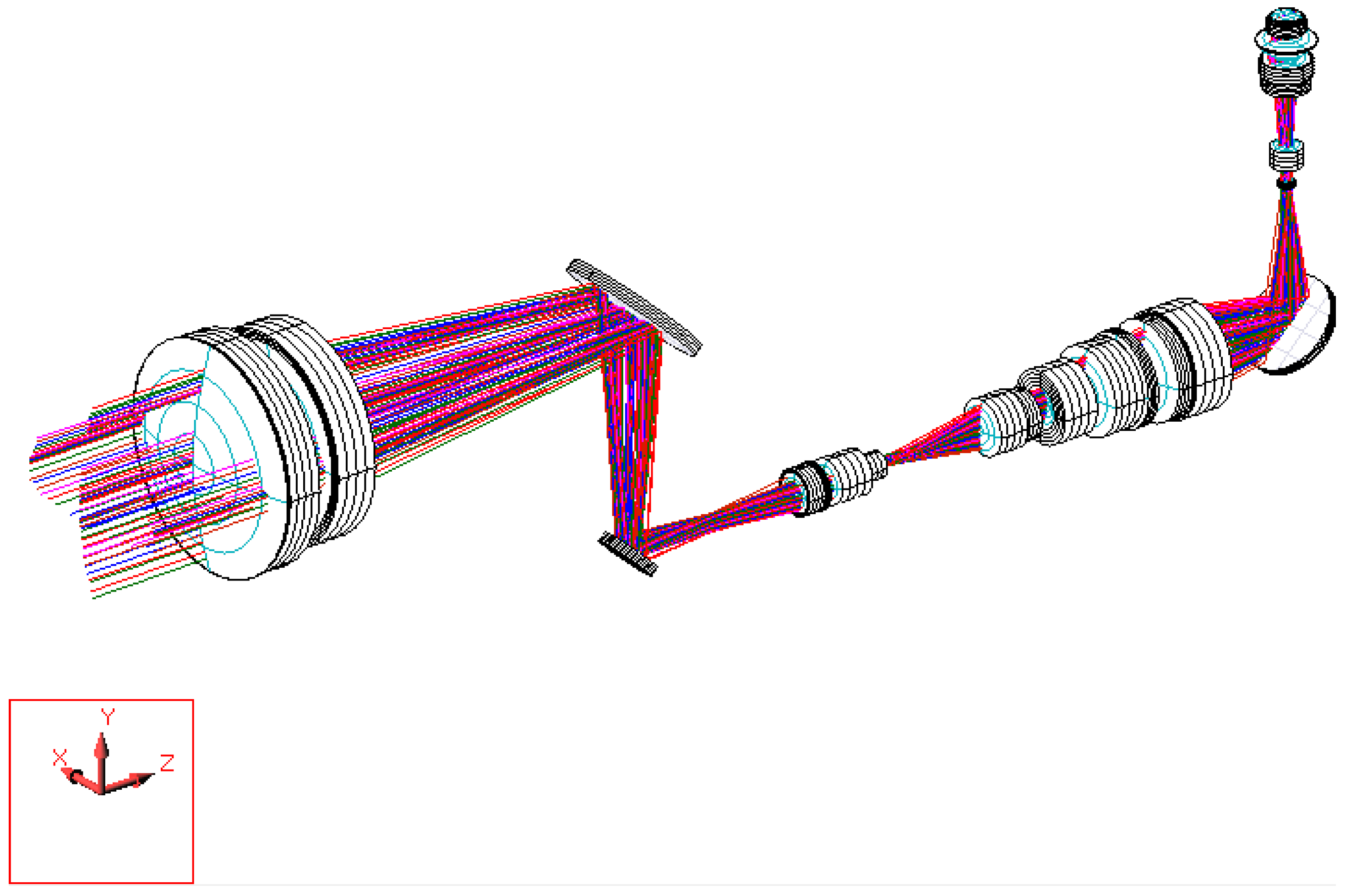
| Objective Lens | Erecting Lens | Eyepiece Lens | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 mm | Focal Length | 30 mm | 2.5 mm | ||
| 176 mm | −45 mm | −22 mm | |||
| −0.7° | 90 mm | −11.061° | |||
| −0.012 | 0.113 | −0.195 | |||
| −2.15 mm | −0.056 | 4.3 mm | |||
| 0.113 | Transverse magnification | −2 | −0.056 | ||
| Item | Design Target |
|---|---|
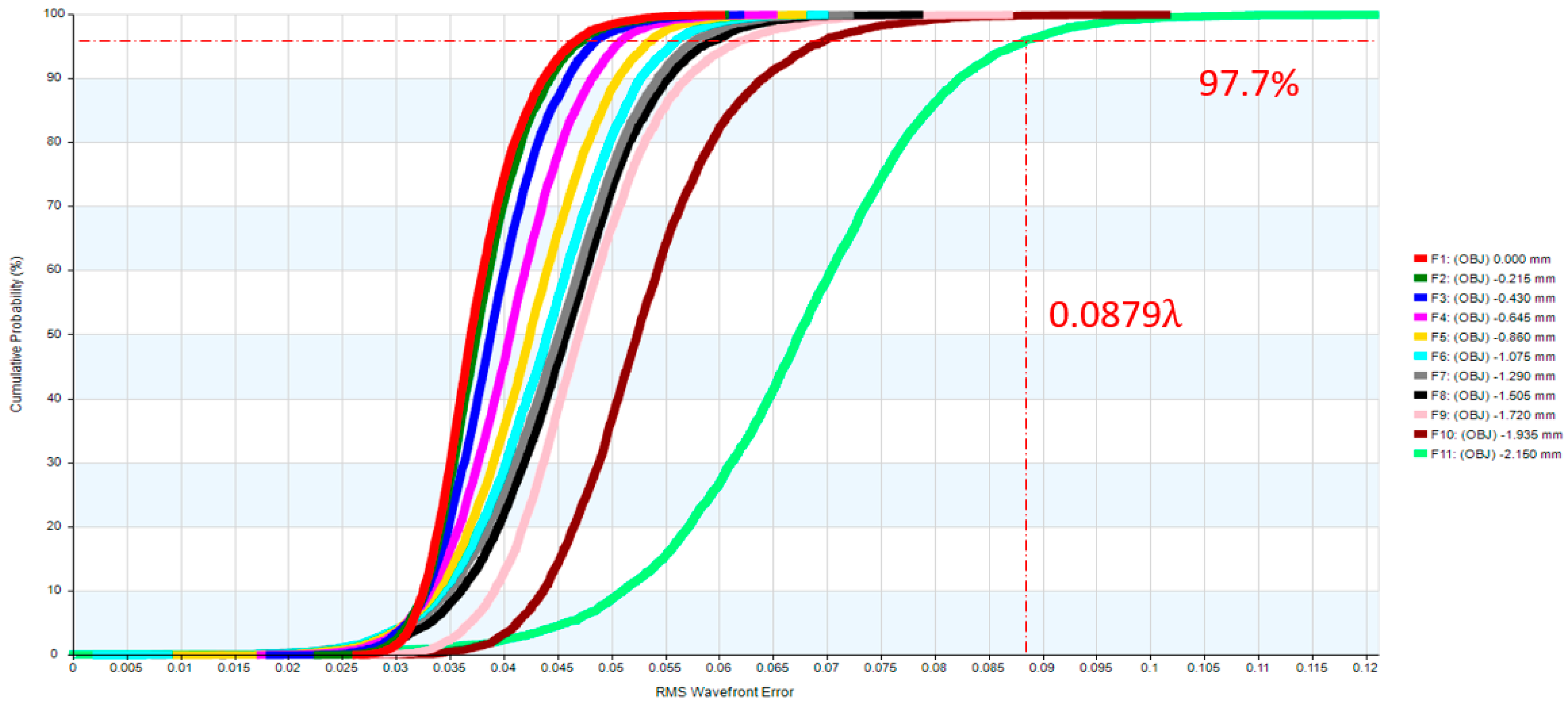
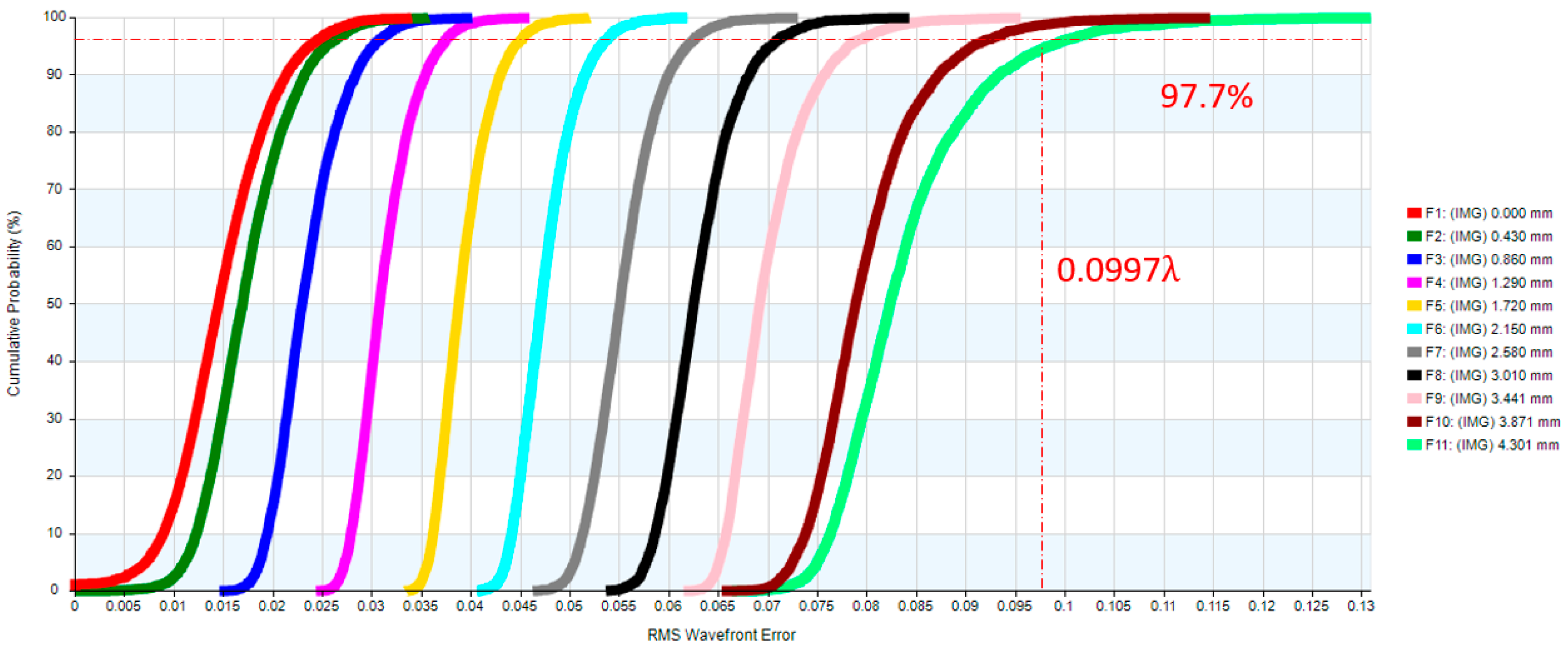
| RMS optical path difference (OPD) | <0.07 λ |
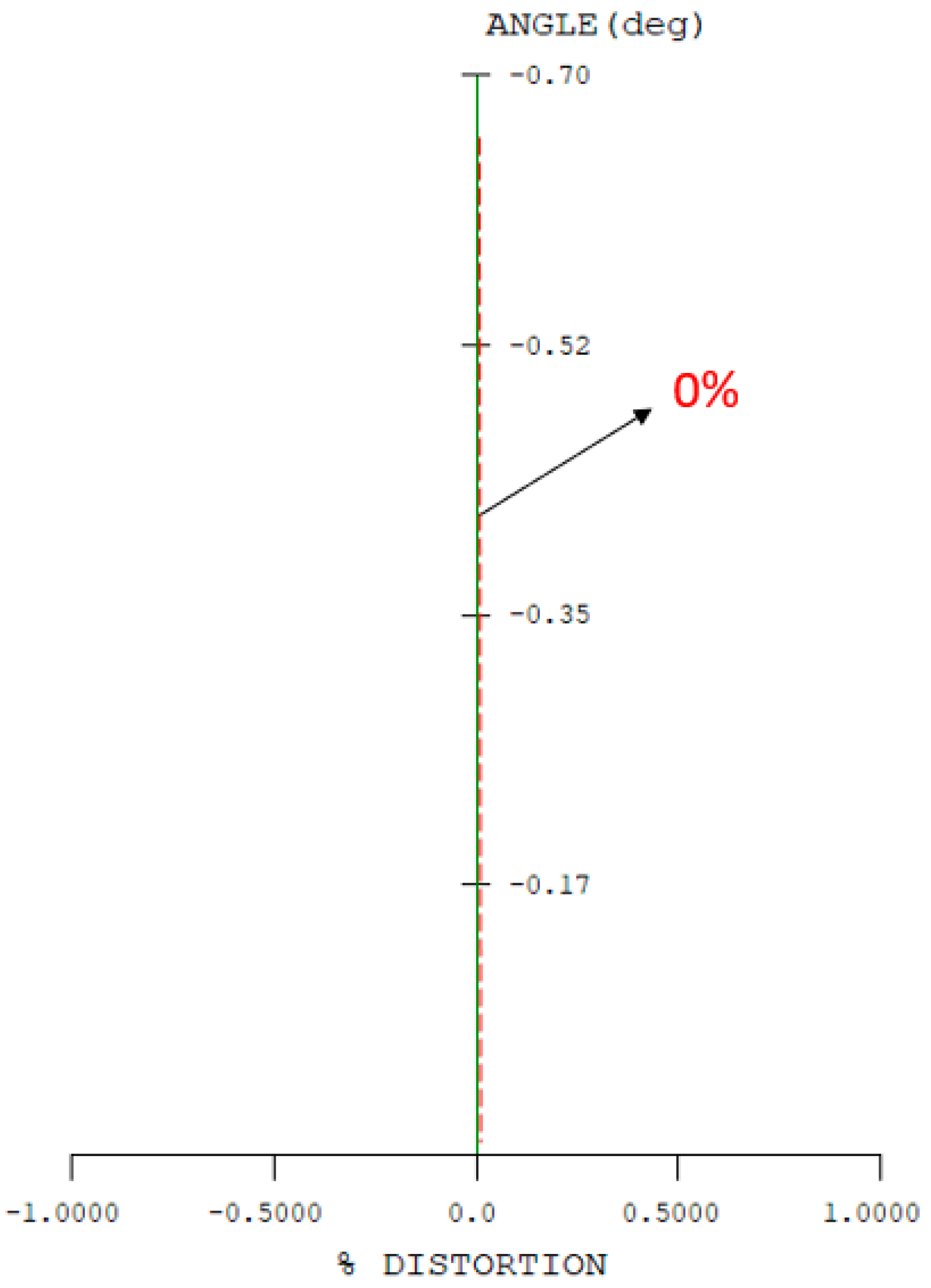
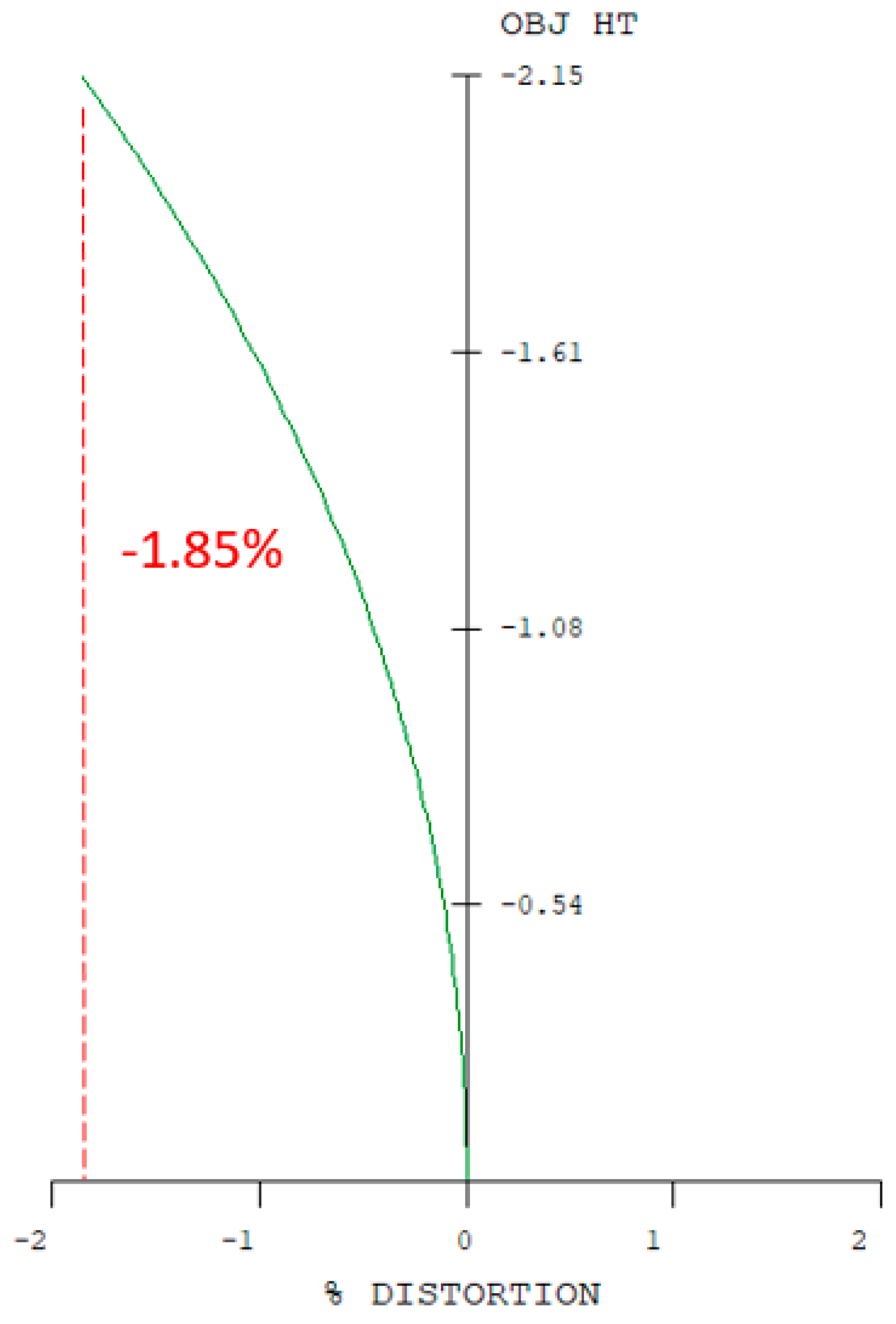
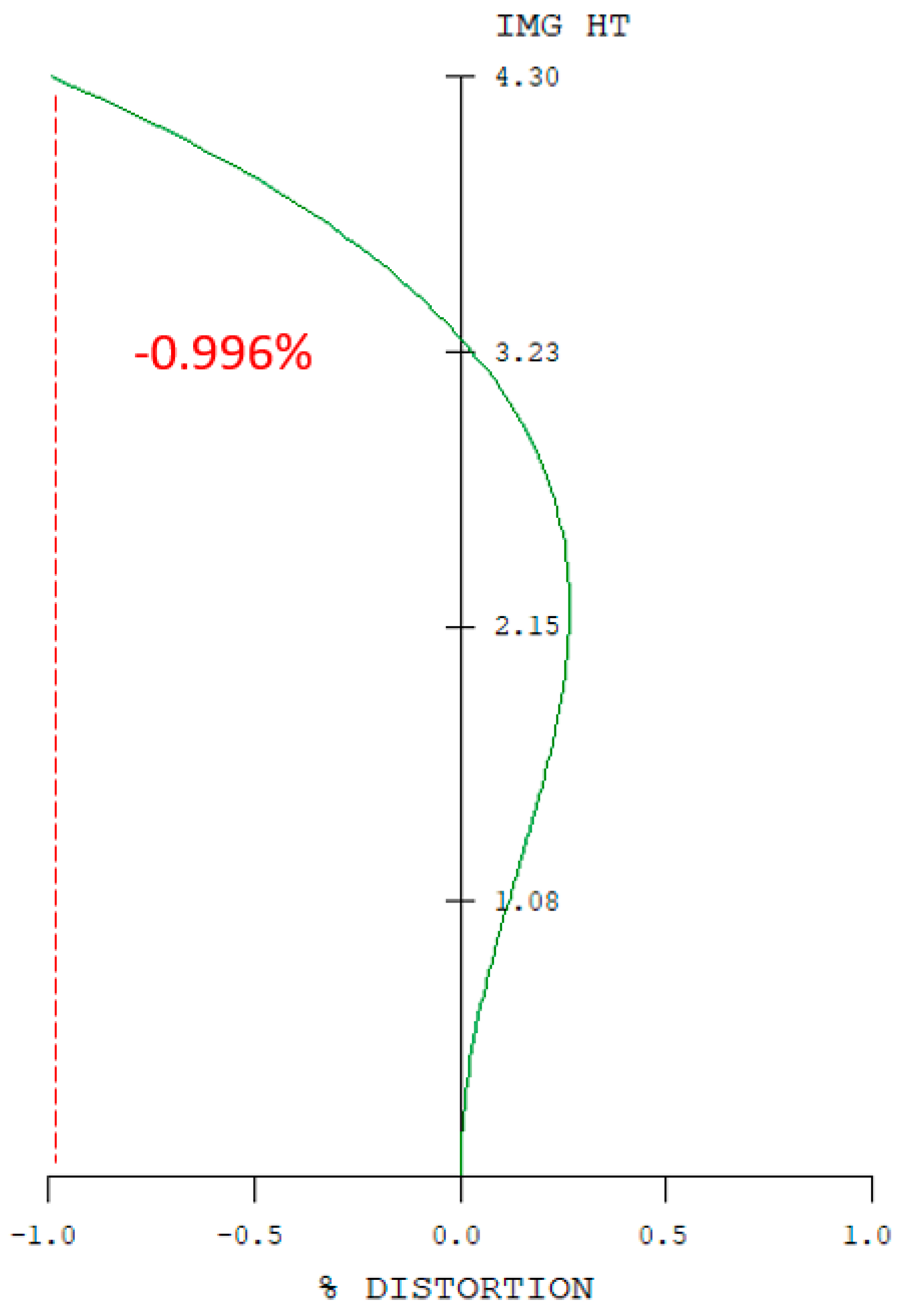
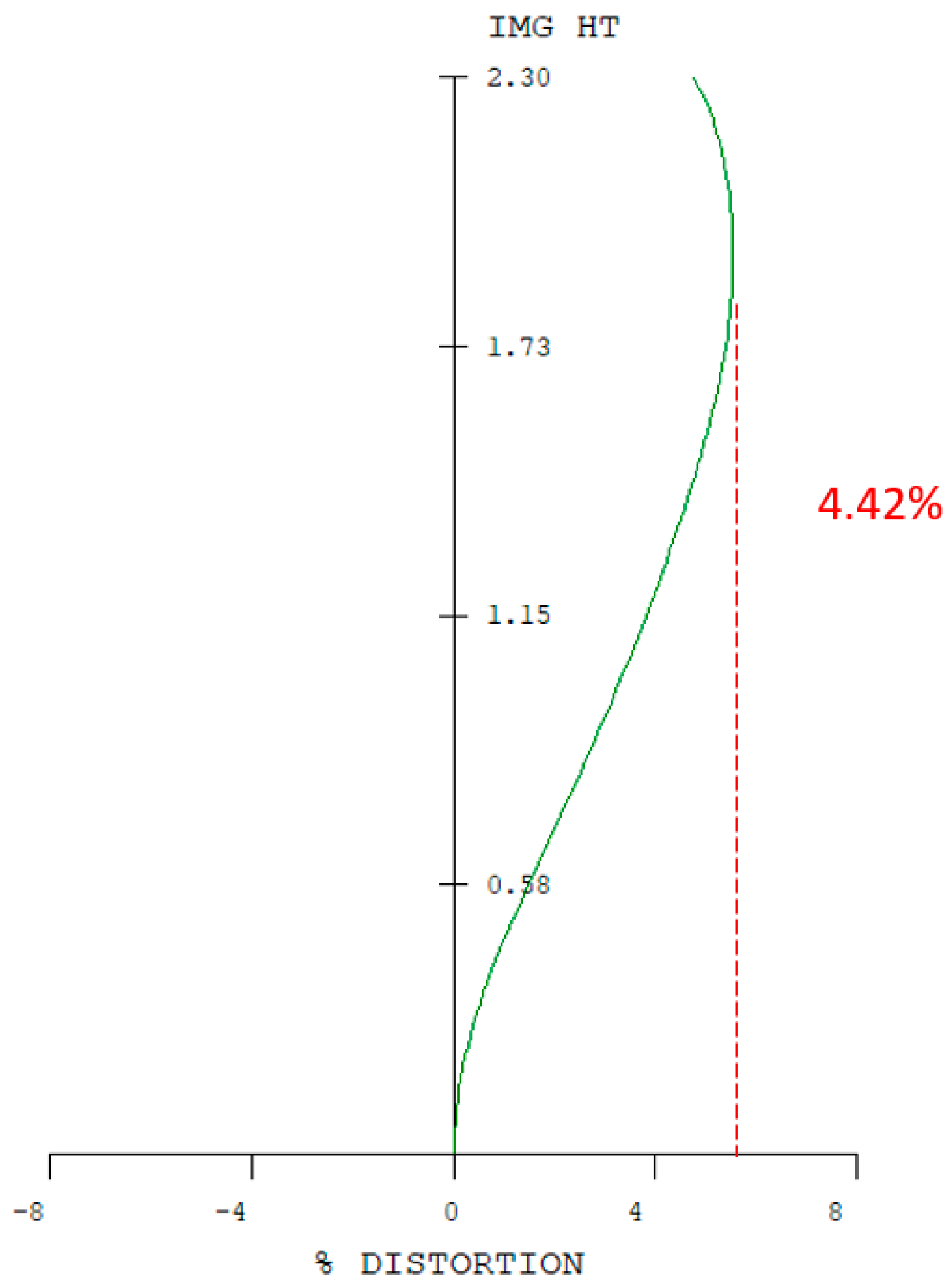
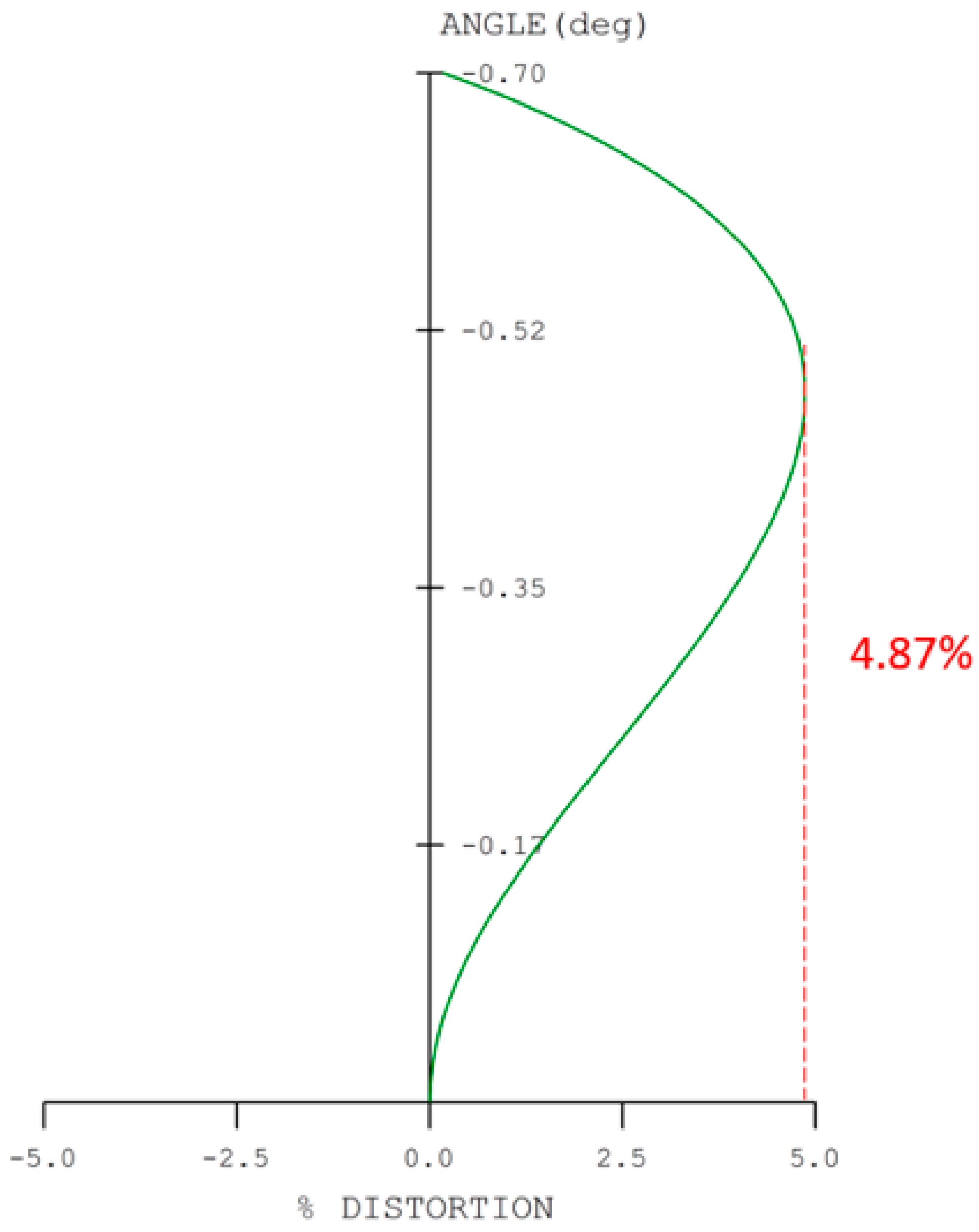
| |Optical distortion| | ≤2% |
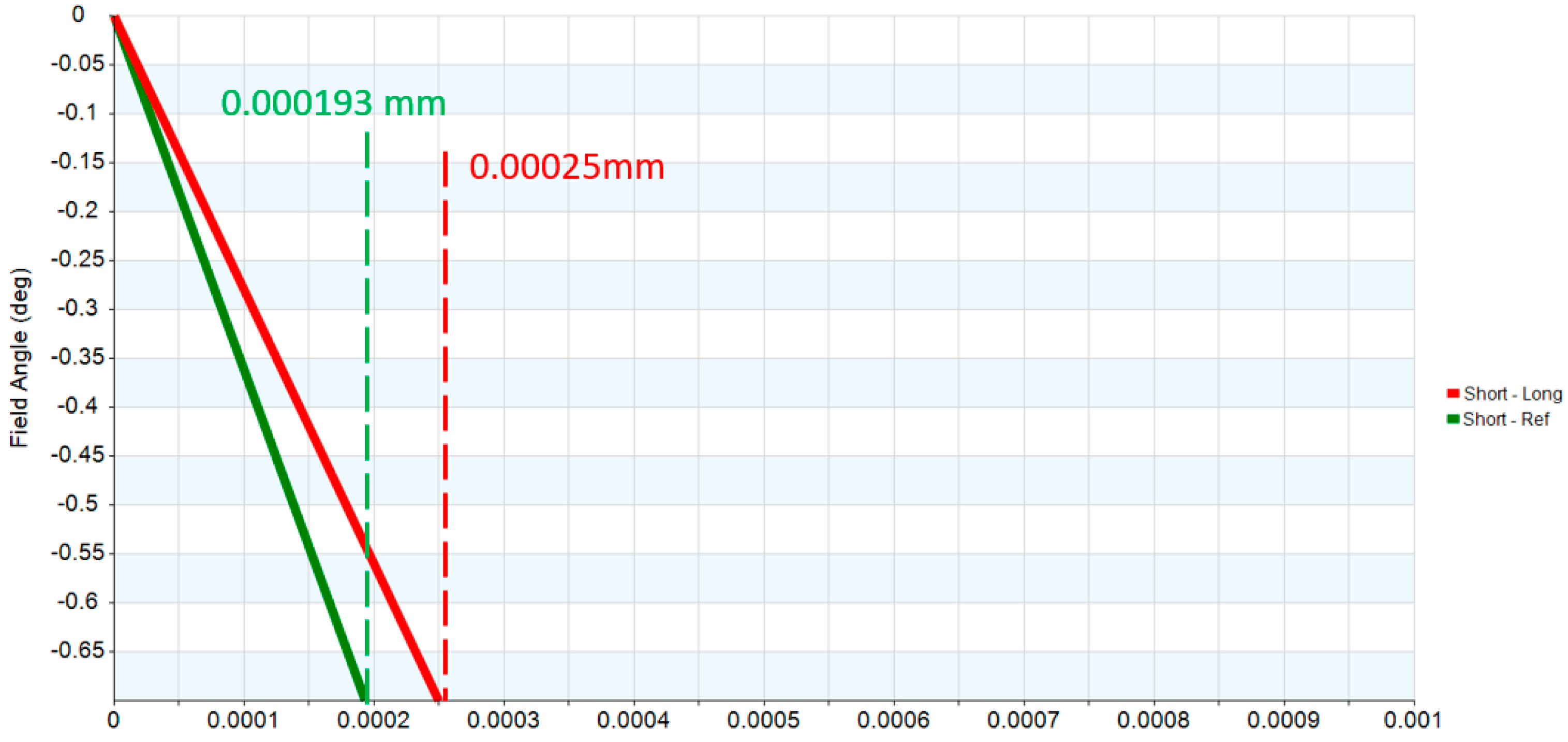
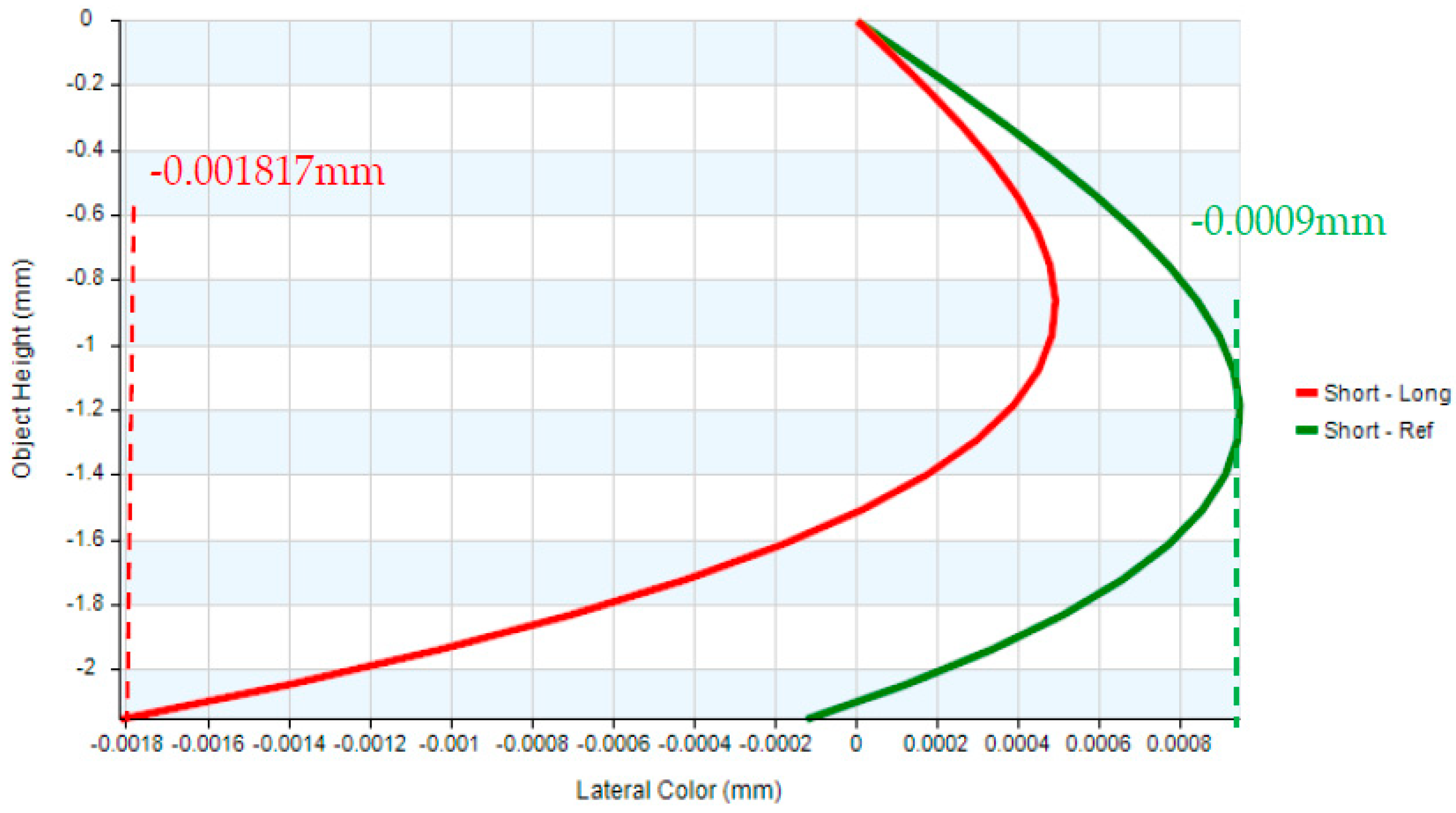
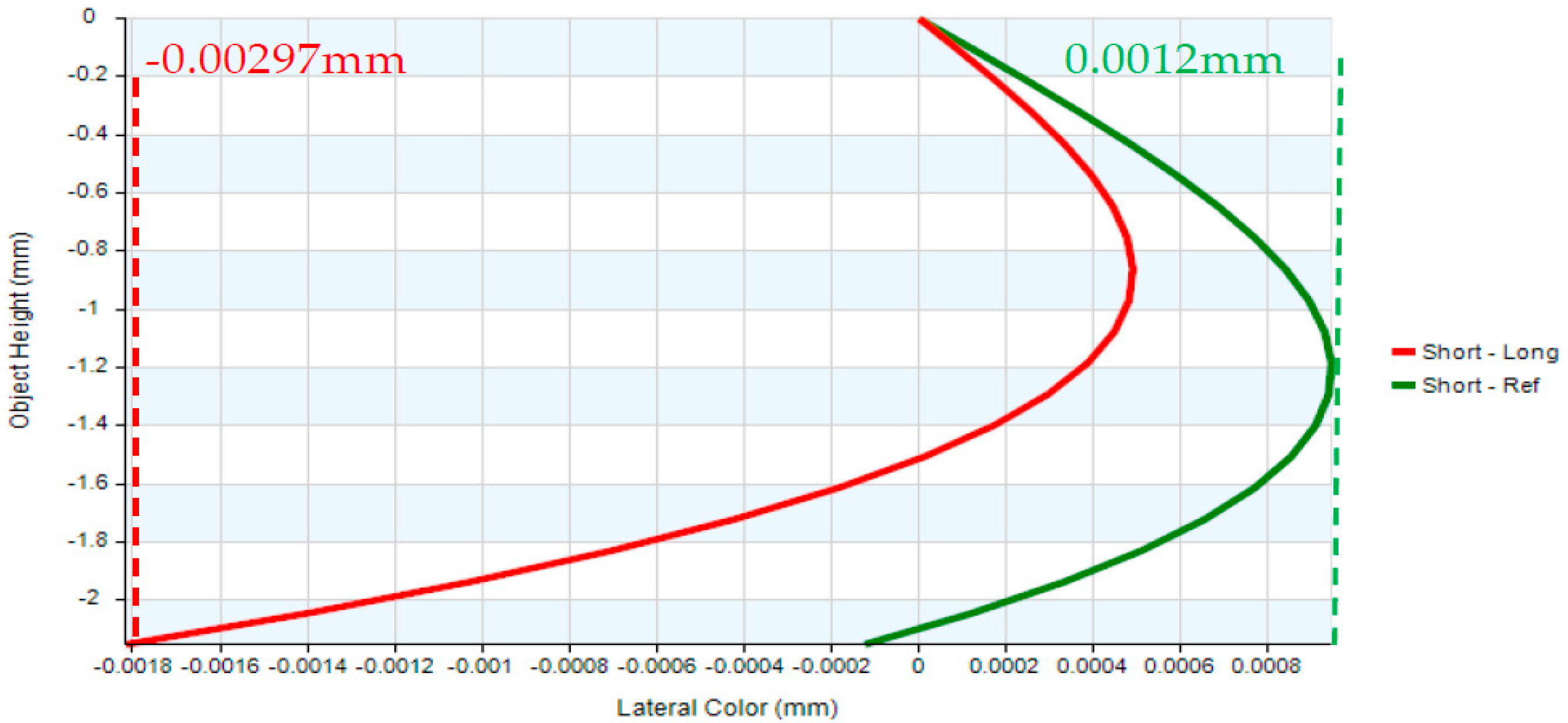
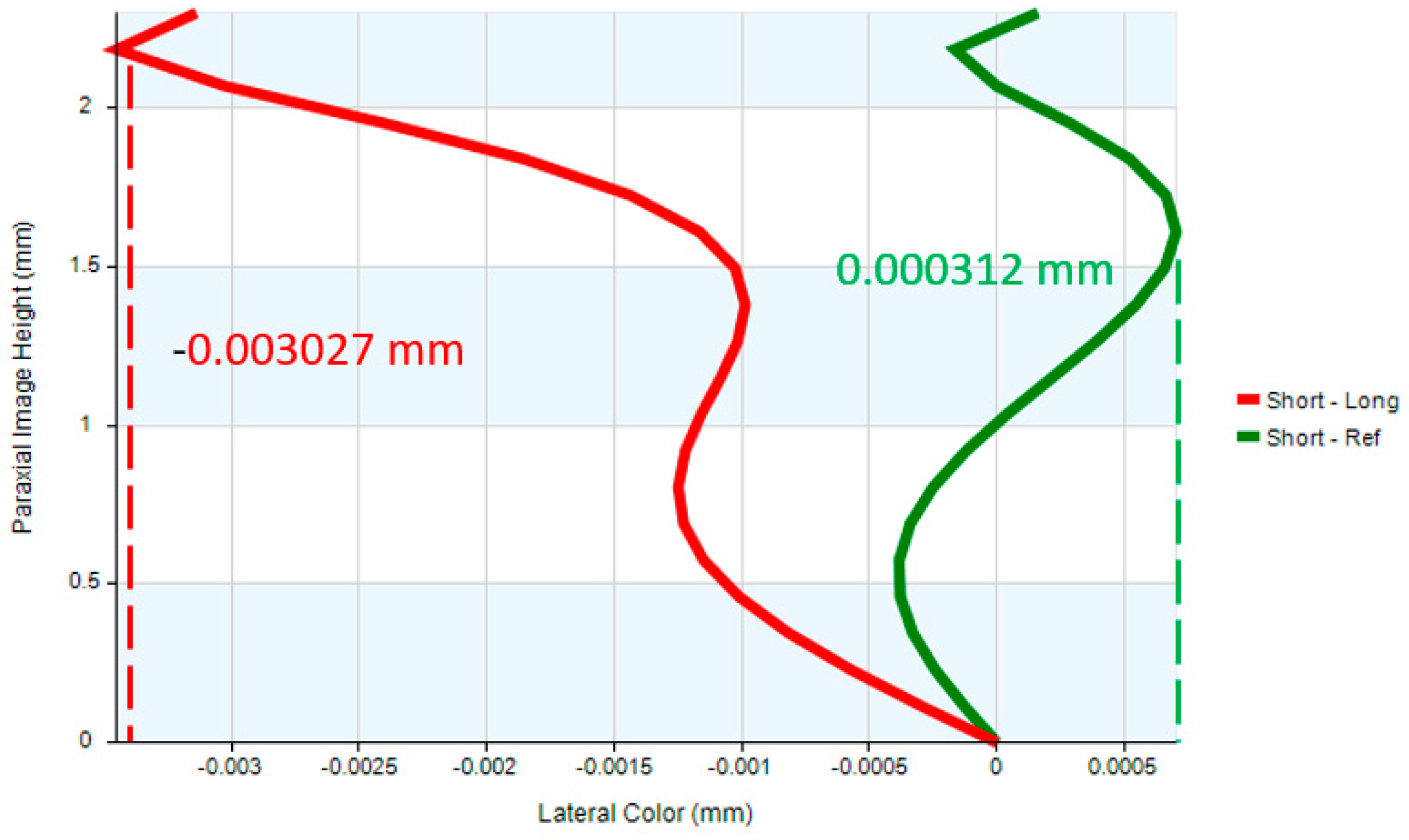
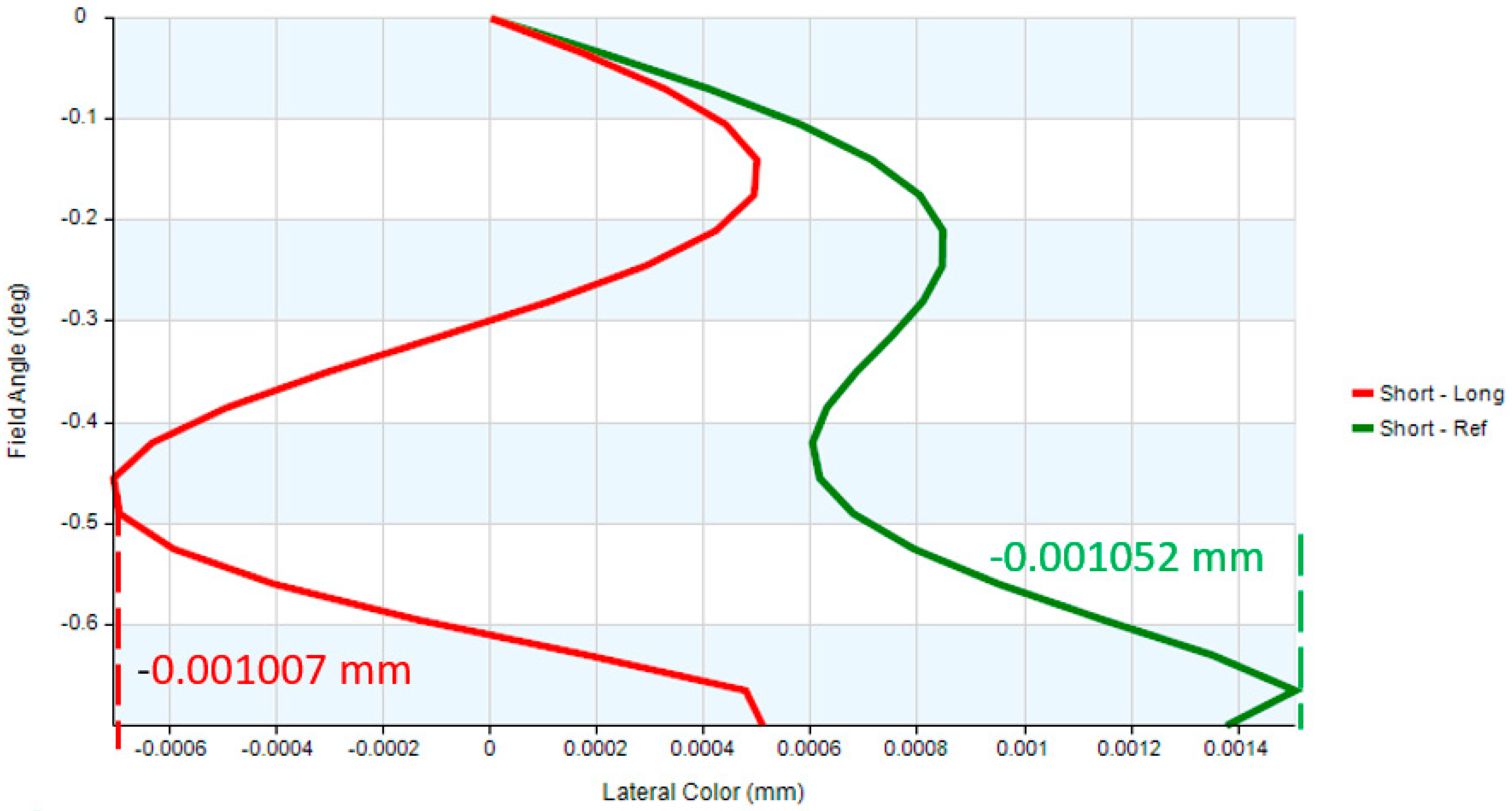
| Lateral color | <1 Airy Disk |
| Conic constant K | −100 < K < 100 |
| The range of wavelengths | 656 nm, 587 nm, 486 nm. |
| Type | Design RMS OPD Value | Design plus Tolerance RMS OPD Value |
|---|---|---|
| DLF (fringe) | 1~8 fringes | 1~8 fringes |
| DLT (mm) | >0.02 mm | 0.01 mm~0.05 mm |
| DLN | >0.0001 | 0.0001~0.0005 |
| DLV | >0.1% | 0.1%~0.5% |
| CYD (fringe) | ||
| CYN (fringe) | ||
| TRX (arcmin) | >0.5 arc min | 1 arc min~3 arc min |
| TRY (arcmin) | >1 arc min | 1 arc min~3 arc min |
| BTY (arcmin) | >1 arc min | 1 arc min~3 arc min |
| BTX (arcmin) | >1 arc min | 1 arc min~3 arc min |
| Omni-Vision Sensor Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Omni Vision |
| Product model | OV5695 |
| Effective pixels | 2631 × 1973 (5 Mega) |
| Pixel size | 1.4 μm × 1.4 μm |
| Area length and width | 3.684 mm × 2.763 mm |
| Diagonal | 4.605 mm |
| Surface No. | Type | Y Radius | Thickness | Glass | Y-Semi Aperture | Conic Constant (K) | 4th Order | 6th Order | 8th Order | 10th Order | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Object | Sphere | Infinity | Infinity | ||||||||
| 1 | Asphere | 65.77 | 7.5 | PSF67_SCHOTT | 20 | −0.22 | −2.2 × 10−7 | 6.36 × 10−11 | −3.01 × 10−12 | ||
| 2 | Sphere | −110 | 6.33 | PSF8_SCHOTT | 19.79 | ||||||
| 3 | Asphere | −244.19 | 7.14 | 19.35 | 64.73 | −4.56 × 10−7 | 1.78 × 10−9 | −4.27 × 10−12 | 6.661 × 10−15 | ||
| 4 | Asphere | −54.65 | 7.5 | POLEFINH | 18.34 | −6.4 | −1.83 × 10−6 | 4.97 × 10−9 | 2.95 × 10−12 | 5.88 × 10−15 | |
| 5 | Asphere | −95.42 | 80.2 | 17.74 | −26.83 | 3.22 × 10−6 | 4.72 × 10−6 | 1.95 × 10−12 | 5.2 × 10−15 | ||
| 6 | Sphere | Infinity | 0 | 13.14 | |||||||
| 7 | Sphere | Infinity | −52 | Reflect | 9.48 | ||||||
| 8 | Sphere | Infinity | 0 | 5.37 | |||||||
| 7 | Sphere | Infinity | 20 | Reflect | 4.18 | ||||||
| Image | Sphere | Infinity | 0 | 2.15 | |||||||
| FIELD | Design RMS OPD Value | Design plus Tolerance RMS OPD Value |
|---|---|---|
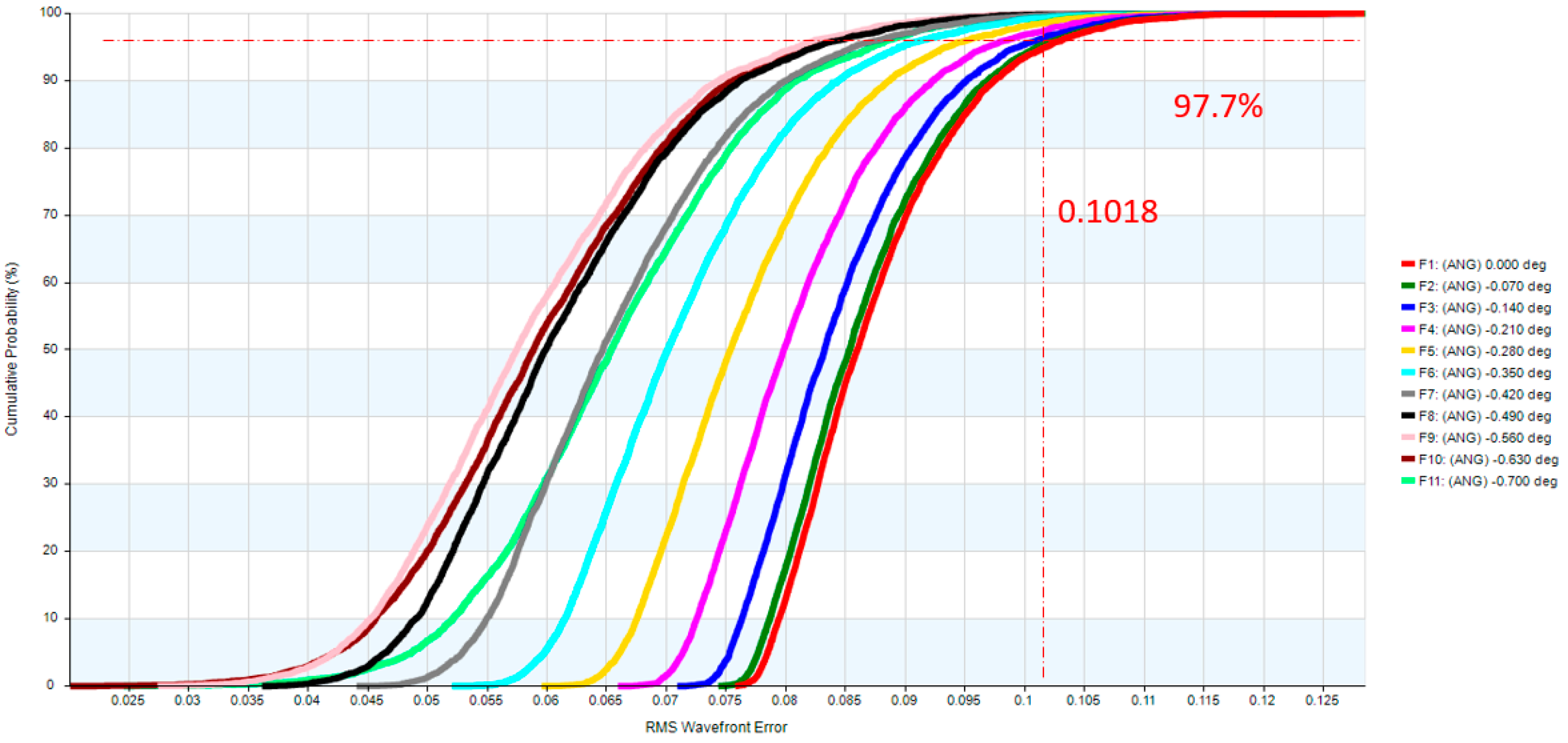
| 0.0 | 0.0767 | 0.1018 |
| 0.1 | 0.0759 | 0.1013 |
| 0.2 | 0.0736 | 0.0997 |
| 0.3 | 0.0736 | 0.0997 |
| 0.4 | 0.0698 | 0.0971 |
| 0.5 | 0.0646 | 0.0937 |
| 0.6 | 0.0594 | 0.0899 |
| 0.7 | 0.0517 | 0.0860 |
| 0.8 | 0.0456 | 0.0827 |
| 0.9 | 0.0425 | 0.0825 |
| 1.0 | 0.0515 | 0.0879 |
| Surface (No.) | Surface Type | Y Radius | Thickness | Glass | Y-Semi Aperture | Conic Constant (K) | 4th Order | 6th Order | 8th Order | 10th Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Object | Sphere | Infinity | 20.69 | |||||||
| 1 (Stop) | Sphere | −186.94 | 3 | NLASF45_SCHOTT | 2.36 | |||||
| 2 | Sphere | 13.74 | 3 | NLAK34_SCHOTT | 2.77 | |||||
| 3 | Sphere | −14.18 | 1 | 3.10 | ||||||
| 4 | Asphere | 11.27 | 7.76 | PSF67_SCHOTT | 3.24 | −0.26 | −1.8 × 10−5 | −1 × 10−6 | 1.09 × 10−7 | −4.4 × 10−9 |
| 5 | Asphere | 4.09 | 5.88 | PLAF37_SCHOTT | 2.45 | −0.29 | −6.13 × 10−4 | −6.7 × 10−7 | −2.48 × 10−6 | |
| 6 | Sphere | 7.40 | 24.68 | 2.16 | ||||||
| 7 | Sphere | 14.69 | 8 | NLASF40_SCHOTT | 5.78 | |||||
| 8 | Sphere | −147.69 | 3 | NFK58_SCHOTT | 4.98 | |||||
| 9 | Sphere | 12.94 | 2.99 | 4.37 | ||||||
| Image | Sphere | Infinity | 0.0000 | 4.22 | ||||||
| Field | Design RMS OPD Value | Design plus Tolerance RMS OPD Value |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.0305 | 0.0466 |
| 0.1 | 0.0310 | 0.0472 |
| 0.2 | 0.0322 | 0.0490 |
| 0.3 | 0.0338 | 0.0516 |
| 0.4 | 0.0356 | 0.0545 |
| 0.5 | 0.0369 | 0.0571 |
| 0.6 | 0.0374 | 0.0589 |
| 0.7 | 0.0373 | 0.0600 |
| 0.8 | 0.0379 | 0.0619 |
| 0.9 | 0.0428 | 0.0694 |
| 1.0 | 0.0579 | 0.0897 |
| Surface (No.) | Surface Type | Y Radius | Thickness | Glass | Y Semi Aperture | Conic Constant (K) | 4th Order | 6th Order | 8th Order | 10th Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Object | Sphere | Infinity | Infinity | |||||||
| 1 (Stop) | Sphere | Infinity | 50 | 1.25 | ||||||
| 2 | Sphere | 30 | 9.18 | NSF66_SCHOTT | 11.47 | |||||
| 3 | Sphere | 25.66 | 8 | NPK52A_SCHOTT | 10.54 | |||||
| 4 | Asphere | −20.88 | 1.43 | 10.52 | −4.13 | 6.27 × 10−6 | 2.36 × 10−8 | −3.85 × 10−11 | −1.99 × 10−13 | |
| 5 | Sphere | 55.47 | 6.27 | NLAK7_SCHOTT | 9.71 | |||||
| 6 | Sphere | −18.63 | 5.84 | NSF57_SCHOTT | 9.17 | |||||
| 7 | Sphere | −39.85 | 1 | 8.48 | ||||||
| 8 | Sphere | 25.24 | 7.85 | PSF67_SCHOTT | 7.29 | |||||
| 9 | Sphere | 8.25 | 3 | 4.45 | ||||||
| Image | Sphere | Infinity | 0 | 4.25 | ||||||
| Field | Design RMS OPD Value | Design plus Tolerance RMS OPD Value |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.0068 | 0.0182 |
| 0.1 | 0.0099 | 0.0200 |
| 0.2 | 0.0155 | 0.0239 |
| 0.3 | 0.0212 | 0.0283 |
| 0.4 | 0.0271 | 0.0335 |
| 0.5 | 0.0342 | 0.0418 |
| 0.6 | 0.0425 | 0.0531 |
| 0.7 | 0.0515 | 0.0652 |
| 0.8 | 0.0590 | 0.0750 |
| 0.9 | 0.0644 | 0.0814 |
| 1.0 | 0.0649 | 0.0997 |
| Half of image high | 2.30 mm |
| Half of view angle | 11.06° |
| EFL | 11.77 mm |
| F-number | 4.71 |
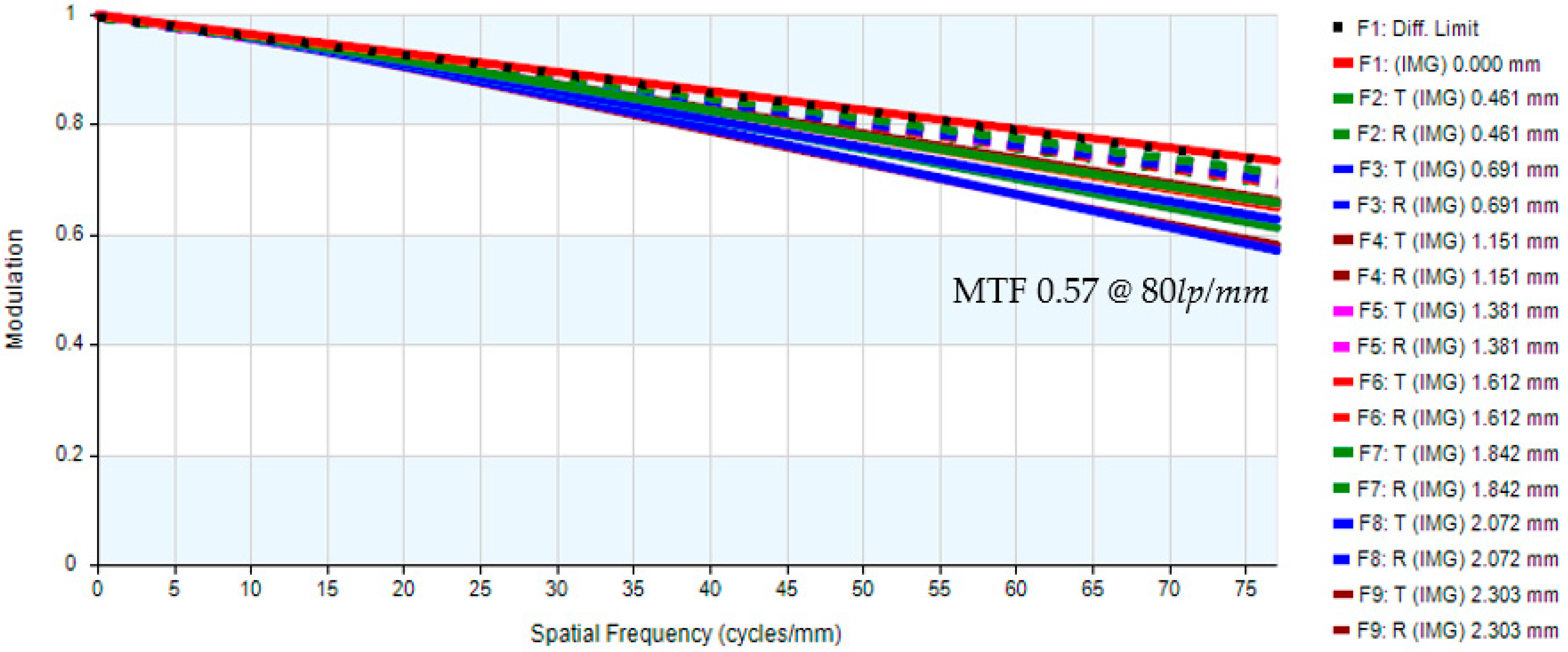
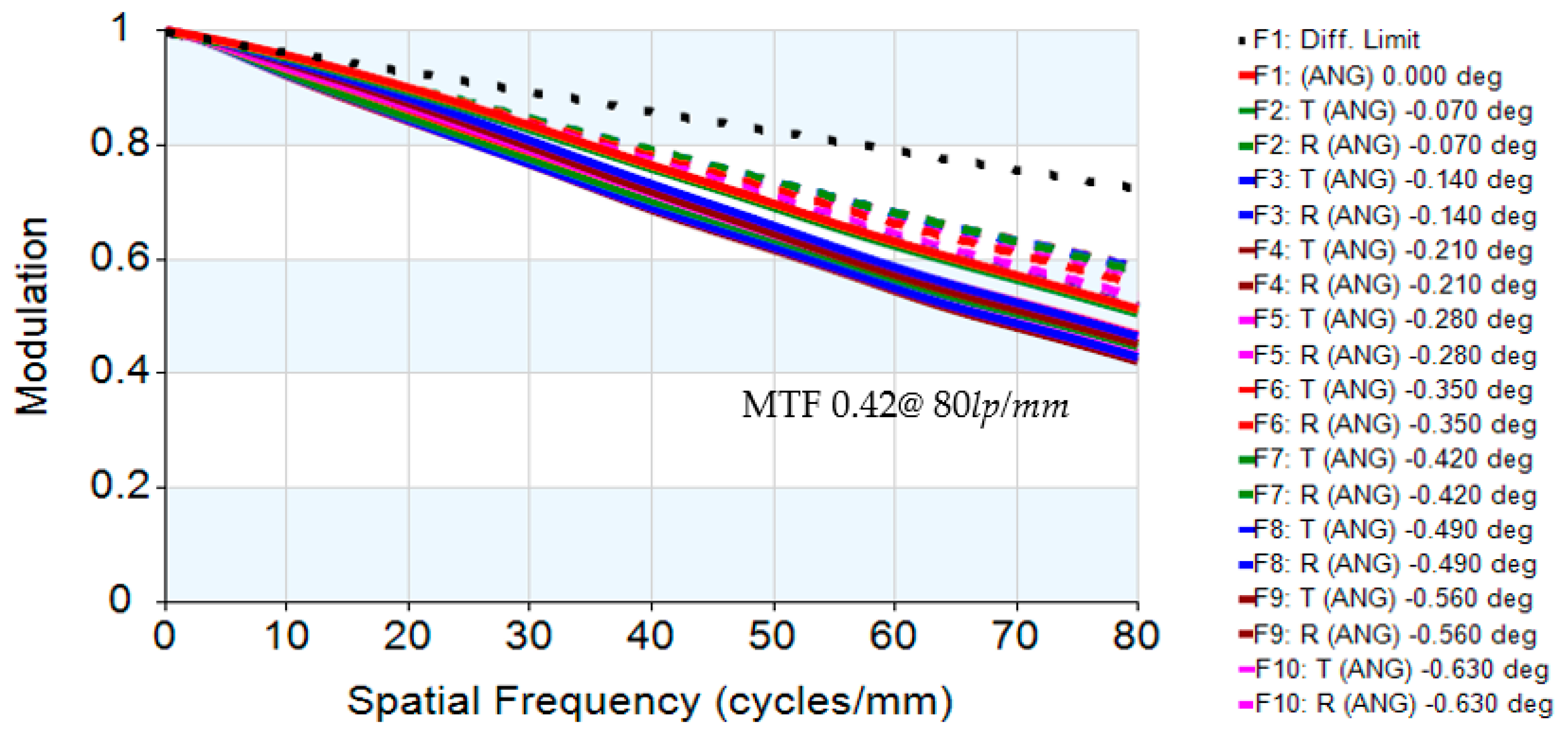
| MTF (80 lp/mm) | >0.5 |
| Lateral color | <3.37 μm |
| Surface (No.) | Surface Type | Y Radius | Thickness | Glass | Y Semi Aperture | Conic Constant (K) | 4th Order | 6th Order | 8th Order | 10th Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Object | Sphere | Infinity | Infinity | |||||||
| 1 (Stop) | Asphere | 29.75 | 1.15 | NKZFS11_SCHOTT | 1.25 | 100 | 1.82 × 10−3 | 2.55 × 10−4 | −1.33 × 10−4 | 1.63 × 10−5 |
| 2 | Asphere | 11.37 | 3.19 | 1.36 | −3.91 | 3.91 × 1000 | 3.76 × 10−3 | 6.12 × 10−4 | −2.55 × 10−4 | |
| 3 | Asphere | 23.82 | 4.8 | NPK51_SCHOTT | 2.23 | −100 | 1.66 × 10−3 | 7.01 × 10−5 | −3.27 × 10−5 | 3.00 × 10−6 |
| 4 | Sphere | −12.59 | 13.23 | 2.76 | ||||||
| 5 | Sphere | −11.06 | 4.67 | NLAK33A_SCHOTT | 3.64 | |||||
| 6 | Sphere | −5.53 | 0.8 | SF2_SCHOTT | 4.25 | |||||
| 7 | Sphere | 597.53 | 0.1 | 4.62 | ||||||
| 8 | Asphere | 5.40 | 4.8 | PLAK35_SCHOTT | 5.26 | −0.63 | 2.70 × 10−4 | −1.98 × 10−5 | 5.69 × 10−7 | −1.08 × 10−8 |
| 9 | Sphere | −31.12 | 1.54 | 4.78 | ||||||
| 10 | Asphere | −33.61 | 1.64 | PSF67_SCHOTT | 3.37 | 83.02 | −1.59 × 10−3 | 7.78 × 10−4 | −6.97 × 10−5 | 2.37 × 10−6 |
| 11 | Asphere | 27.19 | 0.74 | 2.49 | 82.28 | 7.76 × 10−3 | −1.92 × 10−4 | 1.98 × 10−4 | −1.78 × 10−5 | |
| 12 | Sphere | Infinity | 0.7 | BK7_SCHOTT | 2.48 | |||||
| 13 | Sphere | Infinity | 0.66 | 2.45 | ||||||
| Image | Sphere | Infinity | 0 | 2.41 | ||||||
| FIELD | Design RMS OPD Value | Design plus Tolerance RMS OPD Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
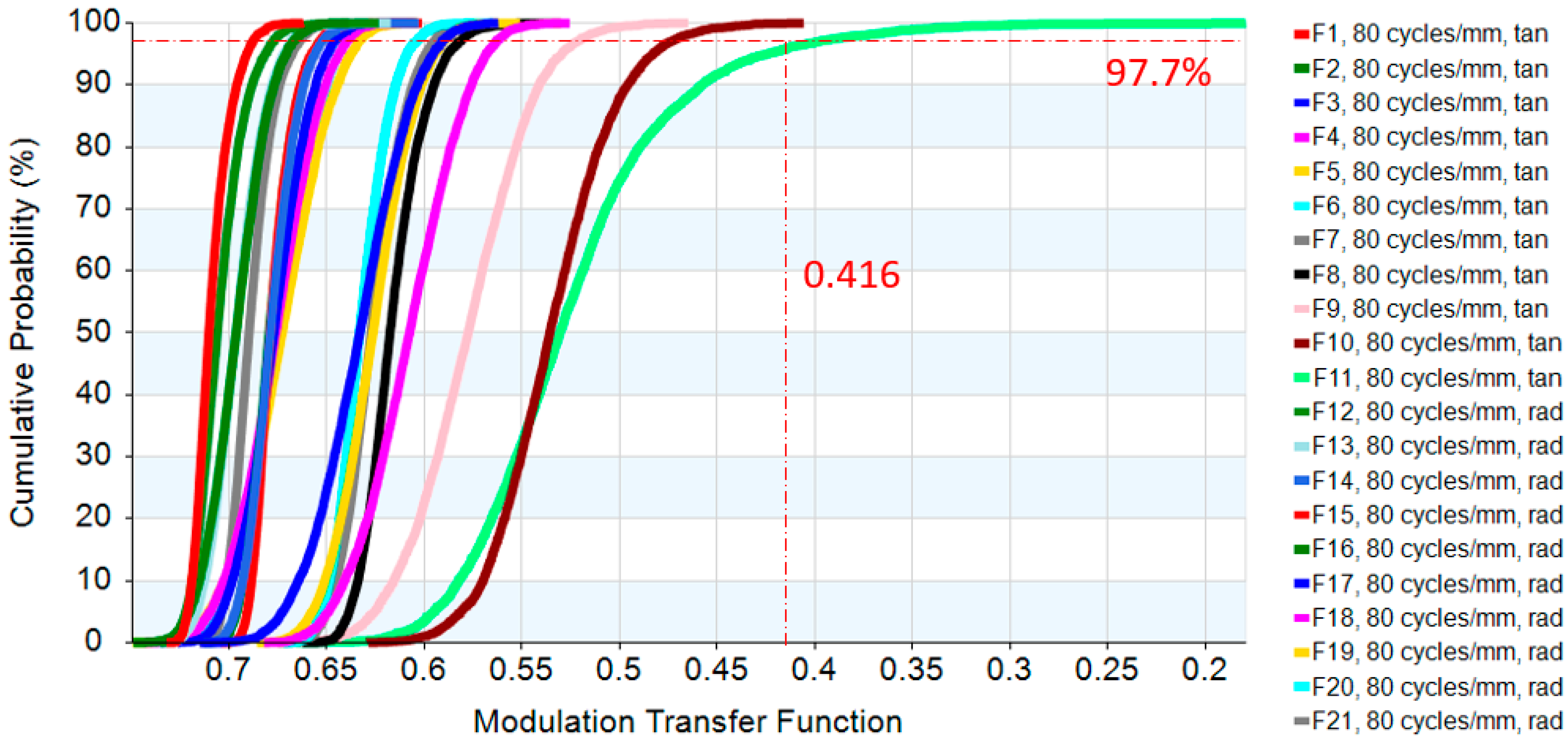
| TAN | 0.0 | 0.7206 | 0.6906 |
| TAN | 0.1 | 0.7076 | 0.6673 |
| TAN | 0.2 | 0.6435 | 0.5886 |
| TAN | 0.3 | 0.6180 | 0.5603 |
| TAN | 0.4 | 0.6382 | 0.5894 |
| TAN | 0.5 | 0.6461 | 0.6061 |
| TAN | 0.6 | 0.6429 | 0.5963 |
| TAN | 0.7 | 0.6340 | 0.5854 |
| TAN | 0.8 | 0.5942 | 0.5181 |
| TAN | 0.9 | 0.5552 | 0.4738 |
| TAN | 1.0 | 0.5662 | 0.4162 |
| RAD | 0.1 | 0.7189 | 0.6800 |
| RAD | 0.2 | 0.7091 | 0.6685 |
| RAD | 0.3 | 0.6900 | 0.6530 |
| RAD | 0.4 | 0.6889 | 0.6569 |
| RAD | 0.5 | 0.6901 | 0.6554 |
| RAD | 0.6 | 0.6887 | 0.6450 |
| RAD | 0.7 | 0.6884 | 0.6375 |
| RAD | 0.8 | 0.6855 | 0.6304 |
| RAD | 0.9 | 0.6879 | 0.6378 |
| RAD | 1.0 | 0.7026 | 0.6669 |
| FRACT | DEG | RMS | STREHL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X Y | 0.00 0.00 | 0.00 0.00 | 0.0438 | 0.927 |
| X Y | 0.00 0.10 | 0.00 −0.07 | 0.0413 | 0.935 |
| X Y | 0.00 0.20 | 0.00 −0.14 | 0.0407 | 0.937 |
| X Y | 0.00 0.30 | 0.00 −0.21 | 0.0414 | 0.935 |
| X Y | 0.00 0.40 | 0.00 −0.28 | 0.0405 | 0.937 |
| X Y | 0.00 0.50 | 0.00 −0.35 | 0.0417 | 0.934 |
| X Y | 0.00 0.60 | 0.00 −0.42 | 0.0403 | 0.938 |
| X Y | 0.00 0.70 | 0.00 −0.49 | 0.0399 | 0.939 |
| X Y | 0.00 0.80 | 0.00 −0.56 | 0.0383 | 0.944 |
| X Y | 0.00 0.90 | 0.00 −0.56 | 0.0355 | 0.951 |
| X Y | 0.00 1.00 | 0.00 −0.70 | 0.0474 | 0.915 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Su, Y.-L.; Sun, W.-S.; Tien, C.-L.; Lin, Y.-C.; Liu, Y.-H. Design of an Afocal Telescope System Integrated with Digital Imaging for Enhanced Optical Performance. Micromachines 2026, 17, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17010062
Su Y-L, Sun W-S, Tien C-L, Lin Y-C, Liu Y-H. Design of an Afocal Telescope System Integrated with Digital Imaging for Enhanced Optical Performance. Micromachines. 2026; 17(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17010062
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yi-Lun, Wen-Shing Sun, Chuen-Lin Tien, Yen-Cheng Lin, and Yi-Hong Liu. 2026. "Design of an Afocal Telescope System Integrated with Digital Imaging for Enhanced Optical Performance" Micromachines 17, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17010062
APA StyleSu, Y.-L., Sun, W.-S., Tien, C.-L., Lin, Y.-C., & Liu, Y.-H. (2026). Design of an Afocal Telescope System Integrated with Digital Imaging for Enhanced Optical Performance. Micromachines, 17(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17010062








