The Cutting Edge Geometric Optimization of the PCBN Tool for the Machining of Cast Iron
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Cutting Simulation of Cast Iron Material
2.1. The Constitutive Model of Cast Iron Material
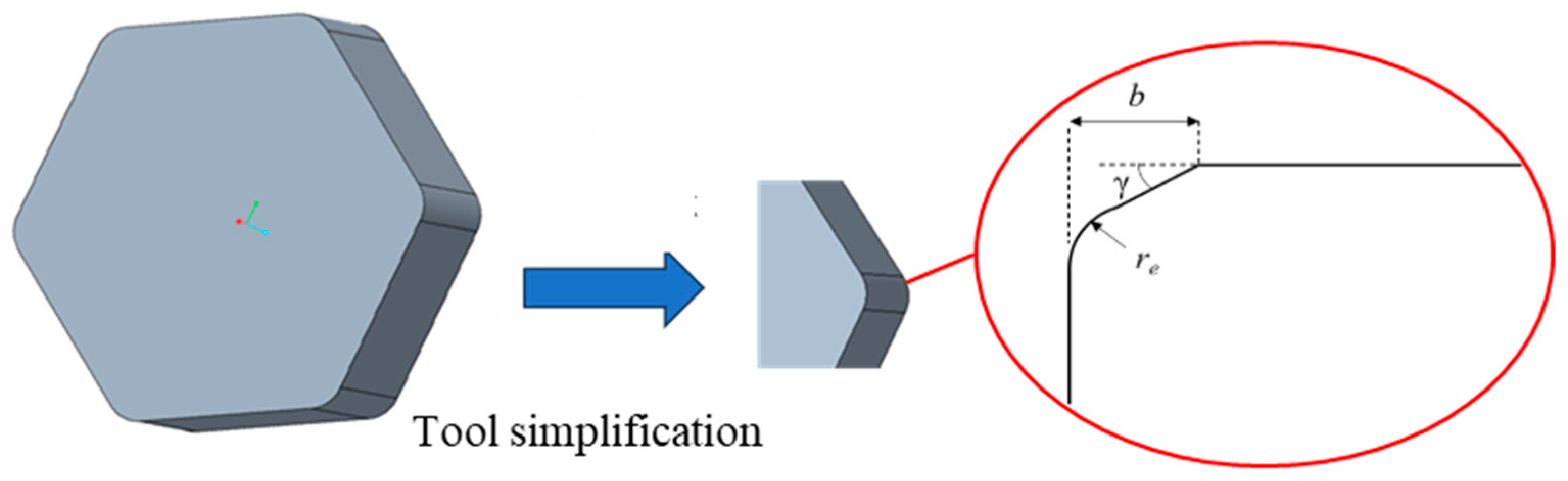
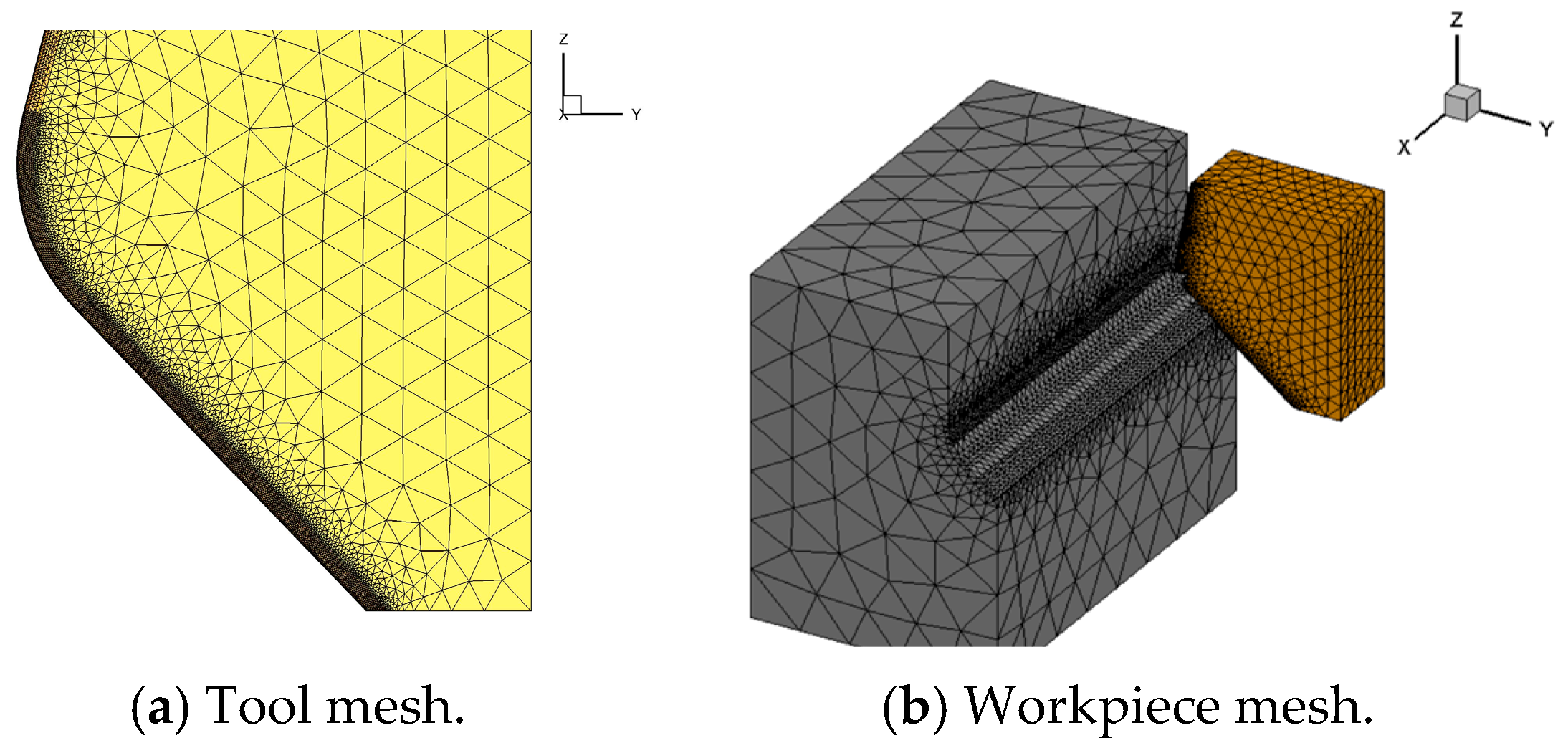
2.2. The Cutting Simulation Model of PCBN Tool
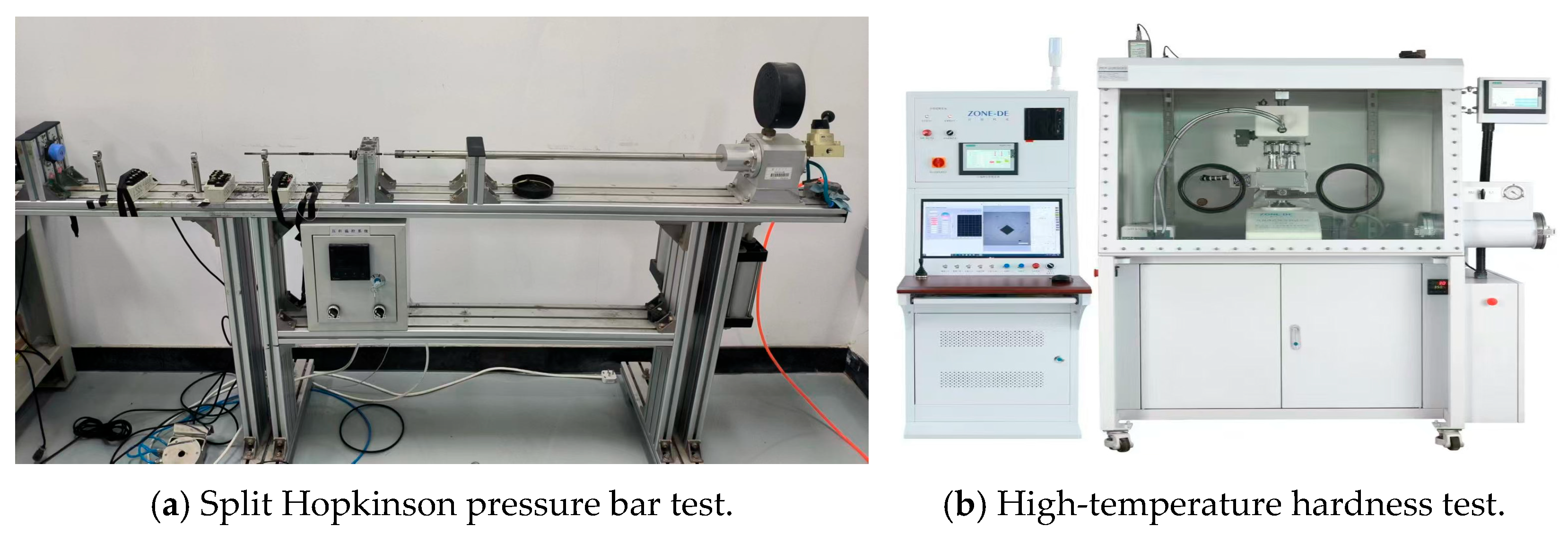
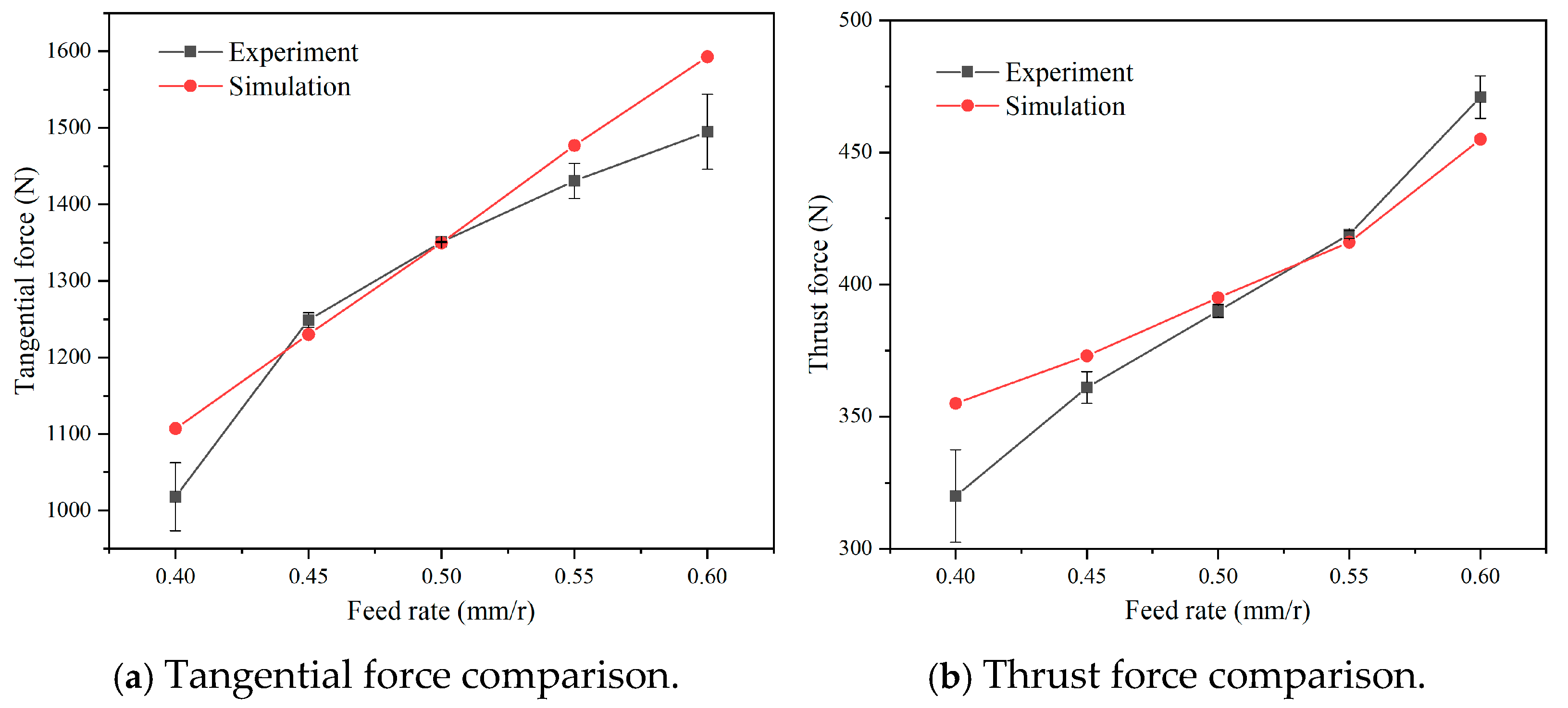
2.3. The Experiment Verification of Cutting Simulation
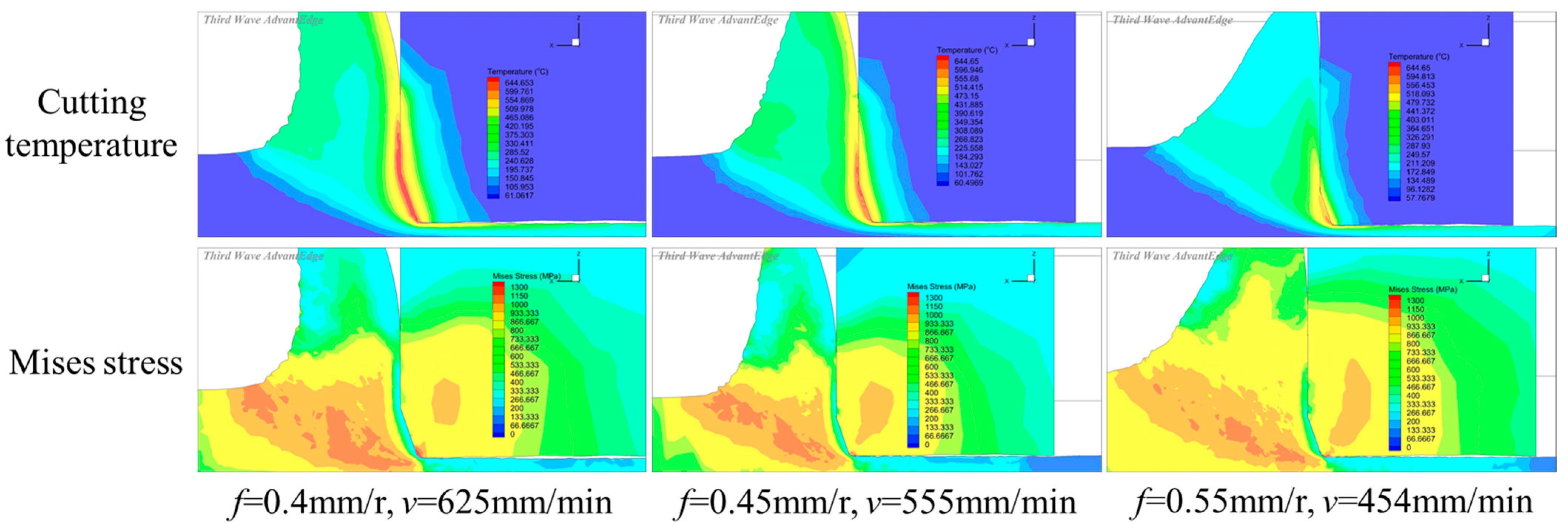
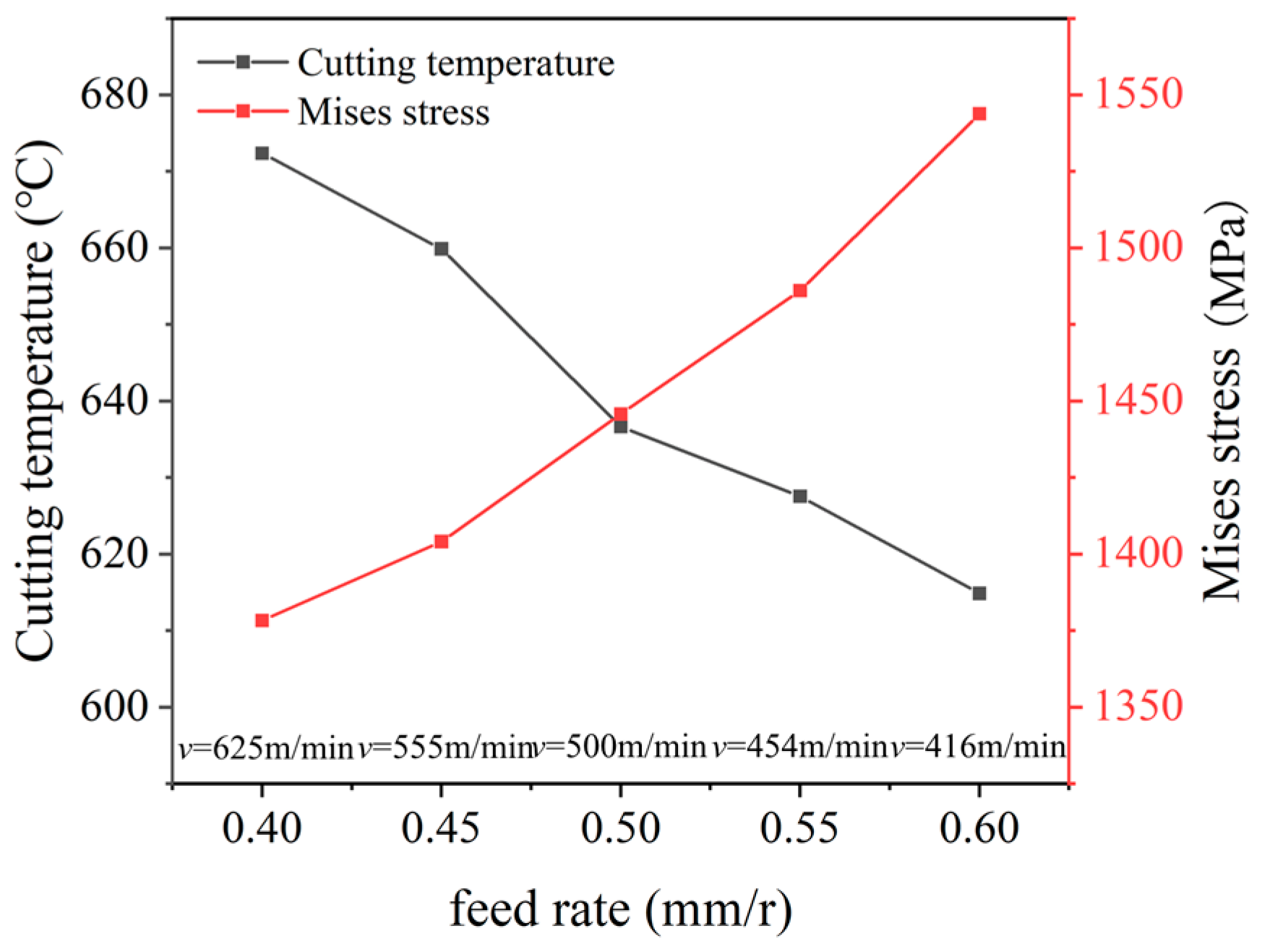
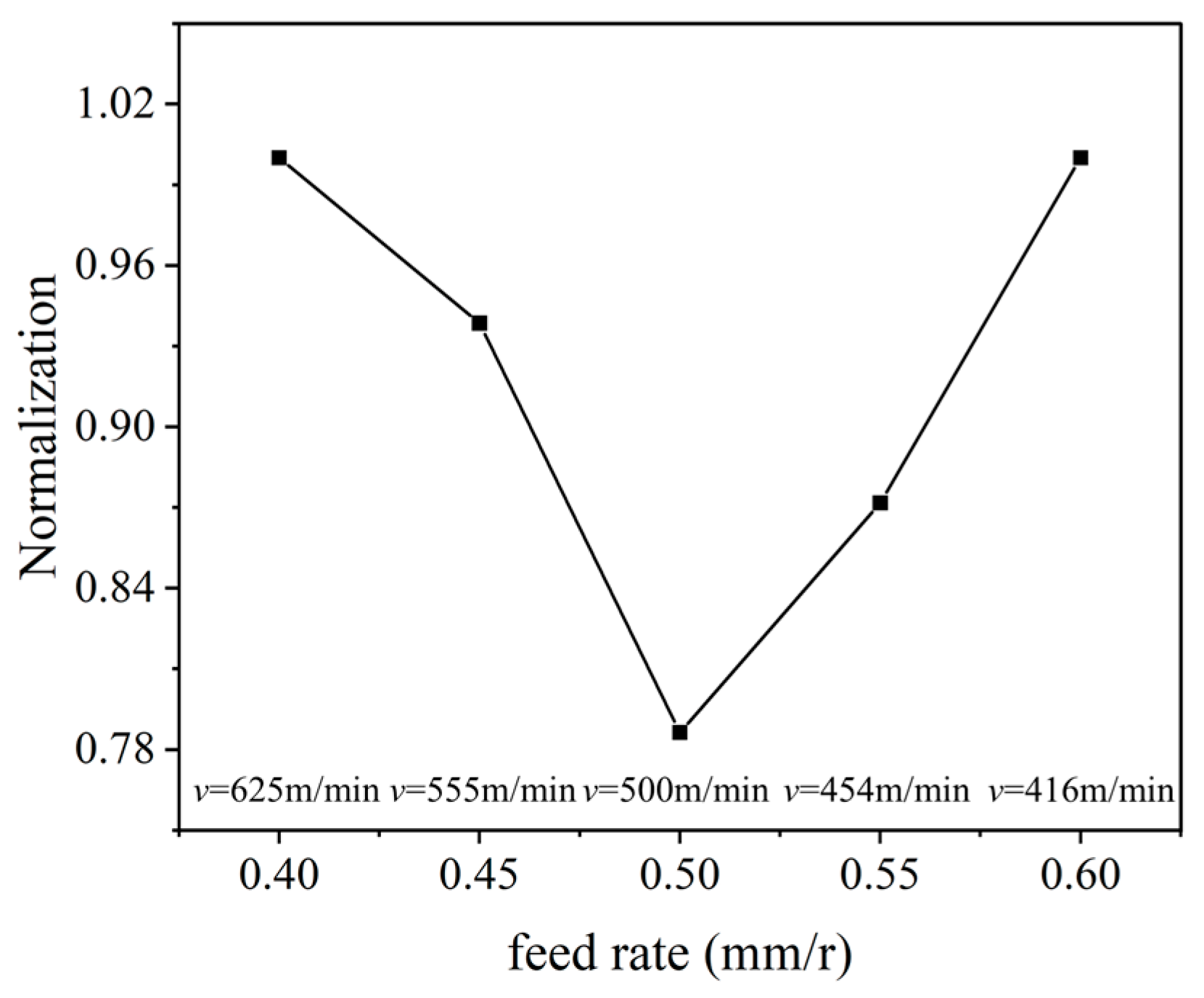
3. The Cutting Parameters’ Optimization Based on Equal Material Removal Rate
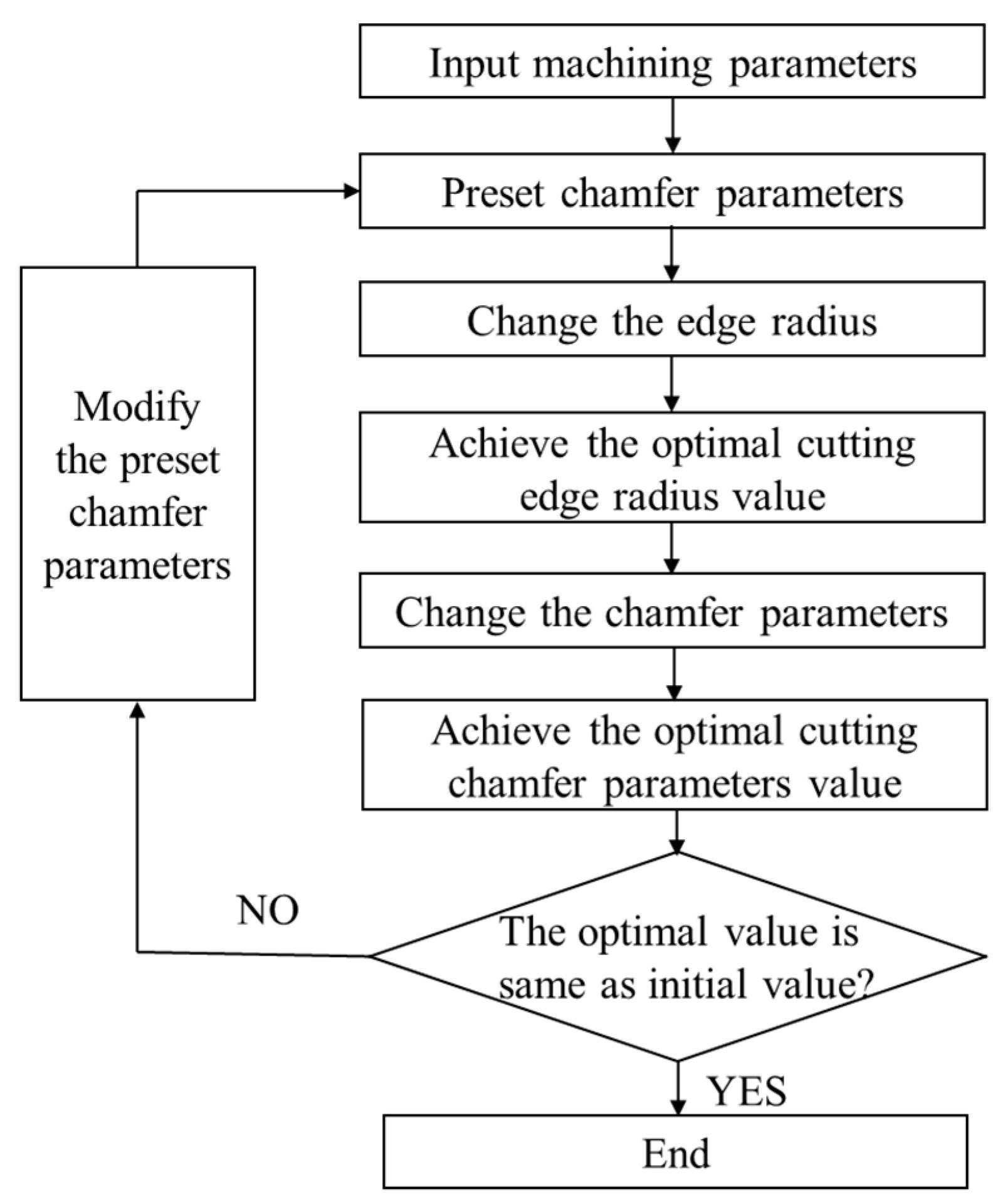
4. The Cutting Edge Geometric Optimization of PCBN Tool
- (1)
- Initialize the cutting simulation, and input the optimal machining parameters and the constitutive model of the cast iron FC220P and PCBN tool.
- (2)
- Preset chamfer parameters, and perform the cutting simulation with different edge radii in the range from 10 μm to 50 μm, to obtain the comprehensive optimal edge radius based on the cutting simulation results.
- (3)
- Based on the optimal edge radius, perform the cutting simulation with different chamfer parameters to obtain the comprehensive optimal chamfer parameters based on the cutting temperature and stress.
- (4)
- If the optimal chamfer parameters are same to the preset value in step (2), end the optimization process. Otherwise, change the preset chamfer parameters in step (1), and then repeat the optimization process until the optimal chamfer parameters and the preset value are consistent.
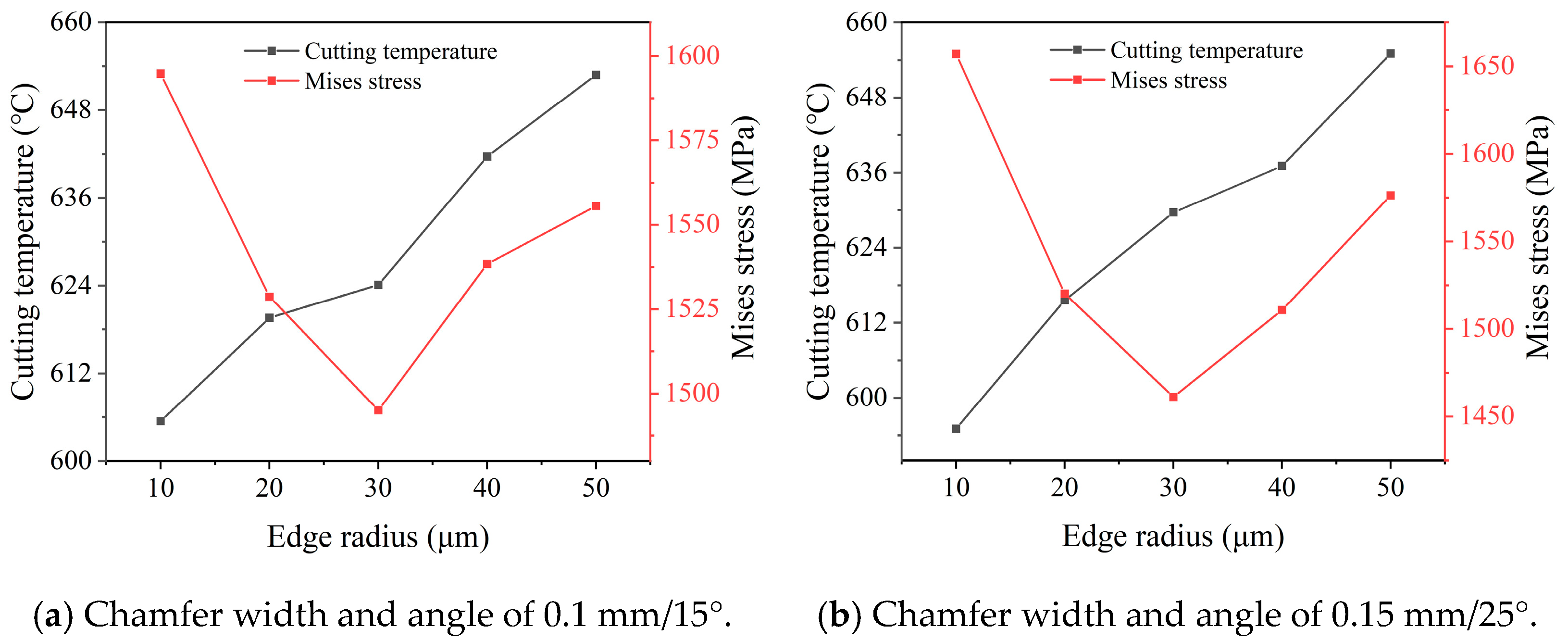
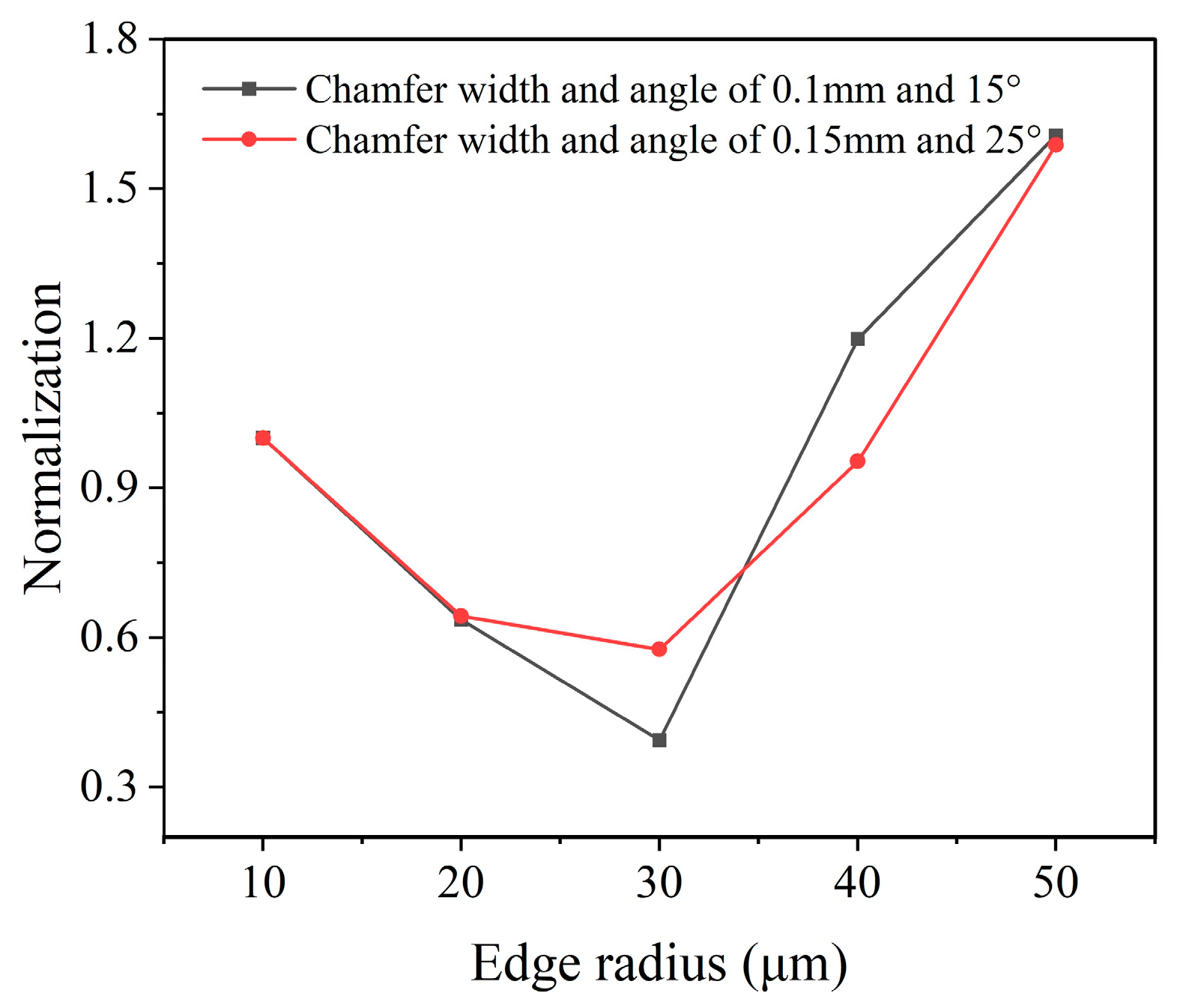
4.1. The Cutting Edge Radius Optimization of PCBN Tool
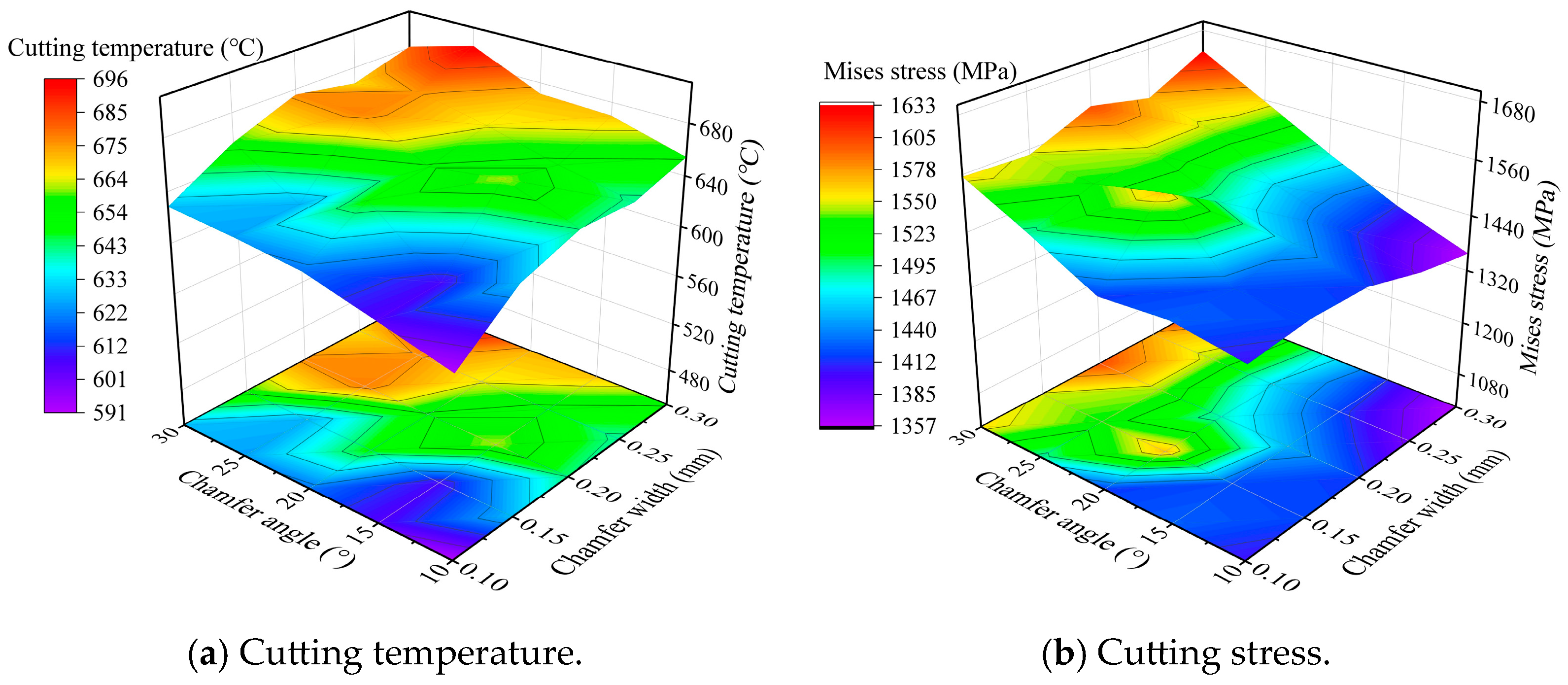
4.2. The Chamfer Parameters’ Optimization of PCBN Tool
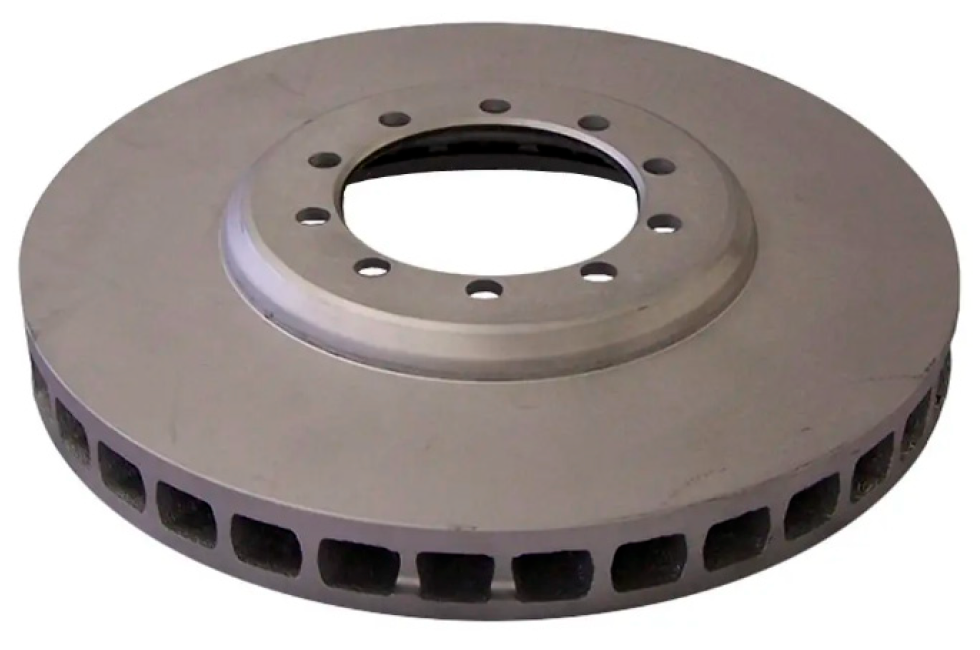
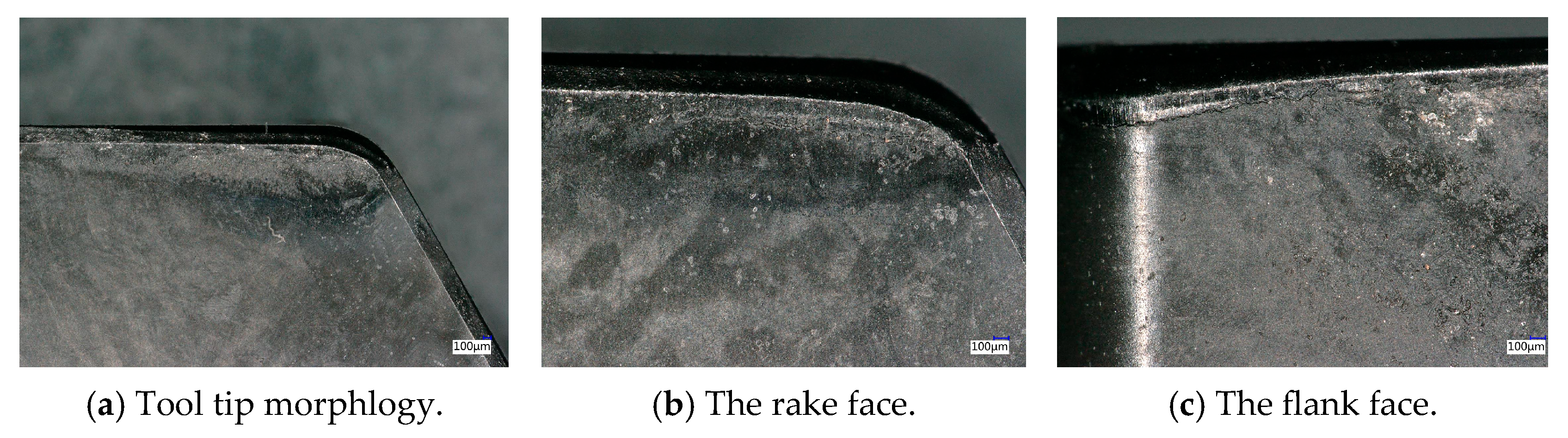
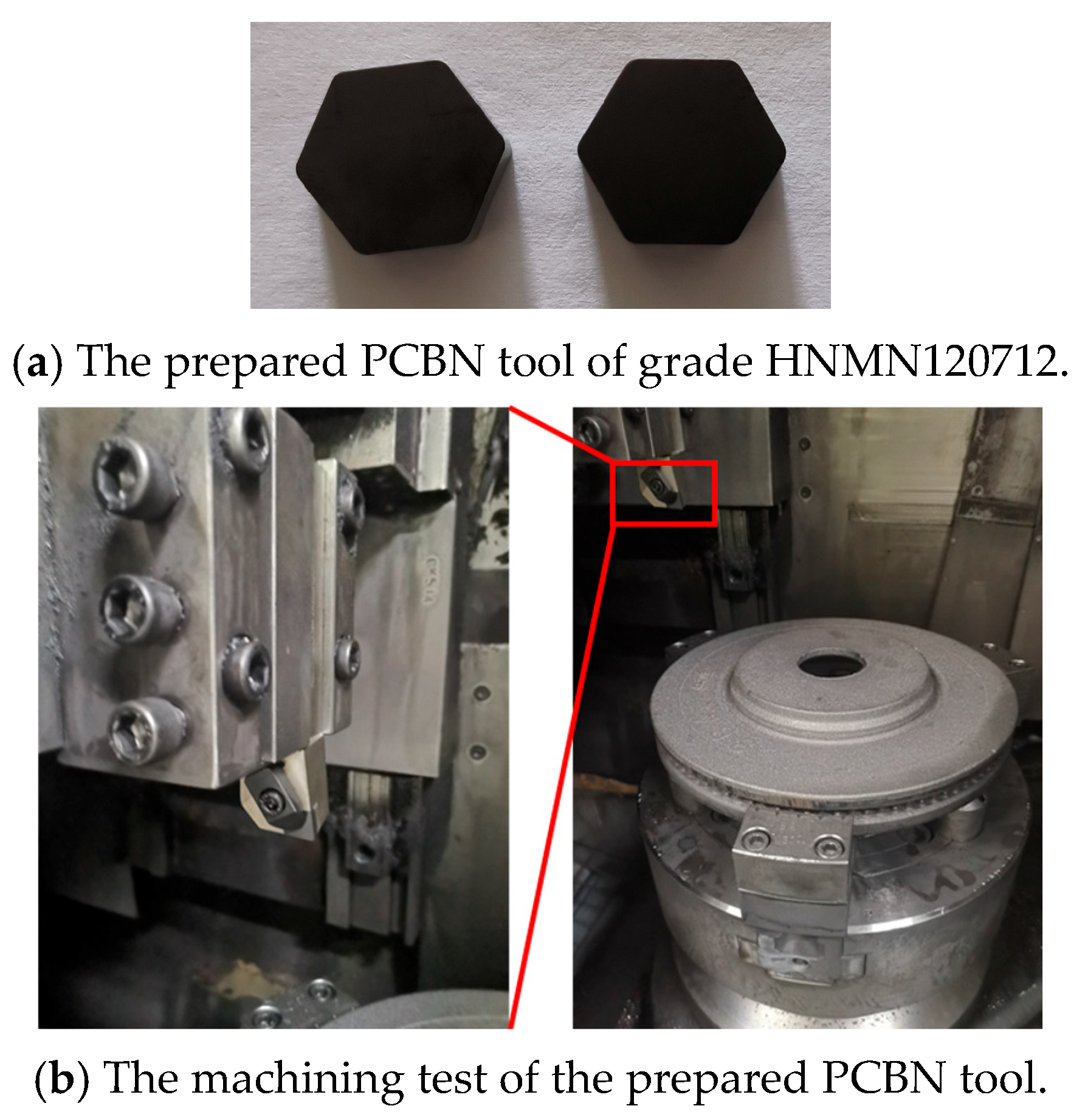
4.3. The Verification of PCBN Tool in Machining of Brake Discs
5. Summary and Conclusions
- The cutting simulation for cast iron F220P with the PCBN tool of grade HNMN120712 was established based on the P-L constitutive model. The established cutting simulation exhibits the largest error of less than 10.7% with the experiment verification. With the equal material removal rate method and considering the production efficiency requirement, the optimal turning parameters were obtained as a cutting depth of 1 mm, feed rate of 0.5 mm/r, and cutting velocity of 500 m/min.
- The edge geometric parameters mainly include the edge radius and chamfer width and angle. The edge geometric parameters were comprehensively optimized in two stages with the normalization coefficient of the cutting temperature and stress. Firstly, the edge radius was optimized to 30 μm, and then, the chamfer width and angle were further optimized to 0.1 mm and 15°.
- The optimized PCBN tool was prepared and then tested in the machining of brake discs made of cast iron F220P. The machining results indicate that the designed PCBN tool exhibits an excellent wear resistance performance and achieves 3.4 times the tool life of the conventional tool.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borawski, A. Conventional and unconventional materials used in the production of brake discs—Review. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2020, 27, 374–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.N.; Vijayakumar, T.; Murali, G. Comprehensive Review on Brake Friction Materials. J. Polym. Compos. 2023, 11, S197–S214. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, A.J.; Boing, D.; Schroeter, R.B. Effect of PCBN tool grade and cutting type on hard turning of high-chromium white cast iron. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yao, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, F. Experimental research on the welding strength of PCBN and cemented carbide materials for cutting tool application. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2024, 119, 106528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, X.; Yao, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Experimental research on the double-sided grinding of PCBN materials with different microstructures. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 129, 107126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, E.; Riemer, H.; Schröter, D.; Henze, S.; Sammler, F.; Barthelmä, F.; Frank, H. Investigation of wear resistance of coated PcBN turning tools for hard machining. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 72, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Q.; Yin, L.; Hänel, A.; Teicher, U.; Penter, L.; Seidel, A.; Harst, S.; Ihlenfeldt, S. Cutting performance of binderless nano-polycrystalline cBN and PcBN milling tools for high-speed milling of hardened steel. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 34757–34773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.; Karthik, R.; Sharma, S.; Ramkumar, J. Finish turning of hardened bearing steel using textured PcBN tools. J. Manuf. Process 2020, 60, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Xu, J.K.; Yu, Z.J. Comparative analysis of cutting performance and dead metal zone in ductile iron machining using PCBN chamfered tools with and without micro-pit texture. J. Manuf. Process 2025, 148, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guo, J.; Wang, D.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, X.L. Experimental study on high-speed hard cutting by PCBN tools with variable chamfered edge. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 4209–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Chen, T.; Qiu, C.Z.; Wang, D.Y.; Liu, X.L. Experimental investigation of high-speed hard turning by PCBN tooling with strengthened edge. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 3785–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Gang, L.; Hui, X.; Liu, J.Q.; Li, S.Y. Study on cutting performance of double-inclined-wall cosine enhanced PCBN tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Li, R.; Zhang, L.B.; Yang, H.D.; Tang, H.H.; Chen, S.H. On the tool wear mechanism of machining Zr-based bulk metallic glasses under varying corner radii. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 624, 122722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Deng, Z.L.; Gao, X.J.; He, Y. Cutting performance of micro-textured PCBN tool. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2021, 4, 023004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, T. Computational modelling of 3D turning: Influence of edge micro-geometry on forces, stresses, friction and tool wear in PcBN tooling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5167–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Alkahtani, M.; Alsultan, M.; Buhl, J.; Gupta, M.K. Chip formation, cutting temperature and forces measurements in hard turning of Gcr15 under the influence of PcBN chamfering parameters. Measurement 2022, 204, 112130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmell, M.; Bushlya, V.; M’Saoubi, R.; Gutnichenko, O.; Zaporozhets, O.; Laakso, S.V.A.; Ståhl, J.E. Investigation of mechanical and thermal loads in pcBN tooling during machining of Inconel 718. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, F.; Wu, X.; Zhao, G.; Shi, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, M. Optimizing the cutting edge geometry of micro drill based on the entropy weight method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 2673–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.K.; Jiang, F.; Guo, B.C.; Wang, F.Z. Optimization and influence of the geometrical parameters of chip breaker for finishing machining of Fe-Cr-Ni stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 3663–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zha, X.M.; Jiang, F. Optimizing the geometric parameters of cutting edge for rough machining Fe-Cr-Ni stainless steel. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, D.; Chen, G. Tool geometry design and microstructure fabrication by micro flat-end milling on soft-brittle LiF surface. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 149, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ma, F.; Wang, Z.; Sha, Z. Power Law Constitutive Model Parameter Identification of 6005A Aluminum Alloy for Machining. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Su, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Yao, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, F. The establishment of constitutive model in the cutting simulation of tool design for cast iron material. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 37, 5142–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Density | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 7.1 g/cm3 | 220 MPa | 180 MPa | 175 HV |
| Parameters | Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting depth ap/mm | 1 | ||||
| Feed rate f/mm/r | 0.4 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.6 |
| Cutting velocity v/m/min | 625 | 555 | 500 | 454 | 416 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Edge radius re/μm | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 |
| Chamfer angle γ/° | 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 |
| Chamfer width b/mm | 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Su, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Yao, H.; Jiang, F. The Cutting Edge Geometric Optimization of the PCBN Tool for the Machining of Cast Iron. Micromachines 2025, 16, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090978
Wu X, Su Z, Zhang C, Zhao X, Yao H, Jiang F. The Cutting Edge Geometric Optimization of the PCBN Tool for the Machining of Cast Iron. Micromachines. 2025; 16(9):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090978
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xian, Zhiqin Su, Chao Zhang, Xuefeng Zhao, Hongfei Yao, and Feng Jiang. 2025. "The Cutting Edge Geometric Optimization of the PCBN Tool for the Machining of Cast Iron" Micromachines 16, no. 9: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090978
APA StyleWu, X., Su, Z., Zhang, C., Zhao, X., Yao, H., & Jiang, F. (2025). The Cutting Edge Geometric Optimization of the PCBN Tool for the Machining of Cast Iron. Micromachines, 16(9), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090978







