Thermal Limitations in Ultrafast Laser Direct Writings in Dielectric Solids
Abstract
1. Introduction
Where and When Does the Temperature Play a Role in the Processes?
2. The Treatment Curve in Scanning Pulsed Laser Mode
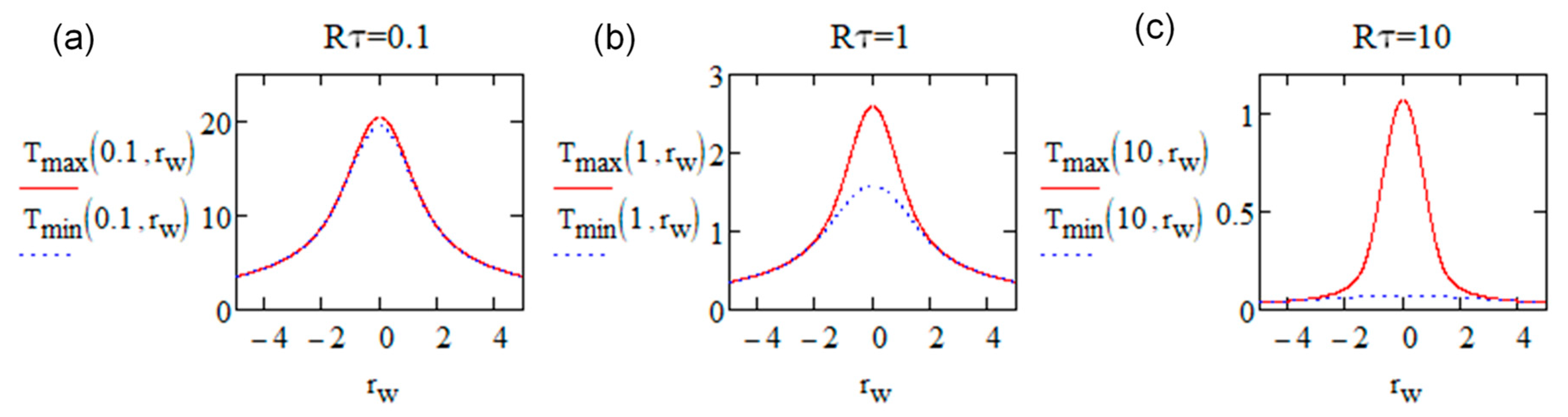
- When is large (ca. ≳ 7), heat accumulation is negligible.
- When , cumulative heating becomes significant, and cannot be neglected. The temperature oscillations are relatively smaller.
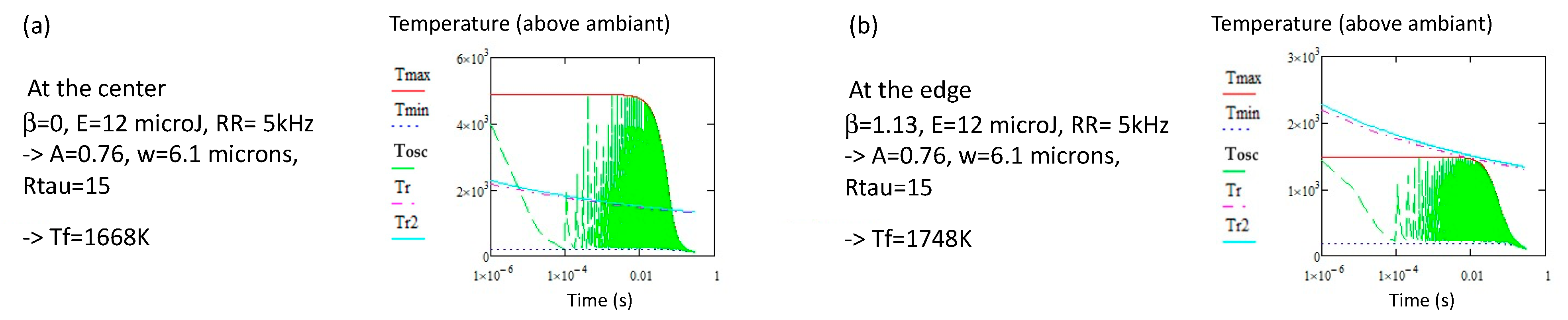
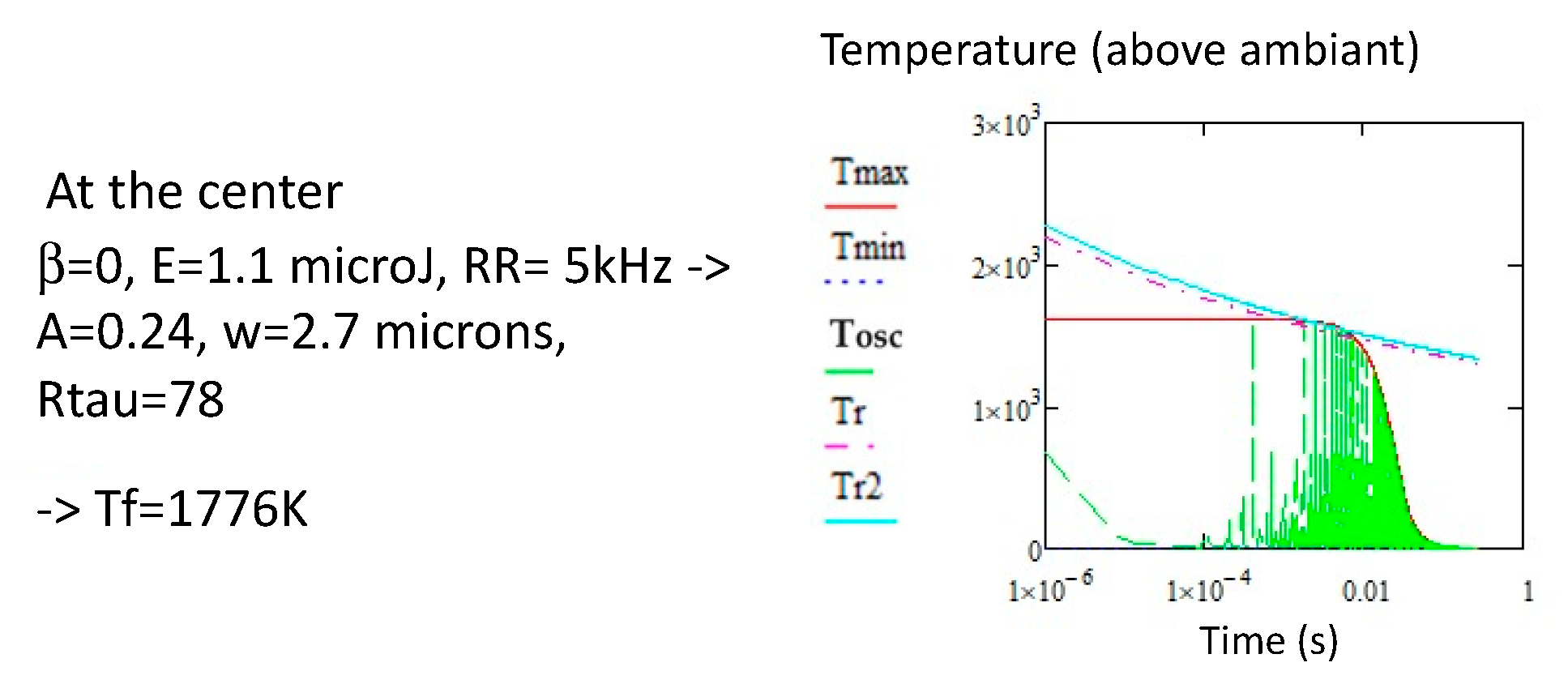
2.1. The Regime of Low Repetition Rate
2.2. The Regime of High Repetition Rate
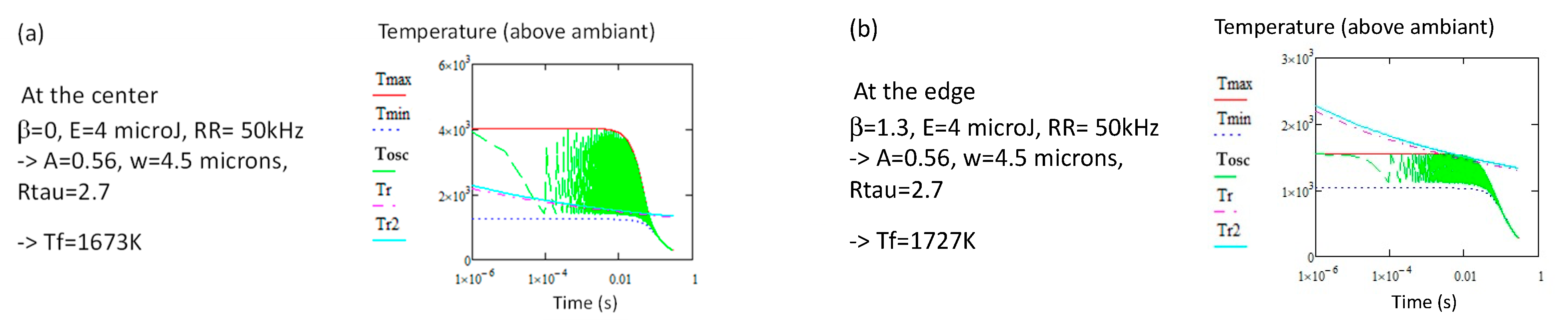
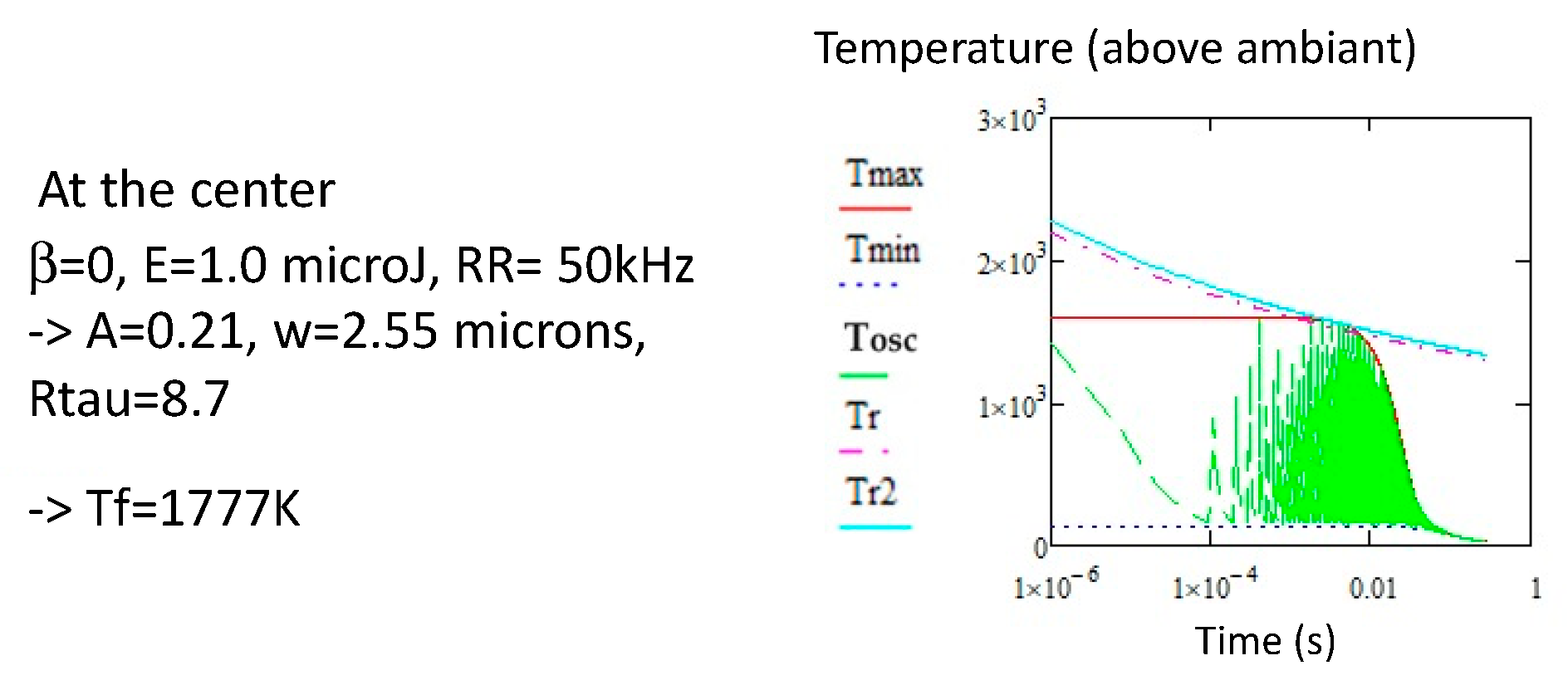
3. Comparison of Thermal Treatment Curve with Transformation/Stability Curves According to the Mechanism
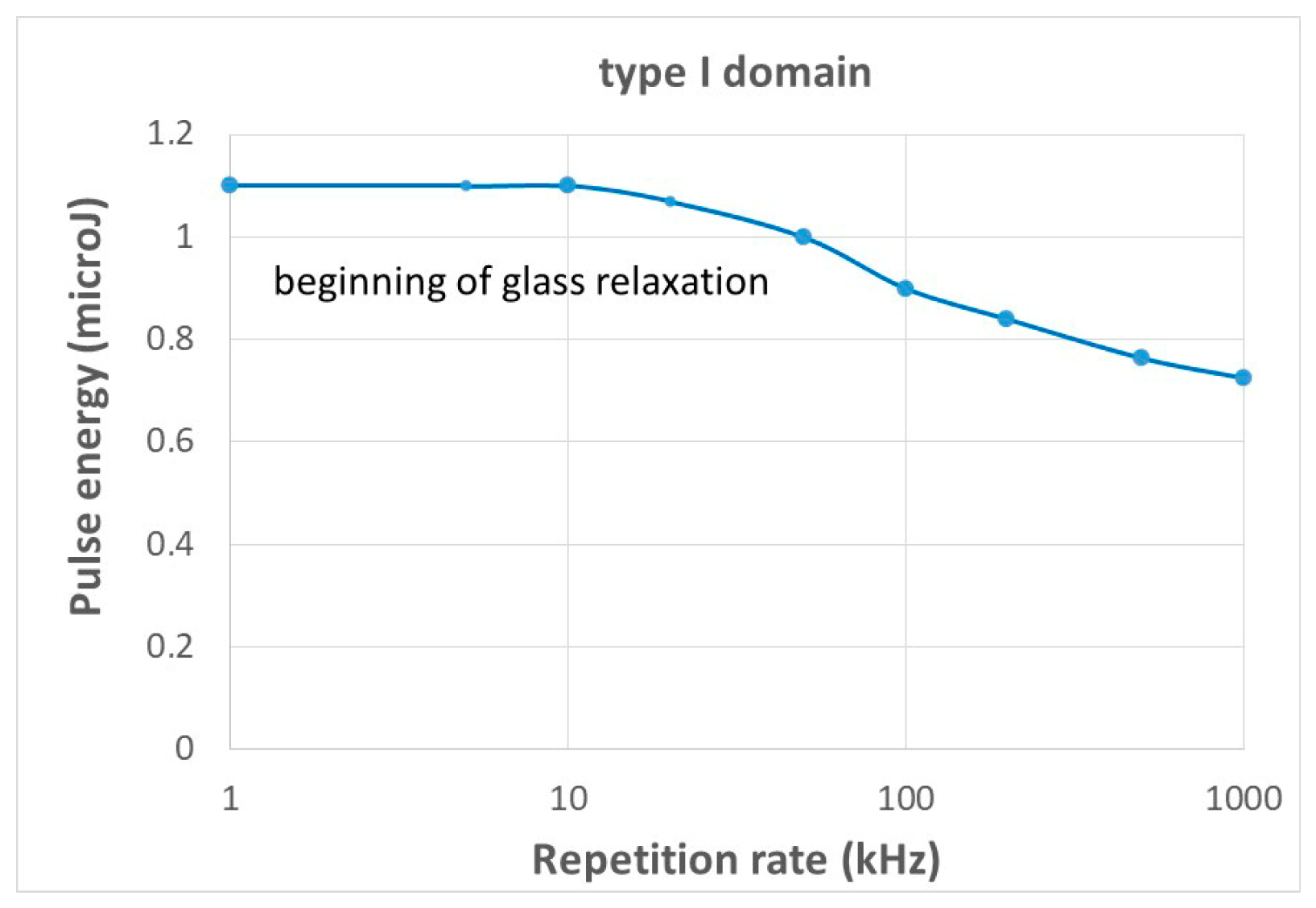
3.1. Type I
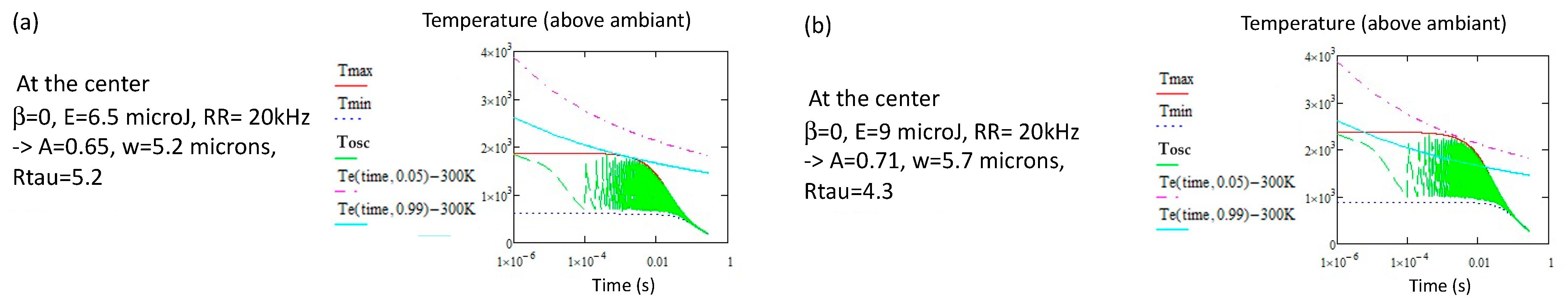
3.2. Type II
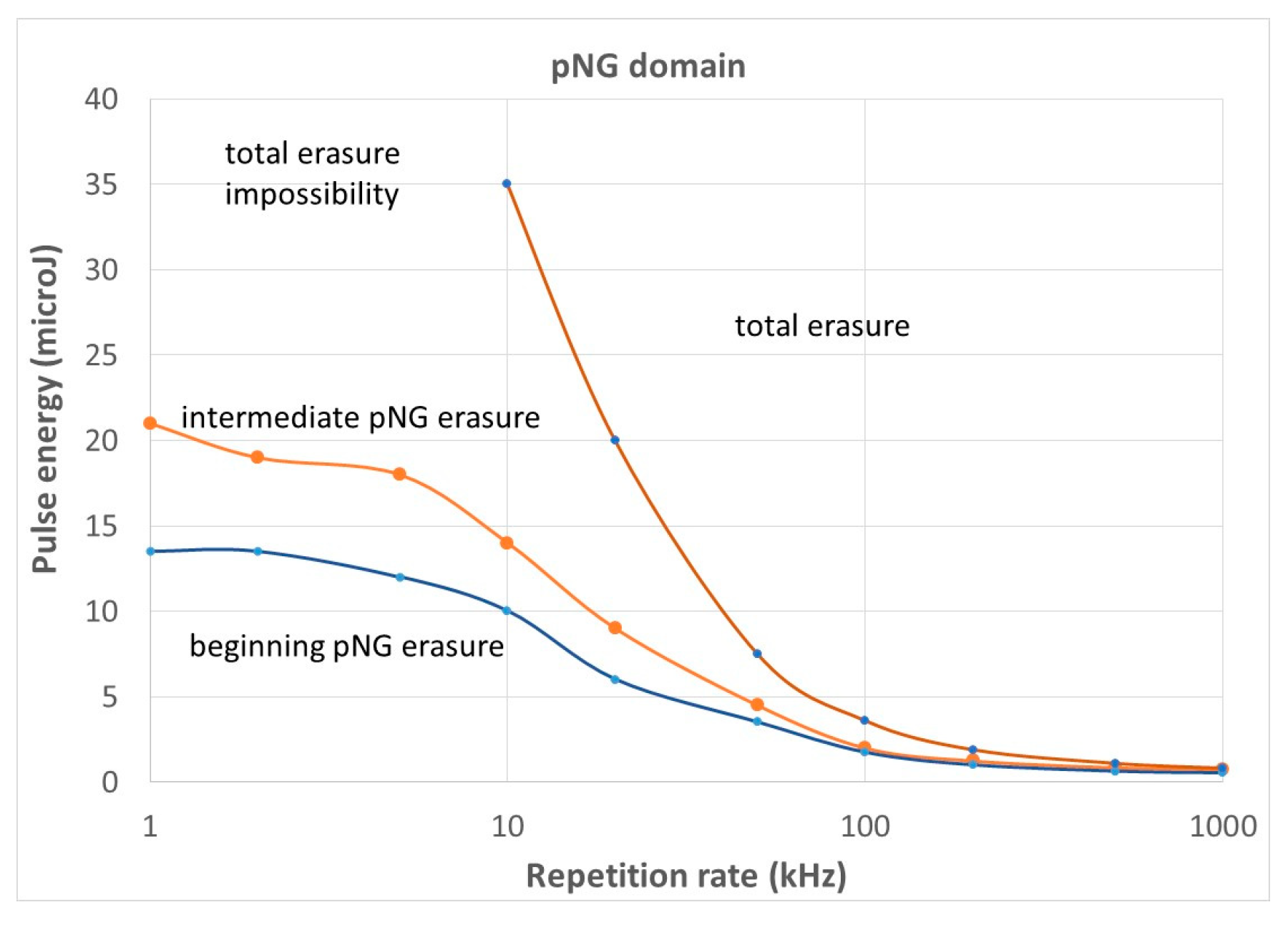
3.2.1. Thermal Stability of Type II (pNG)
3.2.2. Limitation of the Processing Window of Type II
3.3. Type III, the Same Approach as Above (Comparison of Stability and Thermal Treatmentl Curve)
3.4. On VAREPA Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameters | Definitions | Units |
|---|---|---|
| T00 | Temperature increment above room one produced by a single pulse | see equation below |
| Tmin | Minimal temperature of the temperature oscillation at the steady state | see equation below |
| Tmax | Maximal temperature of the temperature oscillation at the steady state | see equation below |
| Tosc | Temperature oscillation at the steady state | ° |
| Tf | Fictive temperature (representative of medium-range order of the glass) | K |
| Tr or Tr2 | Relaxation temperature according to relaxation time for 63 or 87% of relaxed glass fraction (tool definition, see text) | K |
| T(t) | Temperature increment above room one at the distance ,t and at time t This temperature can be either Tmax, Tmin or Tosc according to the discussion. | ° |
| Te | Temperature for erasing 5% or 99% of nanopores involved in type II modifications | K |
| Pulse energy | J | |
| Fraction of absorbed light | none | |
| Period of the pulses | μs | |
| Pulse repetition rate | MHz | |
| Effective beam waist radius (at 1/e) | μm | |
| Thermal conductivity | 1.09 W/(m.K) (1) | |
| Density | 2200 kg/m3 | |
| Specific heat capacity | 703 J/(kg.K) | |
| Thermal diffusivity | 7.06 × 10−7 m2/s | |
| Heat diffusion time | μs | |
| η | Viscosity (2) | |
| none | ||
| A small quantity of computational needs | none | |
| rw | Normalized radius (r/w) | none |
| rwd | Normalized dynamic distance to the focus center (see Equation (A4)) | none |
Appendix B
Appendix B.1. Temperature Distribution Evolution During Laser Writing (Scanning Mode)
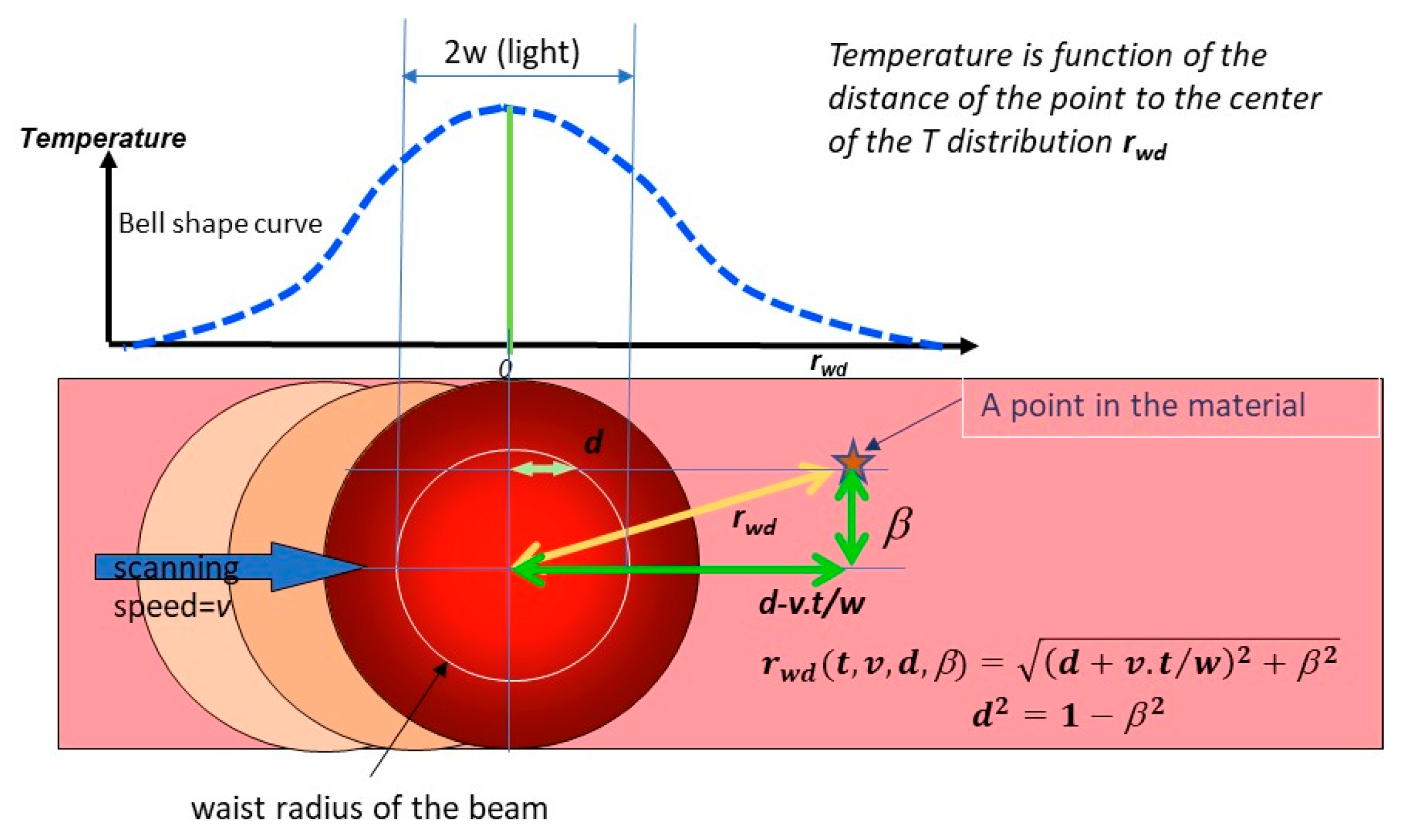
Appendix B.2. Tmin and Tmax
Appendix C

References
- Shchedrina, N.; Cavillon, M.; Ari, J.; Ollier, N.; Lancry, M. Impact of Glass Free Volume on Femtosecond Laser-Written Nanograting Formation in Silica Glass. Materials 2024, 17, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukerstein, M.; Zhukov, V.; Meshcheryakov, Y.; Bulgakova, N. From Localized Laser Energy Absorption to Absorption Delo- calization at Volumetric Glass Modification with Gaussian and Doughnut-Shaped Pulses. Photonics 2023, 10, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Wang, H.; Skuja, L.; Kuehn, B.; Franz, B.; Svirko, Y.; Kazansky, P. Ultrafast Laser Writing in Different Types of Silica Glass. Laser Photonics Rev. 2023, 17, 2200978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, C.B.; Brodeur, A.; Mazur, E. Laser-induced breakdown and damage in bulk transparent materials induced by tightly focused femtosecond laser pulses. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäuerle, D. Laser Processing and Chemistry; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Seuthe, T.; Mermillod-Blondin, A.; Grehn, M.; Bonse, J.; Wondraczek, L.; Eberstein, M. Structural relaxation phenomena in silicate glasses modified by irradiation with femtosecond laser pulses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancry, M.; Poumellec, B.; Canning, J.; Cook, K.; Poulin, J.-C.; Brisset, F. Ultrafast nanoporous silica formation driven by femtosecond laser irradiation. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cang, H.; Labno, A.; Lu, C.; Yin, X.; Liu, M.; Gladden, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Probing the electromagnetic field of a 15-nanometre hotspot by single molecule imaging. Nature 2011, 469, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, A.; Ma, H.; Veiko, V.P.; Colombier, J.-P.; Itina, T.E. On the role of nanopore formation and evolution in multi-pulse laser nanostructuring of glasses. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 124, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, A.; Colombier, J.-P.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J.; Bonse, J.; Itina, T.E. Spontaneous periodic ordering on the surface and in the bulk of dielectrics irradiated by ultrafast laser: A shared electromagnetic origin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grojo, D.; Gertsvolf, M.; Lei, S.; Barillot, T.; Rayner, D.M.; Corkum, P.B. Exciton-seeded multiphoton ionization in bulk SiO2. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 212301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Hnatovsky, C.; Simova, E. Applications of femtosecond laser induced self organized planar nanocracks inside fused silica glass. Laser Photonics Rev. 2008, 2, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.; Jia, F.; Heinrich, M.; Döring, S.; Peschel, U.; Tünnermann, A.; Nolte, S. The role of self-trapped excitons and defects in the formation of nanogratings in fused silica. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancry, M.; Regnier, E.; Poumellec, B. Fictive temperature in silica-based glasses and its application to optical fiber manufacturing. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 63–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K. Fictive pressure effects in structural relaxation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1988, 102, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerfa-Tamezait, D. Modifications D’une Couche Mince Sur Un Substrat, Induites Par L’irradiation Mono-Impulsionnelle UV ns. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Saclay, Bures-sur-Yvette, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsuma, Y.; Kazansky, P.G.; Qiu, J.R.; Hirao, K. Self-organized nanogratings in glass irradiated by ultrashort light pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 247405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poumellec, B.; Lancry, M.; Chahid-Erraji, A.; Kazansky, P. Modification thresholds in femtosecond laser processing of pure silica: Review of dependencies on laser parameters [Invited]. Opt. Mater. Express 2011, 1, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressel, L.; de Ligny, D.; Sonneville, C.; Martinez, V.; Mizeikis, V.; Buividas, R.; Juodkazis, S. Femtosecond laser induced density changes in GeO2 and SiO2 glasses: Fictive temperature effect [Invited]. Opt. Mater. Express 2011, 1, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couairon, A.; Sudrie, L.; Franco, M.; Prade, B.; Mysyrowicz, A. Filamentation and damage in fused silica induced by tightly focused femtosecond laser pulses. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 125435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudrie, L. Propagation Non-Linéaire des Impulsions Laser Femtosecondes Dans la Silice. Université de Paris Sud XI Orsay. 2002. Available online: https://ensta.hal.science/ENSTA-PARIS/tel-01188199 (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Li, P.; Yan, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhang, J. Advanced Transparent Glass-Ceramics via Laser Anisotropic Nanocrystallization. Laser Photonics Rev. 2024, 18, 2301403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Qiu, J.; Mitsuyu, T.; Hirao, K. Space-selective growth of frequency-conversion crystals in glasses with ultrashort infrared laser pulses. Opt. Lett. 2000, 25, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Ma, H.L.; Lu, B.; Yu, B.K.; Zhu, B.; Qiu, J.R. Femtosecond laser-induced oriented precipitation of Ba2TiGe2O8 crystals in glass. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 3912–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T.; Honma, T. Laser patterning and characterization of optical active crystals in glasses. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2013, 1, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Simova, E.; Rajeev, P.; Hnatovsky, C.; Taylor, R.; Rayner, D.; Corkum, P. Optically produced arrays of planar nanostructures inside fused silica. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 57404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, T.T.; Sakakura, M.; Eaton, S.M.; Sotillo, B.; Siegel, J.; Solis, J.; Shimotsuma, Y.; Miura, K. Bespoke photonic devices using ultrafast laser driven ion migration in glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 94, 68–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakura, M.; Lei, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.-H.; Kazansky, P.G. Ultralow-loss geometric phase and polarization shaping by ultrafast laser writing in silica glass. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, A.; Colombier, J.P.; Itina, T.E. From random inhomogeneities to periodic nanostructures induced in bulk silica by ultrashort laser. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 075427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricchi, E.; Klappauf, B.G.; Kazansky, P.G. Form birefringence and negative index change created by femtosecond direct writing in transparent materials. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktafi, I.; Cavillon, M.; Lancry, M.; Poumellec, B. Relation between porosity-based and crystal-based femtosecond laser induced nanogratings in oxide glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Muzi, E.; Cavillon, M.; Lancry, M.; Brisset, F.; Sapaly, B.; Janner, D.; Poumellec, B. Polarization-oriented LiNbO3 nanocrystals by femtosecond laser irradiation in LiO2-Nb2O5-SiO2-B2O3 glasses. Opt. Mater. Express 2021, 11, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Xie, Q.; Cavillon, M.; Neuville, D.R.; Pugliese, D.; Janner, D.; Dai, Y.; Poumellec, B.; Lancry, M. Volume nanogratings inscribed by ultrafast IR laser in alumino-borosilicate glasses. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 15449–15460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Cavillon, M.; Pugliese, D.; Janner, D.; Poumellec, B.; Lancry, M. On the Formation of Nanogratings in Commercial Oxide Glasses by Femtosecond Laser Direct Writing. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poumellec, B.; Cavillon, M.; Lancry, M. Electrostatic Interpretation of Phase Separation Induced by Femtosecond Laser Light in Glass. Crystals 2023, 13, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavillon, M.; Wang, Y.; Poumellec, B.; Brisset, F.; Lancry, M. Erasure of nanopores in silicate glasses induced by femtosecond laser irradiation in the Type II regime. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glezer, E.N.; Milosavljevic, M.; Huang, L.; Finlay, R.J.; Her, T.H.; Callan, J.P.; Mazur, E. Three-dimensional optical storage inside transparent materials. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 2023–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa, M.; Cavillon, M.; Blanchet, T.; Lancry, M.; Laffont, G. Spectral and Microscopic Behavior of Type III Femtosecond Fiber Bragg Gratings at High Temperatures. Micromachines 2025, 16, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poumellec, B.; Lancry, M. Kinetics of Thermally Activated Physical Processes in Disordered Media. Fibers 2015, 3, 206–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, R.; Lancry, M.; Poumellec, B. Usable Analytical Expressions for Temperature Distribution Induced by Ultrafast Laser Pulses in Dielectric Solids. Micromachines 2024, 15, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, R.; Lancry, M.; Cavillon, M.; Poumellec, B. How to Crystallize Glass with a Femtosecond Laser. Crystals 2024, 14, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichkov, B.N.; Momma, C.; Nolte, S.; Von Alvensleben, F.; Tünnermann, A. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl. Phys. A 1996, 63, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Sharafudeen, K.N.; Yue, Y.; Qiu, J. Femtosecond laser induced phenomena in transparent solid materials: Fundamentals and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 76, 154–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattass, R.R.; Mazur, E. Femtosecond laser micromachining in transparent materials. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.M.; Miura, K.; Sugimoto, N.; Hirao, K. Writing waveguides in glass with a femtosecond laser. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1729–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glezer, E.N.; Mazur, E. Ultrafast-laser driven micro-explosions in transparent materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 882–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, C.B.; Brodeur, A.; García, J.F.; Mazur, E. Micromachining bulk glass by use of femtosecond laser pulses with nanojoule energy. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, S.M.; Zhang, H.; Herman, P.R.; Yoshino, F.; Shah, L.; Bovatsek, J.; Arai, A.Y. Heat accumulation effects in femtosecond laser-written waveguides with variable repetition rate. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 4708–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, S.; Zhang, H.; Ng, M.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Ho, S.; Herman, P. Transition from thermal diffusion to heat accumulation in high repetition rate femtosecond laser writing of buried optical waveguides. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 9443–9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, L.; Qiu, J.; Dai, Y.; Ma, H. Femtosecond laser induced coordination transformation and migration of ions in sodium borate glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 121113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Zhu, B.; Dai, Y.; Qian, B.; Qiu, J.; Shimotsuma, Y.; Miura, K.; Hirao, K. Micromodification of element distribution in glass using femtosecond laser irradiation. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Sakakura, M.; Kanehira, S.; Nishi, M.; Shimotsuma, Y.; Hirao, K.; Miura, K. Formation mechanism of element distribution in glass under femtosecond laser irradiation. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 2161–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Dai, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, S.; Lin, G.; Qiu, J. Femtosecond laser induced space-selective precipitation of nonlinear optical crystals in rare-earth-doped glasses. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 6069–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhu, B.; Qiu, J.R.; Ma, H.L.; Lu, B.; Cao, S.X.; Yu, B.K. Direct writing three-dimensional Ba2TiSi2O8 crystalline pattern in glass with ultrashort pulse laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 181109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoubir, A.; Rivero, C.; Grodsky, R.; Richardson, K.; Richardson, M.; Cardinal, T.; Couzi, M. Laser-induced defects in fused silica by femtosecond IR irradiation. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 224117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, O.L. Cooling time of strong glass fibers. J. Appl. Phys. 1958, 29, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tool, A. Relation between inelastic deformability and theram expansion of glass in its annealing range. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1946, 29, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Mauro, J.C. Viscosity of glass-forming systems. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, J.E. Density of vitreous silica. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 349, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritland, H. Relation Between Refractive Index and Density of a Glass at Constant Temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 38, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiuchida, H.; Saito, K.; Ikushima, A.J. Refractive Index, Density and Polarizability of Silica Glass with Various Fictive Temperatures. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, L743–L745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y. Laser Modification of Materials at Micro- and Nanoscale for Photonics and Information Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Wang, H.; Shayeganrad, G.; Svirko, Y.; Kazansky, P. Controlling ultrafast laser writing in silica glass by pulse temporal contrast. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmarchelier, R.; Poumellec, B.; Brisset, F.; Mazerat, S.; Lancry, M. In the Heart of Femtosecond Laser Induced Nanogratings: From Porous Nanoplanes to Form Birefringence. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2015, 5, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Bricchi, E.; Kazansky, P.; Bovatsek, J.; Arai, A. Self-assembled periodic sub-wavelength structures by femtosecond laser direct writing. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 10117–10124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancry, M.; Zimmerman, F.; Desmarchelier, R.; Tian, J.; Brisset, F.; Nolte, S.; Poumellec, B. Nanogratings formation in multicomponent silicate glasses. Appl. Phys. B-Lasers Opt. 2016, 122, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Cavillon, M.; Poumellec, B.; Pugliese, D.; Janner, D.; Lancry, M. Application and validation of a viscosity approach to the existence of nanogratings in oxide glasses. Opt. Mater. 2022, 130, 112576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Petit, S.; Becker, A.; Aközbek, N.; Bowden, C.M.; Chin, S.L. Intensity clamping of a femtosecond laser pulse in condensed matter. Opt. Commun. 2002, 202, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Tempel, L.; Melis, G.P.; Brandsma, T.C. Thermal Conductivity of a Glass: I. Measurement by the Glass–Metal Contact. Glass Phys. Chem. 2000, 26, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.L.F.; Aparicio, C. Data classification with the Vogel–Fulcher–Tammann–Hesse viscosity equation using correspondence analysis. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2007, 398, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, W. Glass Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Rault, J. Origin of the Vogel–Fulcher–Tammann law in glass-forming materials: The α–β bifurcation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2000, 271, 177–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, I.; Horn, A.; Gottmann, J. Local Melting of Glass Material and Its Application to Direct Fusion Welding by Ps-laser Pulses. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2007, 2, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. A Contribution to High Temperature Applications Using Femtosecond Laser Direct Writing in Silica-Based Glasses and Optical Fibers. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Saclay, Orsay, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ashcom, J.B.; Gattass, R.R.; Schaffer, C.B.; Mazur, E. Numerical aperture dependence of damage and supercontinuum generation from femtosecond laser pulses in bulk fused silica. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2006, 23, 2317–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poumellec, B.; Que, R. Thermal Limitations in Ultrafast Laser Direct Writings in Dielectric Solids. Micromachines 2025, 16, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090970
Poumellec B, Que R. Thermal Limitations in Ultrafast Laser Direct Writings in Dielectric Solids. Micromachines. 2025; 16(9):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090970
Chicago/Turabian StylePoumellec, Bertrand, and Ruyue Que. 2025. "Thermal Limitations in Ultrafast Laser Direct Writings in Dielectric Solids" Micromachines 16, no. 9: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090970
APA StylePoumellec, B., & Que, R. (2025). Thermal Limitations in Ultrafast Laser Direct Writings in Dielectric Solids. Micromachines, 16(9), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090970







