Harmonic-Recycling Passive RF Energy Harvester with Integrated Power Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A passive dual-stage rectifier architecture integrating harmonic suppression and secondary rectification is proposed to enhance RF-DC efficiency without additional active components.
- A microstrip stub-based harmonic rejection network is developed to selectively reflect and recycle residual high-frequency energy.
- A theoretical model of system efficiency is established to quantify the performance gain from energy recycling.
- A complete low-power energy storage chain is built by combining the BQ25570 and low-leakage supercapacitor, improving voltage regulation and system endurance.
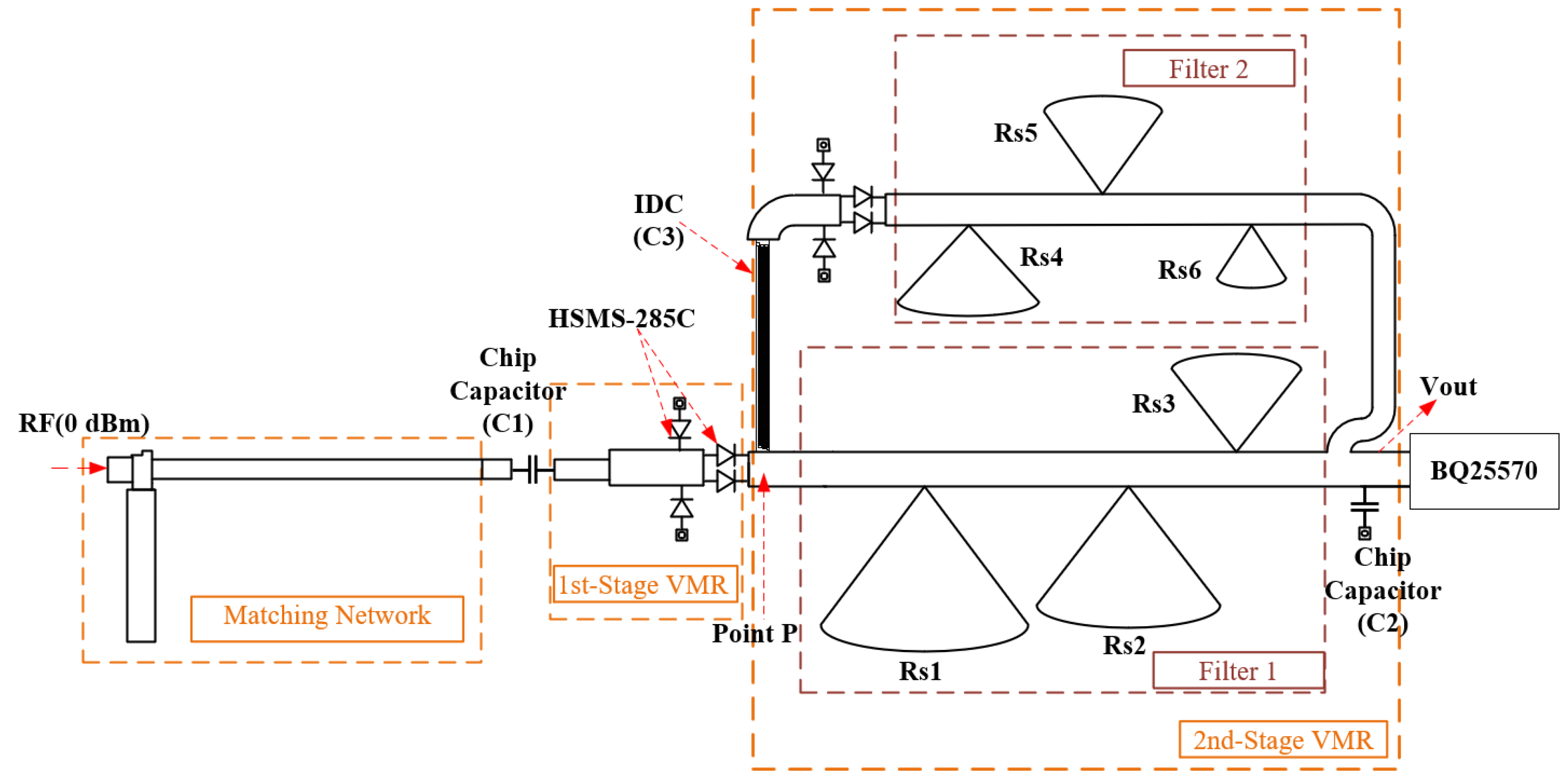
2. Circuit Design
2.1. Rectifier Circuit Design
2.2. Power Management Circuit Design
- BQ25570 supports a cold-start threshold as low as 600 mV, and after startup, it can continue operating with input voltages down to 100 mV [29]. This makes it particularly well-suited for microwatt-level RF energy input.
- Given that the proposed system uses a fully passive RF rectifier without any external microcontroller, the periodic-sampling MPPT strategy of the BQ25570 allows for maximum power point tracking without introducing additional active power consumption.
- As the system replaces traditional batteries with supercapacitors, the BQ25570 integrates supercapacitor charge/discharge management, voltage threshold control, and LDO regulation, thereby providing efficient energy accumulation and a stable voltage supply to the back-end MCU [19].
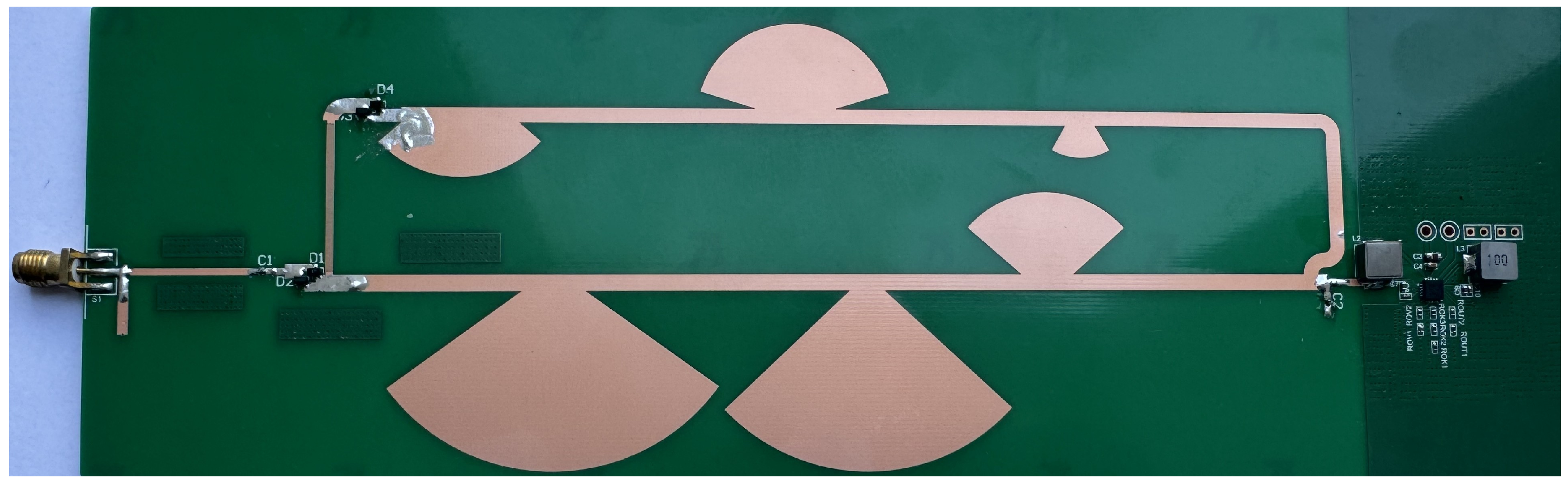
3. System Implementation
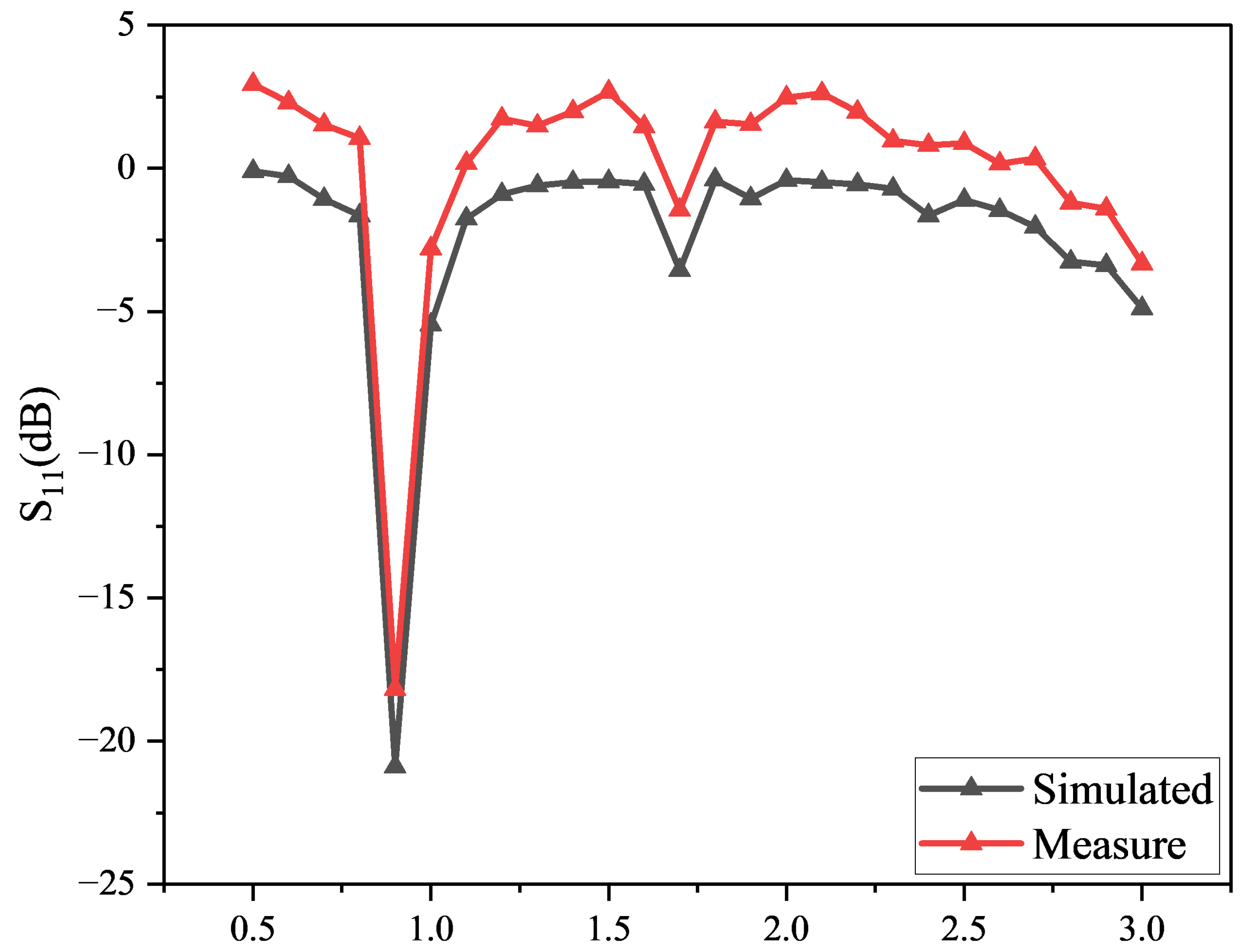
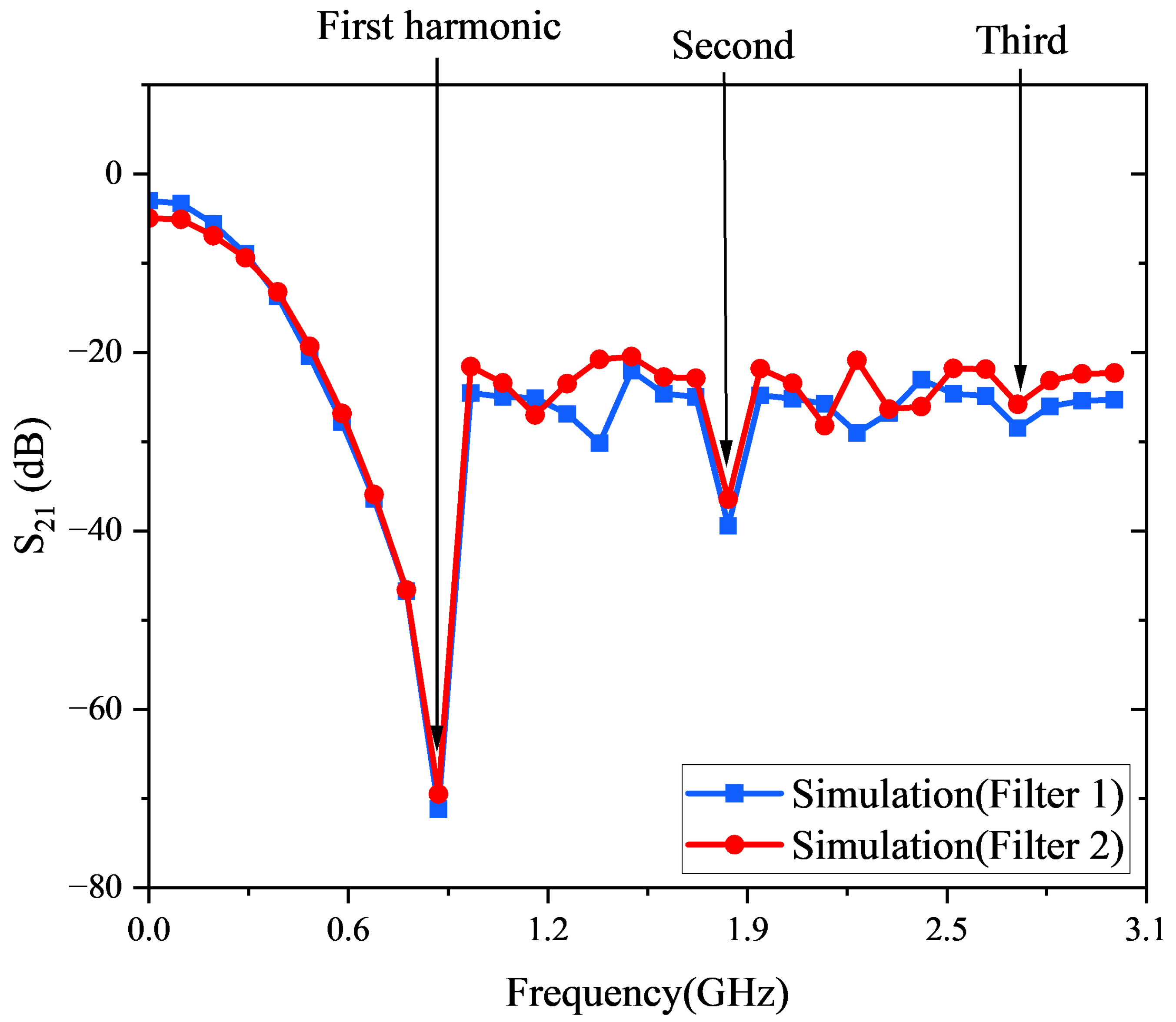
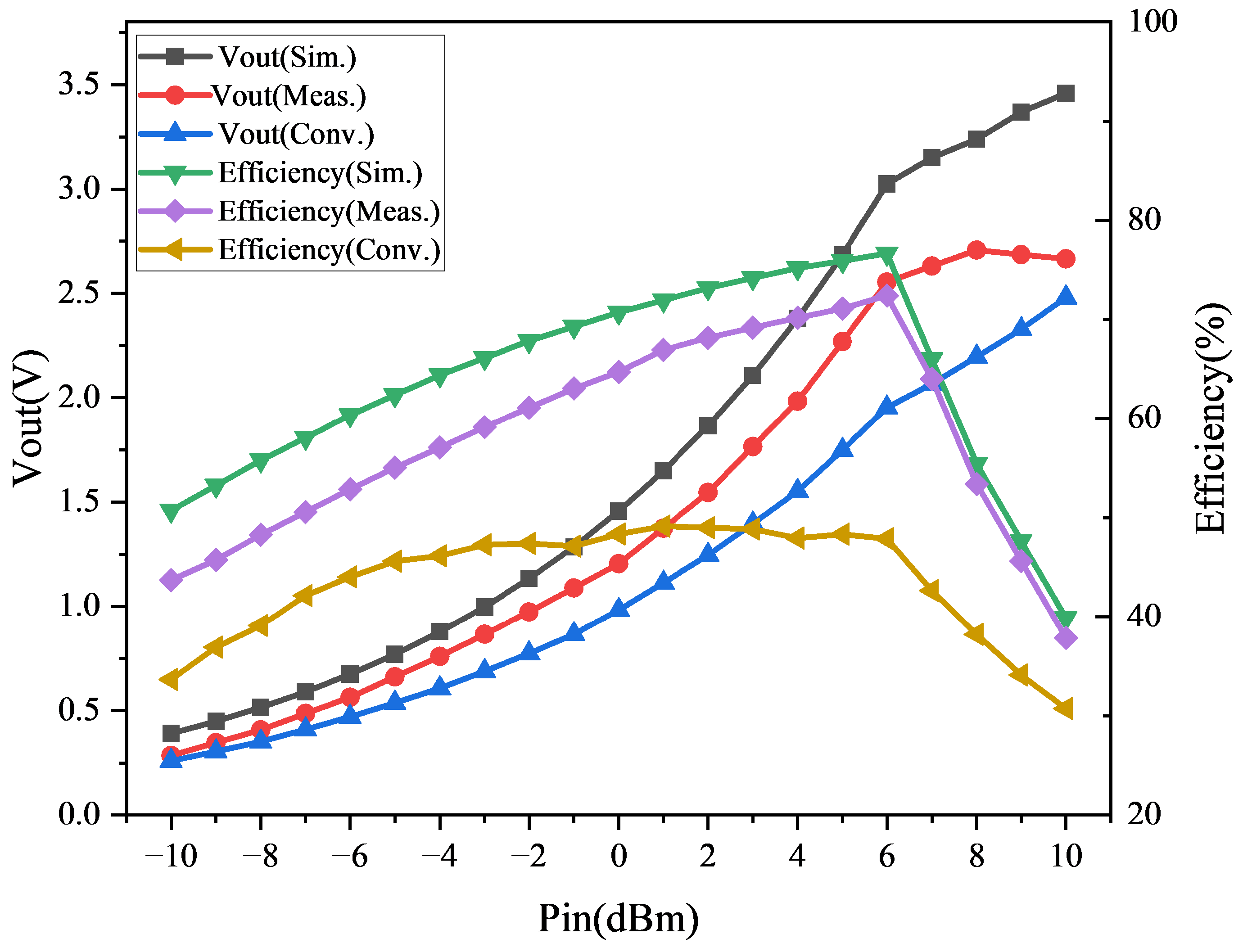
3.1. Implementation and Evaluation of VMR
3.2. Power Management and Energy Output Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| HR-P-RFEH | Harmonic-Recycling Passive RF Energy Harvester |
| MEMS | Micro-Electro-Mechanical System |
| VMR | Voltage Multiplier Rectifier |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| DC | Direct Current |
| LTCC | Low-Temperature Co-Fired Ceramic |
| EH | Energy Harvesting |
| MPPT | Maximum Power Point Tracking |
| VOC | Open-Circuit Voltage |
| SiP | System-in-Package |
| ADS | Advanced Design System |
| FR4 | Flame Retardant 4 (PCB substrate) |
| EM | Electromagnetic |
| DMM | Digital Multimeter |
| VNA | Vector Network Analyzer |
| SOLT | Short-Open-Load-Thru (VNA calibration) |
| S11 | Input Reflection Coefficient |
| S21 | Forward Transmission Coefficient |
| LDO | Low Dropout Regulator |
| MCU | Microcontroller Unit |
| PMU | Power Management Unit |
References
- Guo, L.; Yan, M.; Li, X.; Guan, K.; Chu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, K. RF Power Harvester with Varactor-Enabled Wide-Power-Range Capability for Wireless Power Transfer Applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2024, 73, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhathoki, R.K.; Guragain, D.P. TT-Mote: An Architecture towards Perpetual Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Industry 4.0 (STI), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–18 December 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Refaei, A.; Genevey, S.; Audet, Y.; Savaria, Y. High-Efficiency Wide Input Power Range Three-Phase Radio Frequency Energy Harvester for IoT Applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2024, 73, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, M.; Weddell, A.S.; Beeby, S. Rectennas for Radio-Frequency Energy Harvesting and Wireless Power Transfer: A Review of Antenna Design [Antenna Applications Corner]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2020, 62, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, Z.J.; Ruan, T.; Zhu, M. Power Management Circuit for Wireless Sensor Nodes Powered by Energy Harvesting: On the Synergy of Harvester and Load. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 8671–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citroni, R.; Mangini, F.; Frezza, F. Efficient Integration of Ultra-Low Power Techniques and Energy Harvesting in Self-Sufficient Devices: A Comprehensive Overview of Current Progress and Future Directions. Sensors 2024, 24, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, W.S. Design of Miniaturized Incident Angle-Insensitive 2.45 GHz RF-Based Energy Harvesting System for IoT Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 70, 3781–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Vyas, R.; Bito, J.; Niotaki, K.; Collado, A.; Georgiadis, A.; Tentzeris, M.M. Ambient RF Energy-Harvesting Technologies for Self-Sustainable Standalone Wireless Sensor Platforms. Proc. IEEE 2014, 102, 1649–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, A.; Knox, A.R. Maximum Power Point Tracking Converter Based on the Open-Circuit Voltage Method for Thermoelectric Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zărnescu, G.C.; Pîslaru-Dănescu, L.; Stamatin, I. Hybrid Piezo–Electromagnetic Device Designed to Harvest the Vibrations of the Human Body. Micromachines 2025, 16, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, H.; Cho, J.S.; Lim, K.; Kim, H.-C.; Kim, S.; Rhee, J. A 5.5 W-to-276 W Integrated Photovoltaic Energy Harvesting System with 99.95% MPPT Efficiency and 98.74% Power Conversion Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 40, 4522–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.-W.; Wu, H.-H.; Tsai, D.-L.; Wei, C.-L. Photovoltaic Energy Harvester with Fractional Open-Circuit Voltage Based Maximum Power Point Tracking Circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 2019, 66, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, Z.J.; Zhu, M. Adaptive Maximum Power Point Finding Using Direct Voc/2 Tracking Method with Microwatt Power Consumption for Energy Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8164–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Long, H.; Song, D.; Shariar, H. Energy Harvesting Microelectromechanical System for Condition Monitoring Based on Piezoelectric Transducer Ring. Micromachines 2025, 16, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, G.; You, Z. Optimization Design and Simulation of a Multi-Source Energy Harvester Based on Solar and Radioisotope Energy Sources. Micromachines 2016, 7, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Atoche, A.; Vázquez-Castillo, J.; Osorio-De-La-Rosa, E.; Heredia-Lozano, J.C.; Vinas, J.A.; Cetina, R.Q.; Estrada-Lopez, J.J. An Energy-Saving Data Statistics-Driven Management Technique for Bio-Powered Indoor Wireless Sensor Nodes. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 9507010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, G.; Xia, H.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qian, L.; Liu, L. Configurable Hybrid Energy Synchronous Extraction Interface with Serial Stack Resonance for Multi-Source Energy Harvesting. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2023, 58, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Song, C.; Huang, K.M. A Compact Rectenna Design with Wide Input Power Range for Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 6705–6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xia, H.; Xiao, C. Self-Powered Multi-Input Hybrid Rectifier with Arbitrary Phase Difference and Low Start-Up Voltage for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 40, 4461–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.A.; Choi, Y.; Seo, C. Dual-Band Rectifier Design with High Efficiency Using Simple Dual Band-Stop Network for Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Access 2024, 13, 43218–43223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, B.; Talla, V.; Gollakota, S. Bringing Gesture Recognition to All Devices. In Proceedings of the 11th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI), Seattle, WA, USA, 2–4 April 2014; pp. 303–316. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, T.; Chen, Y.; Song, K.; Lan, G.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Gu, T.; Xu, W. A Simple and Fast Human Activity Recognition System Using Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting. In Adjunct Proceedings of the 2021 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and Proceedings of the 2021 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers (ISWC), Virtual Event, 21–26 September 2021; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 666–671. [Google Scholar]
- Talla, V.; Pellerano, S.; Xu, H.; Kellogg, B.; Yazicioglu, R.F.; Gollakota, S.; Smith, J.R. Wi-Fi RF Energy Harvesting for Battery-Free Wearable Radio Platforms. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on RFID (RFID), San Diego, CA, USA, 15–17 April 2015; pp. 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, T.; Lan, G.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Gu, T.; Xu, W. Eavesdropping Mobile App Activity via Radio-Frequency Energy Harvesting. In Proceedings of the 32nd USENIX Security Symposium, Anaheim, CA, USA, 9–11 August 2023; pp. 3511–3528. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, T.; Sun, Z.; Han, M.; Xie, Y.; Lan, G.; Li, Z.; Gu, T.; Xu, W. REHSense: Towards Battery-Free Wireless Sensing via Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting. In Proceedings of the 25th International Symposium on Theory, Algorithmic Foundations, and Protocol Design for Mobile Networks and Mobile Computing (MobiHoc), Athens, Greece, 4–7 June 2024; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Murch, R.D. Multiport Pixel Rectenna for Ambient RF Energy Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yu, J.; Dong, L. A Wide-Angle and Polarization-Insensitive Rectifying Metasurface for 5.8 GHz RF Energy Harvesting. Micromachines 2025, 16, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, H.J.; Vullers, R.J.M. RF Energy Harvesting and Transport for Wireless Sensor Network Applications: Principles and Requirements. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas Instruments. BQ25570 Nano Power Boost Charger and Buck Converter, Datasheet. 2019. Available online: https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/bq25570.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2025).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, H.; Liao, D. Harmonic-Recycling Passive RF Energy Harvester with Integrated Power Management. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16091053
Li R, Hu Y, Li H, Jin H, Liao D. Harmonic-Recycling Passive RF Energy Harvester with Integrated Power Management. Micromachines. 2025; 16(9):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16091053
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruijiao, Yuquan Hu, Hui Li, Haiyan Jin, and Dan Liao. 2025. "Harmonic-Recycling Passive RF Energy Harvester with Integrated Power Management" Micromachines 16, no. 9: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16091053
APA StyleLi, R., Hu, Y., Li, H., Jin, H., & Liao, D. (2025). Harmonic-Recycling Passive RF Energy Harvester with Integrated Power Management. Micromachines, 16(9), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16091053







