Tribology of EDM Recast Layers Vis-À-Vis TIG Cladding Coatings: An Experimental Investigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
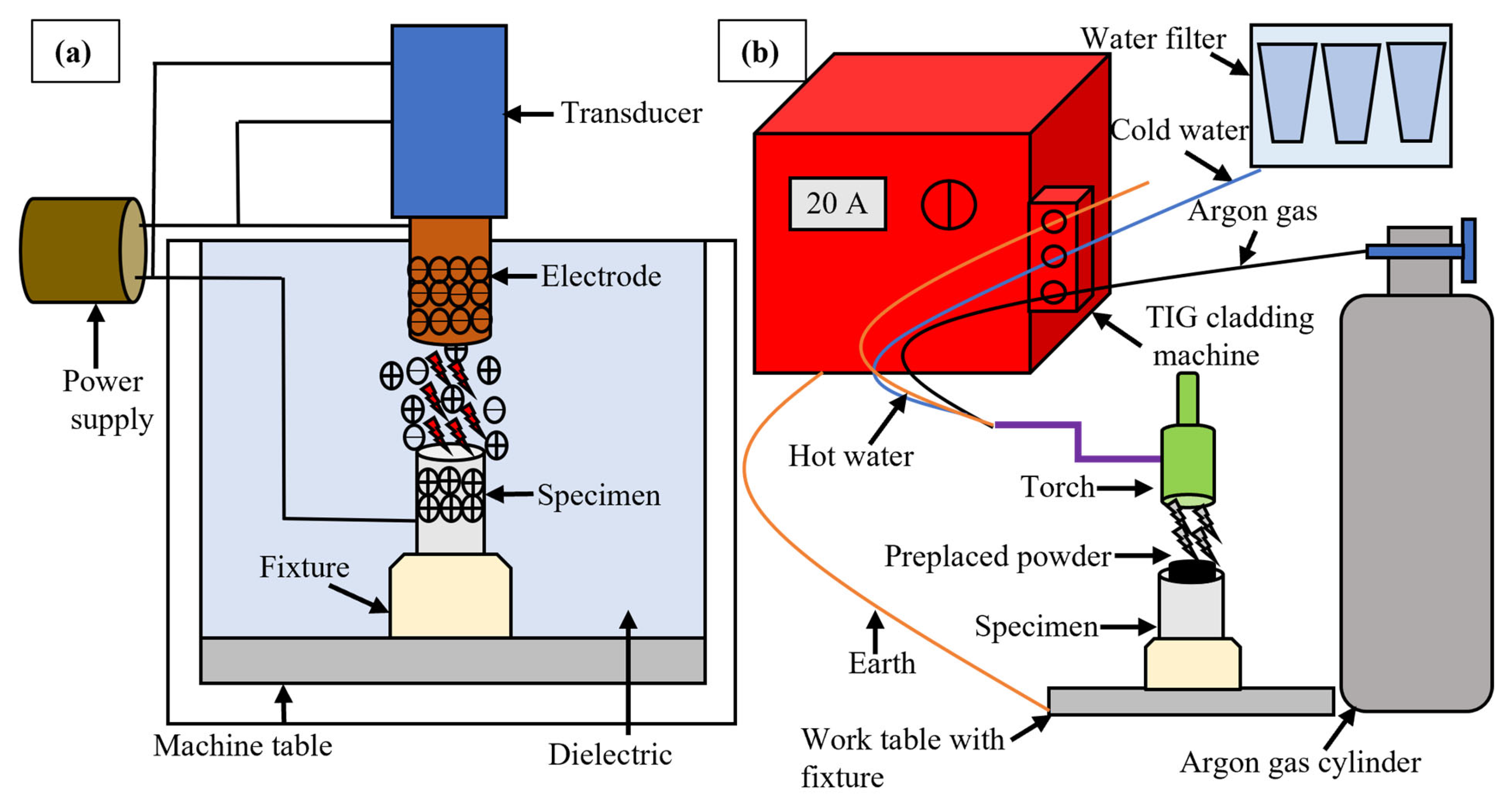
2.2.1. EDM
2.2.2. TIG Cladding Coating
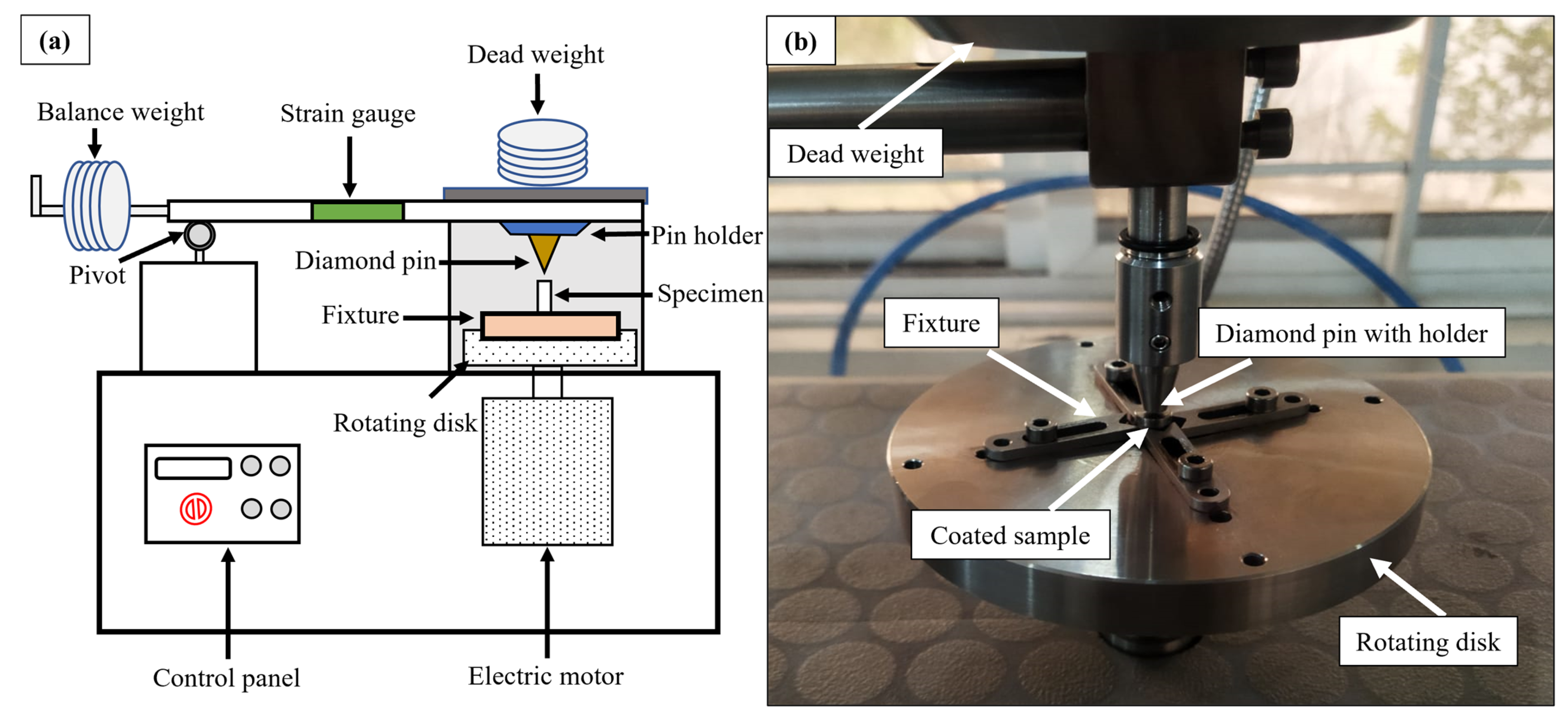
2.2.3. Characterization of Coatings
3. Results and Discussion
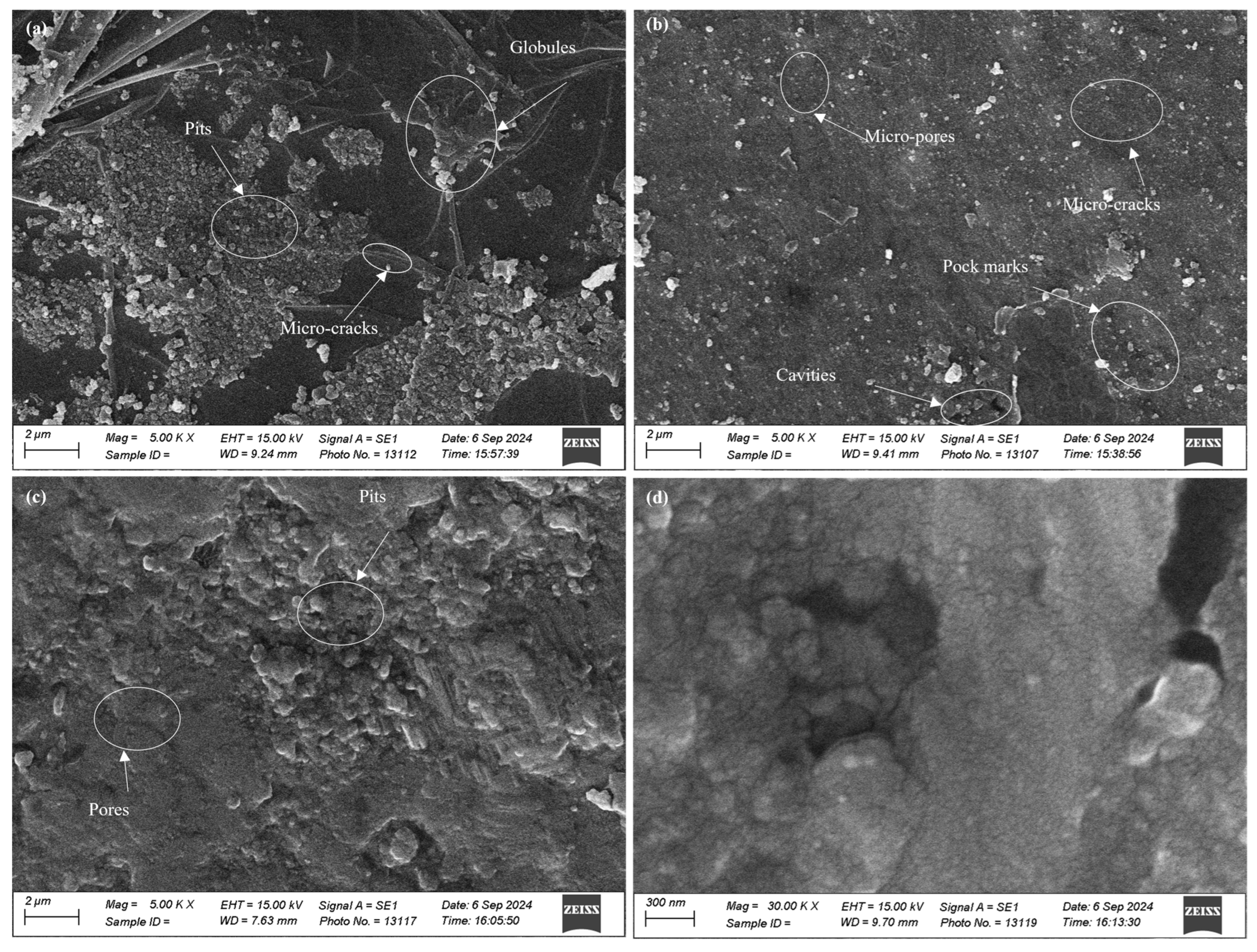
3.1. Surface Morphology
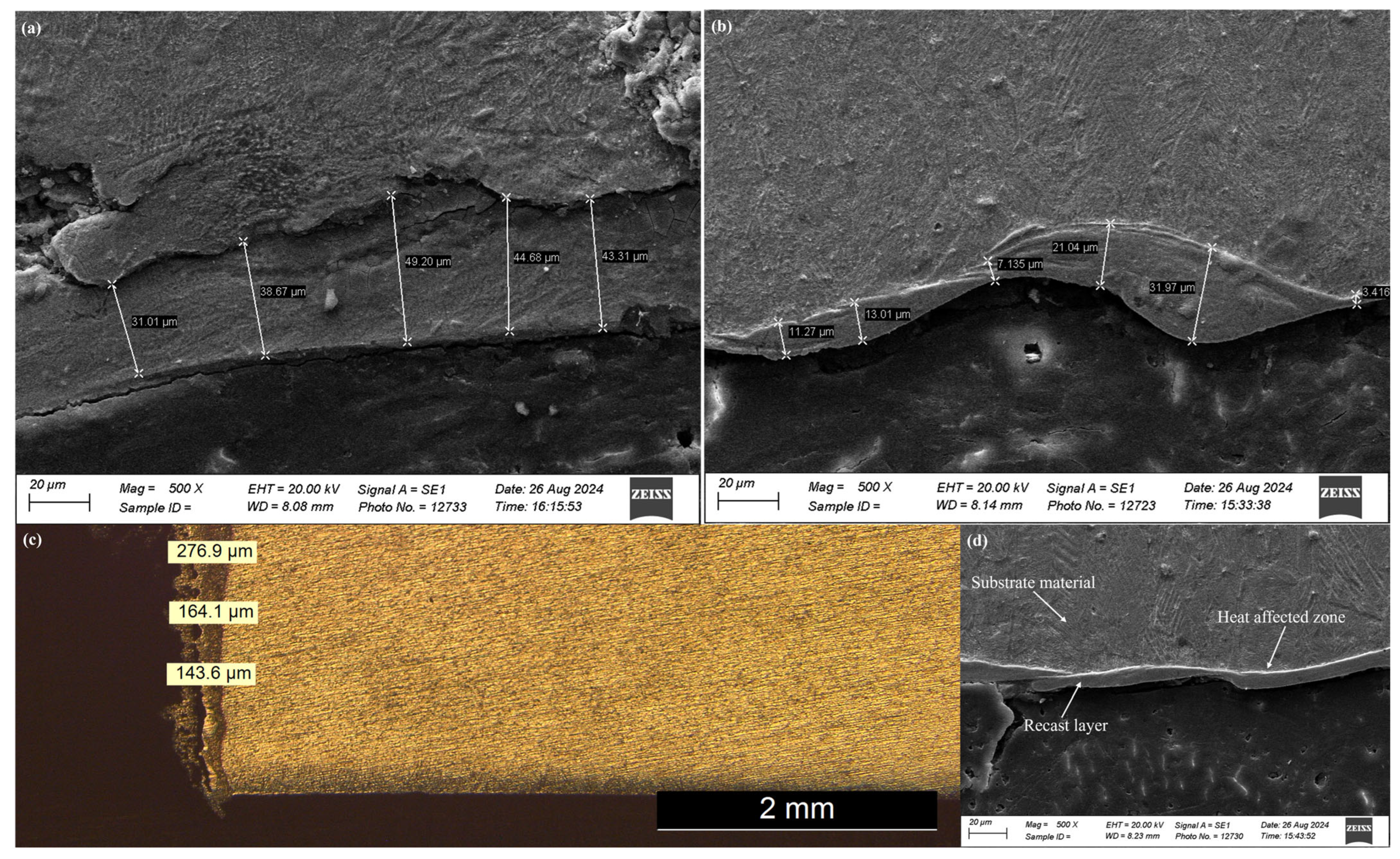
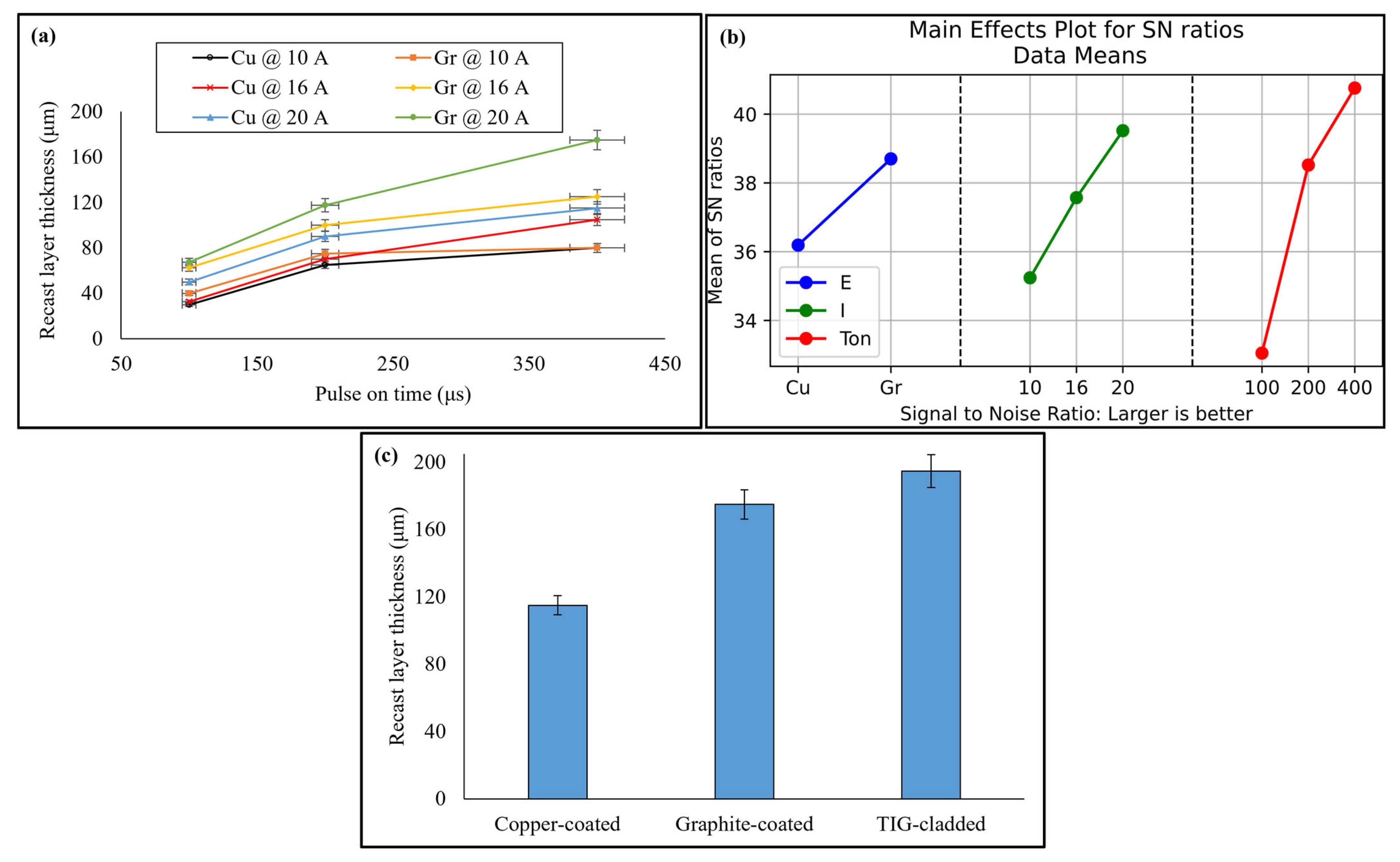
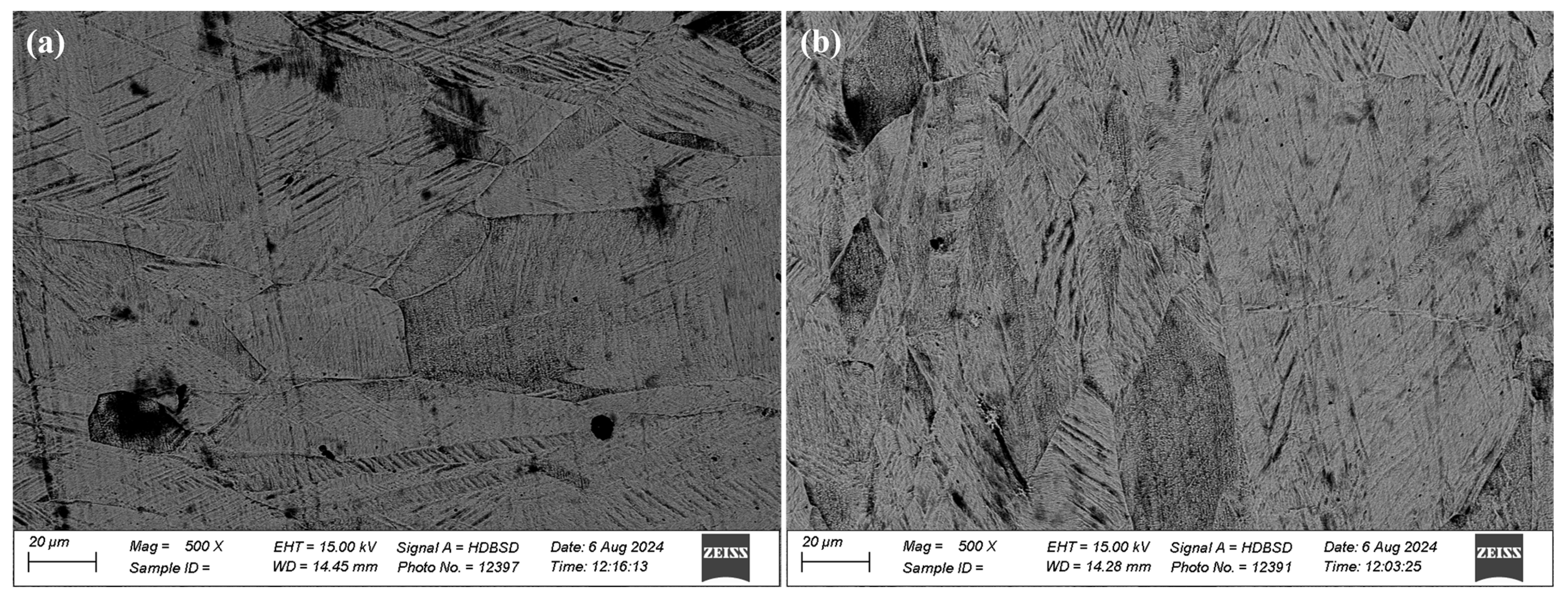
3.2. Recast Layer Thickness and Microstructure
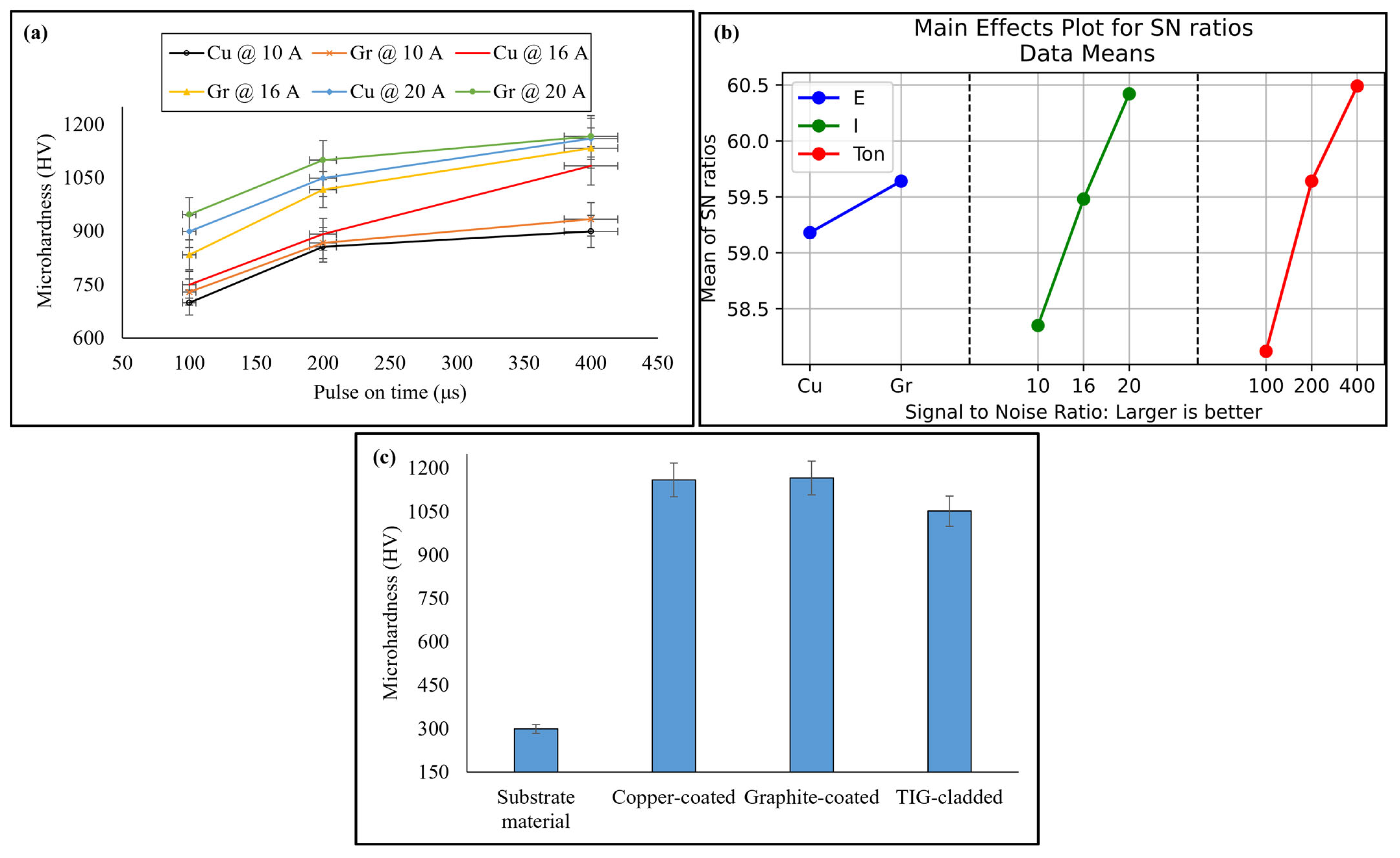
3.3. Microhardness
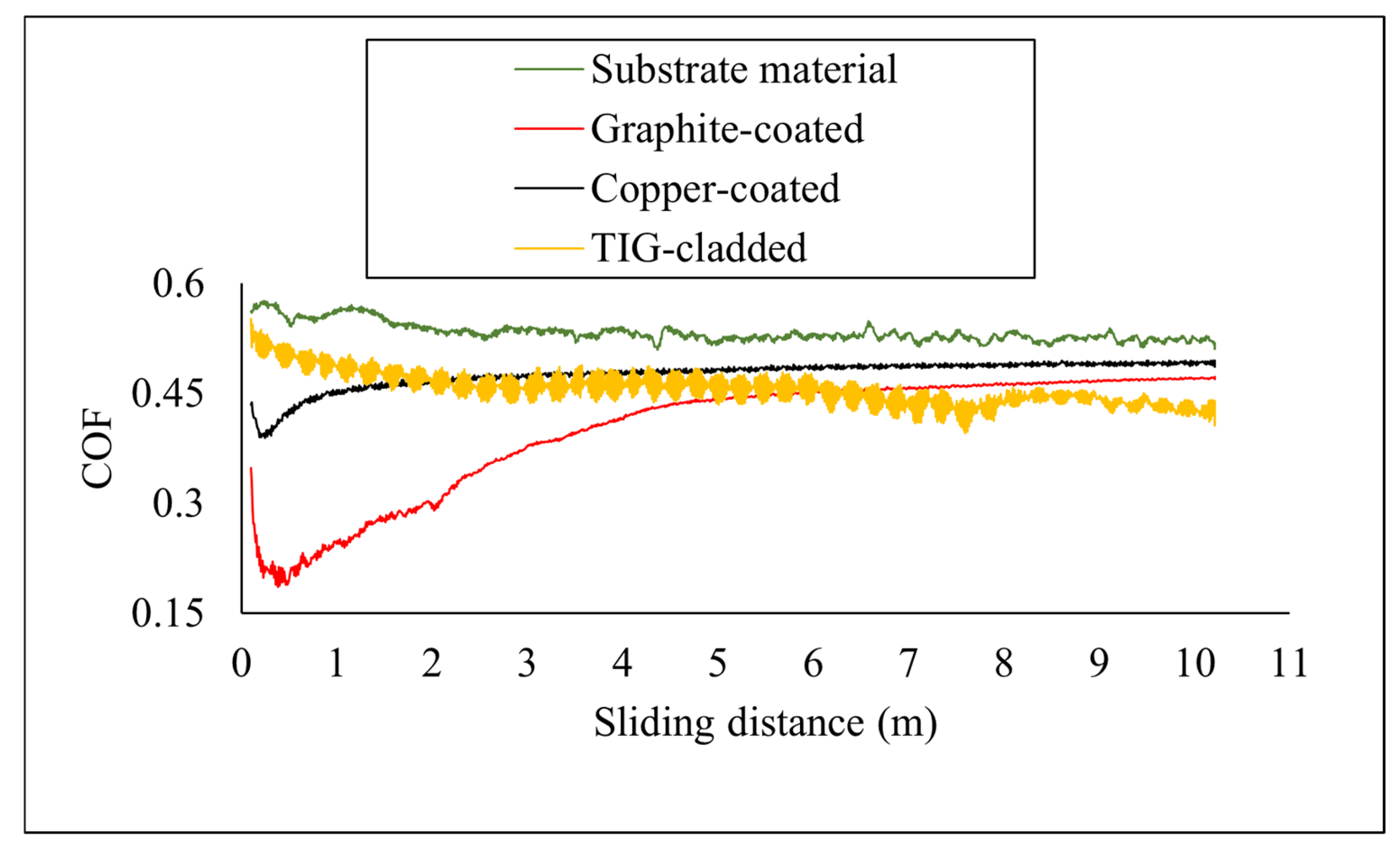
3.4. Tribological Performance
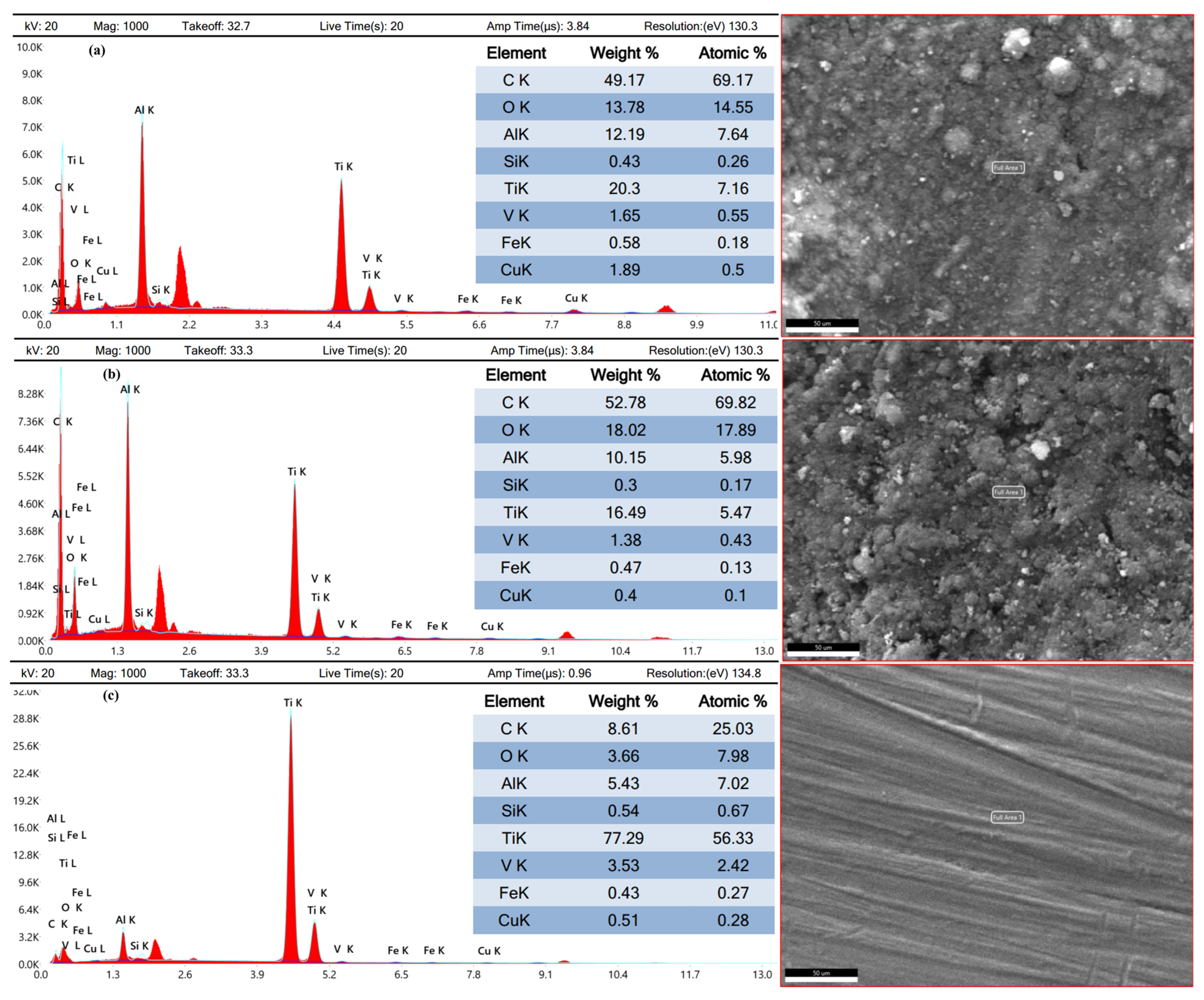
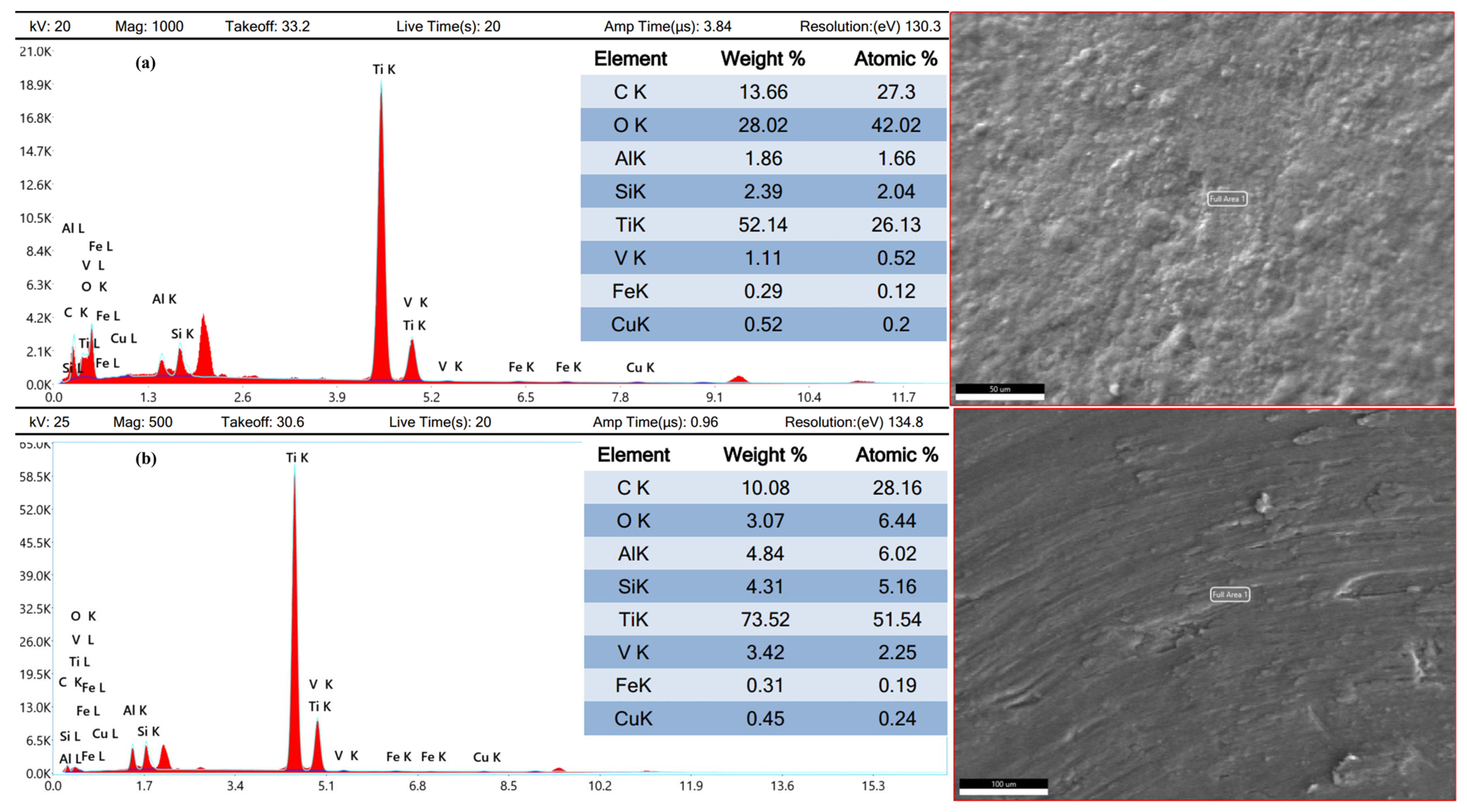
3.5. Worn Products
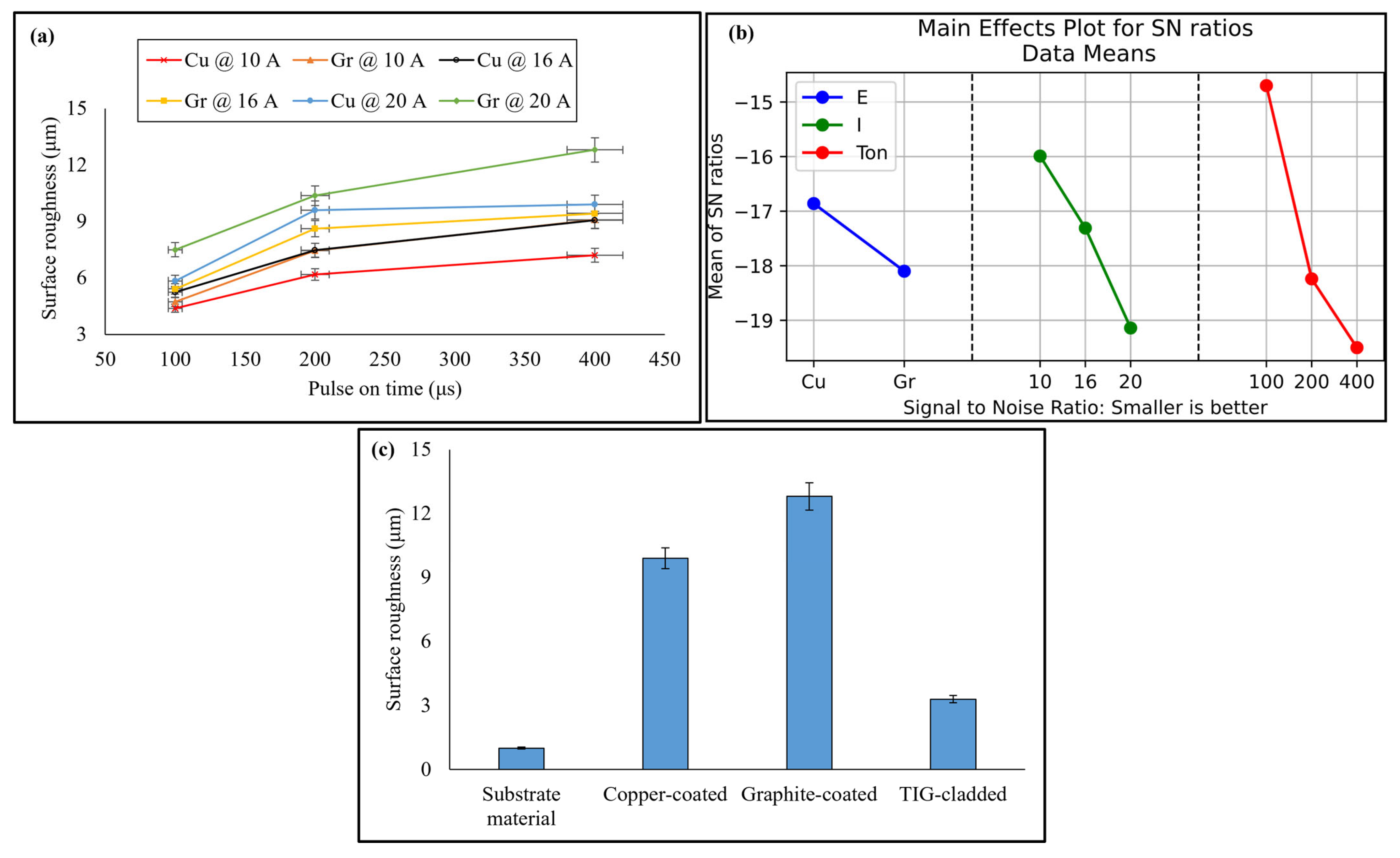
3.6. Surface Roughness
4. Conclusions
- The optimized recast layer was created using a graphite electrode at 20 A discharge current and 400 μs pulse on time. This layer showed an 11.11% lower COF, a 1.57% lower specific wear rate, and a 10.93% higher microhardness compared to TIG cladding coatings.
- The optimized recast layer was also depicted with an altered microstructure, chemical composition, and phase distribution, which resulted in superior tribological performance as compared to the TIG cladding coatings. However, surface roughness, recast layer thickness, and surface morphology of the TIG cladding coating were comparatively better.
- Moreover, the optimized recast layer exhibited superior microhardness (289%), higher wear resistance (74.69%), and lower COF (24.52%) than the substrate material.
- The key factors affecting the tribological performance of the recast layers were pulse on time (electrical) and the graphite electrode (non-electrical).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Podgornik, B. Coated machine elements—Fiction or reality? Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 146–147, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützmacher, P.G.; Rosenkranz, A.; Rammacher, S.; Gachot, C.; Mücklich, F. The influence of centrifugal forces on friction and wear in rotational sliding. Tribol. Int. 2017, 116, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleque, M.A.; Harina, L.; Bello, K.; Azwan, M.; Rahman, M.M. Tribological properties of surface modified Ti-6Al-4V alloy under lubricated condition using Taguchi approach. J. Tribol. 2018, 17, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, S.; Jha, K.; Mandal, A. Deposition of hard solid-lubricating composite coating on Ti-6Al-4V alloy with enhanced mechanical, corrosion, and electrical discharge wear properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 457, 129315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Huang, L.; Jiang, S.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Geng, L. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of TIG cladded TiB reinforced composite coating on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Vacuum 2017, 145, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Anand, M.; Jha, K.; Mandal, A. Parametric optimization and clad characterization of composite coating prepared on Ti-6Al-4V alloy using TiB2-Ni-Yb2 O3 precursor powders. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 308, 128248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, D.T.; Padhee, C.K.; Prasad, R.; Masanta, M. NiTi coating on Ti-6Al-4V alloy by TIG cladding process for improvement of wear resistance: Microstructure evolution and mechanical performances. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2018, 262, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debta, M.K.; Masanta, M. Effect of stand-off-distance on the performance of TIG cladded TiC-Co coating deposited on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 434, 128210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei-Yeboah, J.; Jahan, M.P. Study of Corner and Shape Accuracies in Wire Electro-Discharge Machining of Fin and Gear Profiles and Taper Cutting. Micromachines 2025, 16, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabyrov, N.; Jahan, M.P.; Bilal, A.; Perveen, A. Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Electro-Discharge Machining (EDM)—An Overview. Materials 2019, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wei, T.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Ding, S. Multi-Channel Electrical Discharge Machining of Ti-6Al-4V Enabled by Semiconductor Potential Differences. Micromachines 2025, 16, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manderna, S.K.; Katyal, P.; Gupta, M.; Singh, V. Wear and Corrosion Behaviour of Wire Electrical Dis-charge Machined Ti-6A1-4V alloy. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1225, 012067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshy, J.; Reddy, M.V.K.; Kuriachen, B.; Joy, M.L. Effect of Powder-Mixed Electric Discharge Alloying Using WS2 on the Tribological Performance of Ti6Al4V. Trans. Indian. Inst. Met. 2023, 76, 2413–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiyarasan, U.; Baranitharan, P.; Satheeshkumar, V.; Senthilkumar, C.; Arunkumar, T. Evaluation on Tribological Performance of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Modified Using Powder Composite Electrode-Assisted Electrical Discharge Coating. JOM 2025, 77, 1834–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Kumar, V.; Das, A.K.; Dixit, A.R. Surface modification of Ti-alloy by micro-electrical discharge process using tungsten disulphide powder suspension. J. Manuf. Process 2019, 37, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.T.; Mathew, J.; Kuriachen, B. Transition from EDM to PMEDM—Impact of suspended particulates in the dielectric on Ti6Al4V and other distinct material surfaces: A review. J. Manuf. Process 2021, 64, 1105–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukahara, H.; Minami, H.; Masui, K.; Sone, T.; Demizu, K. Tribological Properties of Surface Modified Layers of Titanium using EDM Process. J. Jpn. Soc. Electr. Mach. Eng. 2004, 38, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, R.; Khanna, S.; Patel, V.K.; Vora, J.; Plaza, S.; de Lacalle, L.N.L. Experimental Investigations of Using Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) and Nano-Graphene Powder in the Electrical Discharge Machining of Tita-nium Alloy. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Qureshi, W.; Umer, M.; Botto, D. Tribological Characterization of Electrical Discharge Ma-chined Surfaces for AISI 304L. Materials 2022, 15, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Thakur, L.; Angra, S. An investigation on the parameter optimization and abrasive wear be-haviour of nanostructured WC-10Co-4Cr TIG weld cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 386, 125474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, D.L.; Na, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Han, X.L.; Wang, J. Effects of TIG Welding Parameters on Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Welded Joint of Ni-base Superalloy. Procedia Eng. 2011, 10, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzner, D.W. Microindentation Hardness Testing of Materials Using ASTM E384. Microsc. Microa-Nalysis 2003, 9, 708–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Ablyaz, T.R.; Shlykov, E.S.; Muratov, K.R.; Bhui, A.S.; Sidhu, S.S. Enhancing Corrosion and Wear Resistance of Ti6Al4V Alloy Using CNTs Mixed Electro-Discharge Process. Micromachines 2020, 11, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillot, N.; Iordanoff, I.; Berthier, Y. Wear modeling and the third body concept. Wear 2007, 262, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasky, J.; Janecek, M.; Harcub, P. Electric discharge machining of Ti-6Al-4V alloy for biomedical use. In WDS’11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference of Doctoral Students—WDS 2011, Prague, Czech Republic, 31 May–3 June 2011; Matfyzpress: Prague, Czech Republic, 2011; pp. 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Datta, S.; Kumar, R. Electro-discharge Machining Performance of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy: Studies on Parametric Effect and Phenomenon of Electrode Wear. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 1553–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasçalık, A.; Çaydaş, U. Electrical discharge machining of titanium alloy (Ti–6Al–4V). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 9007–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, A.; Perveen, A.; Talamona, D.; Jahan, M.P. Understanding Material Removal Mechanism and Effects of Machining Parameters during EDM of Zirconia-Toughened Alumina Ceramic. Micromachines 2021, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Rack, H.J. Phase transformations during cooling in α + β titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolvanen, S.; Pederson, R.; Klement, U. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Welds Produced with Different Processes. Materials 2024, 17, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, F.L.; Stedile, L.J.; Torres, R.D.; Soares, P.C.; Laurindo, C.A.H. Performance and Surface Integrity of Ti6Al4V After Sinking EDM with Special Graphite Electrodes. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Khan, A.; Mehmood, A.; Mehmood, K.; Kousar, H.; Ahmad, S.; Adnan, M.; Sattar, A.; Ali, S. Taguchi-Optimized Friction Stir Welding of Aluminum Alloy AA2219: Investigating the Influence of Process Parameters on Mechanical Properties Via Grain Refinement. Multiscale Sci. En-Gineering 2023, 5, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijo, D.; Masanta, M. In-situ TiC-TiB2 coating on Ti-6Al-4V alloy by tungsten inert gas (TIG) cladding method: Part-II. Mechanical performance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 344, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.T.; Kumar, D.; Joshi, S.N.; Mathew, J.; Kuriachen, B. Monitoring of EDM parameters to develop tribo-adaptive Ti6Al4V surfaces through accretion of alloyed matrix. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2019, 72, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, S.A.; Maleque, M.A. TIG Melted Surface Modified Titanium Alloy for automotive cylinder liner application. Int. J. Automot. Eng. Technol. 2015, 4, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mahajan, A.; Devgan, S.; Sidhu, S.S. Surface alteration of biomedical alloys by electrical discharge treatment for enhancing the electrochemical corrosion, tribological and biological performances. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N.K.; Kumar, S.; Anant, R. TIG assisted surface modification of Ti-6Al-4V with B 4 C, SiC particles. Surf. Eng. 2024, 40, 1047–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahr, K.-H.Z. Microstructure and Wear of Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Áovarikova, I.; Szewczykova, B.; Blaskovits, P.; Hodulova, E.; Lechovic, E. Study and characteristic of abrasive wear mechanisms. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2009, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, M.P.; Kakavand, P.; Alavi, F. A Comparative Study on Micro-electro-discharge-machined Surface Characteristics of Ni-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V with Respect to Biocompatibility. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 10, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taktak, S.; Ulu, S. Wear behaviour of TRD carbide coatings at elevated temperatures. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2010, 62, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.H.; Mao, Y.S.; Wei, M.X.; Wang, S.Q. Wear Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy at 20–400 °C. Tri-Bol. Trans. 2012, 55, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmiris-Obratański, P.; Papazoglou, E.L.; Leszczyńska-Madej, B.; Zagórski, K.; Markopoulos, A.P. A Comprehensive Study on Processing Ti–6Al–4V ELI with High Power EDM. Materials 2021, 14, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafi, M.A.; Jahan, M.P. Functional Surface Generation by EDM—A Review. Micromachines 2022, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nomenclature | Material | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Specimen | TC4 (5.13 wt. % Al, 0.256 wt. % Si, 90.94 wt. % Ti and 4.07 wt. % V) | Diameter = 8 mm, Hm = 300 HV and Ra = 1 μm |
| EDM electrodes | Copper (0.455 wt. % Si, 0.074 wt. % Fe, 96.66 wt. % Cu, 2.79 wt. % Zn and 0.025 wt. % Pb) | Diameter = 10 mm, Hm = 100 HV and Ra = 0.79 μm |
| Graphite (98.97 wt. % C, 0.236 wt. % Al, 0.354 wt. % Si, 0.095 wt. % S and 0.343 wt. % Fe) | Diameter = 10 mm, Hm = 21 HV and Ra = 1.25 μm | |
| TIG cladding electrode | Tungsten thoriated (0.207 wt. % Ni, 0.801 wt. % Zn, 0.222 wt. % Zr, 0.078 wt. % Ni, 95.79 wt. % W and 2.90 wt. % Bi) | Diameter = 2.4 mm |
| Counter-body | Diamond (0.041 wt. % B, 99.93 wt. % C and 0.026 wt. % N) | Diameter = 3 mm |
| Parameters for DOE | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |
| Discharge current (A) | 10 | 16 | 20 |
| Pulse on time (μs) | 100 | 200 | 400 |
| Electrodes | Copper | Graphite | - |
| Other Parameters | Description | ||
| Pulse off time (μs) | 100 | ||
| Gap (mm) | 1 | ||
| Duty factor (%) | 75 | ||
| Dielectric | 406 EDM oil | ||
| Polarity | Positive | ||
| Input Parameters | Current (A) | Voltage (V) | Powder Size (μm) | Speed (mm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | 20 | 15 | 110 | 1 |
| Input Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Applied load (N) | 50 |
| Track radius (mm) | 3 |
| Rotational speed (RPM) | 100 |
| Sliding distance (m) | 10 |
| Temperature (°C) | 25 |
| Humidity (%) | RH 47 |
| Level | hc (Larger Is Better) | Hm (Larger Is Better) | Ra (Smaller Is Better) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | I | TON | E | I | TON | E | I | TON | |
| 1 | 36.19 | 35.24 | 33.05 | 59.18 | 58.35 | 58.12 | −16.86 | −15.99 | −14.70 |
| 2 | 38.70 | 37.57 | 38.52 | 59.64 | 59.48 | 59.64 | −18.10 | −17.31 | −18.24 |
| 3 | 39.52 | 40.76 | 60.42 | 60.49 | −19.14 | −19.50 | |||
| Delta | 2.51 | 4.28 | 7.71 | 0.46 | 2.07 | 2.37 | 1.25 | 3.15 | 4.80 |
| Rank | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
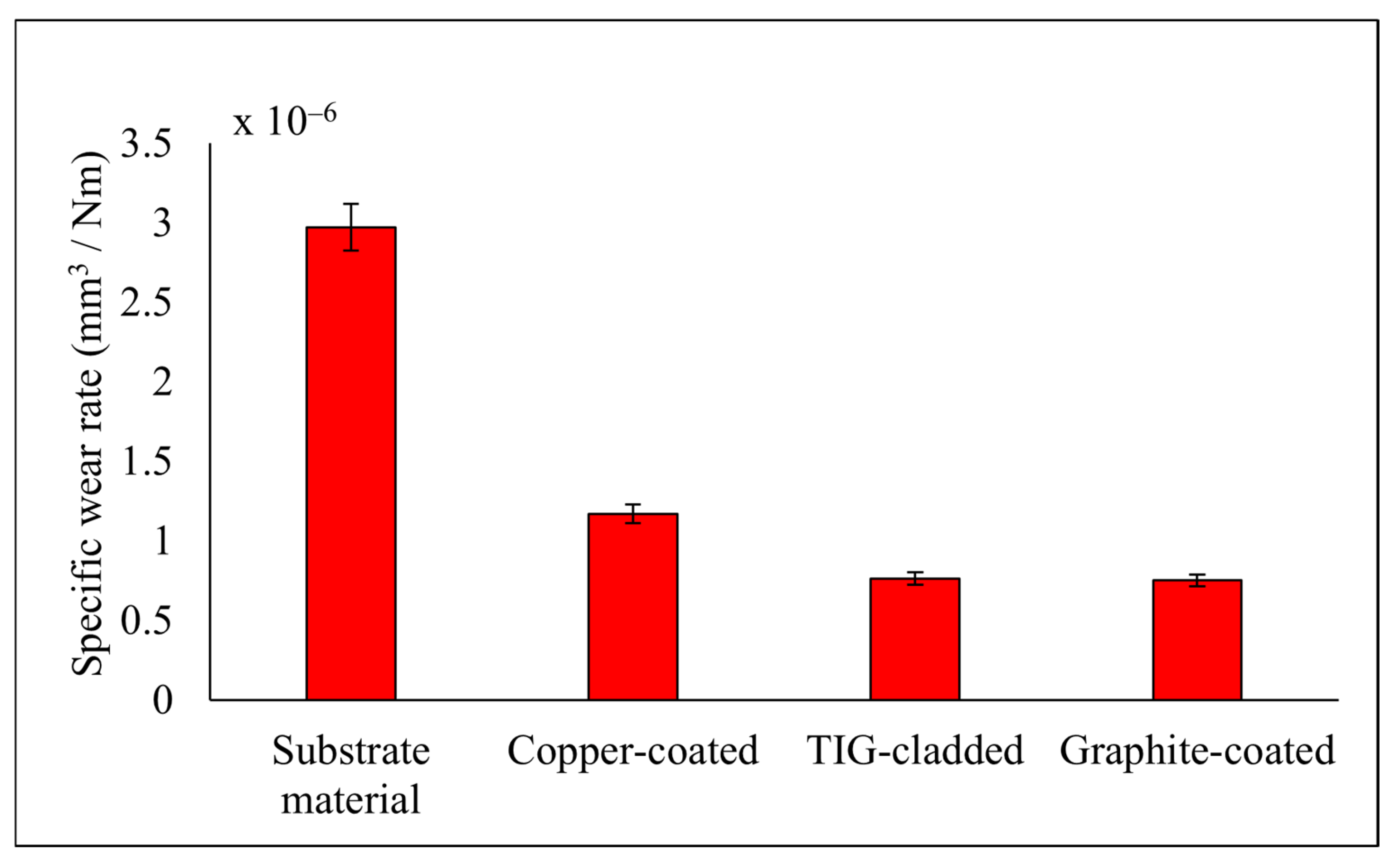
| Sample Nomenclature | COF | Wear Volume (mm3) | Specific Wear Rate (mm3/Nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate material | 0.53 ± 0.03 | 0.001486 | (2.972 ± 0.28) × 10−6 |
| Copper-coated | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 0.000586 | (1.172 ± 0.08) × 10−6 |
| TIG-cladded | 0.45 ± 0.04 | 0.000382 | (7.64 ± 0.09) × 10−7 |
| Graphite-coated | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 0.000376 | (7.52 ± 0.07) × 10−7 |
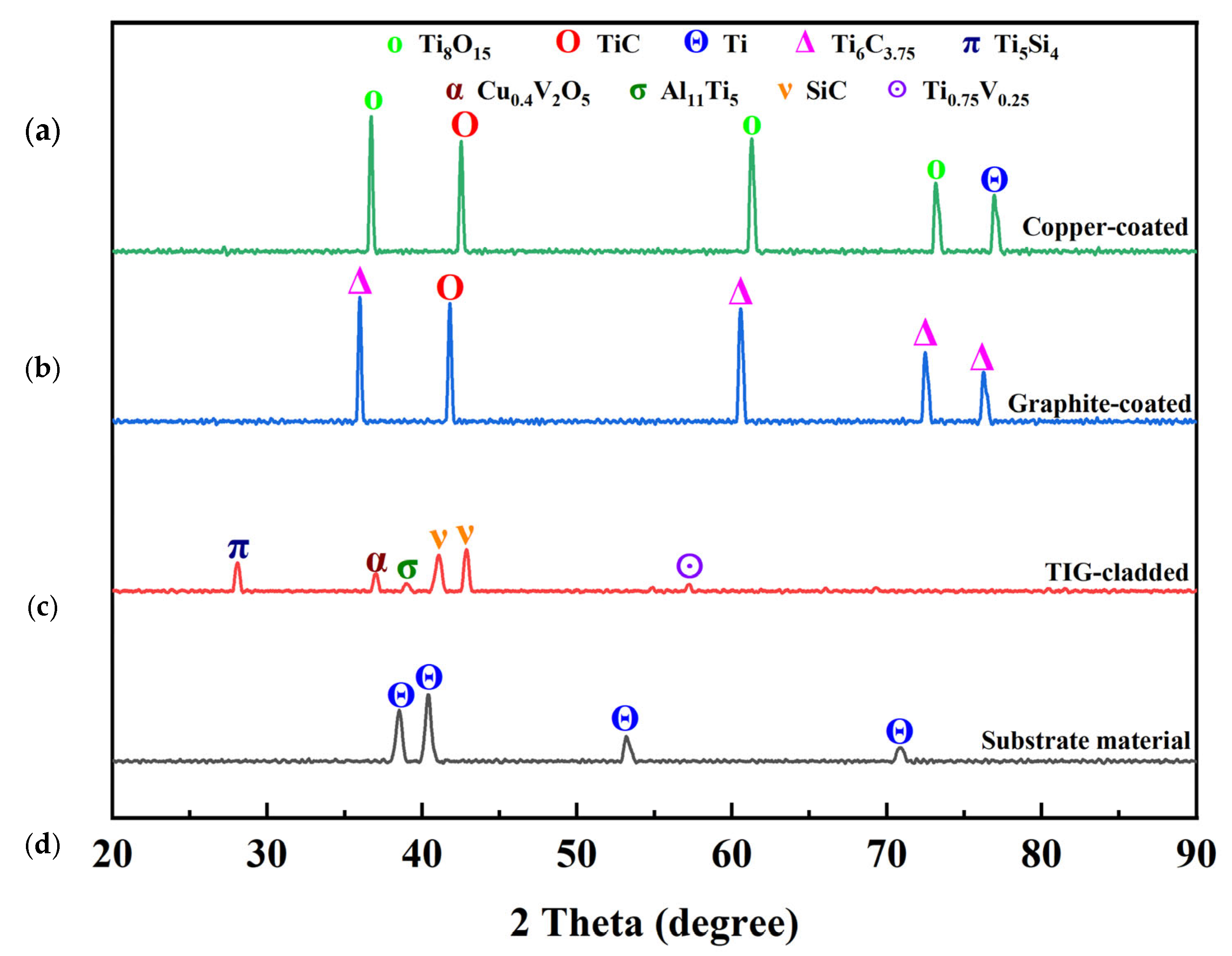
| Symbol | Chemical Formula | JCPD Card | Diffraction Angle (2ϴ°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Δ | Ti6C3.75 | 79-0971 | 35.936, 60.457, 72.378, 76.190 |
| O | TiC | 32-1383 | 41.710, 41.710 |
| Π | Ti5Si4 | 23-1079 | 28.036 |
| A | Cu0.4V2O5 | 18-0464 | 37.200 |
| Σ | Al11Ti5 | 42-1135 | 39.049 |
| V | SiC | 12-1301 | 41.186, 42.823 |
| ʘ | Ti0.75V0.25 | 51-0636 | 57.244 |
| Θ | Ti | 44-1294 | 38.765, 40.170, 53.004, 70.660, 76.218, |
| O | Ti8O15 | 50-0790 | 36.120, 60.870, 72.491 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adnan, M.; Qureshi, W.; Umer, M. Tribology of EDM Recast Layers Vis-À-Vis TIG Cladding Coatings: An Experimental Investigation. Micromachines 2025, 16, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080913
Adnan M, Qureshi W, Umer M. Tribology of EDM Recast Layers Vis-À-Vis TIG Cladding Coatings: An Experimental Investigation. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080913
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdnan, Muhammad, Waqar Qureshi, and Muhammad Umer. 2025. "Tribology of EDM Recast Layers Vis-À-Vis TIG Cladding Coatings: An Experimental Investigation" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080913
APA StyleAdnan, M., Qureshi, W., & Umer, M. (2025). Tribology of EDM Recast Layers Vis-À-Vis TIG Cladding Coatings: An Experimental Investigation. Micromachines, 16(8), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080913






