A Sliding Microfluidic Chip-Integrated Colorimetric Biosensor Using MnO2 Nanoflowers for Rapid Salmonella Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Culture
2.2. Antibody Conjugation on Immunomagnetic Beads
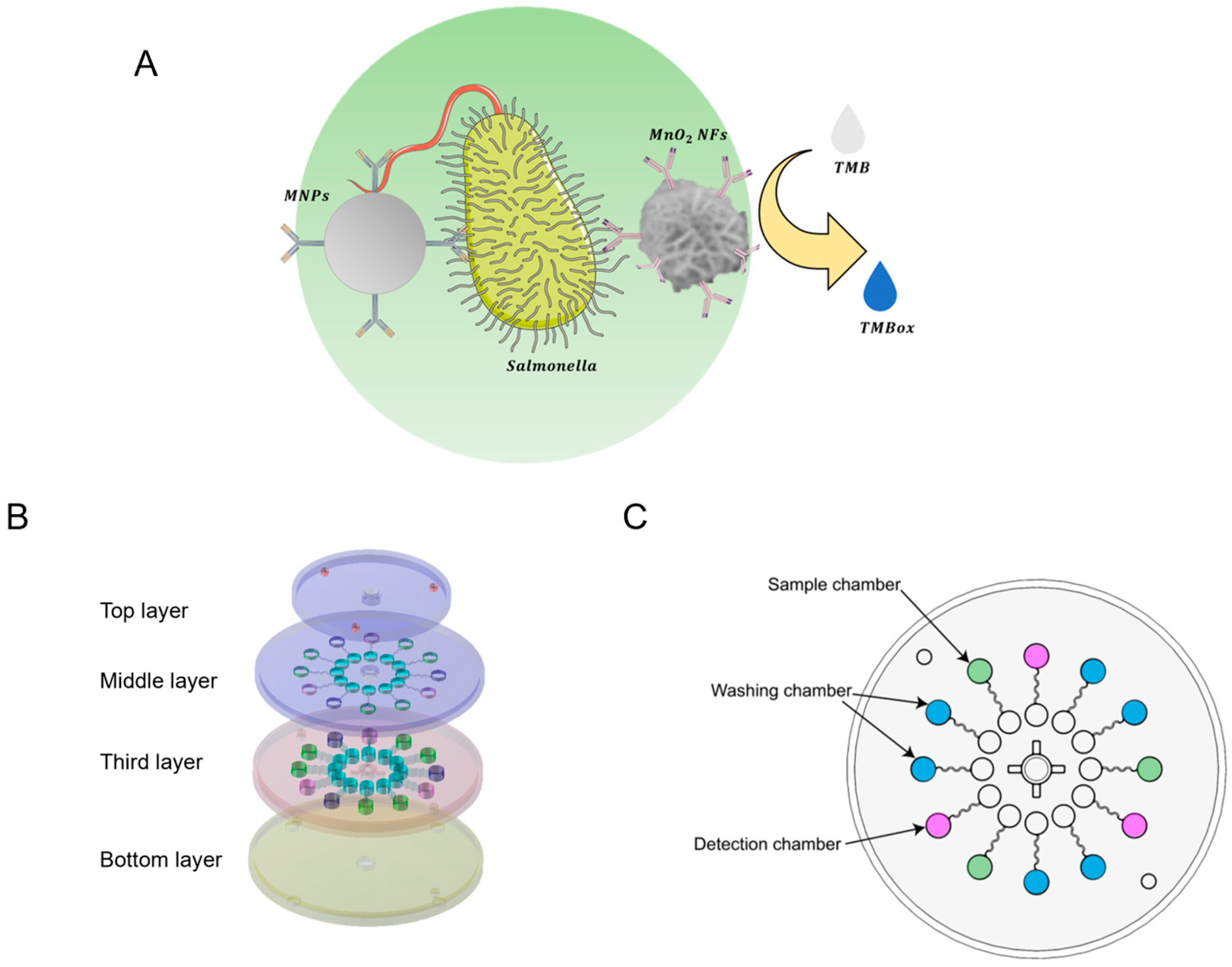
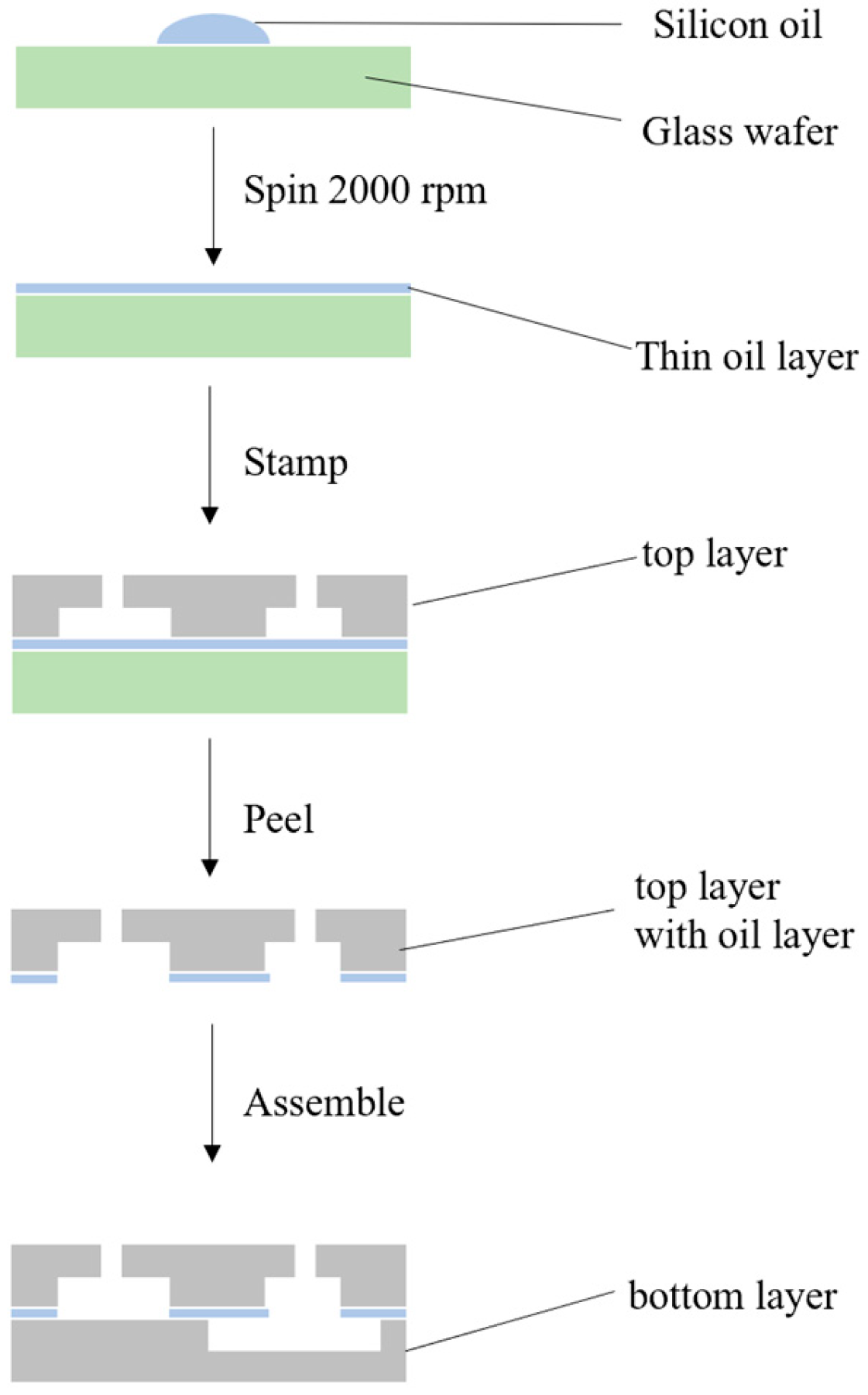
2.3. Design and Fabrication of the Microfluidic Chip
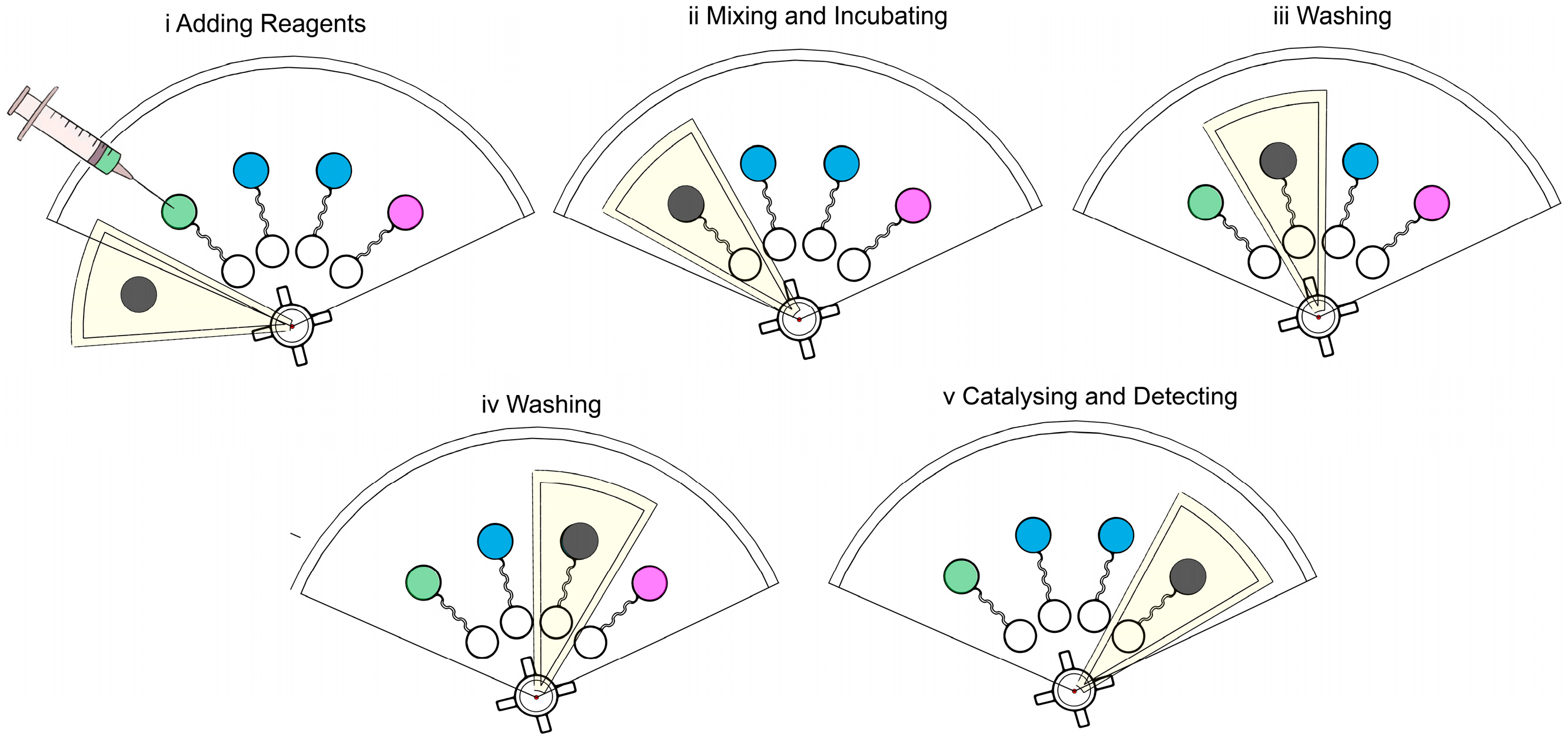
2.4. Implementation of Automated Detection
2.5. Synthesis of MnO2-NH2 Nanoflowers
2.6. Synthesis of Ab-MnO2 Probes
2.7. Detection Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Working Principle of the Biosensor
3.2. Simulations of the Magnetic Field
3.3. Optimization of Parameters
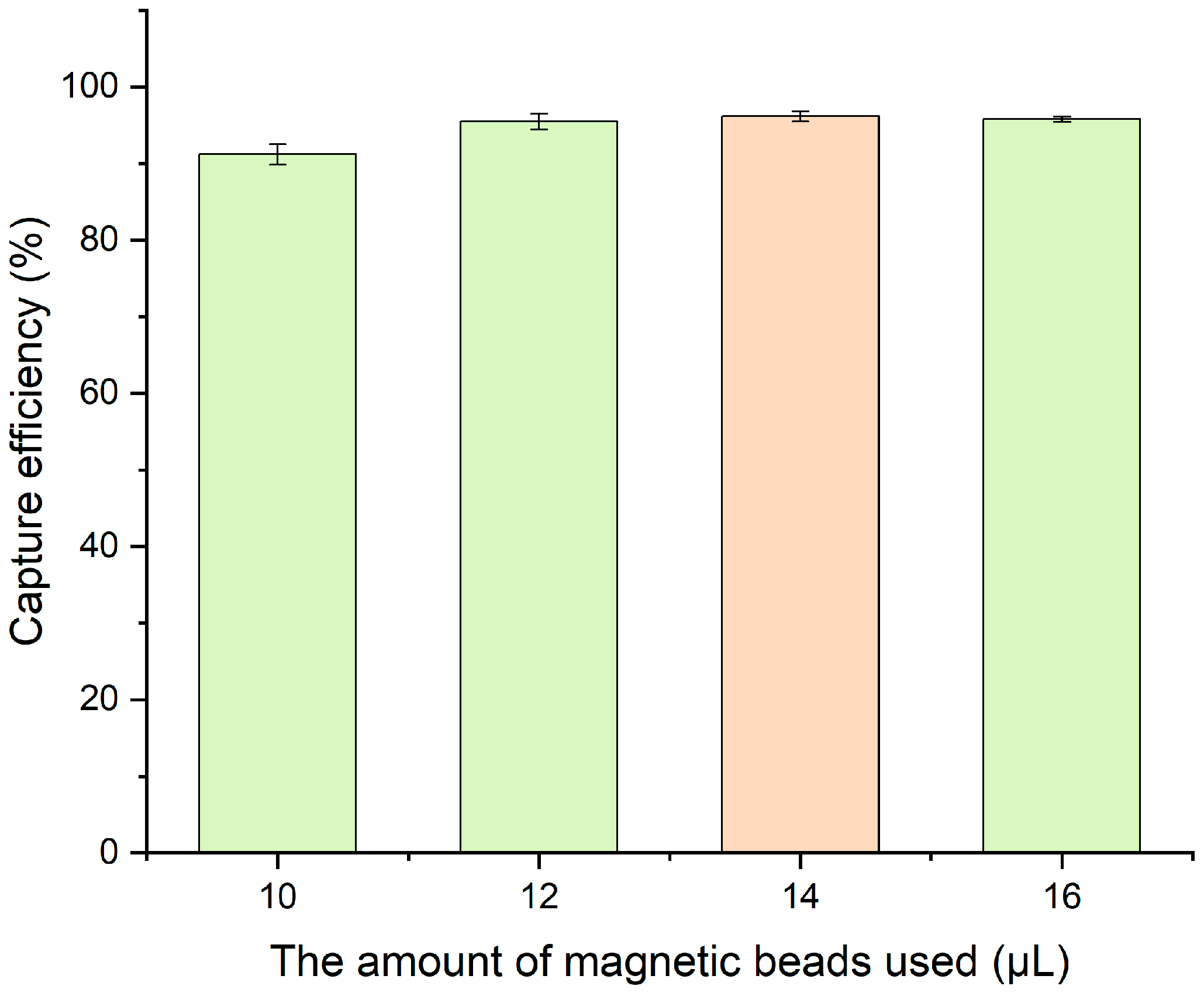
3.3.1. Optimization of Immunomagnetic Bead Volume
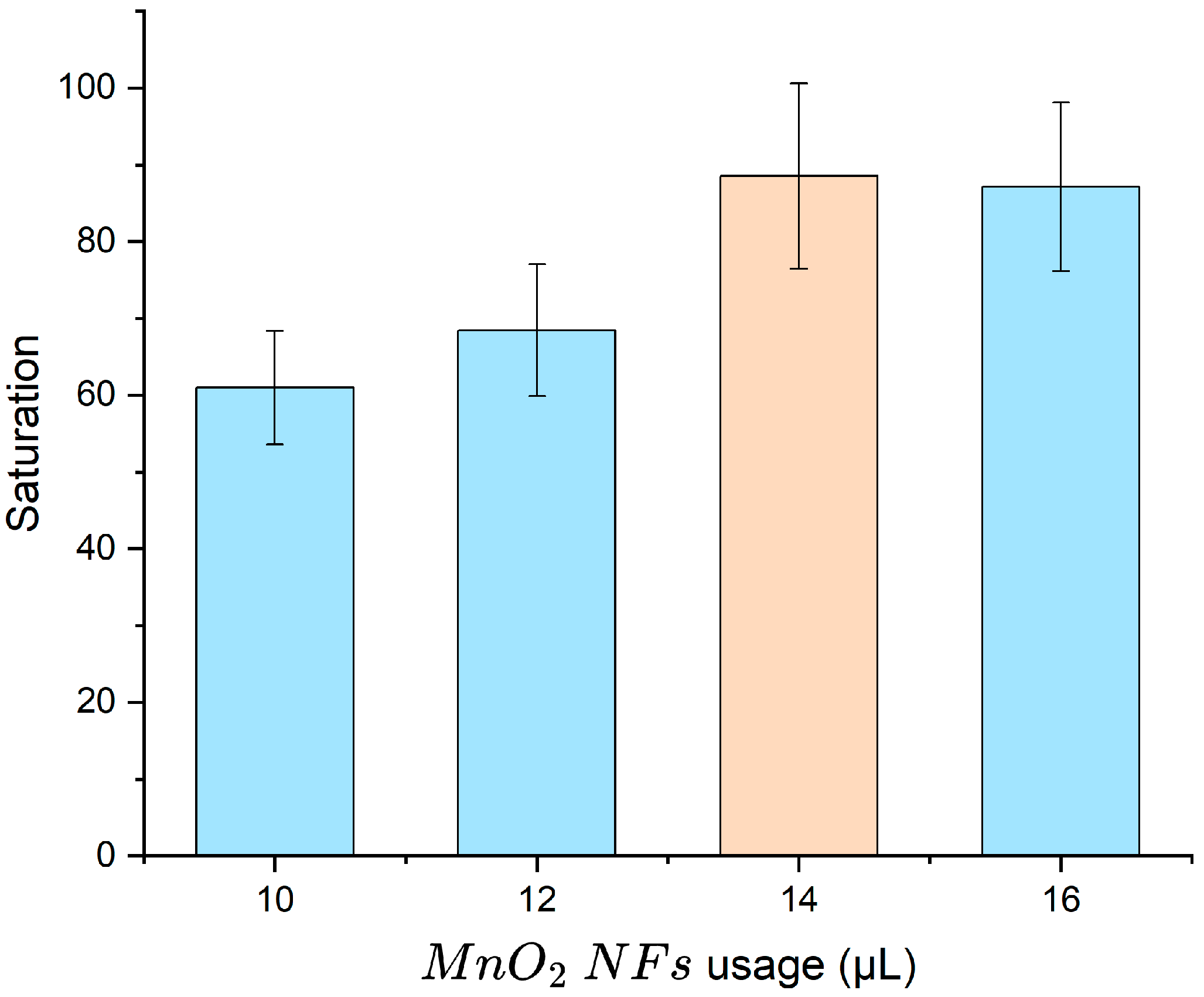
3.3.2. Optimization of MnO2 NF Volume
3.3.3. Optimization of Mixing Time
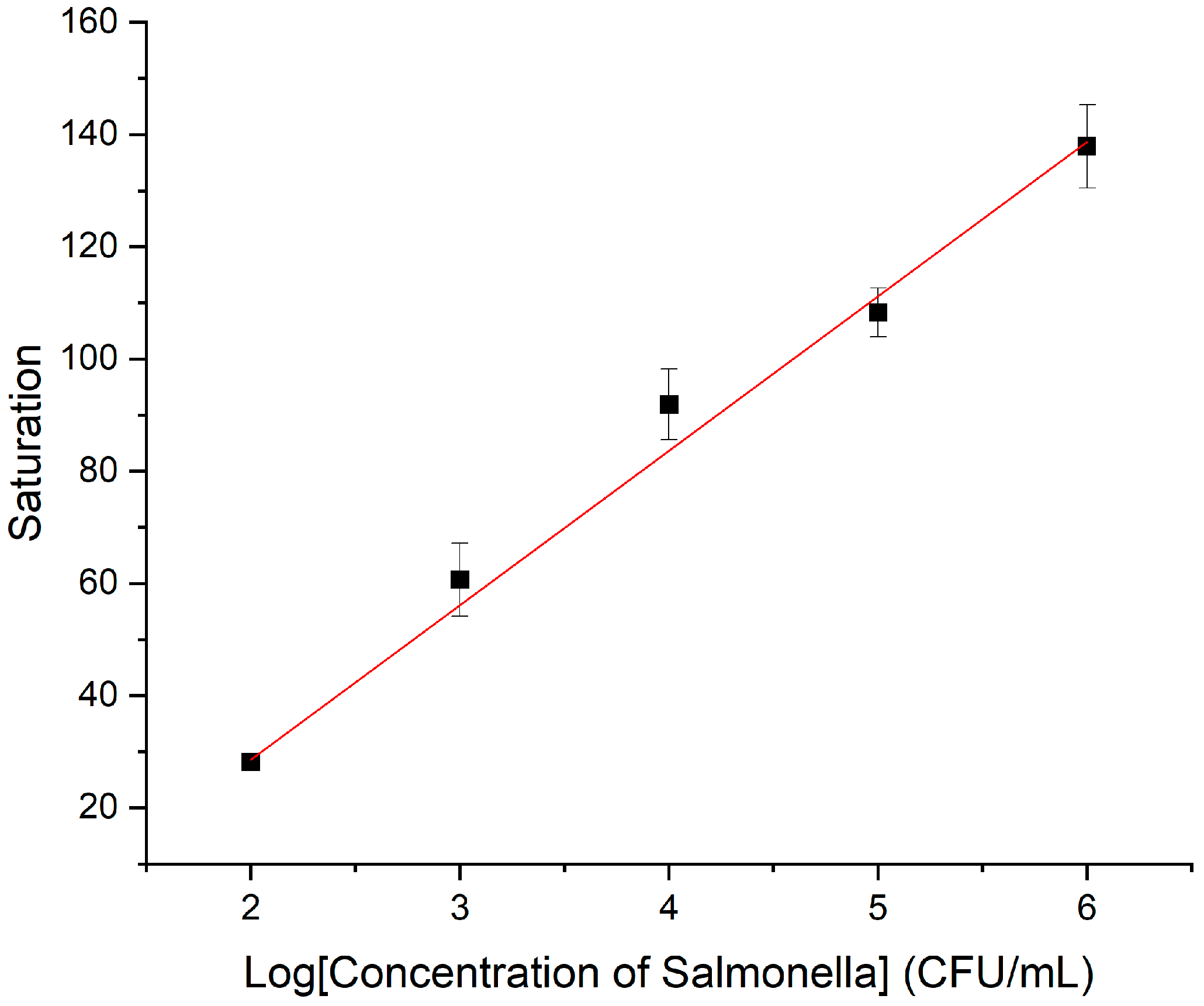
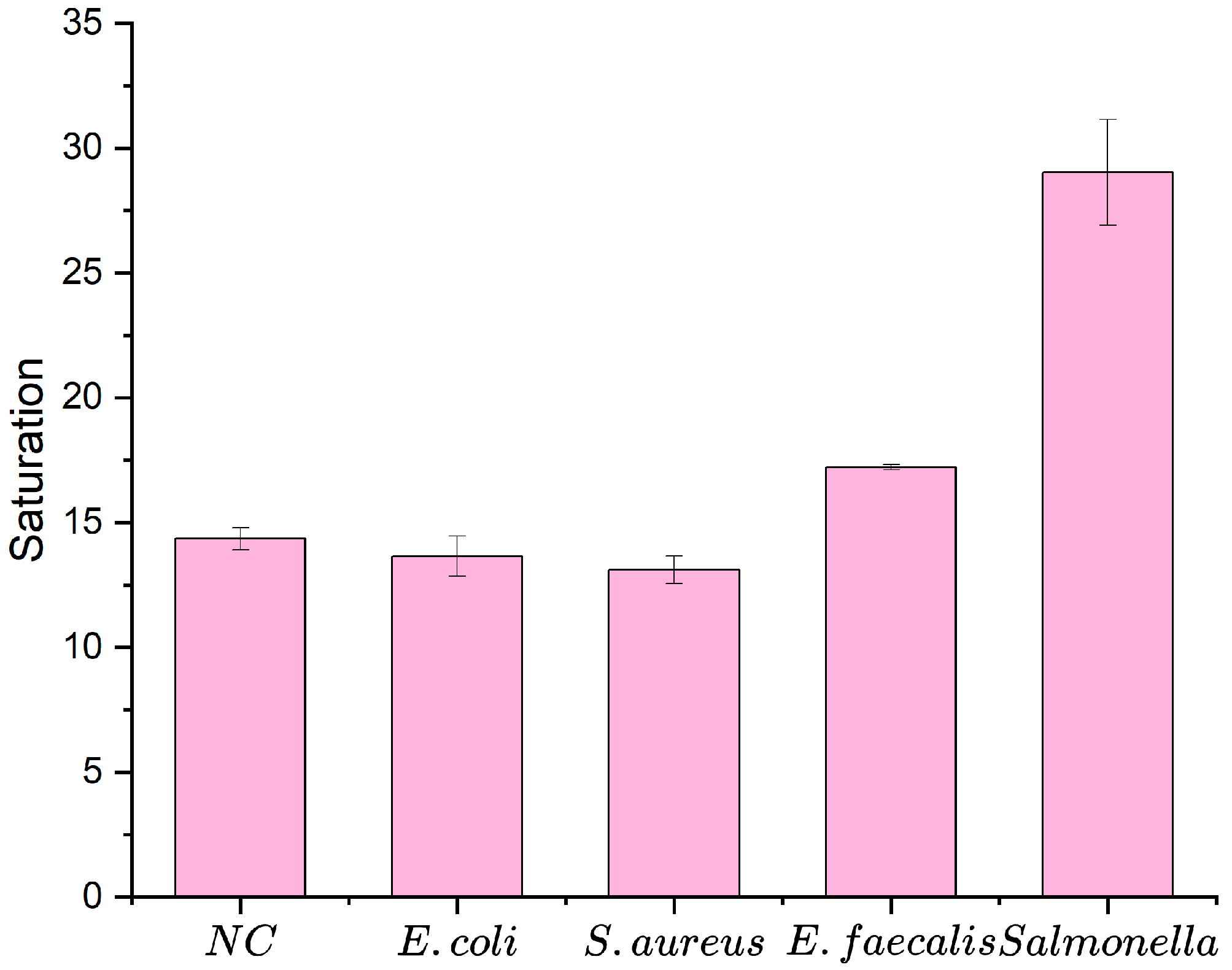
3.4. Performance of the Biosensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fung, F.; Wang, H.-S.; Menon, S. Food safety in the 21st century. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullis, K.; Faloona, F.; Scharf, S.; Saiki, R.; Horn, G.; Erlich, H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: The polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1986, 51, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engvall, E.; Perlmann, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry 1971, 8, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, B.; Habibi, R.; Kett, C.; Chin, W.H.; Barr, J.J.; Tuck, K.L.; Cadarso, V.J. Bacterial concentration and detection using an ultrasonic nanosieve within a microfluidic device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 374, 132769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.I.; Procura, F.; Bueno, D.J. Comparison of 7 culture methods for Salmonella serovar Enteritidis and Salmonella serovar Typhimurium isolation in poultry feces. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3826–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, M.S.; Ahmed, M. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). In Cancer Cell Biology: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 2508, pp. 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Fronczek, C.F. Lab-on-a-Chip Biosensors for the Rapid Detection of Pathogens in Clinical and Field Samples; The University of Arizona: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.J.; Fu, Z.X.; Lu, C.F.; Wu, S.F.; Pan, L.; He, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J. Rapid fabrication of modular 3D paper-based microfluidic chips using projection-based 3D printing. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2024, 7, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.R.G.; Santos, D.R.; Pinio, I.F.; Azevedo, A.M.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Multiplexed microfluidic platform coupled with photodetector array for point-of-need and sub-minute detection of food contaminants. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Belfast, UK, 21–25 January 2018; pp. 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Iseri, E.; Kaya, K.; Heuchel, R.; van der Wijngaart, W. Slip-X-Chip: A Sliding Microfluidic Platform with Cross-Flow. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 35th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems Conference (MEMS), Tokyo, Japan, 9–13 January 2022; pp. 912–914. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Xue, L.; Jin, N.; Duan, H.; Li, M.; Lin, J. Power-free microfluidic biosensing of Salmonella with slide multivalve and disposable syringe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 213, 114458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Liao, M.; Lin, J. An all-in-one microfluidic SlipChip for power-free and rapid biosensing of pathogenic bacteria. Lab Chip 2024, 24, 4039–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanies, O.S.; Kremer, K.R.; Mason, B.M.; Dudley, M.G.; Hlavay, J.M.; Miller, C.T.; Spero, R.C.; Fisher, J.K. A modular microfluidic device that uses magnetically actuatable microposts for enhanced magnetic bead-based workflows. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.B.; Chien, C.C.; You, H.L.; Kuo, F.C.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, G.B. An integrated microfluidic system for antimicrobial susceptibility testing with antibiotic combination. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Huang, P.C.; Lee, G.B. A miniaturized, DNA-FET biosensor-based microfluidic system for quantification of two breast cancer biomarkers. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2021, 25, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.F.; Guzmán-Sastoque, P.; Muñoz-Camargo, C.; Reyes, L.H.; Osma, J.F.; Cruz, J.C. Enhancing magnetic micro-and nanoparticle separation with a cost-effective microfluidic device fabricated by laser ablation of PMMA. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Chen, Y.; Lüders, A.; Bertrand, T.; Hanedan, E.; Nielaba, P.; Nelson, B.J. Scalable high-throughput microfluidic separation of magnetic microparticles. Device 2024, 2, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zeng, T.; Wu, R.B. QM/MM Modeling Aided Enzyme Engineering in Natural Products Biosynthesis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 5018–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.Y.; Fan, D.X.; Chen, Y.; Han, S.Y. Exploring enzyme-MOF (metal-organic framework) catalytic systems: Trade-offs between enzyme activity and MOF stability. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 2605–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, R.; Yan, X. Nanozymes: Next-generation artificial enzymes. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2022, 52, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, R.B.; Yu, L.L.; Li, S.; Fan, J.; Luo, R.; Zhao, J.T. Facile synthesis of hierarchical mesoporous beta-manganese dioxide nanoflowers with extremely high specific surface areas for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 284, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.; Ahmed, M.S.; Jeon, S. δ-MnO2 nanoflowers on sulfonated graphene sheets for stable oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 296, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huo, X.; Jiang, F.; Xi, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. Dual-functional manganese dioxide nanoclusters for power-free microfluidic biosensing of foodborne bacteria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 393, 134242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Jin, N.; Guo, R.; Wang, S.; Qi, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. Microfluidic colorimetric biosensors based on MnO2 nanozymes and convergence–divergence spiral micromixers for rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2674–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Qi, Y.; Si, Y. MnO2 nanozyme-driven polymerization and decomposition mechanisms of 17β-estradiol: Influence of humic acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Spike Concentration (CFU/mL) | Detected Concentration (CFU/mL) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | 63.8 | 99.7 | 5.76 |
| 640 | 607.4 | 94.9 | 5.60 |
| 2600 | 3261.6 | 125.4 | 6.77 |
| 260,000 | 28,252.0 | 108.7 | 4.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhi, X.; An, J.; Wang, Y. A Sliding Microfluidic Chip-Integrated Colorimetric Biosensor Using MnO2 Nanoflowers for Rapid Salmonella Detection. Micromachines 2025, 16, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080904
Niu Y, Jiang J, Zhi X, An J, Wang Y. A Sliding Microfluidic Chip-Integrated Colorimetric Biosensor Using MnO2 Nanoflowers for Rapid Salmonella Detection. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080904
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Yidan, Juntao Jiang, Xin Zhi, Jiahui An, and Yuhe Wang. 2025. "A Sliding Microfluidic Chip-Integrated Colorimetric Biosensor Using MnO2 Nanoflowers for Rapid Salmonella Detection" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080904
APA StyleNiu, Y., Jiang, J., Zhi, X., An, J., & Wang, Y. (2025). A Sliding Microfluidic Chip-Integrated Colorimetric Biosensor Using MnO2 Nanoflowers for Rapid Salmonella Detection. Micromachines, 16(8), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080904




