Design of Low-SAR High-Efficiency Terminal Antenna Using Magnetic Field Homogenization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Both simulation verification and theoretical derivation have been performed to demonstrate the correlation between the SAR and the tangential magnetic field distribution of the antenna.
- (2)
- A magnetic field homogenization design mechanism for reducing the antenna SAR values is proposed. Unlike traditional approaches that introduce reverse currents to reduce the SAR values, this mechanism achieves homogenization of the tangential magnetic field distribution in the antenna near-field region through antenna structure optimization, and effectively reduces the SARs while avoiding degradation of antenna efficiency.
- (3)
- Guided by the magnetic field homogenization mechanism, we design an antenna operating in the N78 band, which simultaneously achieves both high efficiency and low SAR performance.
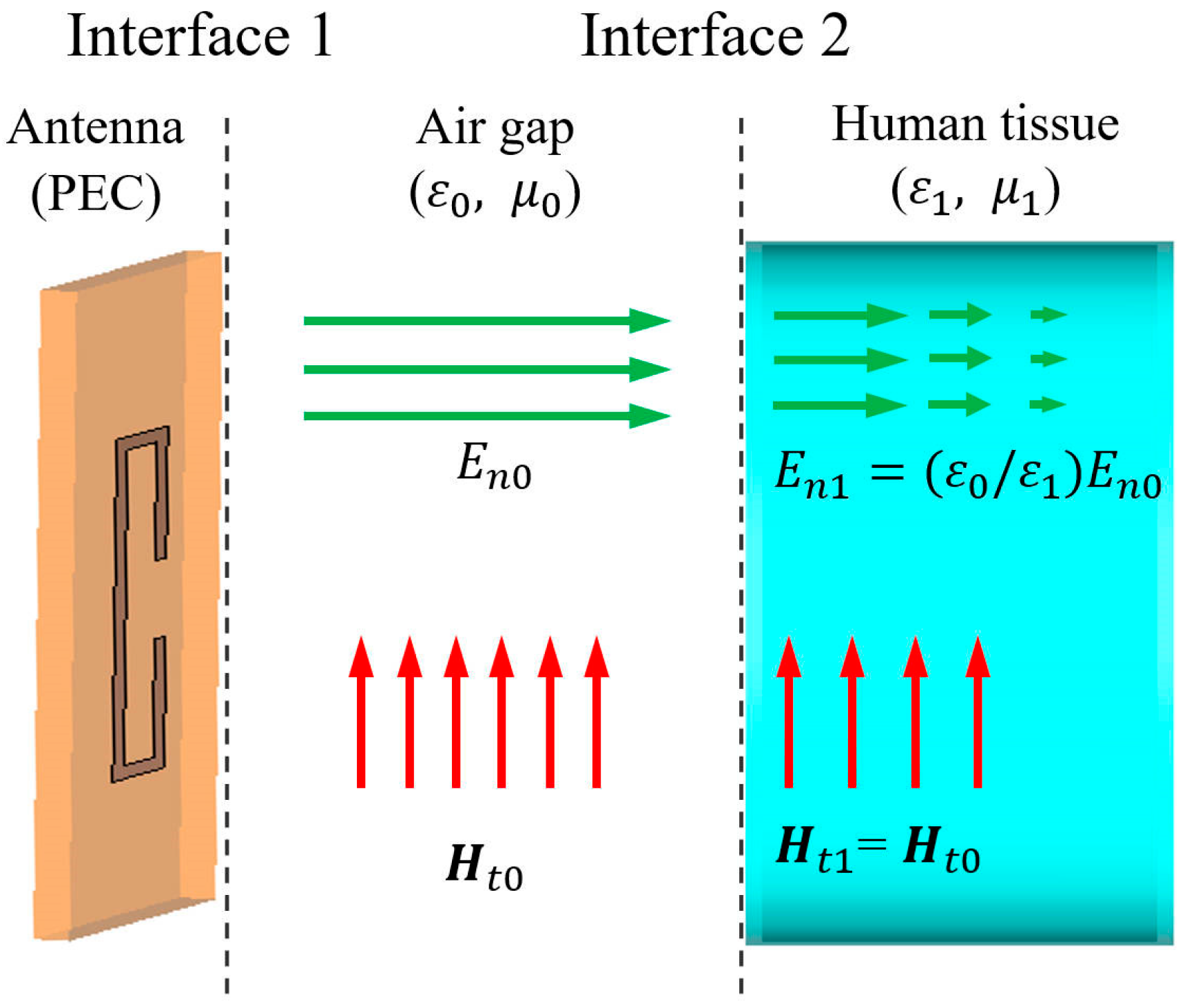
2. Theoretical Analysis of Magnetic Field Homogenization
2.1. Tangential Magnetic Field and SAR Hot Spot Analysis
2.2. SAR Reduction Mechanism Through Magnetic Field Homogenization
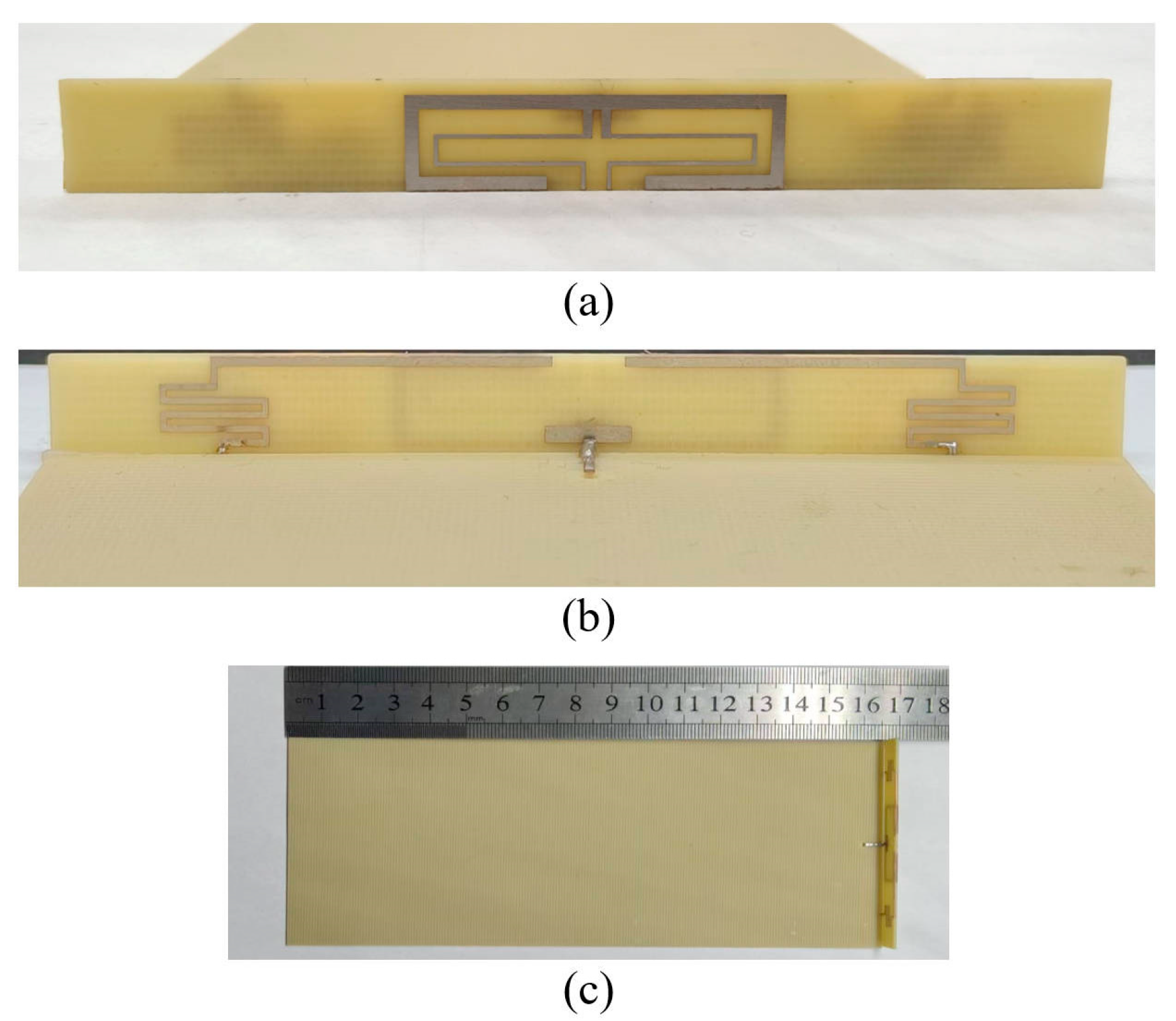
3. Design of Low-SAR Antenna
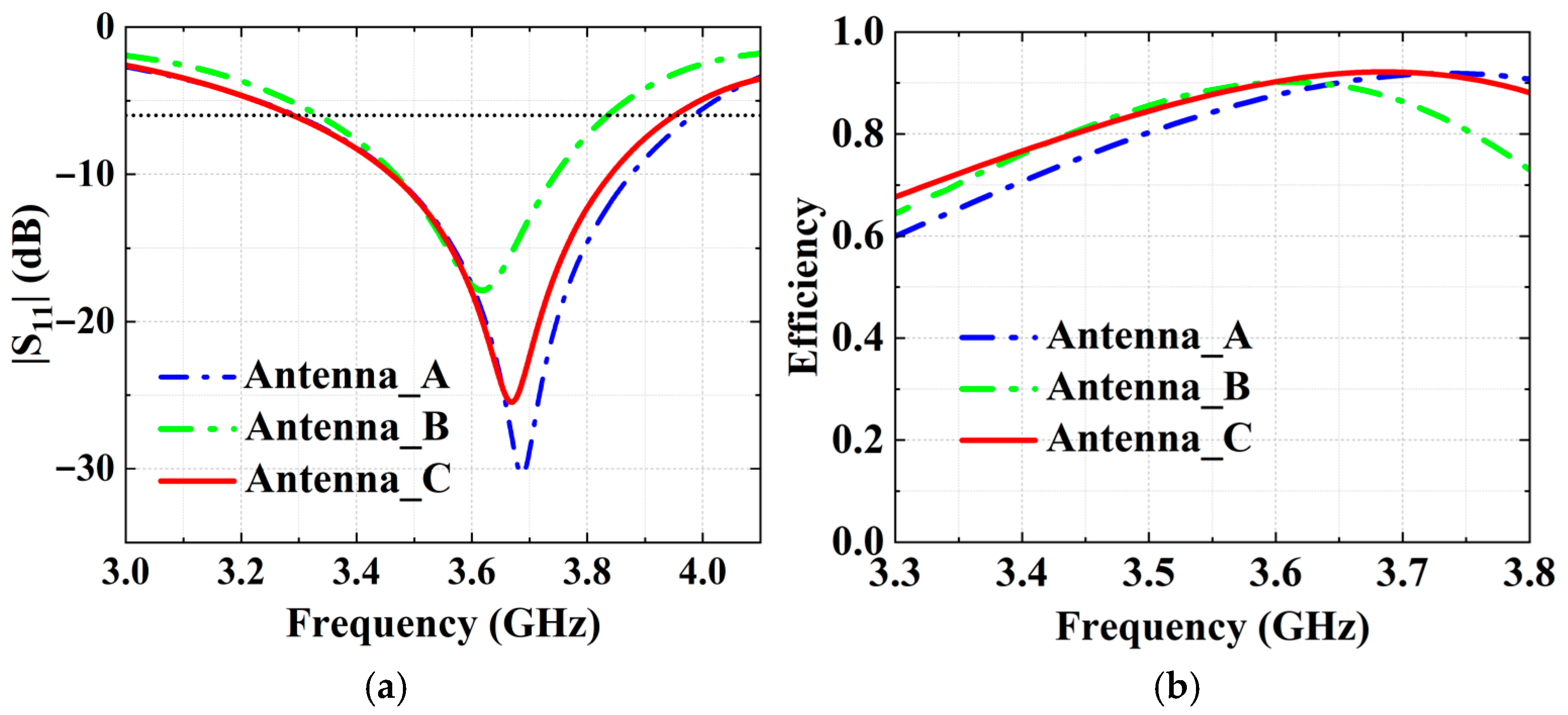
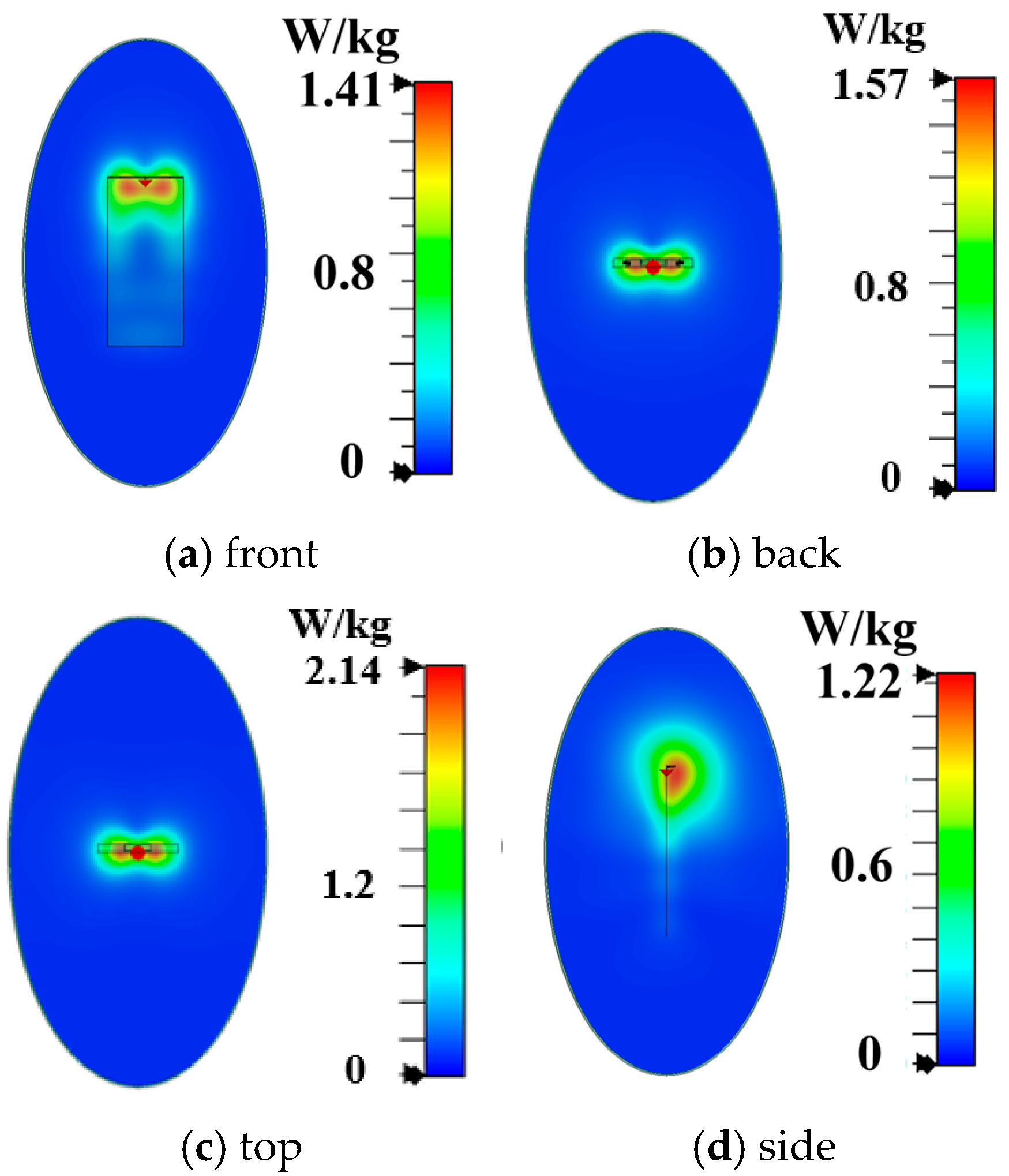
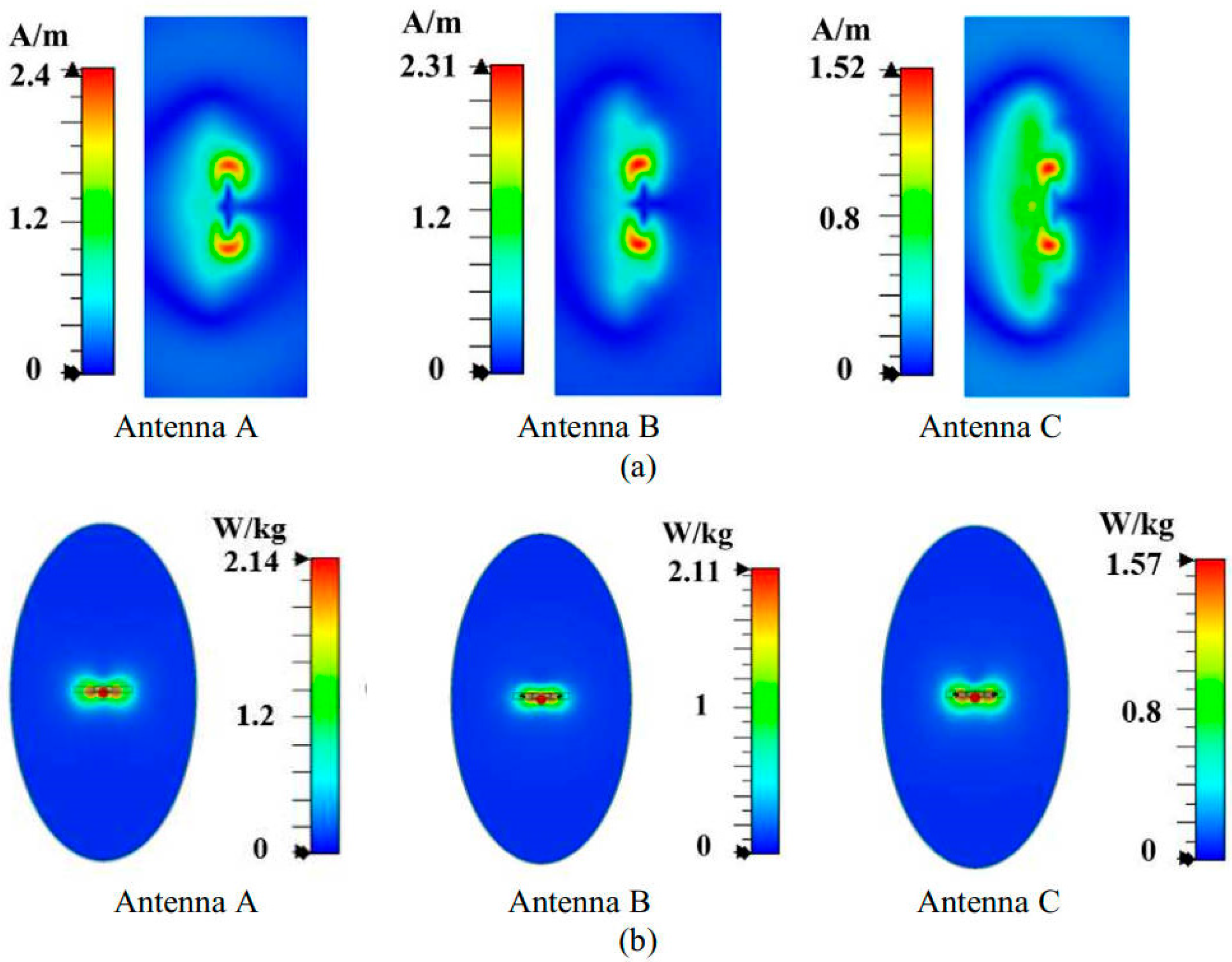
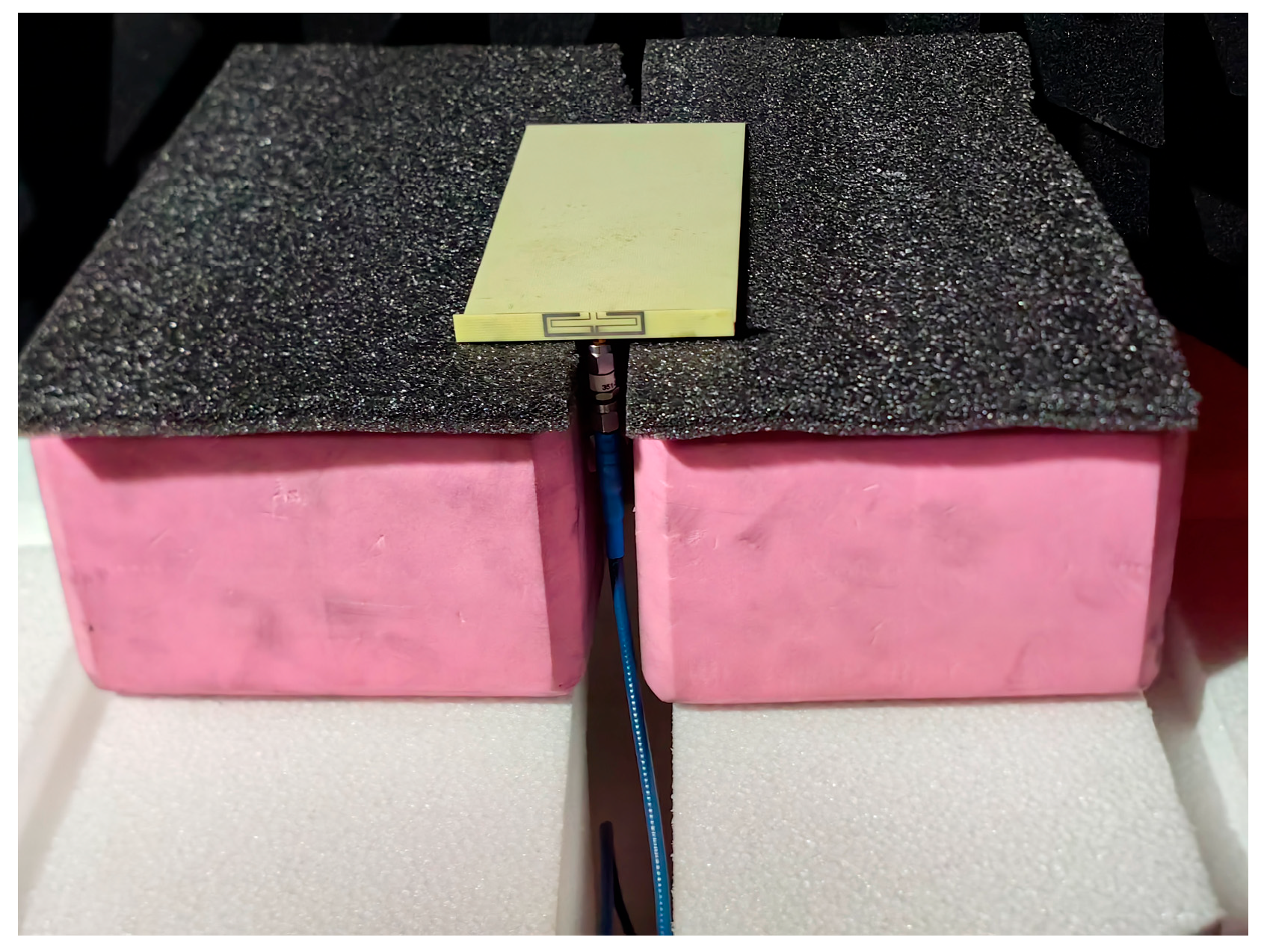
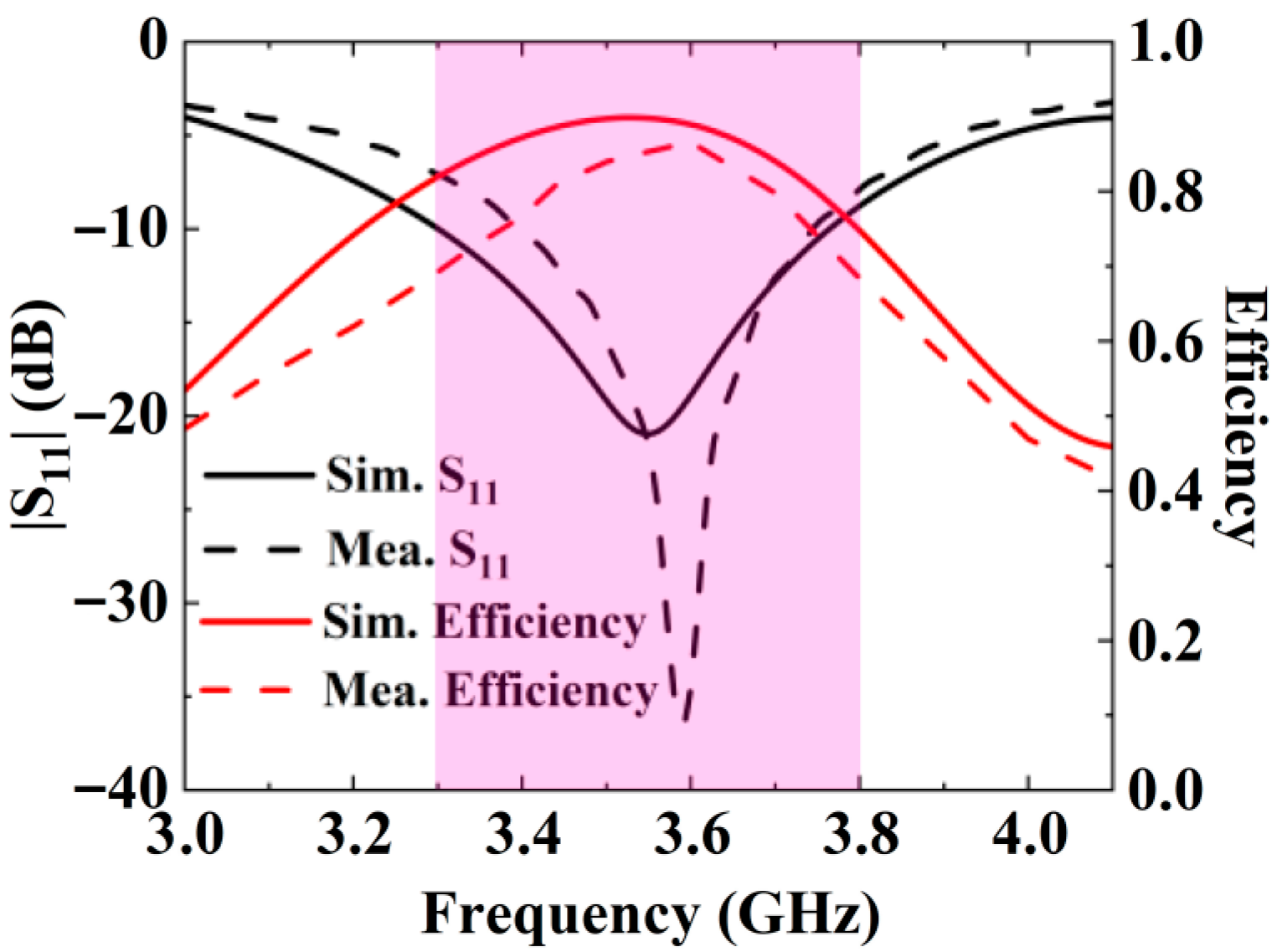
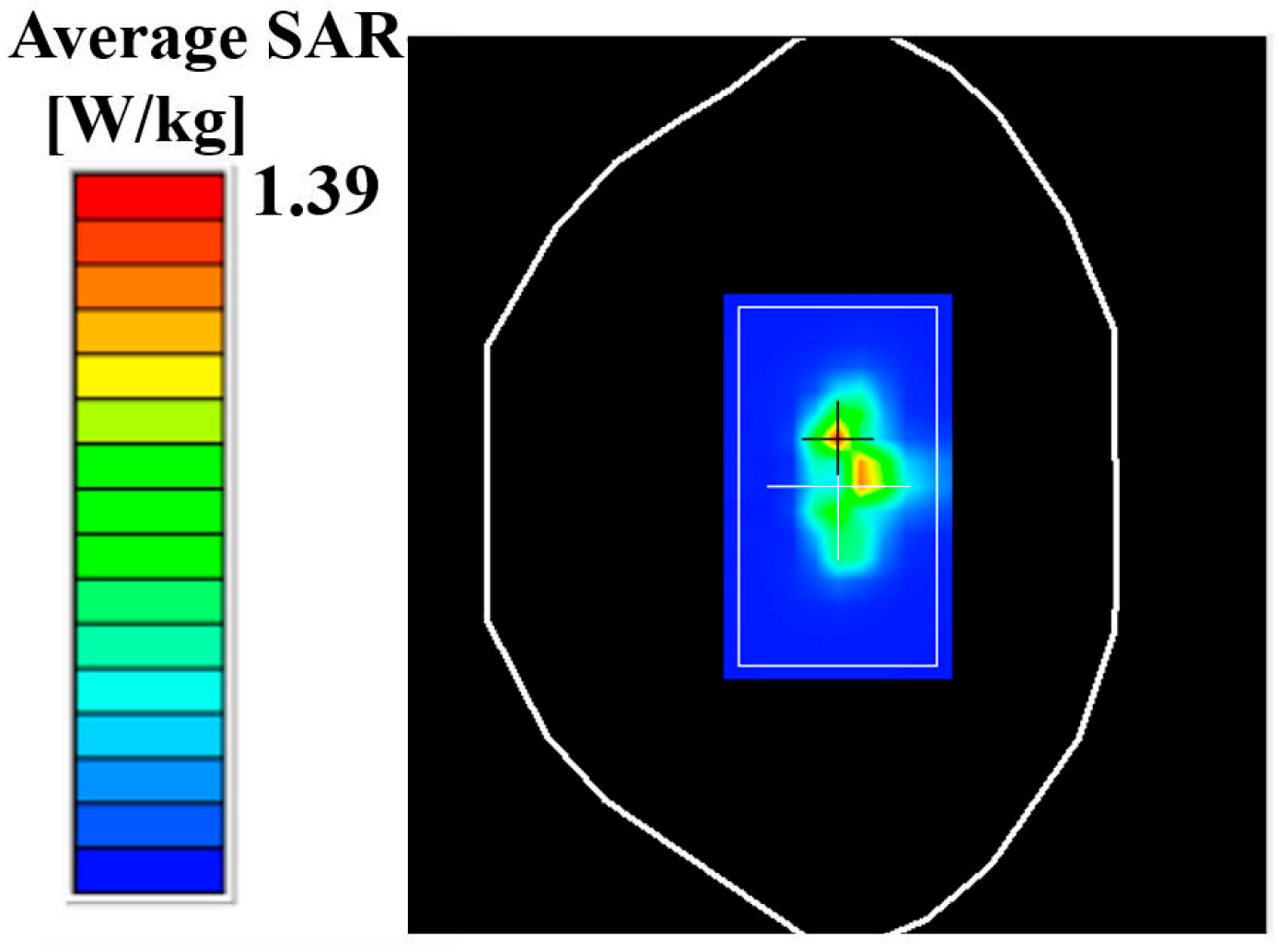
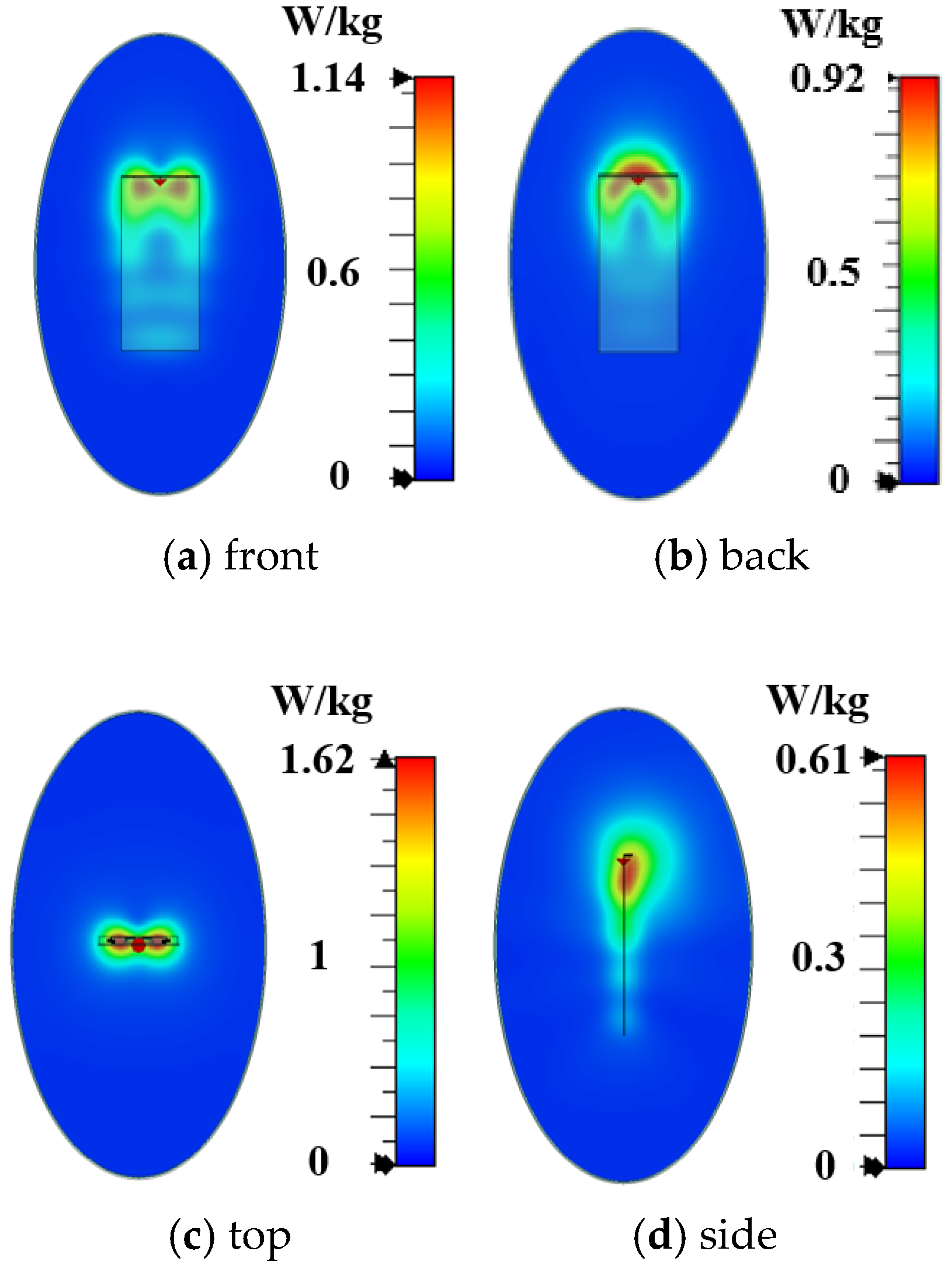
4. Antenna Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEEE Standard C95.1-1991; IEEE Standard for Safety Levels with Respect to Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields, 3 kHz to 300 GHz. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1992. [CrossRef]
- Repacholi, M.H.; Grandolfo, M.; Ahlbom, A. Health issues related to the use of hand-held radiotelephones and base transmitters. Health Phys. 1996, 70, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard C95.1-2019; IEEE Standard for Safety Levels with Respect to Human Exposure to Electric, Magnetic, and Electromagnetic Fields, 0 Hz to 300 GHz. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wong, K. Planar monopole with a coupling feed and an inductive shorting strip for LTE/GSM/UMTS operation in the mobile phone. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 2479–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J. Antenna Design for Mobile Device; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.W.; Wong, Y.W. Quarter-wavelength printed loop antenna with an internal printed matching circuit for GSM/DCS/PCS/UMTS operation in the mobile phone. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Das, S.; Paul, S. SAR reduction for an implantable antenna using ferrite superstrate. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Workshop on Antenna Technology, Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 March 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitra, M.I.; Panagamuwa, C.J.; McEvoy, P.; Vardaxoglou, J.C.; James, J.R. Low SAR ferrite handset antenna design. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.N.; Chen, F.C. Reduction of the peak SAR in the human head with metamaterials. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2006, 54, 3763–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Karthigai, L.S. A Compact Penta-Band Low-SAR Antenna Loaded with Split-Ring Resonator for Mobile Applications. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2022, 2022, 3298866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Chow, K.M.; Fung, L.C.; Leung, S.W. Effect of using conductive materials for SAR reduction in mobile phone. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2005, 44, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouche, Y.B.; Nedil, M.; Ben Mabrouk, I.; Ramahi, O.M.; Elhennawy, H.M. Wearable circularly polarized antenna backed by AMC reflector for WBAN communications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 12838–12852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Atrash, M.; Abdalla, M.A.; Elhennawy, H.M. A wearable dual-band low profile high gain low SAR antenna AMC-backed for WBAN applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 6378–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.A.B.; Nikolaou, S.S.; Antoniades, M.A.; Stevanovic, M.N.; Vryonides, P. Compact EBG-backed planar monopole for BAN wearable applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.P.; Hu, B.; Wang, S.-F.; Yang, C. Wearable circular ring slot antenna with EBG structure for wireless body area network. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, K.S.; Abdullah, H.H.; Abdallah, E.A.; Hashish, E.A. Low-SAR, miniaturized printed antenna for mobile, ISM, and WLAN services. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broas, R.F.J.; Sievenpiper, D.F.; Yablonovitch, E. A high-impedance ground plane applied to a cellphone handset geometry. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2001, 49, 1262–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Hao, Y.; Munoz, M.O.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H. A compact and low-profile MIMO antenna using a miniature circular high-impedance surface for wearable applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Analysis of electromagnetic energy absorption in the human body for mobile terminals. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2020, 1, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Yu, G.G.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.X.; Shi, G.; Wang, S. Design of low-SAR mobile phone antenna: Theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Yu, G.G.; Liu, X.Z.; Cheng, G.S.; Xu, Y.X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G.M. Low-SAR MIMO antenna array design using characteristic modes for 5G mobile phones. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 3052–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Liu, X.Z.; Cheng, G.S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G.M.; Li, K. Low-SAR four-antenna MIMO array for 5G mobile phones based on the theory of characteristic modes of composite PEC-lossy dielectric structures. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Hu, W.; Jiang, W.; Lu, B. Design of low-SAR terminal antenna using characteristic mode manipulation. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2023, 22, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, J.-Q.; Liu, Y.; An, J. Self-decoupling, shared-aperture, eight-antenna MIMO array with MIMO-SAR reduction. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 72, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC/IEEE 62209-1528:2020; IEC/IEEE International Standard—Measurement Procedure for the Assessment of Specific Absorption Rate of Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Fields from Hand-Held and Body-mounted Wireless Communication Devices–Part 1528: Human Models, Instrumentation, and Procedures (Frequency Range of 4 MHz to 10 GHz). IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–284. [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna theory: Analysis and design. IEEE Antennas Propag. Soc. Newsl. 2003, 24, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.D. Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1998; 832p, ISBN 0-471-30932-X. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, R.F. Time-Harmonic Electromagnetic Fields; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1961; ISBN 0-471-20806-X. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.Y.; Yu, D.; Zhang, H.H.; Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Dong, Y.F.; Han, Y.J. High head-hand efficiency and low-SAR mobile phone antenna design based on unidirectional and uniform current distribution. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 72, 5560–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Du, Z. Dual-feed shared-radiator metal-frame fullscreen mobile phone antenna for GPS and LTE bands with a dual-function capacitor. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2023, 71, 8314–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Bandwidth (GHz) | SAR Reduction Mechanism | Back Body SAR (W/kg) | Simulated Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [20] | 0.83 to 1.04; 1.67 to 2.73 | Reverse current | 1.88 (1.06) | >34 |
| [21] | 3.4 to 3.6 | Reverse mode current | 1.01 (0.35) | >50 |
| [24] | 3.4 to 3.6 | Total current equalization | 1.67 (0.60) | >57 |
| [29] | 1.7 to 2.7 | Uniform current | 1.19 (0.31) | >67 |
| [30] | 1.7 to 2.7 | without | 1.53 (0.50) | >60 |
| Prop. | 3.3 to 3.8 | Magnetic field homogenization | 0.92 (0.23) | >78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, S.; Jiao, Y.-C.; Lv, Z.; Zan, L.; Weng, Z. Design of Low-SAR High-Efficiency Terminal Antenna Using Magnetic Field Homogenization. Micromachines 2025, 16, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080856
Xiao S, Jiao Y-C, Lv Z, Zan L, Weng Z. Design of Low-SAR High-Efficiency Terminal Antenna Using Magnetic Field Homogenization. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080856
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Sihan, Yong-Chang Jiao, Ziming Lv, Liupeng Zan, and Zibin Weng. 2025. "Design of Low-SAR High-Efficiency Terminal Antenna Using Magnetic Field Homogenization" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080856
APA StyleXiao, S., Jiao, Y.-C., Lv, Z., Zan, L., & Weng, Z. (2025). Design of Low-SAR High-Efficiency Terminal Antenna Using Magnetic Field Homogenization. Micromachines, 16(8), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080856





