Laser Micromachining for the Nucleation Control of Nickel Microtextures for IR Emission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
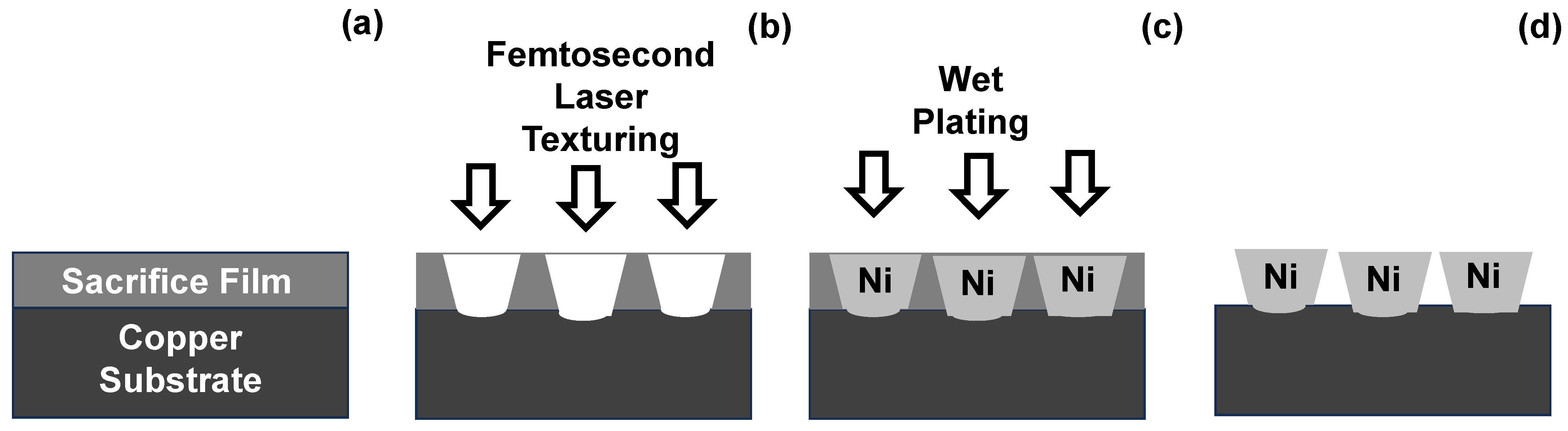
2.1. Femtosecond Laser Microtexturing Method
2.2. Nickel Wet Plating Method
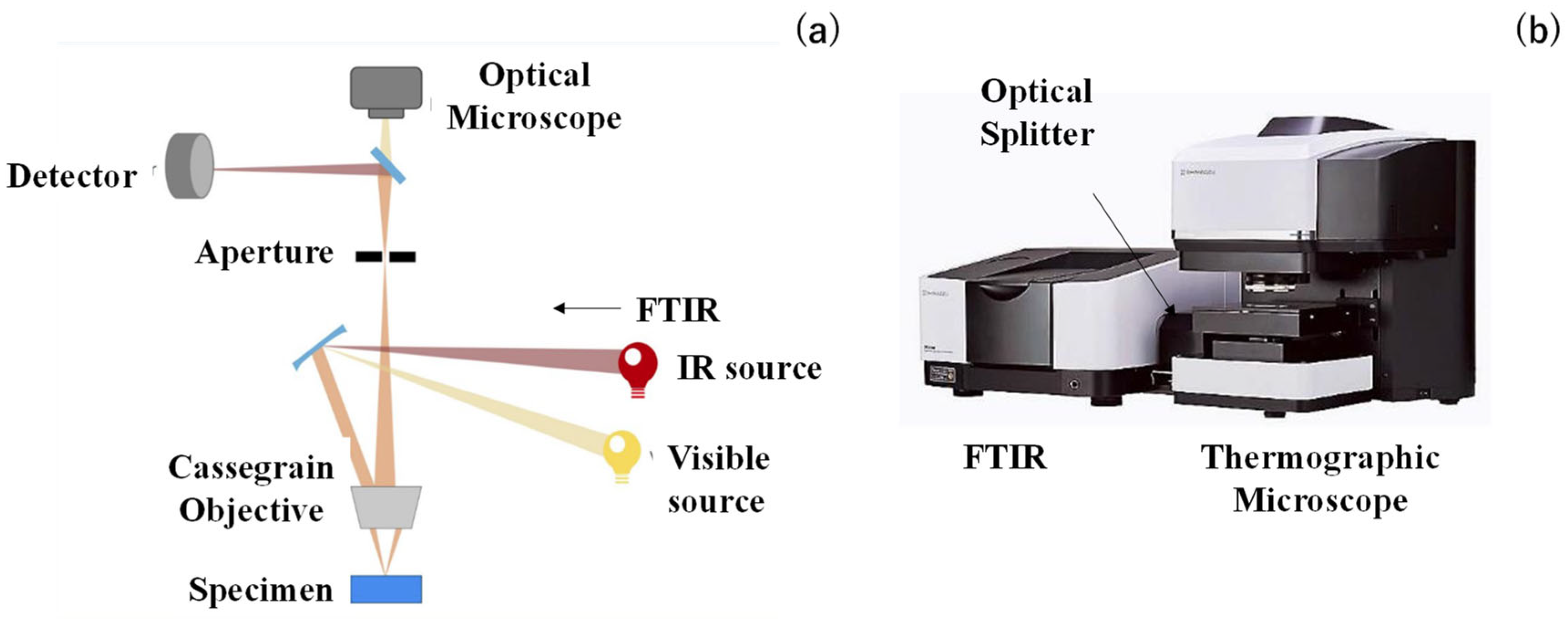
2.3. Geometric Characterization of Microtextures
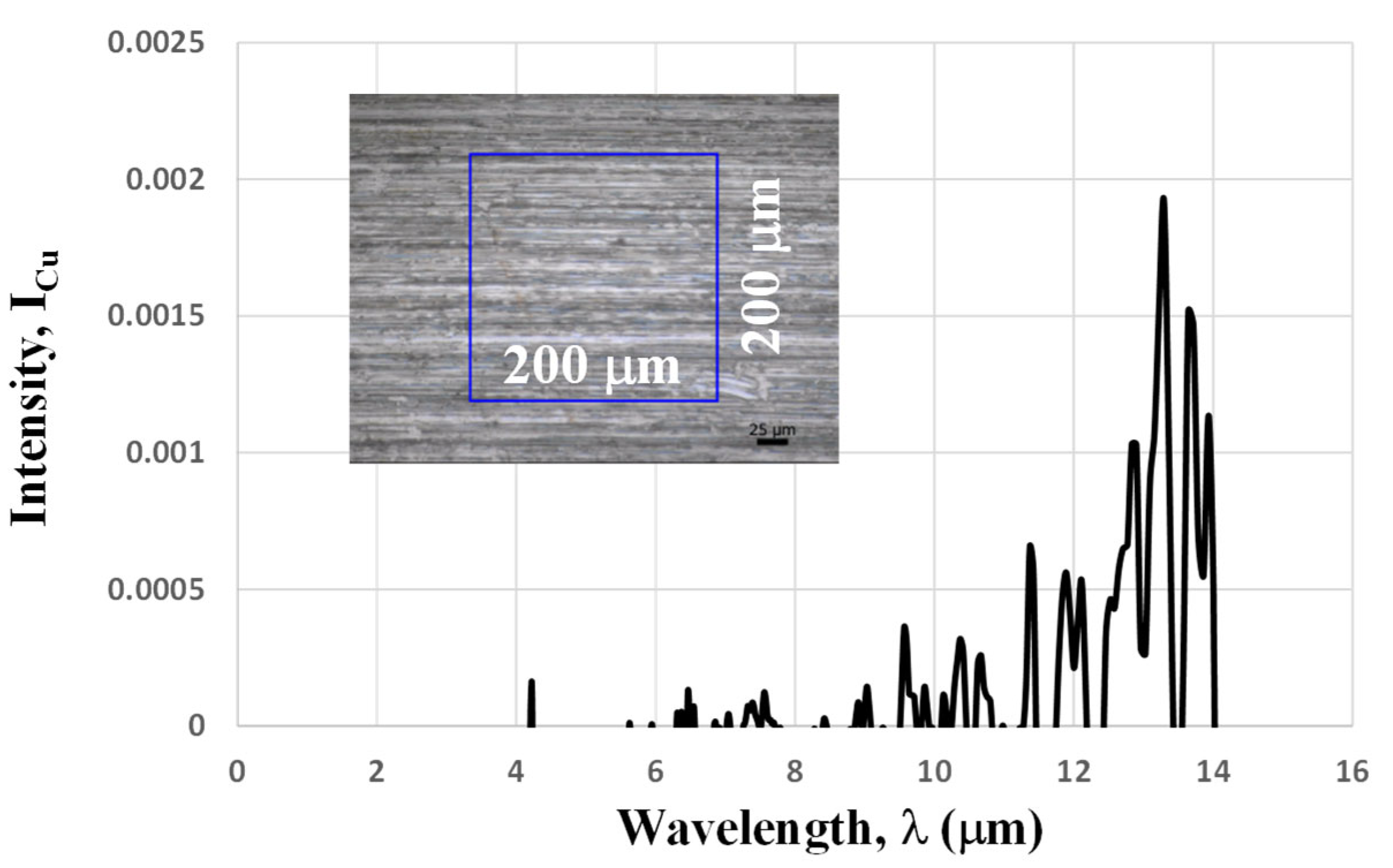
2.4. IR Emissivity Measurement
3. Results
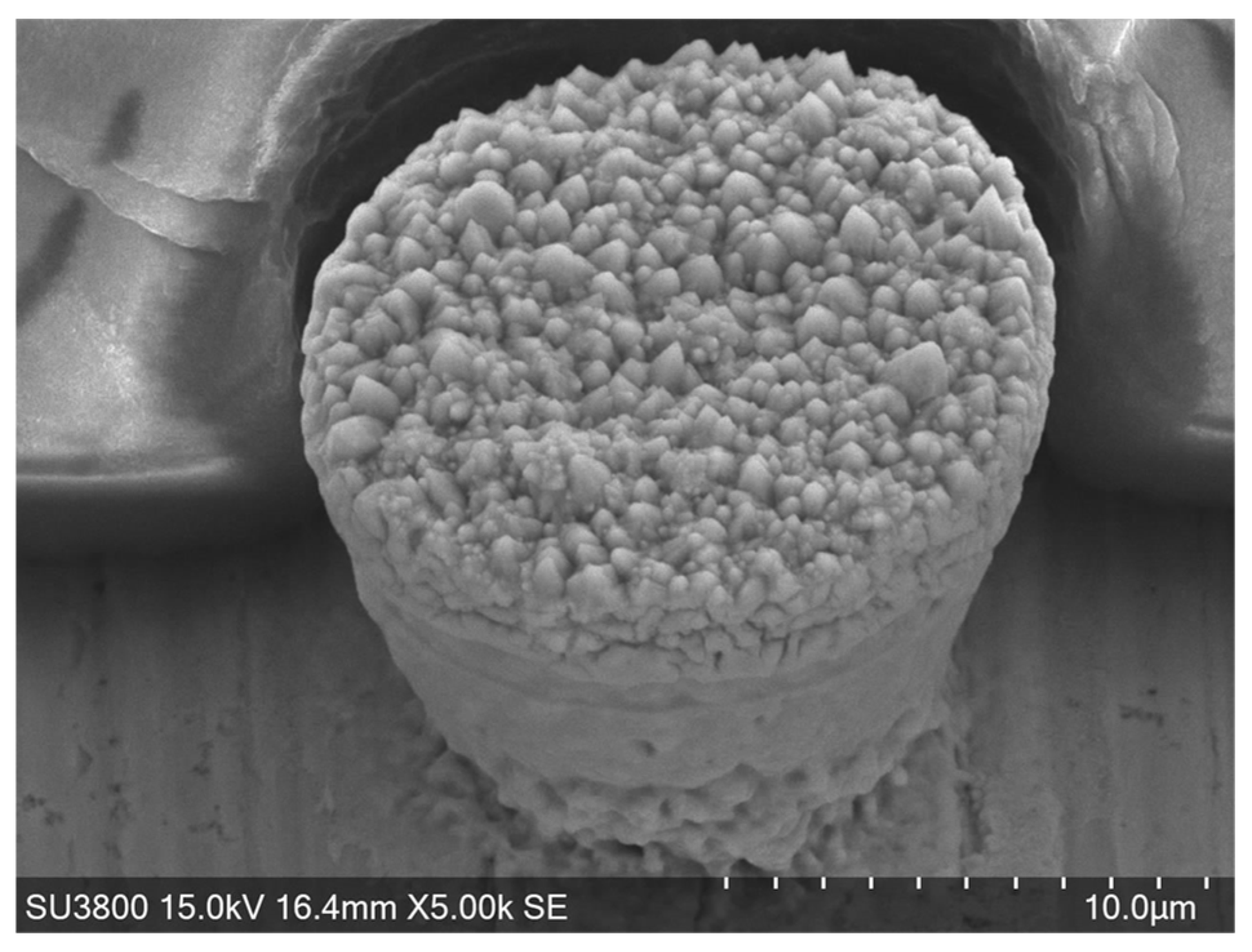
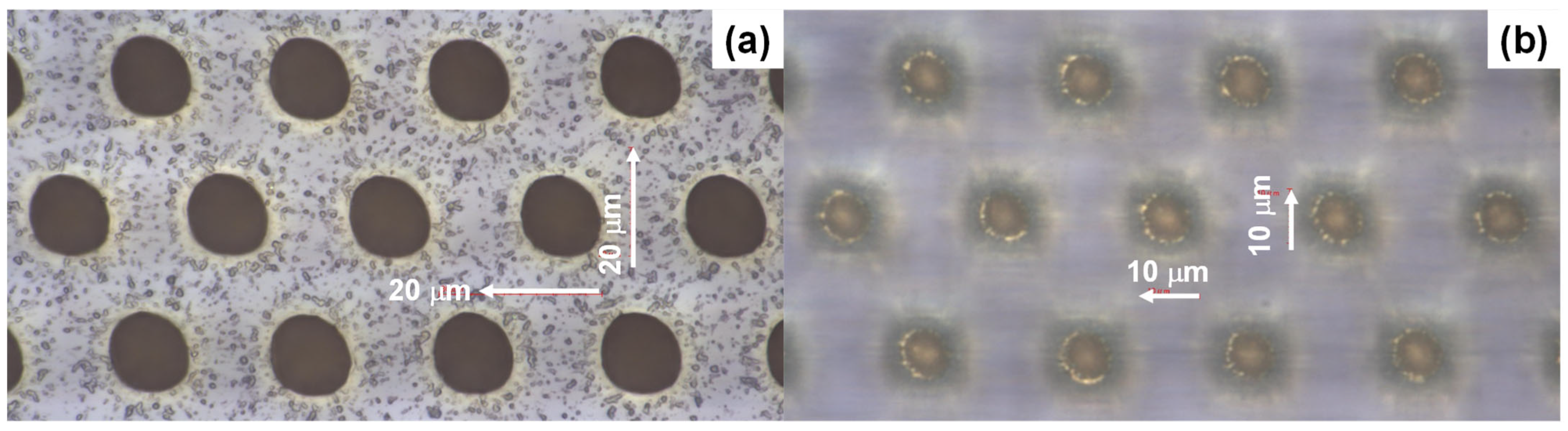
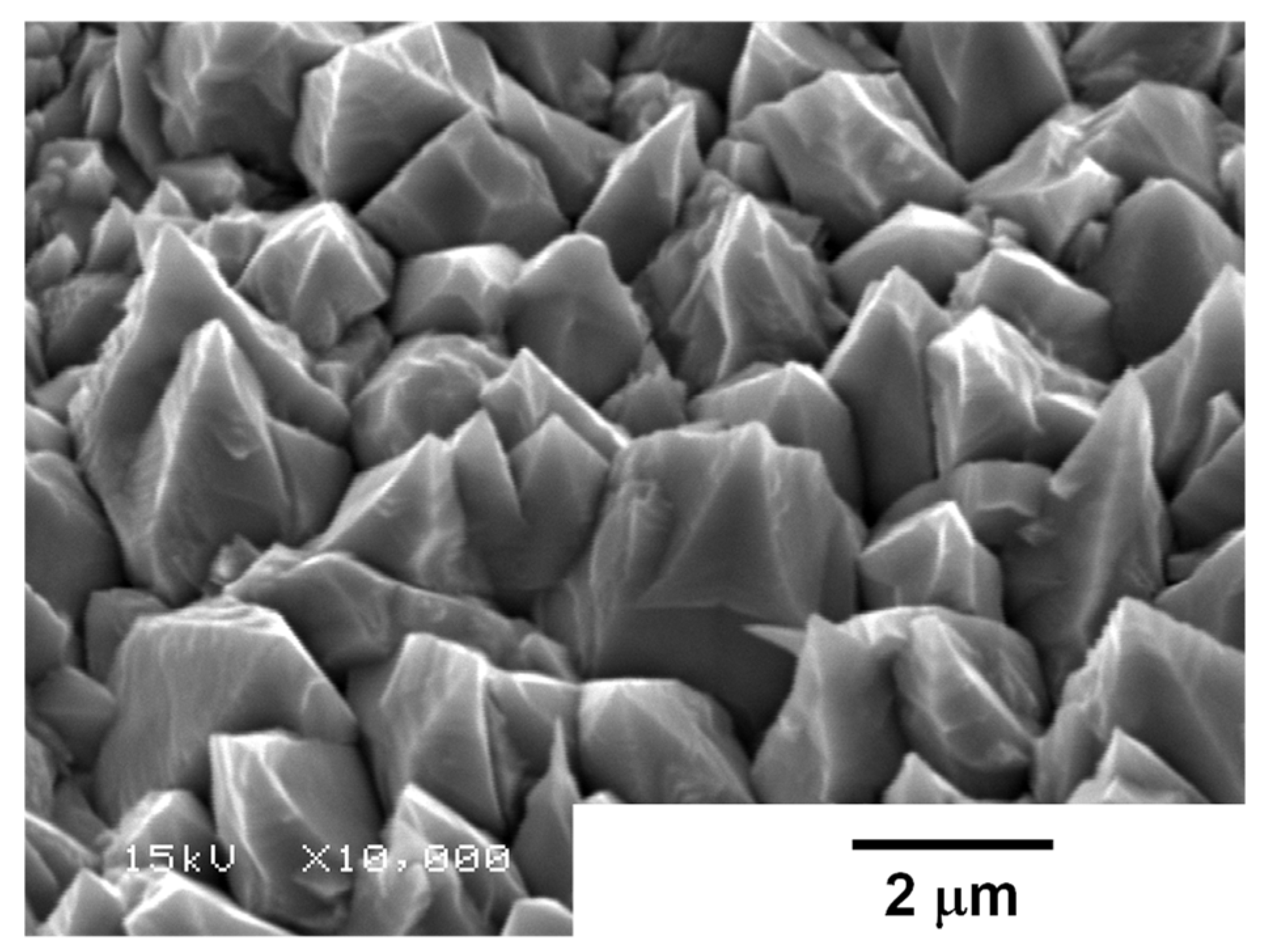
3.1. Femtosecond Laser Microtexturing
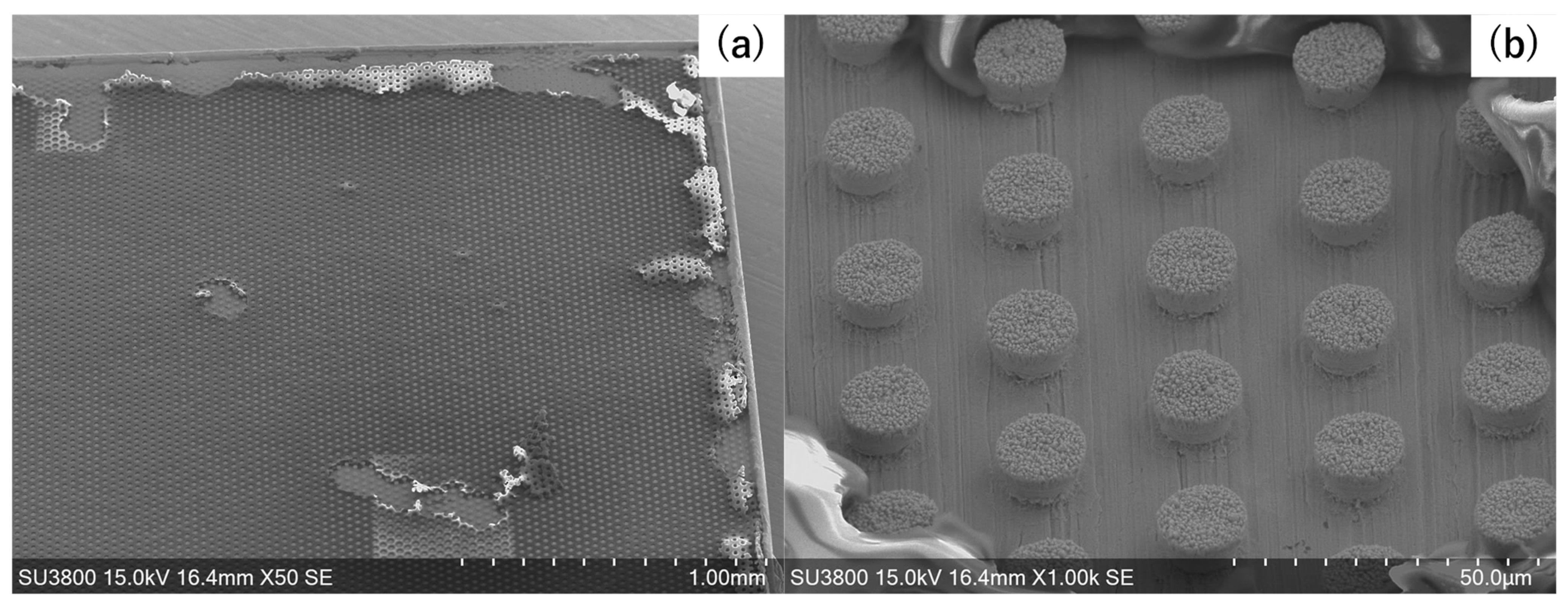
3.2. Nickel Microtexturing via Wet Plating
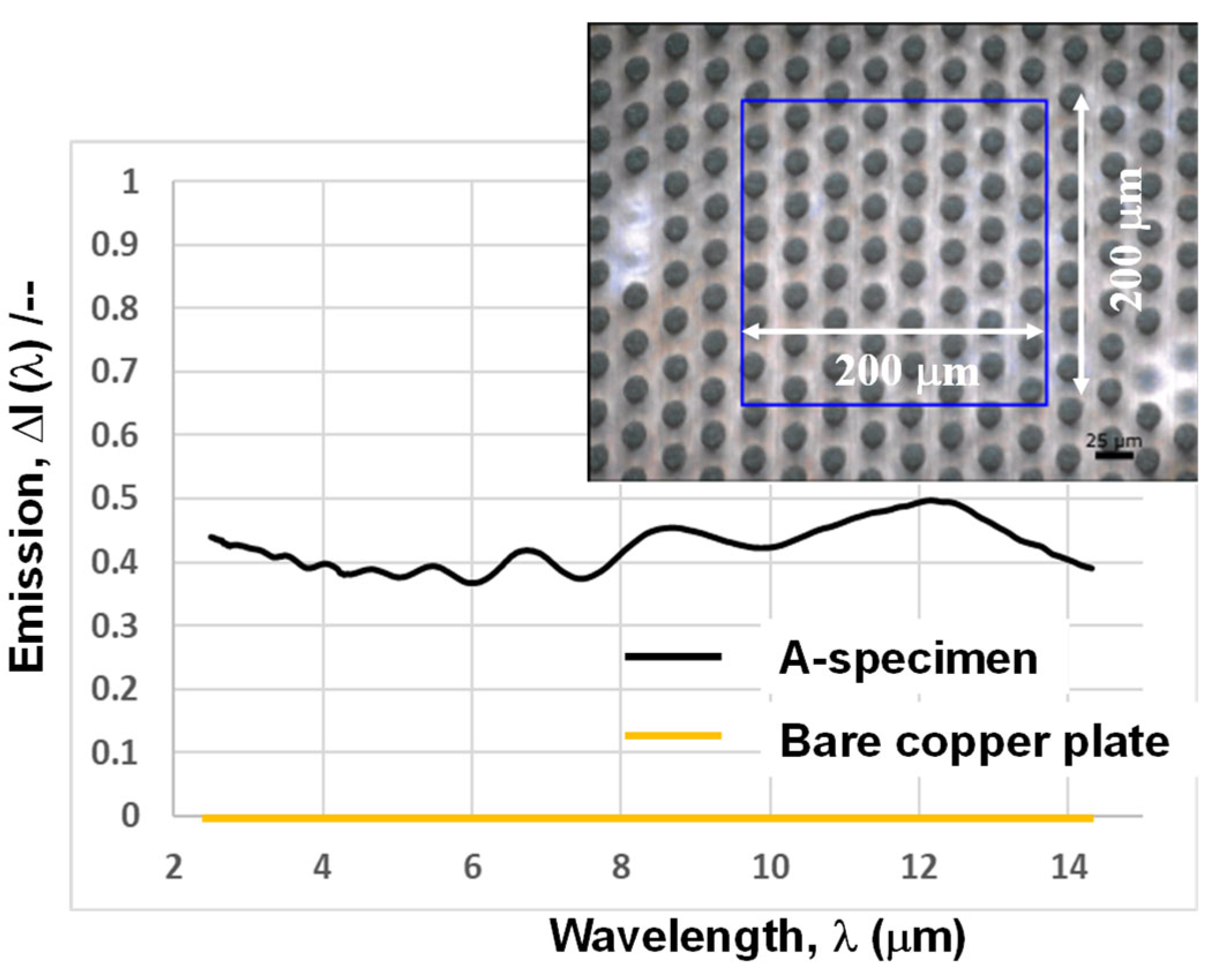
3.3. IR Emissivity of the Micro-Pillared Specimen
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J. From terahertz imaging to terahertz wireless communications. Engineering 2023, 22, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Fukui, R. Active thermographic non-destructive inspection of CFRP. J. Jpn. Soc. Compos. Mater. 2023, 49, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, M. Heat Transfer by Infrared Radiation from Sensor to Sample. Available online: https://ctherm.com/resources/newsroom/thermal-conductivity/heat-transfer-by-ir/ (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Li, W.; Fan, S. Nano-photonic control of thermal radiation for energy applications. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 15995–16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Thang, D.D.; Ishii, S.; Sugavaneshwa, R.P.; Nagao, T. Selective patterned growth of ZnO nanowires/nanosheets and their photoluminescence properties. Opt. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ghanekar, A.; Ricci, M.; Hyde, M.; Gregory, O.; Zheng, Y. A Review of tunable wavelength selectivity of meta-materials in near-field and far-field radiative thermal transport. Materials 2018, 11, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Han, T.; Zheng, X.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Fan, S.; Qiu, C.-W. Transforming heat transfer with thermal metamaterials and devices. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 488–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohiyama, A.; Shimizu, M.; Yugami, H. Unidirectional radiative heat transfer with a spectrally selective planar ab-sorb-er/emitter for high-efficiency solar thermophotovoltaic systems. Appl. Phys. Express 2016, 9, 112302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, T.; Nakata, H.; Nasu, T. Fabrication and characterization of acicular micro-textured copper-sheet device for low temperature heat radiation. J. Micromach. 2023, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, T.; Ebina, S.; Nakata, H.; Nasu, T. Heat Transportation Device. Japanese Patent #2023-056971, 31 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa, T.; Nakata, H.; Nasu, T. Infrared emission for heat radiation from micro-cone textured metallic sheet device with semi-regular alignment. ASME J. Micro Nano-Manuf. 2023, 11, 021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, T.; Inohara, T. Chapter 1 in Micromachining. In Pico- and Femtosecond Laser Micromachining for Surface Texturing; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa, T.; Nakata, H.; Nasu, T. Regularity controlled metallic unit-cell alignment for heat radiation device. In Proceedings of the WCMNM2025, Valletta, Malta, 15–18 September 2025. [Google Scholar]
- List of Metals Emissivity. Available online: https://www.flukeprocessinstruments.com/en-us/service-and-support/knowledge-center/infrared-technology/emissivity-metals (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Ono, M.; Takata, M.; Shirata, M.; Yoshihiro, T.; Tani, T.; Naya, M.; Saiki, T. Self-adaptive control of infrared emissivity in a solution-processed plasmonic structure. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 36048–36060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.C.; Hsiao, T.C.; Wang, W.H.; Chang, S.W.; Chen, H.L. Emissivity and optical properties of thin-film metallic glass in the thermal infrared region. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2301517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, T.; Nakata, H.; Nasu, T. Heat transportation by acicular micro-textured device with semi-regular alignment. Ch. 6. In Heat Transfer—Advances in Fundamentals and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024; Chapter 6; pp. 123–148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Fang, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Machining approach of freeform optics on infrared materials via ultra-precision turning. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.H.; Yu, Y.H.; Sun, H.B. Laser interference fabrication of large-area functional periodic structure surface. Front. Mech. Eng. 2018, 13, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobunaga, N.; Kumagai, S.; Sasaki, M. Bipolar electrostatic driving of isolated micro-resonator for sensing high voltage of battery output with resolution. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2022, 16, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemiya, K.; Koshikawa, H.; Imbe, M.; Yamaki, T.; Shitomi, H. Perfect blackbody sheets from nano-precision microtextured elastomers for light and thermal radiation management. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 5418–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Hwang, T.; Lin, S.; Chen, Y.; Wong, Z.J. Directional thermal emission and display using pixelated non-imaging micro-optics. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4544. [Google Scholar]
- Talebzadeh, N.; Rostami, M.; O’Brien, P.G. Elliptic paraboloid-based solar spectrum splitters for self-powered photobioreactors. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, B.; Pullen, M.G.; Baudisch, M.; Sclafani, M.; Hemmer, M.; Senftleben, A.; Schröter, C.D.; Ullrich, J.; Moshammer, R.; Biegert, J. Strong-field physics with Mid-IR fields. Phys. Rev. X 2015, 5, 021034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perekrestov, V.; Kornyushchenko, A.; Kosminska, Y.; Kubakh, M.; Wilde, G. Self-organization of micro- and nanosystems in the form of patterns. J. Cryst. 2024, 14, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, J.; Dan, Y. Near-infrared and mid-infrared light emission of boron-doped crystalline silicon. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 10941–10947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Procedure | Alignment | Unit Cell Size | Unit Cell Geometry | Duration | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Machining | Limited to small areas | Accurate as designed | Accurate as designed | Fast | Cheap |
| Laser Interference Technique | Applicable to large areas | Nearly Accurate | Not accurate | Fastest | Cheapest |
| Lithography | Applicable to large areas | Accurate | Limited by cylinder or column | Multi-step | Expensive |
| Femtosecond Laser Microtexturing | Applicable to large areas | Accurate As designed | Controllable | Faster | Normal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aizawa, T.; Nakata, H.; Nasu, T. Laser Micromachining for the Nucleation Control of Nickel Microtextures for IR Emission. Micromachines 2025, 16, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060696
Aizawa T, Nakata H, Nasu T. Laser Micromachining for the Nucleation Control of Nickel Microtextures for IR Emission. Micromachines. 2025; 16(6):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060696
Chicago/Turabian StyleAizawa, Tatsuhiko, Hiroki Nakata, and Takeshi Nasu. 2025. "Laser Micromachining for the Nucleation Control of Nickel Microtextures for IR Emission" Micromachines 16, no. 6: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060696
APA StyleAizawa, T., Nakata, H., & Nasu, T. (2025). Laser Micromachining for the Nucleation Control of Nickel Microtextures for IR Emission. Micromachines, 16(6), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060696






