The Preparation of a GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating and the Study of Its Performance Optimization for Pure Titanium Implants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Reagents
2.2. Material Preparation
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Experimental Grouping
2.5. Characterization Methods
2.5.1. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM)
2.5.2. Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
2.5.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.5.4. Raman Spectra (Raman)
2.5.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.5.6. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.6. Physical and Chemical Property Test
2.6.1. Coating Bond Strength
2.6.2. Nanoindentation
2.6.3. Differential Thermal Analysis (TG-DSC)
2.6.4. Water Contact Angle
2.6.5. In Vitro Mineralization Experiments
2.6.6. Electrochemical Analyses
2.7. Cellular Experiments
2.7.1. Cell Culture
2.7.2. DMEM Osteogenic Induction Medium
2.7.3. Cytotoxicity by CCK-8 Assay
2.7.4. ALP Activity Assay
2.7.5. ARS Alizarin Red Assay
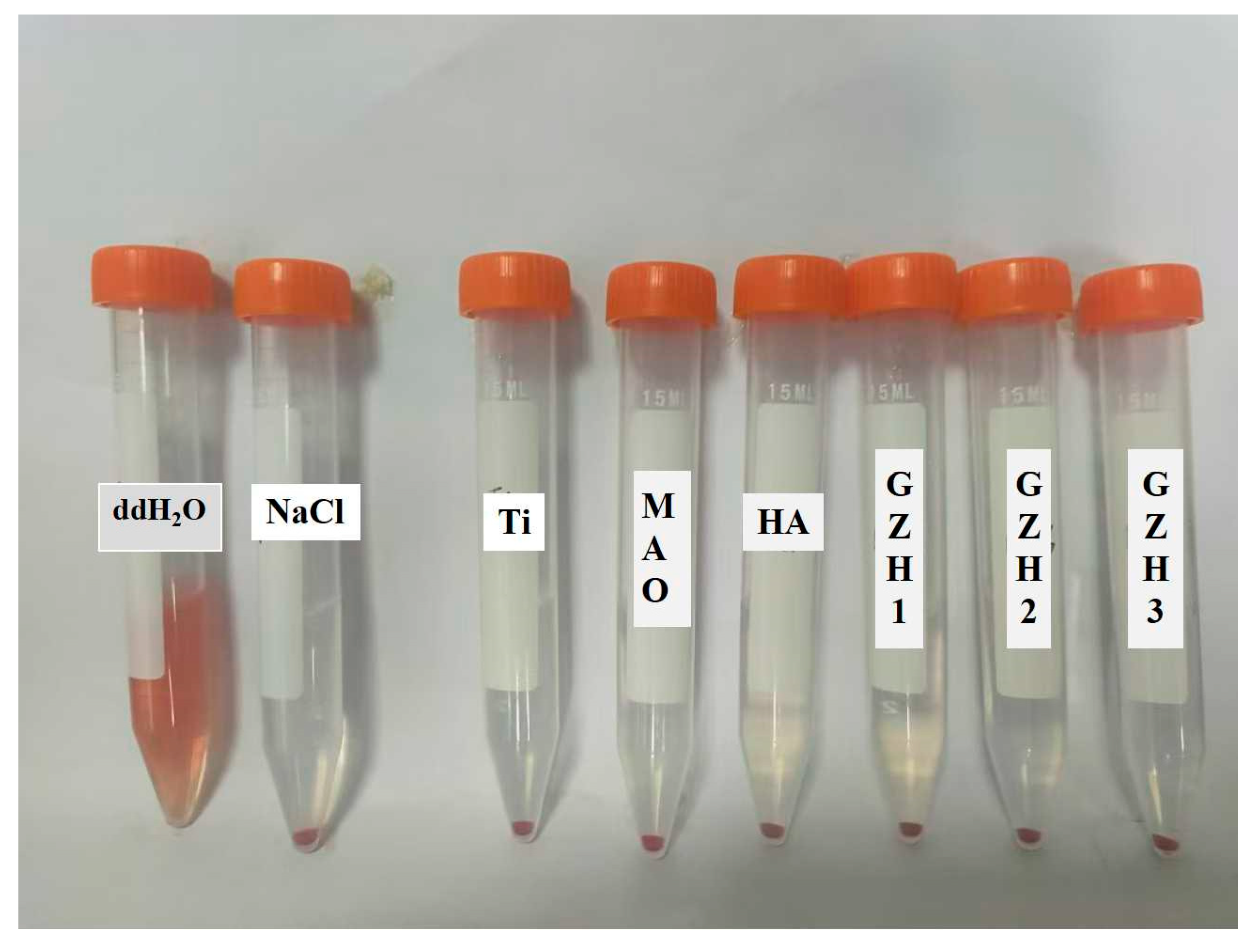
2.7.6. Haemolysis Test
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating
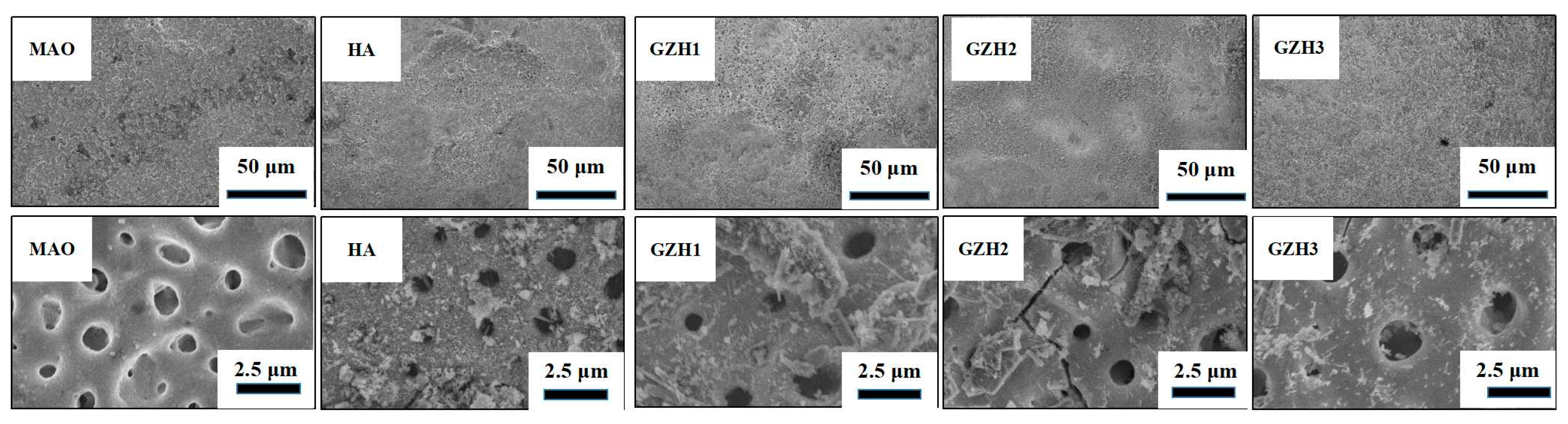
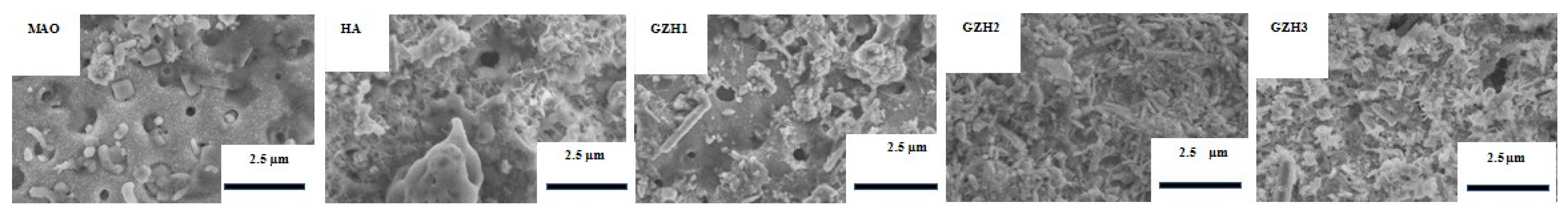
3.1.1. SEM of GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating
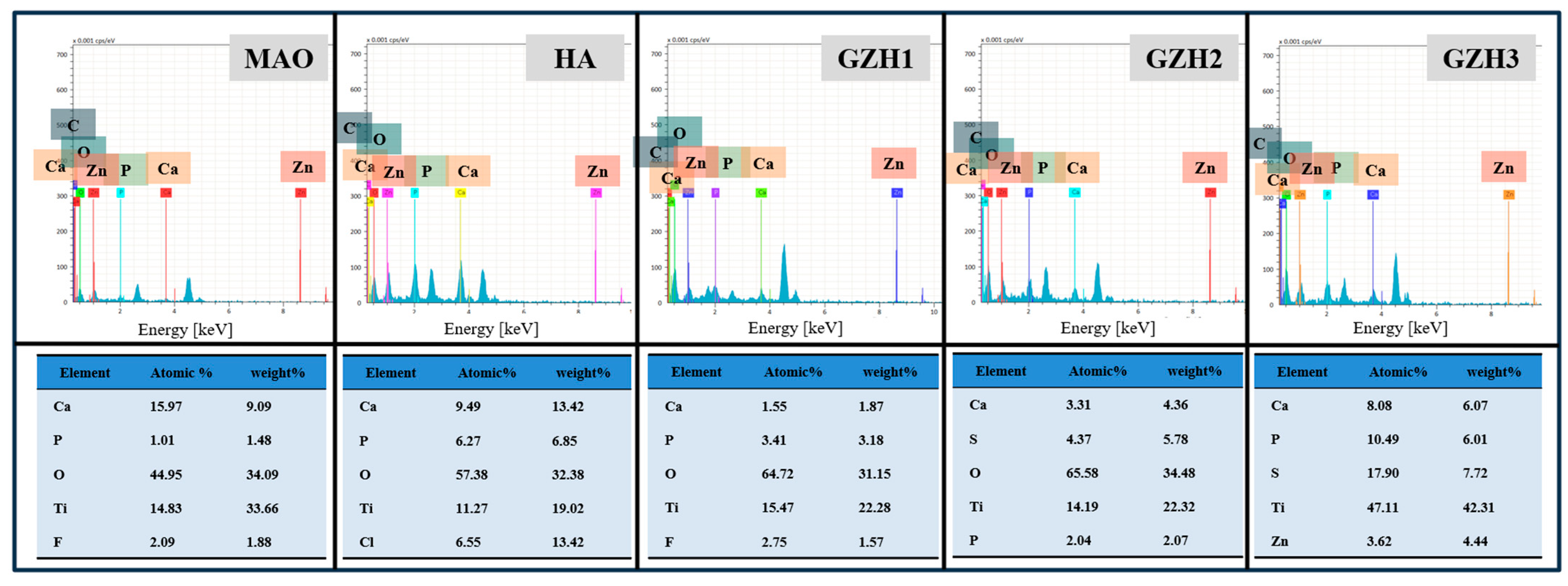
3.1.2. Energy Dispersion Spectrometer (EDS) Analysis
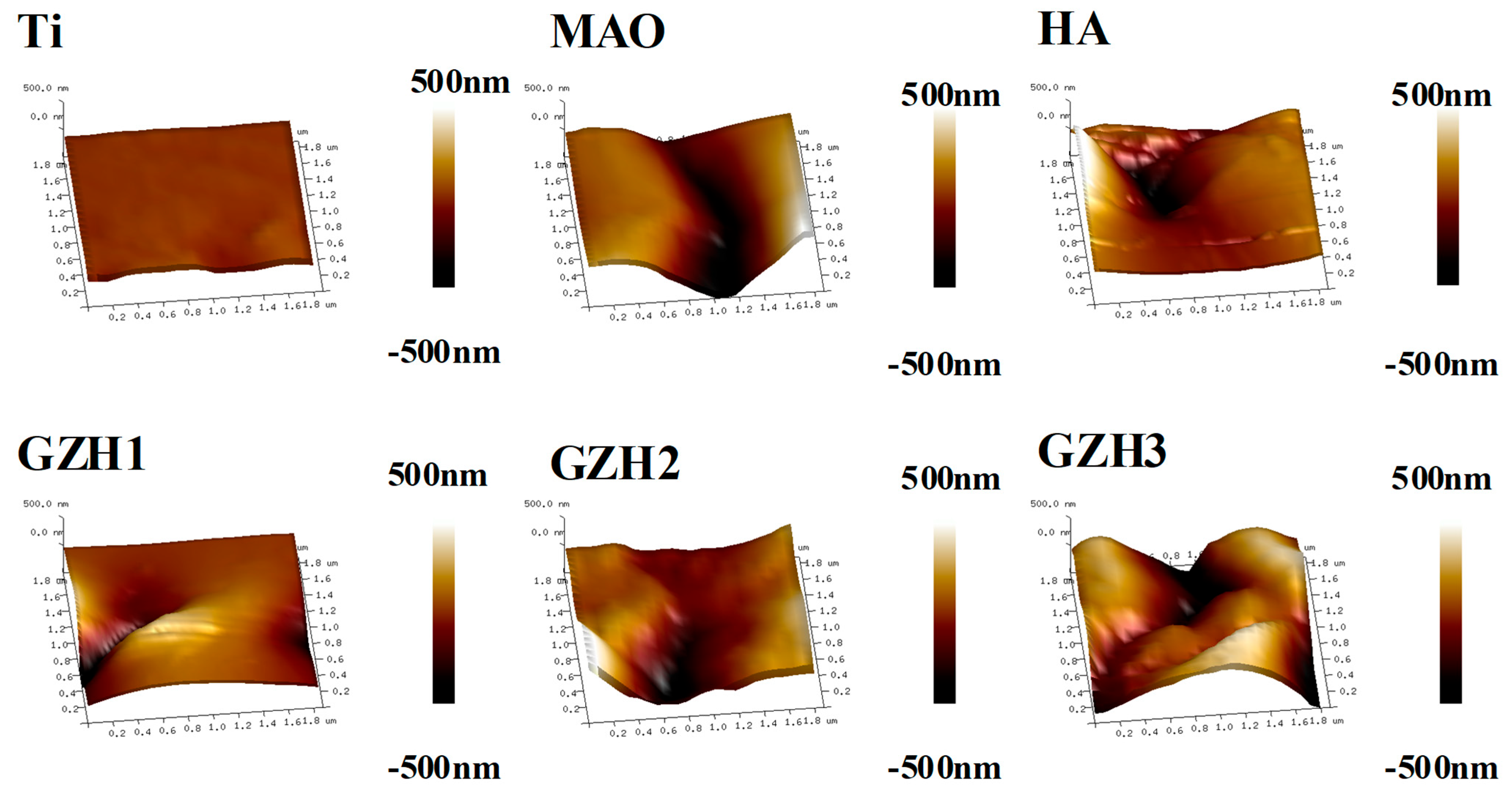
3.1.3. Surface Roughness
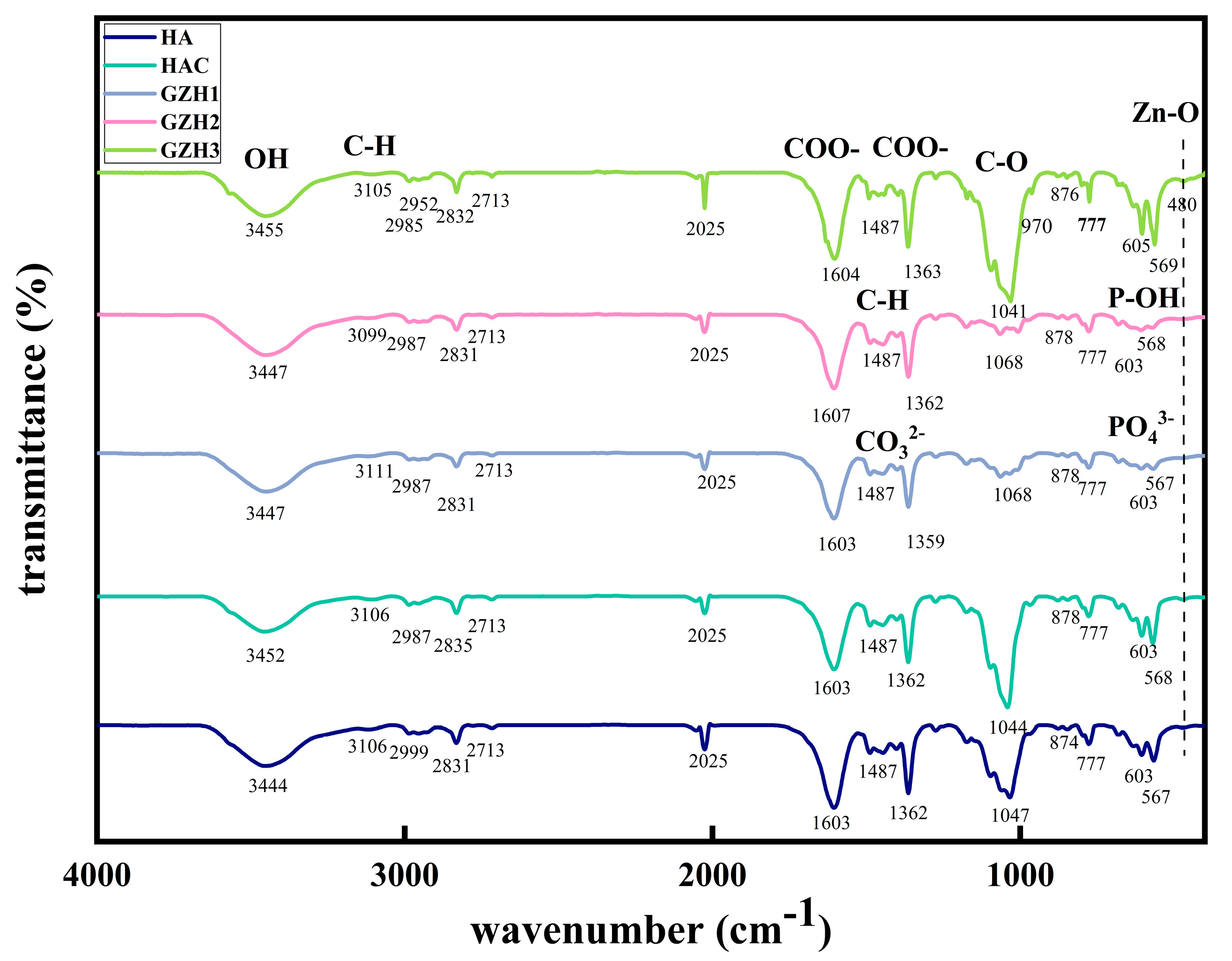
3.1.4. FTIR Spectrum
3.1.5. XRD Test Results
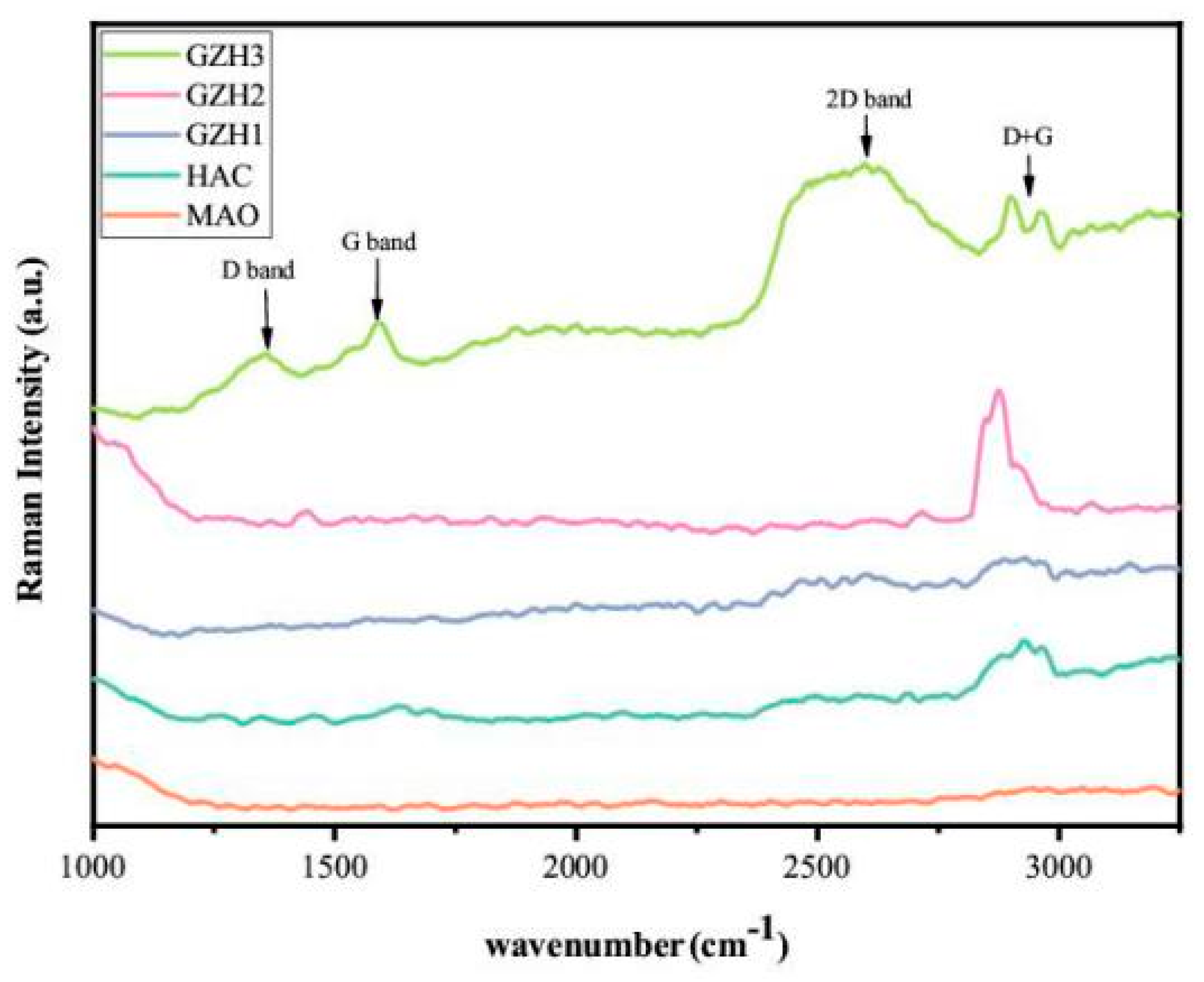
3.1.6. Raman Spectra of GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating
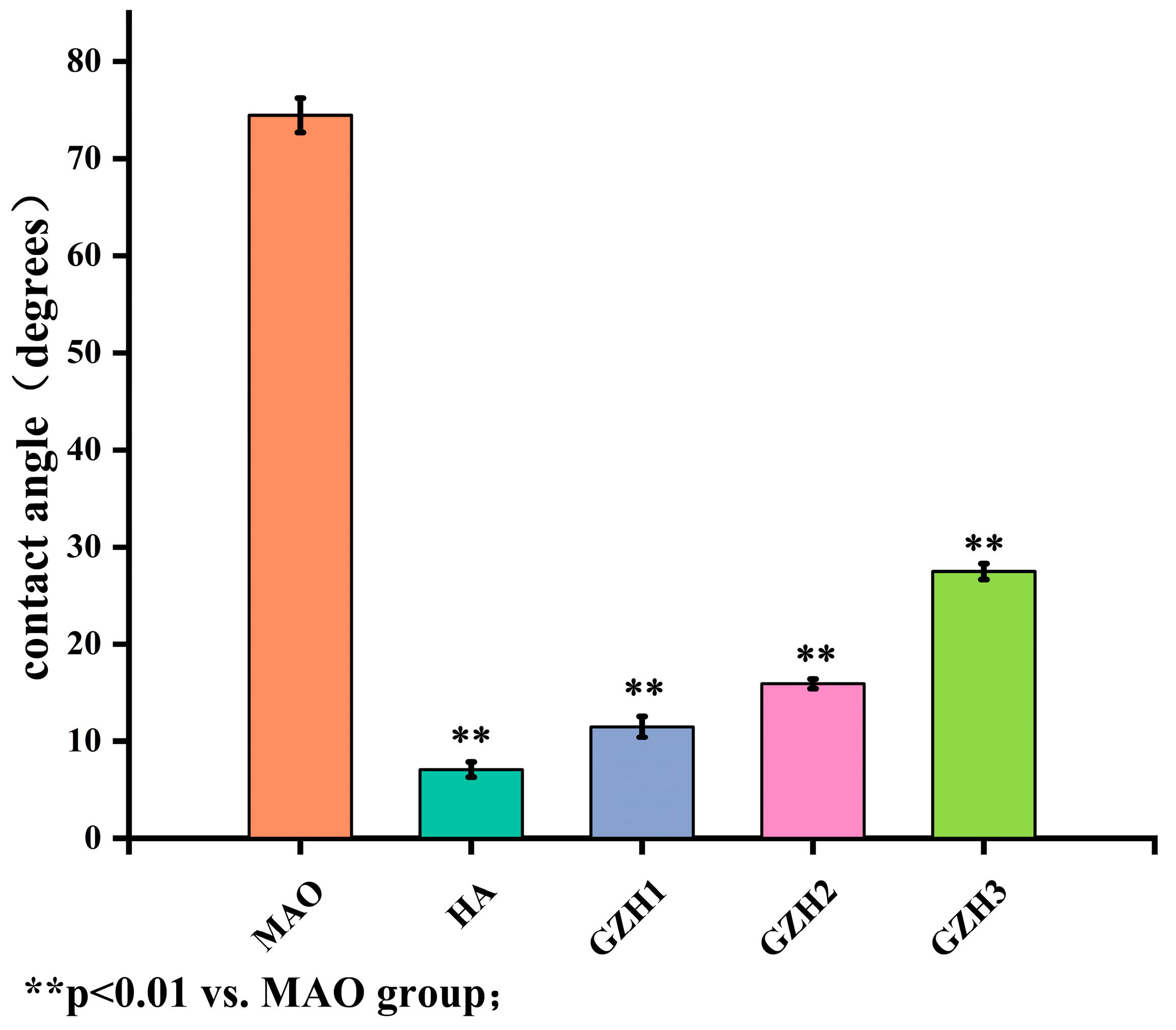
3.2. Surface Wettability Detection Results
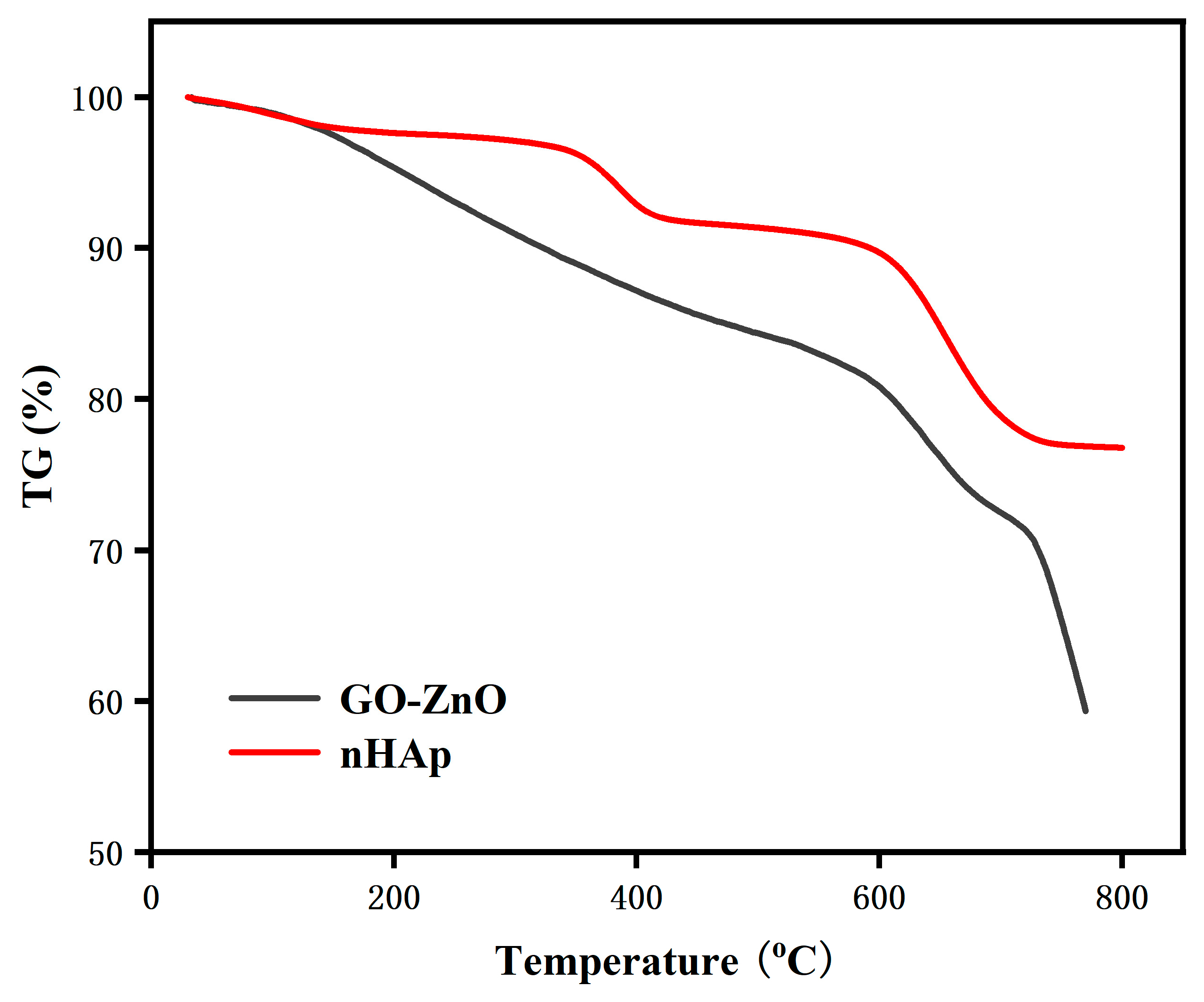
3.3. Differential Thermal Analysis (TG-DSC)
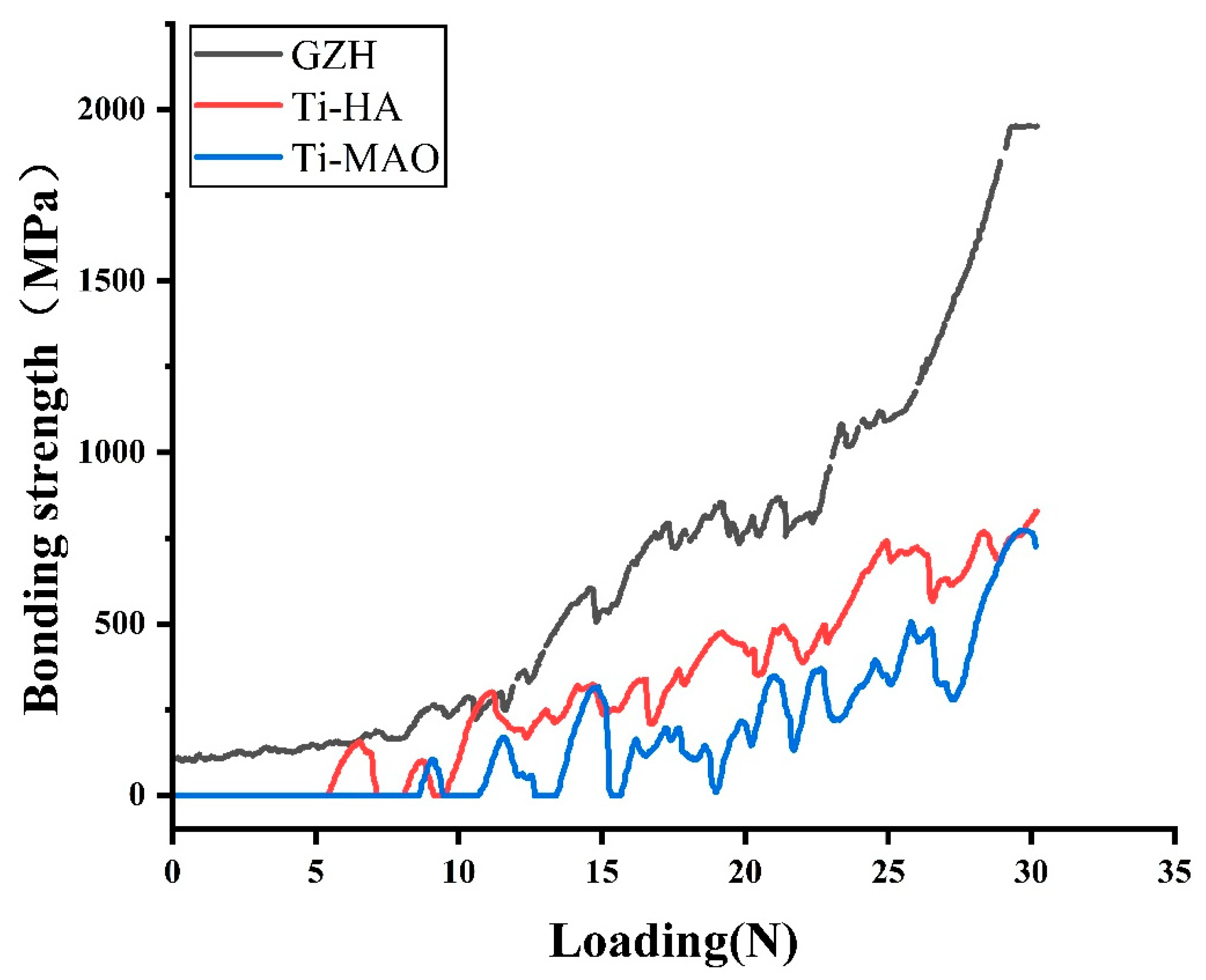
3.4. Adhesion Strength of the Coating
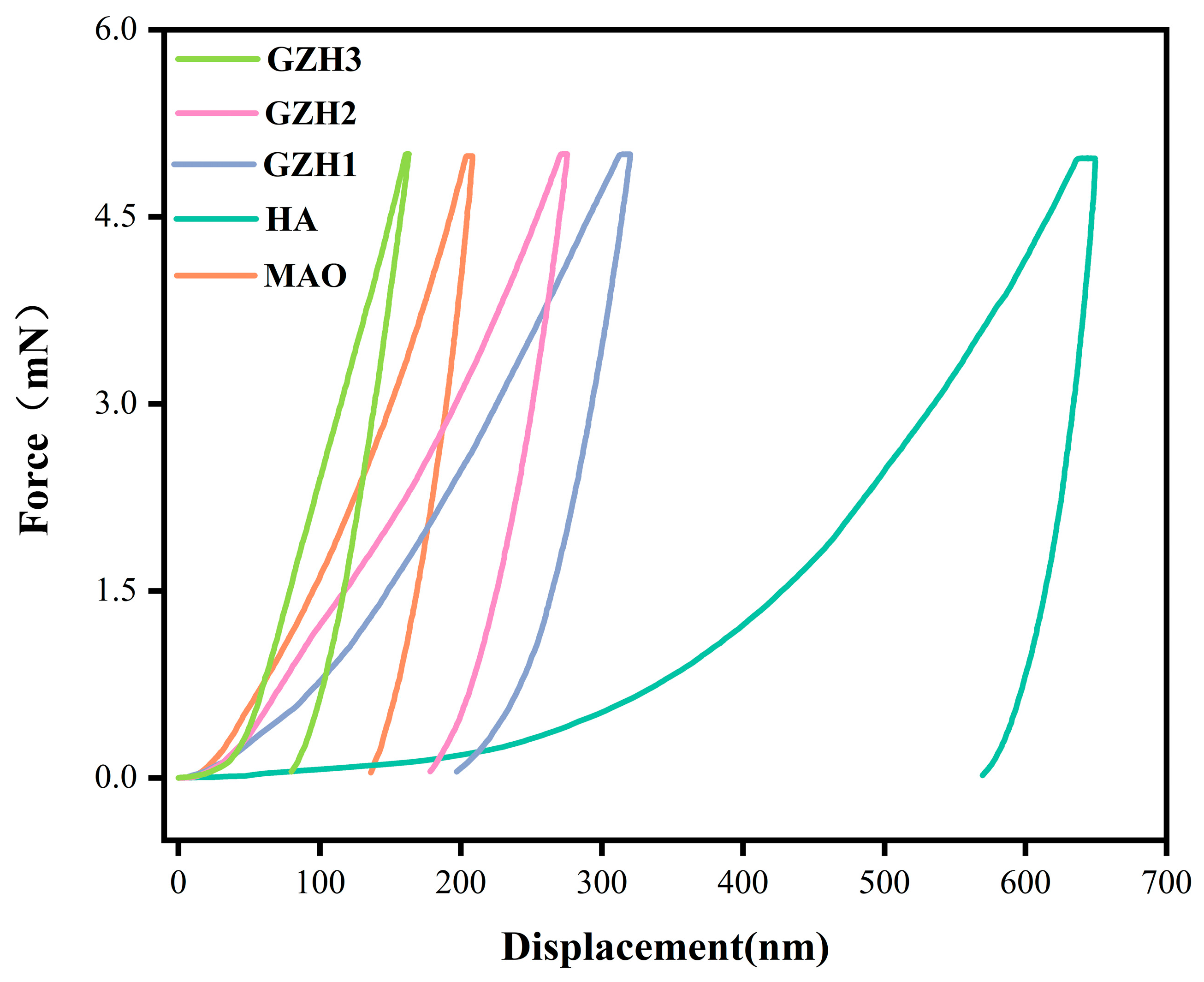
3.5. Nanoindentation
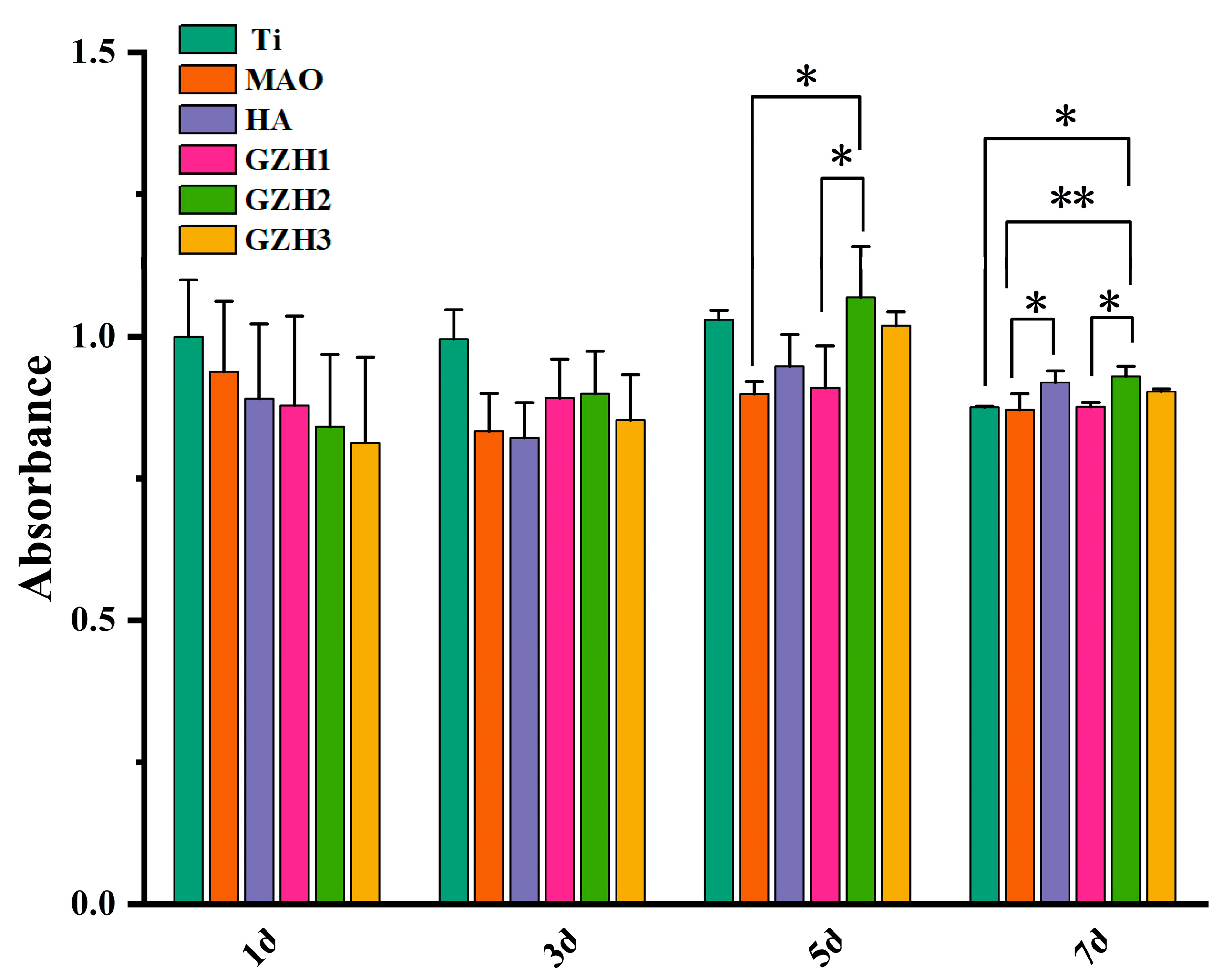
3.6. In Vitro Mineralization Experiments
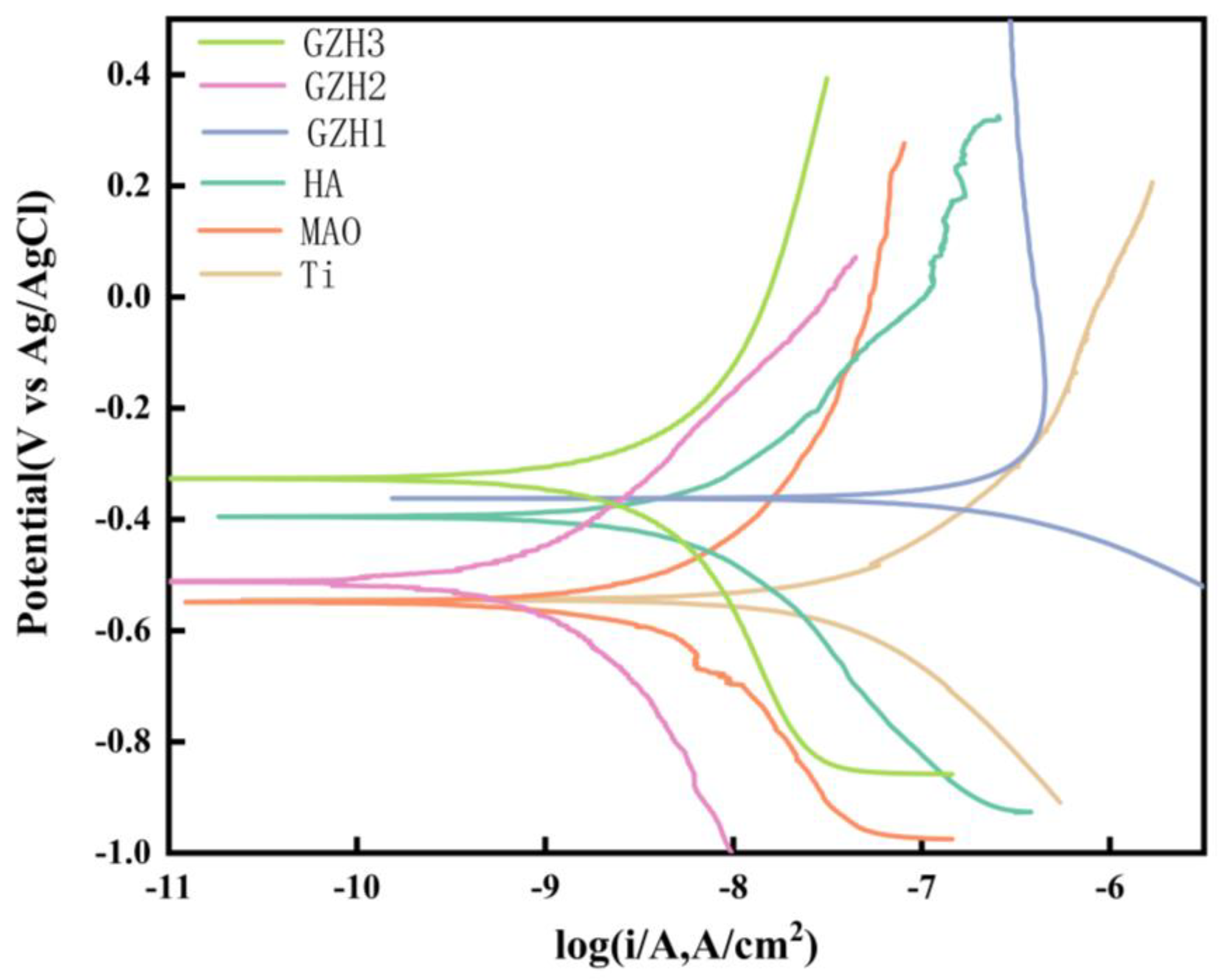
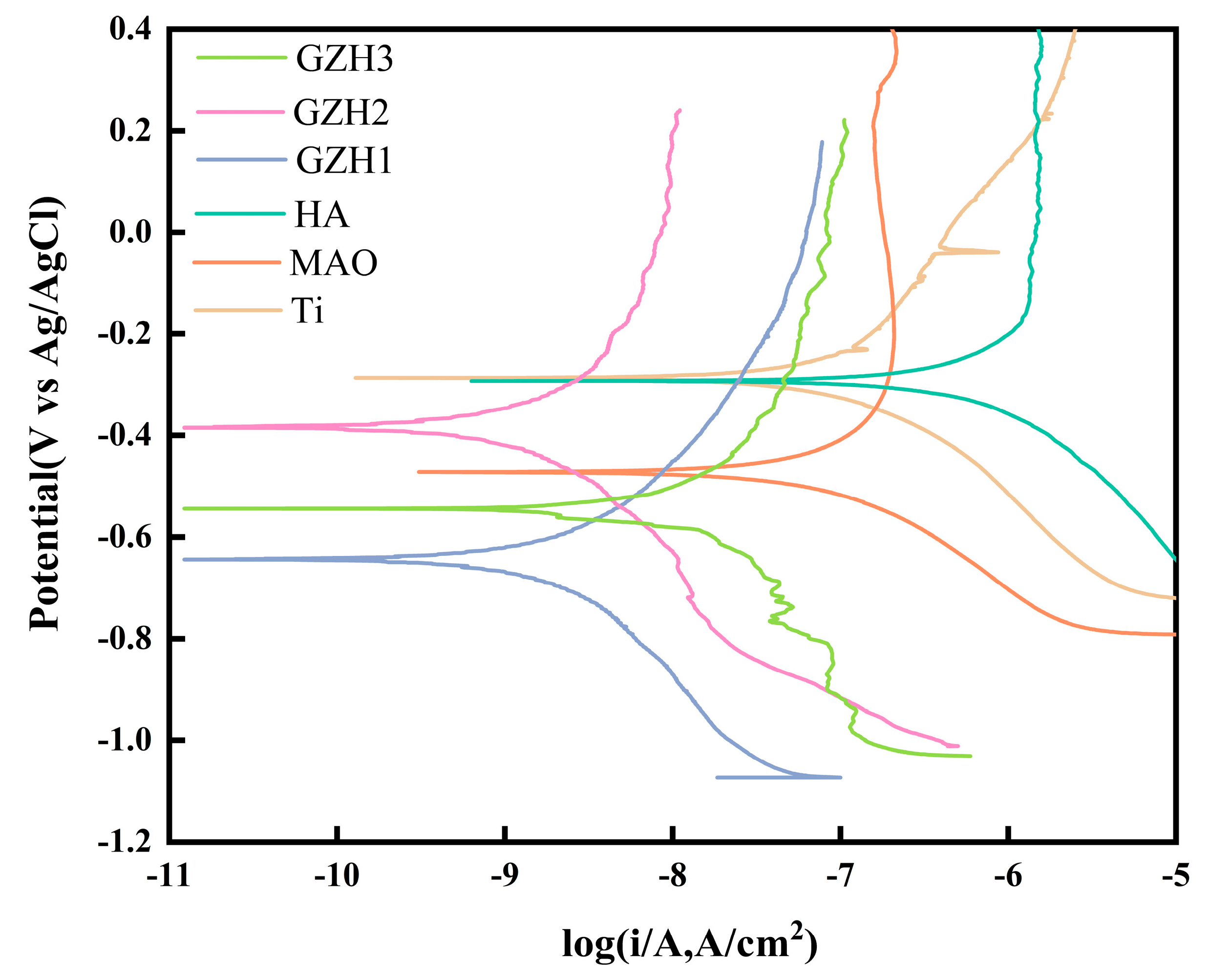
3.7. Electrochemical Test
3.8. MC3T3-E1 Cell Cytological Testing Results
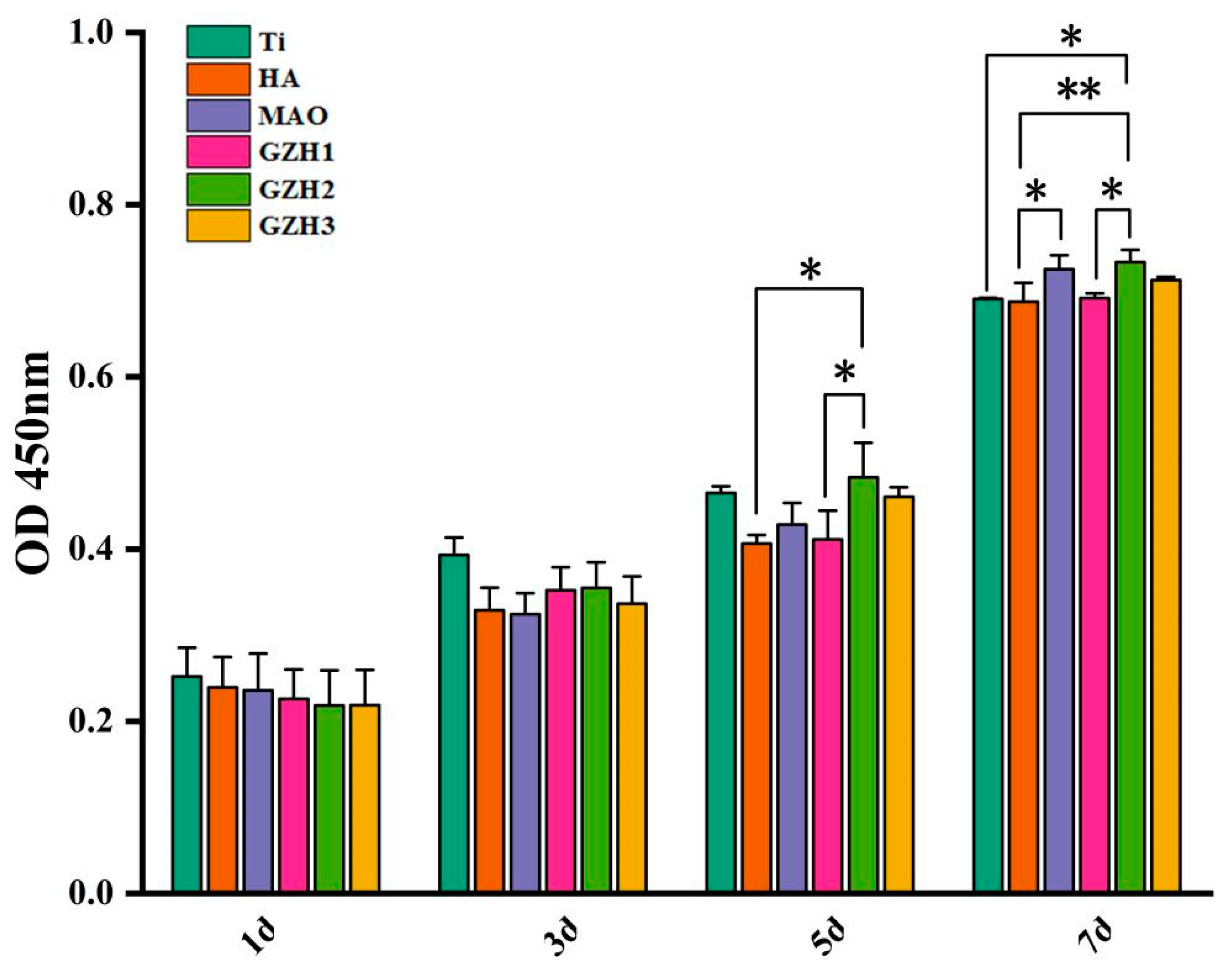
3.8.1. CCK-8 Detection Results of MC3T3-E1 Cell Proliferation on the Surface of Each Group of Samples
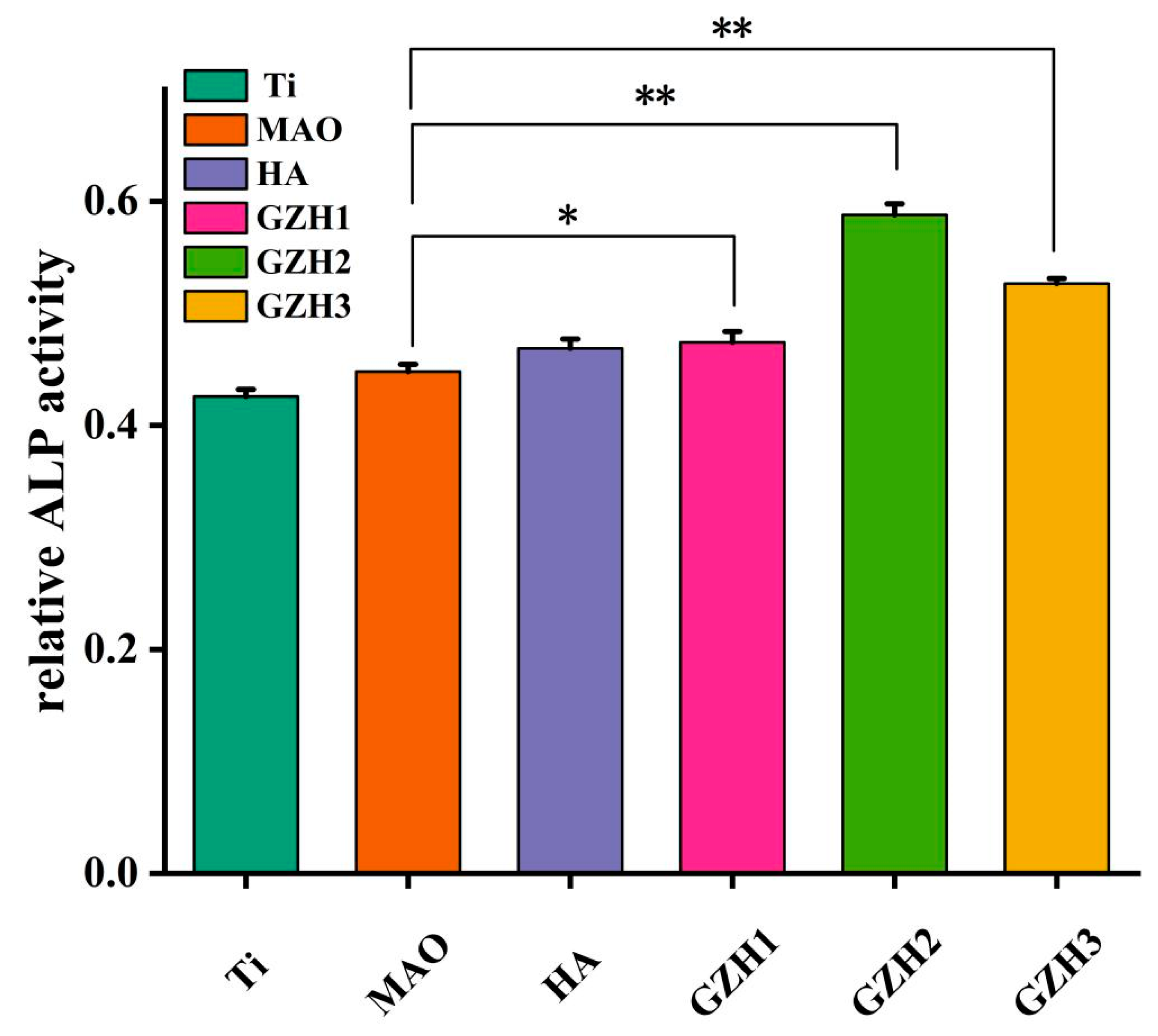
3.8.2. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
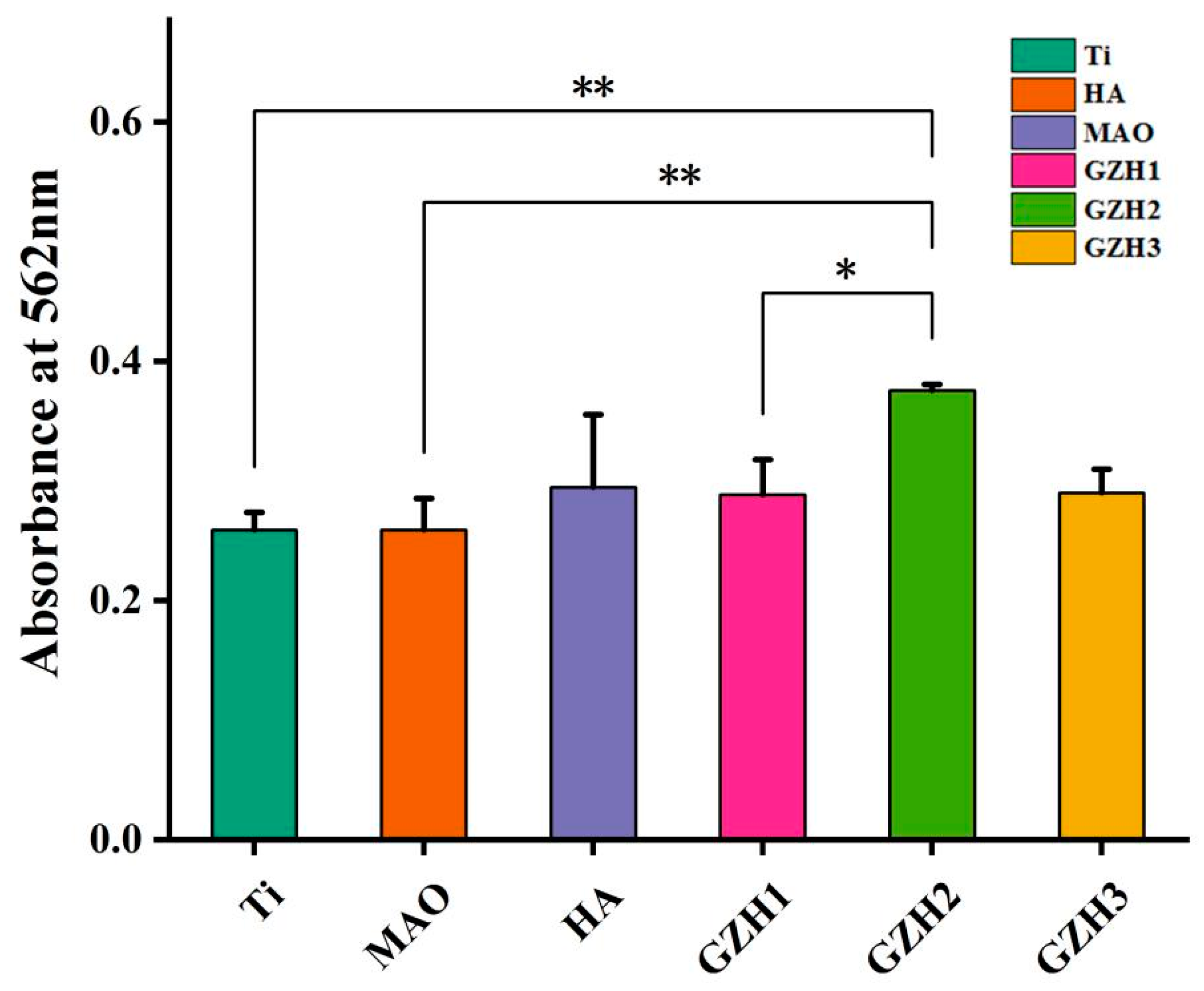
3.8.3. Alizarin Red (ARS)
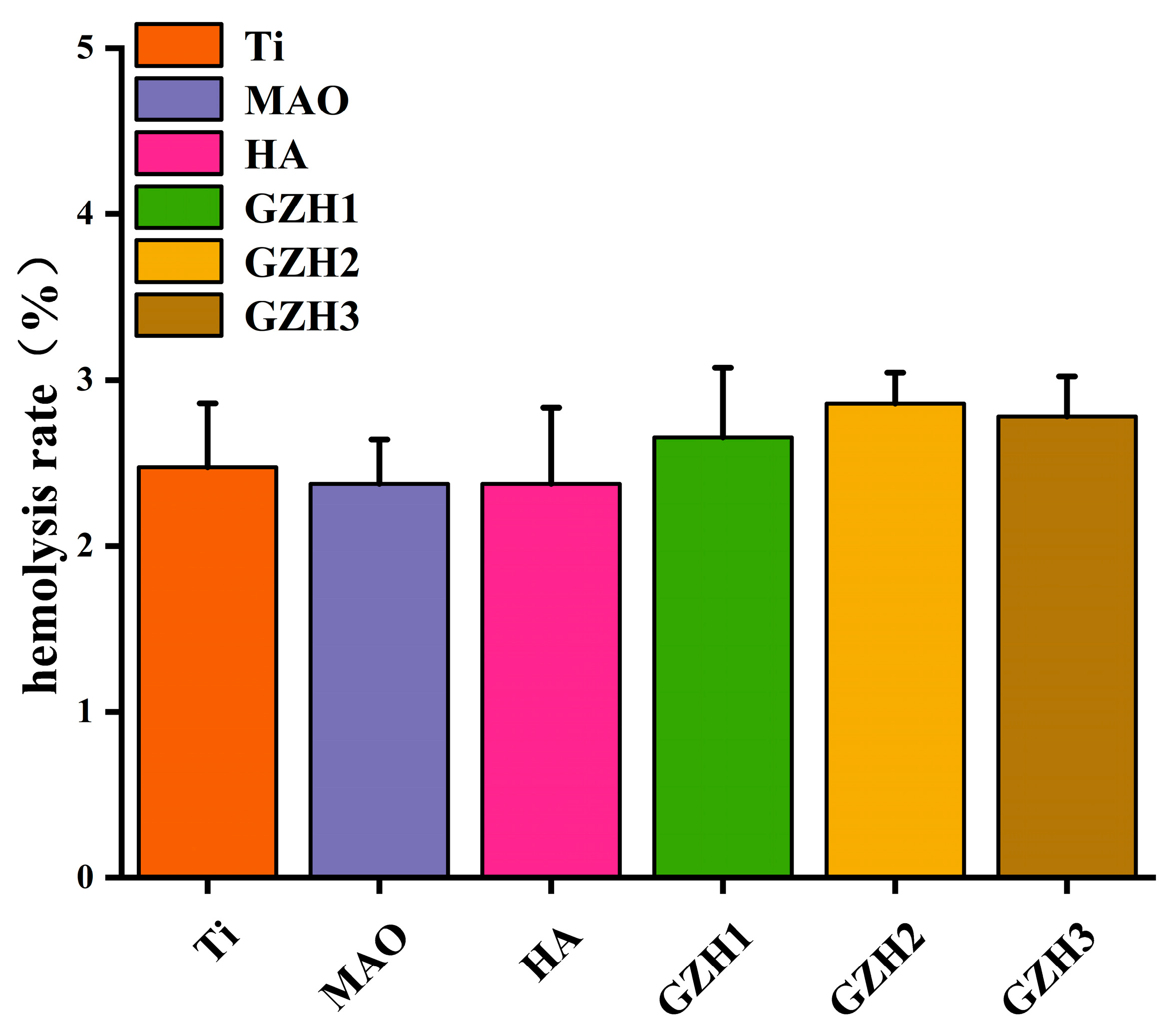
3.8.4. Hemolysis Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barão, V.A.R.; Costa, R.C.; Shibli, J.A.; Bertolini, M.; Souza, J.G.S. Emerging titanium surface modifications: The war against polymicrobial infections on dental implants. Braz. Dent. J. 2022, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Loutan, L.; Garavaglia, G.; Hashim, D. Removal of osseointegrated dental implants: A systematic review of explantation techniques. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Tsoi, J.K.; Matinlinna, J.P. Binary titanium alloys as dental implant materials-a review. Regen. Biomater. 2017, 4, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Chai, F.; Hornez, J.-C.; Li, C.L.; Zhao, Y.M.; Traisnel, M.; Hildebrand, H.F. The corrosion and biological behaviour of titanium alloys in the presence of human lymphoid cells and MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.S.; Viannie, L.R. Piezoelectric barium titanate/hydroxyapatite composite coatings on Ti-6Al-4V alloy via electrophoretic deposition. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, K.; A, V.S.; N, V.; Ramar, K. Surface Coating of Nickel-Titanium (Ni-Ti) Pediatric Rotary File Using Graphene Oxide: A Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e66632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, S.-S.; Zou, D.; Ni, R.-H.; Wei, C.-B.; Wang, H.; Li, W.-S. A novel porous interbody fusion cage modified by microarc oxidation and hydrothermal treatment technology accelerate osseointegration and spinal fusion in sheep. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 31966–31978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitić, D.; Čarkić, J.; Jaćimović, J.; Lazarević, M.; Karišik, M.J.; Toljić, B.; Milašin, J. The Impact of Nano-Hydroxyapatite Scaffold Enrichment on Bone Regeneration In Vivo-A Systematic Review. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikhil, A.; Gugjoo, M.B.; Das, A.; Ahmad, S.M.; Kumar, A. 3D-Printed-Cryogel-Impregnated Functionalized Scaffold Augments Bone Regeneration in Critical Tibia Fracture in Goat. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2402619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Cao, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Qi, H.; Zhou, Q. Nanocrystal hydroxyapatite carrying traditional Chinese medicine for osteogenic differentiation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 244, 114186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanis-Gómez, R.P.; Hernández-Rosas, F.; Olivares-Hernández, J.D.; Rivera-Muñoz, E.M.; Zapatero-Gutiérrez, A.; Méndez-Lozano, N.; Alanis-Gómez, J.R.; Velázquez-Castillo, R. Magnesium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanofibers for Medicine Applications: Characterization, Antimicrobial Activity, and Cytotoxicity Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, K. Bone Morphogenetic Protein 7-Loaded Gelatin Methacrylate/Oxidized Sodium Alginate/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite Hydrogel for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 6359–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungordu Er, S.; Edirisinghe, M.; Tabish, T.A. Graphene-Based Nanocomposites as Antibacterial, Antiviral and Antifungal Agents. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2201523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edrisi, F.; Baheiraei, N.; Razavi, M.; Roshanbinfar, K.; Imani, R.; Jalilinejad, N. Potential of graphene-based nanomaterials for cardiac tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 7280–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orecchioni, M.; Ménard-Moyon, C.; Delogu, L.G.; Bianco, A. Graphene and the immune system: Challenges and potentiality. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105 Pt B, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ding, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Qu, L.; Pei, H.; Yildirimer, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Graphene-based nanomaterials for drug and/or gene delivery, bioimaging, and tissue engineering. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Feng, L.; Shi, X.; Liu, Z. Nano-graphene in biomedicine: Theranostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 530–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Wang, L.; Lv, M.; Tang, Z.; Fan, C. Graphene-based nanomaterials in biosystems. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Huang, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Lin, H.; He, K.; Chen, H.; Jiang, W.; et al. Reduced graphene oxide loaded with tetrahedral framework nucleic acids for combating orthodontically induced root resorption. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Martinsen, K.H.; Klement, U.; Kovtun, A.; Xia, Z.; Silva, P.F.B.; Hryha, E.; Nyborg, L.; Palermo, V. Controllable Coating Graphene Oxide and Silanes on Cu Particles as Dual Protection for Anticorrosion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 38857–38866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tan, Y.; Qi, F.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, A.; Zhao, N.; Ouyang, X. A Micro-Nano Structure Formed by SiC/Graphene Oxide Self-Assembly Improves the Wear Resistance and Corrosion Resistance of an Epoxy-Based Composite Coating. Polymers 2022, 14, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, Q.; Jia, Z.; Xu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xi, T.; Wei, S. Graphene oxide/hydroxyapatite composite coatings fabricated by electrophoretic nanotechnology for biological applications. Carbon 2014, 67, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, M.; Xi, W.; Wei, J. Antimicrobial GL13K Peptide-Decorated ZnO Nanoparticles To Treat Bacterial Infections. Langmuir 2024, 40, 25042–25050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K, S.; Nechikkadan, S.; Theresa, M.; Krishnankutty, R.E. ZnO nanoparticles induced biofilm formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus at sub-inhibitory concentrations. Folia Microbiol. 2024, 69, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, G.; Mohan, P.S.; Mashghan, M.M.; Wong, K.-C.; Abdul-Rahman, P.S.; Vellasamy, K.M.; Hirad, A.H.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Wang, S. Phyto-fabricated ZnO nanoparticles for anticancer, photo-antimicrobial effect on carbapenem-resistant/sensitive Pseudomonas aeruginosa and removal of tetracycline. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 47, 1163–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janduang, S.; Cotchim, S.; Kongkaew, S.; Srilikhit, A.; Wannapob, R.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Limbut, W. Synthesis of flower-like ZnO nanoparticles for label-free point of care detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Talanta 2024, 277, 126330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Beltagi, H.S.; Ragab, M.; Osman, A.; El-Masry, R.A.; Alwutayd, K.M.; Althagafi, H.; Alqahtani, L.S.; Alazragi, R.S.; Alhajri, A.S.; El-Saber, M.M. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles via neem extract and their anticancer and antibacterial activities. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Pan, P.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Cui, X.; Liu, W.; Kan, L. 3D chitosan scaffolds loaded with ZnO nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 245, 114199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnaneshwar, P.V.; Sudakaran, S.V.; Abisegapriyan, S.; Sherine, J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Yusoff, M.M.; Jose, R.; Venugopal, J.R. Ramification of zinc oxide doped hydroxyapatite biocomposites for the mineralization of osteoblasts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 96, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păun, A.G.; Popescu, S.; Ungureanu, C.; Trusca, R.; Pirvu, C. Reduced TiO2 Nanotubes/Silk Fibroin/ZnO as a Promising Hybrid Antibacterial Coating. Chempluschem 2024, 89, e202300450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Wei, Z.; Guo, W. Exploring the Osteogenic Potential of Zinc-Doped Magnesium Phosphate Cement (ZMPC): A Novel Material for Orthopedic Bone Defect Repair. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 30707-2014; Testing Method on Adhesion of Fine Ceramic Coatings―Scratching. China National Standards: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Shami, R.; Sabir, A.; Iqbal, S.S.; Gull, N.; Zohra, R.; Khan, S.M. Synergistic effect of GO/ZnO loading on the performance of cellulose acetate/chitosan blended reverse osmosis membranes for NOM rejection. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.; Surmeneva, M.; Tyurin, A.; Pirozhkova, T.; Shuvarin, I.; Prymak, O.; Epple, M.; Chaikina, M.; Surmenev, R. Fabrication and physico-mechanical properties of thin magnetron sputter deposited silver-containing hydroxyapatite films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baheti, W.F.B. Study on Hydroxyapatite-Graphene Oxide Nano-Coating Promoting Osteogenic Differentiation and Regulating Macrophage Polarization. Ph.D. Thesis, Xinjiang Medical University, Ürümqi, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10993-5:2009(E); Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Han, X.; Ma, J.; Tian, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, B.; Tong, X.; Ma, X. Surface modification techniques of titanium and titanium alloys for biomedical orthopaedics applications: A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 227, 113339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ho, D.K.L.; Pelekos, G.; Fok, M.R. Clinical performance of implant-supported single hybrid abutment crown restoration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2024, 68, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, R.; Shimabukuro, M.; Terauchi, M.; Marukawa, E.; Kawashita, M. Amorphous Magnesium Coating for Achieving Functional Changes from Antibacterial to Osteogenic Activities. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 8565–8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.-H.; An, J.-H.; Seo, Y.-W.; Moon, W.-J.; Park, Y.-J.; Song, H.-J. Osteoblast cell adhesion and viability on nanostructured surfaces of porous titanium oxide layer. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 5682–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issi, C.T.; Yilmaz, B.K.; Kaga, S.; Demirel, H.H.; Kaga, E.; Konya, M.N. Histopathological and radiological evaluation of the efficacy of hydroxyapatite-boric acid and hydroxyapatite-magnesium coated Kirschner wires on fracture healing in femoral diaphyseal fractures: An experimental study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, M.R.; Ramasamy, M.; Jain, D.; Muthu, K.; Marunganathan, V.; Manivannan, C.; Hussain, S.A.; Deepak, P.; Thiyagarajulu, N.; Guru, A.; et al. Synergistic Action of Rutin-Coated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Targeting Biofilm Formation Receptors of Dental Pathogens and Modulating Apoptosis Genes for Enhanced Oral Anticancer Activity. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2024, 38, e70030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; Ruan, X.; Huang, T. Advances in Research on Surface Coatings of Titanium Implants to Enhance Osteogenic Performance. J. Jilin Med. Sci. 2025, 46, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, G.C.; Barbaro, K.; Kuroda, P.A.B.; De Bonis, A.; Teghil, R.; Krasnyuk, I.I., Jr.; Imperatori, L.; Grandini, C.R.; Rau, J.V. Antimicrobial Cu-Doped TiO2 Coatings on the β Ti-30Nb-5Mo Alloy by Micro-Arc Oxidation. Materials 2023, 17, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Zhao, R.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Yue, X. SLM Magnesium Alloy Micro-Arc Oxidation Coating. Materials 2024, 17, 4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashte, S.B.; Kadam, S.; Maffulli, N.; Potty, A.G.; Migliorini, F.; Gupta, A. Osteoinductive potential of graphene and graphene oxide for bone tissue engineering: A comparative study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.-K.; Chun, Y.; Jeong, G.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, W.-J.; Ryu, J.-H.; Cho, H.; Lim, H.-P. Biological Effects of Double-Layered Hydroxyapatite and Zirconium Oxide Depositions on Titanium Surfaces. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 8015–8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, W. Hydrophobic modification and durability protection of cotton garment fabric surfaces by graphene oxide/PGMA composite coatings. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Sreeja, B.; Kumar, K.K.; Padmalaya, G. Static and dynamic analysis of sulfamethoxazole using GO/ZnO modified glassy carbon electrode by differential pulse voltammetry and amperometry techniques. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, R.; Izanloo, S. Development of HAp/GO/Ag coating on 316 LVM implant for medical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 126, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Osgouei, M.; Li, Y.; Wen, C. A comprehensive review of biodegradable synthetic polymer-ceramic composites and their manufacture for biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 4, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Tian, X.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, Y. Analysis of the Effect of Thickness on the Performance of Polymeric Heart Valves. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Yang, D.; Maher, S.; Lima-Marques, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Atkins, G.J.; Losic, D. Micro- and nano-structured 3D printed titanium implants with a hydroxyapatite coating for improved osseointegration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3136–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Song, Y.; Wu, S.; Lv, J.; Xiao, Y.; Ning, Y.; Tian, H.; Liu, B. Dual Stimulus Responsive GO-Modified Tb-MOF toward a Smart Coating for Corrosion Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 29162–29176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Fu, X.; Wang, D.; Peng, F.; Li, H.; Liang, C.; Wang, H. Preparation and characterization of mesoporous HA coating with paclitaxel loaded lignin nanospheres on titanium surface. J. Orthop. 2025, 60, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Lai, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Y. Facile fabrication of linezolid/strontium coated hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide nanocomposite for osteoporotic bone defect. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/TR7405-1984; Biological Evaluation of Dental Materials. ISO: Basel, Switzerland, 1984.




| Chemical Formula | Grade | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| CaCl2 | Analytical reagent | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Na2HPO4 | Analytical reagent | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| C10H14N2Na2O8 | Analytical reagent | Macklin (Shanghai, China) |
| CH3COCH3 | Analytical reagent | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| C2H6O | Analytical reagent | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| NaOH | Analytical reagent | Tianjin Kaitong Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China) |
| KOH | Analytical reagent | Tianjin Kaitong Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. |
| KF | Analytical reagent | Tianjin Kemio Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China) |
| Na3PO4·12H2O | Analytical reagent | Tianjin Ruijinte Chemical Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China) |
| Na2SO3·9H2O | Analytical reagent | Tianjin Hengxing Chemical Reagent Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China) |
| GO/ZnO | Provided by Professor Lu Yuguang’s team of the School of Pharmacy, Jiamusi University (Jiamusi, China) |
| Name | Manufacturer |
|---|---|
| MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts | Provided by Basic Medical College of Jiamusi University (Jiamusi, China) |
| Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit | Beyotime Biotechnology (Shanghai, China) |
| BCA Protein Assay Kit | Beyotime Biotechnology |
| TritionX-100 | Beyotime Biotechnology |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | Gibco company (Shanghai, China) |
| DMEM Medium with High Glucose | Hyclone company (Hyclone, NY, USA) |
| PBS | Hyclone company (Paisley, UK) |
| Trypsin-EDTA Soiution | Gibco company |
| 4% Paraformaldehyde Fix Solution | Solomen company (Shanghai, China) |
| Cell Counting Kit-8 | Beyotime Biotechnology |
| Parameter | MAO | HA | GZH1 | GZH2 | GZH3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H (GPa) | 3.6 ± 1.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 2.7 ± 1.0 | 5.6 ± 1.0 |
| E (GPa) | 93.5 ± 6.0 | 40.8 ± 2.4 | 44.3 ± 3.1 | 53.5 ± 1.0 | 89.6 ± 3.4 |
| H/E | 0.039 | 0.010 | 0.038 | 0.050 | 0.63 |
| Samples | Icorr (A/cm2) | Ecorr (V vs. Ag/AgCl) |
|---|---|---|
| Ti | 3.54 ± 1.89 × 10−7 | −0.46 ± 0.081 |
| MAO | 1.17 ± 1.60 × 10−7 | −0.62 ± 0.125 |
| HA | 2.57 ± 4.00 × 10−7 | −0.34 ± 0.076 |
| GZH1 | 4.45 ± 6.79 × 10−6 | −0.43 ± 0.076 |
| GZH2 | 1.94 ± 3.29 × 10−7 | −0.39 ± 0.107 |
| GZH3 | 4.93 ± 4.24 × 10−7 | −0.45± 0.115 |
| Samples | Icorr (A/cm2) | Ecorr (V vs. Ag/AgCl) |
|---|---|---|
| Ti | 1.77 ± 2.51 × 10−6 | −0.42 ± 0.124 |
| MAO | 2.00 ± 3.01 × 10−7 | −0.63 ± 0.155 |
| HA | 7.41 ± 9.51 × 10−6 | −0.50 ± 0.187 |
| GZH1 | 1.01 ± 1.66 × 10−7 | −0.52 ± 0.103 |
| GZH2 | 0.99 ± 1.39 × 10−8 | −0.40 ± 0.076 |
| GZH3 | 6.66 ± 4.70 × 10−8 | −0.50 ± 0.046 |
| Level | Relative Proliferation Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 | ≥100 |
| 1 | 80–99 |
| 2 | 50–79 |
| 3 | 30–49 |
| 4 | 0–29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Zuo, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zou, J.; Jia, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G. The Preparation of a GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating and the Study of Its Performance Optimization for Pure Titanium Implants. Micromachines 2025, 16, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060637
Wu J, Zuo Y, Xu Z, Wang L, Zou J, Jia Z, Wang C, Zhang G. The Preparation of a GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating and the Study of Its Performance Optimization for Pure Titanium Implants. Micromachines. 2025; 16(6):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060637
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiang, Yu Zuo, Zhaoxi Xu, Lang Wang, Jiaju Zou, Zijian Jia, Chunmei Wang, and Guoliang Zhang. 2025. "The Preparation of a GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating and the Study of Its Performance Optimization for Pure Titanium Implants" Micromachines 16, no. 6: 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060637
APA StyleWu, J., Zuo, Y., Xu, Z., Wang, L., Zou, J., Jia, Z., Wang, C., & Zhang, G. (2025). The Preparation of a GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating and the Study of Its Performance Optimization for Pure Titanium Implants. Micromachines, 16(6), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060637





