The Dielectrophoretic Interactions of Curved Particles in a DC Electric Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mathematical Model
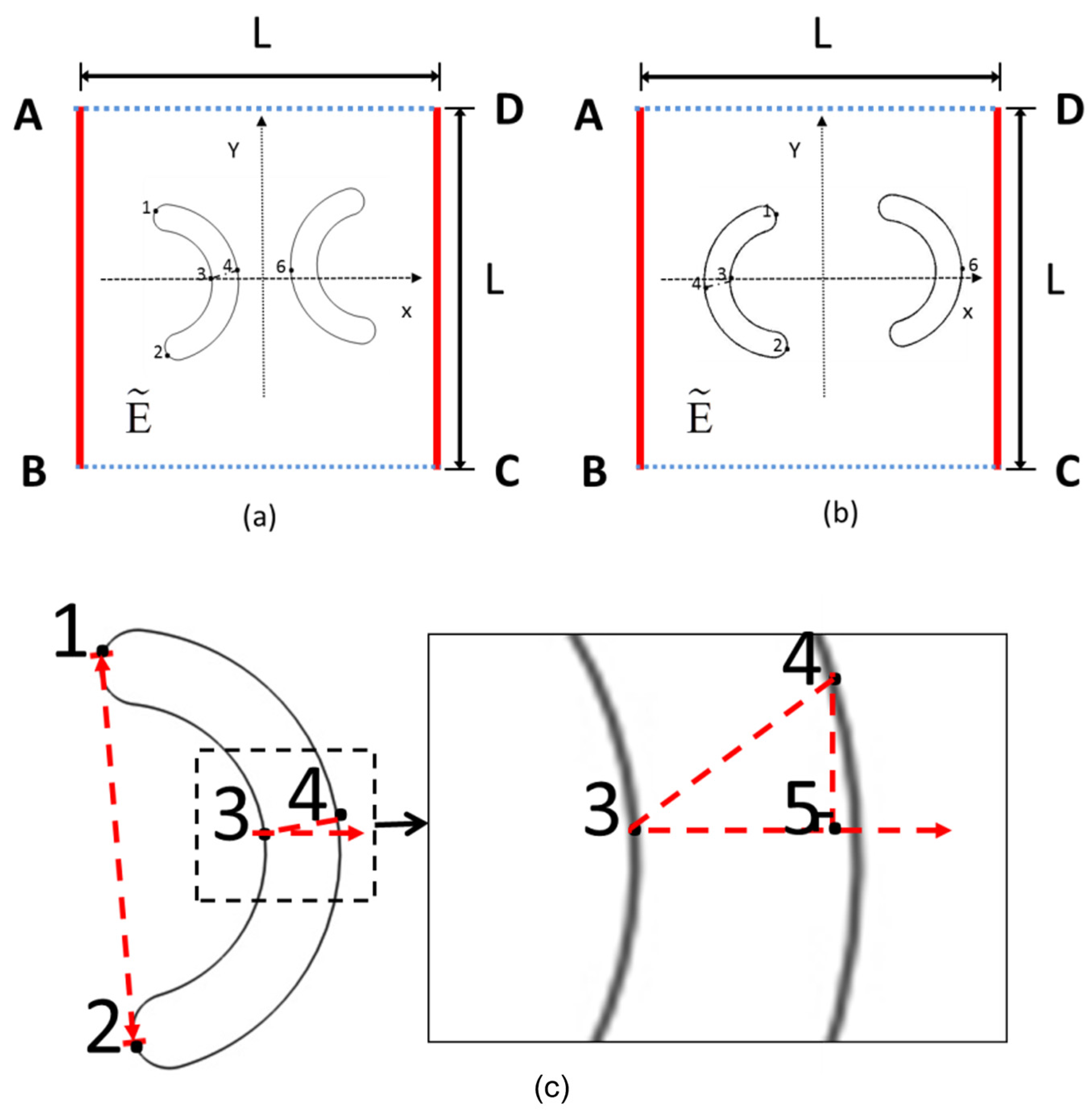
2.2. Boundary Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
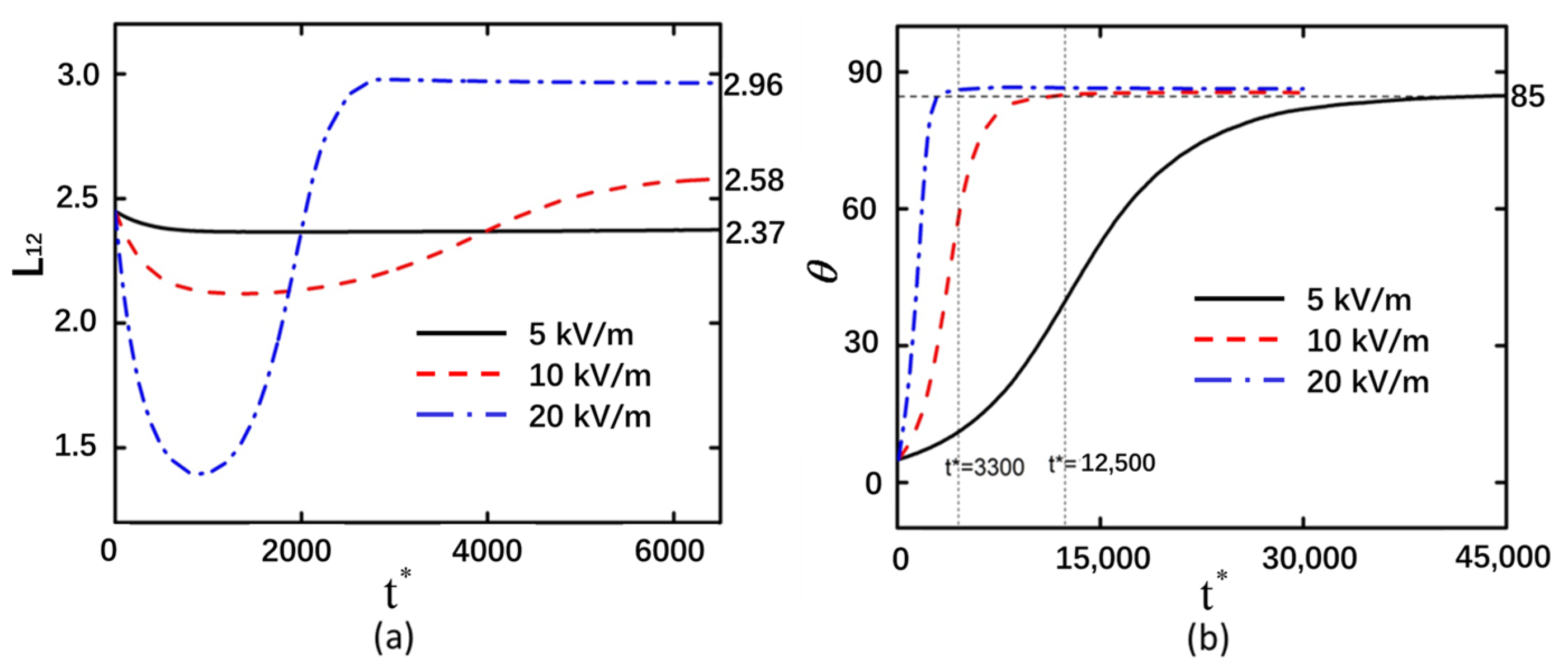
3.1. Electric Field Intensity
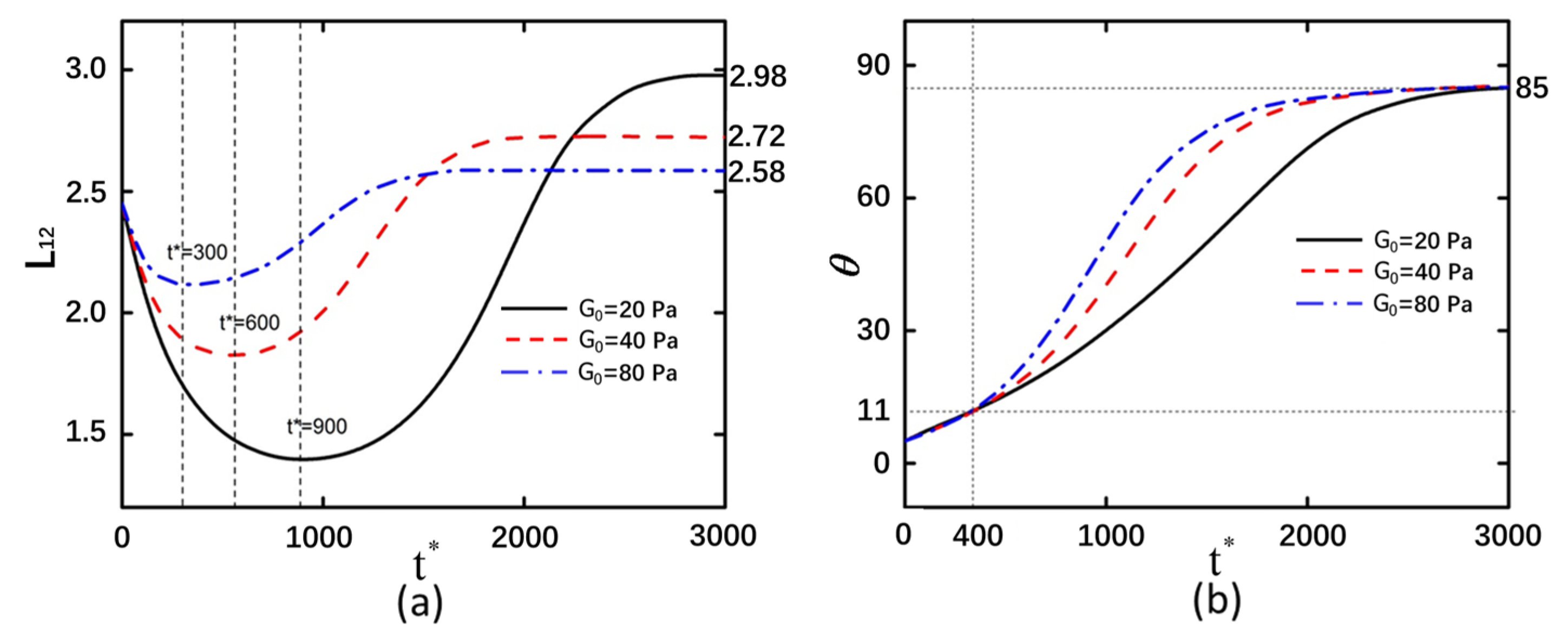
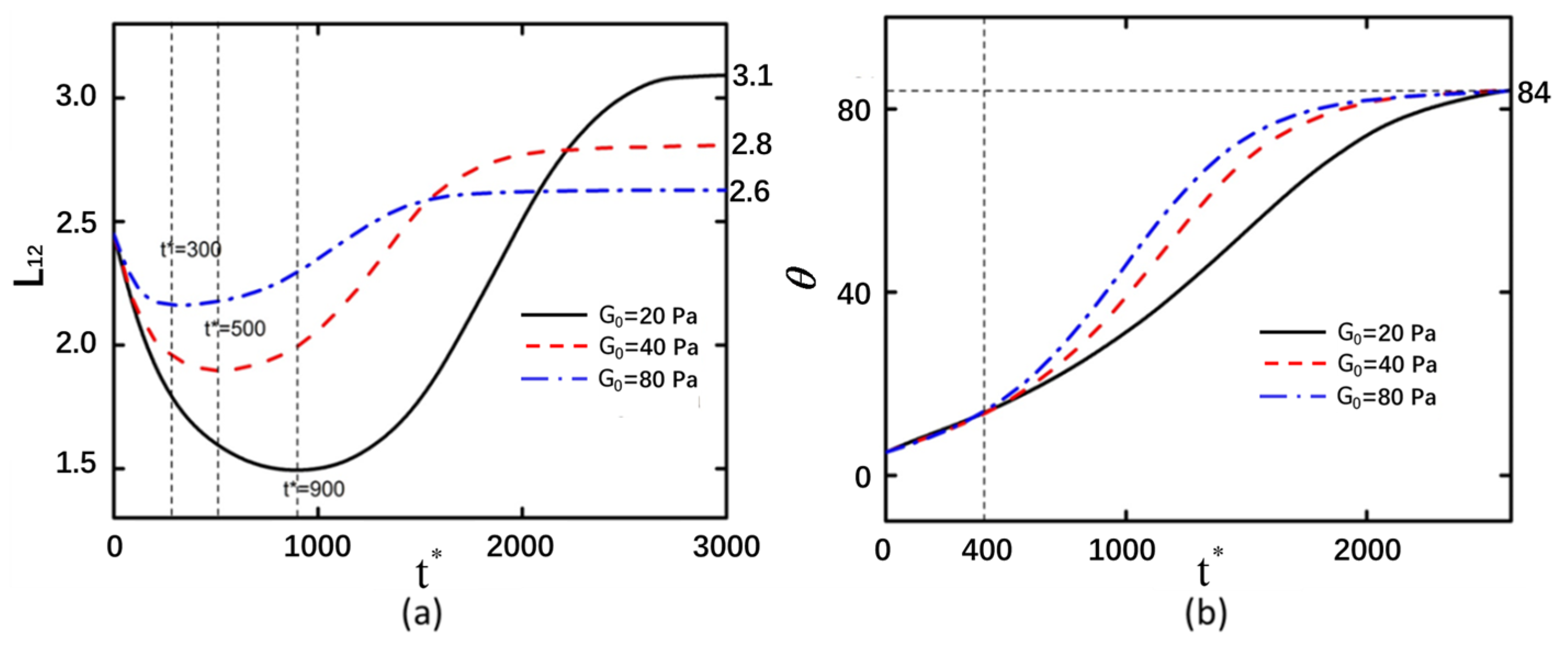
3.2. Shear Modulus
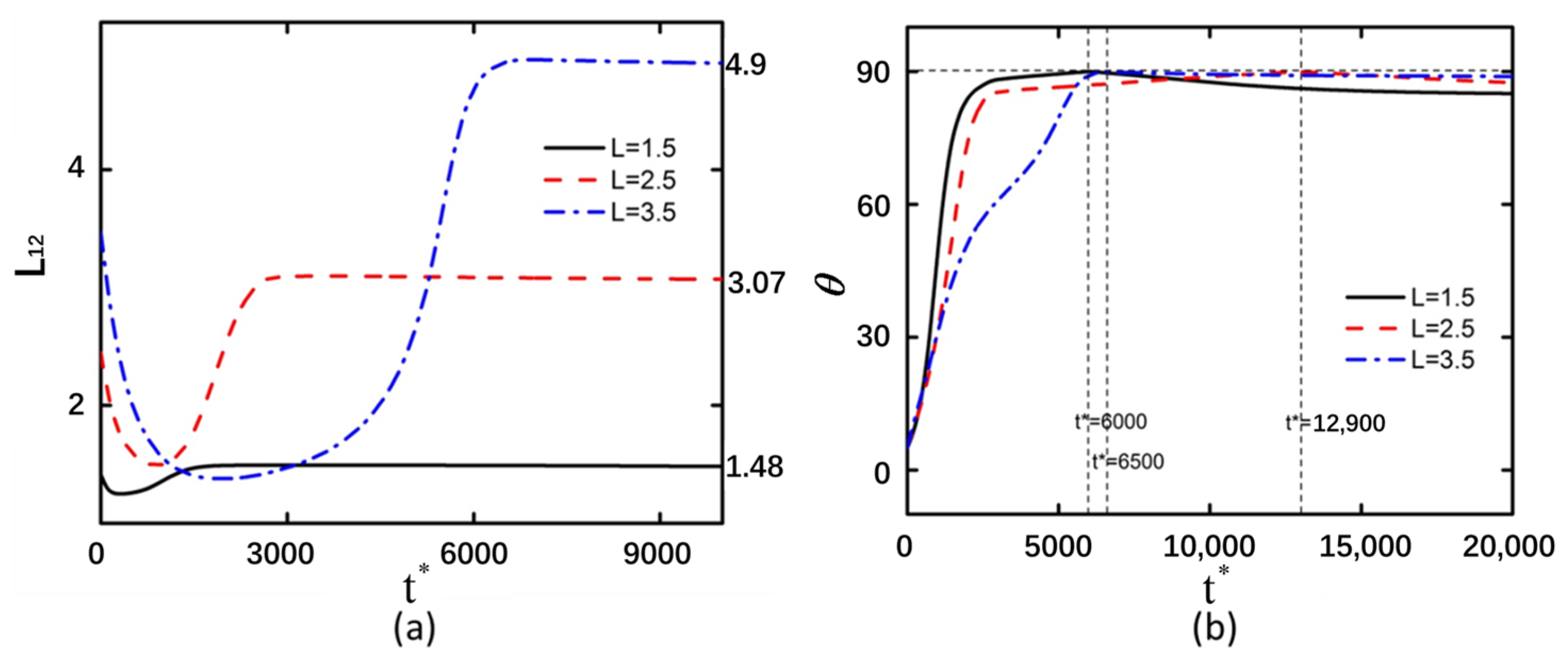
3.3. Curved Particle Length
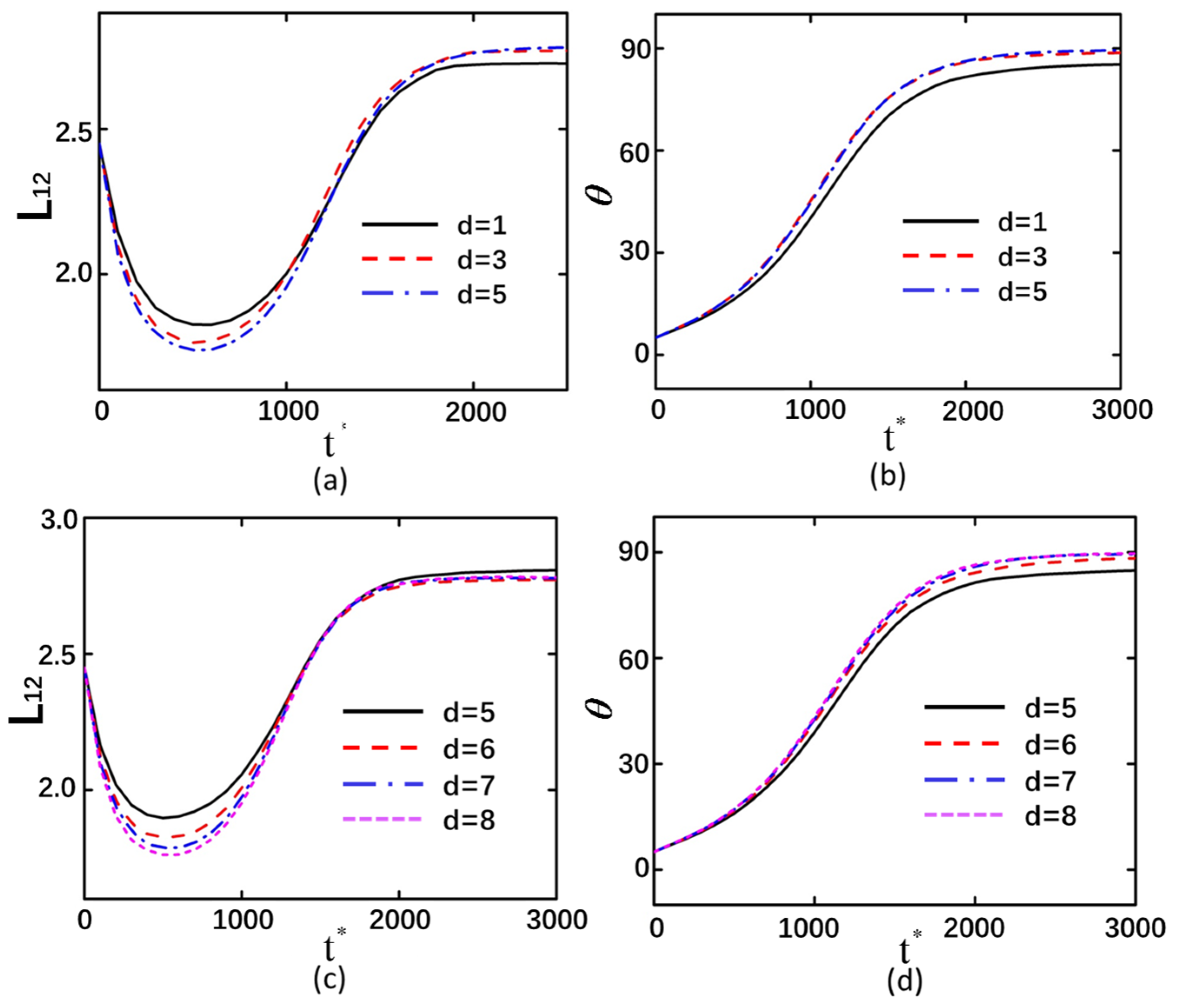
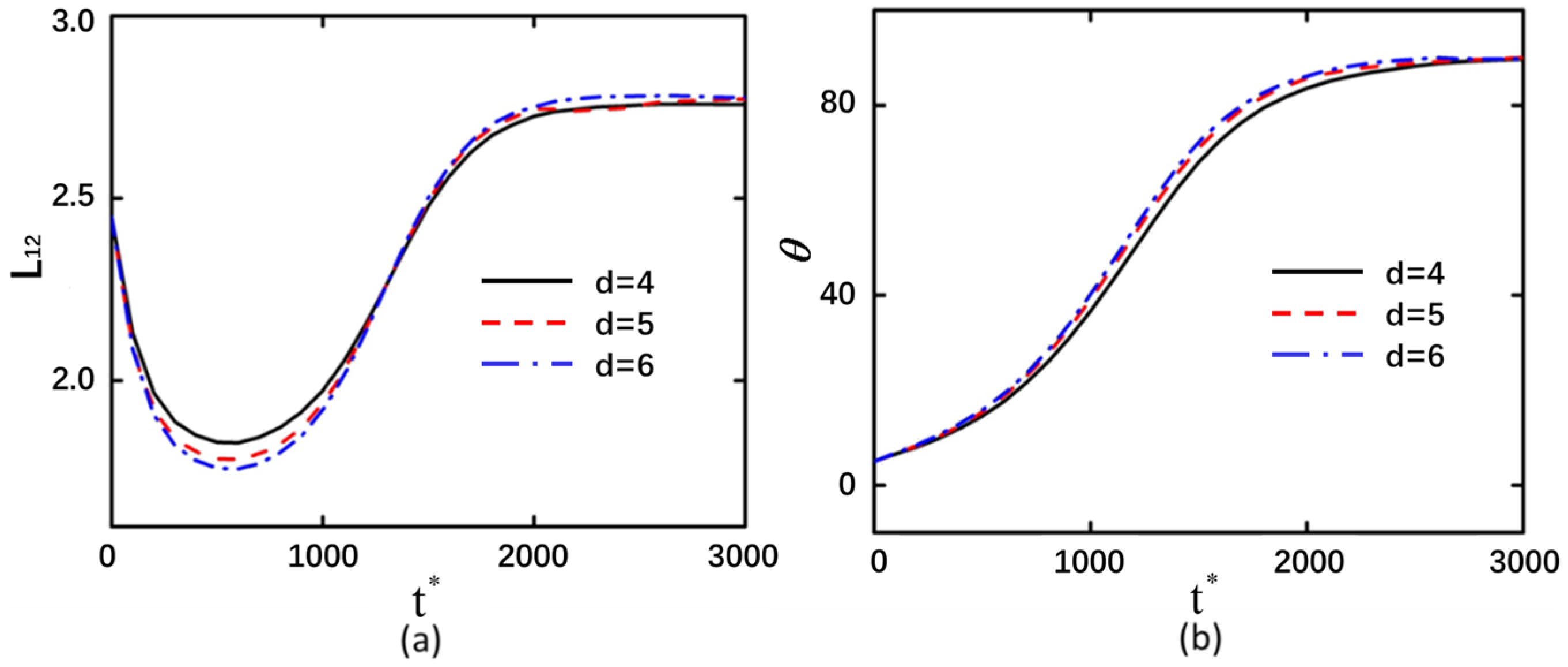
3.4. The Interparticle Distance
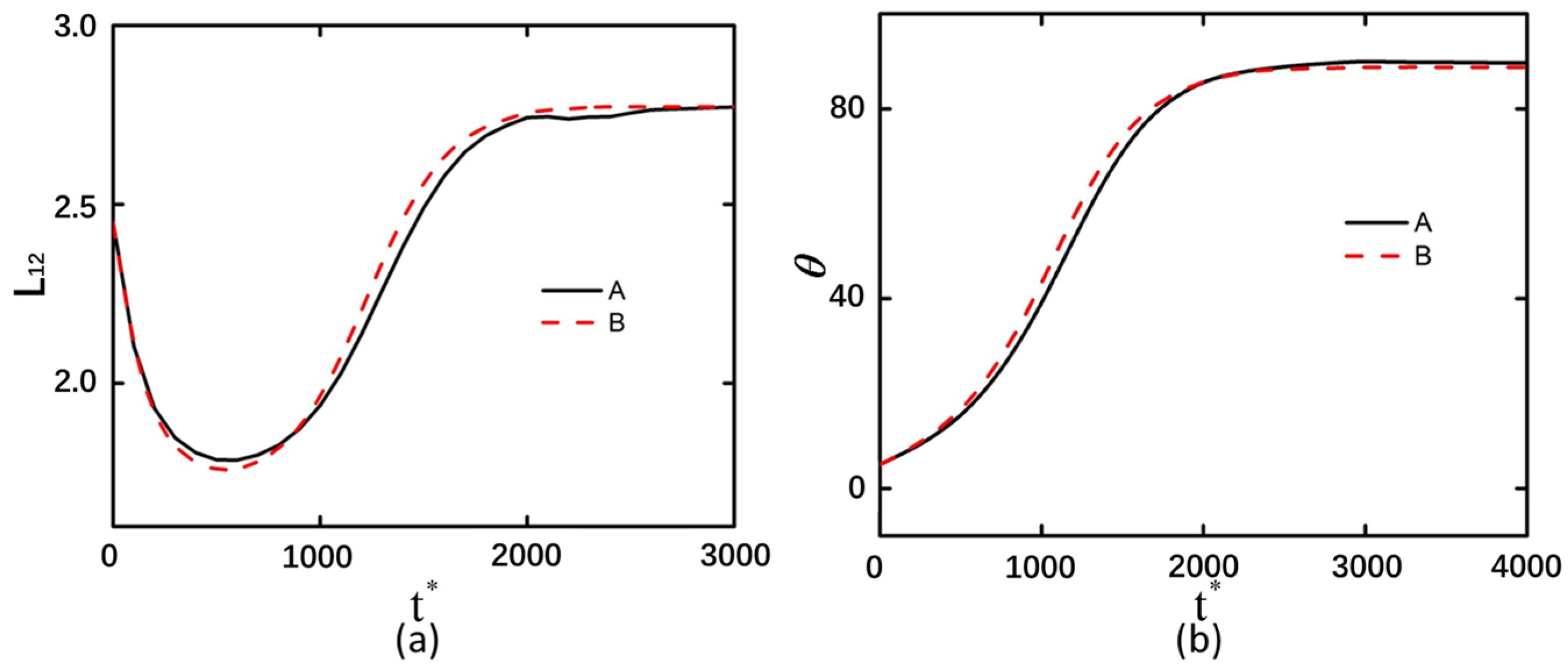
3.5. The Arrangement Pattern of Curved Particles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEP | dielectrophoresis |
| EDL | electrical double layer |
| DC | direct current |
| ALE | arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian |
References
- Lan, M.; Yang, F. Applications of dielectrophoresis in microfluidic-based exosome separation and detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 491, 152067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.S.; Vashi, A.; Roshan, U.; Galogahi, F.M.; Tran, D.T.; Sreejith, K.R.; Nguyen, N.-T. Continuous dielectrophoretic sorting of liquid beads. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 435, 137627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinappi, M.; Yamaji, M.; Kawano, R.; Cecconi, F. Analytical model for particle capture in nanopores elucidates competition among electrophoresis, electroosmosis, and dielectrophoresis. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 15816–15828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavatski, S.; Martin, O.J. Visual and quantitative analysis of the trapping volume in dielectrophoresis of nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 10305–10312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Lee, C.-H.; Noh, H.; Kang, G.; Lee, J.; Bae, J.-H.; Moon, H.; Park, J.; Kong, S.; Baek, M.-C. High-precision extracellular-vesicle isolation-analysis integrated platform for rapid cancer diagnosis directly from blood plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 267, 116863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, J.; Casti, P.; Antonelli, G.; Murdocca, M.; Mencattini, A.; Corsi, F.; D’Orazio, M.; Pecora, A.; De Luca, M.; Curci, G. Cell Electrokinetic Fingerprint: A Novel Approach Based on Optically Induced Dielectrophoresis (ODEP) for In-Flow Identification of Single Cells. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2300923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, X.; He, Z.; Hou, L.; Ge, C.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Detection of prostate specific antigen in whole blood by microfluidic chip integrated with dielectrophoretic separation and electrochemical sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 204, 114057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertsgaard, C.T.; Kim, M.; Choi, J.; Oh, S.-H. Wireless dielectrophoresis trapping and remote impedance sensing via resonant wireless power transfer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Joo, S.W.; Jiang, Y.; Xuan, X.; Qian, S. Transient electrophoretic motion of a charged particle through a converging–diverging microchannel: Effect of direct current-dielectrophoretic force. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ge, J.; Shi, L.; Fan, J.; Liu, Z.; Woo Joo, S. Dielectrophoretic choking phenomenon of a deformable particle in a converging-diverging microchannel. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, N.; Singh, P. Influence of particle-particle interactions and particles rotational motion in traveling wave dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Ji, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Joo, S.W. AC dielectrophoretic deformable particle-particle interactions and their relative motions. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Qian, S. Direct numerical simulation of AC dielectrophoretic particle–particle interactive motions. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2014, 417, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Ji, X.; Shi, L.; Hu, N.; Li, T. Dielectrophoretic interactions of two rod-shaped deformable particles under DC electric field. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 607, 125493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Chen, B.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, J. Iterative dipole moment method for the interaction of multiple dielectrophoretic particles in an AC electrical field. Eur. J. Mech.-B/Fluids 2016, 58, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwizera, E.A.; Sun, M.; White, A.M.; Li, J.; He, X. Methods of generating dielectrophoretic force for microfluidic manipulation of bioparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 2043–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, K.I.; Park, I.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Chang, W.-J.; Bashir, R.; Choi, S.; Lee, S.W. Ultra-sensitive dielectrophoretic surface charge multiplex detection inside a micro-dielectrophoretic device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 210, 114235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, X.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Peng, R.; Wang, Q.; Gong, N.; Pan, X.; Sun, Y. DC dielectrophoresis separation of marine algae and particles in a microfluidic chip. Sci. China Chem. 2012, 55, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, W.; Sharaf, O.Z.; Alazzam, A.; Abu-Nada, E. Dielectrophoresis-field flow fractionation for separation of particles: A critical review. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1637, 461799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, P.-Y.; Chen, I.-A.; Yeh, C.-K.; Chen, P.-Y.; Juang, J.-Y. Size-dependent dielectrophoretic crossover frequency of spherical particles. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 011909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Park, S.; Zhu, J.; Xuan, X.; Beskok, A.; Qian, S. DC electrokinetic particle transport in an L-shaped microchannel. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Shi, L.; Fan, C.; Liang, D.; Weng, S.; Joo, S.W. A novel scalable microfluidic load sensor based on electrokinetic phenomena. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2017, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yu, J.; Gong, J.; Wu, J.; Zong, X.; Luo, Z.; He, X.; Cheng, W.M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Campylobacter jejuni-derived cytolethal distending toxin promotes colorectal cancer metastasis. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 2080–2091.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, R.; Li, F.; Xuan, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Li, X. Vibrio cholerae virulence is blocked by chitosan oligosaccharide-mediated inhibition of ChsR activity. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 2909–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, S.; Schreier, D.; Brand, F.; Drese, K.S.; Cierpka, C.; König, J. Interplay of acoustophoresis and dielectrophoresis in a standing surface acoustic wave field: From spherical to non-spherical particles. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2024, 28, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Khanbareh, H.; Van Der Zwaag, S. Computational modeling of structure formation during dielectrophoresis in particulate composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2016, 112, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Mannoor, M.; Maniyeri, R. Effects of the Reynolds number on two-dimensional dielectrophoretic motions of a pair of particles under a uniform electric field. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Alazzam, A.; Khashan, S.; Abutayeh, M. Lab-on-chip for liquid biopsy (LoC-LB) based on dielectrophoresis. Talanta 2017, 164, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miled, M.A.; Sawan, M. Dielectrophoresis-based integrated lab-on-chip for nano and micro-particles manipulation and capacitive detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-D.; Yang, C.-Y.; Han, A.; Wu, C.-C. A label-free Droplet sorting platform integrating Dielectrophoretic separation for estimating bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance. Biosensors 2024, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Toma, A.; Brunetti, G.; Chiriacò, M.S.; Ferrara, F.; Ciminelli, C. A Novel Hybrid Platform for Live/Dead Bacteria Accurate Sorting by On-Chip DEP Device. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; Zeng, J.; He, X.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Zhu, Y. Intelligent optoelectrowetting digital microfluidic system for real-time selective parallel manipulation of biological droplet arrays. Lab. Chip 2025, 6, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, T.; Hu, H.H. Particle interactions in electrophoresis due to inertia. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2004, 273, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; He, X.H.; Zhao, J.C.; Shi, L.Y.; Wen, L.P. Electrokinetic transport of nanoparticles in functional group modified nanopores. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; Zhao, J.C.; Shi, L.Y.; Zhou, T.; Wen, L.P. Gated nanoparticle transport in a functional group modified nanopore. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 092019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Mauroy, B.; Sharma, A.; Qian, S. Electrokinetic motion of a deformable particle: Dielectrophoretic effect. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2282–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsumi, R.; Hoshino, K.; Hatayama, A. Study of numerical error of a Eulerian–Lagrangian scheme in the presence of particle source. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2021, 264, 107960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-C.; Yang, B. An overview of numerical methods for incompressible viscous flow with moving particles. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 1255–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y. The Dielectrophoretic Interactions of Curved Particles in a DC Electric Field. Micromachines 2025, 16, 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050596
Huang Z, Zhang T, Feng J, Wang Y. The Dielectrophoretic Interactions of Curved Particles in a DC Electric Field. Micromachines. 2025; 16(5):596. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050596
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhiwei, Tong Zhang, Jing Feng, and Yage Wang. 2025. "The Dielectrophoretic Interactions of Curved Particles in a DC Electric Field" Micromachines 16, no. 5: 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050596
APA StyleHuang, Z., Zhang, T., Feng, J., & Wang, Y. (2025). The Dielectrophoretic Interactions of Curved Particles in a DC Electric Field. Micromachines, 16(5), 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050596






