Nonlinear Hysteresis Parameter Identification of Piezoelectric Actuators Using an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer with Logistic Chaos Initialization and a Levy Flight Variant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. BW Model and GWO Algorithm Improvements
2.1. Description of the BW Model
2.2. Description of Classical GWO Algorithm
2.2.1. Initialization
2.2.2. Encirclement
2.2.3. Hunting
2.2.4. Attacking
2.3. GWO Algorithm Improvement
2.3.1. Logistic Chaos Initialization
2.3.2. Convergence Factor Improvement
2.3.3. Levy Flight Variant
2.3.4. Algorithm Workflow
| Algorithm 1. The improved GWO. |
|
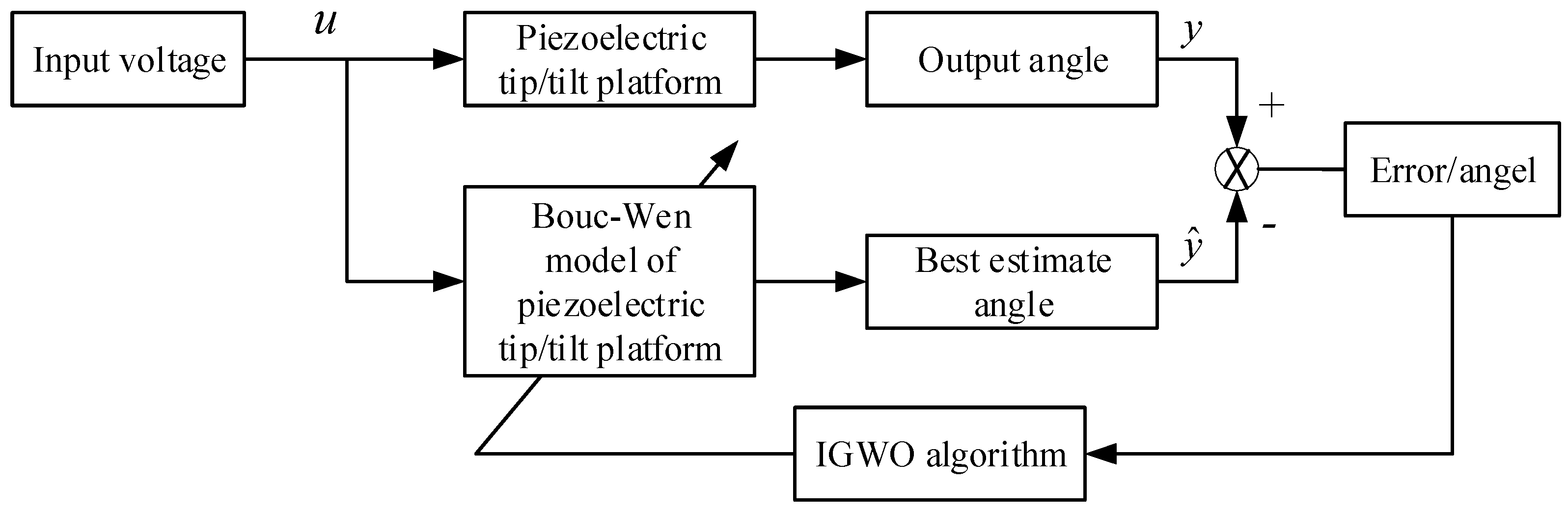
2.4. Principles of Parameter Identification
3. Experimental Verification
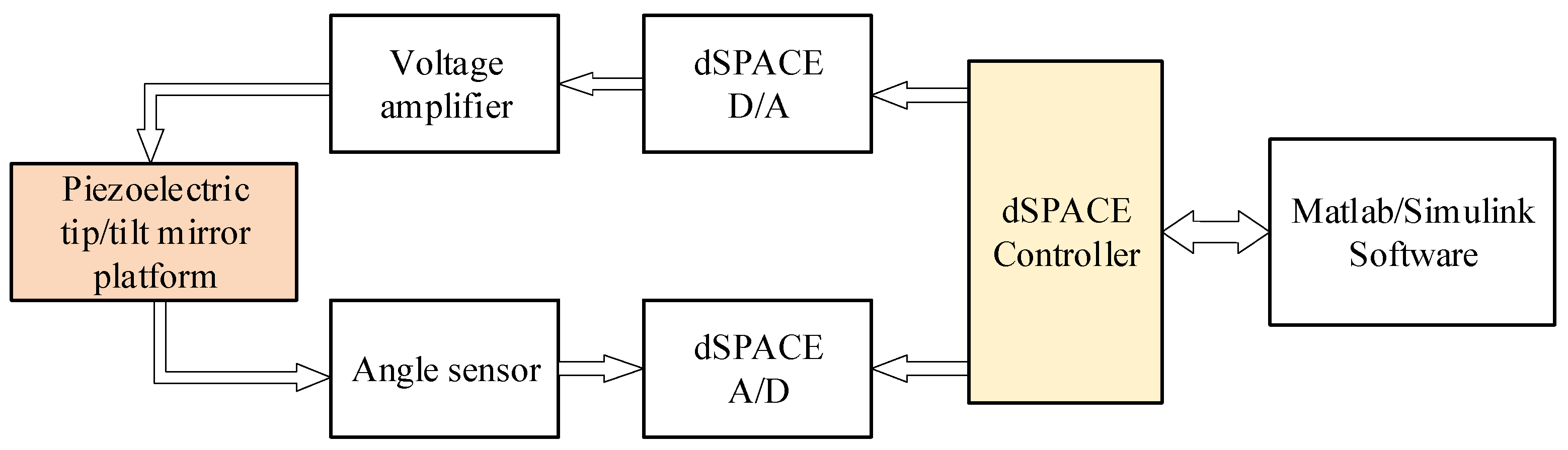
3.1. Experimental Platform Construction
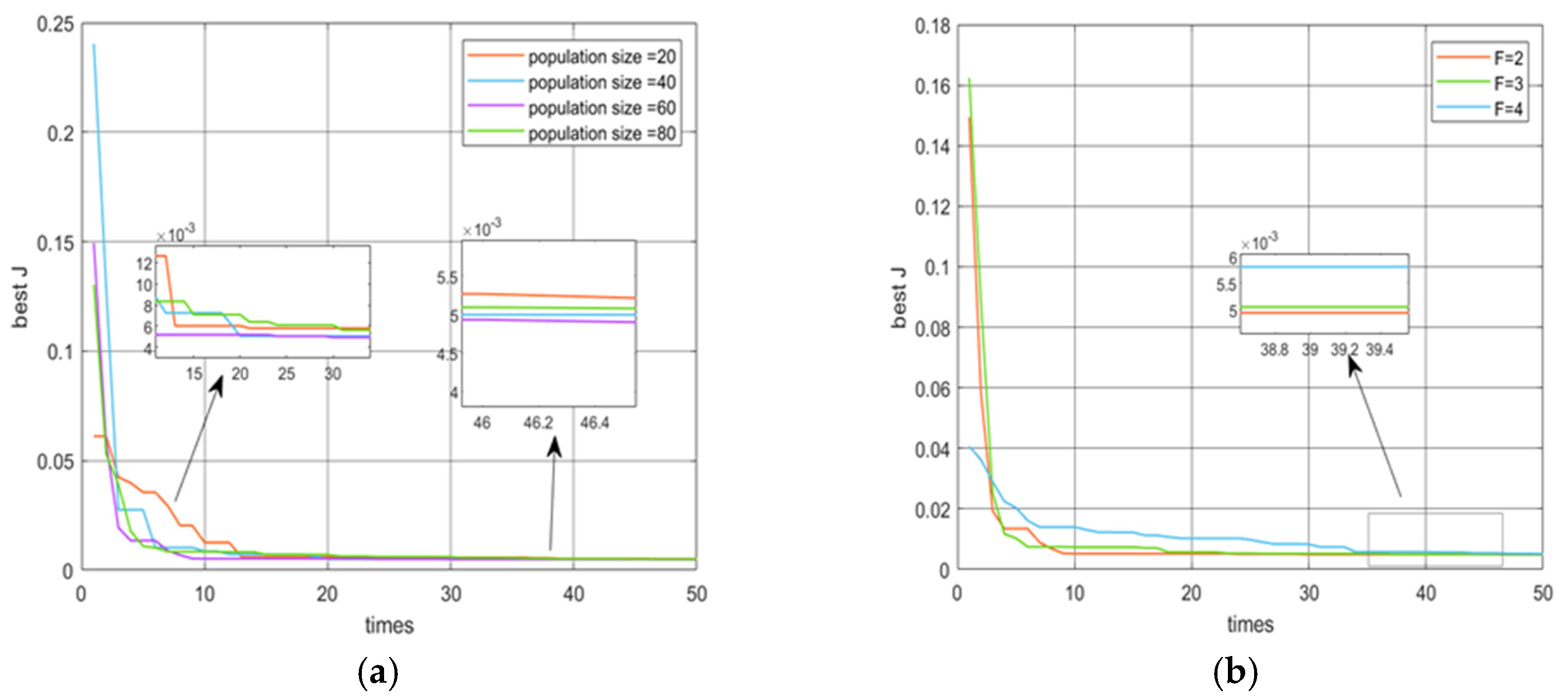
3.2. Selection of Algorithm Parameters
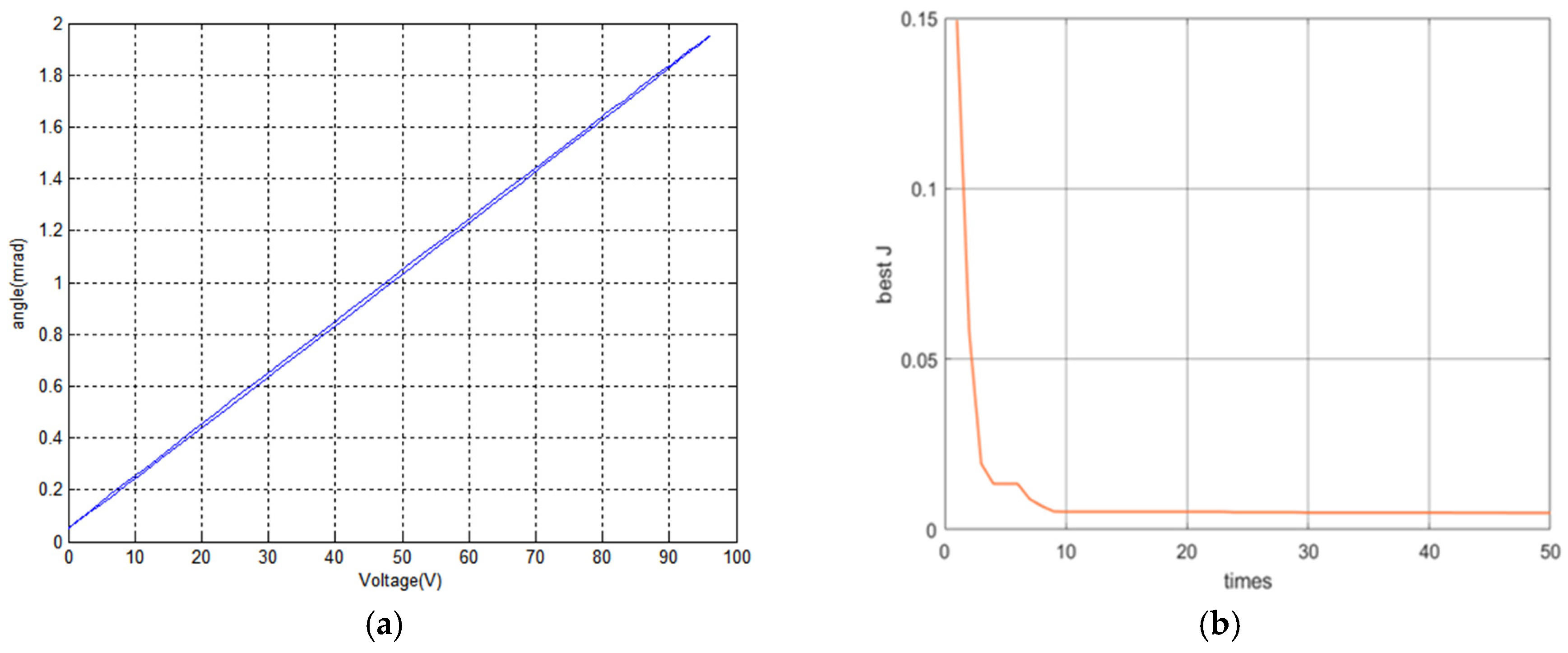
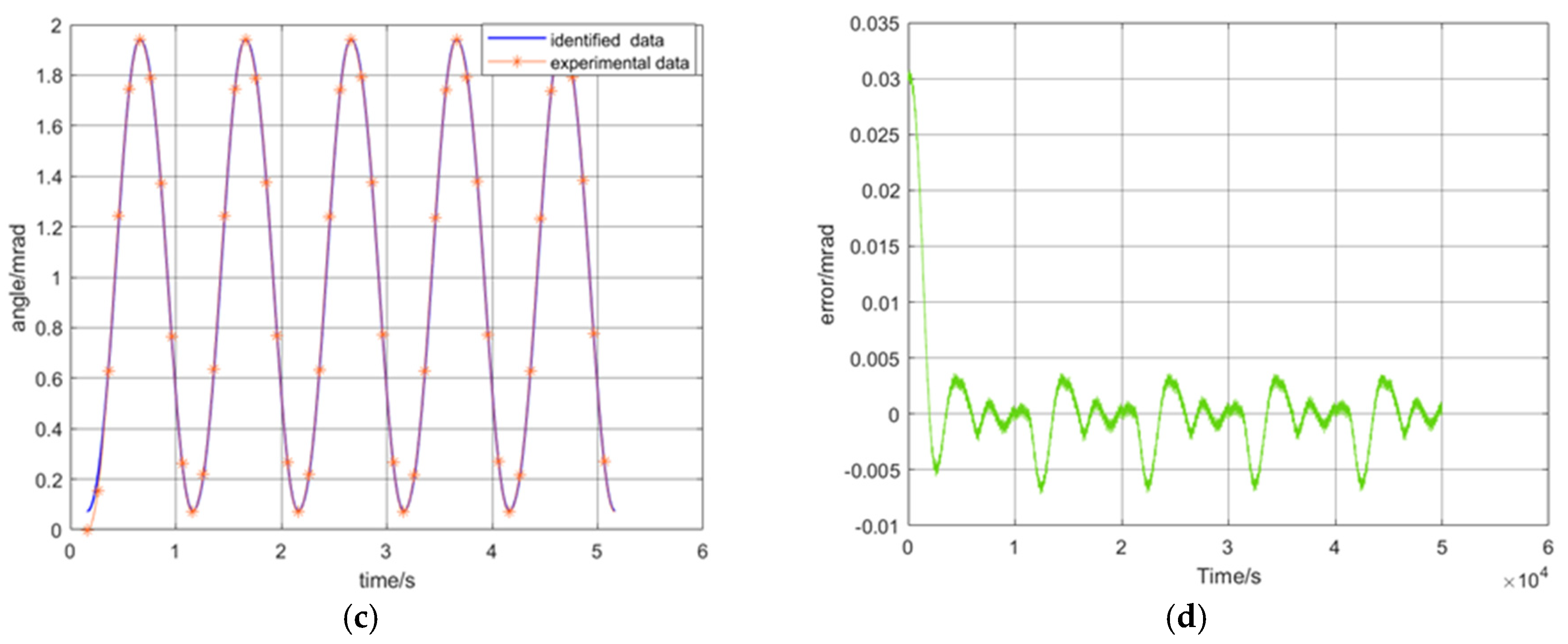
3.3. Parameter Identification Results
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Three Algorithms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GWO | Gray Wolf Optimization |
| IGWO | Improved Gray Wolf Optimization |
| BW | Bouc–Wen |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| FTM | Fast tilt mirror |
| PFTM | Piezoelectric fast tilt mirror |
| KP | Krasnosel’skii–Pokrovskii |
| PI | Prandtl–Ishlinskii |
| NN | Neural network |
| GA | Genetic algorithm |
References
- Xu, T.; Ruan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tang, T. Line of sight control of an image-based tracking system using Youla-Kucera parameterization. Opt. Eng. 2022, 61, 065105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.W.; Zhai, C.P.; Shao, S.B.; Tian, Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Xu, M. Piezoelectric-based large-angle stroke fast steering mirror with high ratio of output range to resolution and self-sensing capability. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2024, 95, 085005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Cao, K.; Li, S.; Wan, Y. Hysteresis Characteristics of Steering Mirror Driven by Piezoelectric Actuator and Its Experimental Research. Acta Opt. Sin. 2018, 38, 0814002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Bai, F.; Chen, G.; Ma, J. Comprehensive approach to modeling and identification of a two-axis piezoelectric fast steering mirror system based on multi-component analysis and synthesis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 127, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Nishida, R.; Shinshi, T. Design and precision tracking control of a high-bandwidth fast steering mirror for laser beam machining. Precis. Eng. 2022, 73, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.A.; Shapiro, A. System Identification and Mathematical Modeling of a Piezoelectric Actuator through A Practical Three-Stage Mechanism. Micromachines 2023, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, K.; Chang, Q. Development of a low capacitance two-axis piezoelectric tilting mirror used for optical assisted micromanipulation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 154, 107602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, K.D.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, W.-G. Development of piezoelectric fast steering mirror with tilt error compensation for portable spectroscopic sensor. J. Eng. Manuf. 2023, 237, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xiong, H.; Song, T.; Zhou, G.; Huang, M.; Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Chen, W. Design of a fast steering mirror driven by piezoelectric ceramics. Opt. Eng. 2022, 61, 024102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.M.; Cao, J.T.; Wang, Z.M.; Ma, X.; Gu, H.; Liu, W. Performance analysis of free space optical communications with FOA-WFS. Opt. Eng. 2024, 32, 28937–28952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strijbosch, N.; Tiels, K.; Oomen, T. Memory-Element-Based Hysteresis: Identification and Compensation of a Piezoelectric Actuator. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2023, 31, 2863–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Daniels, B.; Curti, M.; Tiels, K.; Lomonova, E.A.; Tartakovsky, D.M. Discovery of sparse hysteresis models for piezoelectric materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 122, 214101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierla, M.; Sutor, A.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Kaltenbacher, M. Stageless evaluation for a vector Preisach model based on rotational operators. Compel 2017, 36, 1501–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, M.E.; Borzunov, S.; Meleshenko, P.A.; Sel’vesyuk, N.I. The Preisach model of hysteresis: Fundamentals and applications. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 062008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Model order reduction for the Krasnoselskii-Pokrovskii (KP) model. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 095001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, R.; Lu, K.; Sang, Z.; Ju, B. Research on asymmetric hysteresis modelling and compensation of piezoelectric actuators with PMPI model. Micromachines 2020, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Zhang, X. An enhanced Bouc-Wen model for charactering rate-dependent hysteresis of piezoelectric actuators. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 019902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, A.; Wu, J.L. A novel output feedback disturbance rejection controller for Bouc–Wen hysteresis control systems. Int. J. Control. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Arunkumar, A. Design of State-Constrained Controllers for Bouc–Wen Hysteresis Systems. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2023, 7, 3271–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Zou, D. Modelling and compensation of hysteresis in piezoelectric actuators based on Maxwell approach. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artetxe, E.; Barambones, O.; Calvo, I.; del Rio, A.; Uralde, J. Combined Control for a Piezoelectric Actuator Using a Feed-Forward Neural Network and Feedback Integral Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control. Micromachines 2024, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhao, S.Q.; Fan, Q.Q. A hybrid Genetic algorithm-based parameter identification method for nonlinear hysteretic system with experimental verification. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2023, 24, 2450099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.A.; Xue, B.; Brousseau, E.; Geng, Y.; Yan, Y. Characterizing the electric field- and rate-dependent hysteresis of piezoelectric ceramics shear motion with the Bouc-Wen model. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 367, 115044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Saxena, S.; Sharma, H.; Kamboj, V.K.; Arora, K.; Joshi, G.P.; Cho, W. An integrative TLBO-driven hybrid grey wolf optimizer for the efficient resolution of multi-dimensional, nonlinear engineering problems. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.S.; Deb, S. Cuckoo search: Recent advances and applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouc, R. Forced vibrations of mechanical systems with hysteresis. In Proceedings of the Fourth Conference on Nonlinear Oscillations, Prague, Czech Republic, 5–9 September 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.K. Method for random vibration of hysteretic systems. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1976, 102, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, T.S.; Guo, W. Modeling of a three-layer piezoelectric bimorph beam with hysteresis. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1995, 4, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sireteanu, T.; Giuclea, M.; Mitu, A.M. Identification of an extended Bouc–Wen model with application to seismic protection through hysteretic devices. Comput. Mech. 2010, 45, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Zhang, X. Nonlinear hysteresis modeling of piezoelectric actuators using a generalized Bouc–Wen model. Micromachines 2019, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, N.; Singh, U.; Sohi, B.S. Modified Grey Wolf Optimizer for Global Engineering Optimization. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2016, 2016, 7950348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.Q.; Liu, H.; Ding, G.Y.; Tu, L. A modified Levy flight distribution for solving high-dimensional numerical optimization problems. Math. Comput. Simul. 2023, 204, 376–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Xu, M.H.; Hu, Z.Y. Path Planning of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Based on an Improved Bio-Inspired Tuna Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



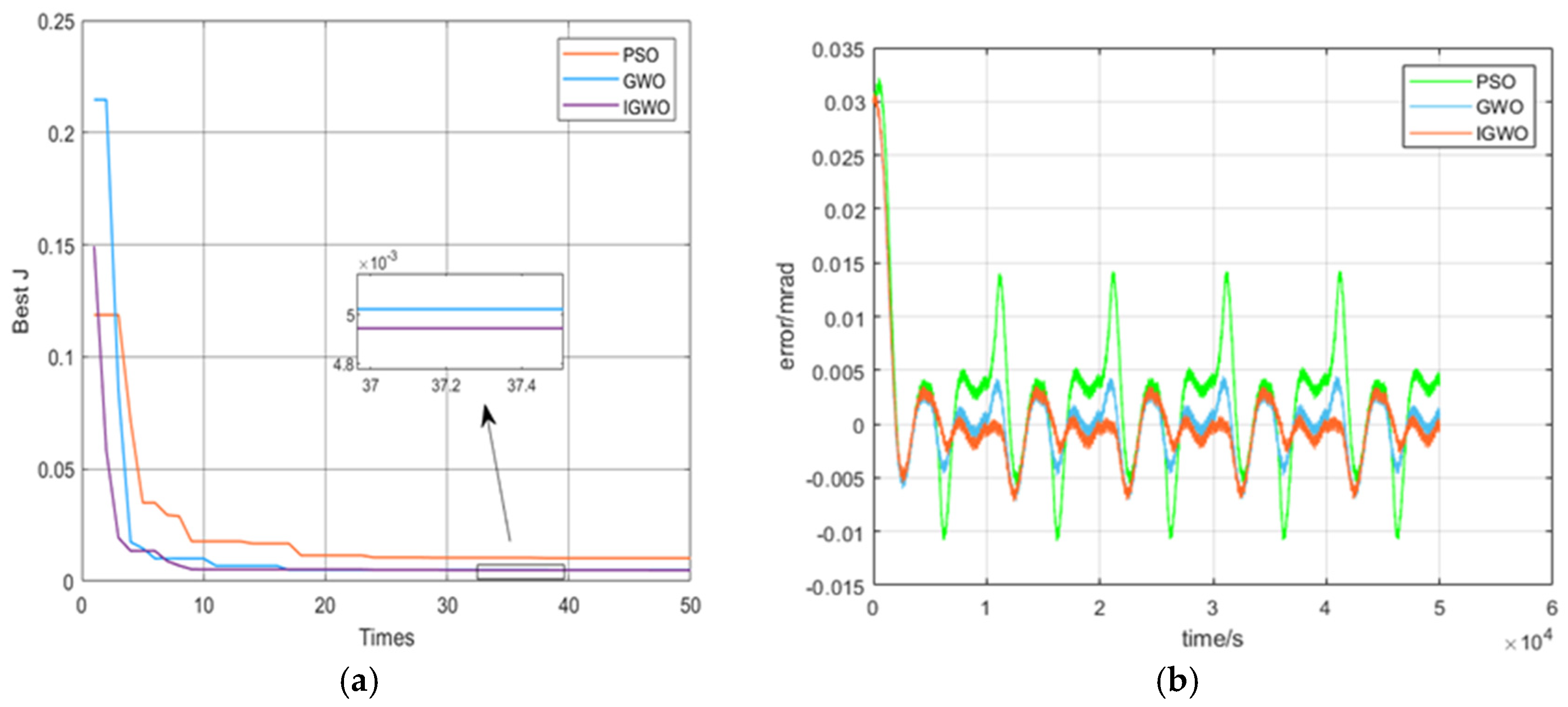

| Algorithm Type | J | α | β | γ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGWO | 1.0406 | 0.2313 | 5.2349 | 2.1457 | |
| GWO | 1.0457 | 0.2249 | 6.8862 | 0.5358 | |
| PSO | 1.0402 | 0.4070 | 7.2397 | 7.4774 |
| Algorithm Type | IGWO | GWO | PSO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Min J | |||
| Max J | |||
| Average value J |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Duan, K.; Cui, J.; Guo, S.; Cui, C.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, F. Nonlinear Hysteresis Parameter Identification of Piezoelectric Actuators Using an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer with Logistic Chaos Initialization and a Levy Flight Variant. Micromachines 2025, 16, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050492
Yan Y, Duan K, Cui J, Guo S, Cui C, Zhou Y, Huang J, Wang G, Zhang D, Zhang F. Nonlinear Hysteresis Parameter Identification of Piezoelectric Actuators Using an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer with Logistic Chaos Initialization and a Levy Flight Variant. Micromachines. 2025; 16(5):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050492
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yonggang, Kangqiao Duan, Jianjun Cui, Shiwei Guo, Can Cui, Yongsheng Zhou, Junjie Huang, Geng Wang, Dengpan Zhang, and Fumin Zhang. 2025. "Nonlinear Hysteresis Parameter Identification of Piezoelectric Actuators Using an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer with Logistic Chaos Initialization and a Levy Flight Variant" Micromachines 16, no. 5: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050492
APA StyleYan, Y., Duan, K., Cui, J., Guo, S., Cui, C., Zhou, Y., Huang, J., Wang, G., Zhang, D., & Zhang, F. (2025). Nonlinear Hysteresis Parameter Identification of Piezoelectric Actuators Using an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer with Logistic Chaos Initialization and a Levy Flight Variant. Micromachines, 16(5), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050492






