Influence of Oil Viscosity on Hysteresis Effect in Electrowetting Displays Based on Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principles of Hysteresis Effect in EWDs
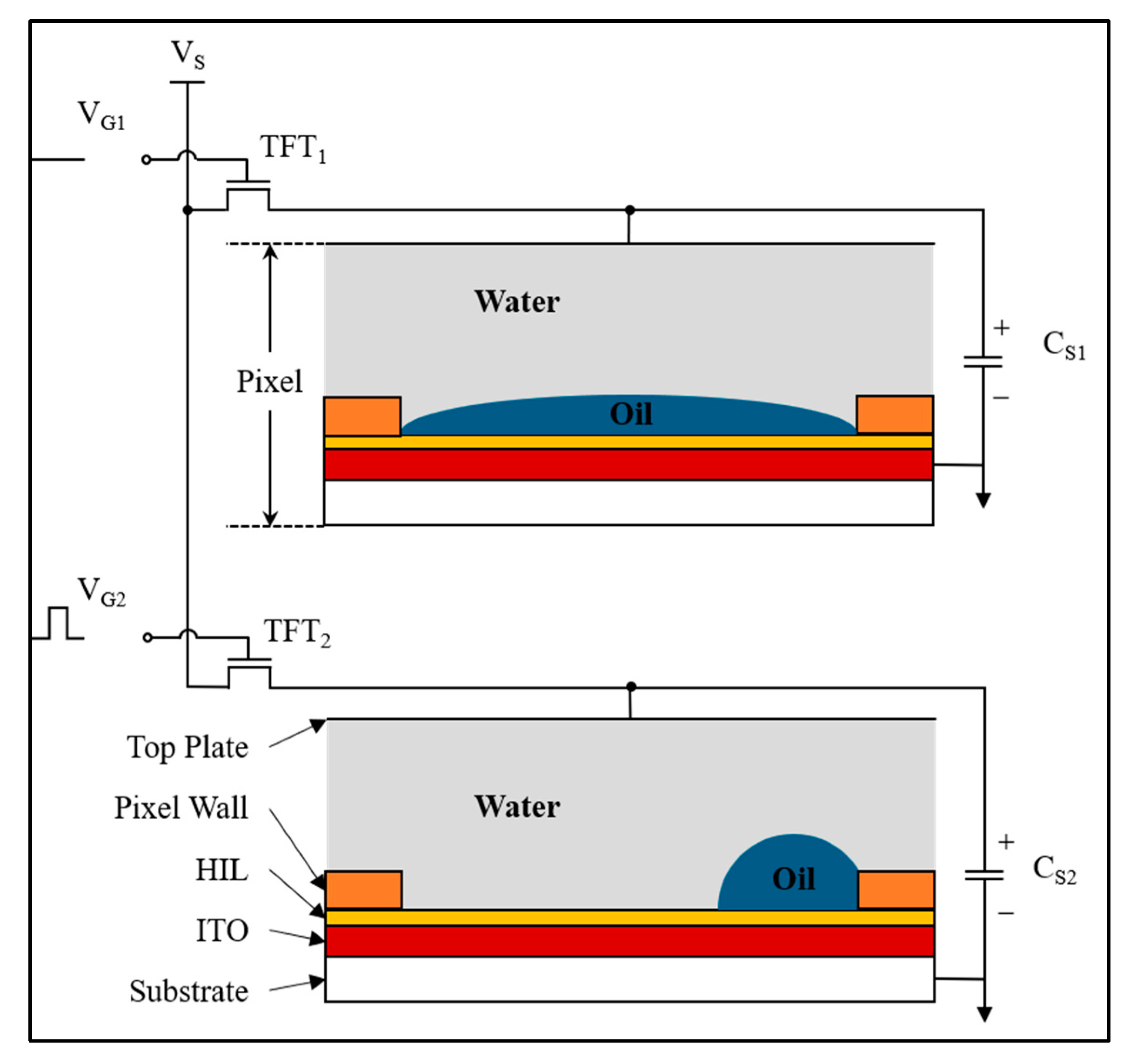
2.1. Driving Principle of EWDs
- Color display mode: When gate signal VG1 is biased at a low level, TFT1 enters the cutoff state, resulting in zero potential storage (CS1 = 0 V). This passive configuration enables spontaneous oil spreading to achieve full-pixel coverage through interfacial tension dominance.
- Substrate exposure mode: Activation of VG2 at a high-level triggers TFT2 conduction, enabling capacitive charging (CS2 = VS). The resultant electrostatic actuation induces oil film retraction to pixel corners, with contraction magnitude being voltage-dependently regulated for precise grayscale modulation.
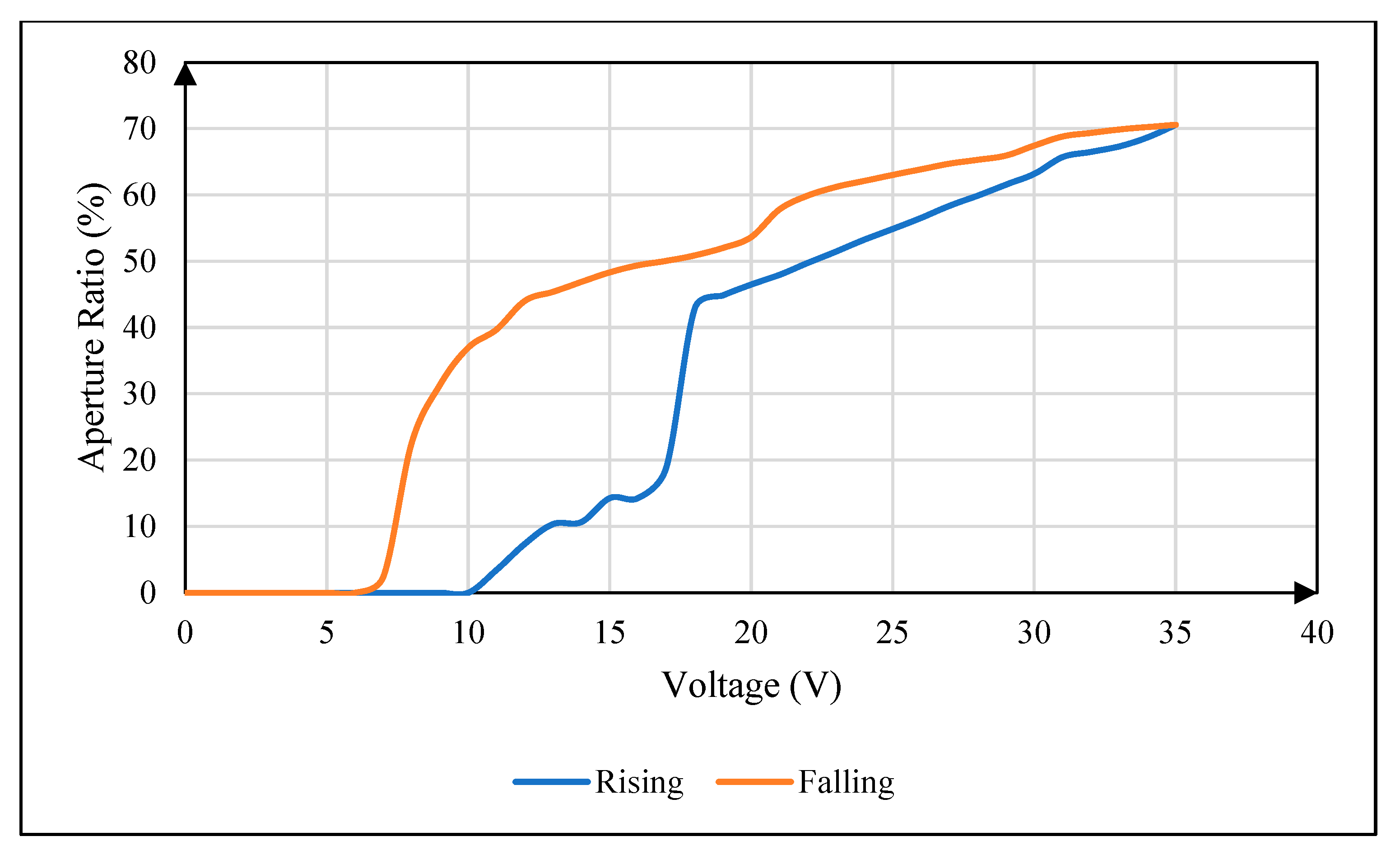
2.2. Hysteresis Effect of EWDs
3. Numerical Methodology
3.1. Governing Equations
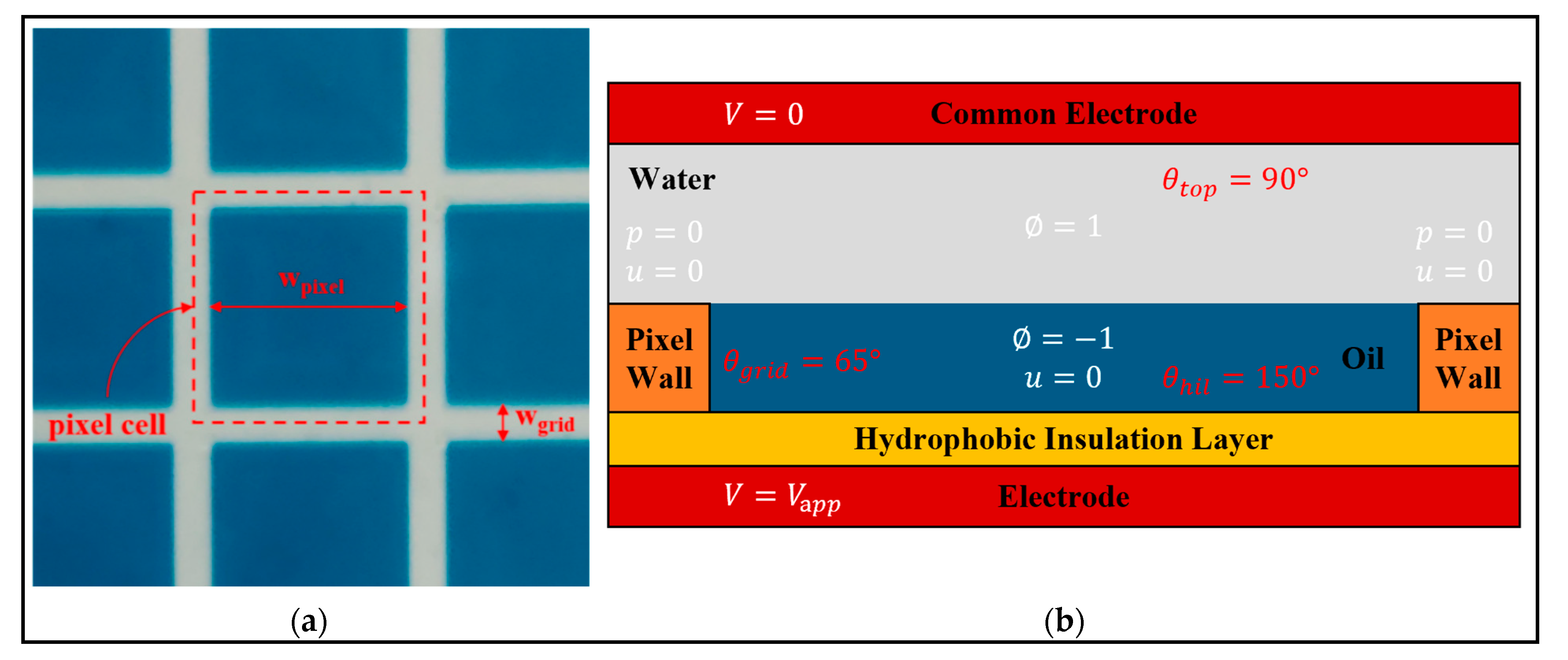
3.2. Boundary Conditions
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
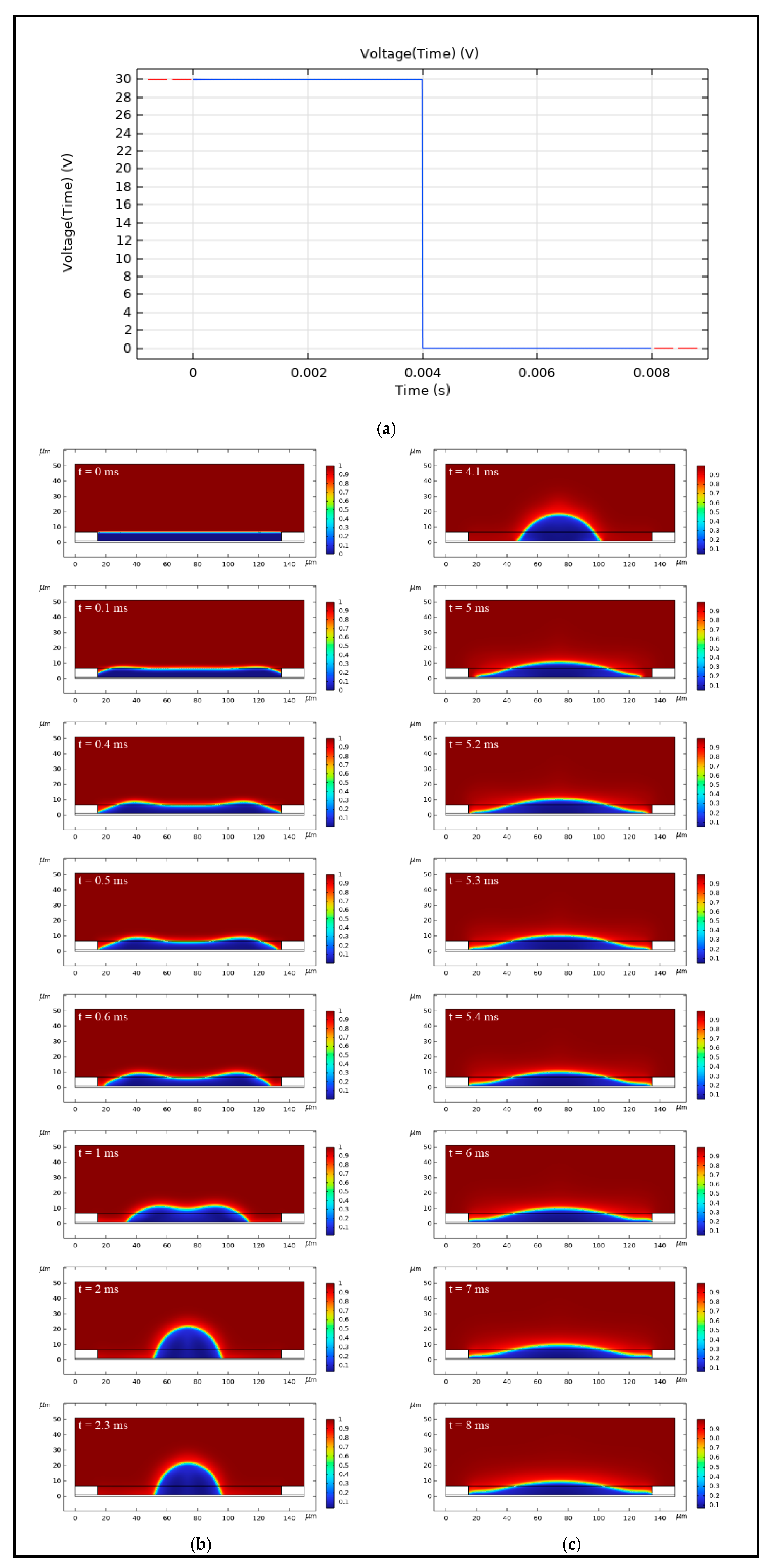
4.1. Simulation of Oil Movement Process
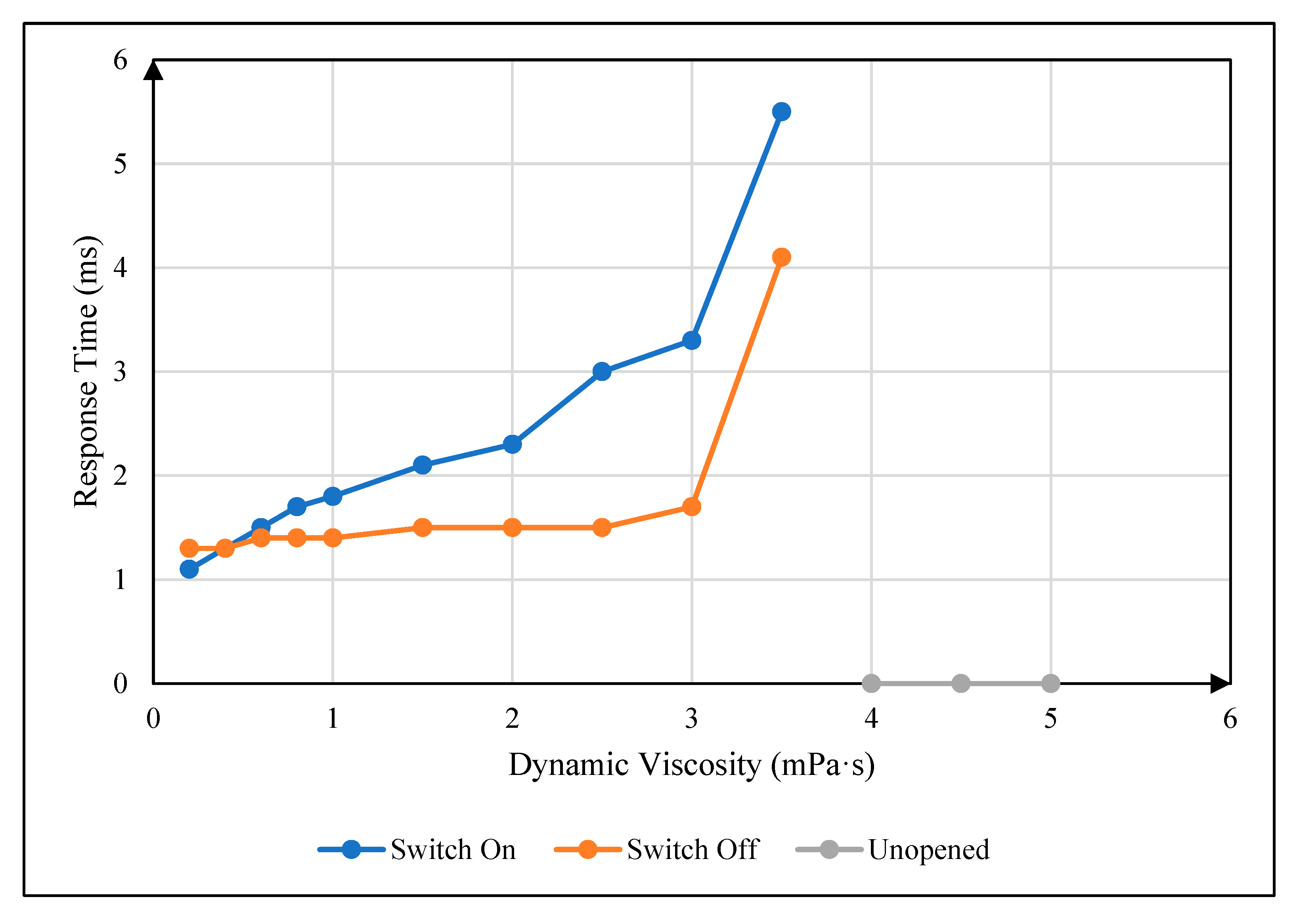
4.2. Influence of Oil Viscosity on Response Time
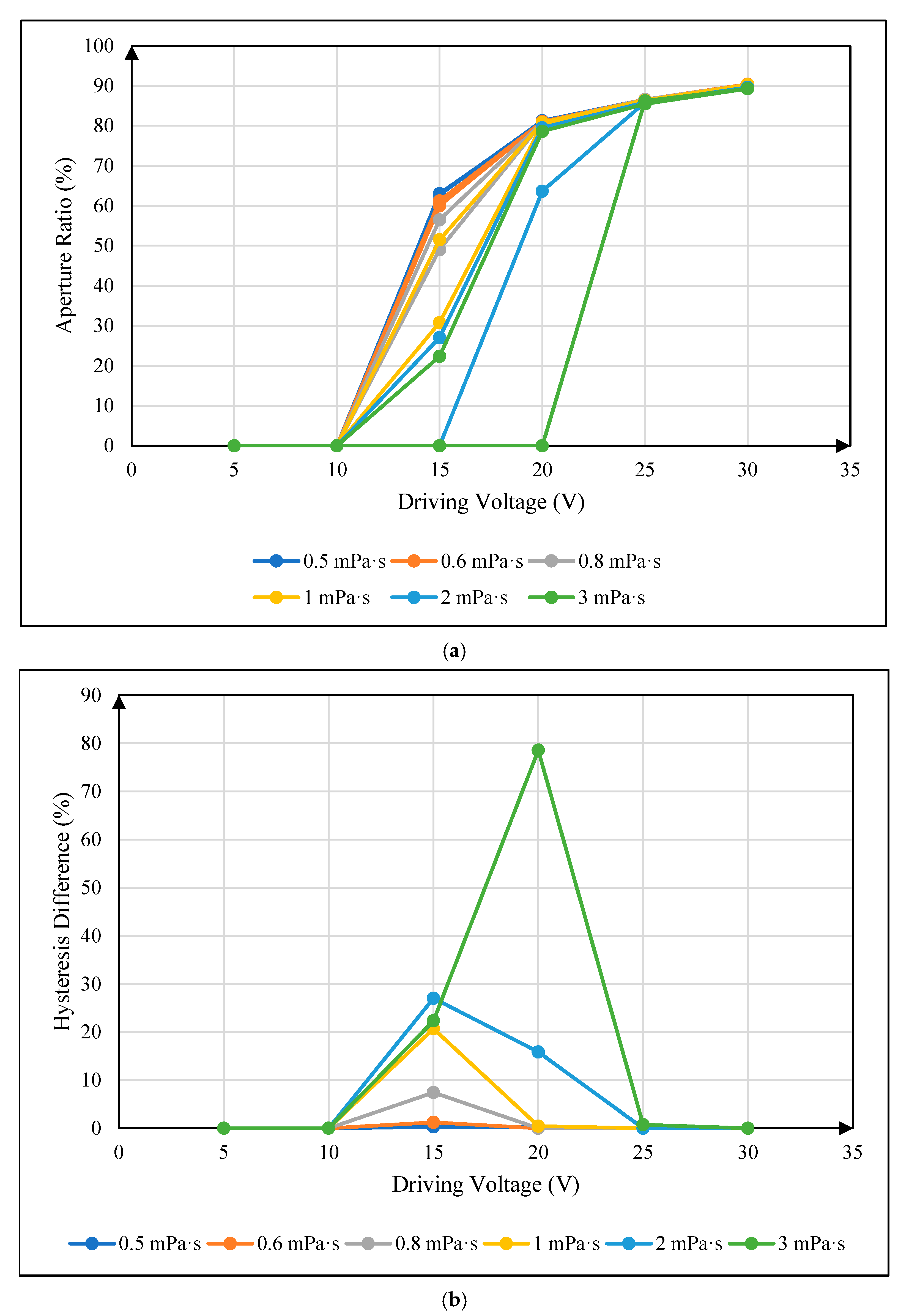
4.3. Influence of Oil Viscosity on Maximum Aperture Ratio
4.4. Influence of Oil Viscosity on Hysteresis Effect
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J. Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 2003, 425, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.; Wheeler, A.R.; Garrell, R.L.; Loo, J.A.; Kim, C.J. An integrated digital microfluidic chip for multiplexed proteomic sample preparation and analysis by MALDI-MS. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, B.; Peseux, J. Variable focal lens controlled by an external voltage: An application of electrowetting. Eur. Phys. J. E 2000, 3, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupenkin, T.; Taylor, J.A. Reverse electrowetting as a new approach to high-power energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Lai, S.; Liu, L.; He, W.; Yi, Z. Driving Waveform Design with Rising Gradient and Sawtooth Wave of Electrowetting Displays for Ultra-Low Power Consumption. Micromachines 2020, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lai, S.; He, W.; Wang, L.; Chi, F.; Zhang, C.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G. Driving Waveform Design of Electrowetting Displays Based on an Exponential Function for a Stable Grayscale and a Short Driving Time. Micromachines 2020, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.S.; Kuo, S.W.; Tsai, Y.H.; Cheng, P.P.; Chen, J.L.; Lan, K.W.; Cheng, W.Y. The Structure and Manufacturing Process of Large Area Transparent Electrowetting Display. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2012, 43, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Heikenfeld, J. Observation and optical implications of oil dewetting patterns in electrowetting displays. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 025027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Feng, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Lin, Y.; He, W.; Zhou, G. Aperture Ratio Improvement by Optimizing the Voltage Slope and Reverse Pulse in the Driving Waveform for Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines 2019, 10, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, R.; Feenstra, B.J.; Hayes, R.A.; Camps, I.G.J.; Boom, R.G.H.; Wagemans, M.M.H.; Feil, H. Gray scales for video applications on electrowetting displays. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2006, 37, 1926–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, A.; Vermeulen, P.; Figura, D.; Spreafico, M.; Meeusen, J.A.; Hampton, M.W.; Novoselov, P. Improved Oil Motion Control and Hysteresis-Free Pixel Switching of Electrowetting Displays. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2012, 42, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fang, H. Hysteresis and saturation of contact angle in electrowetting on a dielectric simulated by the lattice Boltzmann method. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, Q.-C.; Wang, P.; Liang, Z.-C. Contact angle hysteresis in electrowetting on dielectric. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 086801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Peng, R.; He, M. Effect of oil liquid viscosity on hysteresis in double-liquid variable-focus lens based on electrowetting. Int. Conf. Opt. Photonics Eng. 2017, 10250, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Tang, B.; Groenewold, J.; Li, F.; Yue, Q.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, G. Oil motion control by an extra pinning structure in electro-fluidic display. Sensors 2018, 18, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Tang, B.; Henzen, A.; Zhou, G. Photolithography fabricated spacer arrays offering mechanical strengthening and oil motion control in electrowetting displays. Sensors 2020, 20, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Bai, P.F.; Hayes, R.A.; Shui, L.L.; Jin, M.L.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G.F. Novel driving methods for manipulating oil motion in electrofluidic display pixels. J. Disp. Technol. 2016, 12, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Henzen, A. A Multi Waveform Adaptive Driving Scheme for Reducing Hysteresis Effect of Electrowetting Displays. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 618811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eral, H.B.; ’t Mannetje, D.J.C.M.; Oh, J.M. Contact angle hysteresis: A review of fundamentals and applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Deng, Y.; Xu, B.; Henzen, A.; Hayes, R.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G. Asymmetrical Electrowetting on Dielectrics Induced by Charge Transfer through an Oil/Water Interface. Langmuir 2018, 34, 11943–11951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Pak, J.J. Effect of contact angle hysteresis on electrowetting threshold for droplet transport. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 2105–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, A.; Sedev, R.; Ralston, J. Contact angle saturation in electrowetting. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 6268–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzpeyma, A.; Bhaseen, S.; Dolatabadi, A.; Wood-Adams, P. A coupled electro-hydrodynamic numerical modeling of droplet actuation by electrowetting. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 323, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.L.; Lin, C.H.; Lo, K.L.; Lee, K.C.; Cheng, W.Y.; Chen, K.C. 3D electrohydrodynamic simulation of electrowetting displays. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 125024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkiv, V.; Yarin, A.L.; Mashayek, F. Modeling of Droplet Impact onto Polarized and Nonpolarized Dielectric Surfaces. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10169–10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.P.; Yao, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Li, A.F.; Shams, B. Investigation of the Dynamic Contact Angle Using a Direct Numerical Simulation Method. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11736–11744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tang, B.; Dong, B.; Li, H.; Zhou, R.; Guo, Y.; Dou, Y.; Deng, Y.; Groenewold, J.; Henzen, A.V.; et al. Electrowetting on dielectric: Experimental and model study of oil conductivity on rupture voltage. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 195102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.T.; Feng, J.J.; Liu, C.; Shen, J. A diffuse-interface method for simulating two-phase flows of complex fluids. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 515, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, J.W.; Hilliard, J.E. Free Energy of a Nonuniform System. I. Interfacial Free Energy. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 28, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhuang, L.; Bai, P.; Tang, B.; Henzen, A.; Zhou, G. Modeling of Oil/Water Interfacial Dynamics in Three-Dimensional Bistable Electrowetting Display Pixels. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5326–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Zhong, Q.; Sun, H. Driving waveform optimization by simulation and numerical analysis for suppressing oil-splitting in electrowetting displays. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 720515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Mao, Z. Large language models for human–robot interaction: A review. Biomim. Intell. Robot. 2023, 3, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Quantity | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material [31] | density of oil | 880 | kg/m3 | |
| density of water | 998 | kg/m3 | ||
| dynamic viscosity of oil | 0.002 | Pa·s | ||
| dynamic viscosity of water | 0.001 | Pa·s | ||
| dielectric constant of oil | 2.2 | 1 | ||
| dielectric constant of water | 80 | 1 | ||
| dielectric constant of hydrophobic insulating layer | 1.95 | 1 | ||
| dielectric constant of pixel wall | 3.28 | 1 | ||
| Geometric [5] | width of pixel cell | 150 | μm | |
| height of pixel wall | 5.6 | Μm | ||
| width of pixel wall | 15 | μm | ||
| thickness of hydrophobic insulating layer | 1 | μm | ||
| thickness of oil | 5.6 | μm | ||
| Interfacial [17] | surface tension of oil and water | 0.015 | N/m | |
| contact angle of pixel wall | 65 | deg | ||
| contact angle of hydrophobic insulating layer | 150 | deg | ||
| contact angle of top plate | 90 | deg |
| Oil Movement Process | Response Time | Maximum Aperture Ratio | Hysteresis Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| whole process | positive correlation | no correlation | positive correlation |
| whole process [31] | positive correlation [31] | - | positive correlation [14] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Tian, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Lu, J.; Yi, Z.; Zhou, G. Influence of Oil Viscosity on Hysteresis Effect in Electrowetting Displays Based on Simulation. Micromachines 2025, 16, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040479
Li W, Liu L, Zhang T, Tian L, Wang L, Xu C, Lu J, Yi Z, Zhou G. Influence of Oil Viscosity on Hysteresis Effect in Electrowetting Displays Based on Simulation. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040479
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Linwei Liu, Taiyuan Zhang, Lixia Tian, Li Wang, Cheng Xu, Jianwen Lu, Zichuan Yi, and Guofu Zhou. 2025. "Influence of Oil Viscosity on Hysteresis Effect in Electrowetting Displays Based on Simulation" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040479
APA StyleLi, W., Liu, L., Zhang, T., Tian, L., Wang, L., Xu, C., Lu, J., Yi, Z., & Zhou, G. (2025). Influence of Oil Viscosity on Hysteresis Effect in Electrowetting Displays Based on Simulation. Micromachines, 16(4), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040479







