Kinetic Energy Harvesting with a Piezoelectric Patch Using a Bistable Laminate
Abstract
1. Introduction
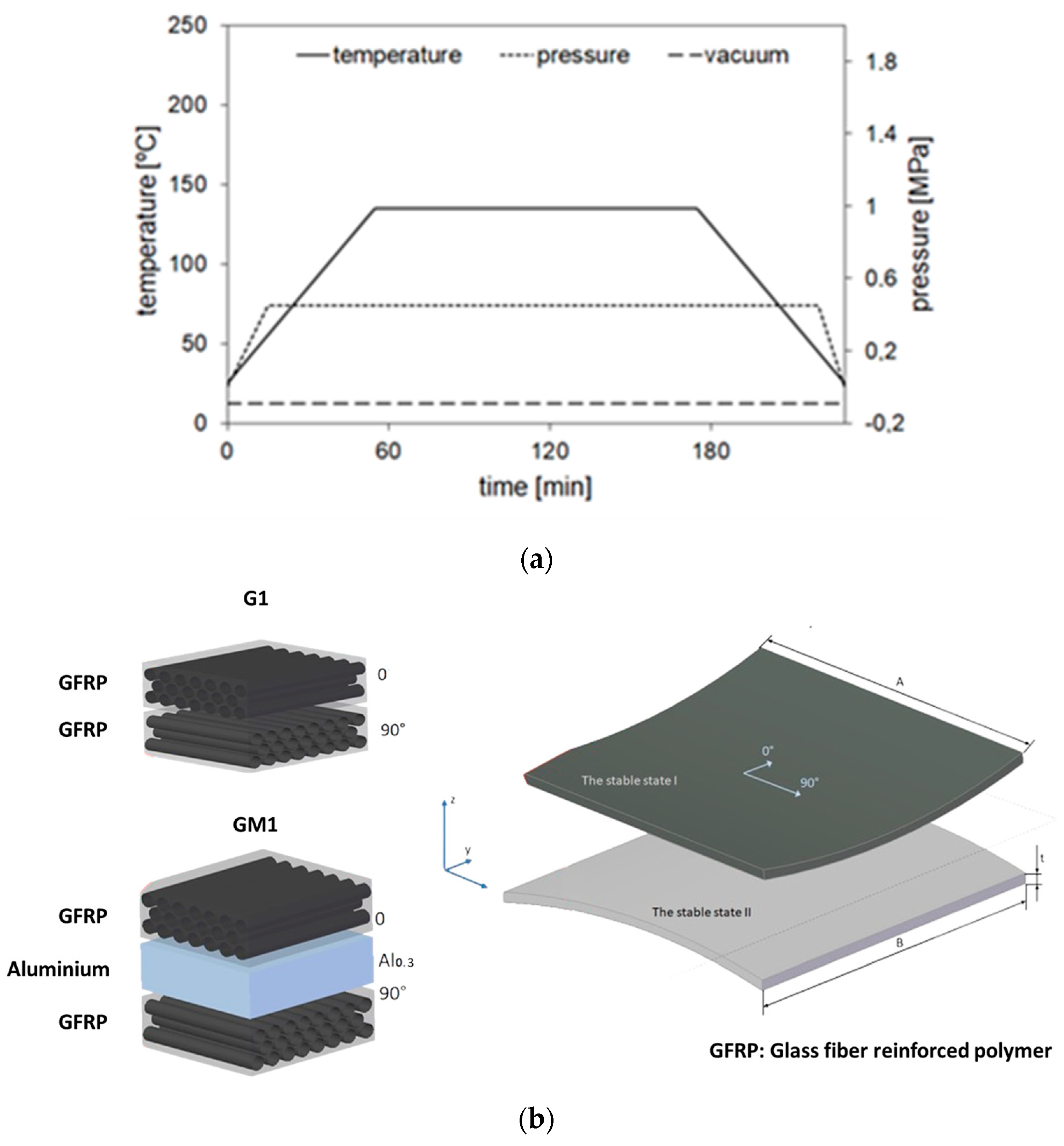
2. Preparation of the Bistable Plates
3. Experimental Investigation
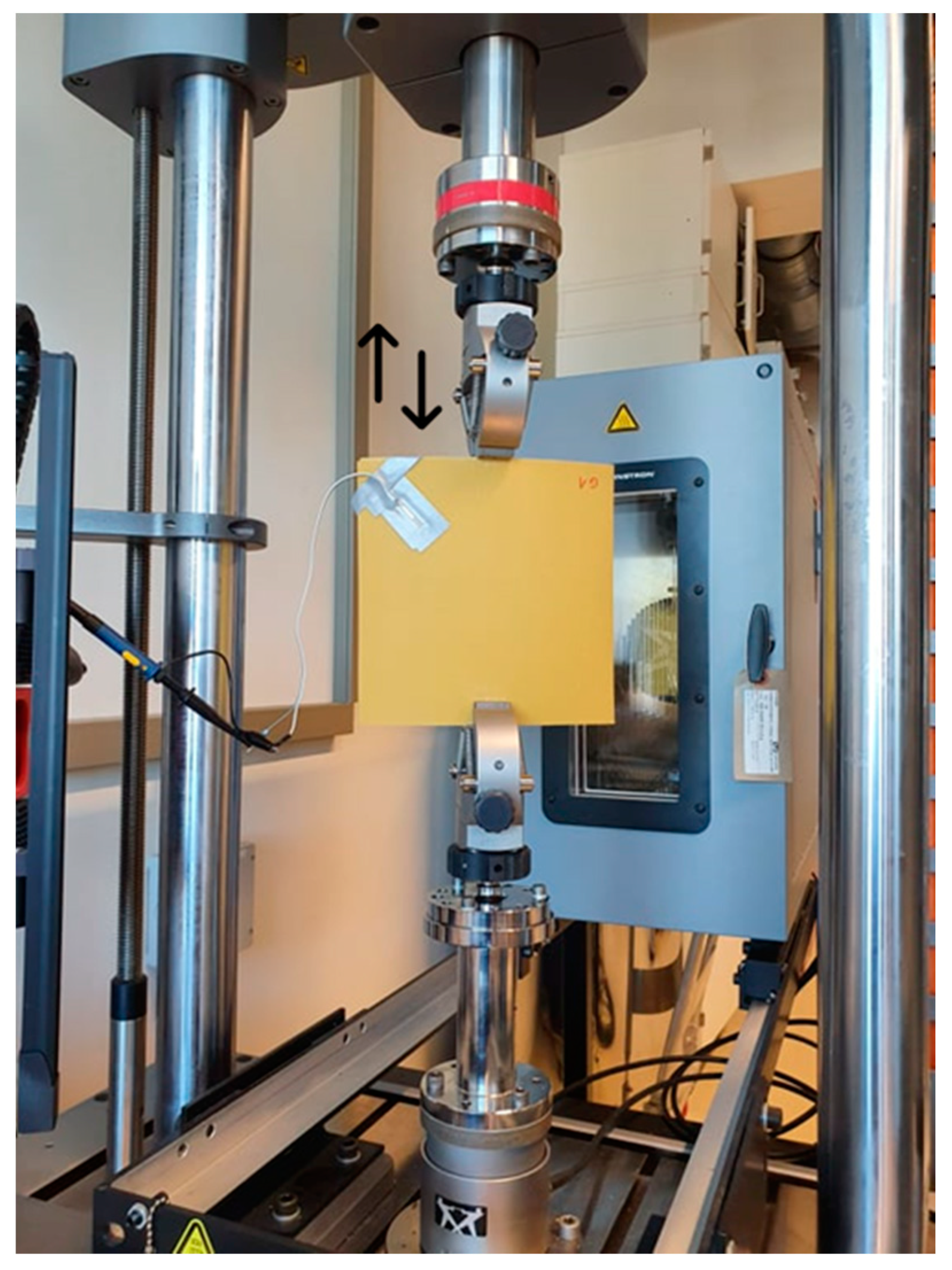
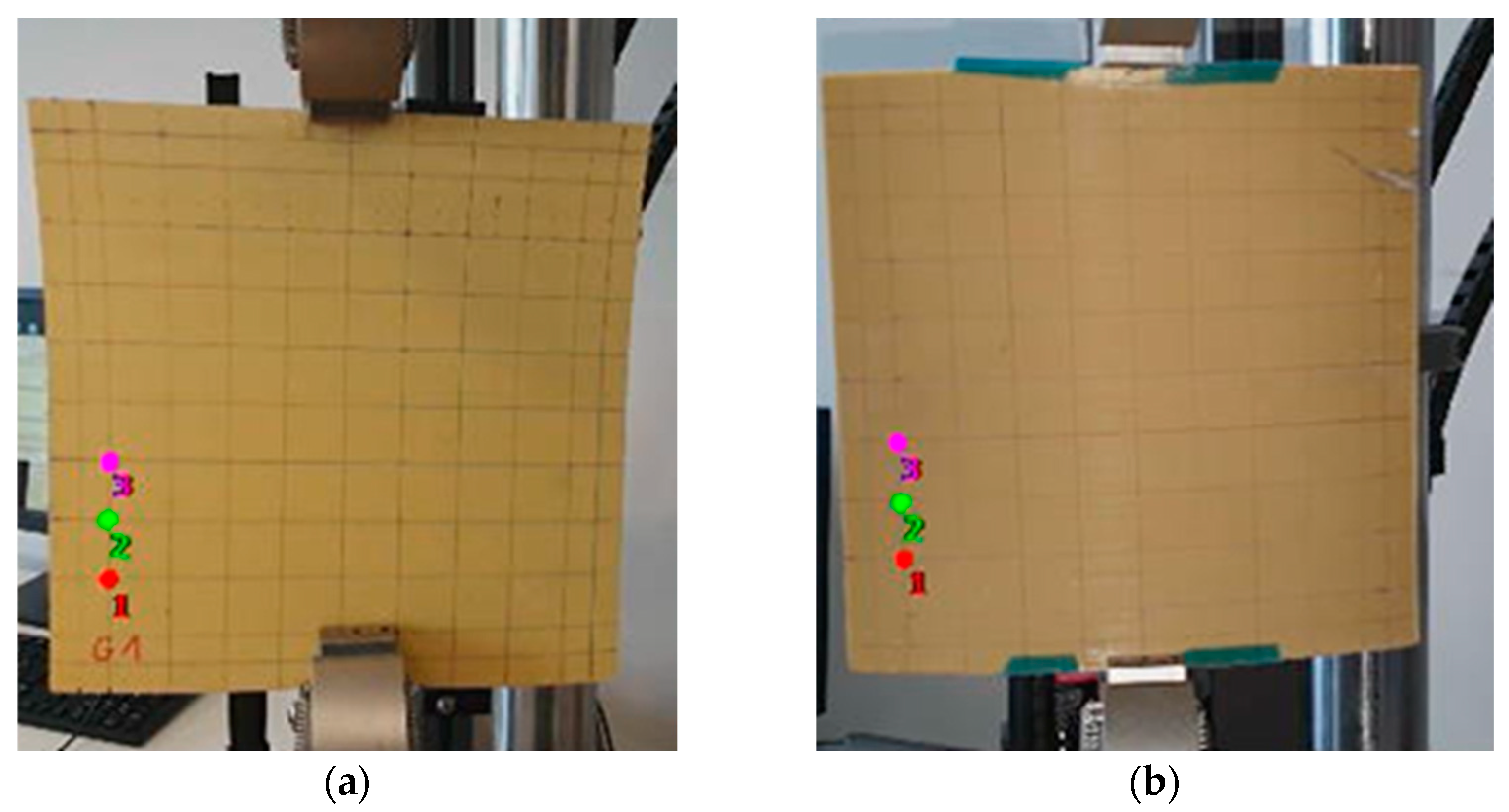
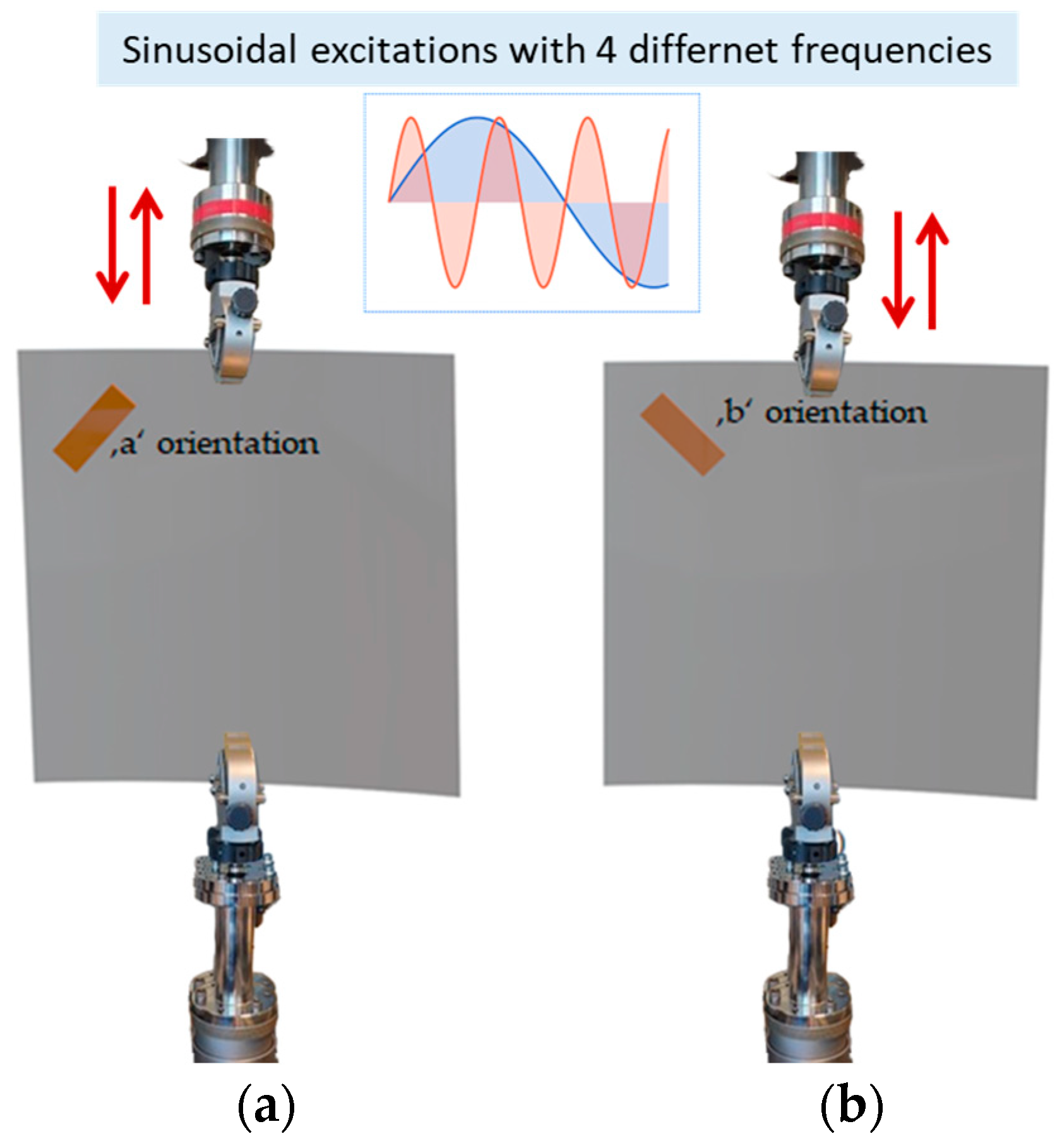
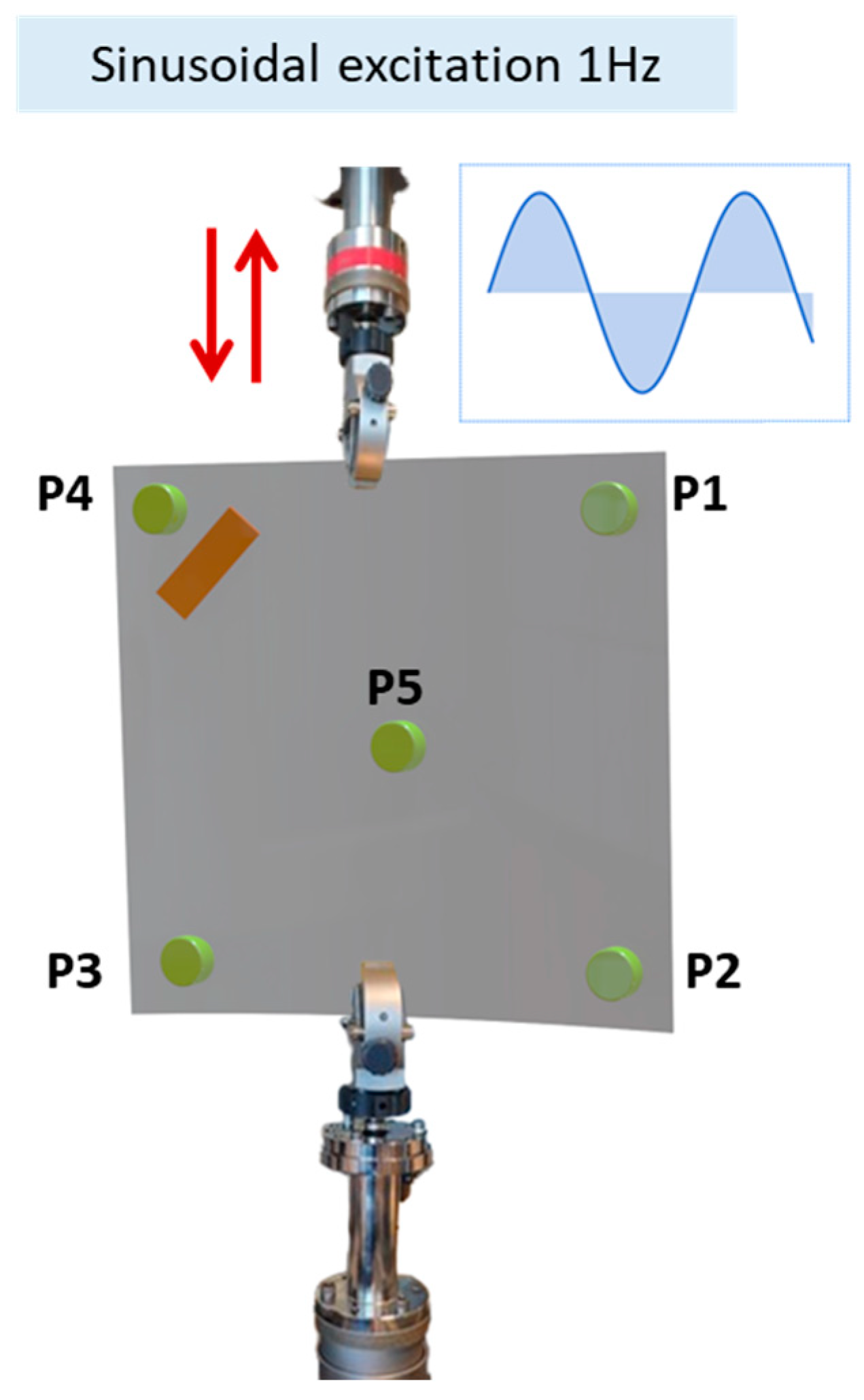
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Evaluation of the Displacement at the Level of the Plate
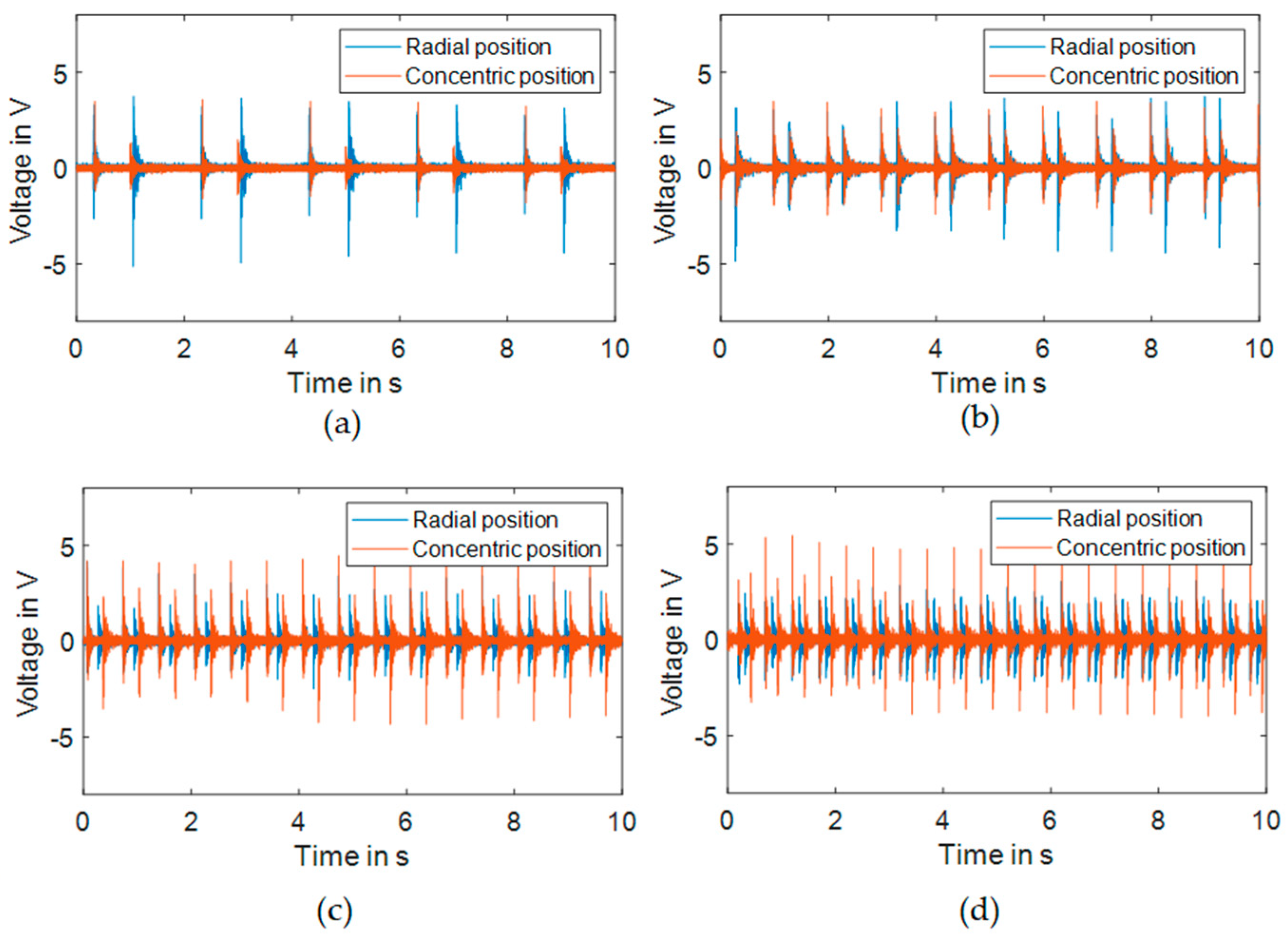
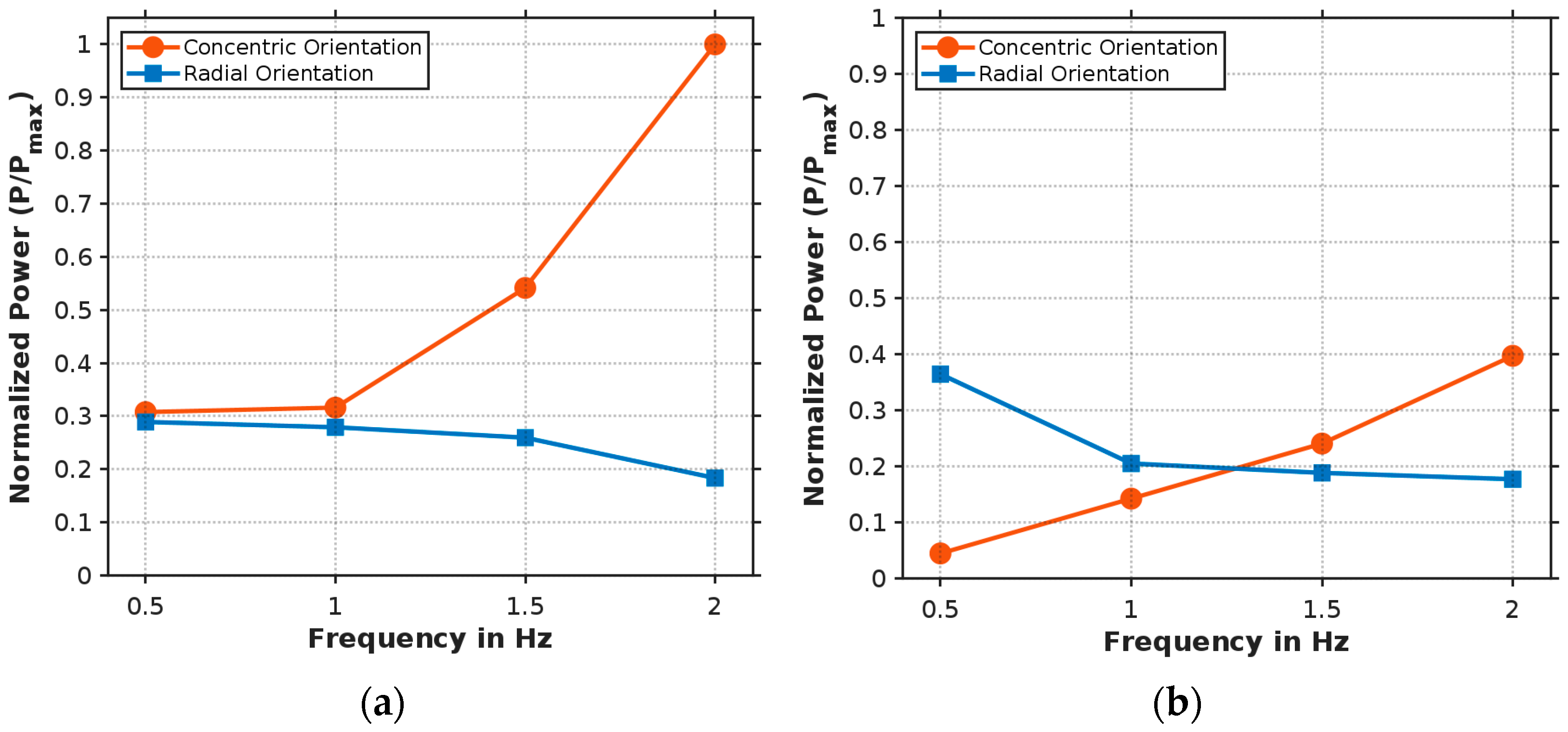
3.3. Effect of the Piezoelectric Direction on the Output Voltage
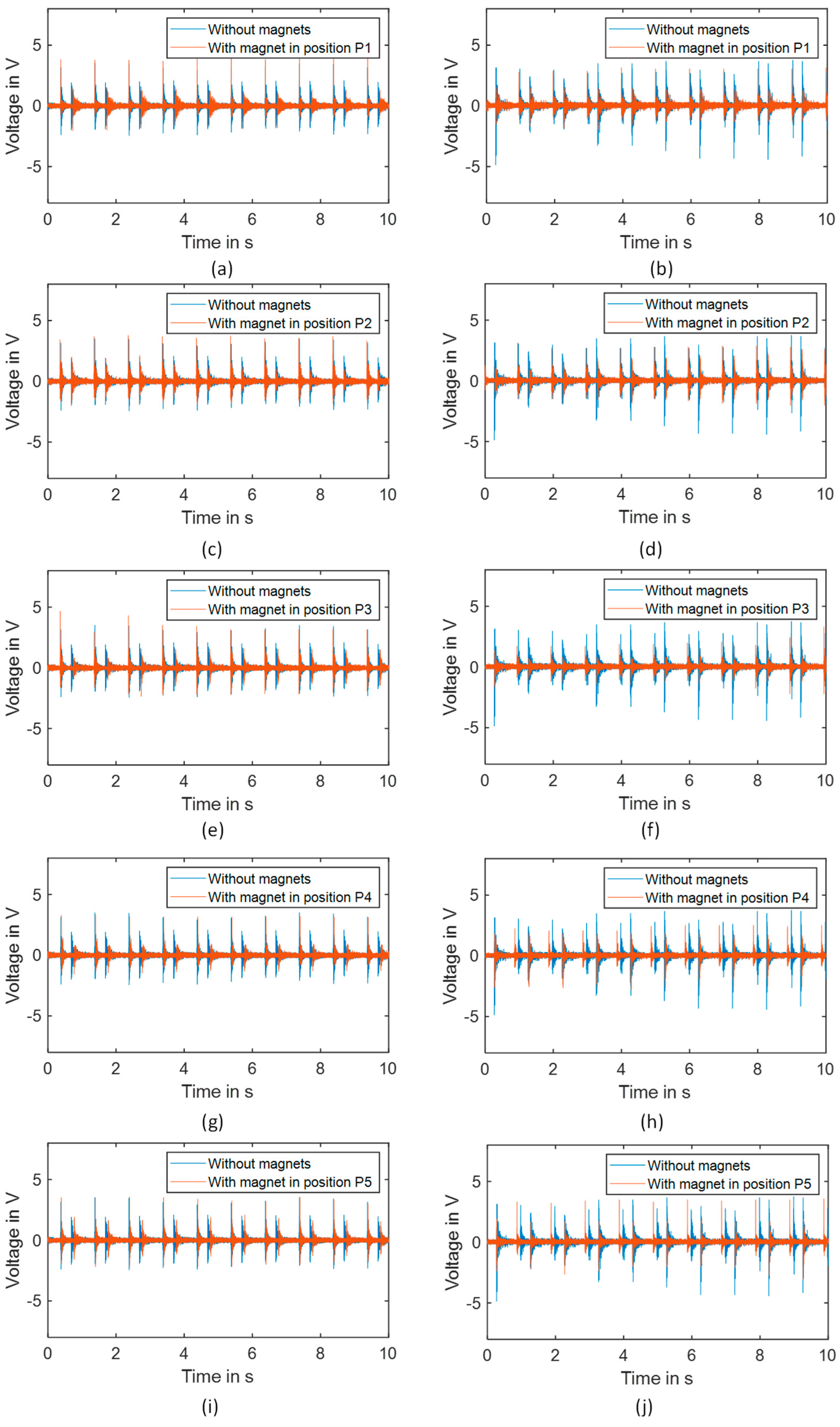
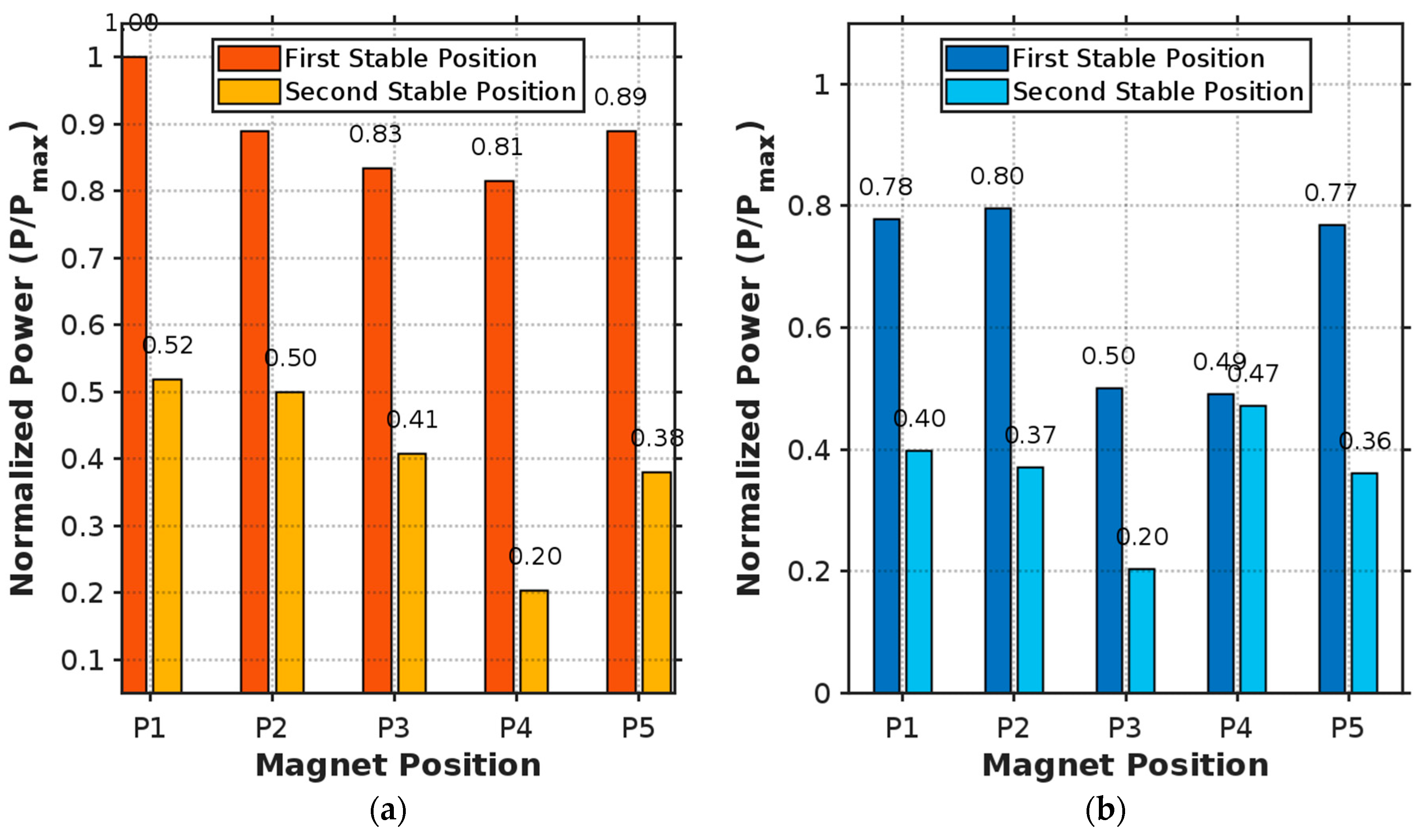
3.4. Effect of Additional Mass on the Output Voltage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ye, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, M.; Zhong, X. Poly-stable energy harvesting based on synergetic multistable vibration. Commun. Phys. 2019, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erturk, A.; Hoffmann, J.; Inman, D.J. A piezomagnetoelastic structure for broadband vibration energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 254102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottone, F.; Vocca, H.; Gammaitoni, L. Nonlinear energy harvesting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 080601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litak, G.; Margielewicz, J.; Gąska, D.; Wolszczak, P.; Zhou, S. Multiple solutions of the tristable energy harvester. Energies 2021, 14, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.M.; Ali, S.F.; Arockiarajan, A. Influence of asymmetric potential on multiple solutions of the bi-stable piezoelectric har-vester. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2022, 231, 1443–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, M.; Mitura, A.; Romeo, F.; Warmiński, J. Nonlinear dynamics of bistable composite cantilever shells: An experimental and modelling study. J. Sound Vib. 2022, 526, 116779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syta, A.; Bowen, C.R.; Kim, H.A.; Rysak, A.; Litak, G. Responses of bistable piezoelectric-composite energy harvester by means of recurrences. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 76–77, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, P.F.; Bowen, C.R.; Salo, A.I.T.; Kim, H.A.; Ive, A. Bistable composite laminates: Effects of laminate composition on cured shape and response to thermal load. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 2220–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, D.N.; Salo, A.I.T.; Bowen, C.R.; Kim, H.A. Characterisation and modelling of the cured shapes of arbitrary layup bistable composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, A.F.; Hagedorn, P.; Erturk, A.; Inman, D.J. A piezoelectric bistable plate for nonlinear broadband energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 104102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syta, A.; Bowen, C.R.; Kim, H.A.; Rysak, A.; Litak, G. Experimental analysis of the dynamical response of energy harvesting devices based on bistable laminated plates. Meccanica 2015, 50, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowiec, M.; Rysak, A.; Betts, D.N.; Bowen, C.R.; Kim, H.A.; Litak, G. Complex response of the bistable laminated plate: Multiscale entropy analysis. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2014, 129, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysak, A.; Bradai, S.; Bieniaś, J.; Jakubczak, P.; Litak, G.; Kanoun, O. Study of bistability behavior relative to the size of the composite plates. In Proceedings of the 17th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Monastir, Tunisia, 20–23 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, D.N.; Kim, H.A.; Bowen, C.R.; Inman, D.J. Optimal configurations of bistable piezo-composites for energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 114104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, S.A.; Inman, D.J. A review on bistable composite laminates for morphing and energy harvesting. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2015, 67, 060803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Suh, I.-Y.; Xiao, X.; Pang, F.; Jeon, J.; Cho, D.S.; Kwon, Y.H.; Kim, S.-W. Triboelectric and piezoelectric technologies for self-powered microbial disinfection. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowska, B.; Ostapiuk, M.; Jakubczak, P.; Droździel, M. The durability of an organic-inorganic sol-gel interlayer in Al-GFRP-CFRP laminates in a saline environment. Materials 2019, 12, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieniaś, J.; Jakubczak, P.; Droździel, M.; Surowska, B. Interlaminar shear strength and failure analysis of aluminium-carbon laminates with a glass fiber interlayer after moisture absorption. Materials 2020, 13, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droździel, M.; Podolak, P.; Nardi, D.; Jakubczak, P. The mechanical effects of kissing bonding defects in hybrid metal-composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2021, 269, 114027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Tensile Strength [MPa] | Young’s Modulus [GPa] | Poisson’s Ratio | Shear Strength [MPa] | Shear Module [GPa] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | 90° | 0° | 90° | 0° | 90° | ±45° | ±45° |
| 1534 | 75 | 46 | 15 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 58 | 5.23 |
| Composite Bistable Plates | Dimensions (a × b) [mm] | Layers Configurations | Plates Thickness (t) [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 200 × 200 | 0/90 | 0.5 |
| GM1 | 200 × 200 | 0/Al/90 | 0.8 |
| Piezolayer Orientation | Cyclic Activation Frequency | Location of Magnet | Amplitude Statistics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Maximum | Standard Deviation | |||
| Concentric | 0.5 Hz | P1 | 0.1045 | 4.8842 | 0.2015 |
| 1 Hz | P1 | 0.1247 | 4.3558 | 0.2174 | |
| 1.5 Hz | P1 | 0.1391 | 4.9333 | 0.2370 | |
| 2 Hz | P1 | 0.1729 | 4.8445 | 0.3143 | |
| Concentric | 1 Hz | P1 | 0.1247 | 4.3558 | 0.2173 |
| P2 | 0.1339 | 3.7783 | 0.2353 | ||
| P3 | 0.1206 | 4.6667 | 0.2166 | ||
| P4 | 0.1101 | 3.6006 | 0.1899 | ||
| P5 | 0.1136 | 3.6895 | 0.1976 | ||
| Radial | 1 Hz | P1 | 0.1438 | 3.3189 | 0.2218 |
| P2 | 0.1451 | 3.14097 | 0.2406 | ||
| P3 | 0.1202 | 3.853 | 0.1846 | ||
| P4 | 0.147 | 2.7335 | 0.253 | ||
| P5 | 0.1255 | 3.7642 | 0.2261 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bradai, S.; Naifar, S.; Wolszczak, P.; Bieniaś, J.; Jakubczak, P.; Rysak, A.; Litak, G.; Kanoun, O. Kinetic Energy Harvesting with a Piezoelectric Patch Using a Bistable Laminate. Micromachines 2025, 16, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040410
Bradai S, Naifar S, Wolszczak P, Bieniaś J, Jakubczak P, Rysak A, Litak G, Kanoun O. Kinetic Energy Harvesting with a Piezoelectric Patch Using a Bistable Laminate. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040410
Chicago/Turabian StyleBradai, Sonia, Slim Naifar, Piotr Wolszczak, Jarosław Bieniaś, Patryk Jakubczak, Andrzej Rysak, Grzegorz Litak, and Olfa Kanoun. 2025. "Kinetic Energy Harvesting with a Piezoelectric Patch Using a Bistable Laminate" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040410
APA StyleBradai, S., Naifar, S., Wolszczak, P., Bieniaś, J., Jakubczak, P., Rysak, A., Litak, G., & Kanoun, O. (2025). Kinetic Energy Harvesting with a Piezoelectric Patch Using a Bistable Laminate. Micromachines, 16(4), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040410












