Pico-Scale Digital PCR on a Super-Hydrophilic Microarray Chip for Multi-Target Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
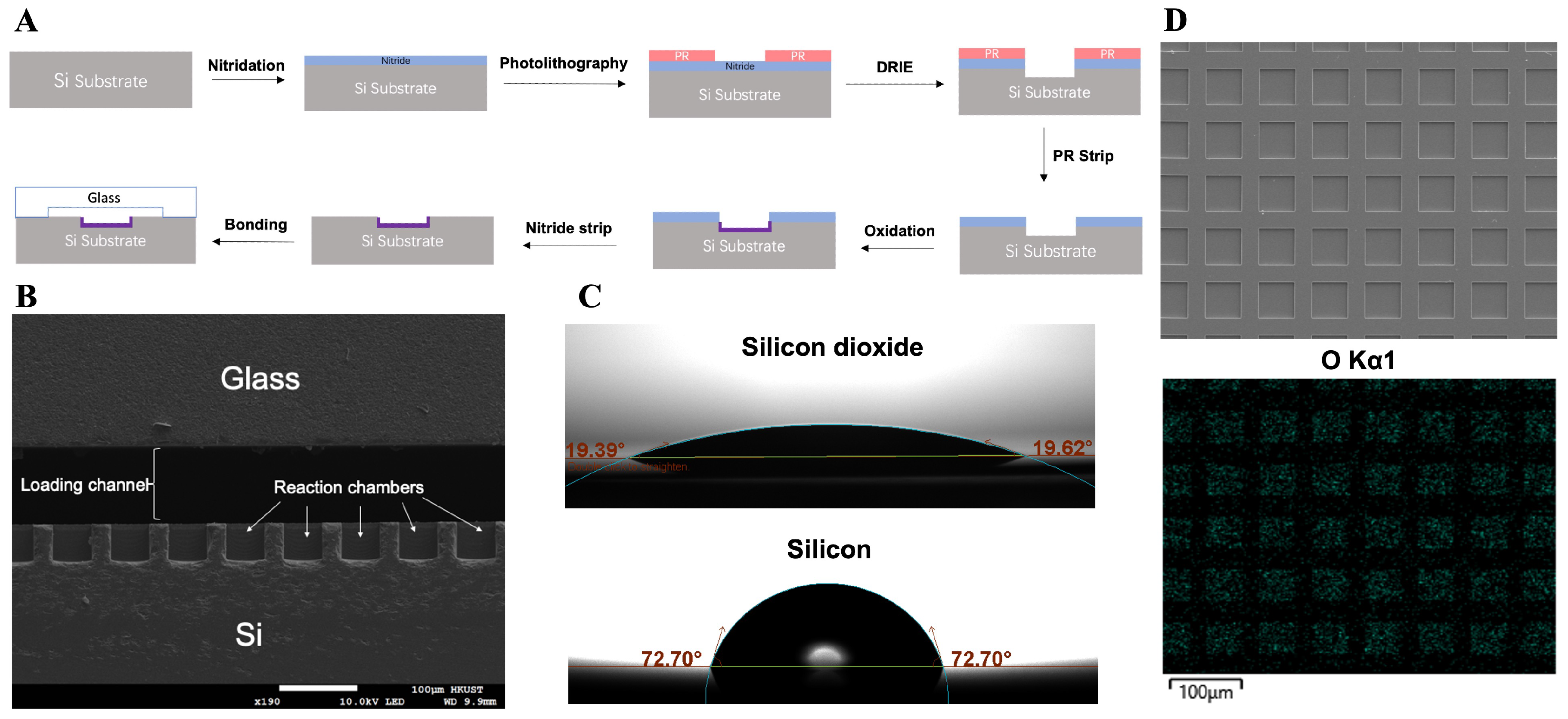
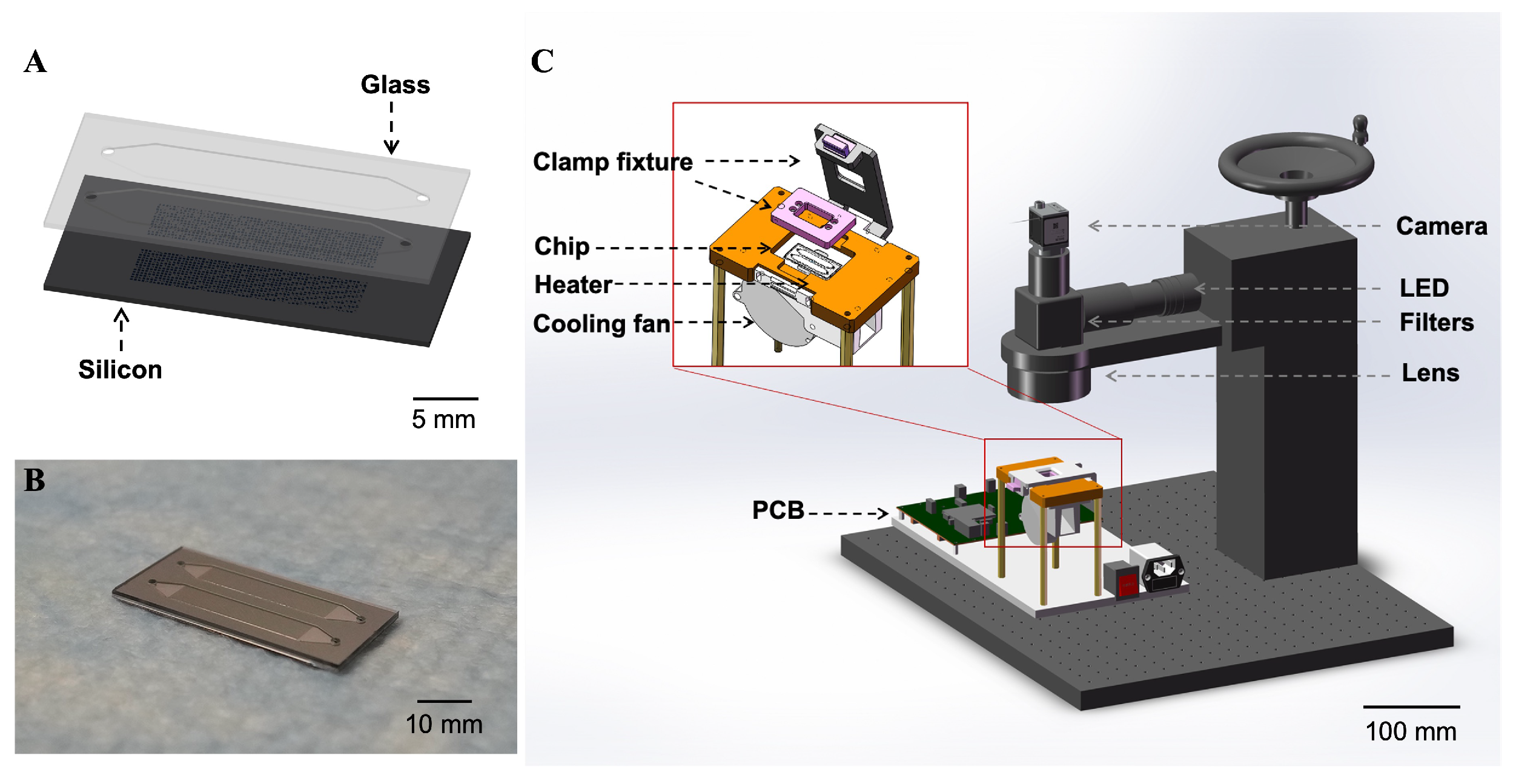
2.1. Fabrication of the dPCR Chip
2.2. Set Up of the dPCR Reaction and Detection System
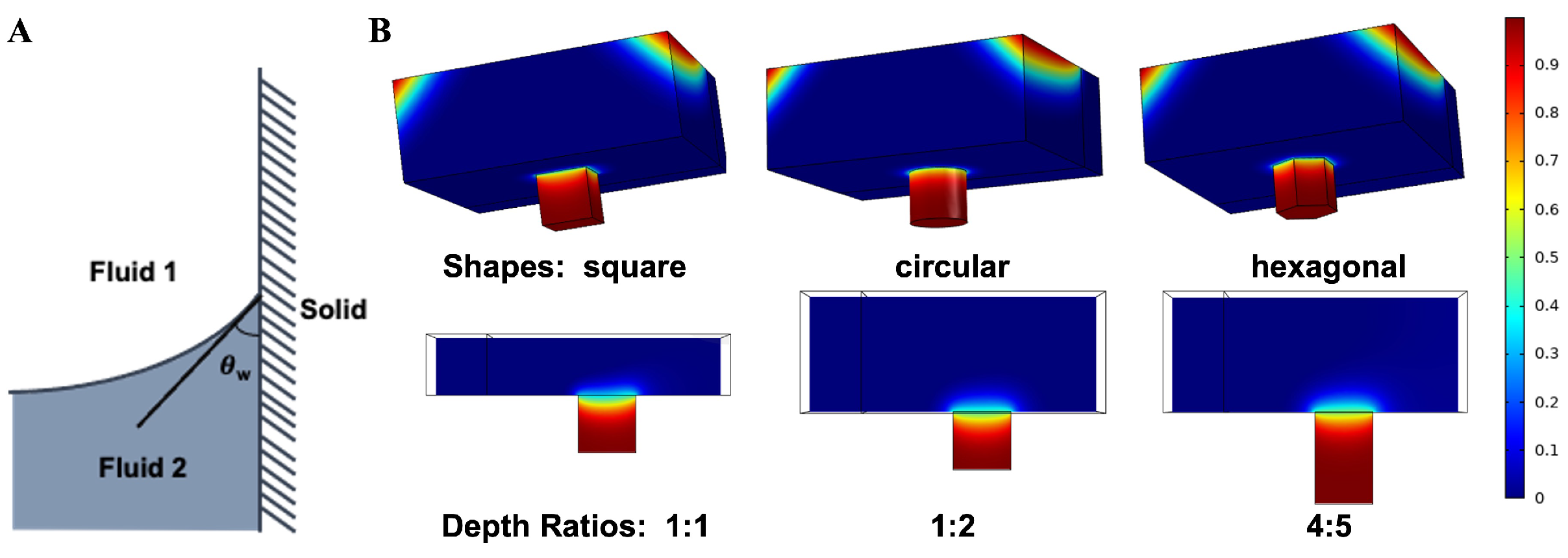
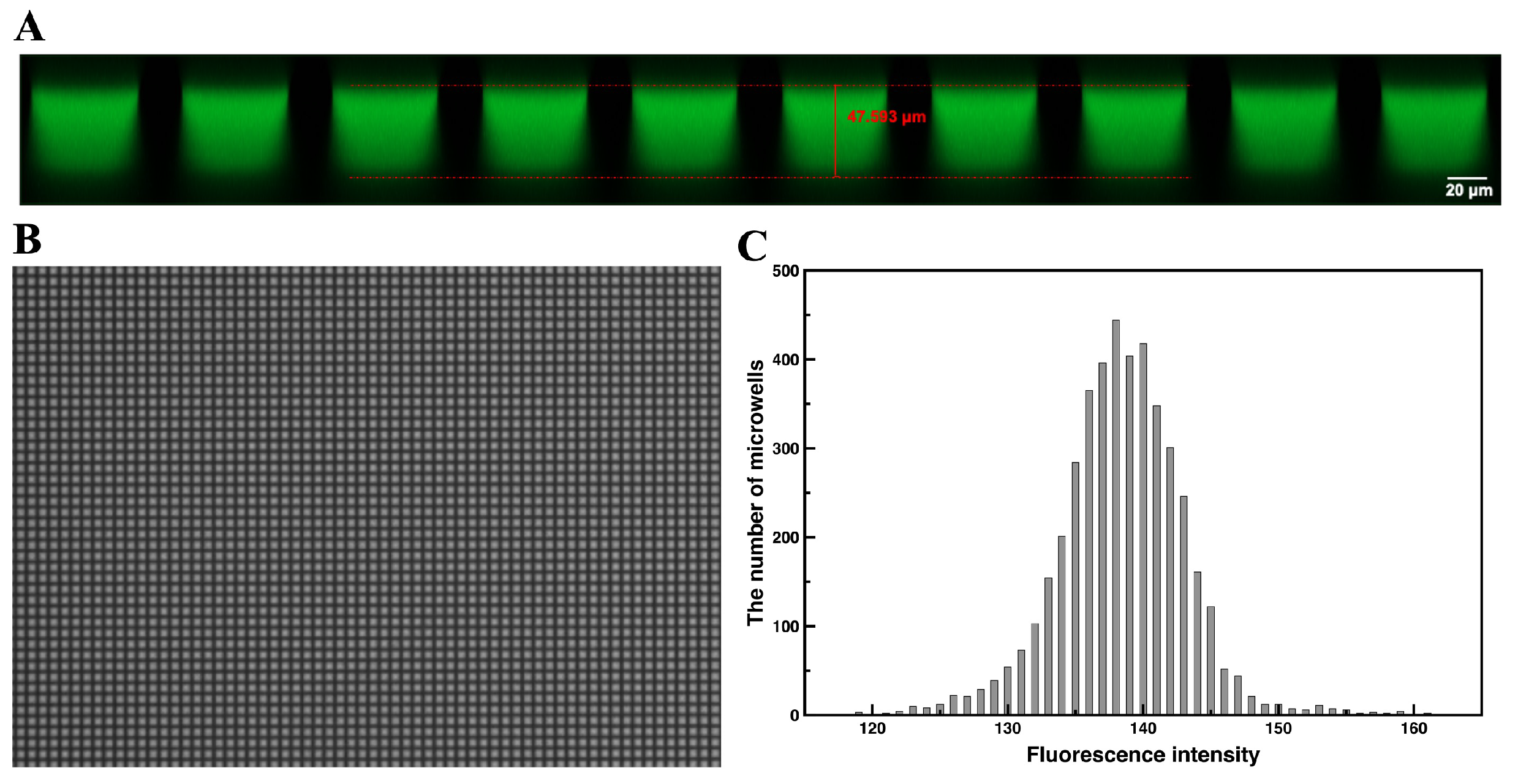
2.3. On-Chip Loading and Distribution
2.4. On-Chip dPCR Analysis
2.4.1. dPCR of HBV
2.4.2. dPCR of Multiple Targets
3. Results
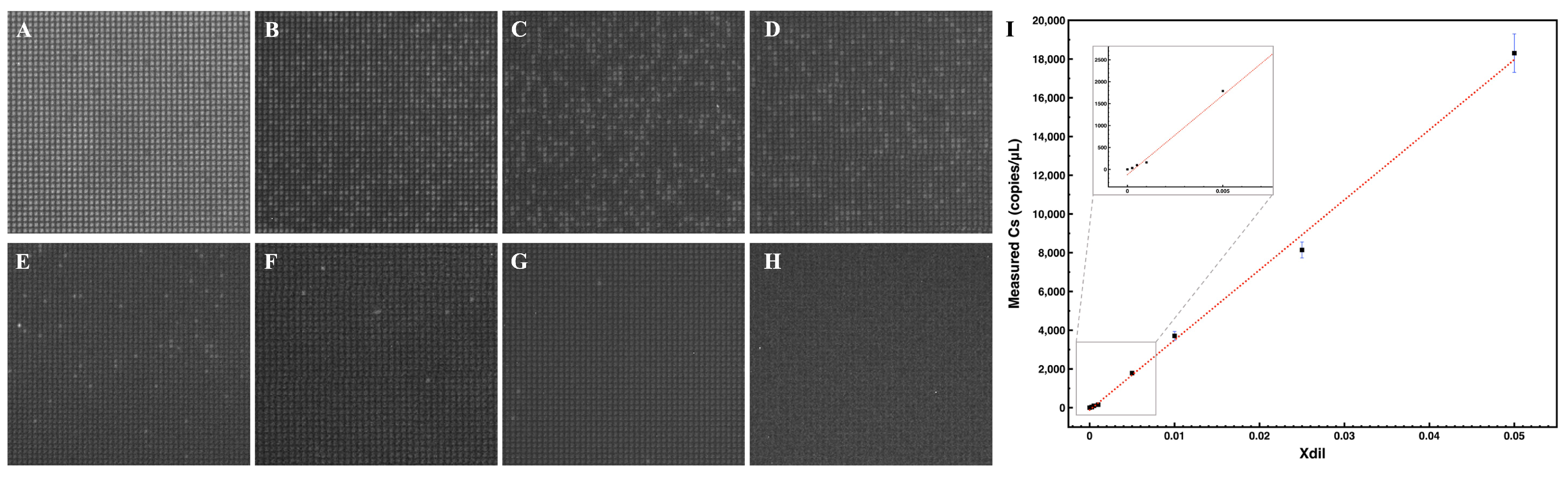
3.1. On-Chip Loading and Distribution
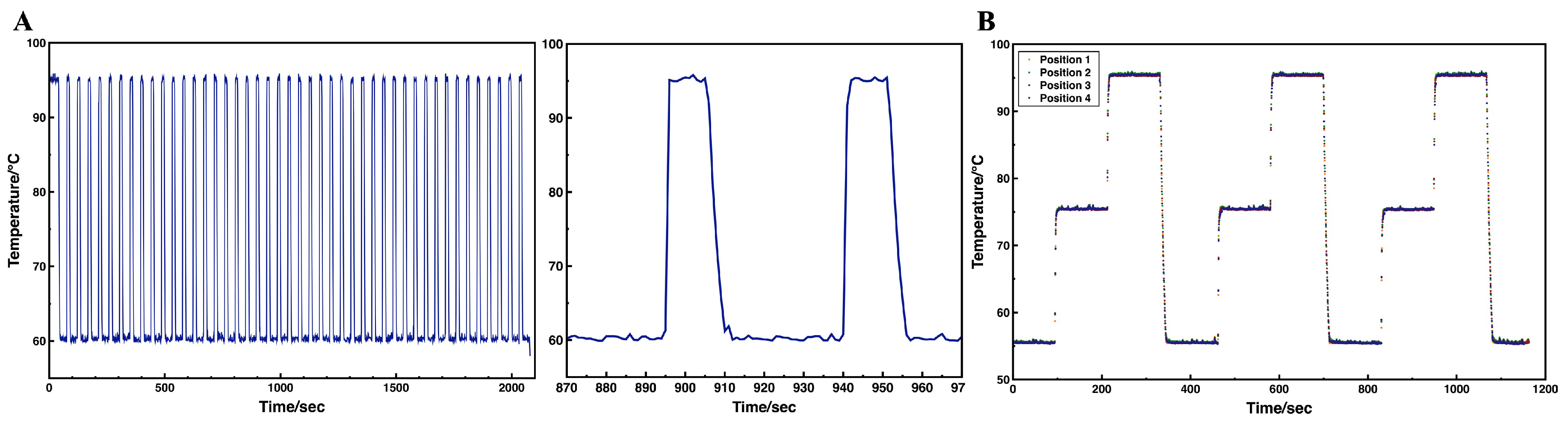
3.2. On-Chip Thermal Performance
3.3. On-Chip dPCR Analysis
3.3.1. dPCR of HBV
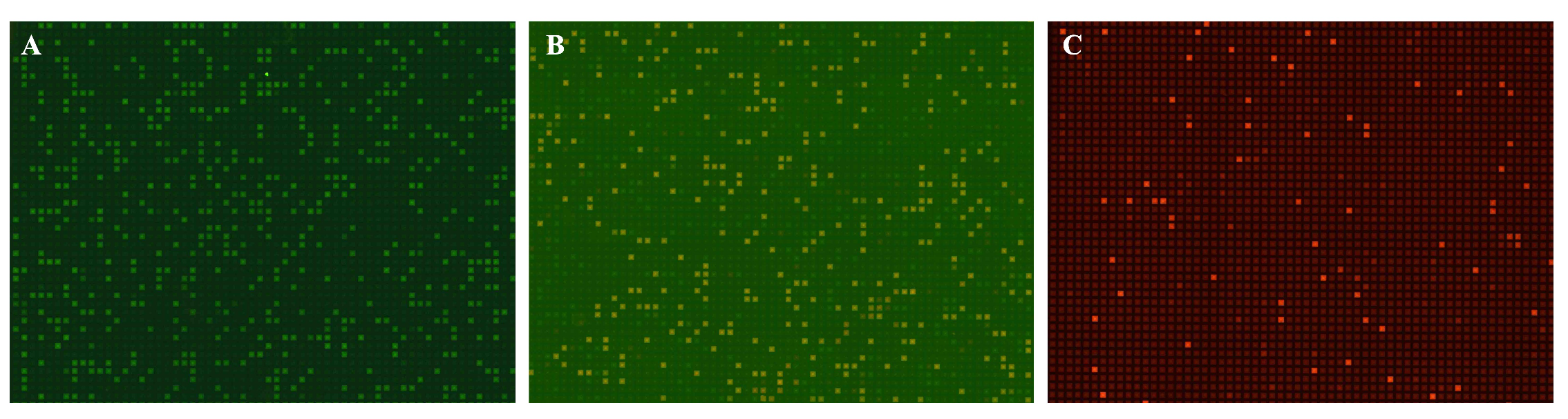
3.3.2. dPCR of Multiple Targets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| dPCR | Digital polymerase chain reaction |
| qPCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| MEMS | Micro-electro-mechanical systems |
| cdPCR | Chamber-based digital polymerase chain reaction |
| ddPCR | Droplet-based digital polymerase chain reaction |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| BRAF | B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| FAM | 5-Carboxyfluorescein |
| TAMARA | 5-Carboxytetramethylrhodamine |
| Cy5 | Invitrogen Cyanine5 |
| LPCVD | Low pressure chemical vapor deposition |
| DRIE | Deep reactive ion etching |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| EDX | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| ST | Single template |
| NTC | No template control |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| POCT | Point-of-care testing |
References
- Basu, A.S. Digital assays part I: Partitioning statistics and digital PCR. Slas Technol. Transl. Life Sci. Innov. 2017, 22, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Digital PCR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9236–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, A.A. Digital PCR: A brief history. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2014, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Deng, R.; Ma, X.; Fan, B.; Liu, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y. A highly integrated digital PCR system with on-chip heating for accurate DNA quantitative analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 253, 116167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, L.; Brodsky, J.; Gablech, I.; Xu, F.; Li, Z.; Korabecna, M.; Neuzil, P. Quantitative or digital PCR? A comparative analysis for choosing the optimal one for biosensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 174, 117676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Li, N.; Lin, J.M. Advances in droplet digital polymerase chain reaction on microfluidic chips. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 1258–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, N.; Lee, Y.T.; Ni, Y.; Koochekpour, R.; Zhu, Y.; Tseng, H.R.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, H. A circulating tumor cell-based digital assay for the detection of EGFR T790M mutation in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5636–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veyer, D.; Wack, M.; Mandavit, M.; Garrigou, S.; Hans, S.; Bonfils, P.; Tartour, E.; Bélec, L.; Wang-Renault, S.F.; Laurent-Puig, P.; et al. HPV circulating tumoral DNA quantification by droplet-based digital PCR: A promising predictive and prognostic biomarker for HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.Y.; Vu, T.; Grunwald, J.T.; Toledano, M.; Zimak, J.; Toosky, M.; Shen, B.; Zell, J.A.; Gratton, E.; Abram, T.J.; et al. An ultrasensitive test for profiling circulating tumor DNA using integrated comprehensive droplet digital detection. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 993–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Pekin, D.; Skhiri, Y.; Baret, J.C.; Le Corre, D.; Mazutis, L.; Salem, C.B.; Millot, F.; El Harrak, A.; Hutchison, J.B.; Larson, J.W.; et al. Quantitative and sensitive detection of rare mutations using droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2156–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basanisi, M.G.; La Bella, G.; Nobili, G.; Raele, D.A.; Cafiero, M.A.; Coppola, R.; Damato, A.M.; Fraccalvieri, R.; Sottili, R.; La Salandra, G. Detection of Coxiella burnetii DNA in sheep and goat milk and dairy products by droplet digital PCR in south Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 366, 109583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; He, X.; Shi, L.; Zhao, L. Quantitative detection of trace VBNC Cronobacter sakazakii by immunomagnetic separation in combination with PMAxx-ddPCR in dairy products. Food Microbiol. 2021, 99, 103831. [Google Scholar]
- Alteri, C.; Cento, V.; Antonello, M.; Colagrossi, L.; Merli, M.; Ughi, N.; Renica, S.; Matarazzo, E.; Di Ruscio, F.; Tartaglione, L.; et al. Detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2 by droplet digital PCR in real-time PCR negative nasopharyngeal swabs from suspected COVID-19 patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlak, R.H.; Jerome, K.R. Viral diagnostics in the era of digital polymerase chain reaction. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didelot, A.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Lupo, A.; Pekin, D.; Li, X.; Atochin, I.; Srinivasan, P.; Zhong, Q.; Olson, J.; Link, D.R.; et al. Multiplex picoliter-droplet digital PCR for quantitative assessment of DNA integrity in clinical samples. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewhey, R.; Warner, J.B.; Nakano, M.; Libby, B.; Medkova, M.; David, P.H.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Samuels, M.L.; Hutchison, J.B.; Larson, J.W.; et al. Microdroplet-based PCR enrichment for large-scale targeted sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Madic, J.; Zocevic, A.; Senlis, V.; Fradet, E.; Andre, B.; Muller, S.; Dangla, R.; Droniou, M. Three-color crystal digital PCR. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2016, 10, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, B.J.; Ness, K.D.; Masquelier, D.A.; Belgrader, P.; Heredia, N.J.; Makarewicz, A.J.; Bright, I.J.; Lucero, M.Y.; Hiddessen, A.L.; Legler, T.C.; et al. High-throughput droplet digital PCR system for absolute quantitation of DNA copy number. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8604–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bio-Rad. QX200 Droplet Digital Systems|Bio-Rad Droplet Digital™ PCR. Available online: https://www.bio-rad.com/life-science/droplet-digital-pcr/droplet-digital-pcr-budgeting?s_kwcid=AL!18120!3!709245417040!e!!g!!biorad%20qx200!21582536543!166846479060&WT.mc_id=241230044812&WT.srch=1&WT.knsh_id=_kenshoo_clickid_&gclid=CjwKCAiAnpy9BhAkEiwA-P8N4iqMn39GauYe6yT2ptRNOXMJwsILqF2gUYyIvAOxAiSTfNUaTG0vSBoCuWAQAvD_BwE&gad_source=1 (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- DPBio. Nebula Digital PCR System. Available online: https://dp-bio.com/platform?id=4 (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- Awashra, M.; Elomaa, P.; Ojalehto, T.; Saavalainen, P.; Jokinen, V. Superhydrophilic/superhydrophobic droplet microarrays of low surface tension biofluids for nucleic acid detection. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 11, 2300596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. OpenArray Technology Overview. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.cn/cn/zh/home/life-science/pcr/real-time-pcr/real-time-openarray/open-array-technology.html?adobe_mc=MCMID%7C90839306120932686505880960015367277842%7CMCAID%3D30984116708B72AE-40000FB356BA8C90%7CMCORGID%3D5B135A0C5370E6B40A490D44%40AdobeOrg%7CTS=1614293705 (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- Broccanello, C.; Gerace, L.; Stevanato, P. QuantStudio™ 12K Flex OpenArray® System as a tool for high-throughput genotyping and gene expression analysis. Quant. Real-Time PCR Methods Protoc. 2020, 2065, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Song, Q.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Lou, K.; Liu, Y.; Wen, W. A rapid digital pcr system with a pressurized thermal cycler. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyries, K.A.; Tropini, C.; VanInsberghe, M.; Doolin, C.; Petriv, O.I.; Singhal, A.; Leung, K.; Hughesman, C.B.; Hansen, C.L. Megapixel digital PCR. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 649–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluidigm. High-Definition Biology; Span Research Through Validation on Biomark HD. Available online: https://fluidigm.my.salesforce.com/sfc/p/#700000009DAw/a/4u0000019cyo/7fyPz7QqSX_v76cIgM9qZxesAbtX5Z3JrJs6Fsyqd_8 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Arkles, B. Hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity and silane surface modification. Gelest Inc. 2011, 215, 547–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yang, S.; Xu, N.; Song, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wen, W. Fabrication of Cost-Effective Microchip-Based Device Using Sandblasting Technique for Real-Time Multiplex PCR Detection. Micromachines 2024, 15, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madadelahi, M.; Agarwal, R.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O.; Madou, M.J. A roadmap to high-speed polymerase chain reaction (PCR): COVID-19 as a technology accelerator. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 246, 115830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zec, H.; O’Keefe, C.; Ma, P.; Wang, T.H. Ultra-thin, evaporation-resistent PDMS devices for absolute quantification of DNA using digital PCR. In Proceedings of the 2015 Transducers-2015 18th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Anchorage, AK, USA, 21–25 June 2015; pp. 536–539. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Xian, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wen, W. A silicon-based PDMS-PEG copolymer microfluidic chip for real-time polymerase chain reaction diagnosis. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Tian, Q.; Yu, B.; Song, B.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, M.; Ma, C.; Jin, W.; et al. A nanoliter self-priming compartmentalization chip for point-of-care digital PCR analysis. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Xu, T.; Wu, L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Jian, X.; Li, X. Overcoming bubble formation in polydimethylsiloxane-made PCR chips: Mechanism and elimination with a high-pressure liquid seal. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2024, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.L.; Loganathan, N.; Agarwalla, S.; Yang, C.; Yuan, W.; Zeng, J.; Wu, R.; Wang, W.; Duraiswamy, S. Current commercial dPCR platforms: Technology and market review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2023, 43, 433–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Mileham, K.F.; Husain, H.; Costa, D.B.; Tracy, P.; Feeney, N.; Sholl, L.M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Redig, A.J.; et al. Assessment of Resistance Mechanisms and Clinical Implications in Patients with EGFR T790M–Positive Lung Cancer and Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopetz, S.; Grothey, A.; Yaeger, R.; Van Cutsem, E.; Desai, J.; Yoshino, T.; Wasan, H.; Ciardiello, F.; Loupakis, F.; Hong, Y.S.; et al. Encorafenib, binimetinib, and cetuximab in BRAF V600E–mutated colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Parameters | Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon | Silicon Dioxide | Glass | |
| 1 (mN/m) | 36.3636 | ||
| 2 (mN/m) | 50.66 | 73.77 | 60.94 |
| 3 (mN/m) | 24.620 | 31.361 | 14.119 |
| 3 (mN/m) | 29.056 | 52.818 | 39.375 |
| 4 (rad) | 1.4485 | 0.9396 | 0.8030 |
| Designs | Shapes | Depth Ratios | Velocities | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Square | Circular | Hexagonal | 1:1 | 1:2 | 4:5 | High | Middle | Low | |
| Filling rates (%) | 96.7338 | 96.7120 | 96.0452 | 92.82 | 96.7338 | 98.6455 | 96.7338 | 96.7674 | 97.4326 |
| Sample Names | FAM | TAMRA | Cy5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple templates | 13,031 | 14,104 | 2273 |
| BRAF ST | 12,494 | 0 | 6 |
| EGFR ST | 0 | 14,495 | 15 |
| GAPDH ST | 0 | 0 | 2280 |
| NTC | 0 | 0 | 17 |
| Multiple templates on Naica system | 13,616 | 15,083 | 2003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xian, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wong, Y.C.; Gao, Y.; Song, Q.; Xu, N.; Wen, W. Pico-Scale Digital PCR on a Super-Hydrophilic Microarray Chip for Multi-Target Detection. Micromachines 2025, 16, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040407
Xian Q, Zhang J, Wong YC, Gao Y, Song Q, Xu N, Wen W. Pico-Scale Digital PCR on a Super-Hydrophilic Microarray Chip for Multi-Target Detection. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040407
Chicago/Turabian StyleXian, Qingyue, Jie Zhang, Yu Ching Wong, Yibo Gao, Qi Song, Na Xu, and Weijia Wen. 2025. "Pico-Scale Digital PCR on a Super-Hydrophilic Microarray Chip for Multi-Target Detection" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040407
APA StyleXian, Q., Zhang, J., Wong, Y. C., Gao, Y., Song, Q., Xu, N., & Wen, W. (2025). Pico-Scale Digital PCR on a Super-Hydrophilic Microarray Chip for Multi-Target Detection. Micromachines, 16(4), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040407






