Compensation of Temperature-Induced Bias Drift in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscopes: An Inherent Data-Driven Architecture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Operation Mechanism of Hemispherical Resonant Gyroscope
3. Mapping Relationship Between Gyroscope Zero-Position Output and Temperature Change
3.1. Single Point Temperature Change and Gyro Bias
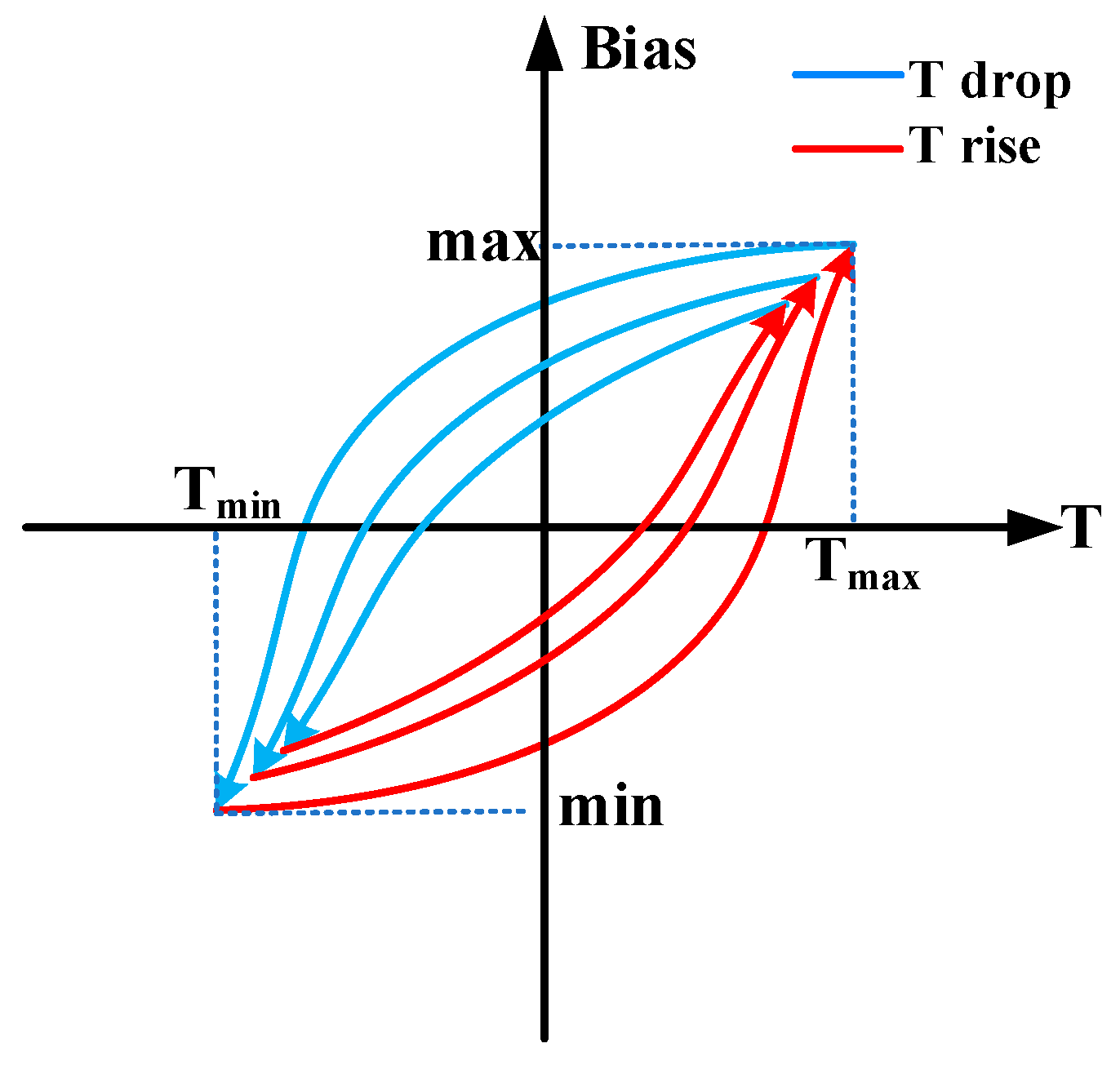
3.2. Hysteresis Effect of Temperature Sequence on Gyro Zero-Rate Output Bias
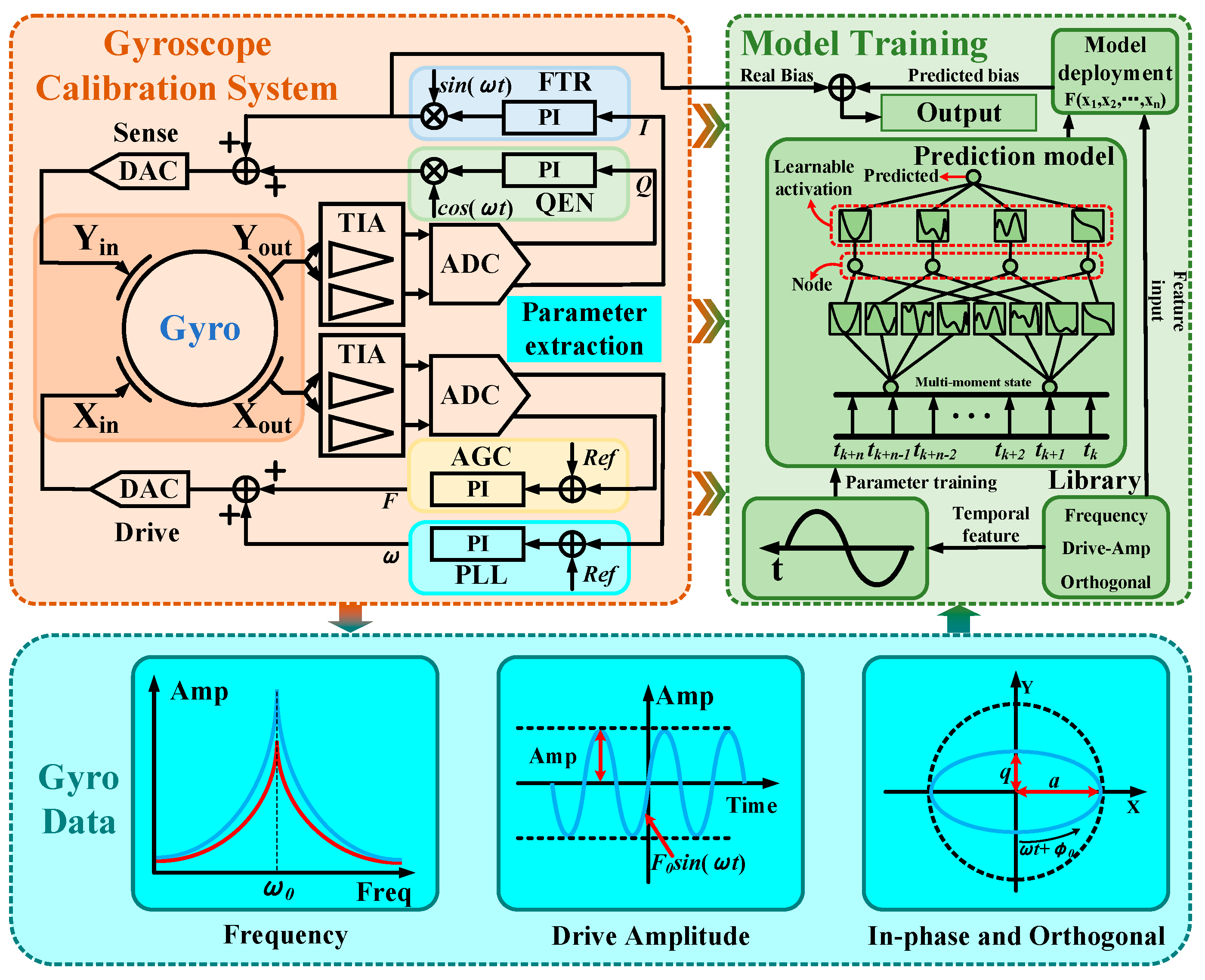
4. Research on Internal Parameter Drive and Zero-Rate Output Bias Compensation Method of Gyroscope
4.1. Temperature Change and Internal Compensation Parameter Selection
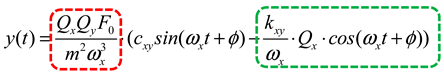
4.2. Look-Up Table Method Based on Gyro Resonant Frequency
4.3. Research on Least-Squares Algorithm with Time Series Characteristics
4.4. Intelligent Compensation Method Based on Internal Parameter Drive
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
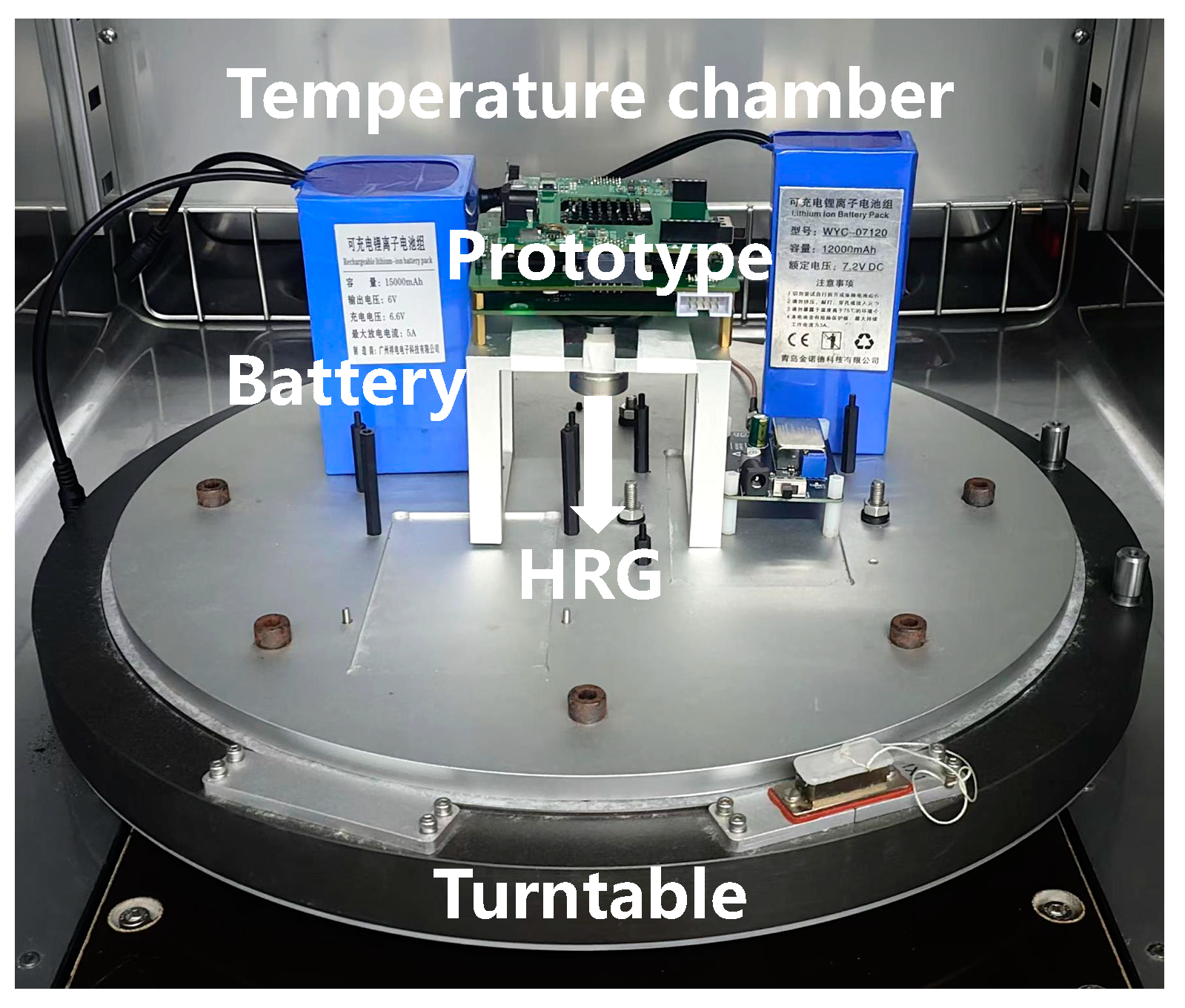
5.1. Experimental Design and Data Collection
5.2. Scheme Verification and Performance Comparison
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Z.; Xi, B.; Yi, G.; Wang, D. A novel model for fully closed-loop system of hemispherical resonator gyroscope under force-to-rebalance mode. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 9918–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelyaev, S.E.; Bodunov, B.P.; Bodunov, S.B. Solid-state wave gyroscope: A new-generation inertial sensor. In Proceedings of the Saint Petersburg International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems (ICINS) 2017, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 29–31 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshekhonov, V.G. The outlook for gyroscopy. Gyroscopy Navig. 2020, 11, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foloppe, Y.; Lenoir, Y. HRG Crystal™ dual core: Rebooting the INS revolution. In Proceedings of the DGON Inertial Sensors and Systems (ISS) 2019, Braunschweig, Germany, 10–11 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.A. Characterization, Control and Compensation of MEMS Rate and Rate-Integrating Gyroscopes. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Perelyaev, S.E. Current State of Wave Solid-State Gyroscopes. Development Prospects in Applied Gyroscopy. In Proceedings of the Saint Petersburg International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems (ICINS), Saint Petersburg, Russian, 29–31 May 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslov, A.A.; Merkuryev, I.V.; Maslov, D.A.; Podalkov, V.V. Scale factor of the wave solid-state gyroscope operating in the angular velocity sensor mode. In Proceedings of the Saint Petersburg International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems (ICINS), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 30 May–1 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhaye, F.; Girault, J.P. SpaceNaute®: HRG technological breakthrough for advanced space launcher inertial reference system. In Proceedings of the 25th Saint Petersburg International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems (ICINS), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 28–30 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T. Review on the current advances, key technology and future trends of hemispherical resonator gyroscope. Opt. Optoelectron. Technol. 2022, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.W.; Xie, W.N.; Xue, Z.W. Design and implementation of inertial measurement unit for satellites based on hemispherical resonant gyroscopes. J. Chin. Lnertial Technol. 2022, 30, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y. Current Status and Development Trend of Gyroscopes in Inertial Navigation in China. J. Sens. Technol. Appl. 2021, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chi, X.; Cui, J.; Lin, L.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yan, G. Research on temperature dependent characteristics and compensation methods for digital gyroscope. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Sensing Technology, Taipei, China, 30 November–3 December 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khooshehmehri, A.; Eslami Majd, A.; Arabsheybani, E. Thermo-elastic damping and anchor loss in the operational modes of a hemispherical shell resonator. J. Comput. Appl. Res. Mech. Eng. (JCARME) 2023, 12, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yi, G.; Zhu, W. An accurate thermoelastic model and thermal output error analysis of a hemispherical resonator gyroscope under varying temperatures. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 170, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Deng, K.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Tang, X.; Luo, H. Self-calibration of hemispherical resonator gyroscopes under drastic changes of ambient temperature based on mode reversal. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 366, 114986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Mei, C. A Review of Theoretical Methods for Resonator Modeling of Hemispherical Resonator Gyro. J. Proj. Rocket. Missiles Guid. 2024, 44, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianmao, X.; Haipeng, Z.; Junzhong, S. Periodic error compensation for quartz MEMS gyroscope drift of INS. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2007, 20, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Xi, B.Q.; Ren, S.Q.; Wang, C.H. Precision enhancement by compensation of hemispherical resonator gyroscope dynamic output errors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2516510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslov, A.A.; Maslov, D.A.; Ninalalov, I.G.; Merkuryev, I.V. Hemispherical resonator gyros (an overview of publications). Gyroscopy Navig. 2023, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkal, D.; Ahamed, M.J.; Ardakani, M.H.A.; Askari, S.; Shkel, A.M. Demonstration of 1 million Q-factor on microglassblown wineglass resonators with out-of-plane electrostatic transduction. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 24, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Singh, S.; Nagourney, T.; Woo, J.K.; Darvishian, A.; Shiari, B.; Najafi, K. High-Q navigation-grade fused-silica micro birdbath resonator gyroscope. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Sensors, Sydney, Australia, 31 October–3 November 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, J.; Wu, J.; Tan, J. Dynamic Friction-Slip Model Based on Contact Theory. Machines 2022, 10, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wang, N.; Xie, R.; Wei, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, C. Study on the Mechanism of Energy Dissipation in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscope. Sensors 2025, 25, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Su, Z.; Yao, X.; Chu, S. Research on the Configuration Optimization of All-Metal Micro Resonant Hemisphere. Sensors 2024, 24, 7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Wu, Z. Self-compensation of bias temperature drift in hemispherical resonator gyro. Aerosp. Control Appl. 2018, 44, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.S.; Jiang, Y.J.; Sun, Z.Q. Modelling Temperature Drift of HRG Based on AR Multi-Variable Model. Chin. J. Sens. Actuators 2009, 22, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, D.; Kong, L.; Hu, Y. Silicon microgyroscope temperature prediction and control system based on BP neural network and Fuzzy-PID control method. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 025101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, L. Temperature compensation method of laser gyroscope based on PSO-BP neural network. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2022, 30, 652–657. [Google Scholar]
- Trusov, A.A.; Phillips, M.R.; Mccammon, G.H. Continuously self-calibrating CVG system using hemispherical resonator gyroscopes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (ISISS) Proceedings, Hapuna Beach, HI, USA, 23–26 March 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.H.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, C.Q. Optimization of Amplitude Control Method of Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscopes Under Force-to-rebalance Mode. Piezoelectrics Acoustooptics 2020, 42, 197. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.X.; Wang, X.L.; Weng, H.N. Temperature compensation of MEMS gyroscope based ongrey model and RBF neural network. J. Chin. Inertial Technol. 2010, 18, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Yang, G.; Cai, Q.; Tu, Y. Nonlinearity Harmonic Error Compensation Method Based on Intelligent Identification for Rate Integrating Resonator Gyroscope. Actuators 2025, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Vaidya, S. Kan: Kolmogorov-arnold networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.19756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Li, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, T.; He, X. Research of Frequency Splitting Caused by Uneven Mass of Micro-Hemispherical Resonator Gyro. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Li, S. Temperature modeling compensation and sensitivity analysis of HRG based on real time sliding window. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2023, 31, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



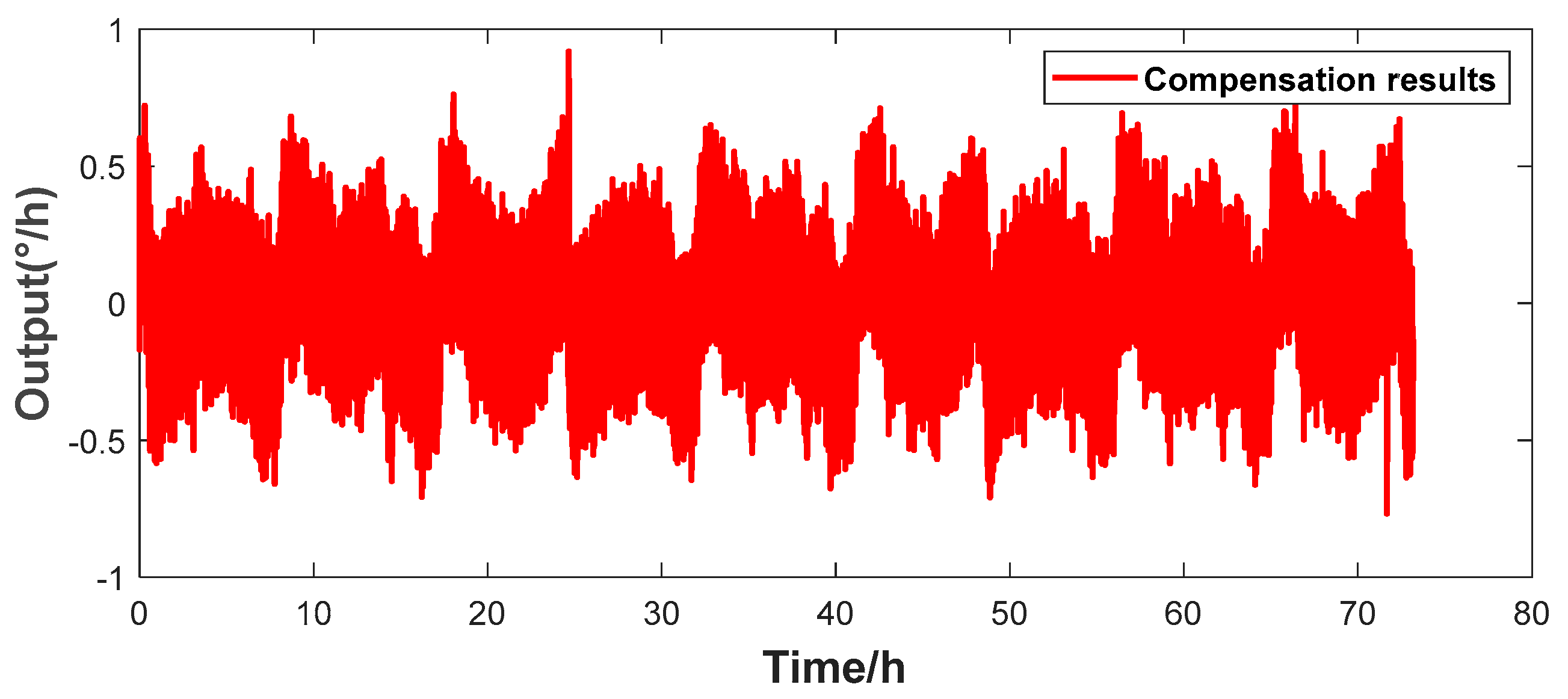
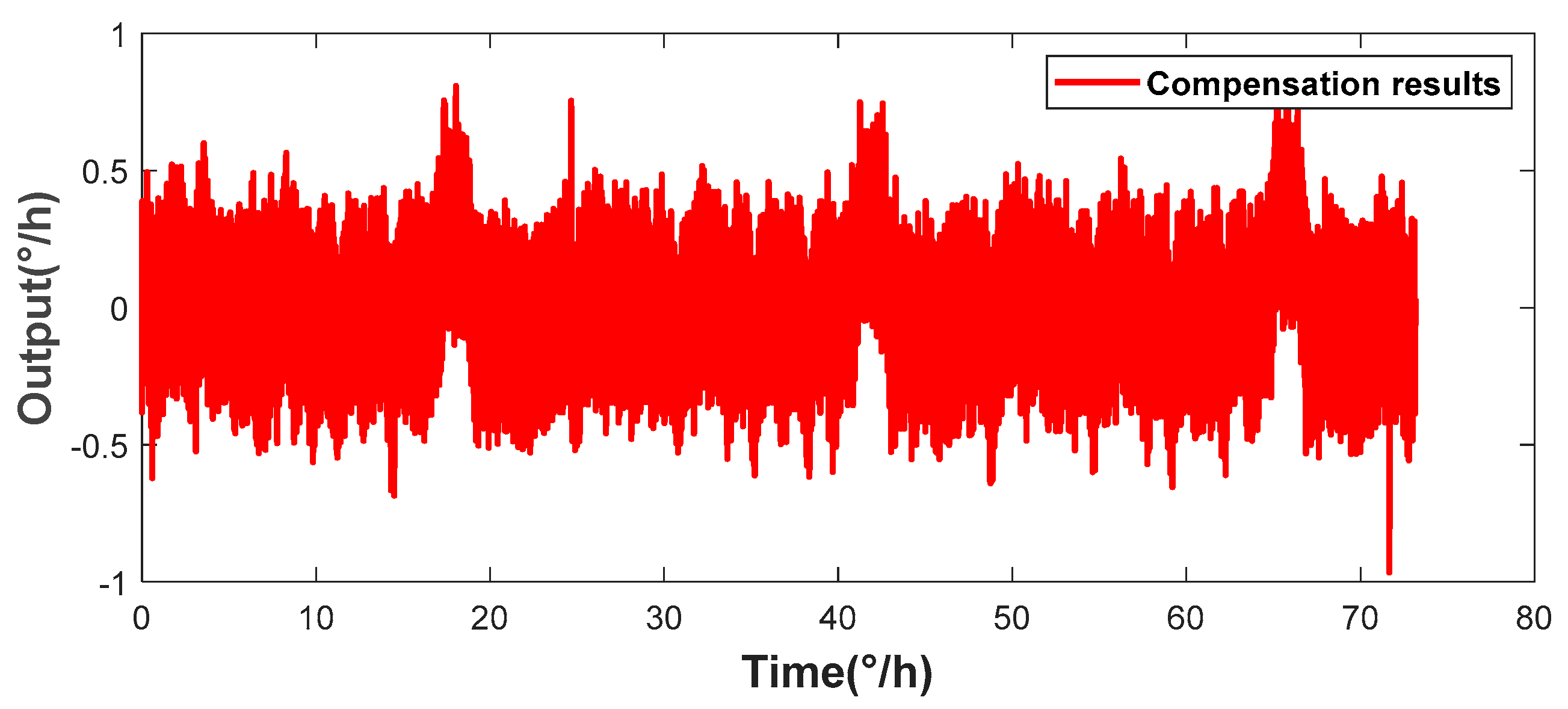

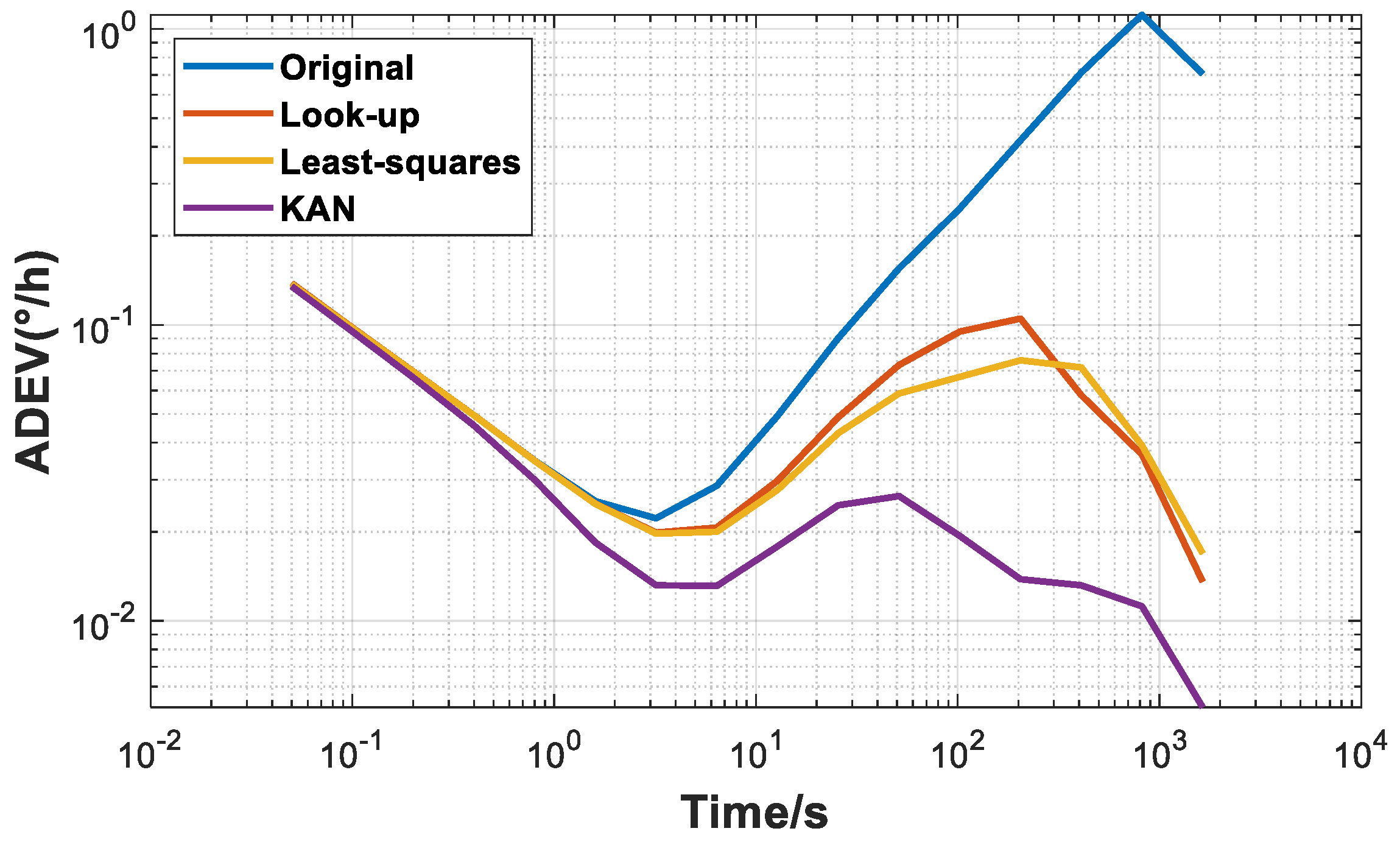
| Bias Instability | Bias Stability | |
|---|---|---|
| Original | 0.022°/h | 1.1392°/h |
| Look-up | 0.0199°/h | 0.1312°/h |
| Least-squares | 0.0197°/h | 0.1076°/h |
| KAN | 0.013°/h | 0.0651°/h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Wen, J.; Han, S.; Li, C. Compensation of Temperature-Induced Bias Drift in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscopes: An Inherent Data-Driven Architecture. Micromachines 2025, 16, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040357
Zhou X, Wen J, Han S, Li C. Compensation of Temperature-Induced Bias Drift in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscopes: An Inherent Data-Driven Architecture. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040357
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaocong, Jiaqiang Wen, Shasha Han, and Chong Li. 2025. "Compensation of Temperature-Induced Bias Drift in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscopes: An Inherent Data-Driven Architecture" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040357
APA StyleZhou, X., Wen, J., Han, S., & Li, C. (2025). Compensation of Temperature-Induced Bias Drift in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscopes: An Inherent Data-Driven Architecture. Micromachines, 16(4), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040357






