Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Thrombospondin-2 Using Nanoparticle Sensors for Cancer Screening and Prognosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Selection of Optimal AuNP Size for Biosensing Probe Preparation
2.3. Sensing Dilution Buffer Preparation
2.4. AuNP Functionalization
2.5. THBS2 Detection Experiments
2.6. Specificity in Different Matrices
2.7. Electronic Reader Design
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
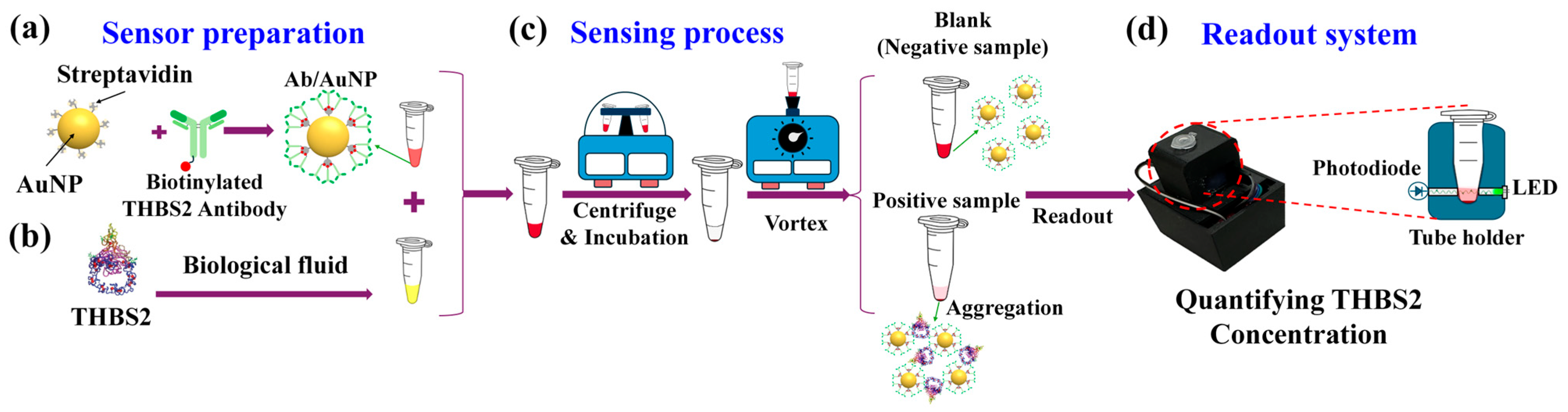
3.1. Sensing Mechanism
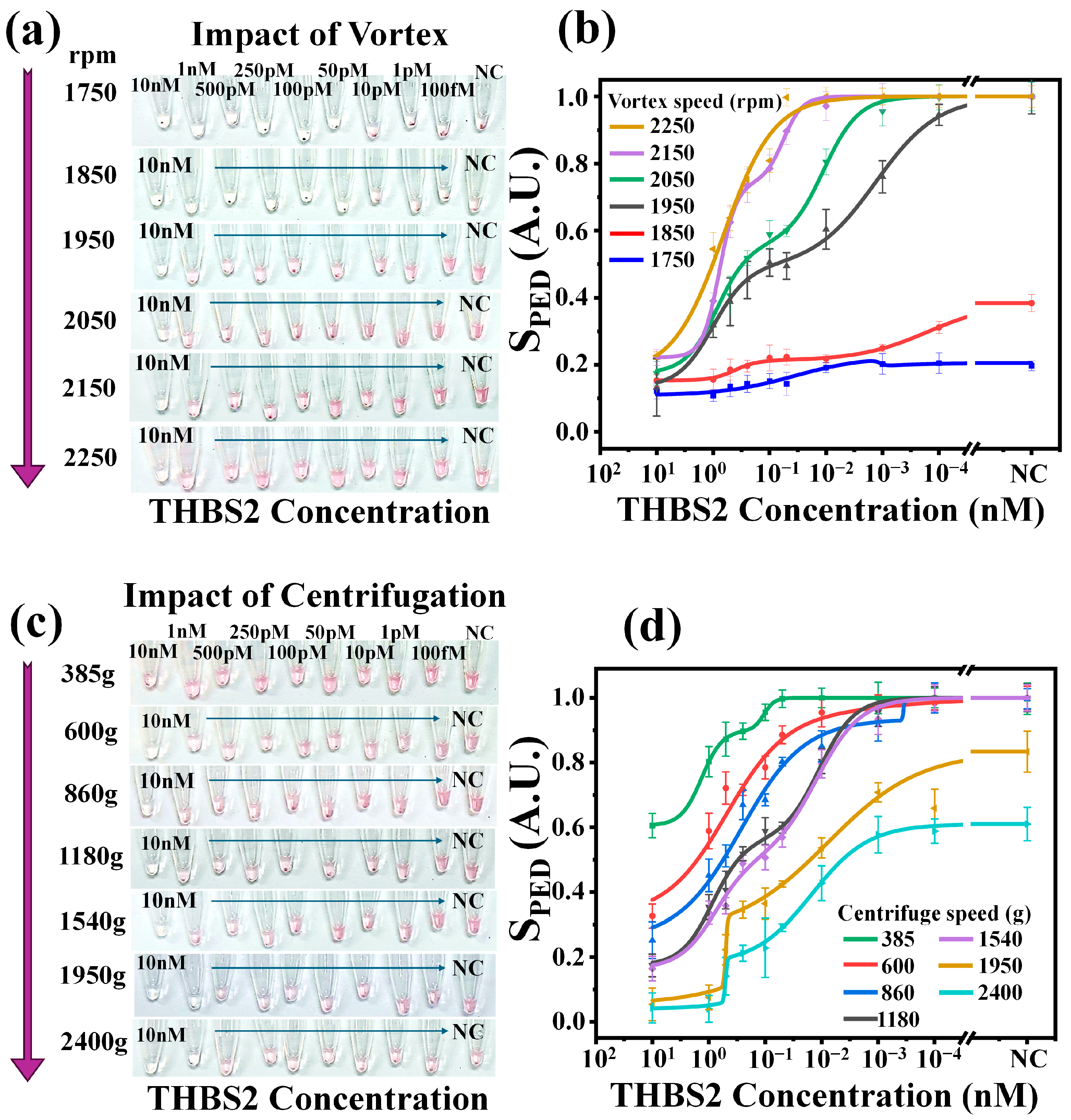
3.2. Sensing Protocol Optimization
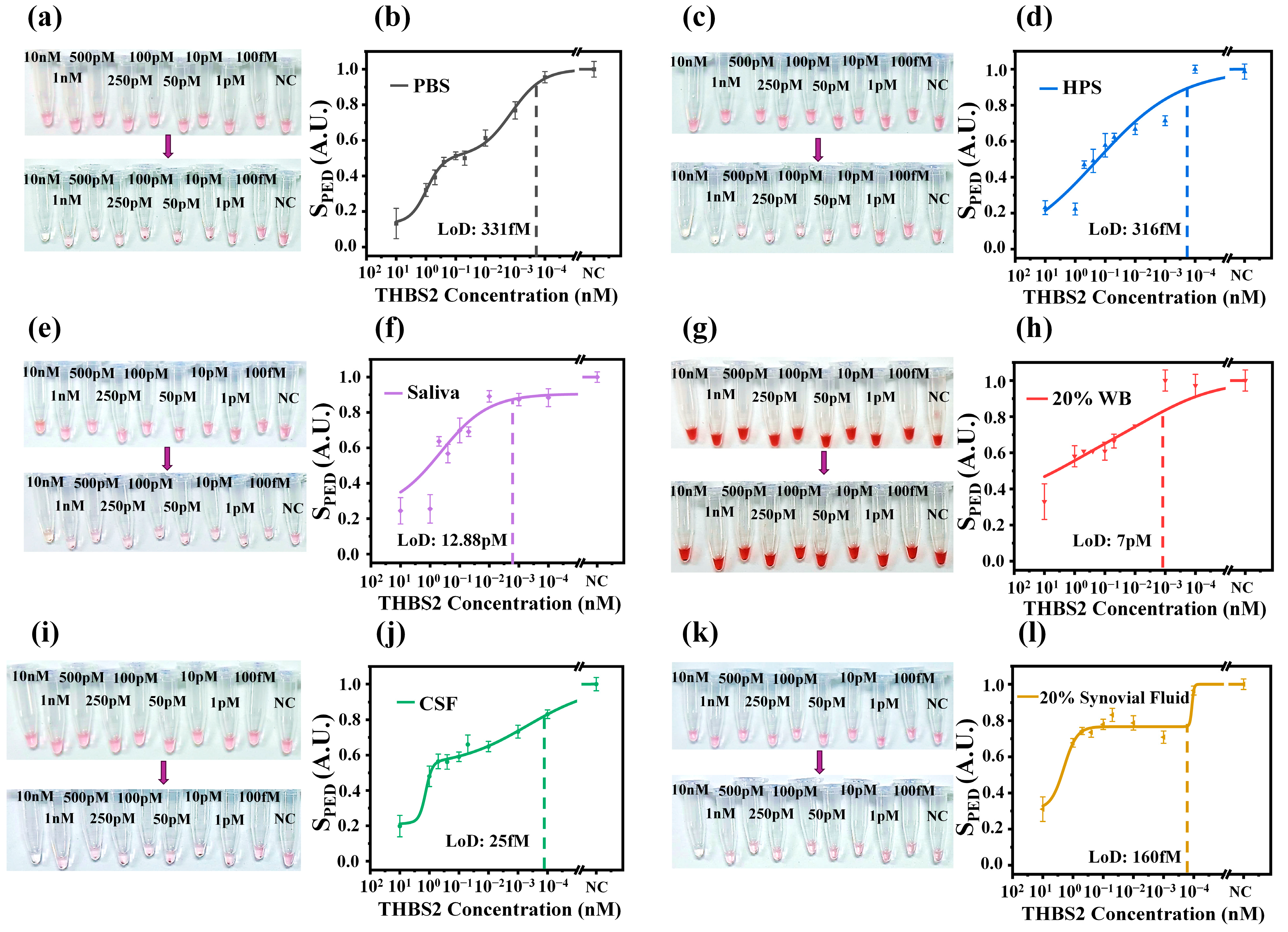
3.3. THBS2 Detection
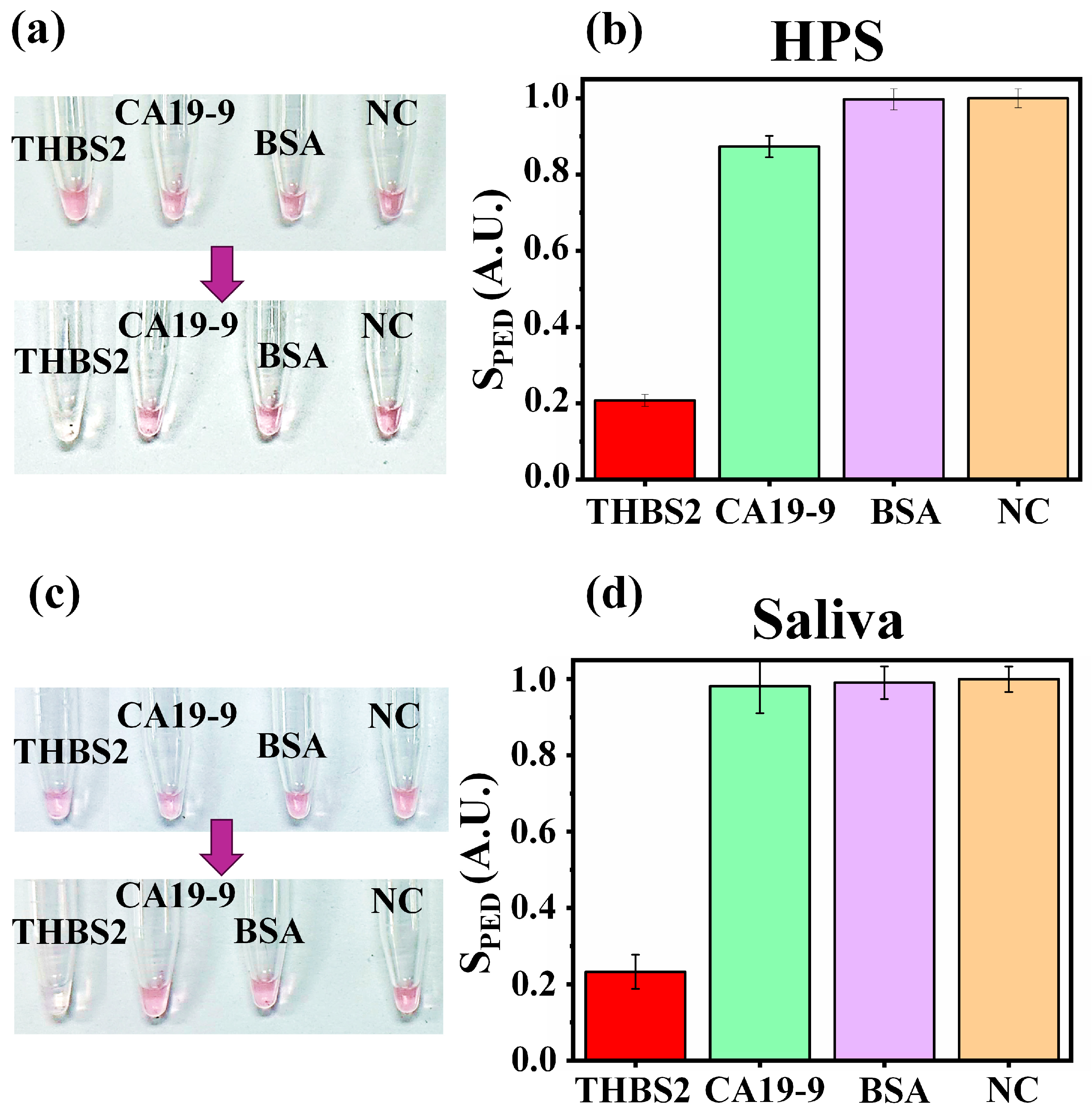
3.4. Specificity Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, B.; Liu, X.-P.; Wang, X. Prognostic and Immunological Role of THBS2 in Colorectal cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1124985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Zheng, L.; Hu, X. RBP4 and THBS2 are serum biomarkers for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92254–92264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Fan, Z. Joint effect of THBS2 and VCAN accelerating the poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Aging 2023, 15, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, J.; Fu, L.; Xia, X.; Pan, F.; Ning, Y. Clinical Value of Serum Thrombospondin-2 Combined with CA19-9 in Early Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 2483964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.-D.; Lin, Z.-B.; Huang, T.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Zhao, Z.; Huangfu, S.-C.; Qiu, S.-H.; Guo, Y.-G.; Pan, J.-H.; et al. Thrombospondin-2 holds prognostic value and is associated with metastasis and the mismatch repair process in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bamlet, W.R.; Oberg, A.L.; Chaffee, K.G.; Donahue, G.; Cao, X.-J.; Chari, S.; Garcia, B.A.; Petersen, G.M.; Zaret, K.S. Detection of early pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with thrombospondin-2 and CA19-9 blood markers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köbel, M.; Kang, E.; Lee, S.; Terzic, T.; Karnezis, A.N.; Ghatage, P.; Woo, L.; Lee, C.; Meagher, N.S.; Ramus, S.J.; et al. Infiltrative pattern of invasion is independently associated with shorter survival and desmoplastic stroma markers FAP and THBS2 in mucinous ovarian carcinoma. Histopathology 2024, 84, 1095–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lin, E.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Huang, J.; Guo, W.; Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Thrombospondin 2 is a Functional Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2022, 28, 1610559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhu, C.; Lu, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, M. Serum THBS2 is a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 15671–15677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-M.; Yu, D.-L.; Hou, G.-X.; Jiang, J.-L.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, X.-F. Serum thrombospondin-2 is a candidate diagnosis biomarker for early non-small-cell lung cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-W.; Yu, J.-S.; Peng, P.-H.; Liu, S.-C.; Chang, Y.-S.; Chang, K.-P.; Wu, C.-C. Secretome profiling of primary cells reveals that THBS2 is a salivary biomarker of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 4796–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Hua, F.; Wang, Y.; Fang, G.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X. MiR-214-3p suppresses cervical cancer cell metastasis by downregulating THBS2. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, I.-W.; Li, C.-F.; Lin, V.C.-H.; He, H.-L.; Liang, P.-I.; Wu, W.-J.; Li, C.-C.; Huang, C.-N. Prognostic impact of thrombospodin-2 (THBS2) overexpression on patients with urothelial carcinomas of upper urinary tracts and bladders. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Iwadare, T.; Wakabayashi, S.; Kuldeep, S.; Nakajima, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Aomura, D.; Zafar, H.; Iwaya, M.; Joshita, S.; et al. Thrombospondin 2 is a key determinant of fibrogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.-H.; Ma, L.-S. THBS2 is a valuable prognosis biomarker in UM. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 6230–6238. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Lin, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Cai, X.; He, Y.; Liu, S. Identification of BGN and THBS2 as metastasis-specific biomarkers and poor survival key regulators in human colon cancer by integrated analysis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W.; Kang, Y.M.; Butterfield, J.; Detmar, M.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Thrombospondin 2 functions as an endogenous regulator of angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Large, T.Y.; Meijer, L.L.; Paleckyte, R.; Boyd, L.N.; Kok, B.; Wurdinger, T.; Schelfhorst, T.; Piersma, S.R.; Pham, T.V.; van Grieken, N.C.; et al. Combined Expression of Plasma Thrombospondin-2 and CA19-9 for Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer and Distal Cholangiocarcinoma: A Proteome Approach. Oncologist 2020, 25, e634–e643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, Y.; Chiba, K.; Karasugi, T.; Nakajima, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Mikami, Y.; Furuichi, T.; Mio, F.; Miyake, A.; Miyamoto, T.; et al. A Functional Polymorphism in THBS2 that Affects Alternative Splicing and MMP Binding Is Associated with Lumbar-Disc Herniation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, P.; Dong, X.; Bai, X.; Lu, H.; Liu, F.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X. Tumor-stroma TGF-β1-THBS2 feedback circuit drives pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression via integrin αvβ3/CD36-mediated activation of the MAPK pathway. Cancer Lett. 2022, 528, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Ikbal, M.A.; Hou, C.-W.; Mohammadi, M.K.; Choi, Y.; Kelbauskas, L.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Hogue, B.G.; Murugan, V.; Diamond, M.S.; et al. Nanoparticle-Supported, Rapid, Digital Quantification of Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Mirjalili, S.; Ikbal, M.D.A.; McClure, S.; Clemens, S.; Solano, J.; Heggland, J.; Zuo, J.; Wang, C. Nanoparticle-Supported, Rapid, and Electronic Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies and Antigens at Attomolar Level. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikbal, M.D.A.; Kang, S.; Chen, X.; Gu, L.; Wang, C. Picomolar-Level Sensing of Cannabidiol by Metal Nanoparticles Functionalized with Chemically Induced Dimerization Binders. ACS Sensors 2023, 8, 4696–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kang, S.; Ikbal, A.; Zhao, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zuo, J.; Gu, L.; Wang, C. Synthetic nanobody-functionalized nanoparticles for accelerated development of rapid, accessible detection of viral antigens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 202, 113971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-Vis spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, D.A.; Pry, T. Limit of Blank, Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2008, 29 (Suppl. S1), S49. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Kitova, E.N.; Klassen, J.S. Dissociation kinetics of the streptavidin-biotin interaction measured using direct electrospray ionization mass spectrometry analysis. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 24, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenberg, D.R.; Varon, E.; Indech, G.; Ben Uliel, T.; Geri, L.; Sharoni, A.; Shefi, O. A streptavidin–biotin system combined with magnetic actuators for remote neuronal guidance. J. Biol. Eng. 2023, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivers, C.E.; Koner, A.L.; Lowe, E.D.; Howarth, M. How the biotin–streptavidin interaction was made even stronger: Investigation via crystallography and a chimaeric tetramer. Biochem. J. 2011, 435, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recombinant Human Thrombospondin-2 Protein, CF. Available online: https://www.rndsystems.com/products/recombinant-human-thrombospondin-2-protein-cf_1635-t2 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Sun, Y.-S.; Zhu, X. Characterization of Bovine Serum Albumin Blocking Efficiency on Epoxy-Functionalized Substrates for Microarray Applications. J. Lab. Autom. 2016, 21, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammadi, M.K.; Mirjalili, S.; Ikbal, M.A.; Xie, H.; Wang, C. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Thrombospondin-2 Using Nanoparticle Sensors for Cancer Screening and Prognosis. Micromachines 2025, 16, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030354
Mohammadi MK, Mirjalili S, Ikbal MA, Xie H, Wang C. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Thrombospondin-2 Using Nanoparticle Sensors for Cancer Screening and Prognosis. Micromachines. 2025; 16(3):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030354
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammadi, Maziyar Kalateh, Seyedsina Mirjalili, Md Ashif Ikbal, Hao Xie, and Chao Wang. 2025. "Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Thrombospondin-2 Using Nanoparticle Sensors for Cancer Screening and Prognosis" Micromachines 16, no. 3: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030354
APA StyleMohammadi, M. K., Mirjalili, S., Ikbal, M. A., Xie, H., & Wang, C. (2025). Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Thrombospondin-2 Using Nanoparticle Sensors for Cancer Screening and Prognosis. Micromachines, 16(3), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030354





