Dynamics Research of the Hopfield Neural Network Based on Hyperbolic Tangent Memristor with Absolute Value
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dual Local Active Memristor Model
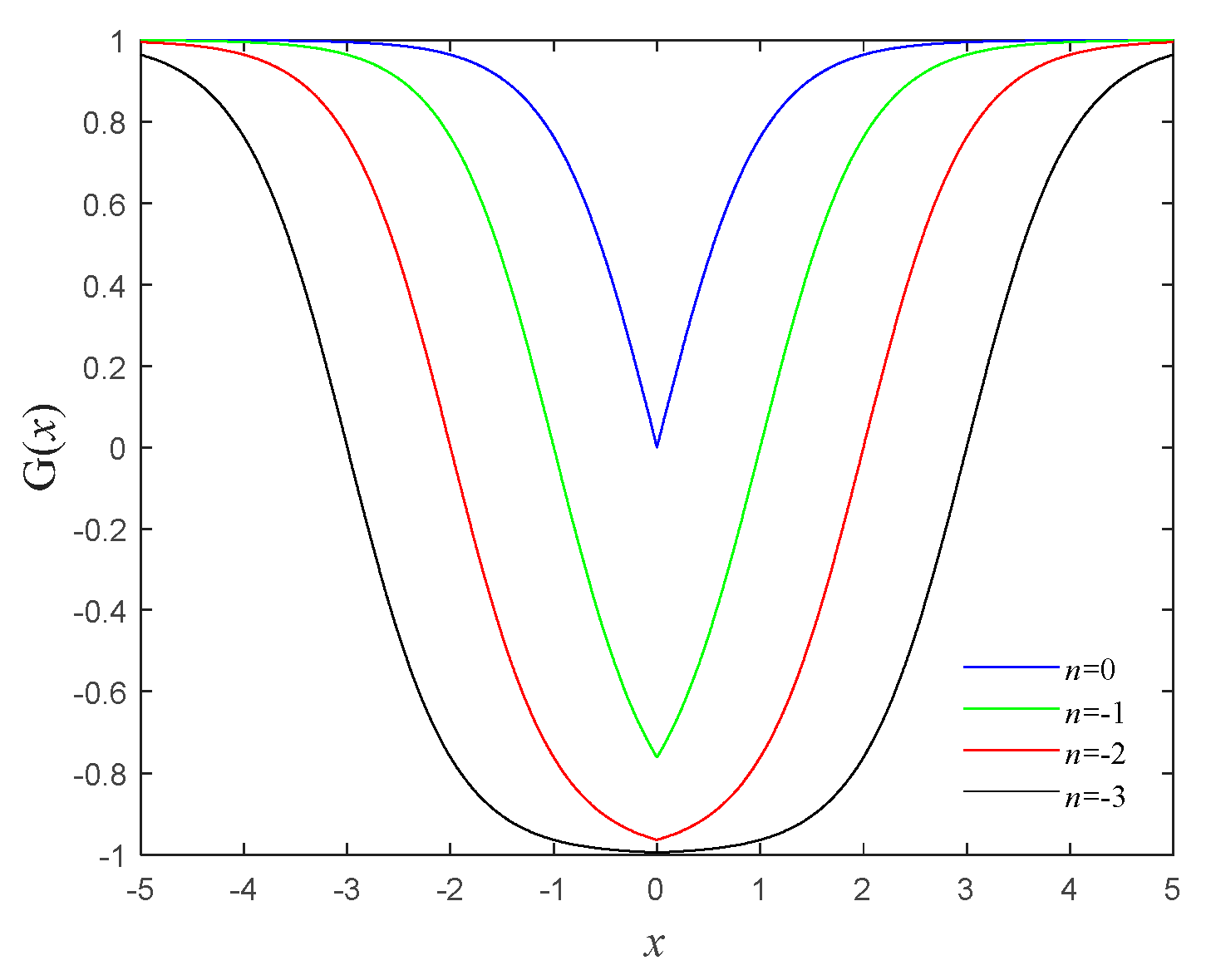
2.1. Mathematical Model of Memristor
2.2. Hysteresis Loop and Time Domain Waveform
2.3. Power-Off Plot and DC Voltage-Current
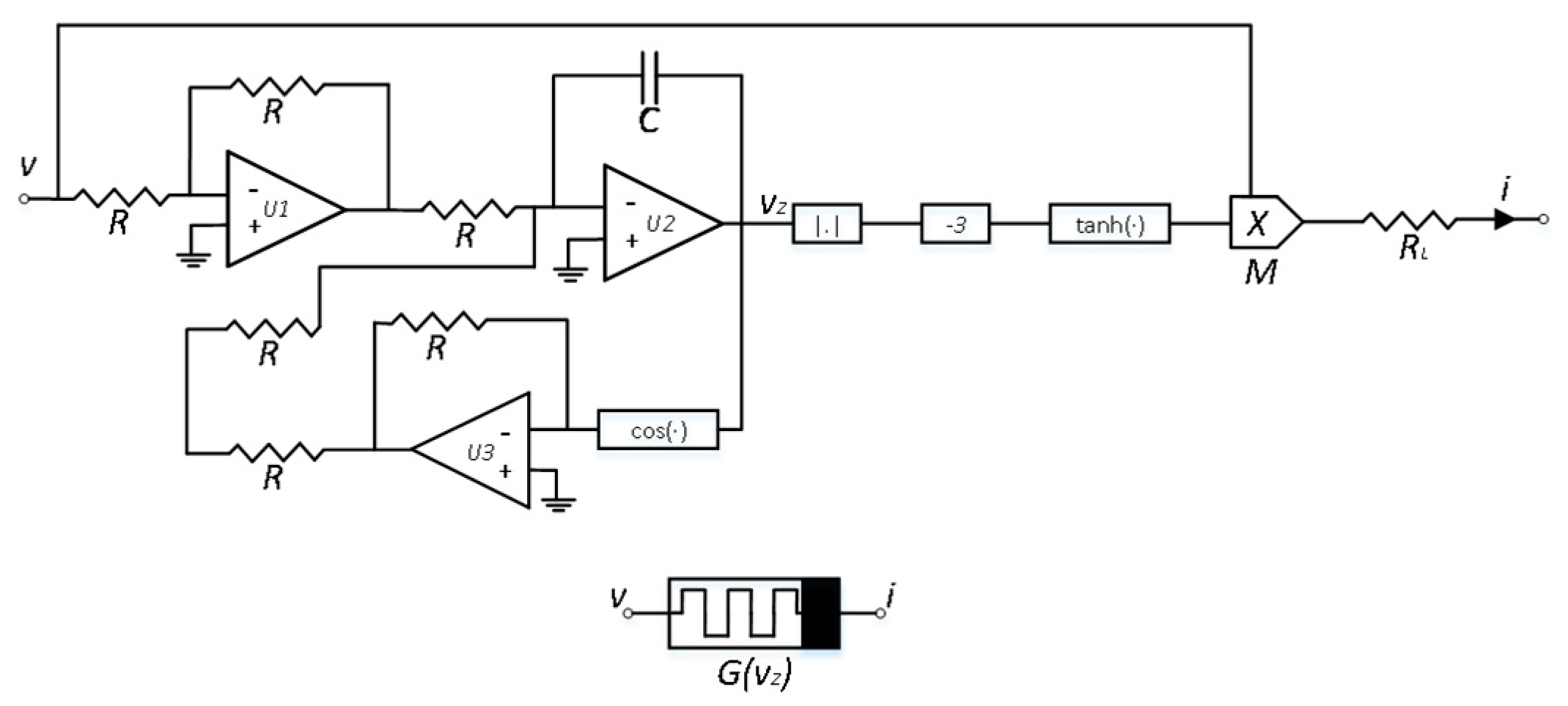
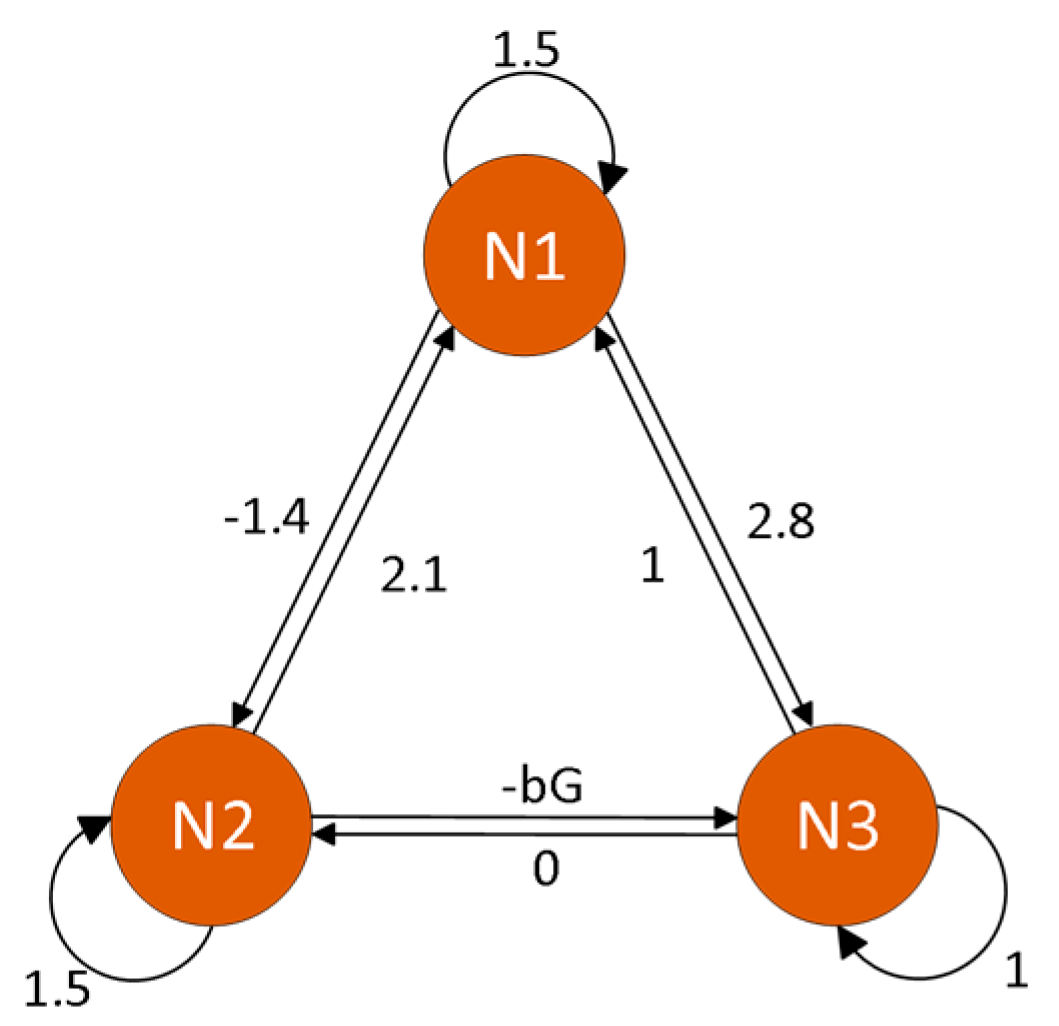
3. Modeling of Memristor-Coupled Three-Neuron HNN
4. Dynamic Analysis of the Memoristor-Coupled Three-Neuron HNN
4.1. Dissipativity
4.2. Equilibrium Point and Its Stability
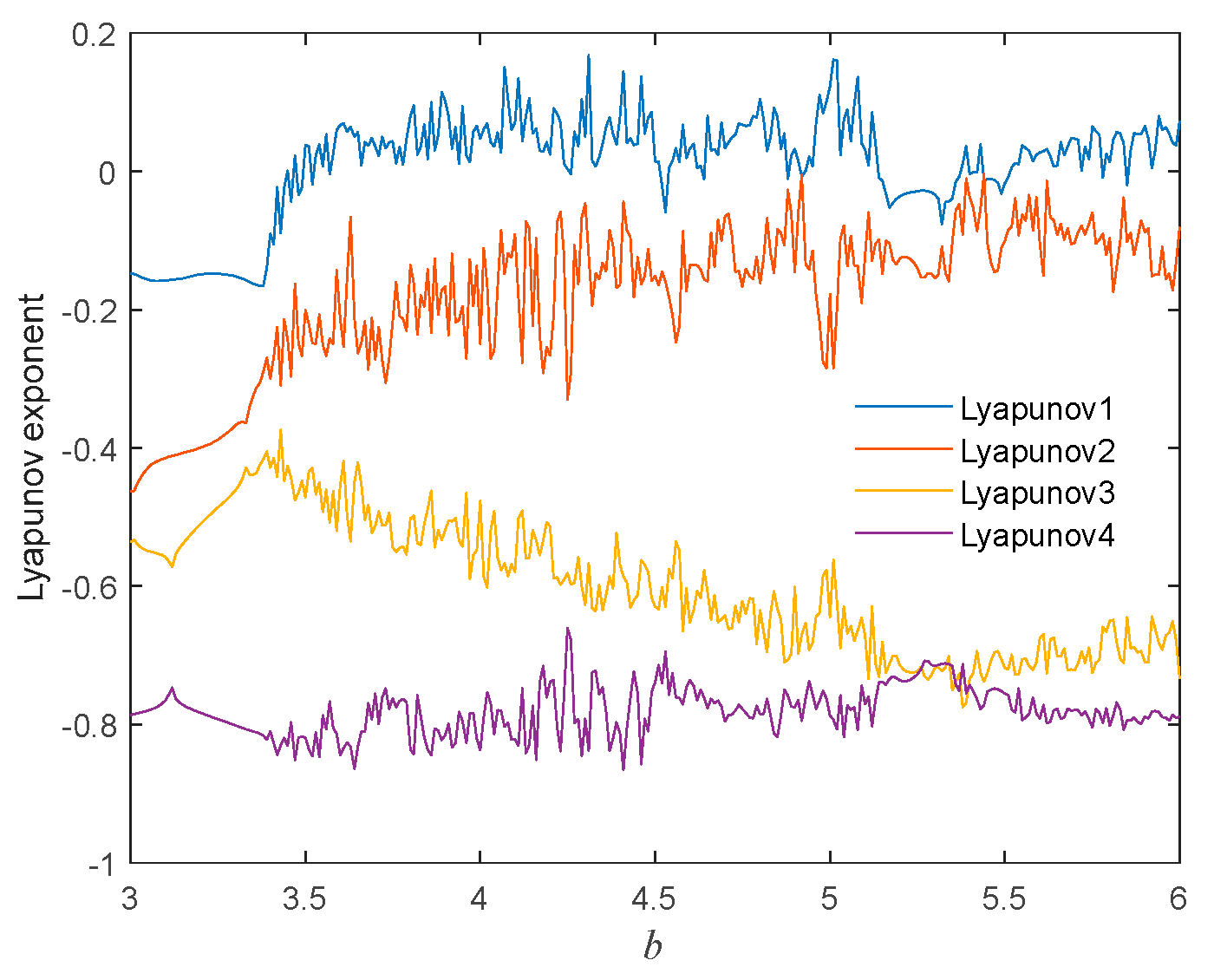
4.3. Bifurcation Diagram and Lyapunov Exponent Spectrum
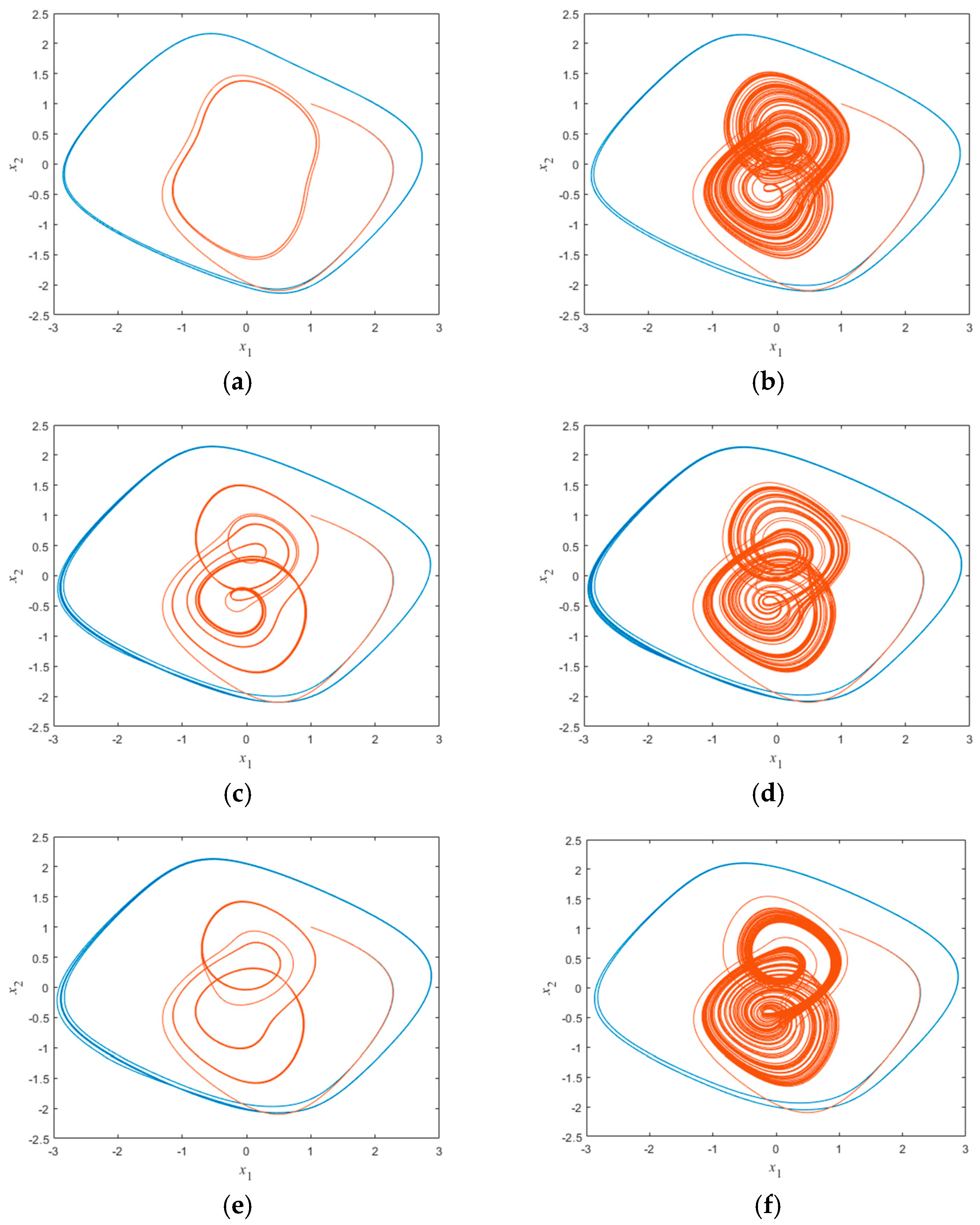
4.4. Two-Dimensional Phase Trajectory Plot
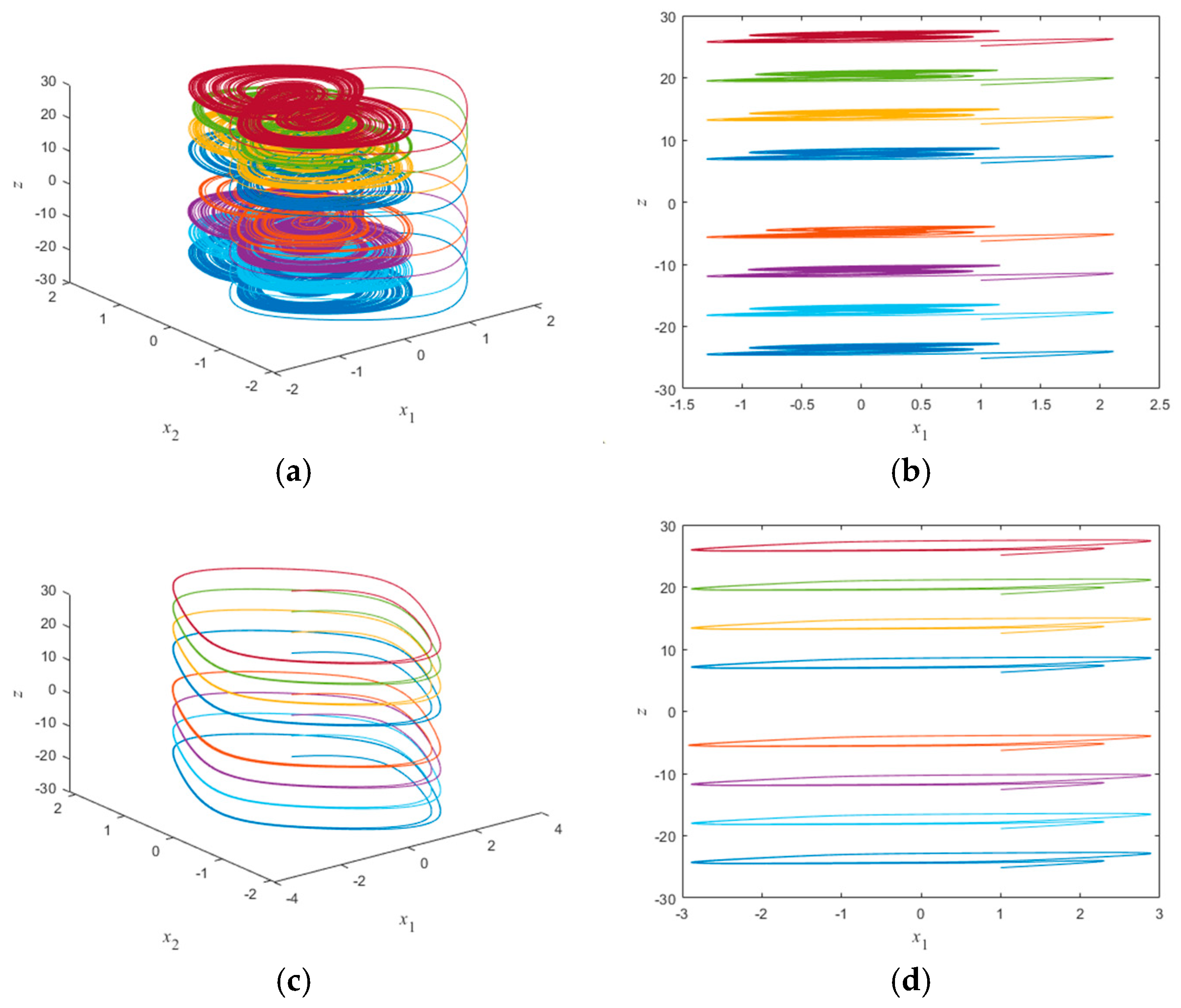
4.5. Super-Multistability Phenomenon
4.6. Comparison of Different Memristor-Coupled Hopfield Neural Networks
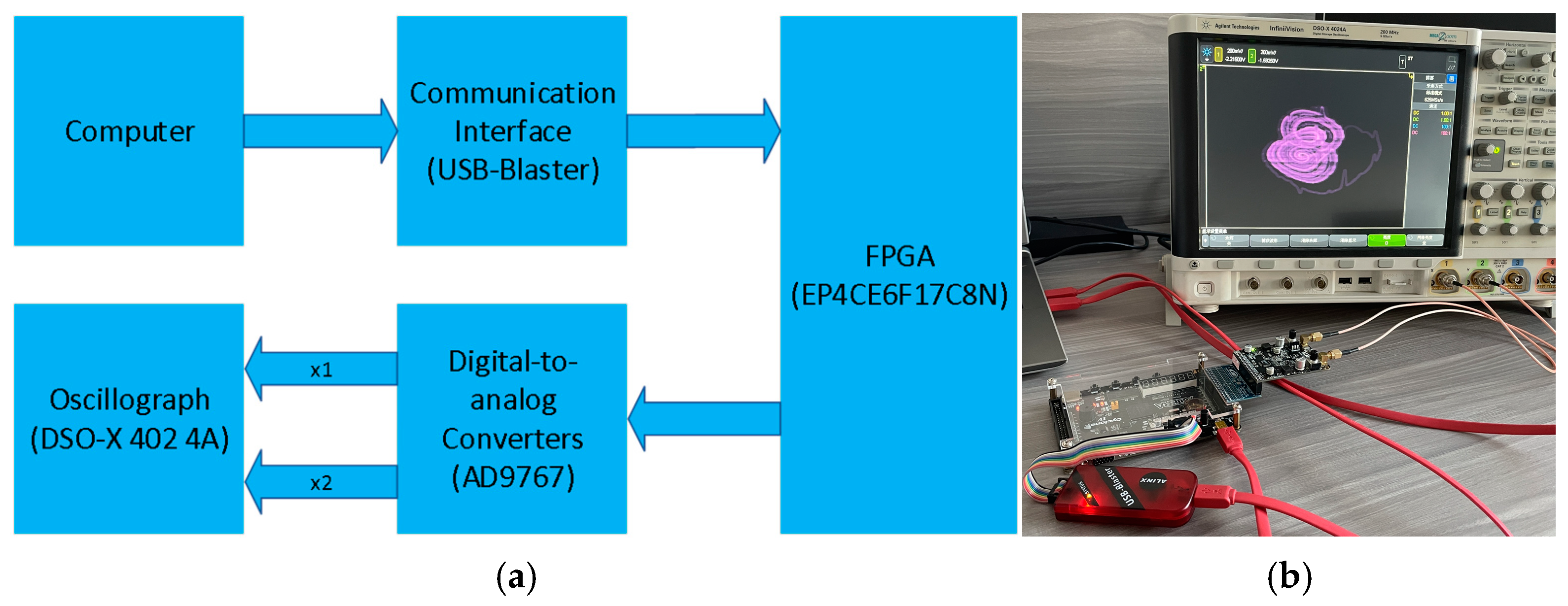
5. FPGA Hardware Implementation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, D.; Wang, M.-Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.-L.; Niu, Y.; Wang, W. Dynamic behaviors analysis of fraction-order neural network under memristive electromagnetic induction. Acta Phys. Sin. 2024, 73, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfield, J.J. Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-state neurons. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3088–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, P.; Roy, A.B. Chaos in a three-dimensional general model of neural network. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 2002, 12, 2271–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yuan, Q. Chaos and transient chaos in simple Hopfield neural networks. Neurocomputing 2005, 69, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Huang, Y. Chaos of a new class of Hopfield neural networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 206, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Tang, W.; Zhang, J. Some novel double-scroll chaotic attractors in Hopfield networks. Neurocomputing 2010, 73, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, P.C. Chaos and hyperchaos in a Hopfield neural network. Neurocomputing 2011, 74, 3361–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ma, J.; Wu, F. Review on memristor application in neural circuit and network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 187, 115361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Cao, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Ahmad, A.M.; Mou, J. A novel neural networks with memristor coupled memcapacitor-synapse neuron. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 189, 115723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yao, W. Firing multistability in a locally active memristive neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 100, 3667–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, J.; Qiao, Y. Initial offset boosting dynamics in a memristive Hopfield neural network and its application in image encryption. Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 2023, 40, 106–116. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zang, H.; Lei, T. Dynamics analysis and circuit implementation of a novel absolute value memristor coupled self-synaptic Hopfield neural network. Electron. Compon. Mater. 2023, 42, 435–444. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Bao, H.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 95, 3385–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Ge, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.; Borah, S. A novel memristive neural network circuit and its application in character recognition. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Hong, Q.; Du, S.; Zhang, J. Design of Artificial Neurons of Memristive Neuromorphic Networks Based on Biological Neural Dynamics and Structures. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 2320–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. If it’s pinched it’s a memristor. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2014, 29, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Yang, L. Discrete memristor applied to construct neural networks with homogeneous and heterogeneous coexisting attractors. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 174, 113807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Hong, Q.; Sun, Y. A multi-stable memristor and its application in a neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3472–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zi, X.; Xiao, F. A tristable locally active memristor and its application in Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 108, 1697–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, C.; He, S.; Li, Z. A novel compound exponential locally active memristor coupled Hopfield neural network. Acta Phys. Sin. 2024, 73, 130501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, G.; Raut, G.; Chandra, M.; Vishvakarma, S.K. VLSI implementation of transcendental function hyperbolic tangent for deep neural network accelerators. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 84, 104270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. Local activity is the origin of complexity. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 2005, 15, 3435–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascoli, A.; Slesazeck, S.; Mähne, H.; Tetzlaff, R.; Mikolajick, T. Nonlinear Dynamics of a Locally-Active Memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2015, 62, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Yao, W.; Tan, Y. Chaotic dynamics in a neural network with different types of external stimuli. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2020, 90, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. Everything you wish to know about memristors but are afraid to ask. Radioengineering 2015, 24, 319–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, M.; Ma, M. Coexisting firing patterns and phase synchronization in locally active memristor coupled neurons with HR and FN models. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 104, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiher, M.; Herzig, M.; Tetzlaff, R.; Ascoli, A.; Mikolajick, T.; Slesazeck, S. Pattern formation with locally active s-type NbOx memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2019, 66, 2627–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C. Influences of electromagnetic radiation distribution on chaotic dynamics of a neural network. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 369, 124840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sun, L.; Qiao, Y. Dynamical analysis and circuit implementation of a memristor synapse-coupled ring Hopfield neural network. Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 2022, 39, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Q.; Kuate, P.D.K.; Liu, F.; Lu, H.H.C. An extremely simple chaotic system with infinitely many coexisting attractors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokar, E.; Abolfathi, H.; Ahamadi, M.; Ahmadi, M. An Eefficient uniform-segmented neuron model for large-scale neuromorphic circuit design: Simulation and FPGA synthesis results. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 2336–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Bao, H.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Hua, Z.; Bao, B. Memristive Rulkov neuron model with magnetic induction effects. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform. 2022, 18, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xu, C.; Hong, Q. Neural bursting and synchronization emulated by neural networks and circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 3397–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Iu, H.H.-C.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y. A chaotic memristive Hindmarsh-Rose neuron with hybrid offset boosting. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 185, 115150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Tang, Q.; Yi, C.; Yang, Y. Constructing Memristive Hindmarsh–Rose Neuron with Countless Coexisting Firings. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 2024, 34, 2450113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
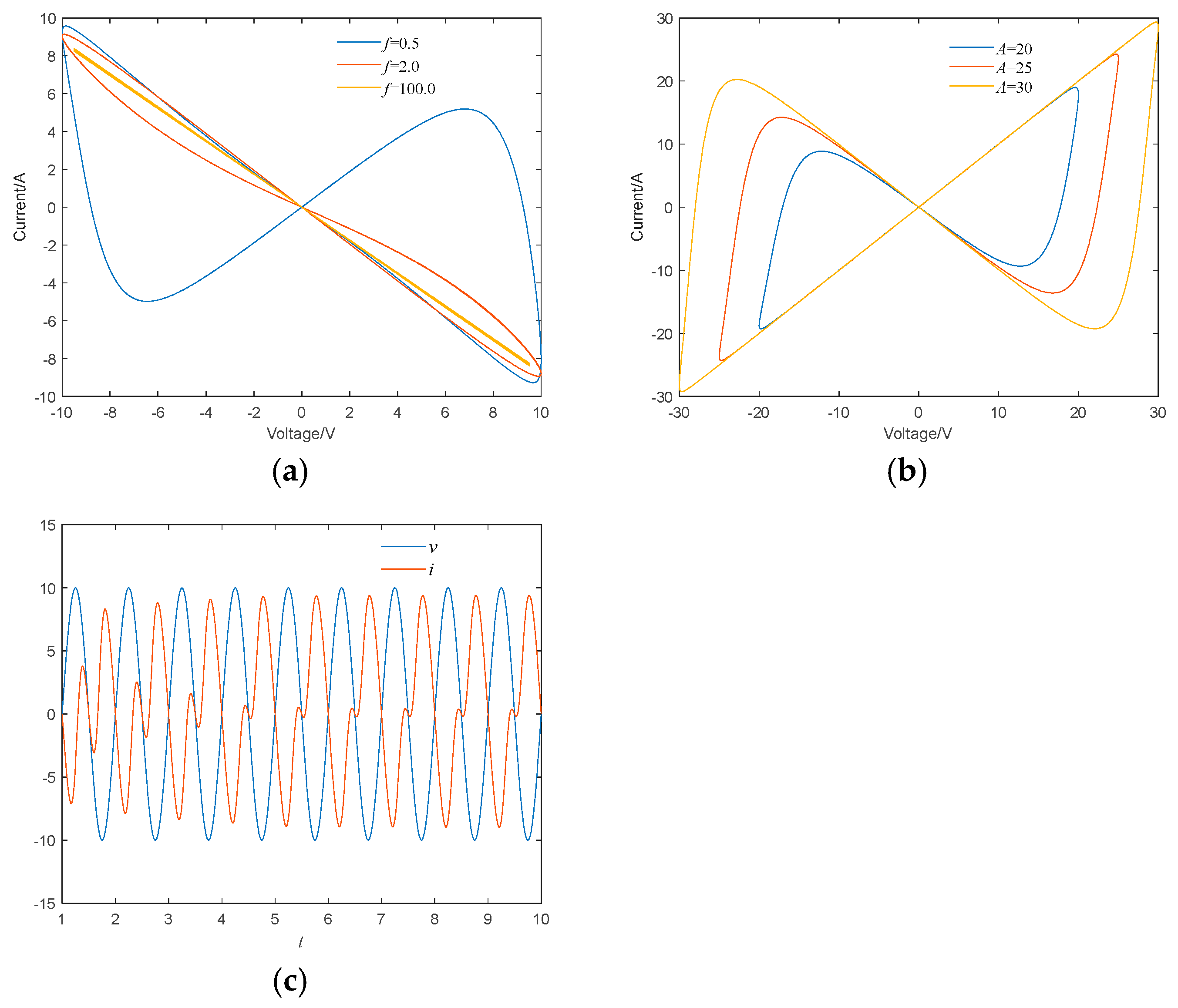




| b | k | Eigenvalue | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5748 | Unstable saddle point | ||
| 1.5421 | Unstable saddle point | ||
| 0.4222 ± 1.3302i; 1.8445 | Unstable saddle point | ||
| 1 | 0.4222 ± 1.3302i; 1.8445 | Unstable saddle point | |
| 3 | 1.5421 | Unstable saddle point | |
| 5 | 1.5748 | Unstable saddle point |
| System | The Type of G(x) | Local Active Memristor | Super-Multistability Phenomenon | Digital Circuit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [11] | linear function | no | no | no |
| Ref. [12] | absolute value function | no | no | no |
| Ref. [13] | linear function | no | no | no |
| Ref. [19] | quadratic function | yes | no | no |
| Ref. [20] | compound exponential function | yes | no | yes |
| This paper | hyperbolic tangent function | yes | yes | yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Xu, H. Dynamics Research of the Hopfield Neural Network Based on Hyperbolic Tangent Memristor with Absolute Value. Micromachines 2025, 16, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16020228
Gao H, Xu H. Dynamics Research of the Hopfield Neural Network Based on Hyperbolic Tangent Memristor with Absolute Value. Micromachines. 2025; 16(2):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16020228
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Huiyan, and Hongmei Xu. 2025. "Dynamics Research of the Hopfield Neural Network Based on Hyperbolic Tangent Memristor with Absolute Value" Micromachines 16, no. 2: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16020228
APA StyleGao, H., & Xu, H. (2025). Dynamics Research of the Hopfield Neural Network Based on Hyperbolic Tangent Memristor with Absolute Value. Micromachines, 16(2), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16020228







