Automated Imaging and Analysis of Platelet, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Activities Using a Novel Flow Chip-Based System at Physiological Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Blood Donors and Blood Collection
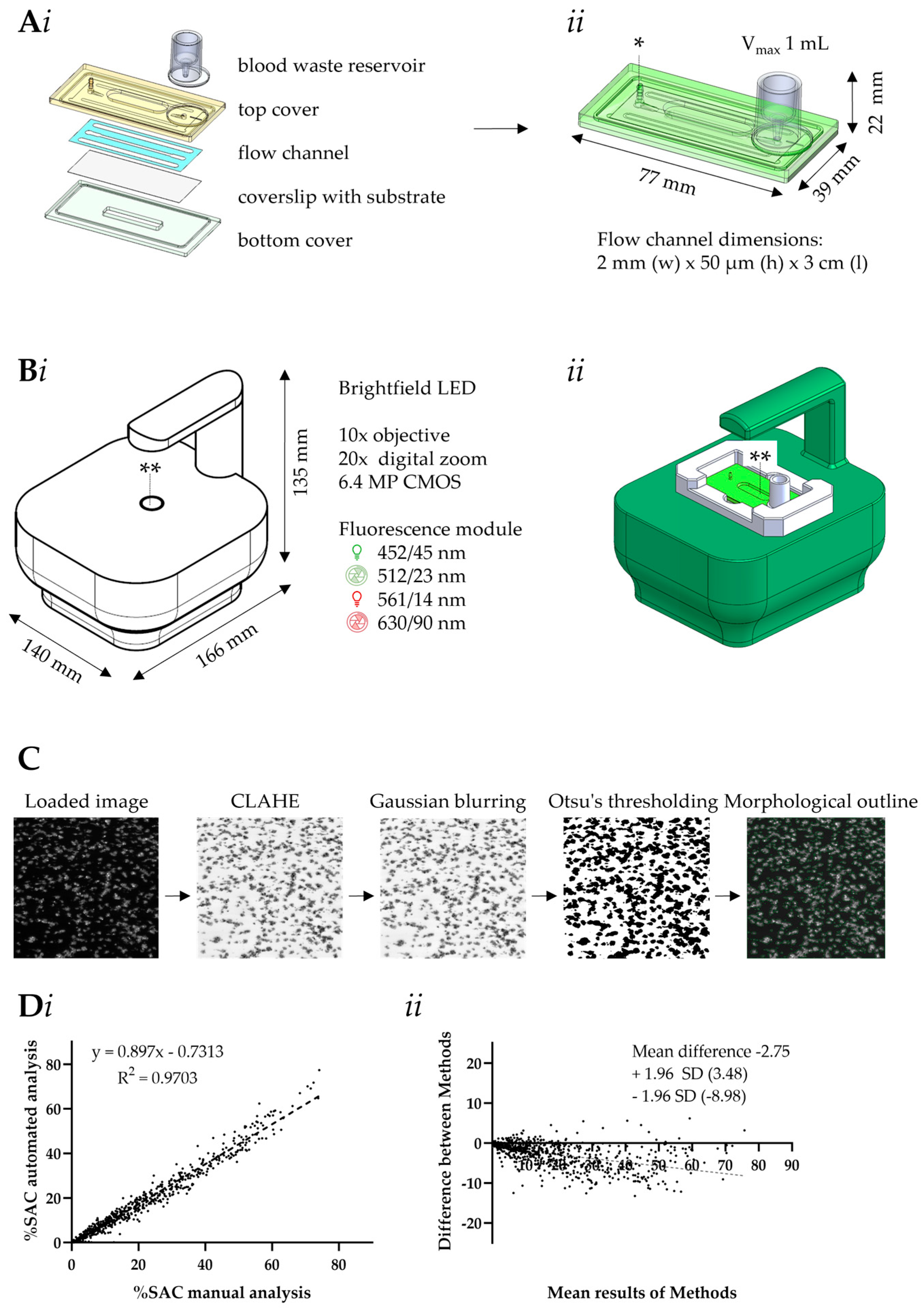
2.3. Design of Microfluidic MC-2S Device
2.4. Scripts for Automated Microscopic Image Analysis
2.5. Quantification by MC-2S of Platelet, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Activities
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
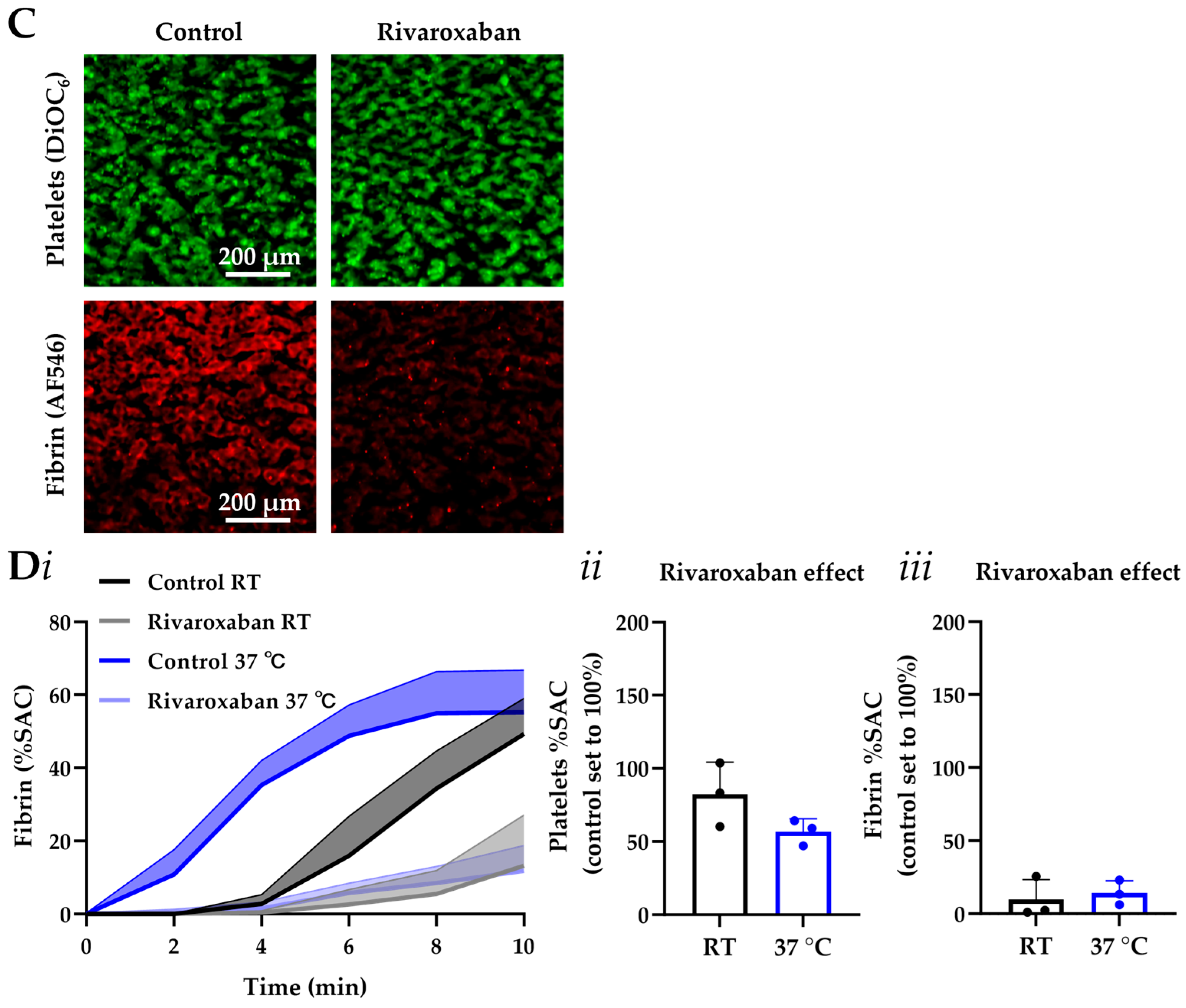
3.1. Platelet Activation to Thrombus Formation Assessed with MC-2S
3.2. MC-2S Chip for Platelet Function Testing
3.3. MC-2S Chip for Measurement of Coagulation Under Flow
3.4. MC-2S Chip for Measurement of Post-Thrombus Fibrinolysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baaten, C.C.; Meacham, S.; de Witt, S.M.; Feijge, M.A.; Adams, D.J.; Akkerman, J.W.; Cosemans, J.M.; Grassi, L.; Jupe, S.; Kostadima, M.; et al. A synthesis approach of mouse studies to identify genes and proteins in arterial thrombosis and bleeding. Blood 2018, 132, e35–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Marini, F.; Solari, F.A.; Swieringa, F.; de Laat, B.; De Simone, I.; Grassi, L.; Gui, X.; Li, K.; Middleton, E.A.; et al. Human and mouse platelet transcriptomes and proteomes for phenotyping 3474 genes with hemostatic and platelet traits. Blood VTH 2025, 2, 10068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangin, P.H.; Gardiner, E.E.; Nesbitt, W.S.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Korin, N.; Lam, W.A.; Panteleev, M.A. In vitro flow based systems to study platelet function and thrombus formation: Recommendations for standardization. Communication from the SSC on Biorheology of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Pasalic, L.; Lippi, G. Towards 50 years of platelet function analyser (PFA) testing. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 61, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, J.; Karczmarska-Wódzka, A.; Bugieda, J.; Sobczak, P. The use of total thrombus formation analysis system as a tool to assess platelet function in bleeding and thrombosis risk: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzano, D.; Quiroga, T. Diagnostic challenges of inherited mild bleeding disorders: A bait for poorly explored clinical and basic research. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouritorghabeh, H.; Monard, A.; Heubel-Moenen, F.; Leentjens, J.; Stroobants, A.; Henskens, Y. The utility of total thrombus-formation analysis system (T-TAS) in the thrombosis and hemostasis field: A scoping review. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2025, 47, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, S.L.; Rossi, J.M. Point of care whole blood microfluidics for detecting and managing thrombotic and bleeding risks. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3667–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeves, K.B.; Onasoga, A.A.; Wufsus, A.R. The use of microfluidics in hemostasis: Clinical diagnostics and biomimetic models of vascular injury. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2013, 20, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Herbig, B.A.; Li, R.; Colace, T.V.; Muthard, R.W.; Neeves, K.B.; Diamond, S.L. In microfluidico: Recreating in vivo hemodynamics using miniaturized devices. Biorheology 2015, 52, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Bresette, C.A.; Ku, D.N. Advancing microfluidic point-of-care platelet function tests: Opportunities and challenges from bench to market. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1507972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Liao, J.; Chen, Y.; Deng, S.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Tian, N.; Song, Y.; et al. Recent advances in microfluidic technology of arterial thrombosis investigations. Platelets 2024, 35, 2316743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, M.; van Geffen, J.P.; Stegner, D.; Adams, D.; Braun, A.; de Witt, S.M.; Elvers, M.; Kuijpers, M.J.; Kunzelmann, K.; Oury, C.; et al. Comparative analysis of microfluidics thrombus formation in multiple genetically modified mice: Link to thrombosis and hemostasis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, J.; Nagy, Z.; Di Nunzio, G.; Smith, C.W.; Geer, M.J.; Al Ghaithi, R.; van Geffen, J.P.; Heising, S.; Boothman, L.; Tullemans, B.M.; et al. Maintenance of platelet homeostasis by the kinase-phosphatase pair Csk-CD148 in mice. Blood 2018, 131, 1122–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geffen, J.P.; Brouns, S.L.; Batista, J.; McKinney, H.; Kempster, C.; Nagy, M.; Sivapalaratnam, S.; Baaten, C.; Bourry, N.; Frontini, M.; et al. High-throughput elucidation of thrombus formation reveals sources of platelet function variability. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.; Lambourne, J.J.; Javierre, B.M.; Grassi, L.; Kreuzhuber, R.; Ruklisa, D.; Rosa, I.M.; Tome, R.A.; Elding, H.; van Geffen, J.P.; et al. Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternkopf, M.; Nagy, M.; Baaten, C.C.; Wirth, J.; Theelen, W.; Mastenbroek, T.M.; Lehrke, M.; Winnerling, B.; Baerts, L.; Marx, N.; et al. Native, intact glucagon-like peptide 1 is a natural suppressor of thrombus growth under physiological flow conditions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, e65–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullemans, B.M.; Veninga, A.; Fernandez, D.I.; Aarts, M.J.; Eble, J.A.; van der Meijden, P.E.; Heemskerk, J.W.; Kuijpers, M.J. Multiparameter evaluation of the platelet-inhibitory effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors used for cancer treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herfs, L.; Swieringa, F.; Jooss, N.; Kozlowski, M.; Heubel-Moenen, F.C.; van Oerle, R.; Machiels, P.; Henskens, Y.; Heemskerk, J.W. Multiparameter microfluidics assay of thrombus formation reveals increased sensitivity to contraction and antiplatelet agents at physiological temperature. Thromb. Res. 2021, 203, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouns, S.; van Geffen, J.P.; Campello, E.; Swieringa, F.; Spiezia, L.; van Oerle, R.; Provenzale, I.; Verdoold, R.; Farndale, R.W.; Clemetson, K.J.; et al. Platelet-primed interactions of coagulation and anticoagulation pathways in flow-dependent thrombus formation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, C.S.; Swieringa, F.; Mastenbroek, T.G.; Lionikiene, A.S.; Lancé, M.D.; van der Meijden, P.E.; Heemskerk, J.W.; Mutch, N.J. Plasminogen associates with phosphatidylserine-exposing platelets and contributes to thrombus lysis under flow. Blood 2015, 125, 2568–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witt, S.M.; Swieringa, F.; Cavill, R.; Lamers, M.M.; van Kruchten, R.; Mastenbroek, T.; Baaten, C.; Coort, S.; Pugh, N.; Schulz, A.; et al. Identification of platelet function defects by multi-parameter assessment of thrombus formation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kruchten, R.; Cosemans, J.M.; Heemskerk, J.W. Measurement of whole blood thrombus formation using parallel-plate flow chambers: A practical guide. Platelets 2012, 23, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casa, L.D.; Ku, D.N. Geometric design of microfluidic chambers: Platelet adhesion versus accumulation. Biomed. Microdevices 2014, 16, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, O.; Münzer, P.; Alnaggar, N.; Geue, S.; Tegtmeyer, R.; Rath, D.; Droppa, M.; Seizer, P.; Heitmeier, S.; Heemskerk, J.W.; et al. Inhibitory mechanisms of very low-dose rivaroxaban in non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.J.; Crowther, M.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Gibson, C.M.; Curnutte, J.T.; Lawrence, J.H.; Yue, P.; Bronson, M.D.; Lu, G.; Conley, P.B.; et al. Full study report of andexanet alfa for bleeding associated with factor Xa inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönichen, C.; Sun, S.; Middelveld, H.; Huskens, D.; de Groot, P.G.; Heemskerk, J.W.; Roest, M.; de Laat, B. Functionally distinct anticoagulant mechanisms of endothelial cells. Thromb. Res. 2024, 244, 109208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medcalf, R.L. Fibrinolysis: From blood to the brain. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Vatankhah, P.; Goh, T.; Michelis, R.; Kyanian, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Ju, L.A. Hemodynamic analysis for stenosis microfluidic model of thrombosis with refined computational fluid dynamics simulation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, B.M.; Porada, C.D.; Atala, A.; Almeida-Porada, G. Microfluidic devices for studying coagulation biology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 112, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyau, S.; Ho-Tin-Noé, B.; Bourrienne, M.C.; Boulaftali, Y.; Jandrot-Perrus, M. Microfluidic modeling of thrombolysis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 2626–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swieringa, F.; Heemskerk, J.W.; Assinger, A. Platelet activation and signaling in thrombus formation. Blood 2025, 146, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, P.K.; Liang, X.M.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hu, M.; Wu, Y.; Gao, D. Comprehensive multiparameter evaluation of platelet function using a highly sensitive membrane capacitance sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 228, 115192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.K.; Heilmann, E.J.; Sio, R.; Garcia, C.; Davidson, R.M.; Ostgaard, R.A. Description of an in vitro platelet function analyzer-PFA-100. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2024, 50, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, D.; DiNardo, J.A. TEG and ROTEM: Technology and clinical applications. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, A. Thrombin generation assay and its application in the clinical laboratory. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, G.A.; Besser, M.W. The place of viscoelastic testing in clinical practice. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.A.; Ku, D.N. Structure of shear-induced platelet aggregated clot formed in an in vitro arterial thrombosis model. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2872–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthard, R.W.; Diamond, S.L. Side view thrombosis microfluidic device with controllable wall shear rate and transthrombus pressure gradient. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| MC-2S | PFA-200 | T-TAS | TEG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runtime | 8 min | 5 min | 10 min | 15–20 min |
| Sample volume | 500 µL whole blood | 800 µL whole blood | 350 µL whole blood | 2–3 mL whole blood |
| Wall shear rate | 1000 s−1 | 5000–6000 s−1 | 2000 s−1 | low |
| Output type | Kinetics of platelet and fibrin deposition (%SAC), thrombus morphology and contraction score | Closure time (CT) of platelet aggregates | Occlusion times (OC, OSC), thrombus profile (area-under-the flow-curve) | Clot elasticity initiation, clot propagation and lysis |
| Application | Haemostasis and thrombosis susceptibility | VWF and platelet activation test | Haemostasis and thrombosis susceptibility | Transfusion science and medicine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gui, X.; Tullemans, B.M.E.; de Laat, B.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Swieringa, F. Automated Imaging and Analysis of Platelet, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Activities Using a Novel Flow Chip-Based System at Physiological Temperature. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111253
Gui X, Tullemans BME, de Laat B, Heemskerk JWM, Swieringa F. Automated Imaging and Analysis of Platelet, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Activities Using a Novel Flow Chip-Based System at Physiological Temperature. Micromachines. 2025; 16(11):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111253
Chicago/Turabian StyleGui, Xiang, Bibian M. E. Tullemans, Bas de Laat, Johan W. M. Heemskerk, and Frauke Swieringa. 2025. "Automated Imaging and Analysis of Platelet, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Activities Using a Novel Flow Chip-Based System at Physiological Temperature" Micromachines 16, no. 11: 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111253
APA StyleGui, X., Tullemans, B. M. E., de Laat, B., Heemskerk, J. W. M., & Swieringa, F. (2025). Automated Imaging and Analysis of Platelet, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Activities Using a Novel Flow Chip-Based System at Physiological Temperature. Micromachines, 16(11), 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111253







