Research on a Phase-Shift-Based Discontinuous PWM Method for 24V Onboard Thermally Limited Micro Voltage Source Inverters
Abstract
1. Introduction
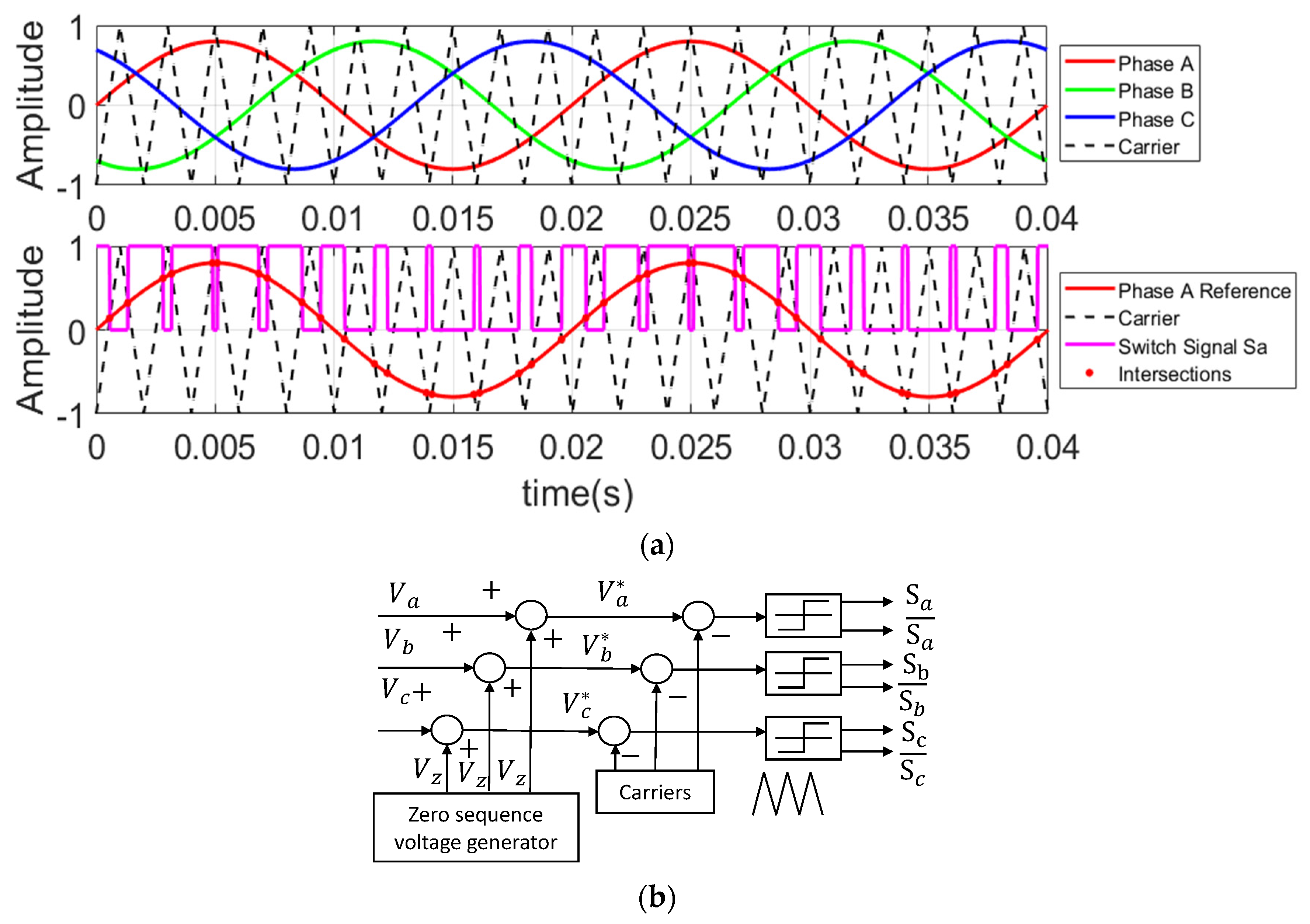
2. Discontinuous PWM Modulation Method with Phase Shift Angle
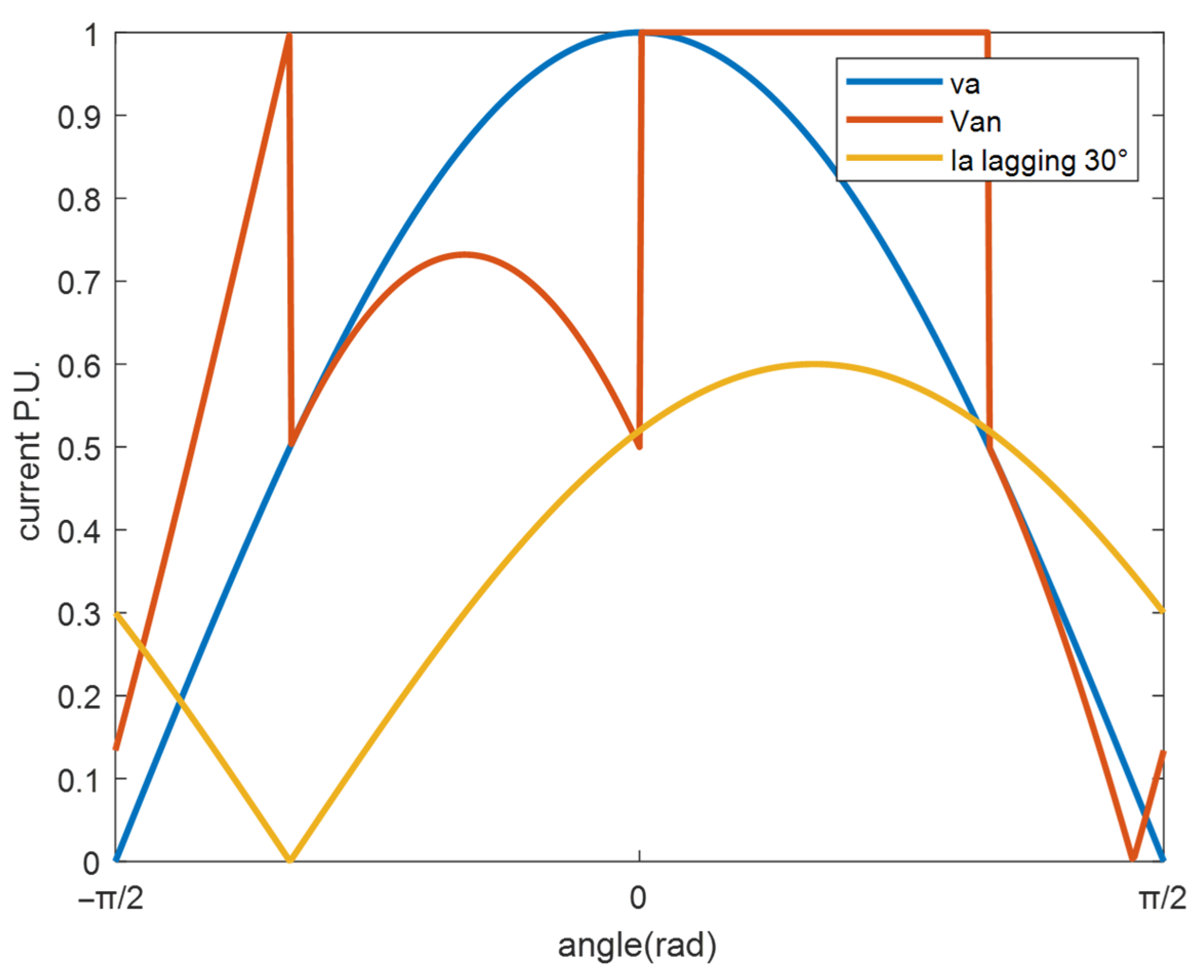
2.1. Basic Principle of Zero-Sequence Voltage Injection
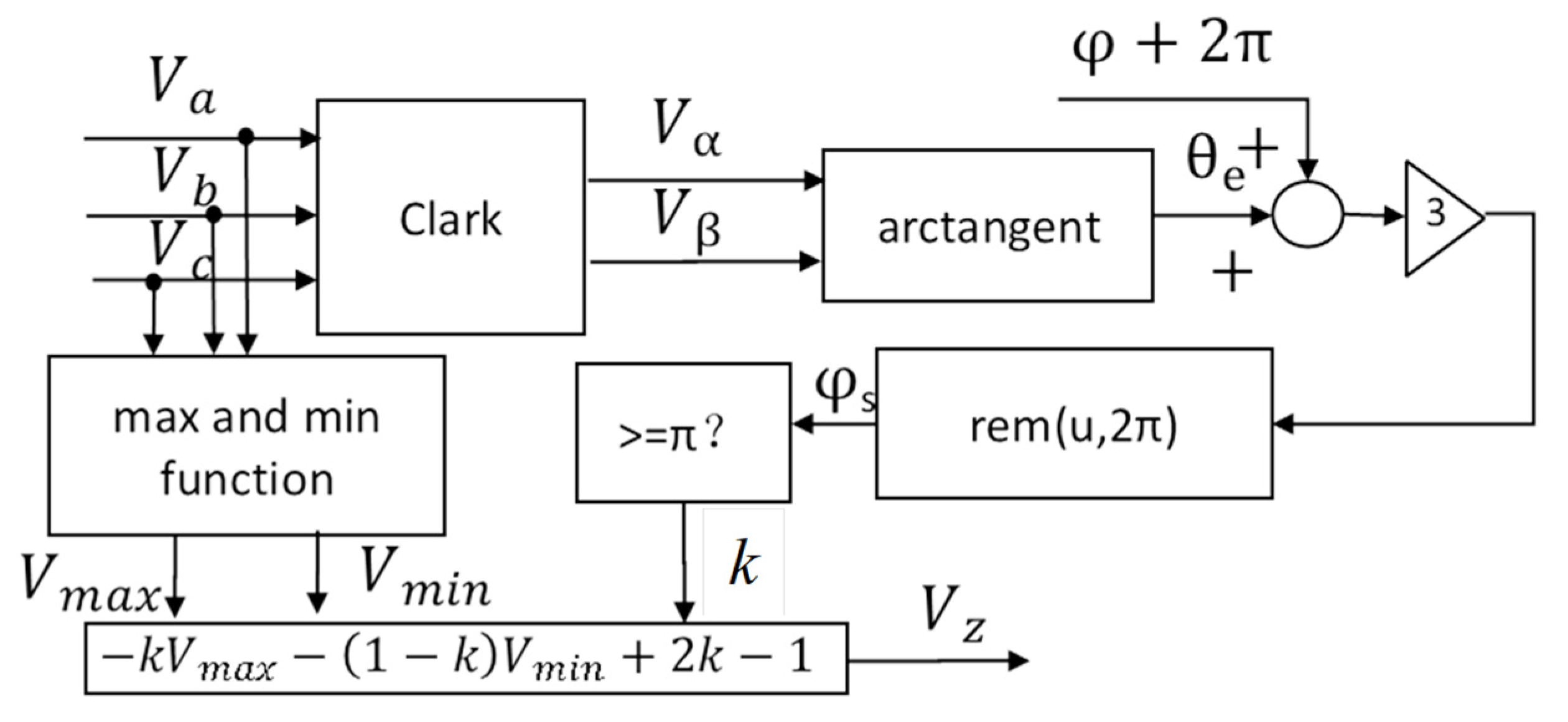
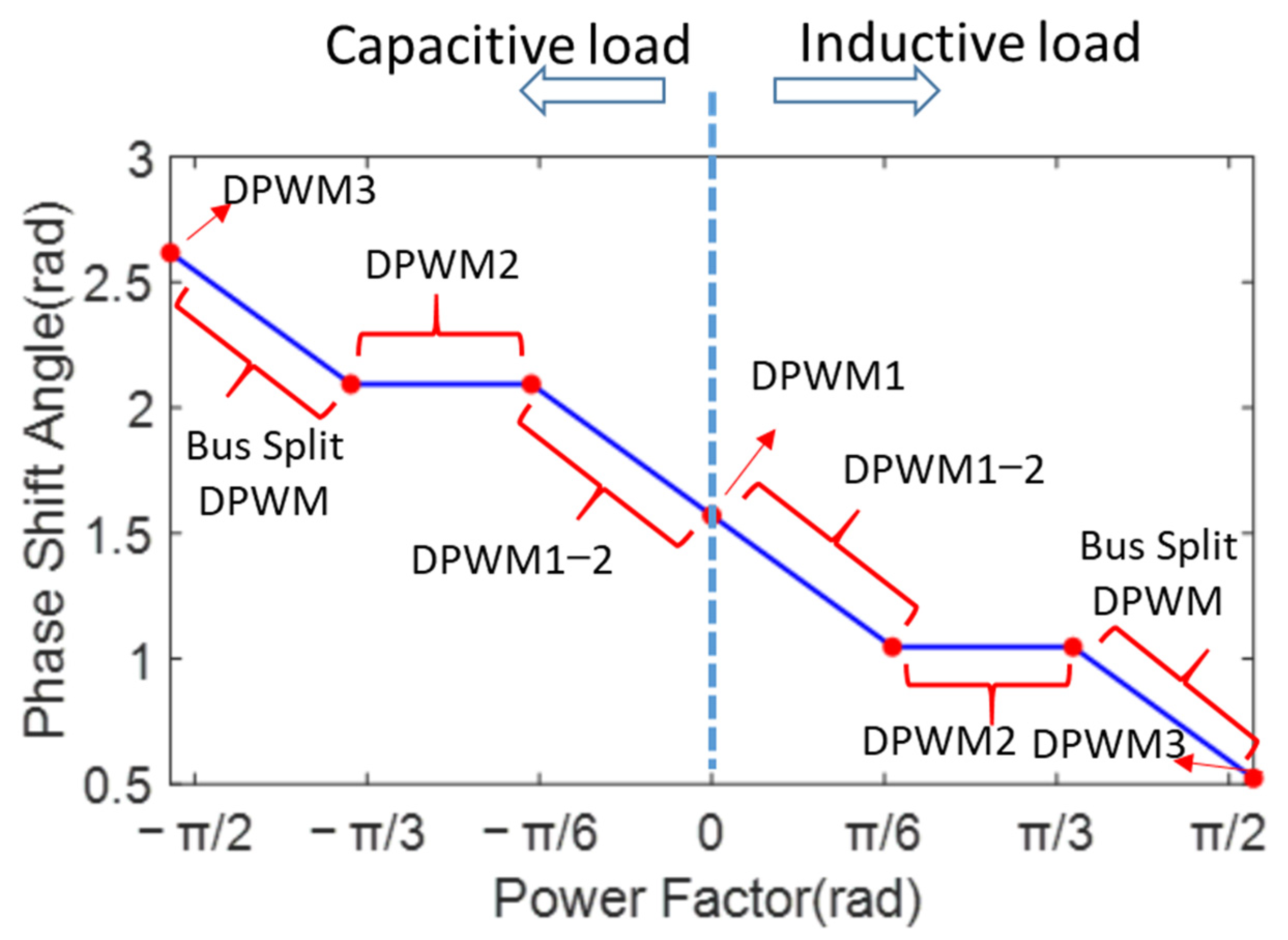
2.2. Zero-Sequence Voltage Generation Method with Phase Shift Angle
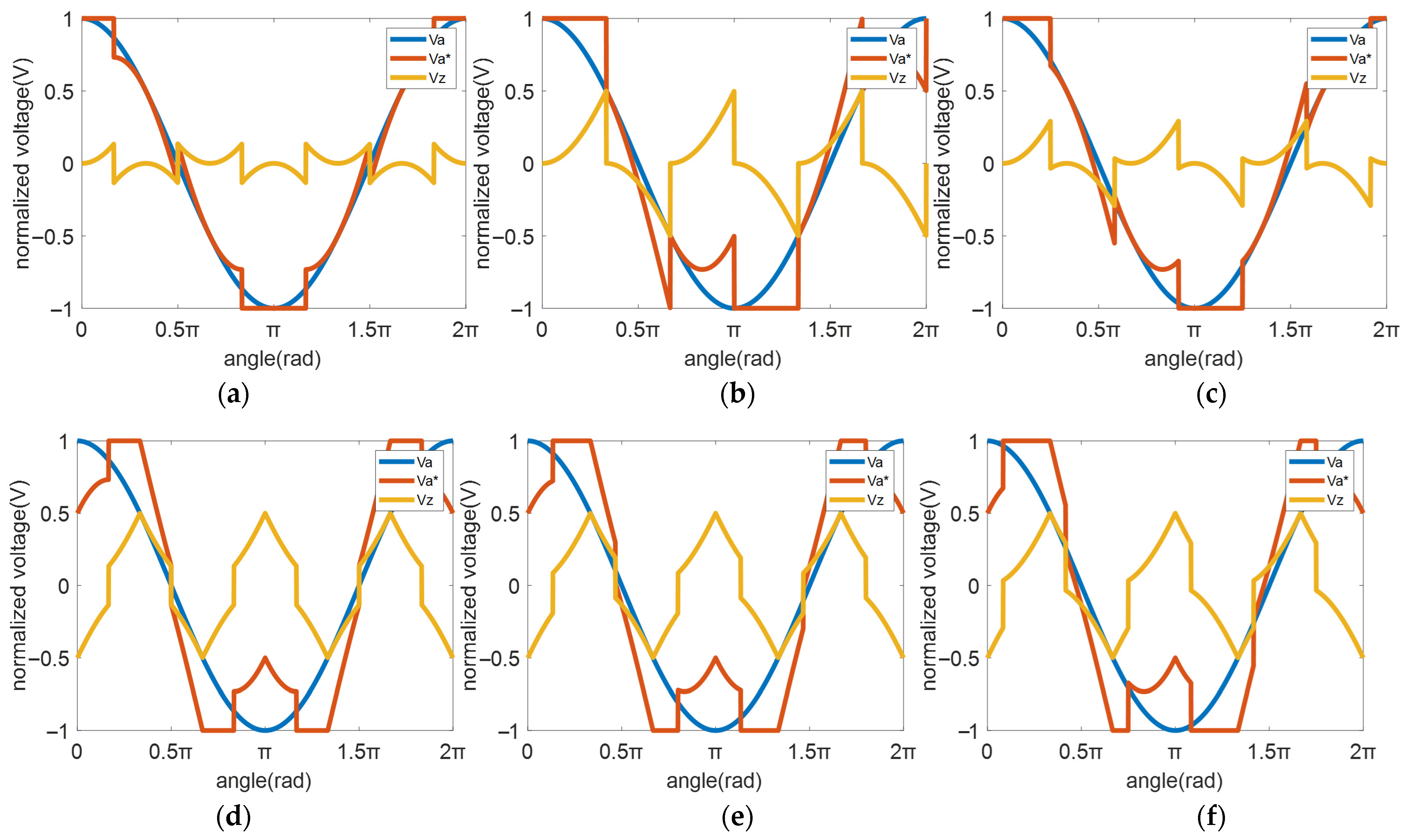
3. Analysis of Switching Characteristics and Harmonic Performance for All DC Bus-Clamping DPWM Modes
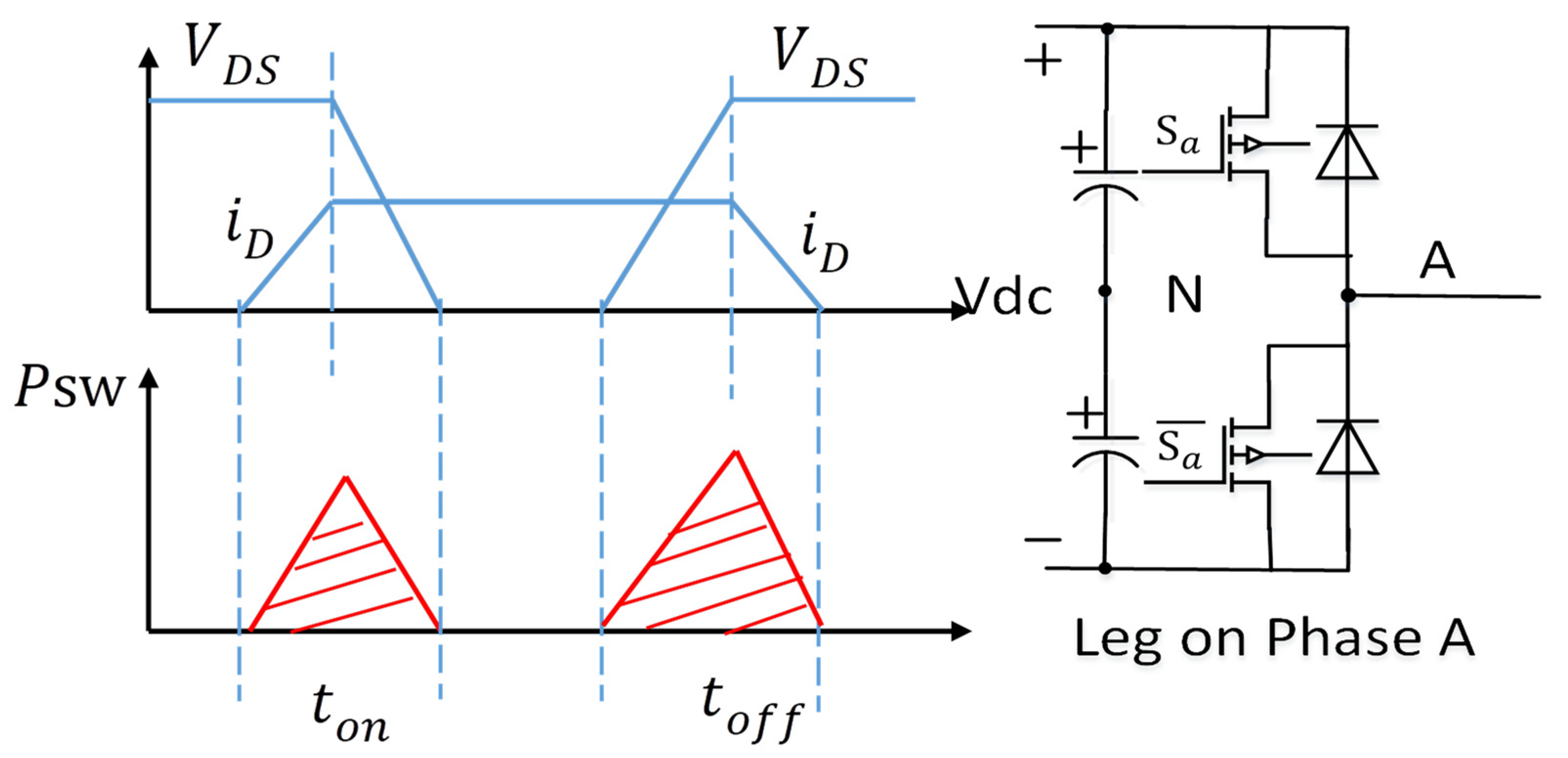
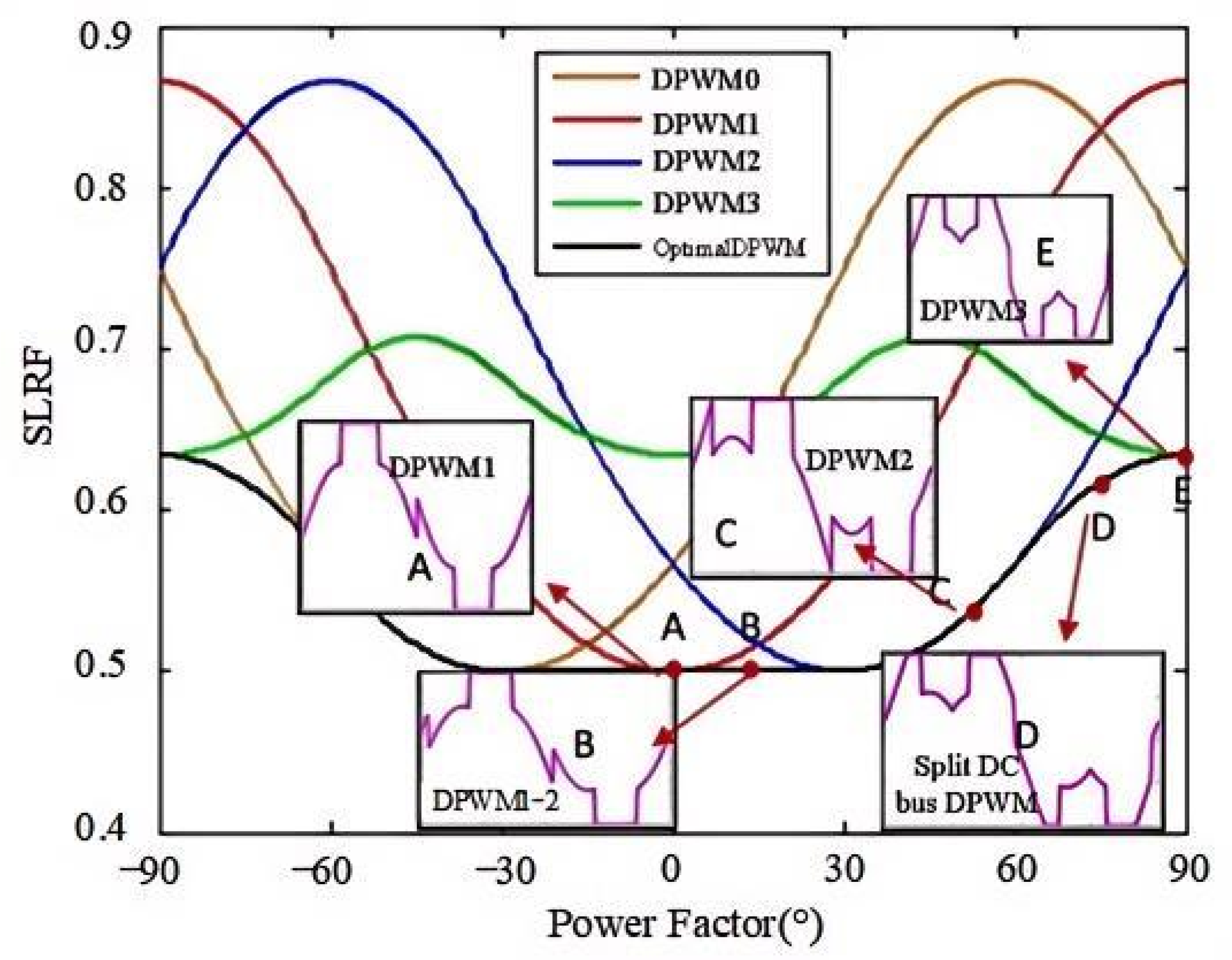
3.1. Analysis of DPWM Switching Characteristics
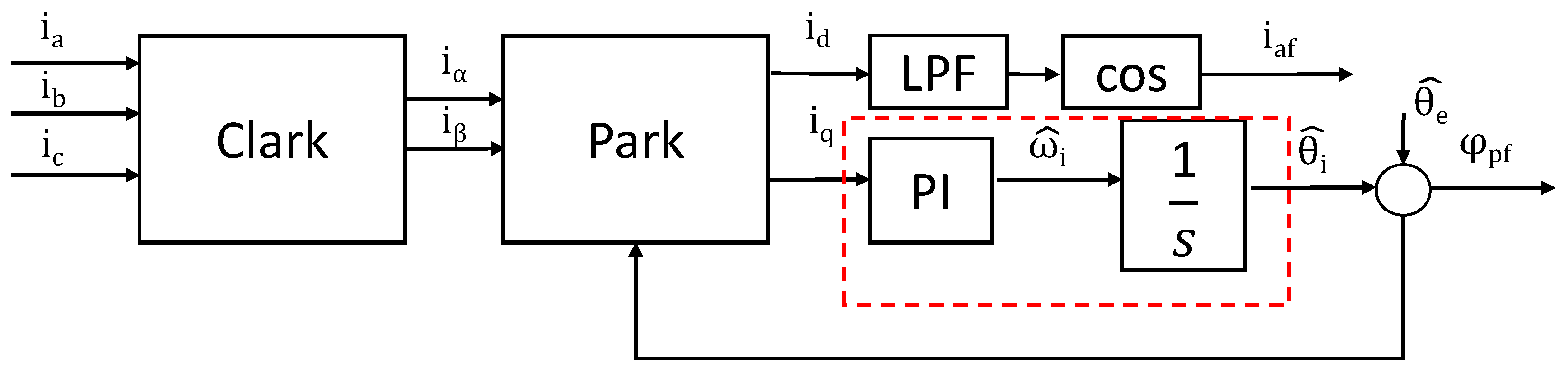
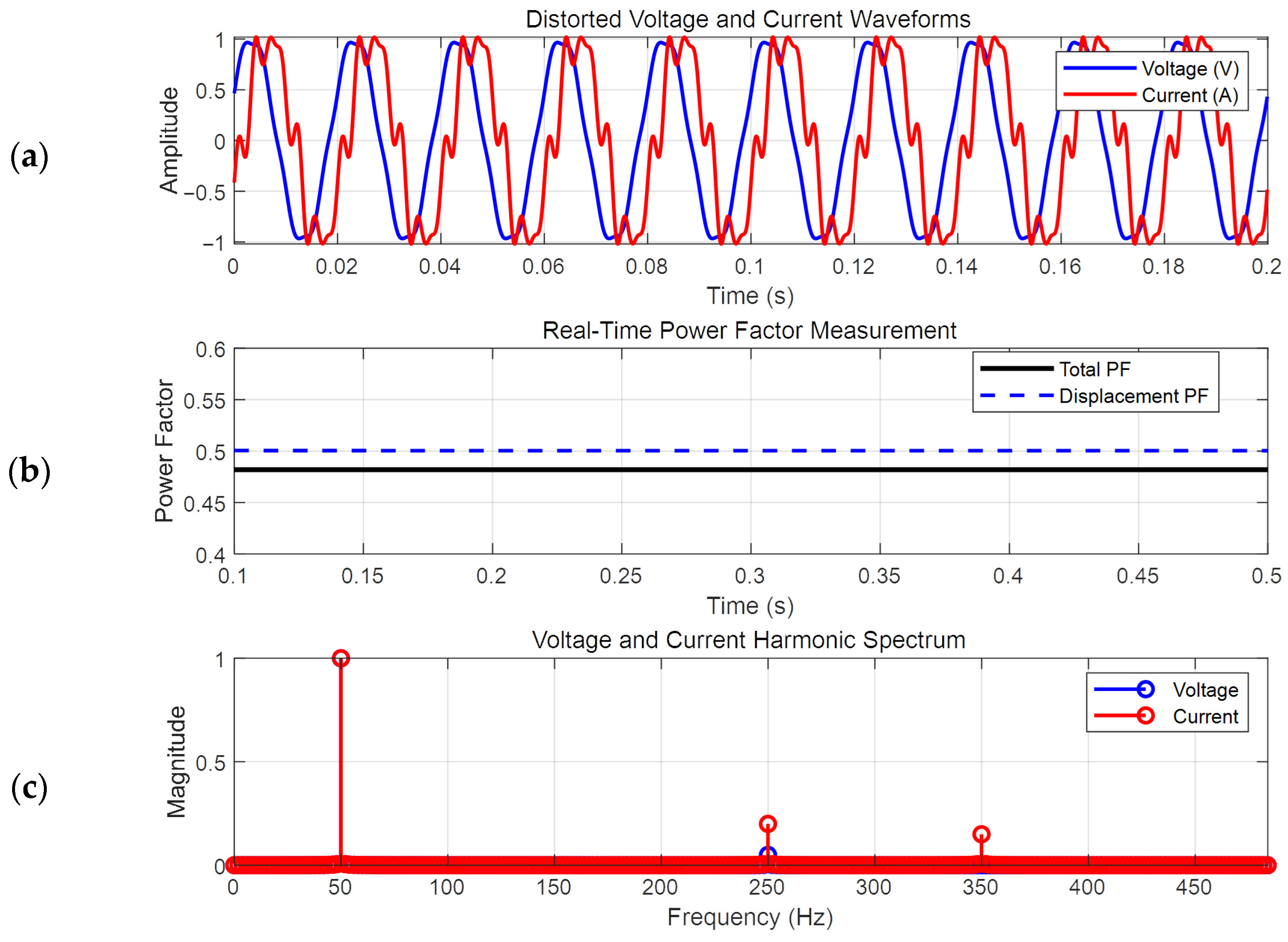
3.2. Real-Time Power Factor Extraction Using SRF-PLL
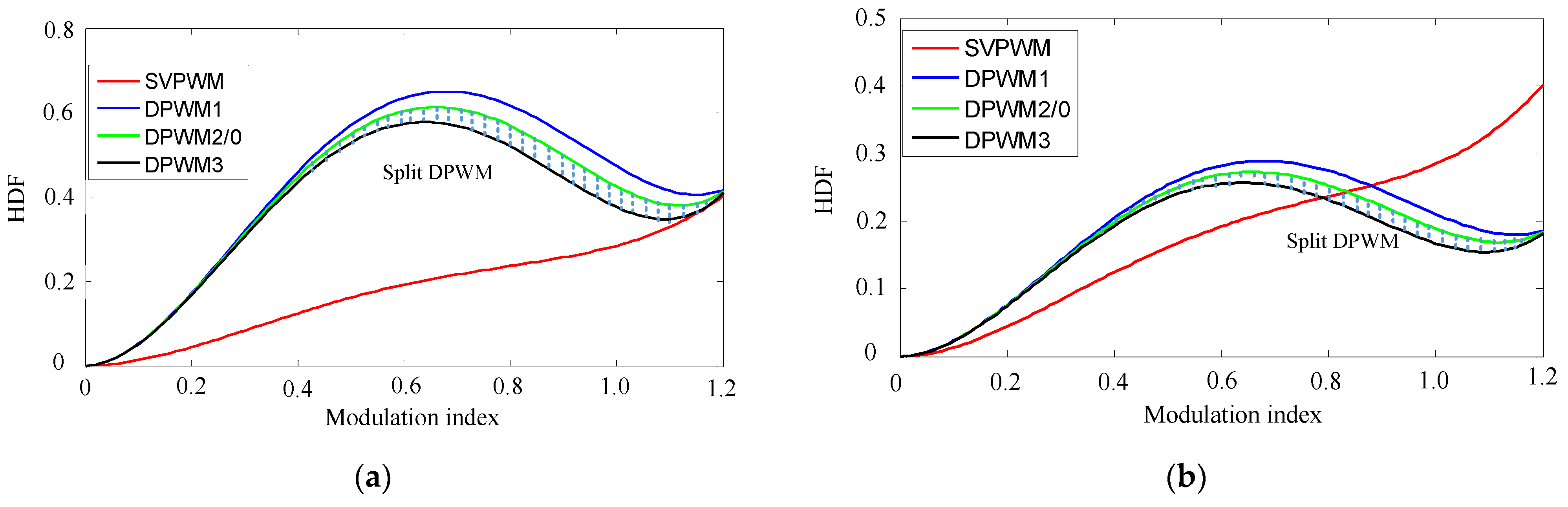
3.3. Harmonic Characteristics Analysis
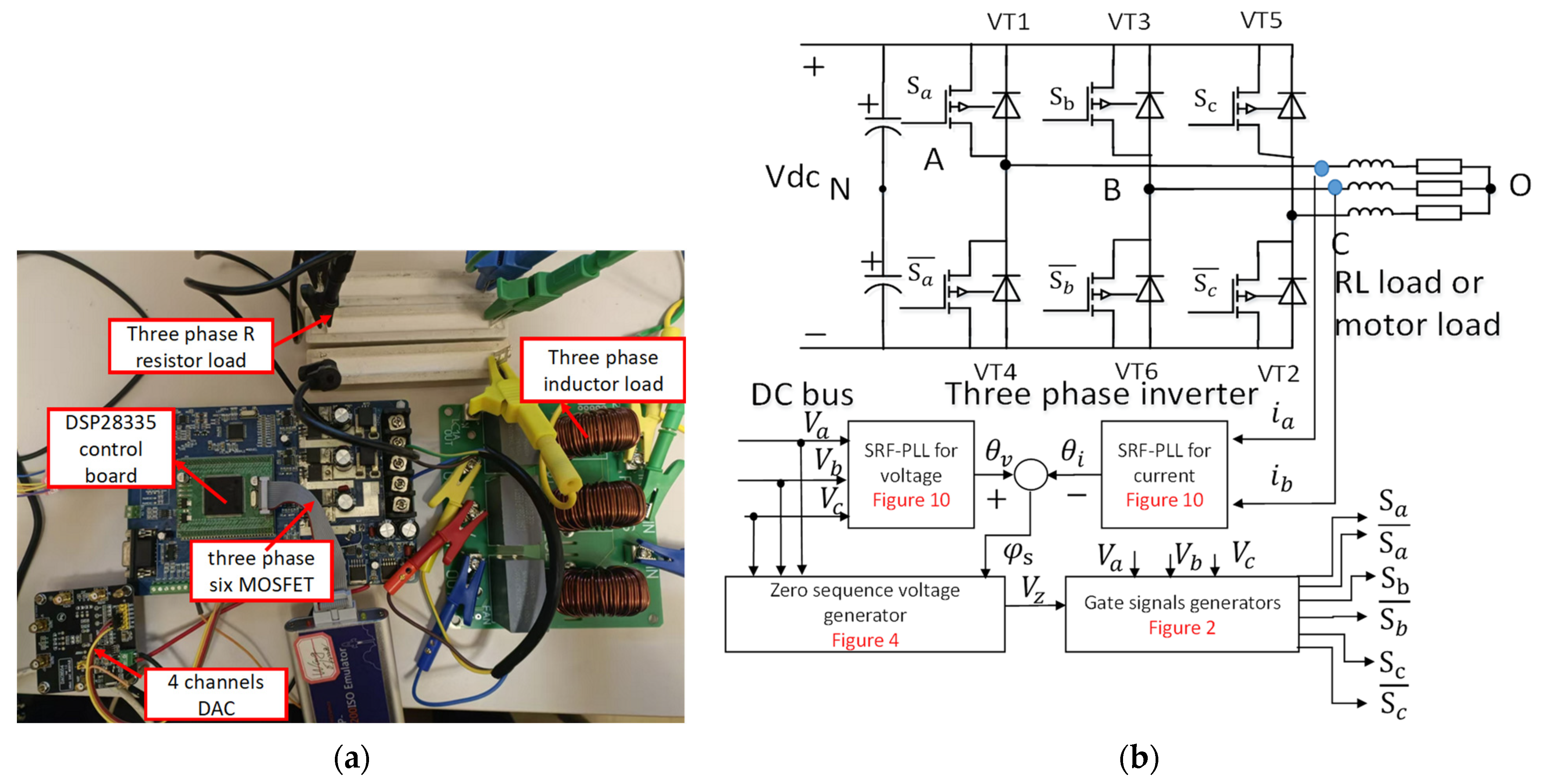
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Inverter Efficiency Test
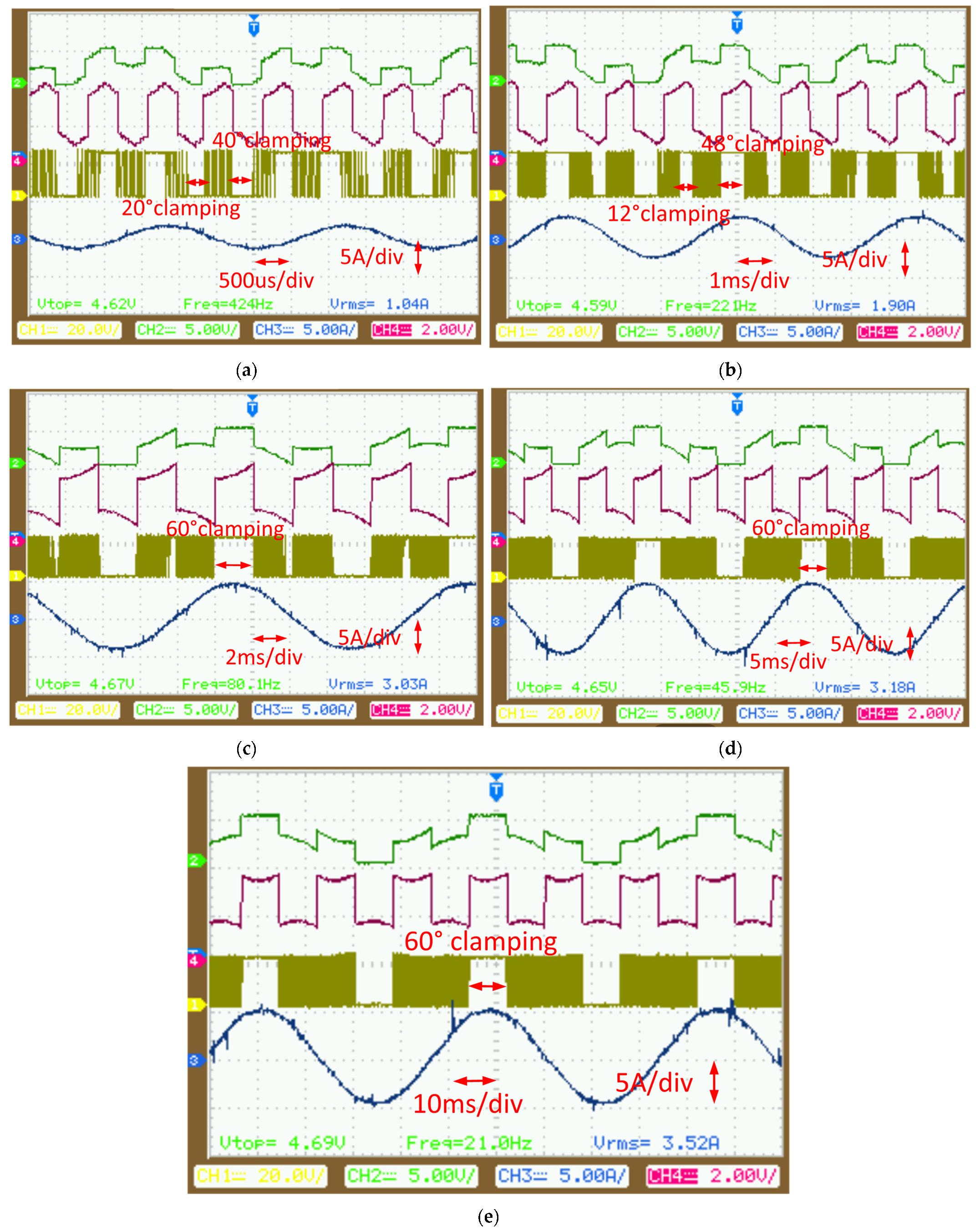
4.2. Testing for Different Modulation Strategies with Different Power Factors
4.3. Testing for Harmonics
5. Conclusions
- (1).
- Switching Loss Reduction: It maintains 40% lower switching losses compared with CPWM even under extremely low-power-factor conditions, significantly improving inverter efficiency over the full operating range.
- (2).
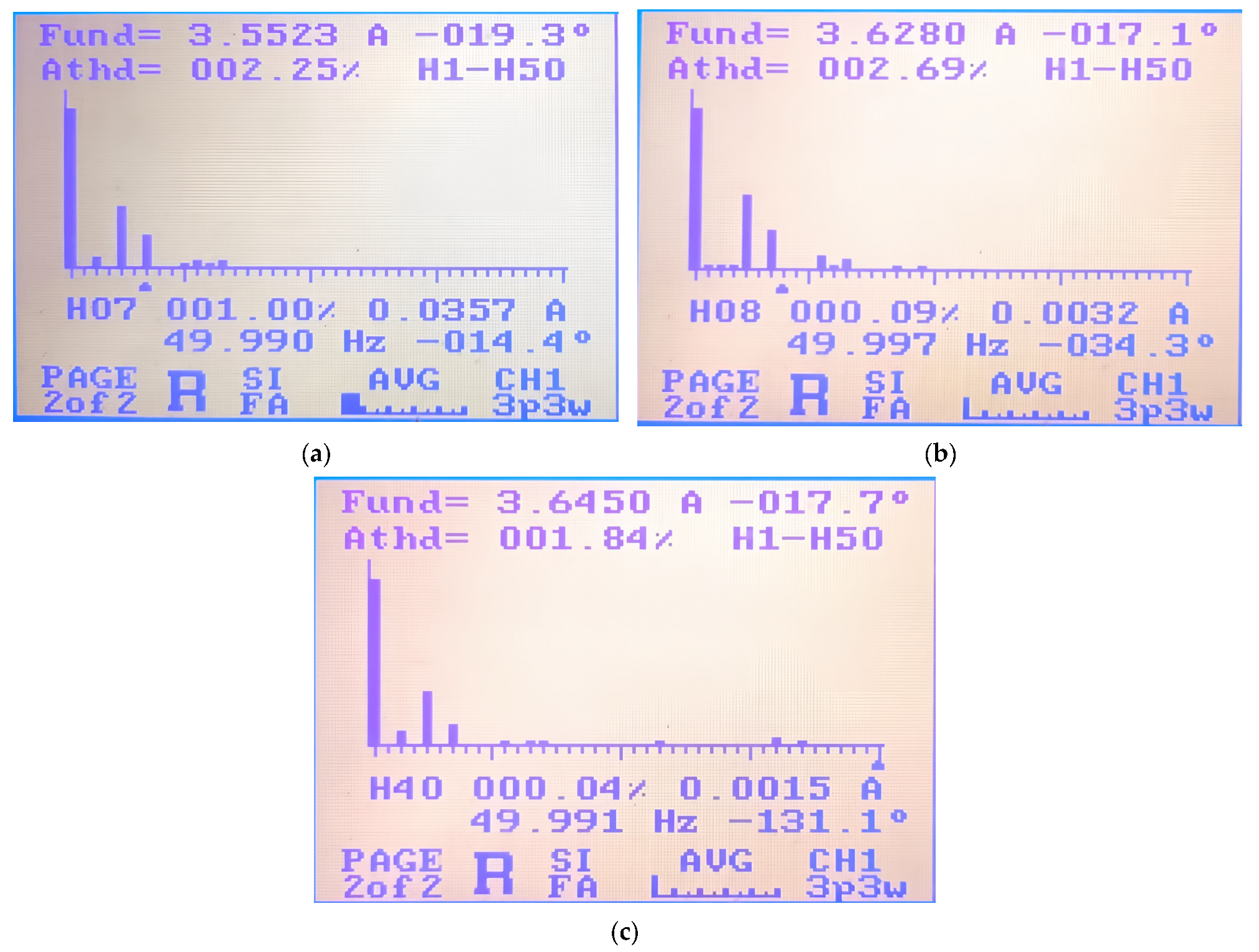
- Improved Waveform Quality: It reduces the current THD from 2.25% to 1.84% at high modulation indices compared to traditional SVPWM while preserving equivalent switching losses.
- (3).
- Robust Dynamic Performance: It demonstrates seamless adaptation to power factor transients and extreme operational conditions, ensuring stable and efficient operation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irudayaraj, S.S.; Emadi, A. Micromachines: Principles of operation, dynamics, and control. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electric Machines and Drives, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15 May 2005; pp. 1108–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunseye, A.; Johnson, D.O. Development of a Microcontroller-Based 6/12/18/24 V Power Inverter Circuit. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. Comput. Sci. 2017, 10, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, Q.; Han, P.; Mei, N. A review of converter circuits for ambient micro energy harvesting. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarhoseini, S.M.; Kale, A.S.; Koniers, P.M.; Boone, A.C.; Bentor, J.; Bioes, A.; Zhao, H.; Xuan, X. Charge-Based Separation of Microparticles Using AC Insulator-Based Dielectrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 13672–13678. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Guo, W.; Tao, Y.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Meng, X.; Yang, R.; Xue, R.; Ren, Y. Ambient Moisture-Driven Self-Powered Iontophoresis Patch for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2401371. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Mascarella, D.; Joos, G. Interleaved SVPWM and DPWM for dual three-phase inverter-PMSM: An automotive application. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Dearborn, MI, USA, 15–18 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ayano, H.; Nakagaki, T.; Iguchi, Y.; Matsui, Y.; Itoh, J.-I. Theoretical study of rampwise DPWM technique to reduce motor acoustic noise. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 8102–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wei, M.; Xie, C.; Deng, F.; Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C. Triangle carrier-based DPWM for three-level NPC inverters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 6, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, R.; Ju, P.; Ji, C.; Zou, Y.; Ming, Y.; Xing, Y. A modified DPWM with neutral point voltage balance capability for three-phase Vienna rectifiers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, C.; Duan, S.X.; Wang, T.; Liu, P. A carrier-based discontinuous PWM method with varying clamped area for Vienna rectifier. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 7177–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiminoaei, L.; Rodriguez, P.; Blaabjerg, F.; Malinowski, M. Reduction of switching losses in active power filters with a new generalized discontinuous-PWM strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wei, M.; Xie, C.; Deng, F.; Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C. A generalized discontinuous PWM based neutral point voltage balancing method for three-level NPC voltage source inverter with switching losses reduction. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Tampa, FL, USA, 26–30 March 2017; pp. 1816–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Artal-Sevil, J.S.; Bernal-Agustín, J.L.; Beyza, J.; Ruiz-Paredes, H.F. Generalized Discontinuous PWM strategy applied to a grid-connected Modular Multilevel Converter. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Autumn Meeting on Power, Electronics and Computing (ROPEC), Ixtapa, Mexico, 13–15 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- An, S.L.; Sun, X.D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Ren, B. Study on the novel generalized discontinuous SVPWM strategies for three-phase voltage source inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2012, 9, 781–789. [Google Scholar]
- Hava, A.M.; Kerkman, R.J.; Lipo, T.A. A high-performance generalized discontinuous PWM algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shafi, M.A.; Knight, A.M.; Mcmahon, R. Comparison of the effects of continuous and discontinuous PWM schemes on power losses of voltage-sourced inverters for induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 26, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.G.; Lipo, T.A. Pulse Width Modulation for Power Converters: Principles and Practice; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Sha, D.; Zhang, J. Current ripple prediction and DPWM-based variable switching frequency control for full ZVS range three-phase inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. DPWM Control Strategy of Auxiliary Inverter for Urban Rail Transit Based on Adaptive Power Factor. Proc. CSEE 2021, 41, 356–365. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.-Q.; Diao, L.-J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.-G.; Wang, L. Performance Optimization of the Minimum-Loss PWM Algorithm for Three Phase Voltage Inverter. Proc. CSEE 2016, 36, 3005–3016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Tan, G.; Ye, Z.; Li, H. Pulse Width Modulation Strategy for Three-phase Voltage Source Inverters Based on Multi-objective Satisfactory Optimization. Proc. CSEE 2016, 36, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, G.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Ye, Z. A generalized algorithm to eliminate spikes of common-mode voltages for CMVRPWM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 6698–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Yoo, A.; Hong, C. A carrier-based adjustable discontinuous PWM for three-phase voltage source inverter. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 September 2015; pp. 2870–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Hobraiche, J.; Patin, N.; Friedrich, G.; Vilain, J.-P. A direct digital technique implementation of general discontinuous pulse width modulation strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 58, 4445–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Hari, V.S.S.P.K.; Narayanan, G.; Ayyanar, R. Space-vector-based hybrid pulsewidth modulation techniques for reduced harmonic distortion and switching loss. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 25, 760–774. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel, A.E. Powers in nonsinusoidal situations-a review of definitions and physical meaning. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2002, 5, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, G.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Wu, M.C. Measuring harmonics by an improved FFT-based algorithm with considering frequency variations. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Island of Kos, Greece, 21–24 May 2006; 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy, P.; Misra, B.; Nayak, B. Phase-locked loop based synchronization schemes for three-phase unbalanced and distorted grid: A review. Int. J. Appl. Power Eng. 2024, 13, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula, W.J.; Tavares, G.H.M.; Soares, G.M.; Almeida, P.; Braga, H.A.C. Switching losses prediction methods oriented to power MOSFETs—A review. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.J.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, X.; Fu, Y.; Kumar, P. Power MOSFET switching loss analysis: A new insight. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2006 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Forty-First IAS Annual Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 October 2006; Volume 3, pp. 1438–1442. [Google Scholar]




| PWM Mode | Input Power (W) | Output Power (W) | Losses on Control Chip and Peripherals (W) | Losses on Micro Inverter (W) | Efficiency for Inverter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVPWM | 62.114 | 40.2 | 3.75 | 18.16 | 64.72% |
| DPWM1 | 63.5208 | 42.8 | 3.75 | 16.97 | 67.38% |
| DPWM1–2 | 60.2646 | 40.8 | 3.74 | 15.72 | 67.70% |
| DPWM2 | 59.5825 | 40.4 | 3.74 | 15.44 | 67.81% |
| DPWM45/15 | 59.26624 | 39.6 | 3.74 | 15.92 | 66.82% |
| DPWM3 | 62.42674 | 41.3 | 3.74 | 17.39 | 66.16% |
| PWM Mode | Input Power (W) | Output Power (W) | Losses on Control Chip and Peripherals (W) | Losses on Micro Inverter (W) | Efficiency for Inverter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVPWM | 16.35 | 9.5 | 3.76 | 3.09 | 58.11% |
| DPWM1 | 16.15 | 9.78 | 3.76 | 2.61 | 60.58% |
| DPWM1–2 | 16.19 | 10.1 | 3.76 | 2.33 | 62.37% |
| DPWM2 | 15.84 | 9.946 | 3.76 | 2.14 | 62.78% |
| DPWM45/15 | 15.75 | 10.12 | 3.76 | 1.87 | 64.25% |
| DPWM3 | 15.16 | 9.7 | 3.76 | 1.70 | 64.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Xia, C. Research on a Phase-Shift-Based Discontinuous PWM Method for 24V Onboard Thermally Limited Micro Voltage Source Inverters. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101128
Wang S, Xia C. Research on a Phase-Shift-Based Discontinuous PWM Method for 24V Onboard Thermally Limited Micro Voltage Source Inverters. Micromachines. 2025; 16(10):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101128
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuo, and Chenyang Xia. 2025. "Research on a Phase-Shift-Based Discontinuous PWM Method for 24V Onboard Thermally Limited Micro Voltage Source Inverters" Micromachines 16, no. 10: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101128
APA StyleWang, S., & Xia, C. (2025). Research on a Phase-Shift-Based Discontinuous PWM Method for 24V Onboard Thermally Limited Micro Voltage Source Inverters. Micromachines, 16(10), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101128






