High-Performance Silicon Nanowire Array Biosensor for Combined Detection of Colorectal Cancer Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
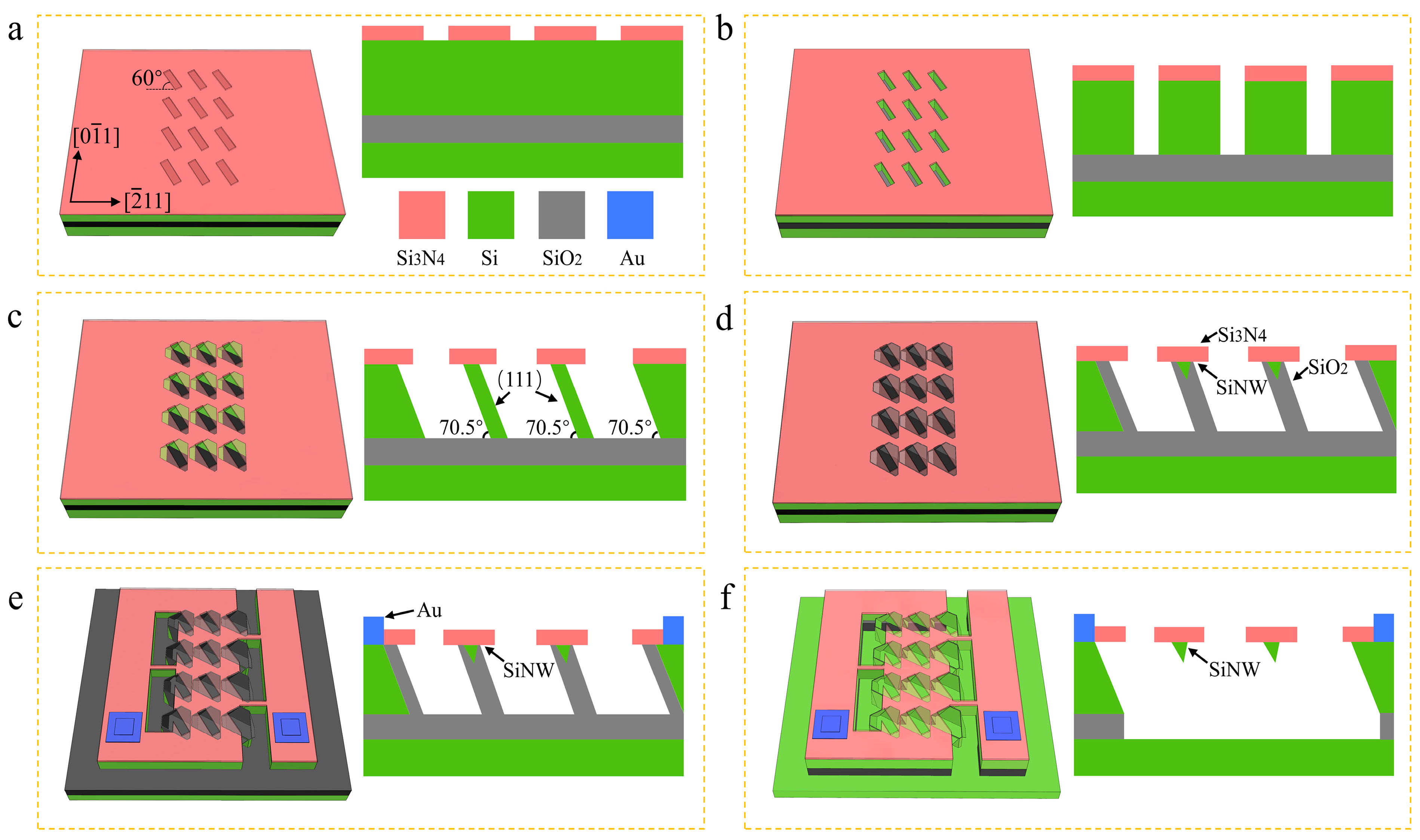
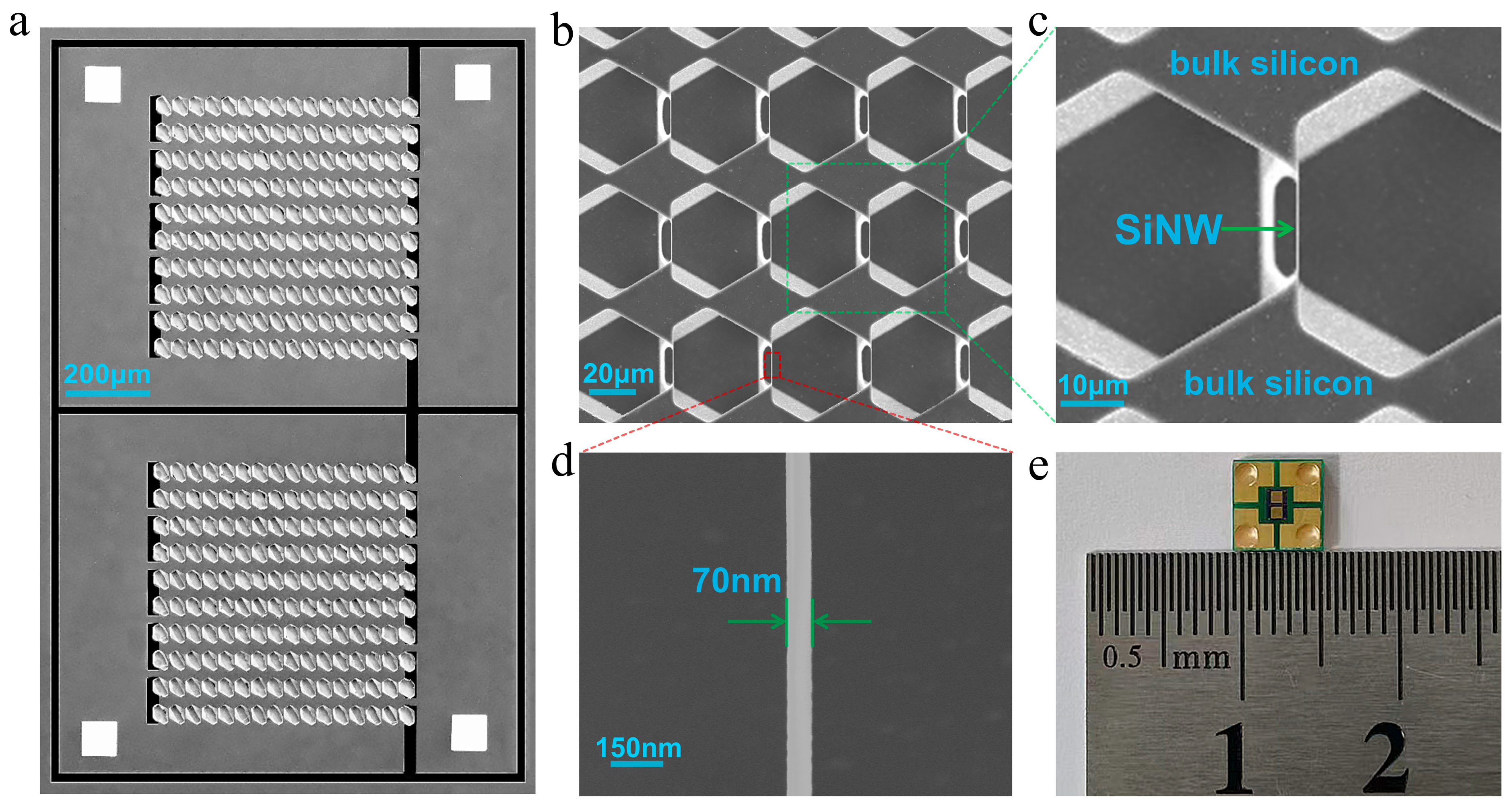
2.1. The Fabrication of SiNW Array Biosensor
2.2. The Reagents and Test Equipment
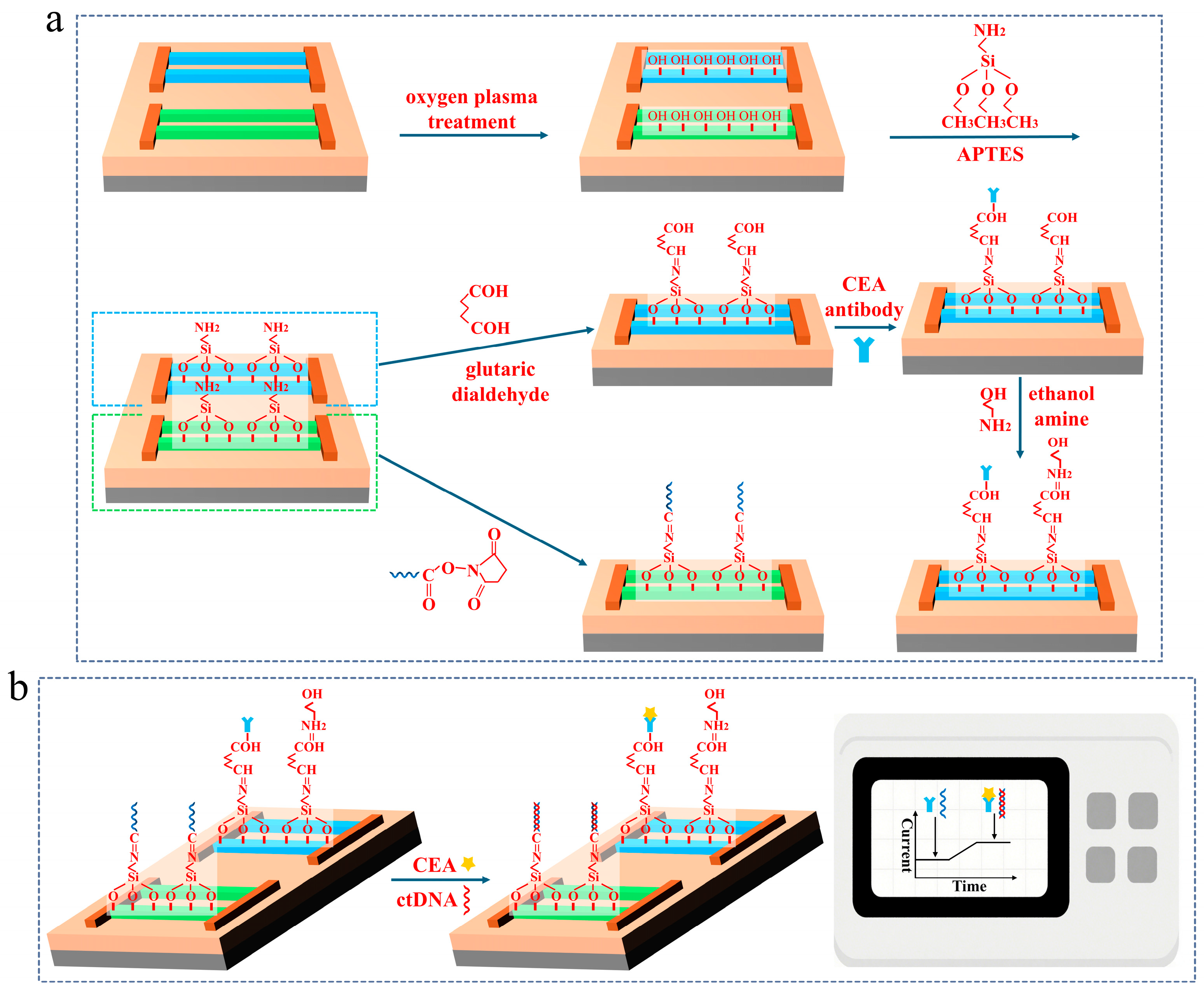
2.3. The Surface Modification of the SiNW Array Biosensor
3. Results
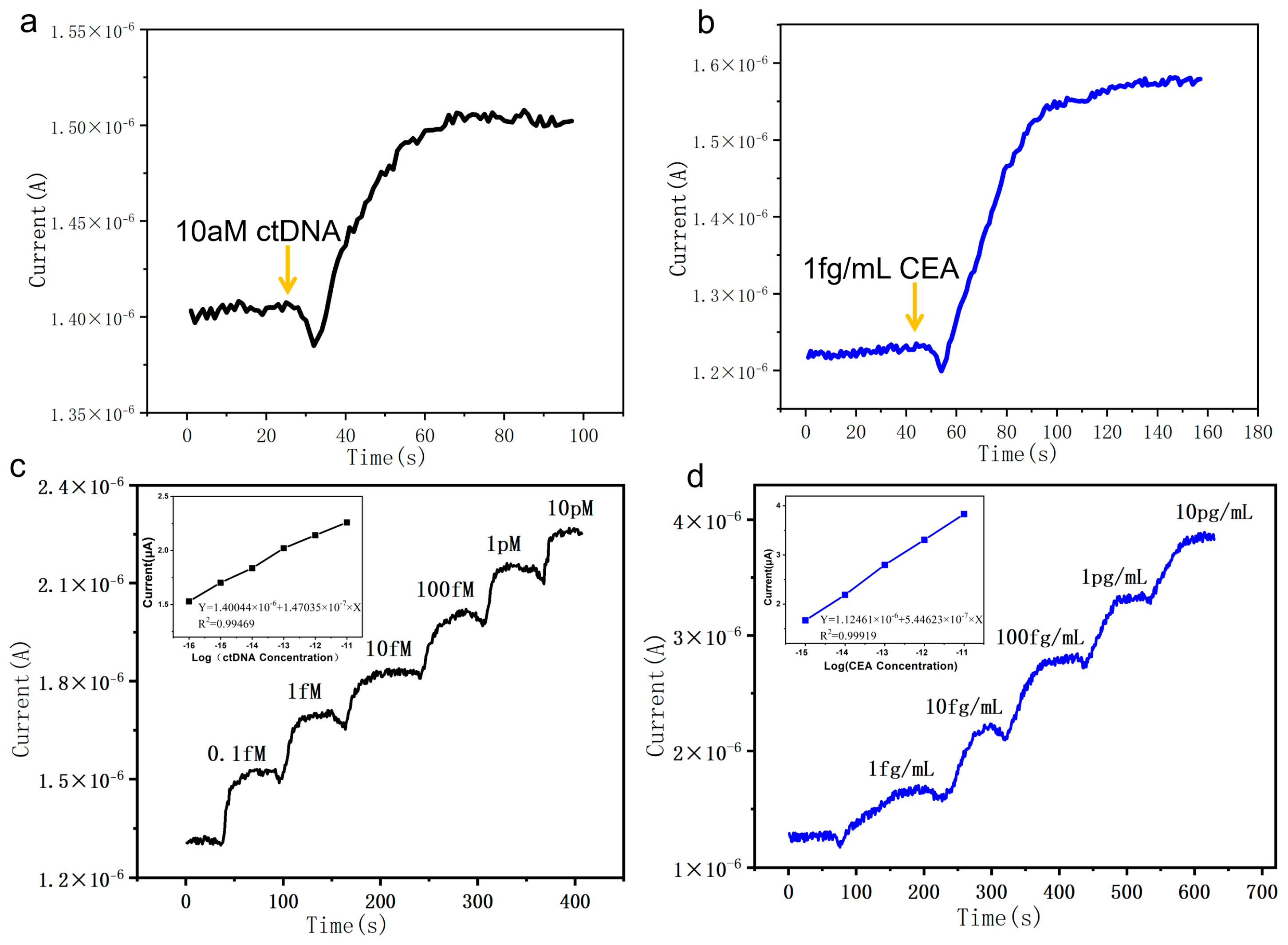
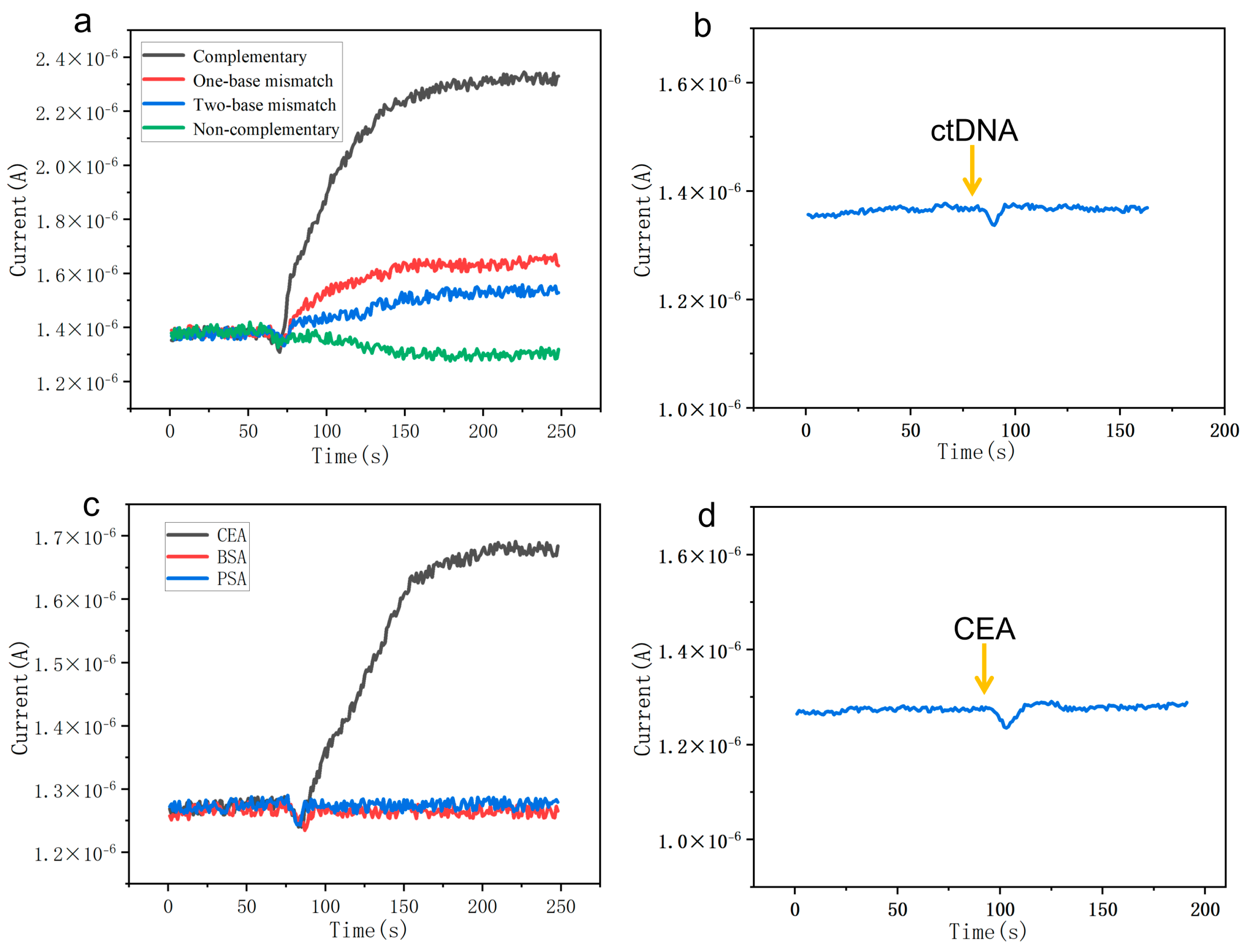
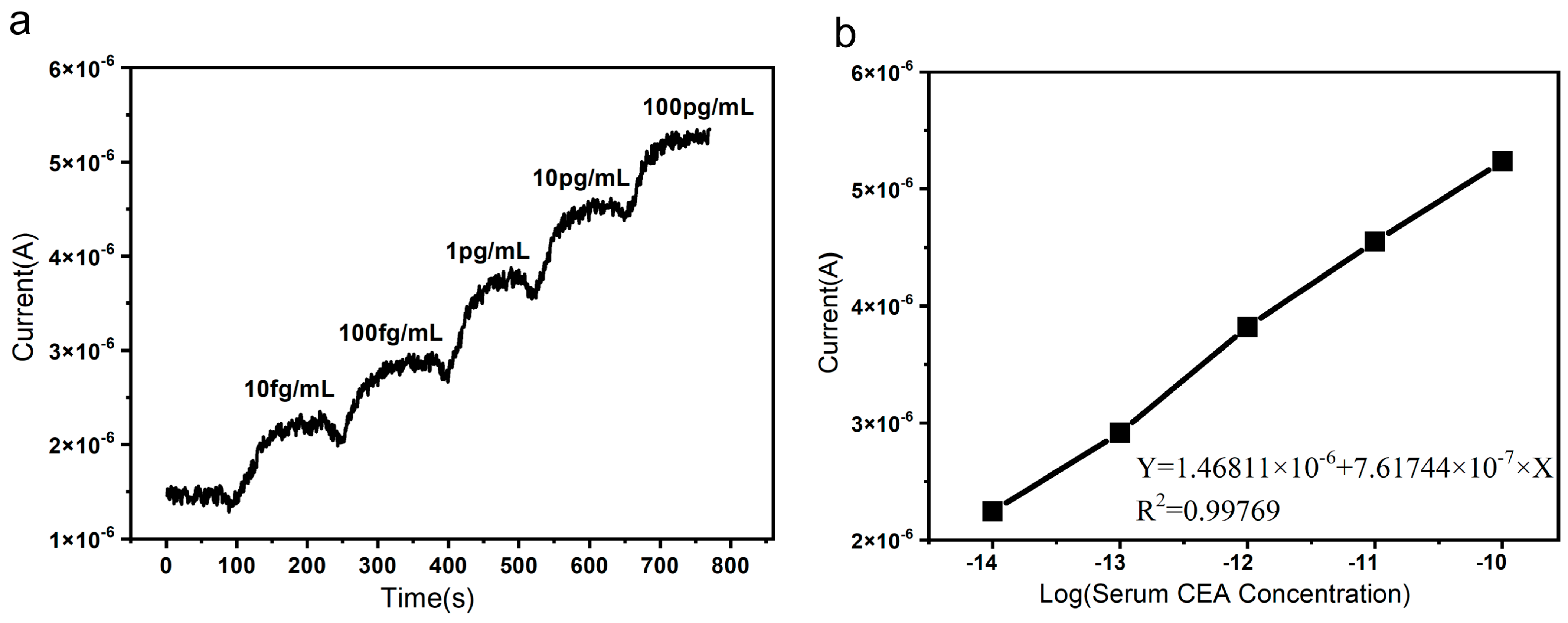
3.1. The Detection and Sensitivity of the SiNW Array Biosensor
3.2. The Specificity of the SiNW Array Biosensor
3.3. The Detection in Human Serum Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamrasnarodom, J.; Rajborirug, P.; Pisespongsa, P.; Pasupa, K. Optimizing colorectal polyp detection and localization: Impact of RGB color adjustment on CNN performance. MethodsX 2025, 14, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Feng, X.; Jia, C.; Li, J.; Yin, H.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; et al. Uncovering the underlying mechanism of yuanhuacine against colorectal cancer by transcriptomics and experimental investigations. Phytomedicine 2025, 140, 156570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rochais, M.; Brahim, I.; Zeghlache, R.; Redoulez, G.; Guillard, M.; Le Noac’h, P.; Castillon, M.; Bourhis, A.; Uguen, A. Automated classification of tertiary lymphoid structures in colorectal cancer using TLS-PAT artificial intelligence tool. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamzari, K.A.M.A.; Constantinou, C. Navigating the Colorectal Cancer Maze: Unveiling Pathways to Diagnosis, Management, Pathophysiology and Prevention. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Akasu, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Fujita, S.; Moriya, Y. Long-term results of hepatectomy after hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for initially unresectable hepatic colorectal metastases. J. Gastrointest. Surg. Off. J. Soc. Surg. Aliment. Tract 2009, 13, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Lee, J.K. Colonoscopy: Advanced and Emerging Techniques—A Review of Colonoscopic Approaches to Colorectal Conditions. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2017, 30, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriza, C.; Emmert, M.; Wahlster, P.; Niederländer, C.; Kolominsky-Rabas, P. An international review of the main cost-effectiveness drivers of virtual colonography versus conventional colonoscopy for colorectal cancer screening: Is the tide changing due to adherence? Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, e629–e636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paimela, H.; Malila, N.; Palva, T.; Hakulinen, T.; Vertio, H.; Järvinen, H. Early detection of colorectal cancer with faecal occult blood test screening. J. Br. Surg. 2010, 97, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colapietro, P.; Brunetti, G.; Panciera, C.; Elicio, A.; Ciminelli, C. Shining the Path of Precision Diagnostic: Advancements in Photonic Sensors for Liquid Biopsy. Biosensors 2025, 15, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Sledge, G.W.; Jeffrey, S.S. Liquid biopsy enters the clinic—Implementation issues and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, A.R.; Mojtahed, A.; Schneider, J.L.; Kanter, K.; Van Seventer, E.E.; Fetter, I.J.; Fish, M.G.; Teshome, B.; Fosbenner, K.; Nadres, B.; et al. Serial ctDNA monitoring to predict response to systemic therapy in metastatic gastrointestinal cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, J.; Cohen, D.J.; Wang, Y.; Christie, M.; Simons, K.; Lee, M.; Wong, R.; Kosmider, S.; Ananda, S.; McKendrick, J.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analyses as Markers of Recurrence Risk and Benefit of Adjuvant Therapy for Stage III Colon Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, Y.S.; Wu, H.X.; Wang, Z.X.; Jin, Y.; Yao, Y.C.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, S.; He, M.M.; et al. Genomic temporal heterogeneity of circulating tumour DNA in unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer under first-line treatment. Gut 2021, 71, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liatsou, E.; Kollias, I.; Trapali, M.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I. Liquid Biopsies in the Early Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Tailored Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Mu, T.; Gu, J.; Xu, M.; Chen, S. The Method of Minimal Residual Disease Detection With Circulating Tumor DNA and Its Clinical Applications in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Rep. 2025, 8, e70167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalti, R.; Pepe, F.; Cassese, G.; Russo, G.; Malapelle, U.; Carlomagno, C.; Giglio, M.C.; Falco, G.; Alagia, M.; De Simone, G.; et al. Prognostic role of postoperative persistence of ctDNA molecular signature after liver resection for colorectal liver metastases: Preliminary results from a prospective study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Surg. Oncol. Br. Assoc. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 51, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamfjord, J.; Guren, K.T.; Glimelius, B.; Sorbye, H.; Pfeiffer, P.; Dajani, O.; Lingjærde, O.C.; Tveit, K.M.; Spindler, K.-L.G.; Pallisgaard, N.; et al. Exploring Early Kinetic Profiles of CEA, ctDNA and cfDNA in Patients With RAS-/BRAF-Mutated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Color. Cancer 2024, 24, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kildusiene, I.; Dulskas, A.; Smailyte, G. Value of combined serum CEA, CA72-4, and CA19-9 marker detection in diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Tech. Coloproctol. 2024, 28, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, G.; Li, H.; Shen, Y.; Tan, Z.; Qian, H. The combined evaluation of preoperative serum CEA and postoperative tissue CEA as a prognostic factor in stages 0–IV colorectal cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Med. 2025, 11, 1447041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, F.; Yoshida, Y.; Yamada, T.; Tanaka, K.; Hayashi, T.; Shimaoka, H.; Sakamoto, R.; Aisu, N.; Yoshimatsu, G.; Hasegawa, S. Site-Specific Mutations on KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF Corelate With the Frequency of ctDNA in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Rep. 2025, 8, e70292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, J.; Carroll, G.; Zhao, J.; Pockney, P.; Scott, R.J. The Prognostic Utility of KRAS Mutations in Tissue and Circulating Tumour DNA in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Gastroenterol. Insights 2024, 15, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavacchi, D.; Gelmini, S.; Calabri, A.; Rossi, G.; Simi, L.; Caliman, E.; Mancini, I.; Salvianti, F.; Petroni, G.; Guidolin, A.; et al. Early changes in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) predict treatment response in metastatic KRAS-mutated colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, P.; Huang, T.; Song, L.; Xu, R. Circulating Tumor DNA Is Capable of Monitoring the Therapeutic Response and Resistance in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Combined Target and Chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 10466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosuke, K.; Yoshihiro, O.; Yuki, K.; Atsushi, O.; Takafumi, S.; Hiromichi, I.; Yoshihiro, M.; Eiji, S.; Yosuke, I.; Kensei, Y.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Tumor Markers (CEA and CA19-9) on Patients with Resectable Colorectal Liver Metastases Stratified by Tumor Number and Size: Potentially Valuable Biologic Markers for Preoperative Treatment. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 7338–7347. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Shi, Q.; Su, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Carcinoembryonic antigen as a predictor of treatment outcomes in cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2531255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, B.; Gu, Y.-C.; Ying, S.-F.; Tao, B.-R.; Li, Y.-T.; Chen, Z.-M.; Sun, R.-Q.; Yi, C.-H.; Geng, Y.; et al. The Significance of CEA Levels Normalization After Neoadjuvant Therapy in Patients With Initially Resectable Colorectal Liver Metastases. J. Surg. Res. 2025, 313, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Meng, P.; Li, S.; Tan, J.; Su, B.; Cheng, Q.; Yang, X. Detection of two markers for pancreatic cancer (CEA, CA199) based on a nano-silicon sphere-cyclodextrin recognition platform. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 75, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiio, L.K.; Onyatta, J.O.; Ndangili, P.M.; Oloo, F.; Santamaria, C.; Montuenga, L.M.; Mbui, D.N. Ultrasensitive immunosensor for multiplex detection of cancer biomarkers carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and yamaguchi sarcoma viral oncogene homolog 1 (YES1) based on eco-friendly synthesized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2024, 266, 124934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, X.; Cao, W.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. Sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for CEA detection based on Ag/MoS2@Fe3O4 and an analogous ELISA method with total internal reflection microscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Wang, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, X. Label-free fluorimetric detection of CEA using carbon dots derived from tomato juice. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlert, T.; Tug, S.; Brahmer, A.; Neef, V.; Heid, F.; Werner, C.; Jansen-Winkeln, B.; Kneist, W.; Lang, H.; Gockel, I.; et al. Establishing PNB-qPCR for quantifying minimal ctDNA concentrations during tumour resection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindler, K.L.G.; Pallisgaard, N.; Vogelius, I.; Jakobsen, A. Quantitative cell-free DNA, KRAS, and BRAF mutations in plasma from patients with metastatic colorectal cancer during treatment with cetuximab and irinotecan. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinmay, K.; Sunil, K. The Application of Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials in Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment: A Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e29059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Jamil, M.; Ke, G.; Dong, N. The role of nanoparticles and nanomaterials in, cancer diagnosis and treatment: A comprehensive review. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 5751–5784. [Google Scholar]
- Jandas, P.; Luo, J.; Prabakaran, K.; Chen, F.; Fu, Y.Q. Highly stable, love-mode surface acoustic wave biosensor using Au nanoparticle-MoS2-rGO nano-cluster doped polyimide nanocomposite for the selective detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 246, 122800. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, H.; Miao, P. Ultrasensitive assay of ctDNA based on DNA triangular prism and three-way junction nanostructures. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 32, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiri, H.; Abdolahad, M.; Gharooni, M.; Hosseini, S.A.; Janmaleki, M.; Azimi, S.; Hosseini, M.; Mohajerzadeh, S. Monitoring the spreading stage of lung cells by silicon nanowire electrical cell impedance sensor for cancer detection purposes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, L.D.; Meng, G.W.; Li, G.H.; Jin-Phillipp, N.Y.; Phillipp, F. Synthesis of Ordered Single Crystal Silicon Nanowire Arrays. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Li, Z.; Pisano, A.P.; Williams, R.S. Selective surface functionalization of silicon nanowires via nanoscale joule heating. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3106–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Sun, B.; Liu, D.; Lee, S.T. Hybrid heterojunction solar cell based on organic-inorganic silicon nanowire array architecture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19408–19415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Yan, D.; Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, W.; Linxi, D.; Wang, G.; et al. A high-performance NO2 gas sensor based on silicon nanowire array. Physica Scripta 2025, 100, 095404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Yusof, N.; Hashim, U.; Hushiarian, R.; Nuzaihan, M.N.; Hamidon, M.; Zawawi, R.; Fathil, M. Enhanced sensing of dengue virus DNA detection using O2 plasma treated-silicon nanowire based electrical biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 942, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Guo, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y. A dual biomarker detection platform for quantitating circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). Nanotheranostics 2018, 2, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, W.; Xie, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, M. Ultrasensitive Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA of Lung Cancer via an Enzymatically Amplified SERS-Based Frequency Shift Assay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 18145–18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Tang, Y.; Chen, G.; Han, K. A nanoflow cytometric strategy for sensitive ctDNA detection via magnetic separation and DNA self-assembly. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 6039–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hua, G.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Wang, F.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Zhou, X.; Ye, S.-F.; Danyang, L.; et al. Upconversion nanoparticle and gold nanocage satellite assemblies for sensitive ctDNA detection in serum. Analyst 2020, 145, 5553–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tao, M.; Luo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Situ, B.; Ye, X.; Chen, P.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, L. A novel nest hybridization chain reaction based electrochemical assay for sensitive detection of circulating tumor DNA. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1107, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Cui, H.; Wu, L.; Yang, N.; Zhou, W.; Chu, P.K.; Yu, X.-F. Sensitive and selective ctDNA detection based on functionalized black phosphorus nanosheets. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanska, B.; Lukaszewski, Z.; Hermanowicz-Szamatowicz, K.; Gorodkiewicz, E. An immunosensor for the determination of carcinoembryonic antigen by Surface Plasmon Resonance imaging. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 609, 113964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, G.; Lin, J.; Wang, S. Micro-plate magnetic chemiluminescence immunoassay and its applications in carcinoembryonic antigen analysis. Sci. China Chem. 2010, 53, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Maceira, T.; García-Maceira, F.I.; González-Reyes, J.A.; Torres-Sánchez, L.A.; Aragón-Gómez, A.B.; García-Rubiño, M.E.; Paz-Rojas, E. Covalent Immobilization of Antibodies through Tetrazine-TCO Reaction to Improve Sensitivity of ELISA Technique. Biosensors 2021, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Hong, X.; Zhao, S. The application of CdTe/CdS in the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen by fluorescence polarization immunoassay. J. Fluoresc. 2012, 22, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Cao, K.; Wu, M.; Zhao, C.; Li, H.; Hong, C. An electrochemical immunosensor for CEA detection based on Au-Ag/rGO@PDA nanocomposites as integrated double signal amplification strategy. Microchem. J. 2019, 151, 104223. [Google Scholar]
| Methods | Detection Limit (μM) | Test Range (μM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| SERS frequency shift assay | 9.0 × 10–9 | 10–9~10–2 | [44] |
| Nucleic acid biosensor | 2 × 10−6 | 5 × 10−3~1 | [45] |
| NIR fluorescent nanoprobes | 6.3 × 10−6 | 5 × 10−6~10−3 | [46] |
| Electrochemical biosensor | 3 × 10–6 | 5 × 10–4~5 × 10–2 | [47] |
| Fluorescent biosensor | 5 × 10−8 | 5 × 10−8~8×10−5 | [48] |
| SiNW array biosensor | 10−11 | 10−10~10−5 | This work |
| Methods | Detection Limit (pg/mL) | Test Range (pg/mL) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface plasmon resonance | 120 | 400~20,000 | [49] |
| Chemiluminescence immunoassay | 610 | 610~250,000 | [50] |
| Click Chemistry-Based ELISA | 540~660 | 0~200,000 | [51] |
| Fluorescent biosensor | 210 | 210~200,000 | [52] |
| Electrochemical Immunosensor | 0.286 | 1~80,000 | [53] |
| SiNW array biosensor | 0.001 | 0.001~10 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Yi, J.; Liu, W.; Qu, X.; Liu, C.; Viriri, S.; Yang, G.; Yang, X.; et al. High-Performance Silicon Nanowire Array Biosensor for Combined Detection of Colorectal Cancer Biomarkers. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101089
Zeng J, Liu M, Chen X, Yi J, Liu W, Qu X, Liu C, Viriri S, Yang G, Yang X, et al. High-Performance Silicon Nanowire Array Biosensor for Combined Detection of Colorectal Cancer Biomarkers. Micromachines. 2025; 16(10):1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101089
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Jiaye, Mingbin Liu, Xin Chen, Jintao Yi, Wenhe Liu, Xinjian Qu, Chaoran Liu, Serestina Viriri, Guangguang Yang, Xun Yang, and et al. 2025. "High-Performance Silicon Nanowire Array Biosensor for Combined Detection of Colorectal Cancer Biomarkers" Micromachines 16, no. 10: 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101089
APA StyleZeng, J., Liu, M., Chen, X., Yi, J., Liu, W., Qu, X., Liu, C., Viriri, S., Yang, G., Yang, X., & Yang, W. (2025). High-Performance Silicon Nanowire Array Biosensor for Combined Detection of Colorectal Cancer Biomarkers. Micromachines, 16(10), 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101089







