Efficient Data Transfer and Multi-Bit Multiplier Design in Processing in Memory
Abstract
1. Introduction
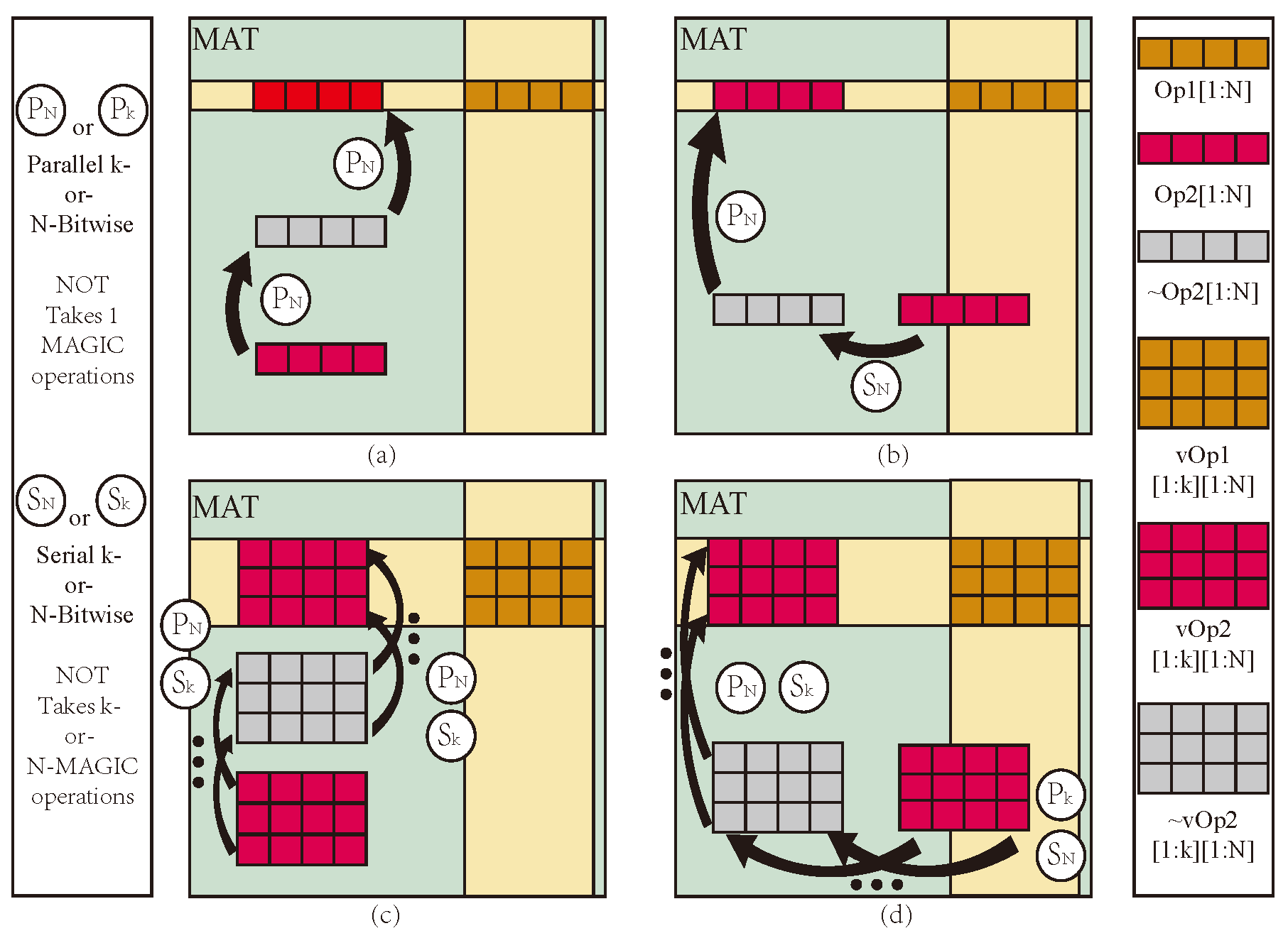
- Improved data transfer efficiency in PiM MPU by reserving a row and column at the edge of the array for logic assistant based on AND and OA logic.
- A multi-bit multiplier with fewer execution steps and devices and lower latency and power consumption is designed based on alternating crossbar array architecture and MIMO logic operations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Transfer in MPU
- Intra-MAT refers to a situation where the operands must be transferred within a MAT.
- Intra-Bank refers to a situation where operands are transferred between MATs where the operands must be transferred from one MAT to another within the same Bank.
- Inter-Bank refers to the operands between Banks that must be transferred from one Bank to another within the same chip.
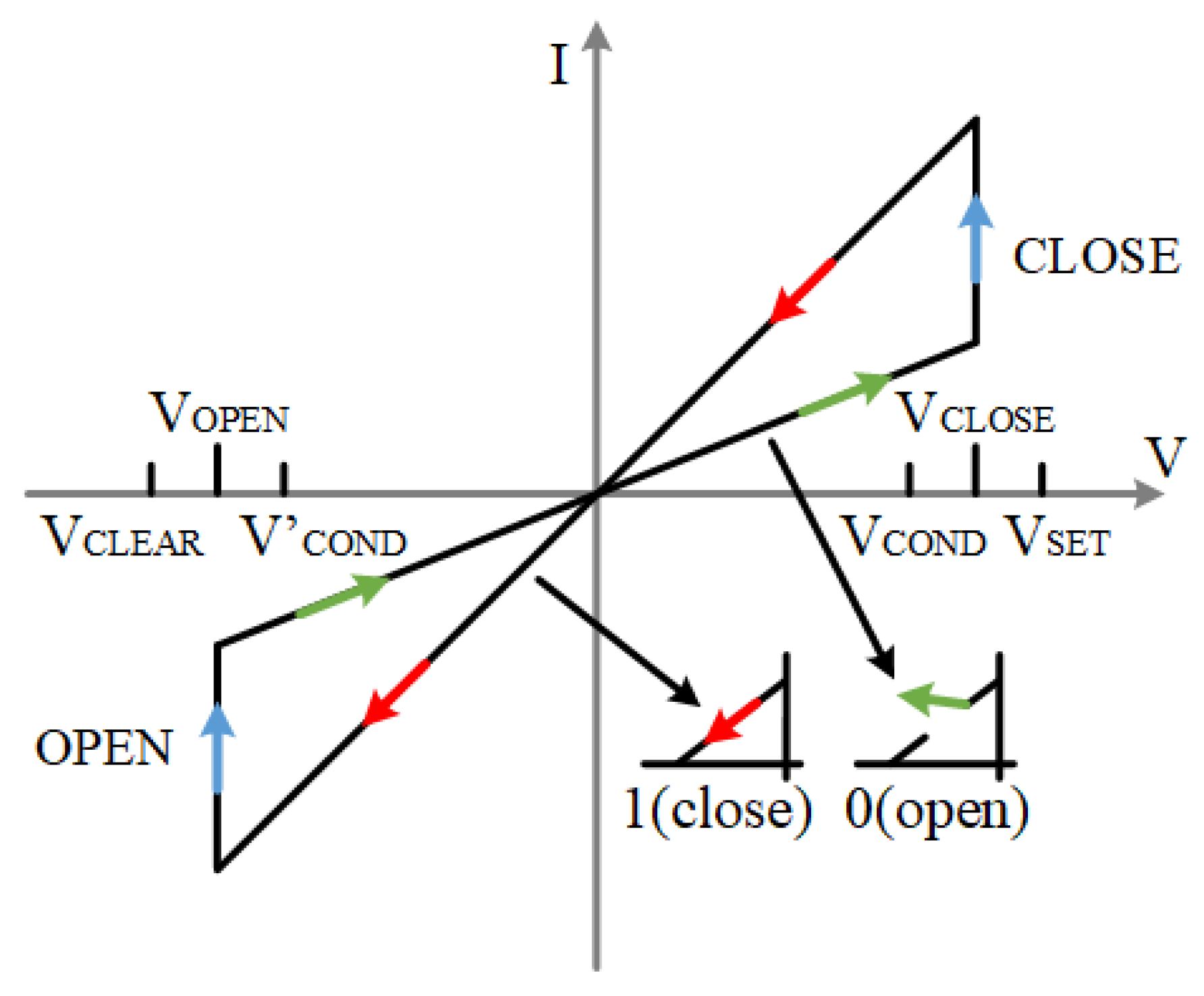
2.2. Memristor Model
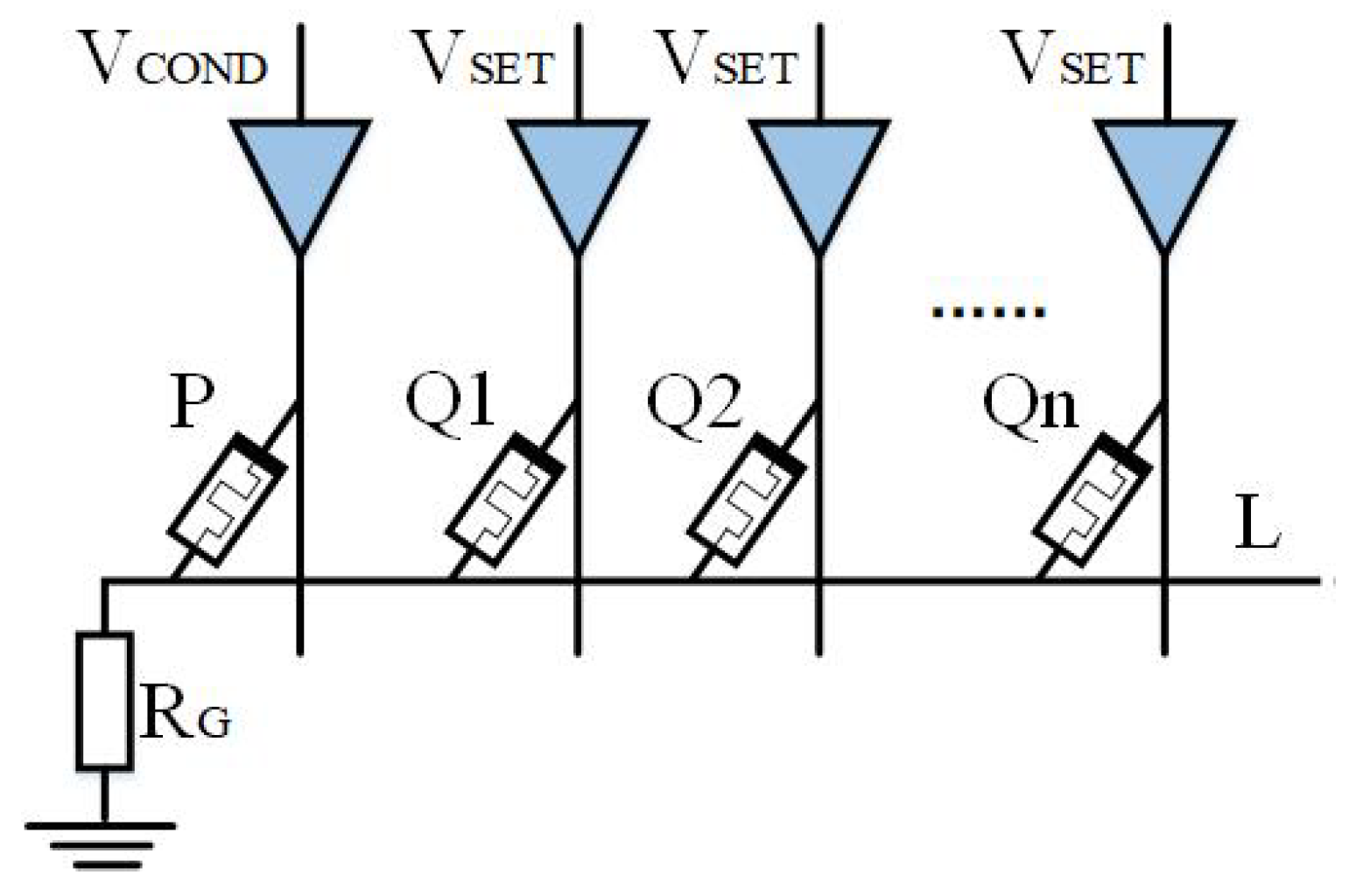
2.3. Basic Logic Operation
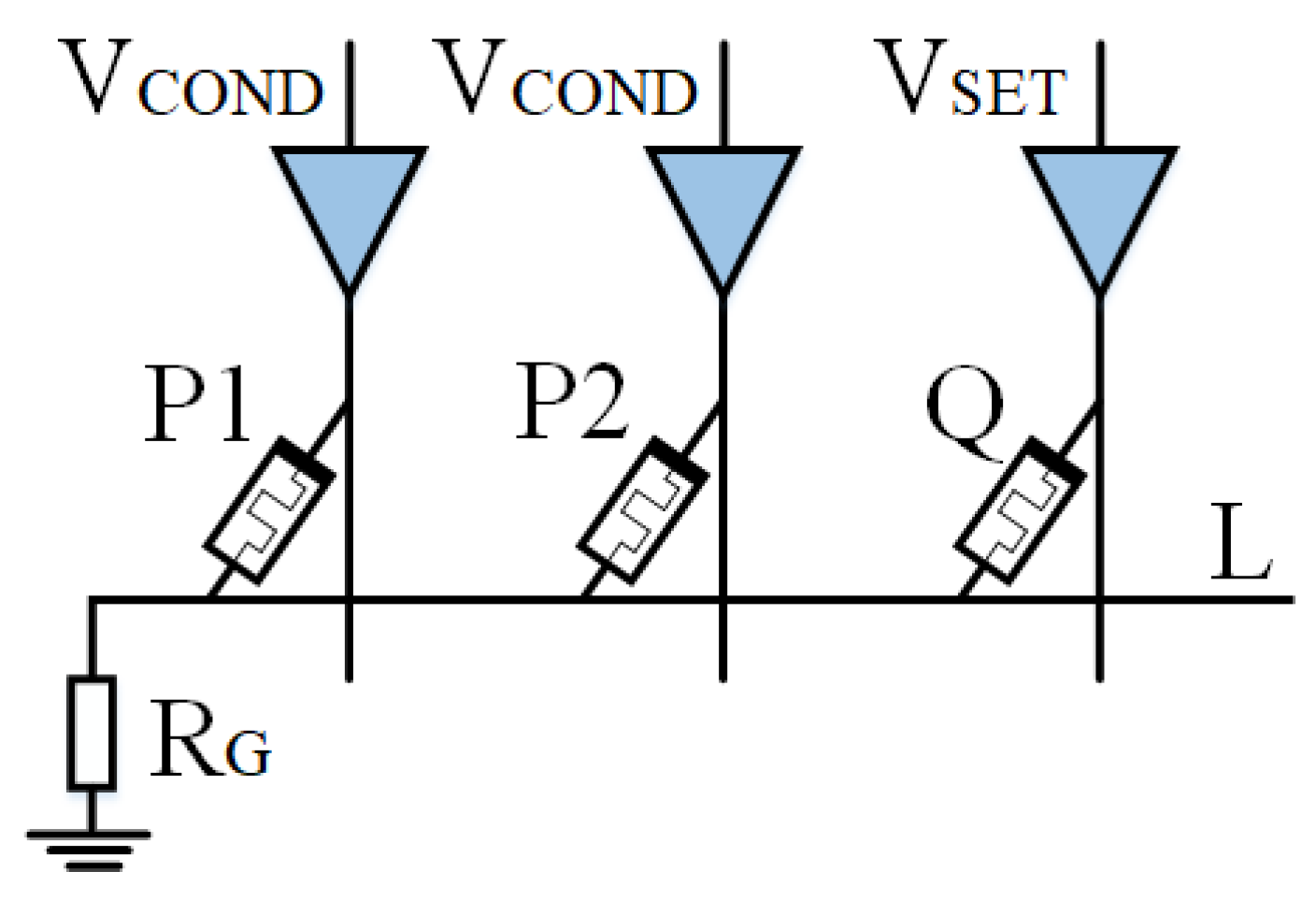
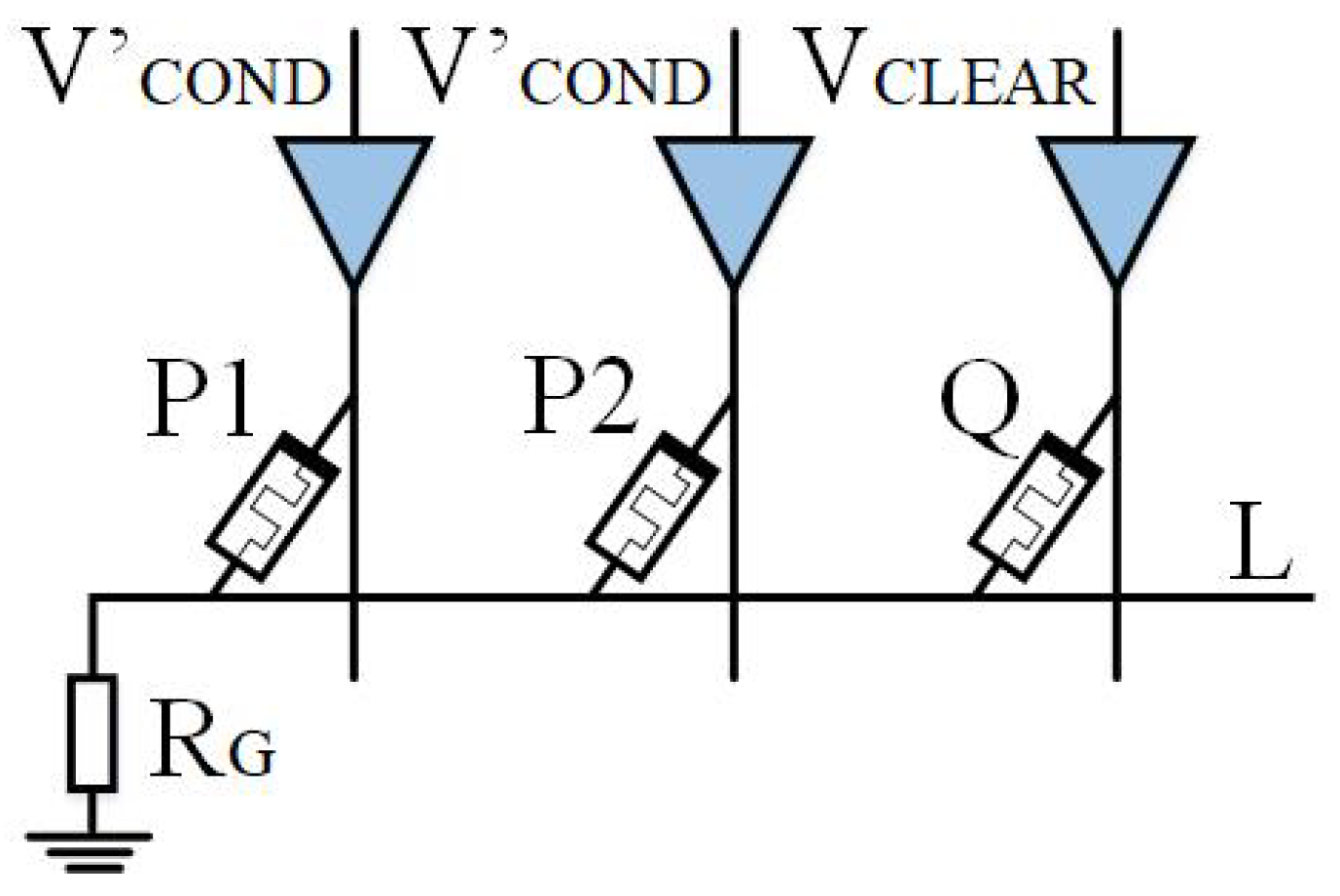
2.3.1. Multi-Input Implicative Logic Circuit Design
- Case 1: When memristors P1 and P2 are both in high impedance state (), is equal to . Because , the voltage on is almost zero. Therefore, the voltage drop across the memristor Q is , wherein . Therefore, the memristor Q is switched to a low-resistance state.
- Cases 2, 3, and 4: When one or two input memristors are in a low-resistance state, the resistance is less than the resistance . Because , the voltage on is . The voltage drop across memristor Q is . The Q resistance state of memristor remains unchanged.
2.3.2. Multi-Output Implicative Logic Circuit Design
2.4. Alternating Crossbar Array
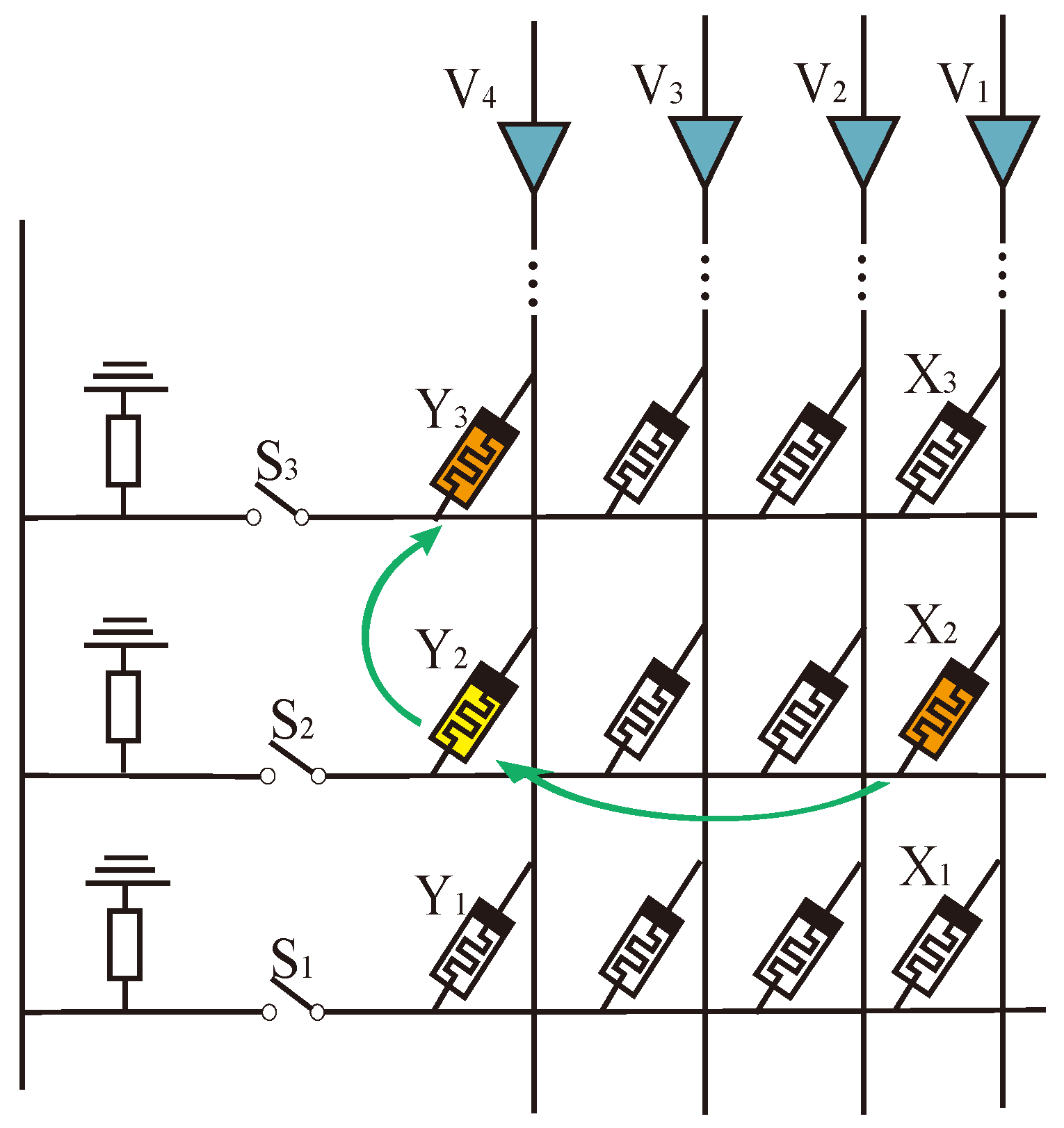
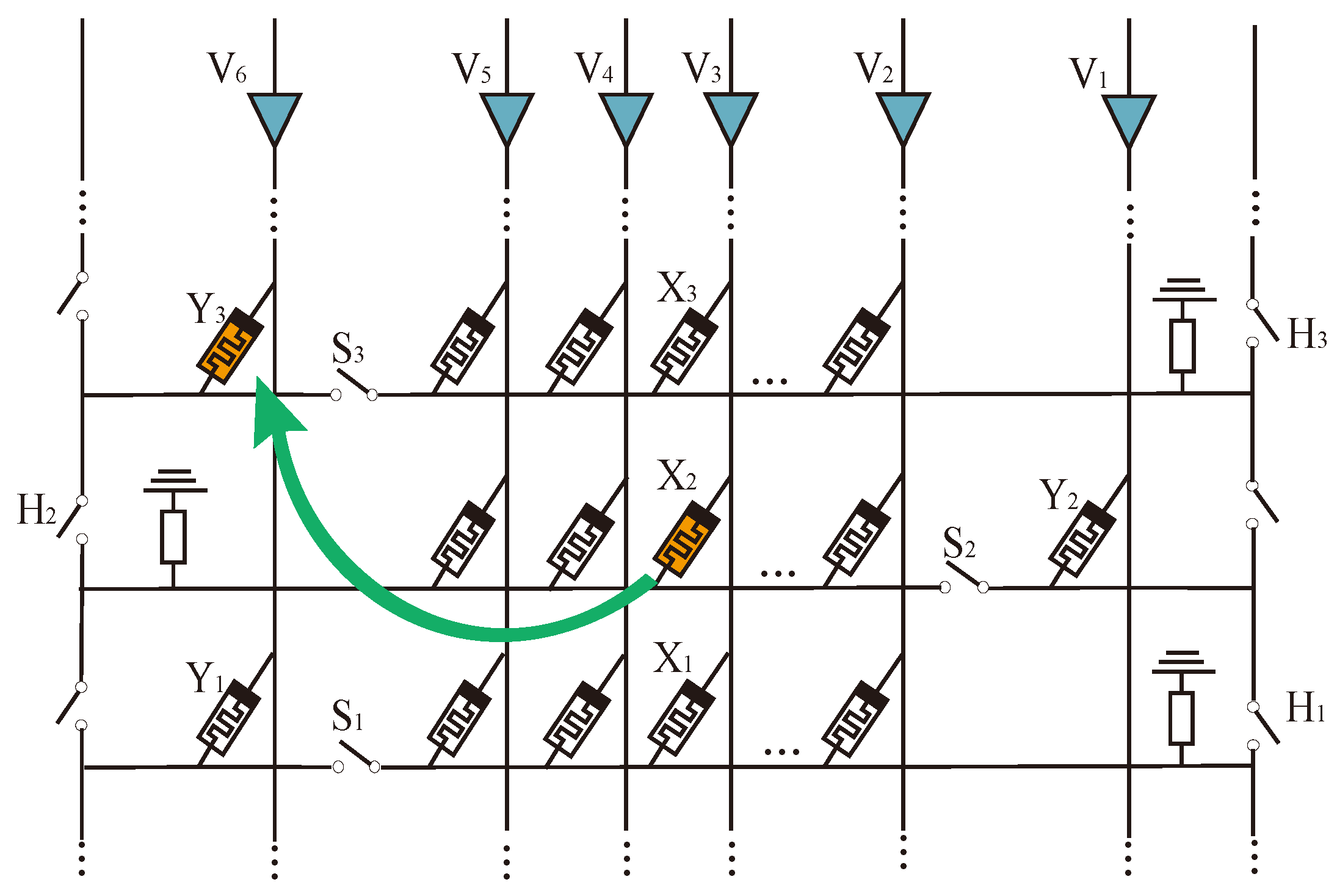
3. Data Transfer within MAT
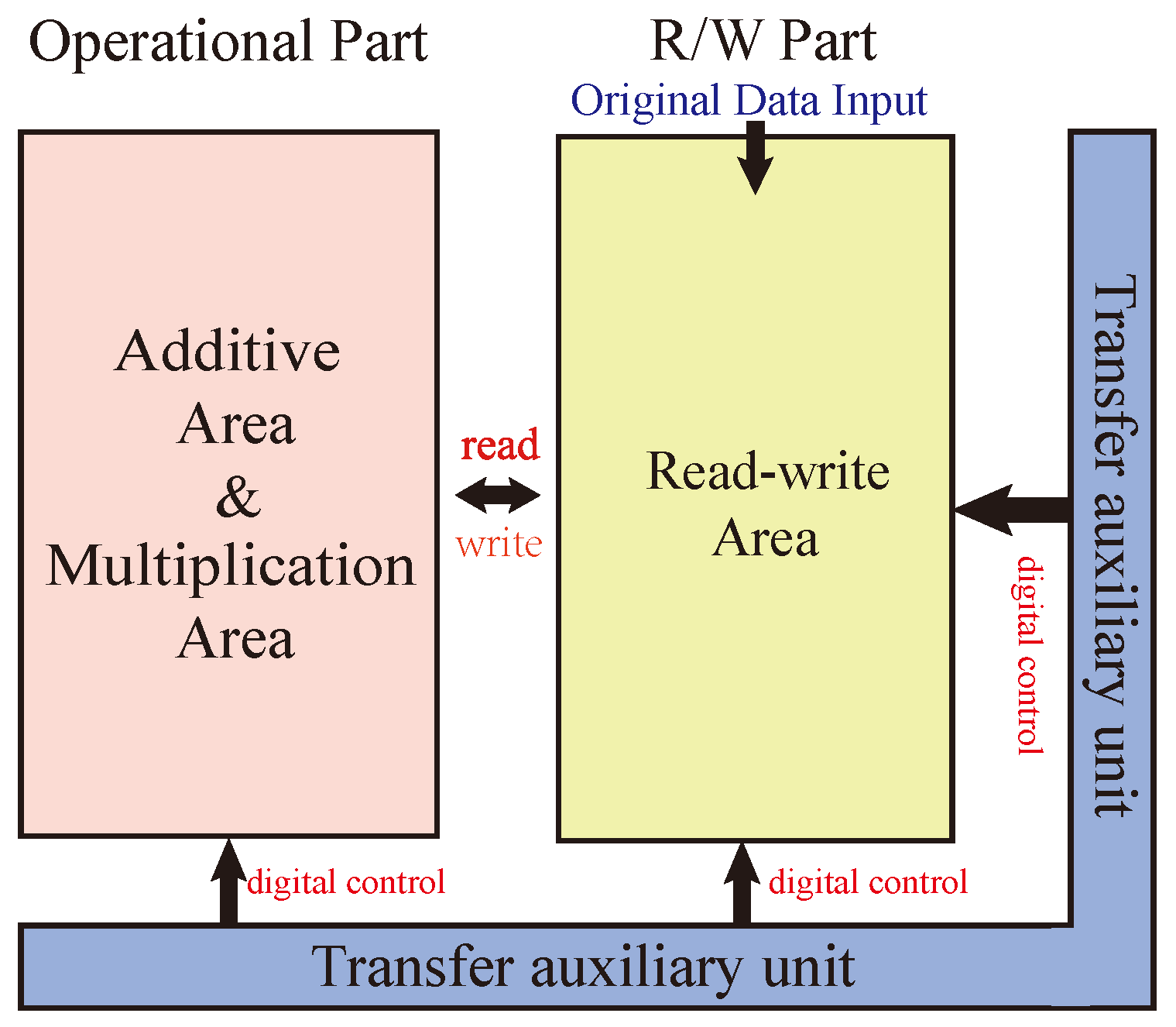
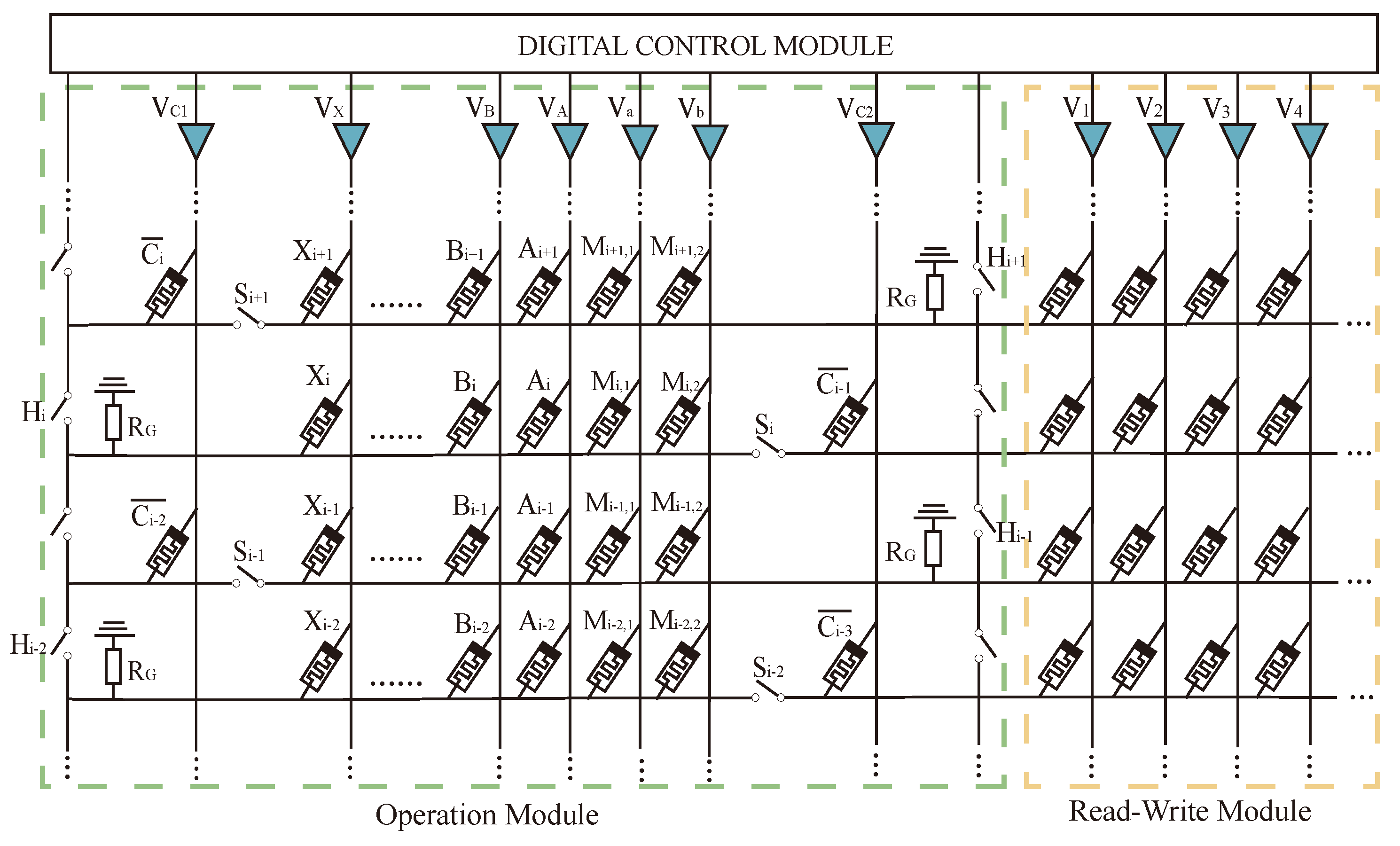
3.1. Structure of mMPU
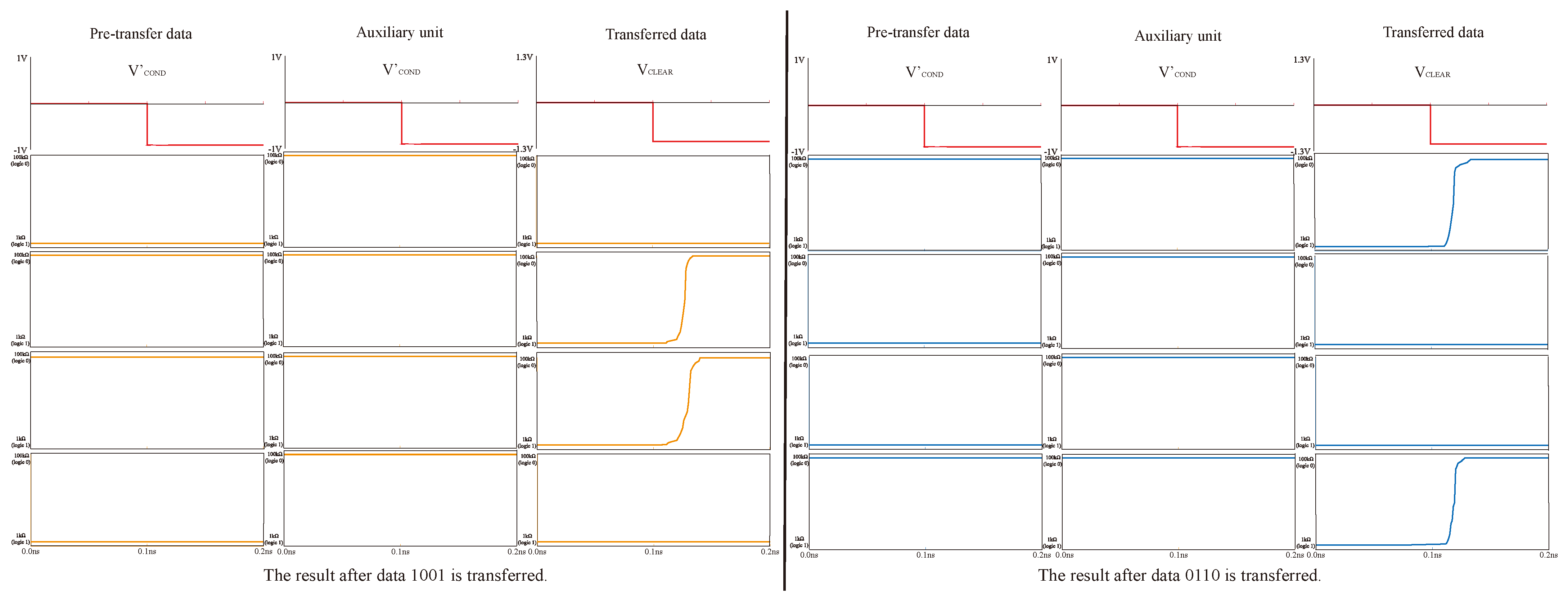
3.2. Design of Data Movement Method
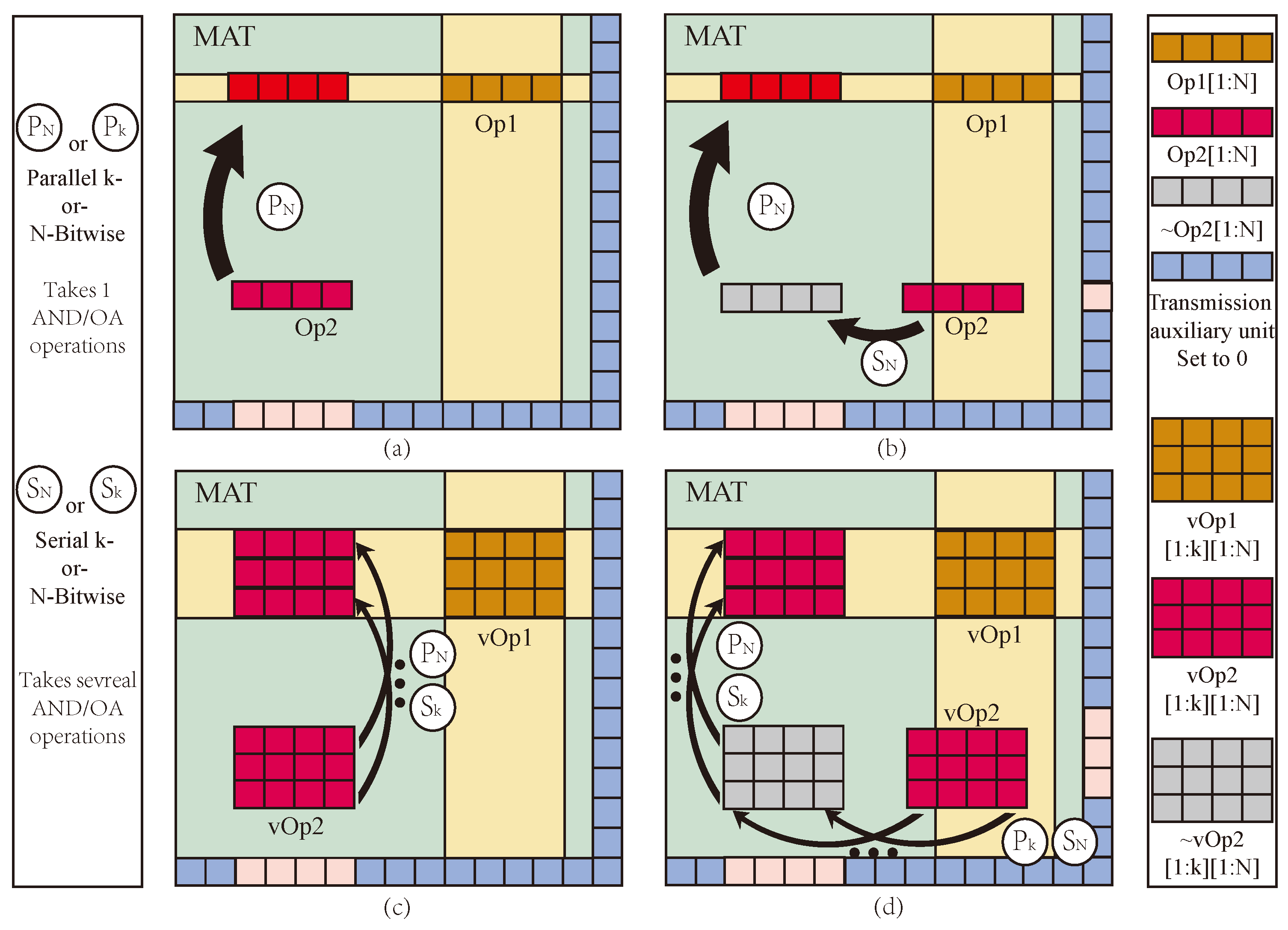
4. Mul-Bit Multiplier Design
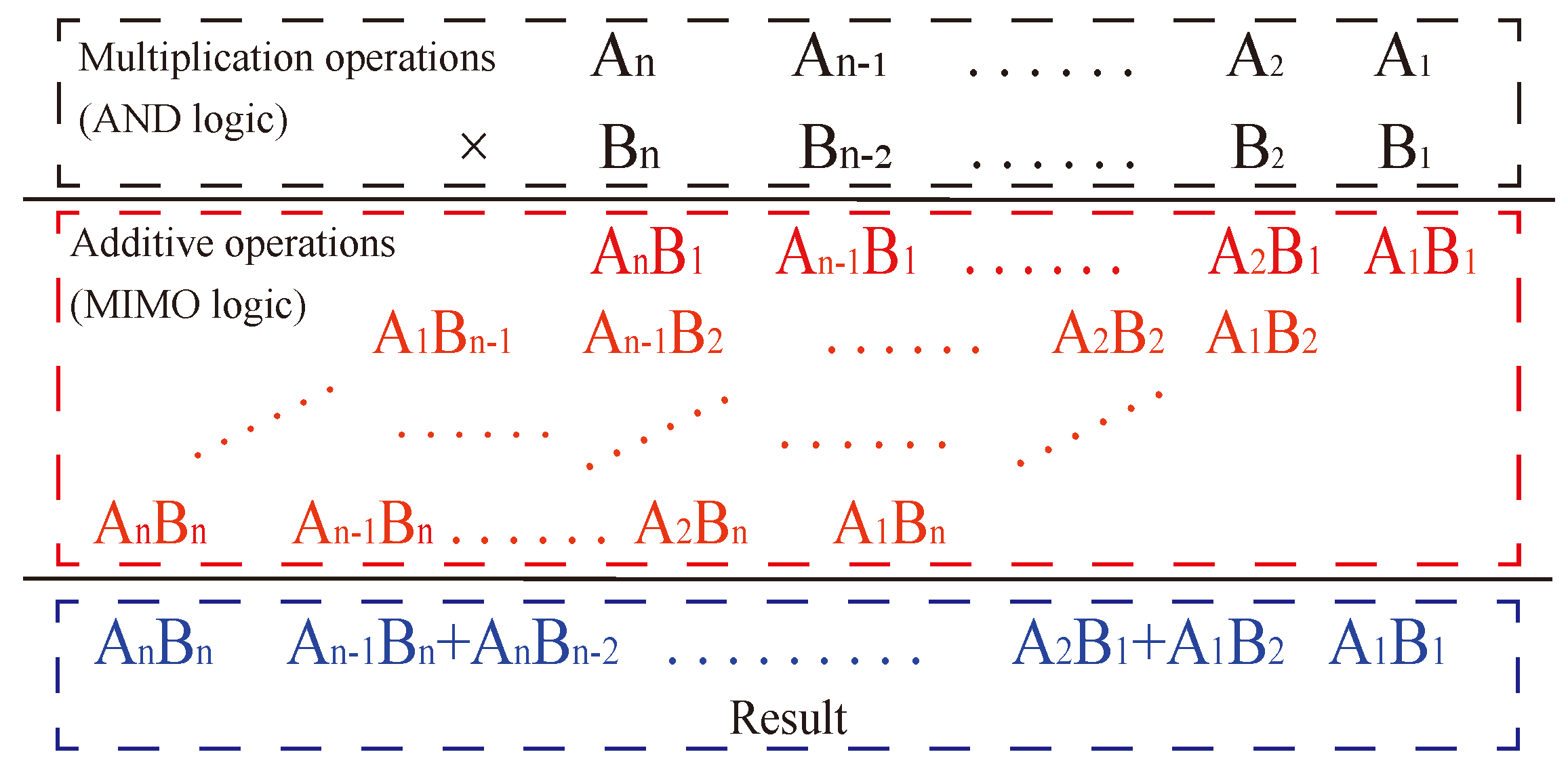
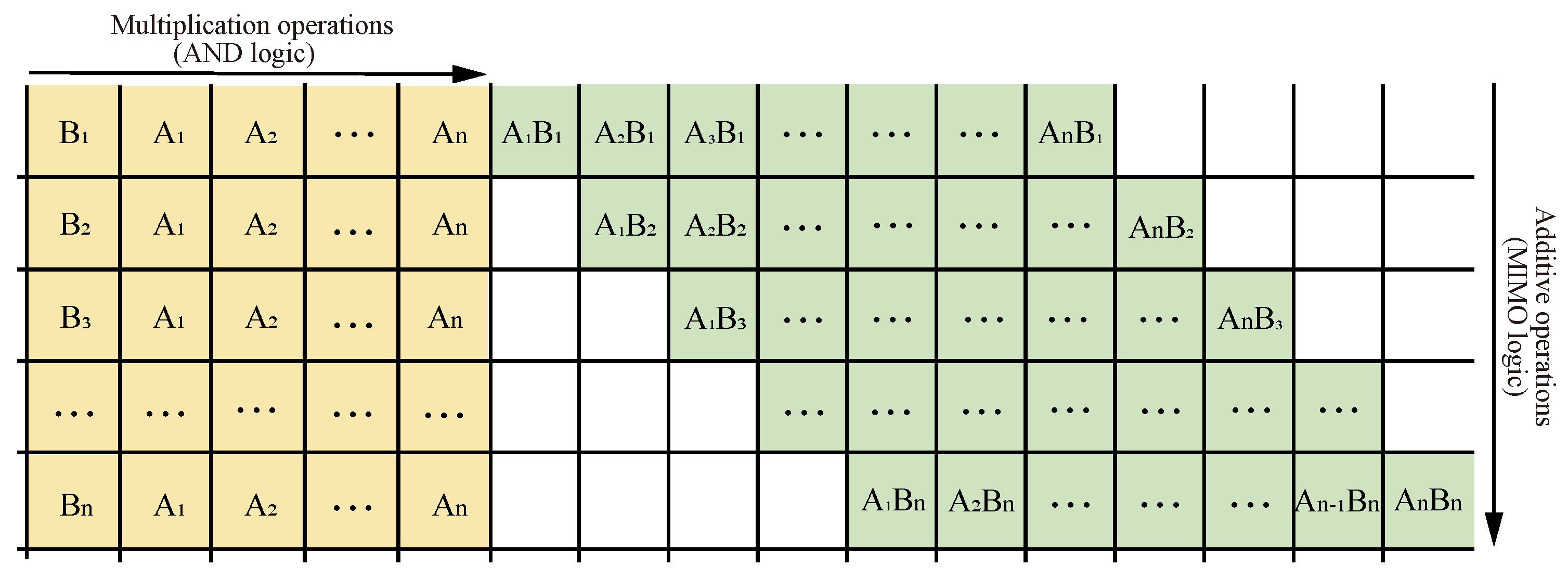
4.1. Multiplier Principle
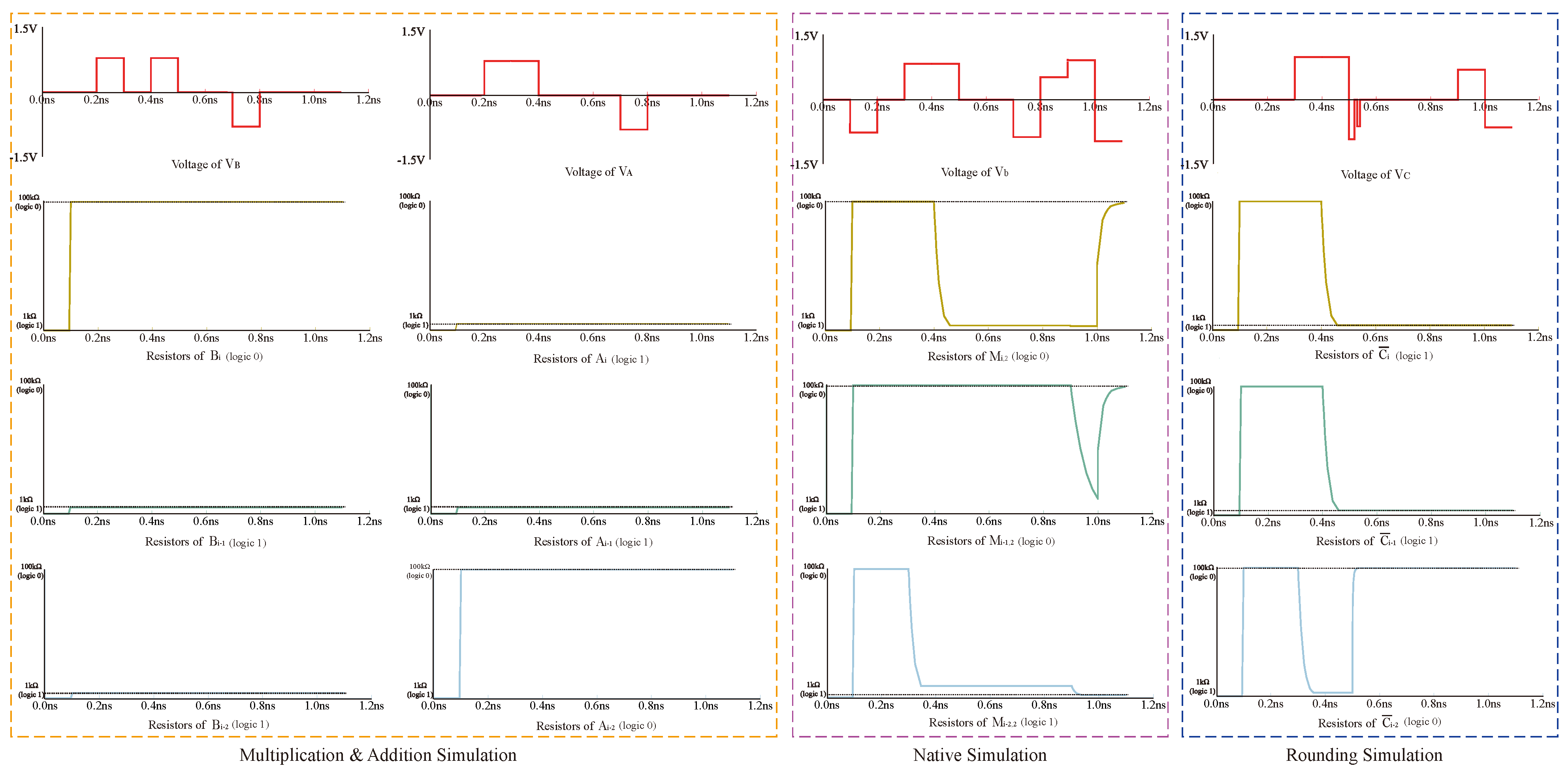
4.2. Multiplier Operations
5. Simulation and Analysis
5.1. Simulation
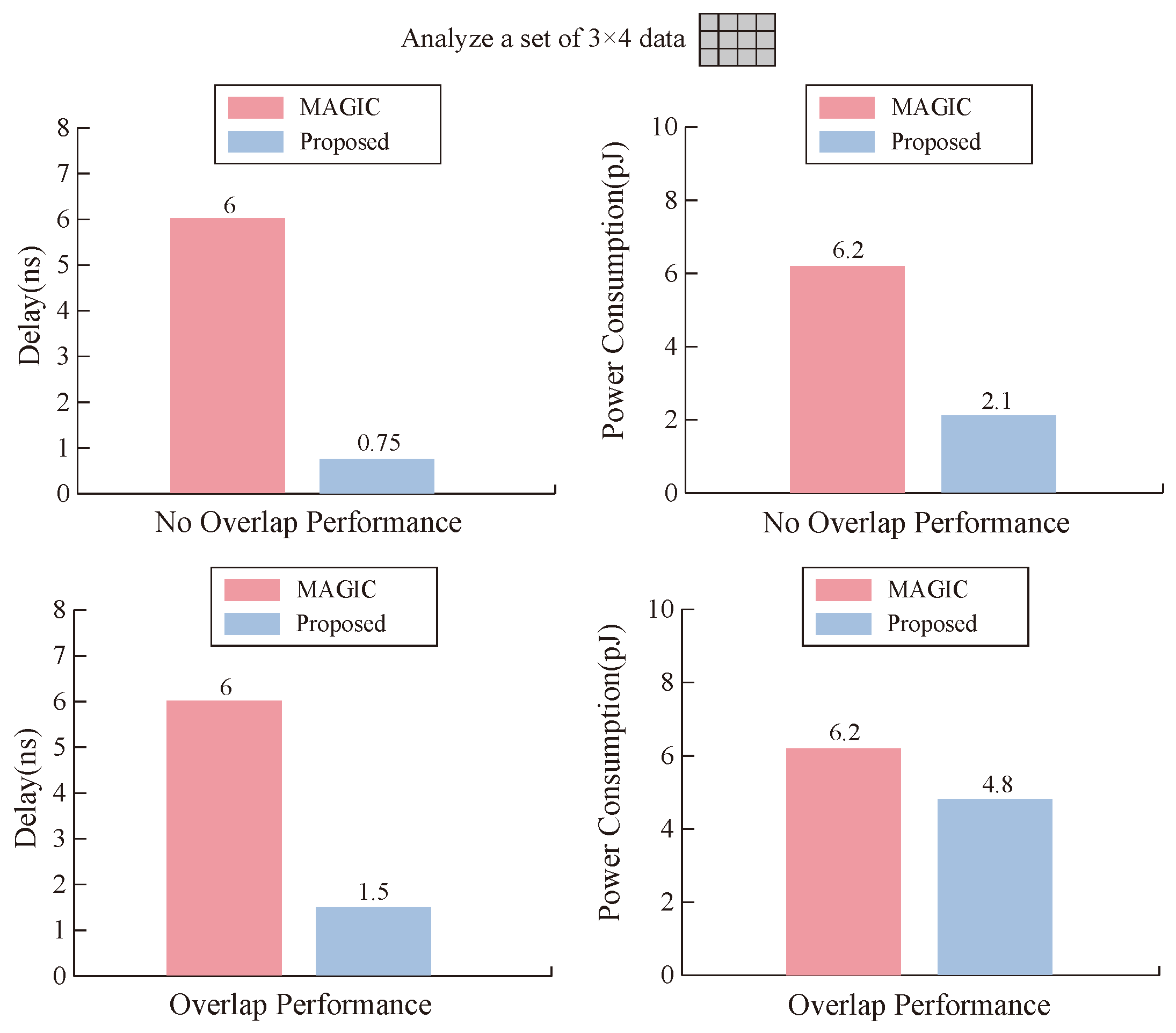
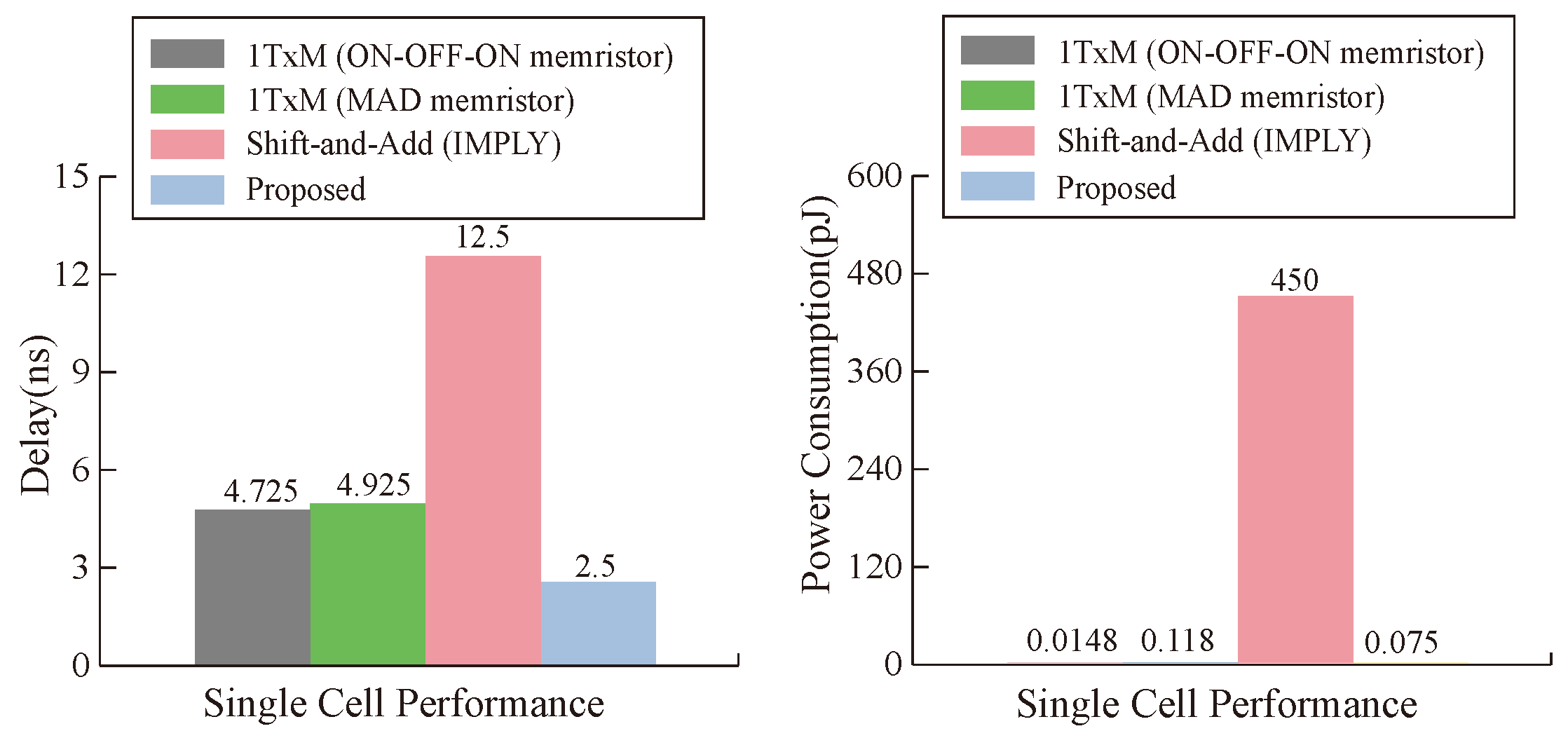
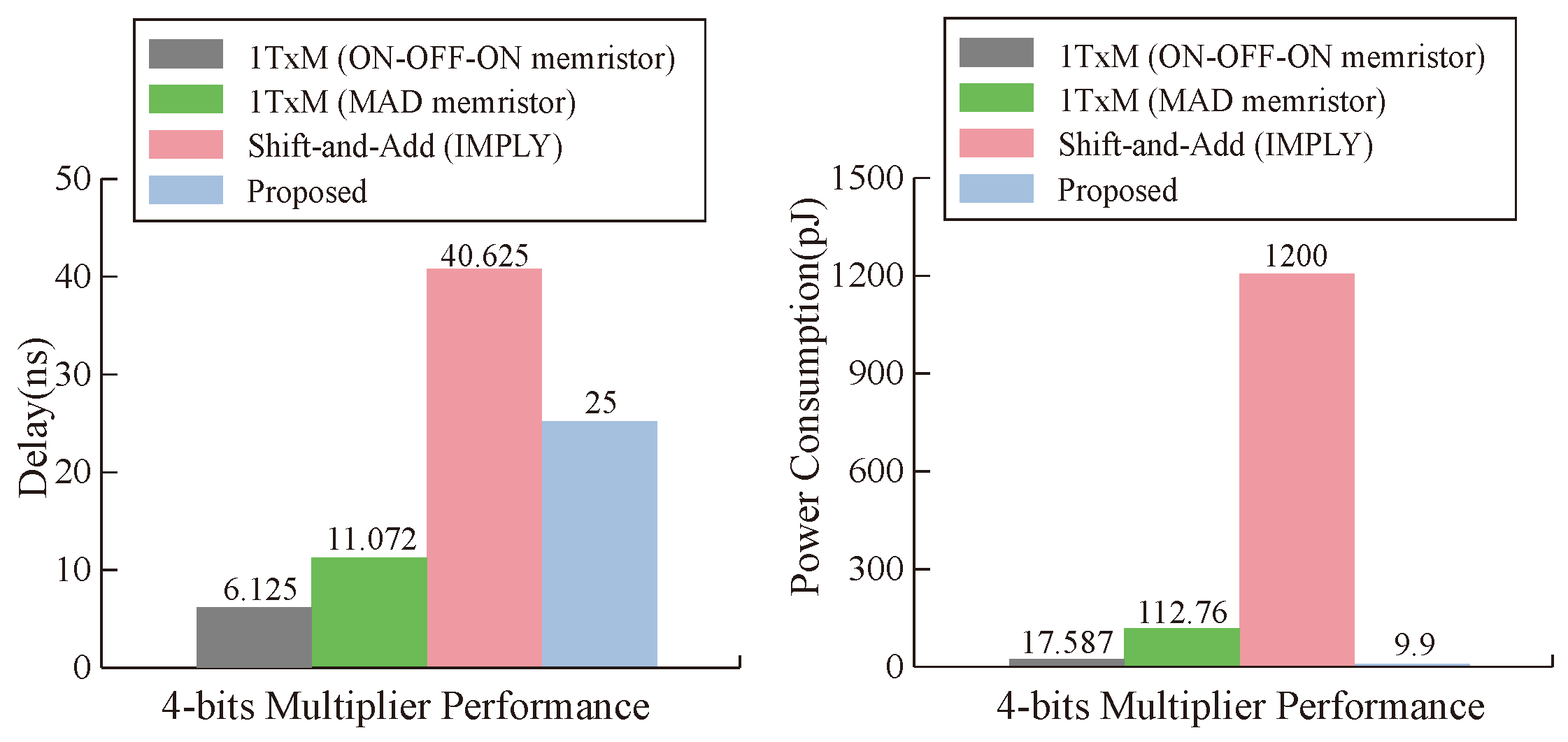
5.2. Analysis and Comparison
| Design | Number of Memristors | Number of Steps | Number of Switches | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | n = 32 | Imp. | Total | n = 32 | Imp. | Total | n = 32 | Imp. | |
| Shift & Add [51] | 7n + 1 | 225 | −89% | 2n2+21n | 2720 | 53% | 8n−1 | 255 | 50% |
| Array [47] | 7n2 − 8n + 9 | 6921 | 69% | 24n − 35 | 733 | −73% | 8n2 − 8n + 9 | 7945 | 98% |
| SEMI-SERIAL [48] | 2n2 + n + 2 | 2082 | −3% | [n](10n + 2) + 4n + 2 | 1740 | 26% | 12[n/2] + [(n − 1)/2] | 207 | 38% |
| Proposed | 2n2+3n | 2144 | - | n2 + 8n − 8 | 1272 | - | 4n | 128 | - |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahn, J.; Hong, S.; Yoo, S.; Mutlu, O.; Choi, K. A scalable processing-in-memory accelerator for parallel graph processing. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Portland, OR, USA, 13–17 June 2015; pp. 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, R.B.; Kvatinsky, S. Memory processing cell for in-memory processing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Nanoscale Architectures (NANOARCH), Beijing, China, 18–20 July 2016; pp. 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ke, S.; Jin, Y.; Wen, X.; Ye, C. A review of memristor: Material and structure design, device performance, applications and prospects. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2023, 24, 2162323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Ramadan, M.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A. VTEAM: A General Model for Voltage-Controlled Memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2015, 62, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lin, H.; Deng, Z. Nonvolatile CMOS Memristor, Reconfigurable Array, and Its Application in Power Load Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 6130–6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Bao, B.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, P. Chaotic and periodic bursting phenomena in a memristive Wien-bridge oscillator. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 83, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, J.; Ma, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. Adaptive biomimetic neuronal circuit system based on Myelin sheath function. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 3669–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Sun, K.; Qin, P. Memristor-based circuit design of episodic memory neural network and its application in hurricane category prediction. Neural Netw. 2024, 174, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Iu, H.H.C. Memristor-coupled asymmetric neural networks: Bionic modeling, chaotic dynamics analysis and encryption application. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 166, 112905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Hong, Q.; Du, S.; Zhang, J. Design of Artificial Neurons of Memristive Neuromorphic Networks Based on Biological Neural Dynamics and Structures. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2023, 71, 2320–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, F.; Cui, L.; Lin, H. Dynamics analysis and image encryption application of Hopfield neural network with a novel multistable and highly tunable memristor. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 693–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Pek Jun, T.; Lei, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, T.; Ge, C.; Huang, R.; Yang, Y. A neuromorphic physiological signal processing system based on VO2 memristor for next-generation human-machine interface. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Can, L.; Zhongrui, W.; Yunning, L.; Hao, J.; Wenhao, S.; Mingyi, R.; Ye, Z.; Upadhyay, N.K.; Barnell, M. Three-dimensional memristor circuits as complex neural networks. Nat. Electron. 2020, 3, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Yu, F. Dynamics analysis and hardware implementation of multi-scroll hyperchaotic hidden attractors based on locally active memristive Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 1511–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Hu, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, X.; Bao, H. Memristor-induced mode transitions and extreme multistability in a map-based neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 3765–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, G. Generating Any Number of Diversified Hidden Attractors via Memristor Coupling. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 4945–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Lu, Y. Synchronization in scale-free neural networks under electromagnetic radiation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2024, 34, 033116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, E.; Poikonen, J.H.; Laiho, M.; Kanerva, P. Large-Scale Memristive Associative Memories. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2014, 22, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Z. A Compact Scheme of Reading and Writing for Memristor-Based Multivalued Memory. IEEE Trans.-Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 37, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y. Memristive cluster based compact high-density nonvolatile memory design and application for image storage. Micromachines 2022, 13, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Kang, K.; Sun, Y.; Hong, Q.; Wang, C. A multi-value 3D crossbar array nonvolatile memory based on pure memristors. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2022, 231, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh, M.; Joshi, A. Design and Optimization of Nonvolatile Multibit 1T1R Resistive RAM. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2014, 22, 1815–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, M.; Kang, K.; Zhu, S.; Sun, Y. Design of heterogeneous memristor based 1T2M multi-value memory crossbar array. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2018, 37, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Teimoory, M.; Amirsoleimani, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Ahmadi, M. A 2M1M Crossbar Architecture: Memory. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2018, 26, 2608–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, I.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jang, H.W. Memristive devices for new computing paradigms. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Wu, H.; Gao, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.J.; Qian, H. Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network. Nature 2020, 577, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, P.; Li, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y. Prime: A novel processing-in-memory architecture for neural network computation in reram-based main memory. ACM Sigarch Comput. Archit. News 2016, 44, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Wu, H.; Gao, B.; Eryilmaz, S.B.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, N.; Shi, L.; et al. Face classification using electronic synapses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hur, R.; Kvatinsky, S. Memristive memory processing cell (MPU) controller for in-memory processing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on the Science of Electrical Engineering (ICSEE), Eilat, Israel, 16–18 November 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Talati, N.; Ali, A.H.; Hur, R.B.; Wald, N.; Ronen, R.; Gaillardon, P.; Kvatinsky, S. Practical challenges in delivering the promises of real processing-in-memory machines. In Proceedings of the Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 19–23 March 2018; pp. 1628–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Ambrosi, E.; Bricalli, A.; Ielmini, D. Logic computing with stateful neural networks of resistive switches. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T. Hybrid memristor-cmos (memos) based logic gates and adder circuits. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.06735. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Shen, S.; Jin, P.; Wang, G.; Liang, Y. Design of memristor-based combinational logic circuits. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 40, 5825–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghetti, J.; Snider, G.S.; Kuekes; Yang, J.J.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. ‘Memristive’switches enable ‘stateful’logic operations via material implication. Nature 2010, 464, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Belousov, D.; Liman, S.; Satat, G.; Wald, N.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A.; Weiser, U.C. MAGIC—Memristor-aided logic. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2014, 61, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Liao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Hong, Q.; Zhang, J. An efficient memristive alternating crossbar array and the design of full adder. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 20331–20345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Satat, G.; Wald, N.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A.; Weiser, U.C. Memristor-based material implication (IMPLY) logic: Design principles and methodologies. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2023, 22, 2054–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohani, S.G.; TaheriNejad, N. An improved algorithm for IMPLY logic based memristive full-adder. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Windsor, ON, USA, 30 April–3 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rohani, S.G.; Taherinejad, N.; Radakovits, D. A Semiparallel Full-Adder in IMPLY Logic. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2020, 28, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Peng, M.; Jiang, H.; Hong, Q.; Sun, Y. HMIAN: A hierarchical mapping and interactive attention data fusion network for traffic forecasting. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 25685–25697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirsoleimani, A.; Alibart, F.; Yon, V.; Xu, J.; Pazhouhandeh, M.R.; Ecoffey, S.; Beilliard, Y.; Genov, R.; Drouin, D. In-Memory Vector-Matrix Multiplication in Monolithic Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor-Memristor Integrated Circuits: Design Choices, Challenges, and Perspectives. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghiri, S.; Nemati, A.; Feizi, S.; Amirsoleimani, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Ahmadi, M. A memristor based binary multiplier. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Windsor, ON, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Guckert, L.; Swartzlander, E.E. Dadda Multiplier designs using memristors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on IC Design and Technology (ICICDT), Austin, TX, USA, 23–25 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Teimoory, M.; Amirsoleimani, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Ahmadi, M. A hybrid memristor-CMOS multiplier design based on memristive universal logic gates. Int. Midwest Symp. Circuits Syst. 2018, 26, 1422–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Shafik, R.; Bunnam, T.; Chen, K.; Yakovlev, A. Self-Amplifying Current-Mode Multiplier Design using a Multi-Memristor Crossbar Cell Structure. In Proceedings of the 2020 27th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Glasgow, UK, 23–25 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Radakovits, D.; TaheriNejad, N.; Cai, M.; Delaroche, T.; Mirabbasi, S. A memristive multiplier using semi-serial imply-based adder. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2020, 67, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Kang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Han, R.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ma, W.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; et al. Reconfigurable nonvolatile logic operations in resistance switching crossbar array for large-scale circuits. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9758–9764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Shafik, R.; Bunnam, T.; Chen, K.; Yakovlev, A. Optimized multi-memristor model based low energy and resilient current-mode multiplier design. In Proceedings of the 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 1–5 February 2021; pp. 1230–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Guckert, L.; Swartzlander, E.E. Optimized memristor-based multipliers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| P1 | P2 | Q | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| case 1 | 0 | 0 | q | 1 |
| case 2 | 0 | 1 | q | q |
| case 3 | 1 | 0 | q | q |
| case 4 | 1 | 1 | q | q |
| P1 | P2 | Q | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| case 1 | 0 | 0 | q | 0 |
| case 2 | 0 | 1 | q | q |
| case 3 | 1 | 0 | q | q |
| case 4 | 1 | 1 | q | q |
| P | Q | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|
| case 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| case 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| case 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| case 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Step | Operation | Voltage | The Logical Value after Operation in: | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Read and Input the Data (R/W Part to Multiplier area of Operational Part) | Digital Control | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | The multiplication area performs AND logic operation. | Digital Control | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | The addition region performs addition operation/ | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5 | |||||
| 6 | |||||
| 7 | (carry-out) | ||||
| 8 | 0 | - | |||
| 9 | 0 | - | |||
| 10 | - | ||||
| 11 | - | ||||
| 12 | (sum) | - | |||
| a | p | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 200 | 1250 | 1250 | 1 V | V | 1 k | 100 k | V | V | V | −0.8 V | 500 |
| Time Delay (ns) | Power Consumption (pJ) | |
|---|---|---|
| Single Memristor | 0.25 | 0.075 |
| OA | 0.31 | 0.227 |
| AND | 0.271 | 0.161 |
| MIMO IMPLY | 0.263 | 0.235 |
| ONO | 0.28 | 0.229 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, M.; Sun, Y. Efficient Data Transfer and Multi-Bit Multiplier Design in Processing in Memory. Micromachines 2024, 15, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060770
Sun J, Li Z, Jiang M, Sun Y. Efficient Data Transfer and Multi-Bit Multiplier Design in Processing in Memory. Micromachines. 2024; 15(6):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060770
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jingru, Zerui Li, Meiqi Jiang, and Yichuang Sun. 2024. "Efficient Data Transfer and Multi-Bit Multiplier Design in Processing in Memory" Micromachines 15, no. 6: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060770
APA StyleSun, J., Li, Z., Jiang, M., & Sun, Y. (2024). Efficient Data Transfer and Multi-Bit Multiplier Design in Processing in Memory. Micromachines, 15(6), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060770







