A Novel Small Form-Factor Handheld Optical Coherence Tomography Probe for Oral Soft Tissue Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
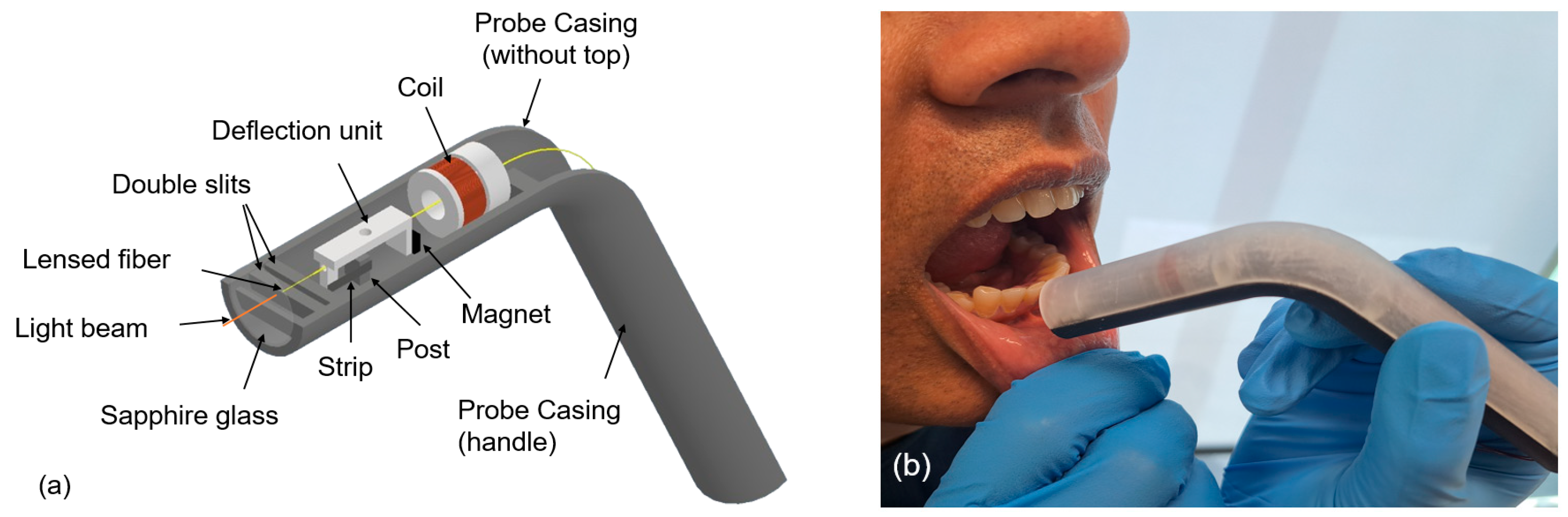
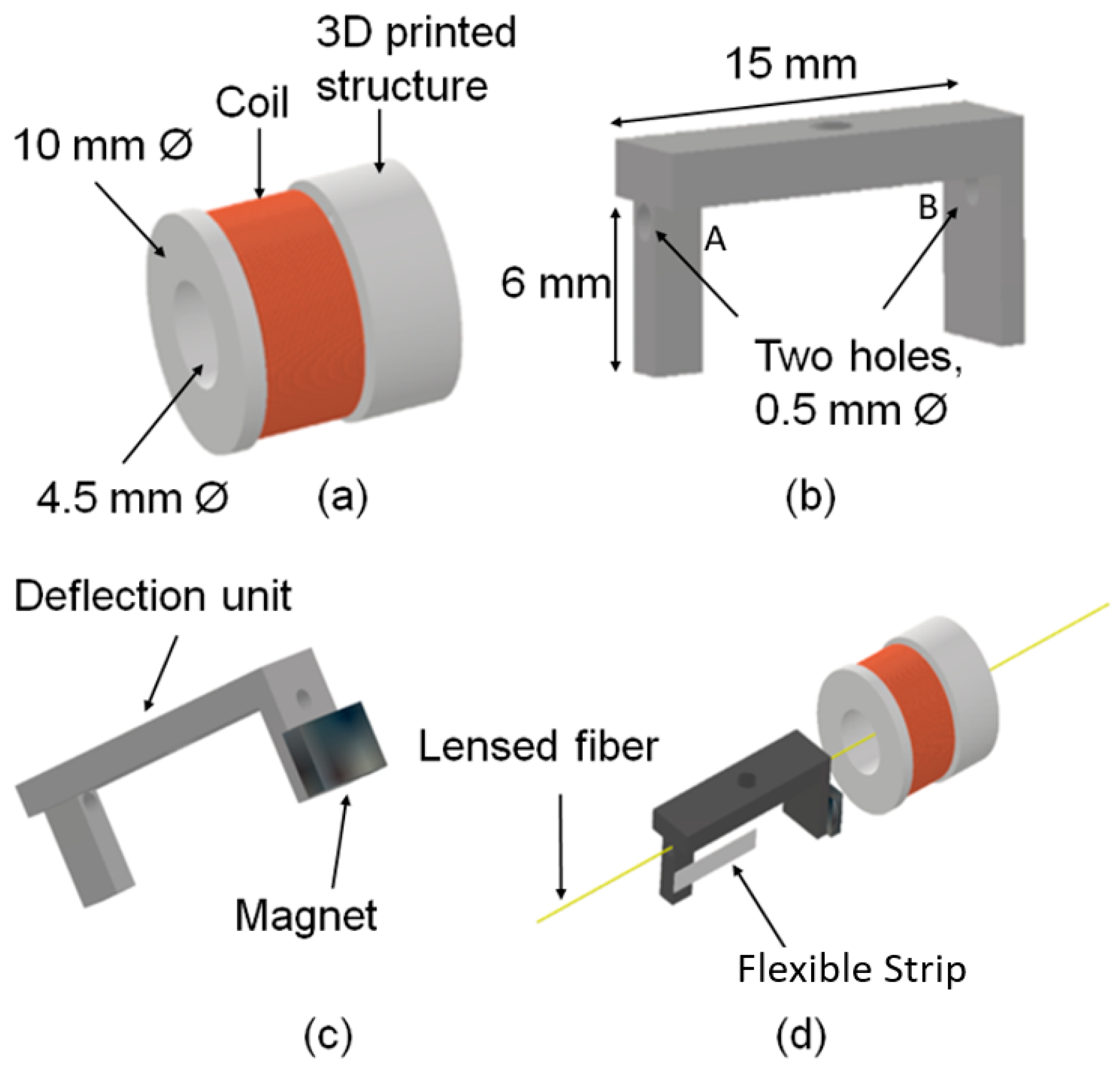
2.1. Handheld Angular Probe Casing
| Distance between the lensed fiber and the sapphire glass: | 1 mm |
| Distance between the sapphire glass and the first slit: | 1.75 mm |
| Width of each slit: | 2 mm |
| Distance between the double slits: | 1 mm |
| Distance between the double slits and the deflection unit: | 3 mm |
| Distance between the magnet and the coil: | 4 mm |
2.2. Deflection Mechanism
2.3. Lensed Fiber
2.4. Back-End System
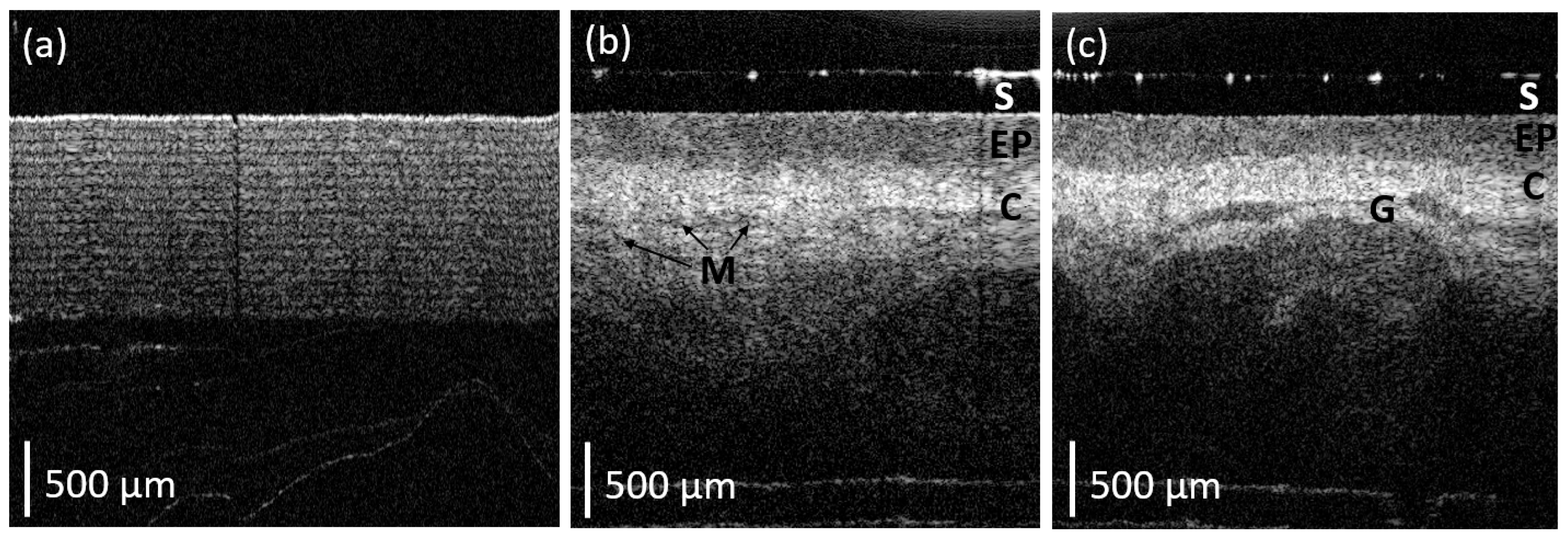
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OCT | Optical Coherence Tomography |
| GRIN | Graded Index |
| NC | No Core |
| FOV | Field of View |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, S.; Teng, T.-H.K.; Bessarab, D.; Aoun, S.; Baxi, S.; Thompson, S.C. Factors contributing to delayed diagnosis of cancer among Aboriginal people in Australia: A qualitative study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, A.; Nguyen, E.; Puah, L.L.; Soong, J.; Keesing, S. Experiences of People with Cancer from Rural and Remote Areas of Western Australia Using Supported Accommodation in Perth While Undergoing Treatment. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hussain, S.; Mubeen, I.; Ullah, N.; Shah, S.S.U.D.; Khan, B.A.; Zahoor, M.; Ullah, R.; Khan, F.A.; Sultan, M.A. Modern Diagnostic Imaging Technique Applications and Risk Factors in the Medical Field: A Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5164970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Huang, R.; Yin, S.; Zeng, Z.; Xie, N.; Ma, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Prediction of subsequent osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture on CT radiography via deep learning. VIEW 2022, 3, 20220012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shu, W.; Zhao, L.; Wan, J. Advanced mass spectrometric and spectroscopic methods coupled with machine learning for in vitro diagnosis. View 2023, 4, 20220038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.B.; Güneri, P.; Boyacioglu, H.; Abt, E. The limitations of the clinical oral examination in detecting dysplastic oral lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Amer. Dent. Assoc. 2012, 143, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilder-Smith, P.; Holtzman, J.; Epstein, J.; Le, A. Optical diagnostics in the oral cavity: An overview. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, W. Optical Coherence Tomography: Technology and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Amsterdam, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aumann, S.; Donner, S.; Fischer, J.; Müller, F. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Principle and Technical Realization. In High Resolution Imaging in Microscopy and Ophthalmology: New Frontiers in Biomedical Optics [Internet]; Bille, J.F., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Chapter 3. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554044/ (accessed on 14 August 2019). [CrossRef]
- Walther, J.; Golde, J.; Albrecht, M.; Quirk, B.C.; Scolaro, L.; Kirk, R.W.; Gruda, Y.; Schnabel, C.; Tetschke, F.; Joehrens, K.; et al. A Handheld Fiber-Optic Probe to Enable Optical Coherence Tomography of Oral Soft Tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed Eng. 2022, 69, 2276–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruda, Y.; Albrecht, M.; Buckova, M.; Haim, D.; Lauer, G.; Koch, E.; Joehrens, K.; Schnabel, C.; Golde, J.; Li, J.; et al. Characteristics of Clinically Classified Oral Lichen Planus in Optical Coherence Tomography: A Descriptive Case-Series Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, J.; Schnabel, C.; Tetschke, F.; Rosenauer, T.; Golde, J.; Ebert, N.; Baumann, M.; Hannig, C.; Koch, E. In vivo imaging in the oral cavity by endoscopic optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 071207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Yang, Z.; Liang, W.; Shang, J.; Liang, Y.; Wan, S. Low-cost, ultracompact handheld optical coherence tomography probe for in vivo oral maxillofacial tissue imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 046003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dental Instruments Packet, University of California, San Diego Pre-Dental Society. Available online: https://ucsdpds.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/pds-instrument-supply-manual-1.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Scolaro, L.; Lorenser, D.; McLaughlin, R.A.; Quirk, B.C.; Kirk, R.W.; Sampson, D.D. High-sensitivity anastigmatic imaging needle for optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 5247–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorlabs: VEG210–Manual. Available online: https://www.thorlabs.com/newgrouppage9.cfm?objectgroup_id=9533&pn=VEG210 (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Gambino, A.; Martina, E.; Panzarella, V.; Ruggiero, T.; El Haddad, G.; Broccoletti, R.; Arduino, P.G. Potential use of optical coherence tomography in oral potentially malignant disorders: In-vivo case series study. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoudi, B.; Lindenmaier, A.; Standish, B.A.; Allo, G.; Bizheva, K.; Vitkin, A. Noninvasive in vivo structural and vascular imaging of human oral tissues with spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.; Jang, W.H.; Xiao, P.; Kim, B.; Wang, T.; Li, Q.; Lee, J.Y.; Chung, E.; Kim, K.H. In vivo wide-field reflectance/fluorescence imaging and polarization sensitive optical coherence tomography of human oral cavity with a forward-viewing probe. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kushwaha, A.K.; Ji, M.; Sethi, S.; Jamieson, L.; McLaughlin, R.A.; Li, J. A Novel Small Form-Factor Handheld Optical Coherence Tomography Probe for Oral Soft Tissue Imaging. Micromachines 2024, 15, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060742
Kushwaha AK, Ji M, Sethi S, Jamieson L, McLaughlin RA, Li J. A Novel Small Form-Factor Handheld Optical Coherence Tomography Probe for Oral Soft Tissue Imaging. Micromachines. 2024; 15(6):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060742
Chicago/Turabian StyleKushwaha, Alok K., Minqi Ji, Sneha Sethi, Lisa Jamieson, Robert A. McLaughlin, and Jiawen Li. 2024. "A Novel Small Form-Factor Handheld Optical Coherence Tomography Probe for Oral Soft Tissue Imaging" Micromachines 15, no. 6: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060742
APA StyleKushwaha, A. K., Ji, M., Sethi, S., Jamieson, L., McLaughlin, R. A., & Li, J. (2024). A Novel Small Form-Factor Handheld Optical Coherence Tomography Probe for Oral Soft Tissue Imaging. Micromachines, 15(6), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060742






