Effect of Al2O3 and ZrO2 Filler Material on the Microstructural, Thermal and Dielectric Properties of Borosilicate Glass-Ceramics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Preparation of Powders and Sintered Ceramics
2.2. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, J.; Zhang, B.; Huang, W.; Yang, H. The effect of composition on Li2(Mg0.3Zn 0.7)Ti3O8-xTiO2 microwave dielectric ceramics for low temperature co-fired ceramics technology application. Mater. Lett. 2013, 95, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hao, M.; Xiao, M.; Zheng, Z. Crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of novel BiMg2MO6 (M = P,V) ceramics with low sintering temperature. J. Mater. 2021, 6, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, K.; Wu, S.; Xiao, M. Microwave dielectric properties of low temperature co-fired ceramics LiMg1-xAxPO4 (A = Mn, Ca, 0.02 ≤ x ≤ 0.08). Mater. Lett. 2019, 255, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hao, X.; Song, L.; Li, Z.; Song, L. Synthesis and characterization of single phase and low temperature co-fired cordierite glass-ceramics from perlite. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 2016, 448, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Su, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Gao, F.; Han, X.; Liang, Z.; Li, Q. Enhancement of structural and microwave properties of Zn2+ ion-substituted Li2MgSiO4 ceramics for LTCC applications. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Nemati, A.; Banijamali, S. Fabrication and microwave dielectric characterization of cordierite/BZBS (Bi2O3-ZnO-B2O3-SiO2) glass composites for LTCC applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 882, 160722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitani, M.K.; Ebadzadeh, T.; Banijamali, S.; Riahifar, R.; Rüssel, C.; Abkenar, S.K.; Ren, H. High quality factor microwave dielectric diopside glass-ceramics for the low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) applications. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 2018, 487, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecha, K.; Maeder, T.; Jacq, C.; Ryser, P. Structuration of the low temperature co-fired ceramics (LTCC) using novel sacrificial graphite paste with PVA-propylene glycol-glycerol-water vehicle. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemethmuller, S.; Roosen, A.; Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F.; Neubauer, J. Quantitative analysis of crystalline and amorphous phases in glass-ceramic composites like LTCC by the rietveld method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 2632–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Ren, L.; Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Gong, W.; Cai, M.; Zhou, H. Microstructure, sinterability and properties of CaO-B2O3-SiO2 glass/Al2O3 composites for LTCC application. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6791–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, E.; Tang, B.; Zhong, C. Sintering behaviors and thermal properties of Li2SiO3-based ceramics for LTCC applications. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 27312–27323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, K.; Sun, W.; Chen, X.; Ruan, H. Phase composition, singtering behavior and microwave dielectric properties of M2BiLi2V3O12 (M = Zn, Ca) low temperature co-fired ceramics. Mater. Lett. 2018, 217, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Du, T.; Wu, H.; Xing, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y. Low-temperature sintering LiF-doped Li4Mg3[Ti0·6(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.4]2O9 microwave dielectric ceramics for LTCC applications. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 2584–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Barcelona, P.; Blanes, M.; Padilla, J.; Ramos, F.; Cirera, A.; Xuriguera, E. Study of mixing process of low temperature co-fired ceramics photocurable suspension for digital light processing stereolithography. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 15931–15938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Tripathi, P.; Parkash, O.; Kumar, D. Low Temperature Sintering and Characterization of MgO-B2O3-SiO2 Glass-Ceramics for LTCC Substrate Applications. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2016, 75, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeno, K.; Li, M.; Fujimori, H. Development of novel temperature-stable Al2O3–TiO2-based dielectric ceramics featuring superior thermal conductivity for LTCC applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, R.; Supancic, P.; Krautgasser, C.; Morrell, R.; Danzer, R. Subcritical crack growth in Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics under biaxial loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2013, 100, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, R.; Supancic, P.; Kraleva, I.; Morrell, R.; Danzer, R. Strength reliability of 3D low temperature co-fired multilayer ceramics under biaxial loading. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Lin, C.; Han, L.; Gui, H.; Song, J.; Liu, T.; Lu, A. Influence of Y2O3 substitution for B2O3 on the structure and properties of alkali-free B2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 glasses containing alkaline-earth metal oxides. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 2019, 553, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhou, J. A simple and an effective method for the fabrication of densified glass-ceramics of low temperature co-fired ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıbuğa, D.; Akkaşoğlu, U.; Çiçek, B.; Balcı-Çağıran, Ö. Enhanced Sinterability, Thermal Conductivity and Dielectric Constant of Glass-Ceramics with PVA and BN Additions. Materials 2022, 15, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Tao, H.; Li, P.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, H. Properties of borosilicate glass/Al2O3 composites with different Al2O3 concentrations for LTCC applications. J Mater Sci. Mater Electron. 2020, 31, 14069–14077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Xiao, M.; Chen, L.; Sun, J.; Ding, J.; Li, X.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, X.; et al. Influence of silicon carbide nanowires on the properties of Bi–B–Si–Zn–Al glass based low temperature co-fired ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 25382–25389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cai, D.; Yang, Z.; Duan, X.; He, P.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Thermal properties and thermal shock resistance of BAS-BN composite ceramics. Ceram Int. 2019, 45, 8181–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobuta, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Terakado, N.; Onoue, N.; Shinozaki, T.; Fujiwara, T. Crystallization of nanostructured ZrO2 phase in borosilicate glass: Impact of Al2O3 on tetragonal-to-monoclinic phase transformation. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2018, 501, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzawy, E.; El-Kheshen, A.; Zawrah, M. Densification and properties of glass/cordierite composites. Ceram. Int. 2005, 31, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.; Monteiro, R.; Graça, M.; Ferreira Da Silva, M.G. Structural, electrical and thermal properties of borosilicate glass-alumina composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 538, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Z. The effects of B2O3 on the microstructure and properties of lithium aluminosilicate glass-ceramics for LTCC applications. Mater. Lett. 2018, 212, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruys, A. Alumina Ceramics Biomedical and Clinical Applications, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 71–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, M.; Alizadeh, P.; Rahimipour, M.R. Sintering behavior and mechanical properties of mica-diopside glass–ceramic composites reinforced by nano and micro-sized zirconia particles. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 2012, 358, 3304–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acchar, W.; Torquato, W.; Sousa, C. Using ZrO2 or Al2O3 particles to enhance the mechanical properties of a LZSA glass-ceramic matrix. Matéria 2009, 14, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, J.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Tian, X. High Performance of Low-Temperature-Cofired Ceramic with Al2O3/BN Biphasic Ceramics Based on B2O3–Bi2O3–SiO2–ZnO Glass. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 1901486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Long, Q.; Duan, D. Effects of ZrO2 on properties of BaO–Al2O3–B2O3–SiO2 composites for LTCC applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 2824–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilaç, O.; Duran, C. Al2O3/glass/hBN composites with high thermal conductivity and low dielectric constant for low temperature cofired ceramic applications. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2021, 9, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, D.; Sun, H.; Hu, C.; Chen, S. Design and preparation of a novel degradable low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) composites. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 7001–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
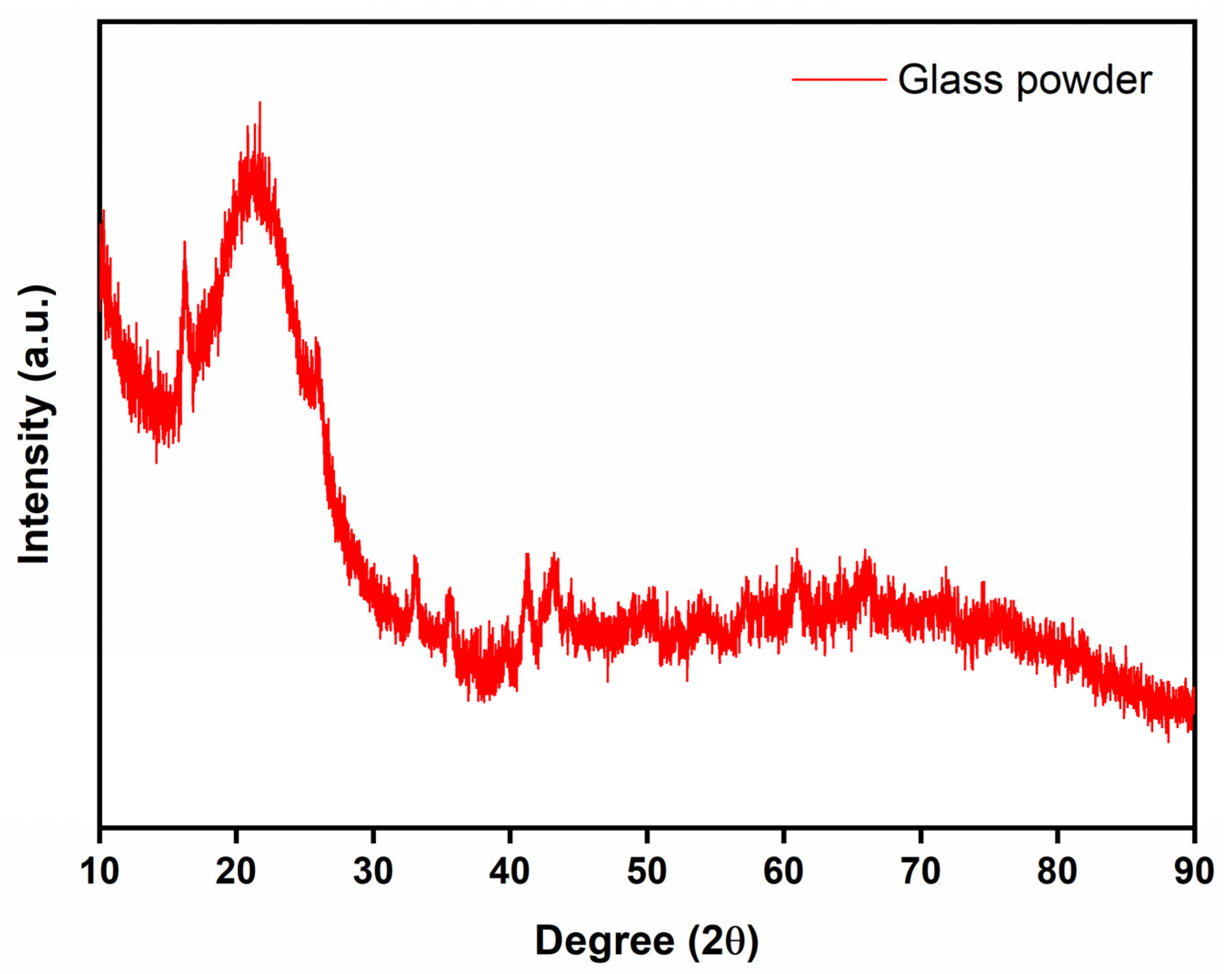
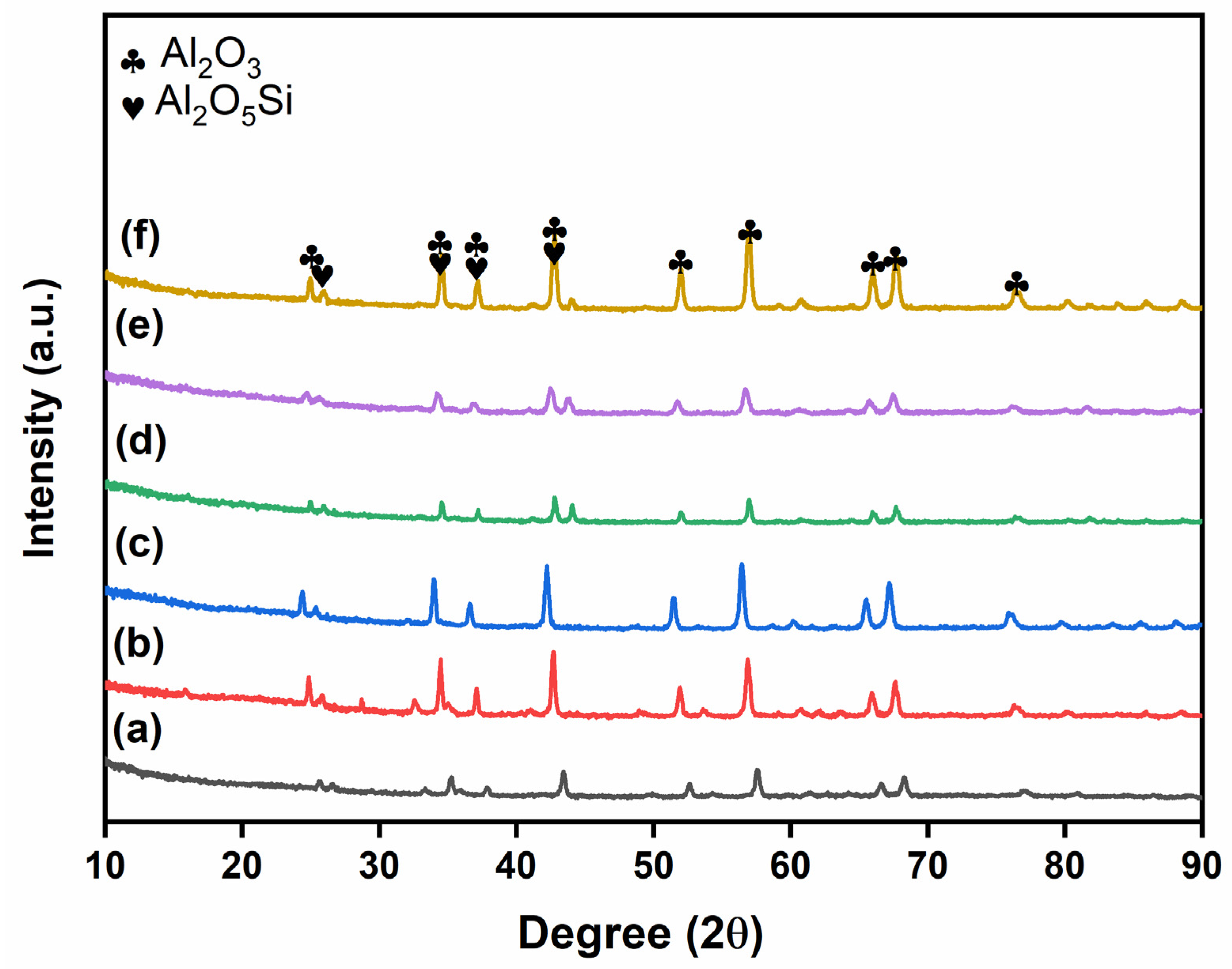
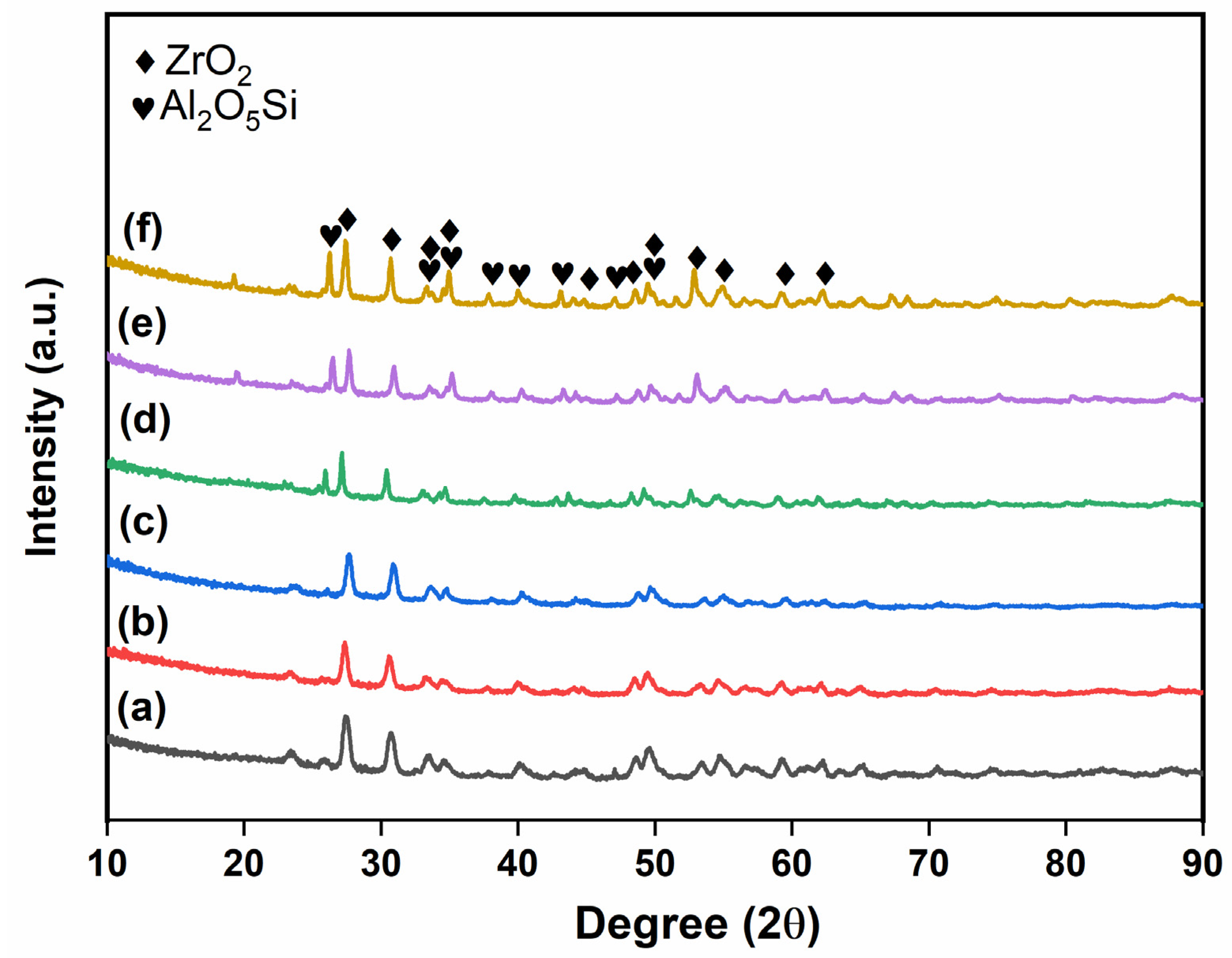
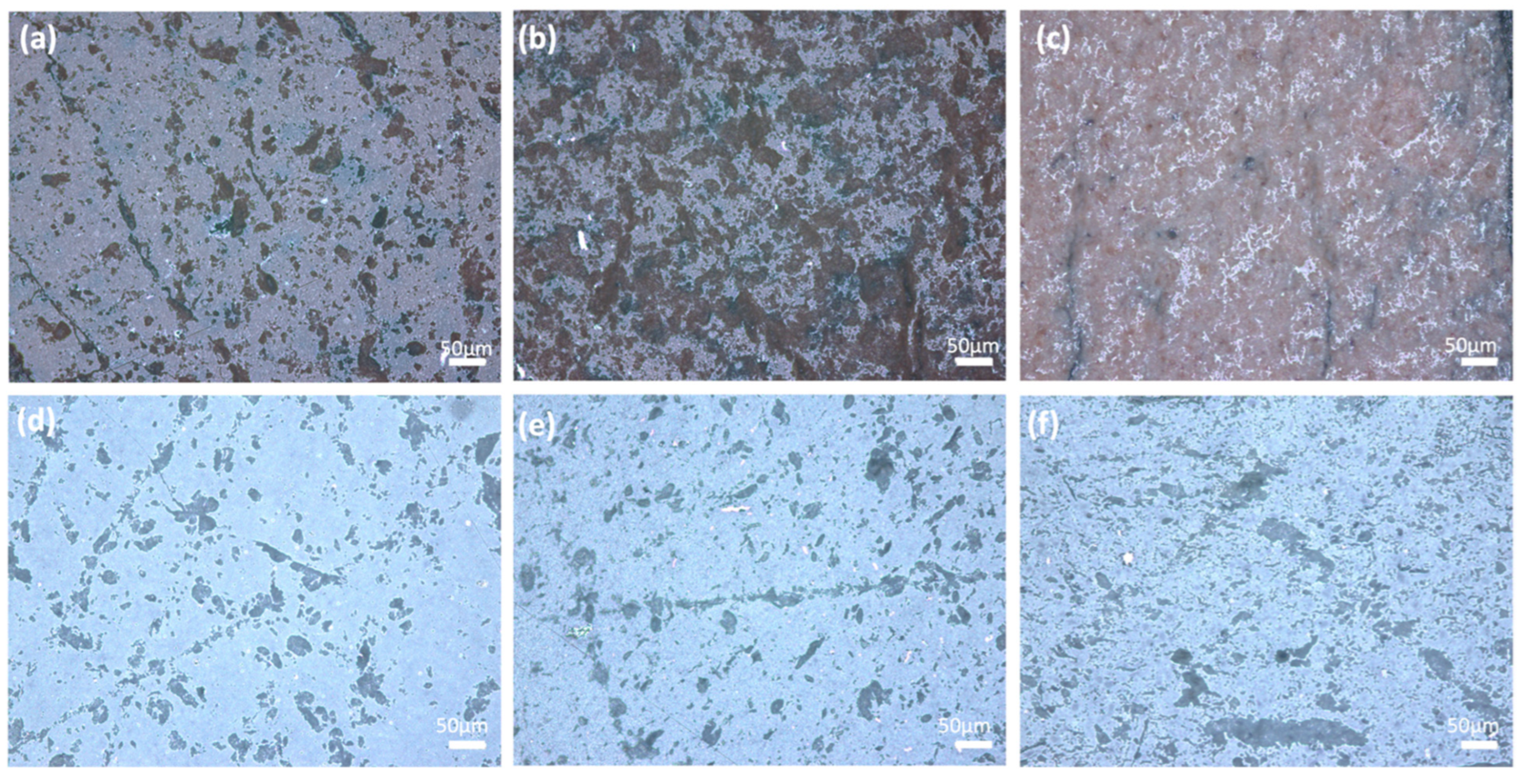
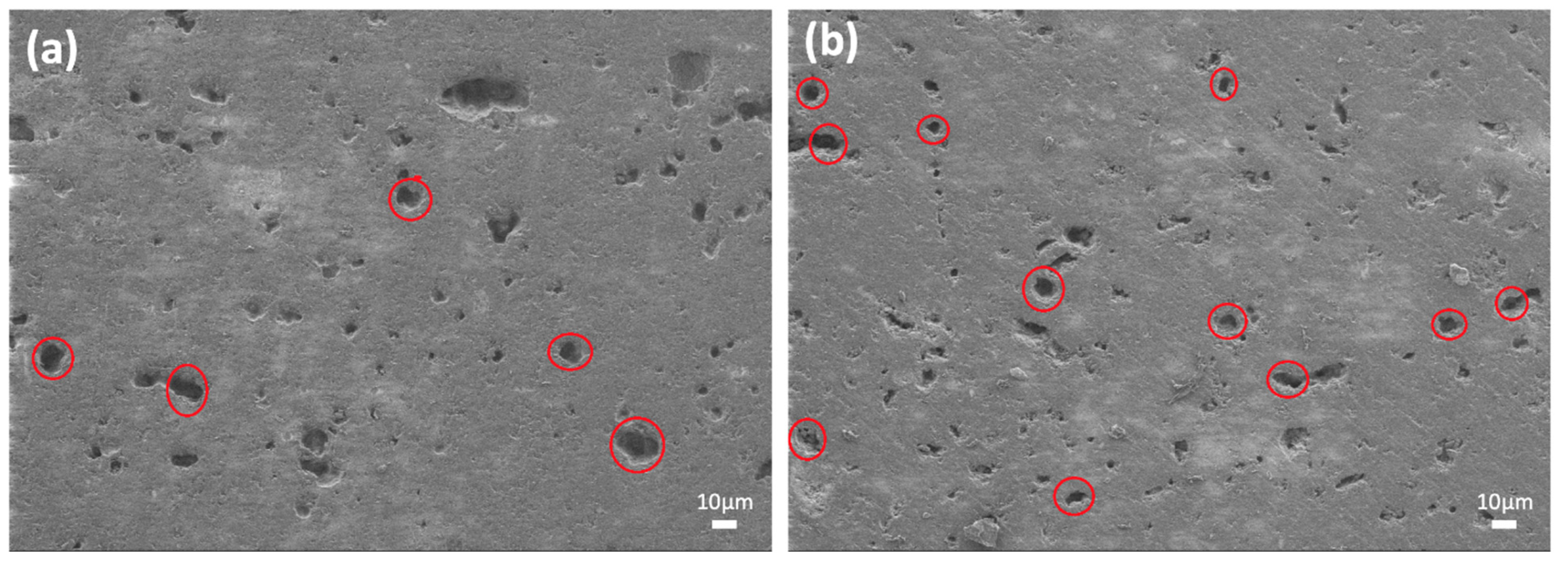
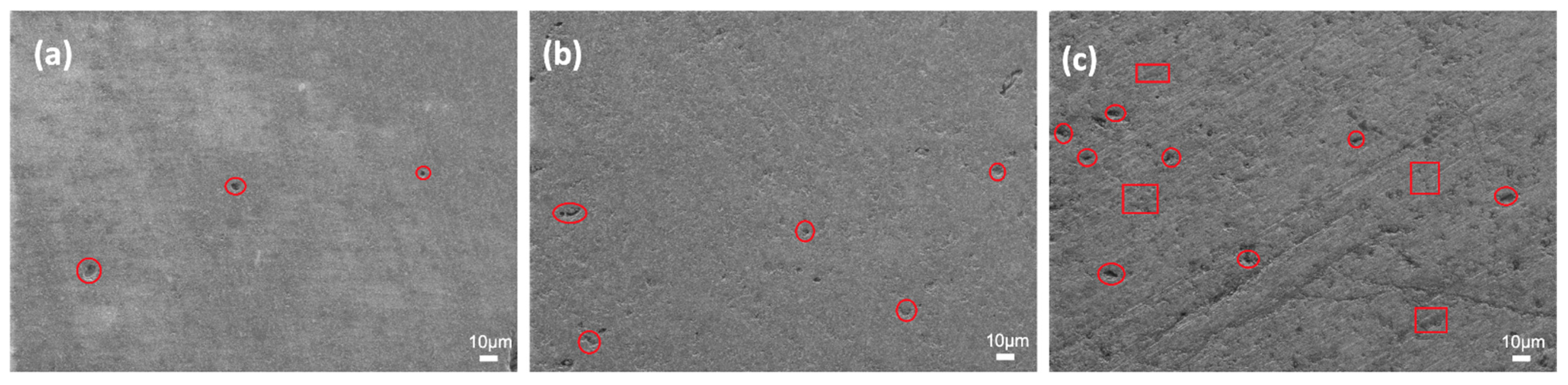
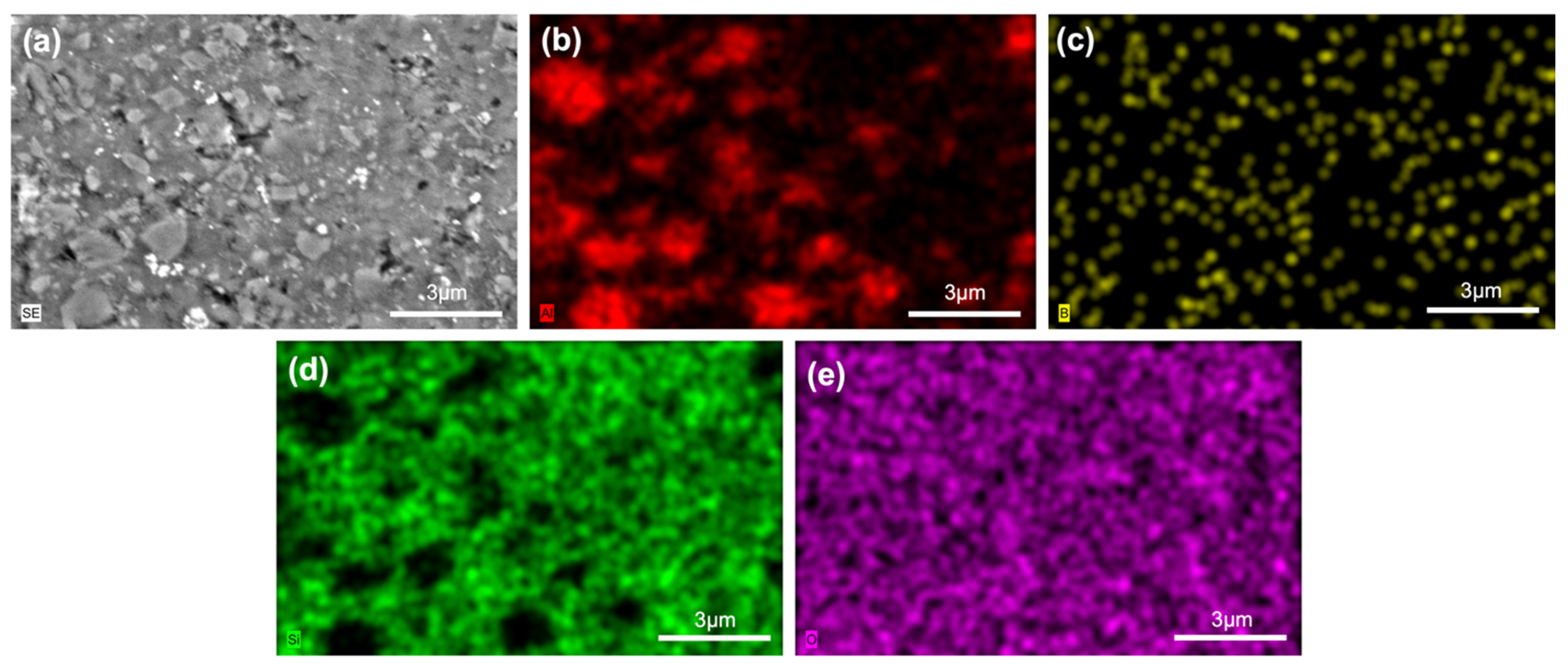

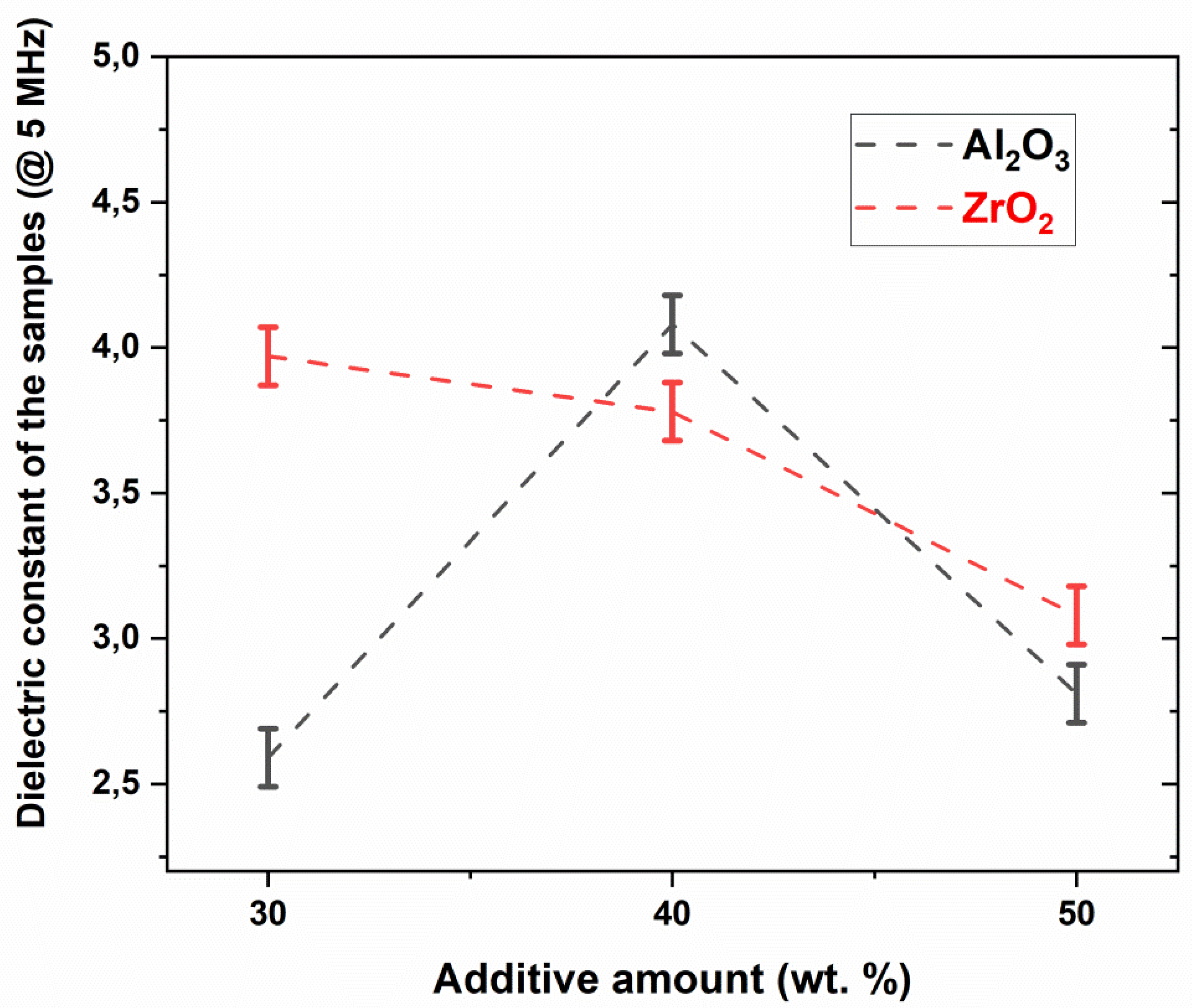
| Sample Name | wt.% of Glass Powder | wt.% of Al2O3 Filler | wt.% of ZrO2 Filler | Sintering Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30Al-Ar | 70 | 30 | - | 950 °C, Ar |
| 40Al-Ar | 60 | 40 | - | 950 °C, Ar |
| 50Al-Ar | 50 | 50 | - | 950 °C, Ar |
| 30Al-O | 70 | 30 | - | 950 °C, air |
| 40Al-O | 60 | 40 | - | 950 °C, air |
| 50Al-O | 50 | 50 | - | 950 °C, air |
| 30Zr-Ar | 70 | - | 30 | 950 °C, Ar |
| 40Zr-Ar | 60 | - | 40 | 950 °C, Ar |
| 50Zr-Ar | 50 | - | 50 | 950 °C, Ar |
| 30Zr-O | 70 | - | 30 | 950 °C, air |
| 40Zr-O | 60 | - | 40 | 950 °C, air |
| 50Zr-O | 50 | - | 50 | 950 °C, air |
| Sample Name | Average Density (g/cm3) | Relative Density (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 30Al-Ar | 2.399 | 75.99 |
| 40Al-Ar | 2.665 | 72.86 |
| 50Al-Ar | 2.710 | 62.74 |
| 30Al-O | 2.435 | 77.11 |
| 40Al-O | 2.581 | 70.77 |
| 50Al-O | 2.799 | 64.80 |
| 30Zr-Ar | 2.748 | 100.00 |
| 40Zr-Ar | 2.967 | 100.00 |
| 50Zr-Ar | 3.012 | 93.48 |
| 30Zr-O | 2.500 | 90.99 |
| 40Zr-O | 2.761 | 93.07 |
| 50Zr-O | 3.022 | 93.76 |
| Sample Name | Diffusivity (mm2/s) | Standard Deviation (mm2/s) | Average Thermal Conductivity (W/K.m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30Al-O | 0.443 | 0.102 | 1.336 |
| 40Al-O | 0.472 | 0.017 | 1.507 |
| 30Zr-Ar | 0.992 | 0.133 | 2.904 |
| 40Zr-Ar | 0.976 | 0.138 | 2.869 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arıbuğa, D.; Karaahmet, O.; Balcı-Çağıran, Ö.; Çiçek, B. Effect of Al2O3 and ZrO2 Filler Material on the Microstructural, Thermal and Dielectric Properties of Borosilicate Glass-Ceramics. Micromachines 2023, 14, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030595
Arıbuğa D, Karaahmet O, Balcı-Çağıran Ö, Çiçek B. Effect of Al2O3 and ZrO2 Filler Material on the Microstructural, Thermal and Dielectric Properties of Borosilicate Glass-Ceramics. Micromachines. 2023; 14(3):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030595
Chicago/Turabian StyleArıbuğa, Dilara, Oğuz Karaahmet, Özge Balcı-Çağıran, and Buğra Çiçek. 2023. "Effect of Al2O3 and ZrO2 Filler Material on the Microstructural, Thermal and Dielectric Properties of Borosilicate Glass-Ceramics" Micromachines 14, no. 3: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030595
APA StyleArıbuğa, D., Karaahmet, O., Balcı-Çağıran, Ö., & Çiçek, B. (2023). Effect of Al2O3 and ZrO2 Filler Material on the Microstructural, Thermal and Dielectric Properties of Borosilicate Glass-Ceramics. Micromachines, 14(3), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030595







