Amorphous ITZO-Based Selector Device for Memristor Crossbar Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
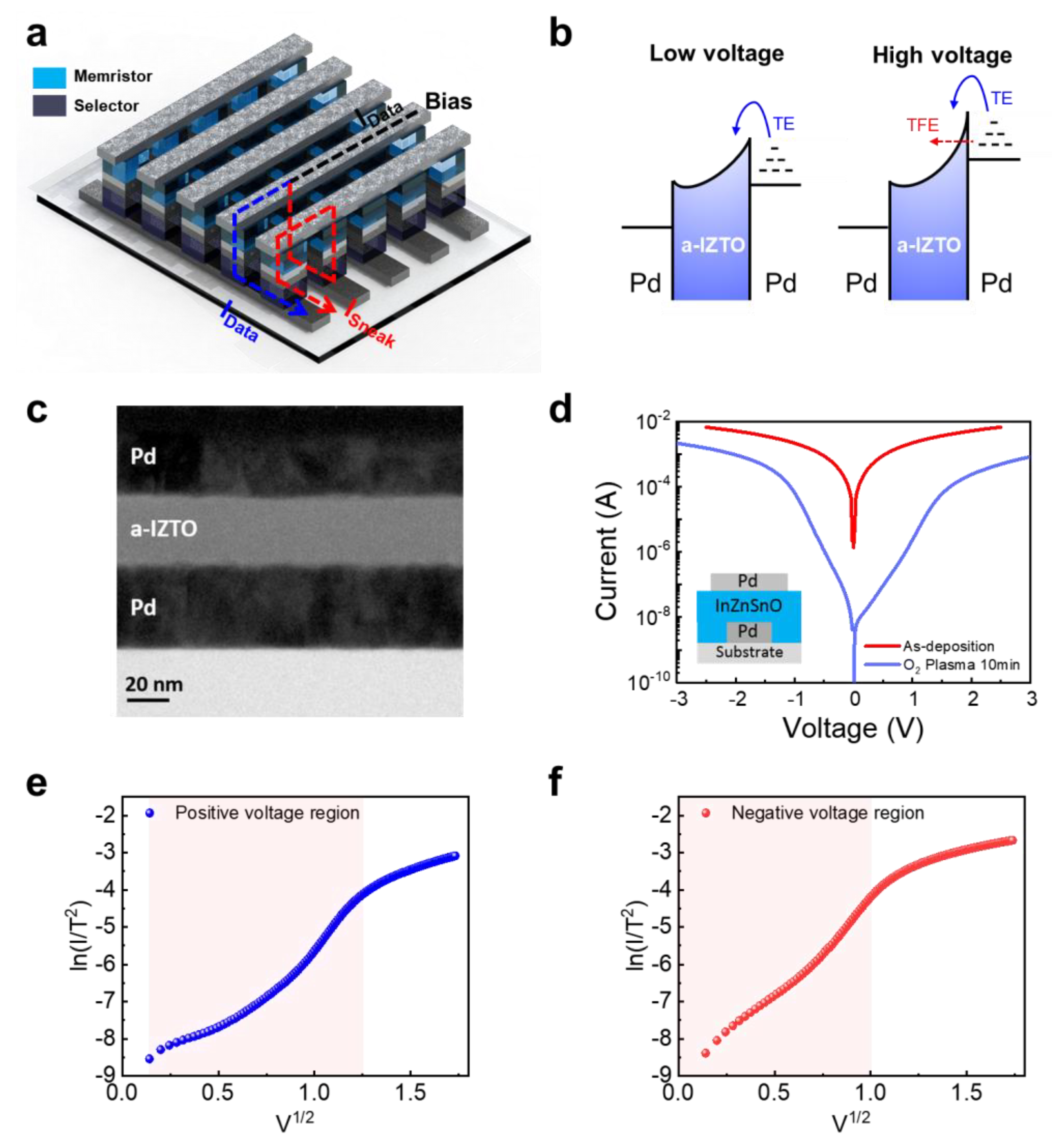
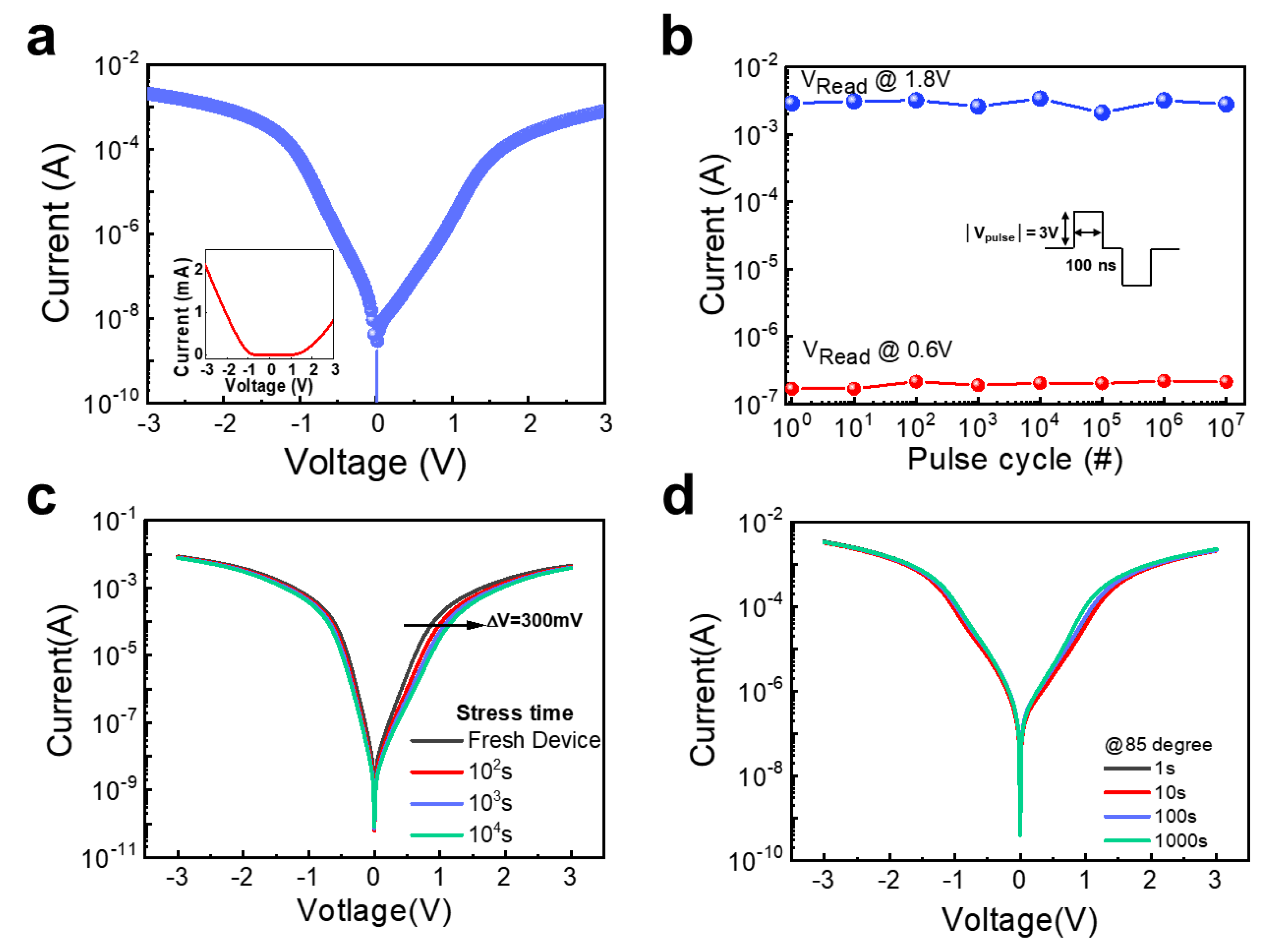
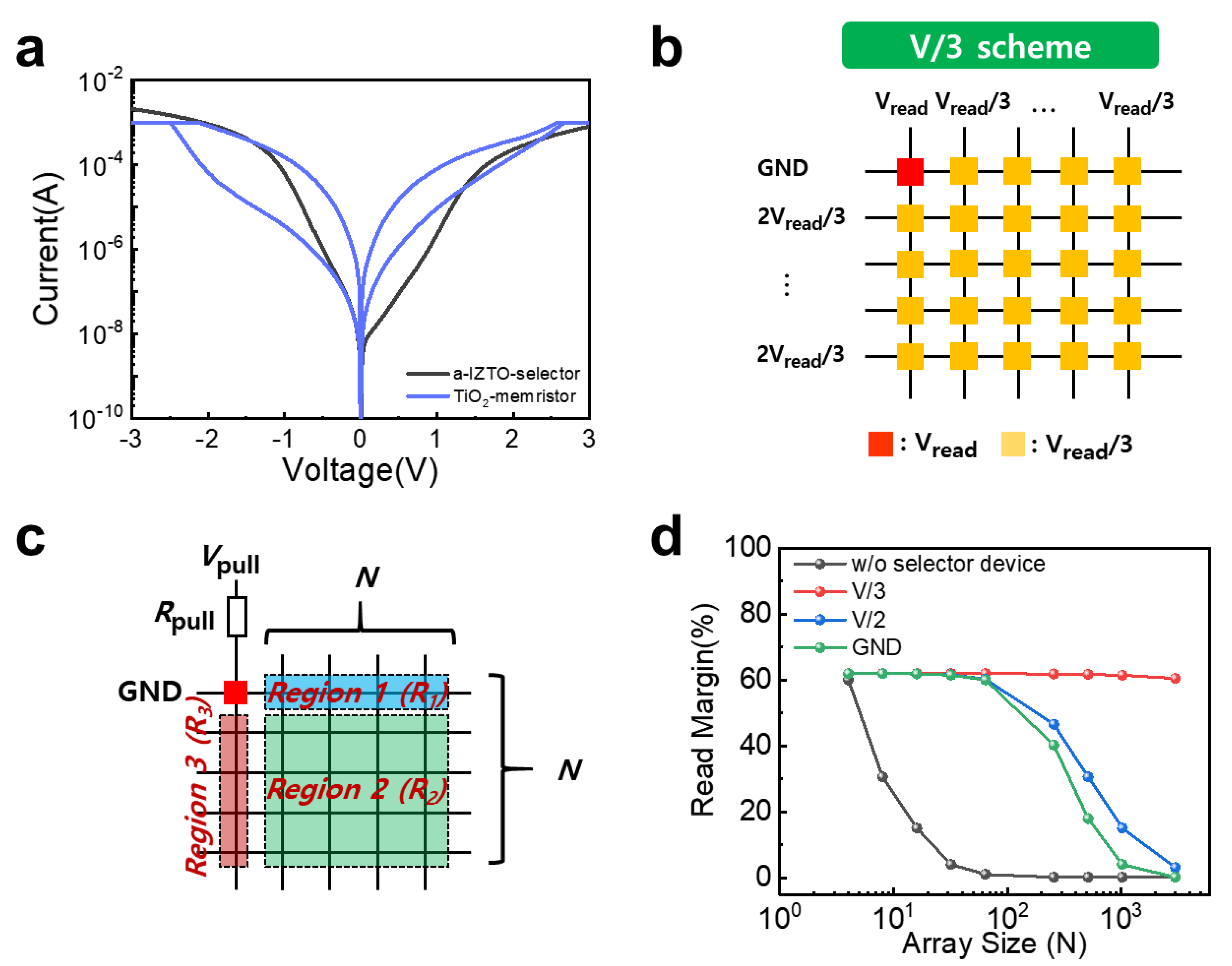
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waser, R.; Aono, M. Nanoionics-based resistive switching memories. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Lee, C.B.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.R.; Chang, M.; Hur, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, C.J.; Seo, D.H.; Seo, S.; et al. A fast, high-endurance and scalable non-volatile memory device made from asymmetric Ta2O5-x/TaO2-x bilayer structures. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Loh, L.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Li, B.; Bosman, M.; Ang, K.-W. Anomalous resistive switching in memristors based on two-dimensional palladium diselenide using heterophase grain boundaries. Nat. Electron. 2021, 4, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, F.M.; Hsu, C.-L.; Abbey, T.; Chang, L.-Y.; Rajasekaran, S.; Prodromakis, T.; Tseng, T.-Y. Conduction channel configuration controlled digital and analog response in TiO2-based inorganic memristive artificial synapses. APL Mater. 2021, 9, 121103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Wang, S.; Lu, N. High-Stability Memristive Devices Based on Pd Conductive Filaments and Its Applications in Neuromorphic Computing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 17844–17851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balatti, S.; Ambrogio, S.; Ielmini, D. Normally-off Logic Based on Resistive Switches—Part I: Logic Gates. IEEE Trans. Electr. Dev. 2015, 62, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinerio, M.; Ciocchini, N.; Ielmini, D. Logic computation in phase change materials by threshold and memory switching. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5975–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, B.C.; Yang, S.Y.; Seong, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, J.; Im, S.G.; Choi, S.-Y. Zero-Static-Power Nonvolatile Logic-in-Memory Circuits for Flexible Electronics. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 2459–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghetti, J.; Snider, G.S.; Kuekes, P.J.; Yang, J.J.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. ‘Memristive’ switches enable ‘stateful’ logic operations via material implication. Nature 2010, 464, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strukov, D.B.; Likharev, K.K. Defect-Tolerant Architectures for Nanoelectronic Crossbar Memories. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, G. Computing with hysteretic resistor crossbars. Appl. Phys. A 2005, 80, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Wu, H.; Gao, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.J.; Qian, H. Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network. Nature 2020, 577, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, P.; Ye, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Kang, J. A learnable parallel processing architecture towards unity of memory and computing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.J.; Zhang, J.; Norris, K.; Gibson, G.; Kim, K.M.; Jackson, W.; Zhang, M.X.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.J.; Williams, R.S. Trilayer Tunnel Selectors for Memristor Memory Cells. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 356–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, J.; Bai, G.; Zhong, G.; Wang, B.; Ling, Y.; Chen, Q.; Bao, L.; Wu, L.; Cai, Y.; et al. Self-Selective Resistive Device With Hybrid Switching Mode for Passive Crossbar Memory Application. IEEE Electr. Dev. Lett. 2020, 41, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.H.; Kumar, T.; Narayanan, S.; Nazarian, H. Cross-Point Resistive RAM Based on Field-Assisted Superlinear Threshold Selector. IEEE Trans. Electr. Dev. 2015, 62, 3477–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, R.; Sun, Z.; Feng, W.; Lin, P.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L.; et al. Memristive Crossbar Arrays for Storage and Computing Applications. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.-H.; Park, J.; Kim, H. Memristor Crossbar Circuit for Ternary Content-Addressable Memory with Fine-Tuning Operation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 220325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Lee, D.; Cho, S.H.; Hur, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Seo, D.H.; Kim, D.S.; Yang, M.S.; Lee, S.; Hwang, E.; et al. A plasma-treated chalcogenide switch device for stackable scalable 3D nanoscale memory. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-J.; Tseng, Y.-M.; Hsu, C.-W.; Hou, T.-H. Bipolar Nonlinear Ni/TiO2/Ni Selector for 1S1R Crossbar Array Application. IEEE Electr. Dev. Lett. 2011, 32, 1427–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-C.; Shahrjerdi, D.; Banerjee, S.K. Highly Non-linear and Reliable Amorphous Silicon Based Back-to-Back Schottky Diode as Selector Device for Large Scale RRAM Arrays. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, N143–N147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, Y.; Hatayama, S.; An, J.; Hong, J.; Ando, D.; Song, Y.; Sutou, Y. Bidirectional Selector Utilizing Hybrid Diodes for PCRAM Applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Feng, F.; Xie, Y. Design of vanadium oxide structures with controllable electrical properties for energy applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5157–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Son, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; You, B.K.; Park, K.I.; Lee, H.K.; Byun, M.; Lee, K.J. Flexible Crossbar-Structured Resistive Memory Arrays on Plastic Substrates via Inorganic-Based Laser Lift-Off. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7480–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-J.; Tseng, Y.-M.; Luo, W.-C.; Hsu, C.-W.; Hou, T.-H. One Selector-One Resistor (1S1R) Crossbar Array for High-density Flexible Memory Applications. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Electron Devices Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 5–7 December 2011; pp. 733–736. [Google Scholar]
- Hosono, H. Ionic amorphous oxide semiconductors: Material design, carrier transport, and device application. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.Q.; Wager, J.F.; Hoffman, R.L.; Jeong, J.; Keszler, D.A. High mobility transparent thin-film transistors with amorphous zinc tin oxide channel layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 013503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Kim, H.; Kim, I.-D. Overview of electroceramic materials for oxide semiconductor thin film transistors. J. Electroceram. 2013, 32, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Ikenaga, E.; Yanagi, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Hosono, H. Depth analysis of subgap electronic states in amorphous oxide semiconductor, a-In-Ga-Zn-O, studied by hard x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 073726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A. Surface oxygen vacancy origin of electron accumulation in indium oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 261910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierwagen, O.; Speck, J.S.; Nagata, T.; Chikyow, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Kobayashi, K. Depletion of the In2O3 (001) and (111) surface electron accumulation by an oxygen plasma surface treatment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 172101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wenckstern, H.; Splith, D.; Schmidt, F.; Grundmann, M.; Bierwagen, O.; Speck, J.S. Schottky contacts to In2O3. APL Mater. 2014, 2, 046104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Tsukazaki, A.; Gunji, R.Y.; Ueno, K.; Ohtomo, A.; Fukumura, T.; Kawasaki, M. Schottky contact on a ZnO (0001) single crystal with conducting polymer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 142113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, R.; Monakhov, E.V.; Grossner, U.; Svensson, B.G. Electrical characteristics of palladium Schottky contacts to hydrogen peroxide treated hydrothermally grown ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 193507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, R.; Monakhov, E.V.; Svensson, B.G.; Diplas, S. Surface passivation and interface reactions induced by hydrogen peroxide treatment of n-type ZnO (0001). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 132101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbacker, H.L.; Strzhemechny, Y.M.; White, B.D.; Smith, P.E.; Look, D.C.; Reynolds, D.C.; Litton, C.W.; Brillson, L.J. Role of near-surface states in ohmic-Schottky conversion of Au contacts to ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 012102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, T.; Bierwagen, O.; White, M.E.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Speck, J.S. Study of the Au Schottky contact formation on oxygen plasma treated n-type SnO2 (101) thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 033707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migani, A.; Sousa, C.; Illas, F. Chemisorption of atomic chlorine on metal surfaces and the interpretation of the induced work function changes. Surf. Sci. 2005, 574, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.-Y. Impact of amorphous titanium oxide film on the device stability of Al/TiO2/Al resistive memory. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 102, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.-D.; Choi, S.-J. Numerical study of read scheme in one-selector one-resistor crossbar array. Solid State Electron. 2015, 114, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.C.; Nam, Y.; Koo, B.J.; Choi, J.; Im, S.G.; Park, S.-H.K.; Choi, S.-Y. Memristive Logic-in-Memory Integrated Circuits for Energy-Efficient Flexible Electronics. Adv. Funt. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-P.; Hussain, A.M.; Hwang, D.-K.; Woo, S.-H.; Lyu, H.-K.; Baek, S.-H.; Jang, Y.; Kim, J.-H. Work Function Modification of Indium–Tin Oxide by Surface Plasma Treatments Using Different Gases. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 021601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungho, K.; Jiantao, Z.; Lu, W.D. Crossbar RRAM Arrays: Selector Device Requirements During Write Operation. IEEE Trans. Electr. Dev. 2014, 61, 2820–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.H.; Seo, M.-J.; Jang, B.C. Amorphous ITZO-Based Selector Device for Memristor Crossbar Array. Micromachines 2023, 14, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030506
Kim KH, Seo M-J, Jang BC. Amorphous ITZO-Based Selector Device for Memristor Crossbar Array. Micromachines. 2023; 14(3):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030506
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ki Han, Min-Jae Seo, and Byung Chul Jang. 2023. "Amorphous ITZO-Based Selector Device for Memristor Crossbar Array" Micromachines 14, no. 3: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030506
APA StyleKim, K. H., Seo, M.-J., & Jang, B. C. (2023). Amorphous ITZO-Based Selector Device for Memristor Crossbar Array. Micromachines, 14(3), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030506




