Impedance-Frequency Response of Closed Electrolytic Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. Equation System
- (i).
- Poisson equation:where is the absolute permittivity of the electrolyte solution assumed to have a constant value, is the electric potential, the time, the elementary charge, and the local concentrations of the two ionic types.
- (ii).
- Nernst–Planck equations:where are the ionic fluxes (mol/(m2s), is the Boltzmann constant, and the absolute temperature.
- (iii).
- Continuity equations:
2.2. Boundary Conditions
2.3. Dimensionless Variables
3. Equation System Solution
4. Results
4.1. Steady State
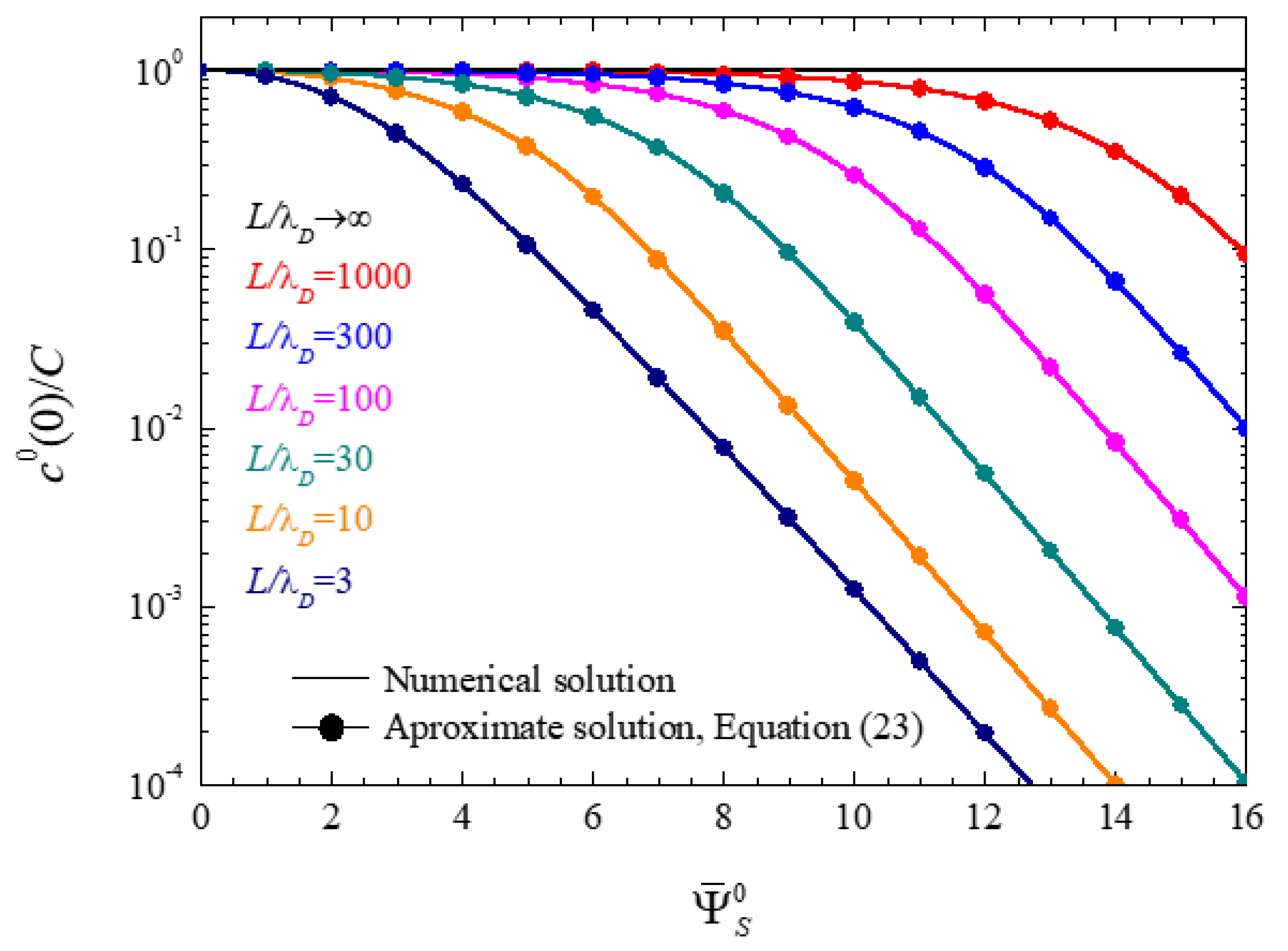
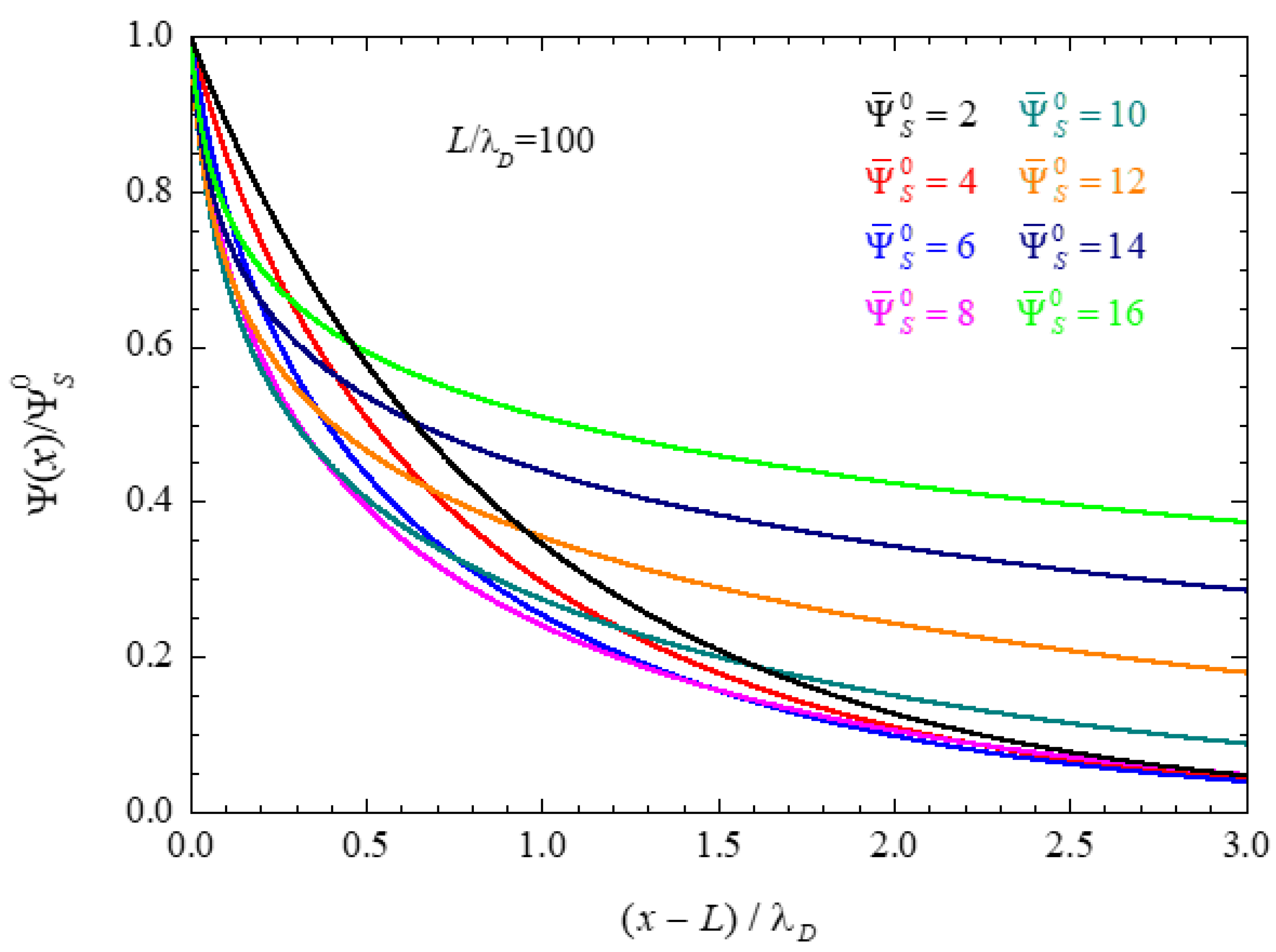
4.1.1. Ionic Concentrations at the Central Plane of Closed Electrolytic Cells
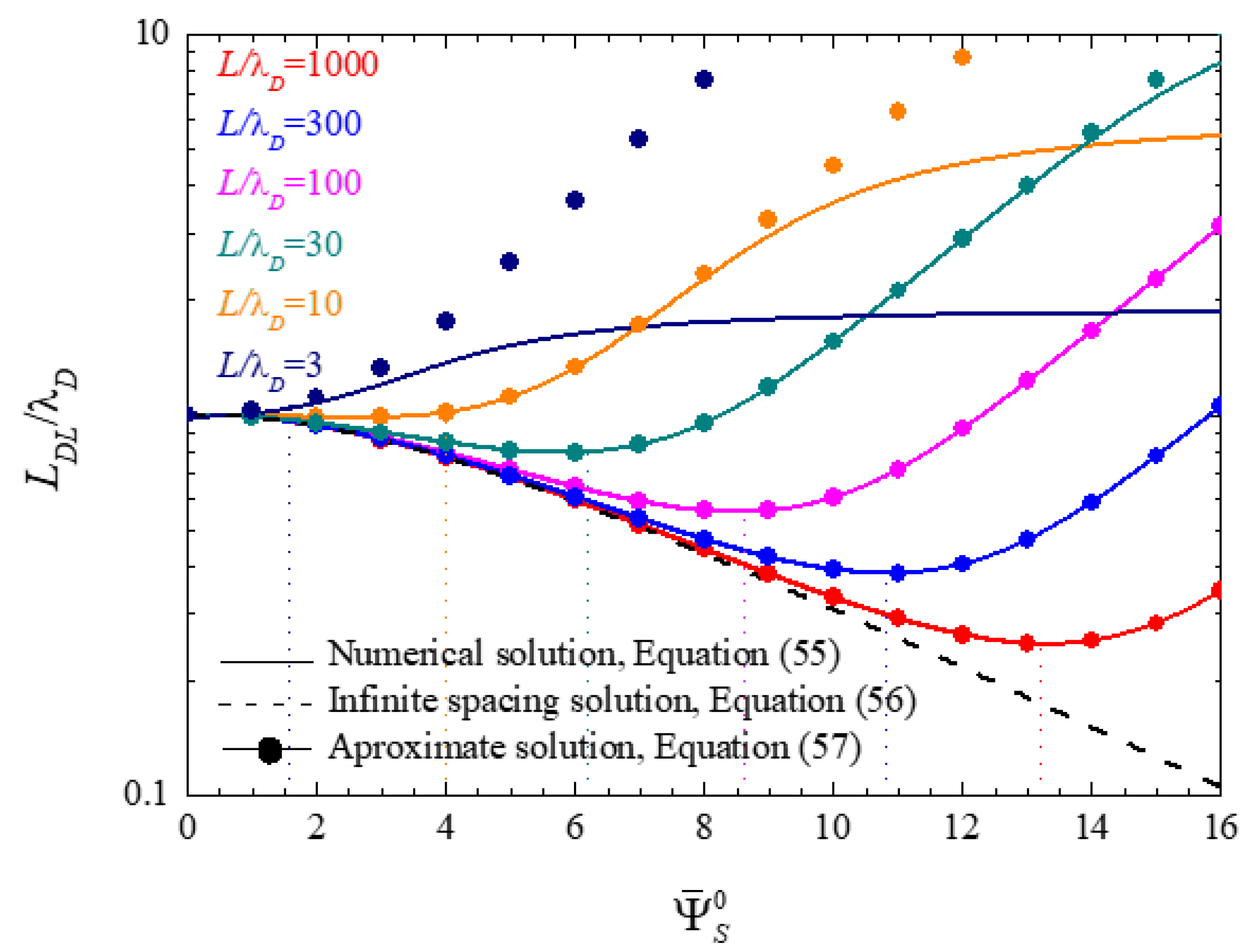
4.1.2. Electric Double Layer Thickness
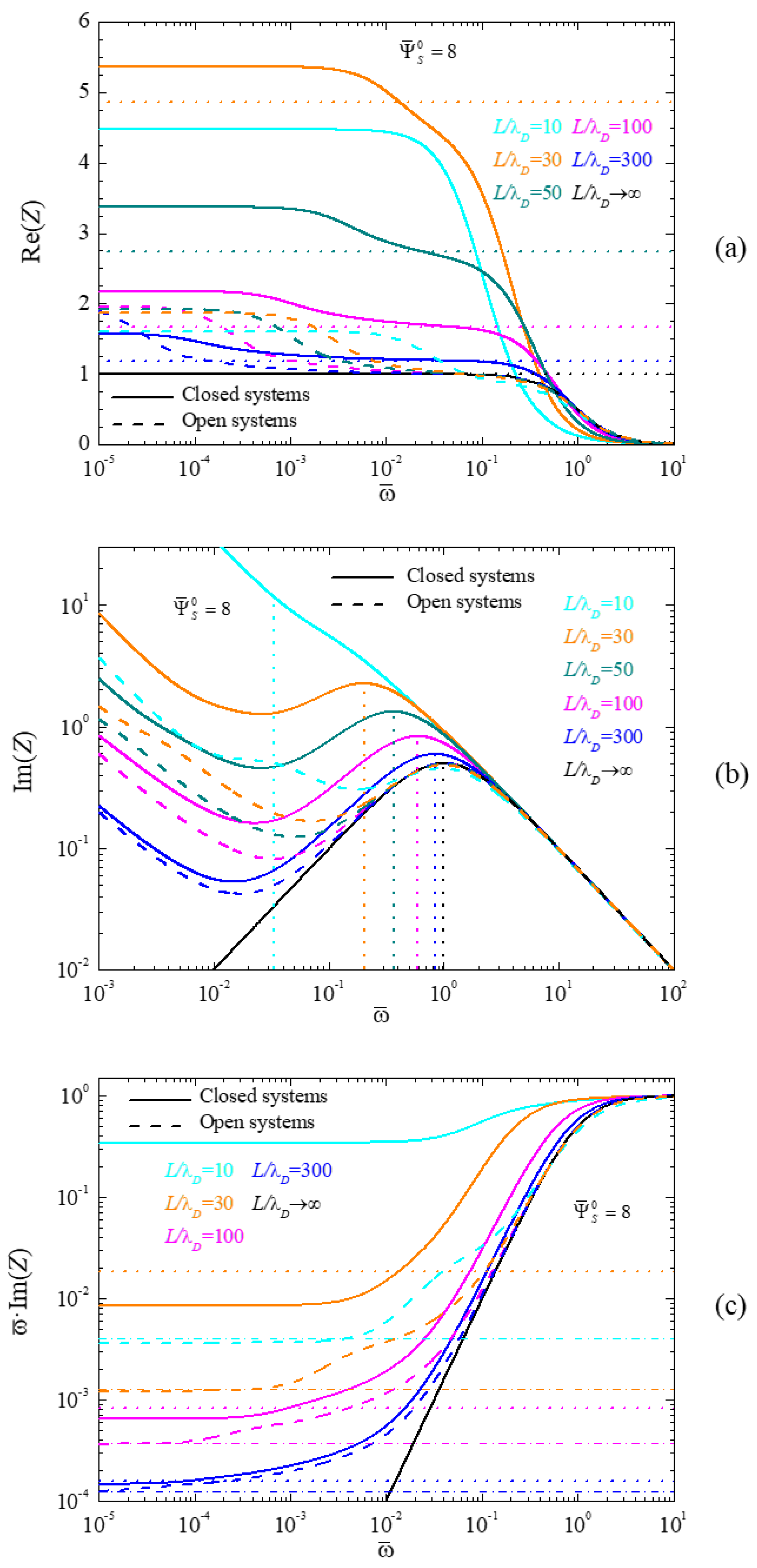
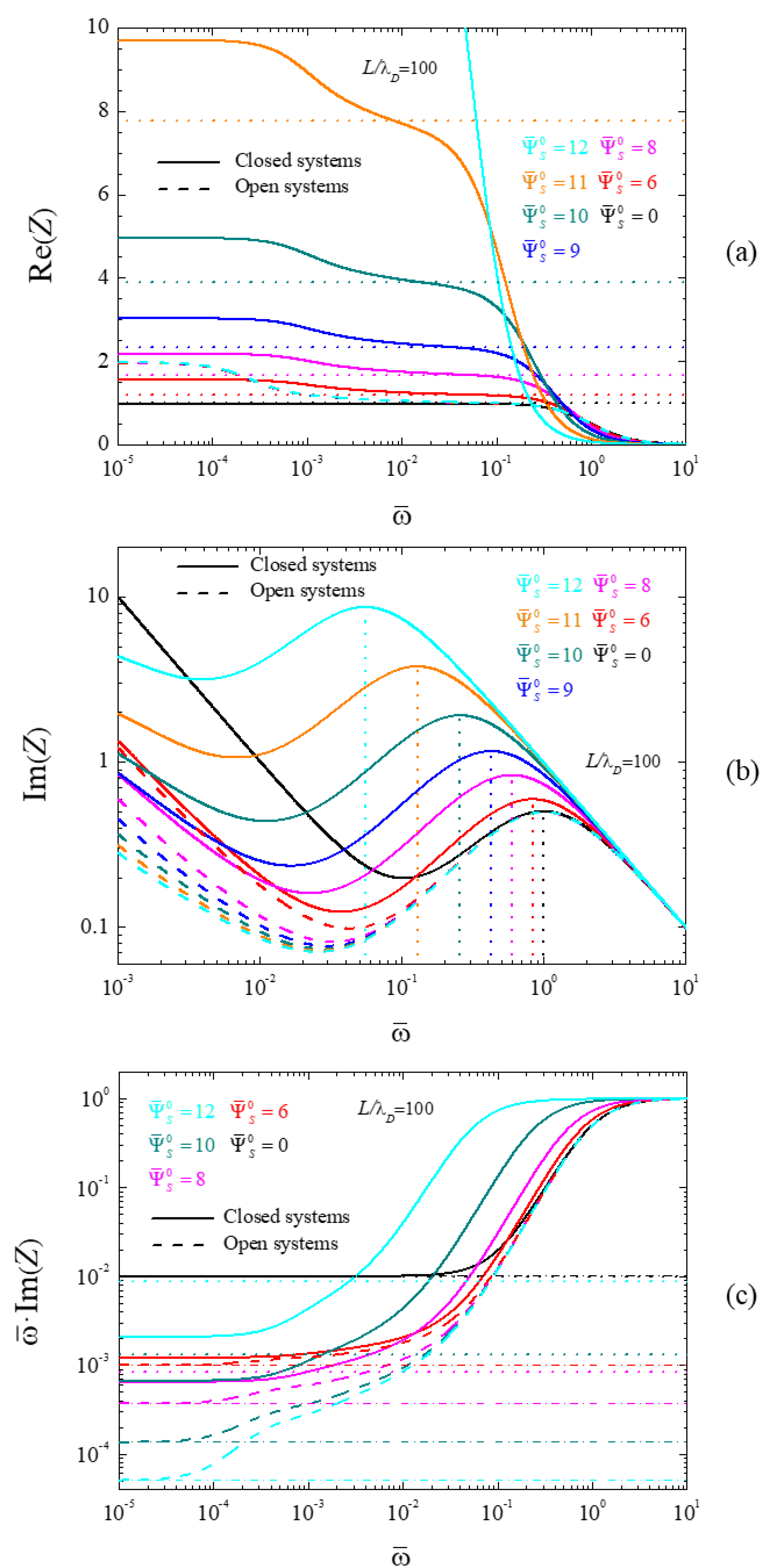
4.2. Frequency Response
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Proof of Equation (27)
Appendix A.2. Proof of Equation (58)
Appendix A.3. Proof of Equation (61)
References
- Barsoukov, E.; Macdonald, J.R. Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment and Applications; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Brumleve, T.R.; Buck, R.P. Numerical solution of the Nernst-Planck and Poisson equation system with applications to membrane electrochemistry and solid state physics. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1978, 90, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, T.B.; Compañ, V. Complex permittivity of a conducting, dielectric layer containing arbitrary binary Nernst–Planck electrolytes with applications to polymer films and cellulose acetate membranes. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1995, 91, 4235–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horno, J.; Moya, A.A.; González-Fernández, C.F. Simulation and interpretation of electrochemical impedances using the network method. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1996, 402, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R. Theory of ac Space-Charge Polarization Effects in Photoconductors, Semiconductors, and Electrolytes. Phys. Rev. 1953, 92, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R. Binary electrolyte small-signal frequency response. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1974, 53, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumleve, T.R.; Buck, R.P. Transmission line equivalent circuit models for electrochemical impedances. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1981, 126, 73–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamnik, J.; Maier, J. Treatment of the Impedance of Mixed Conductors Equivalent Circuit Model and Explicit Approximate Solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R. Effects of Various Boundary Conditions on the Response of Poisson Nernst Planck Impedance Spectroscopy Analysis Models and Comparison with a Continuous-Time Random-Walk Model. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 13370–13380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelidis, I.; Macdonald, J.R.; Barbero, G. Poisson–Nernst–Planck Model with Chang-Jaffe, Diffusion, and Ohmic Boundary Conditions. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 025503–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, E.K.; Zola, R.S.; Rossato, R.; Ribeiro, H.V.; Vieira, D.S.; Evangelista, L.R. Asymptotic behaviors of the Poisson-Nernst-Planck model, generalizations and best adjust of experimental data. Electrochimica Acta 2017, 226, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Khoo, E.; Bazant, M.Z. Electrochemical impedance of electrodiffusion in charged medium under dc bias. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 042204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexe-Ionescu, A.L.; Barbero, G.; Evangelista, L.R. Electric response of asymmetric electrolytic cells to small AC signals. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 873, 114378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.K.; Huang, J. Impedance Response of Electrochemical Interfaces: Part I. Exact Analytical Expressions for Ideally Polarizable Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 167, 166517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, R.P. Diffuse layer charge relaxation at the ideally polarized electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1969, 23, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R. Double layer capacitance and relaxation in electrolytes and solids. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1970, 66, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirkel, P.A.; van der Ploeg, J.P.M.; Koper, G.J.M. Electrode effects in dielectric spectroscopy of colloidal suspensions. Physica A 1997, 235, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, A.D.; Saville, D.A. A broad frequency range dielectric spectrometer for colloidal suspensions Cell design calibration and validation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 257, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.; Paul, R.; Kalert, K.V.I.S. Theory of Frequency-Dependent Polarization of General Planar Electrodes with Zeta Potentials of Arbitrary Magnitude in Ionic Media, Part 2. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 230, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, G.; Alexe-Ionescu, A.L. Role of the diffuse layer of the ionic charge on the impedance spectroscopy of a cell of liquid. Liq. Cryst. 2005, 32, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalioto, F.; Duarte, A.R.; Barbero, G.; Neto, A.M.F. Dielectric Dispersion of Water in the Frequency Range from 10 mHz to 30 MHz. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 3467–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, E.K.; Evangelista, L.R.; Taghizadeh, L.; Pasterk, D.; Zola, R.S.; Sandev, T.; Heitzinger, C.; Petreska, I. Reliability of Poisson–Nernst–Planck Anomalous Models for Impedance Spectroscopy, J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 7885–7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Jaffe, G. Polarization in Electrolytic Solutions. Part I. Theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzi, E.K.; Evangelista, L.R.; Barbero, G. Fractional Diffusion Equation and Impedance Spectroscopy of Electrolytic Cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 11371–11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, P.A.; de Paula, J.L.; Lenzi, E.K.; Evangelista, L.R. Anomalous Diffusion Governed by a Fractional Diffusion Equation and the Electrical Response of an Electrolytic Cell. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 114704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, J.R.; Evangelista, L.R.; Lenzi, E.K.; Barbero, G. Comparison of Impedance Spectroscopy Expressions and Responses of Alternate Anomalous Poisson-Nernst-Planck Diffusion Equations for Finite-Length Situations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 7648–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, D.; Gavish, N. Finite domain effects in steady state solutions of Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2019, 79, 1030–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, J.J.; Horno, J.; Grosse, C. On the use of the infinite solution hypothesis in electrochemical cells for the calculation of their differential capacitance. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 904, 115925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, J.J.; Horno, J.; Grosse, C. Combined Ionic Size and Electrode Spacing Effects on the Differential Capacitance of Confined Electrolytic Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 9154–9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Thornton, K.; Ajdari, A. Diffuse-charge dynamics in electrochemical systems. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 021506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, G.; Gliozzi, A.S.; Scalerandi, M.; Scarfone, A.M. Effects of a dc bias on electrical impedance spectroscopy in electrolytic cells. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, A.; Shaik, V.A.; Chakraborty, S. Effects of finite ionic size and solvent polarization on the dynamics of electrolytes probed through harmonic disturbances. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 042307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, R.F.; Khair, A.S. Moderately nonlinear diffuse-charge dynamics under an ac voltage. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 032305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.; Cooley, J.W. The numerical solution of the time-dependent Nernst-Planck equations. Biophys. J. 1965, 5, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyklema, J. Fundamentals of Colloid and Interface Science; Solid/Liquid Interfaces; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-García, J.J.; Horno, J.; Grosse, C. Impedance-Frequency Response of Closed Electrolytic Cells. Micromachines 2023, 14, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020368
López-García JJ, Horno J, Grosse C. Impedance-Frequency Response of Closed Electrolytic Cells. Micromachines. 2023; 14(2):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020368
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-García, José Juan, José Horno, and Constantino Grosse. 2023. "Impedance-Frequency Response of Closed Electrolytic Cells" Micromachines 14, no. 2: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020368
APA StyleLópez-García, J. J., Horno, J., & Grosse, C. (2023). Impedance-Frequency Response of Closed Electrolytic Cells. Micromachines, 14(2), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020368





