Scattering of Metal Colloids by a Circular Post under Electric Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analysis of the Physical Problem
2.1. Particle Repulsion with Its Image Dipole
2.2. ICEO Repulsion from Insulating Walls
2.3. Dielectrophoresis and Dipolophoresis
2.4. Particle Trajectory and Comparisons between Mechanisms
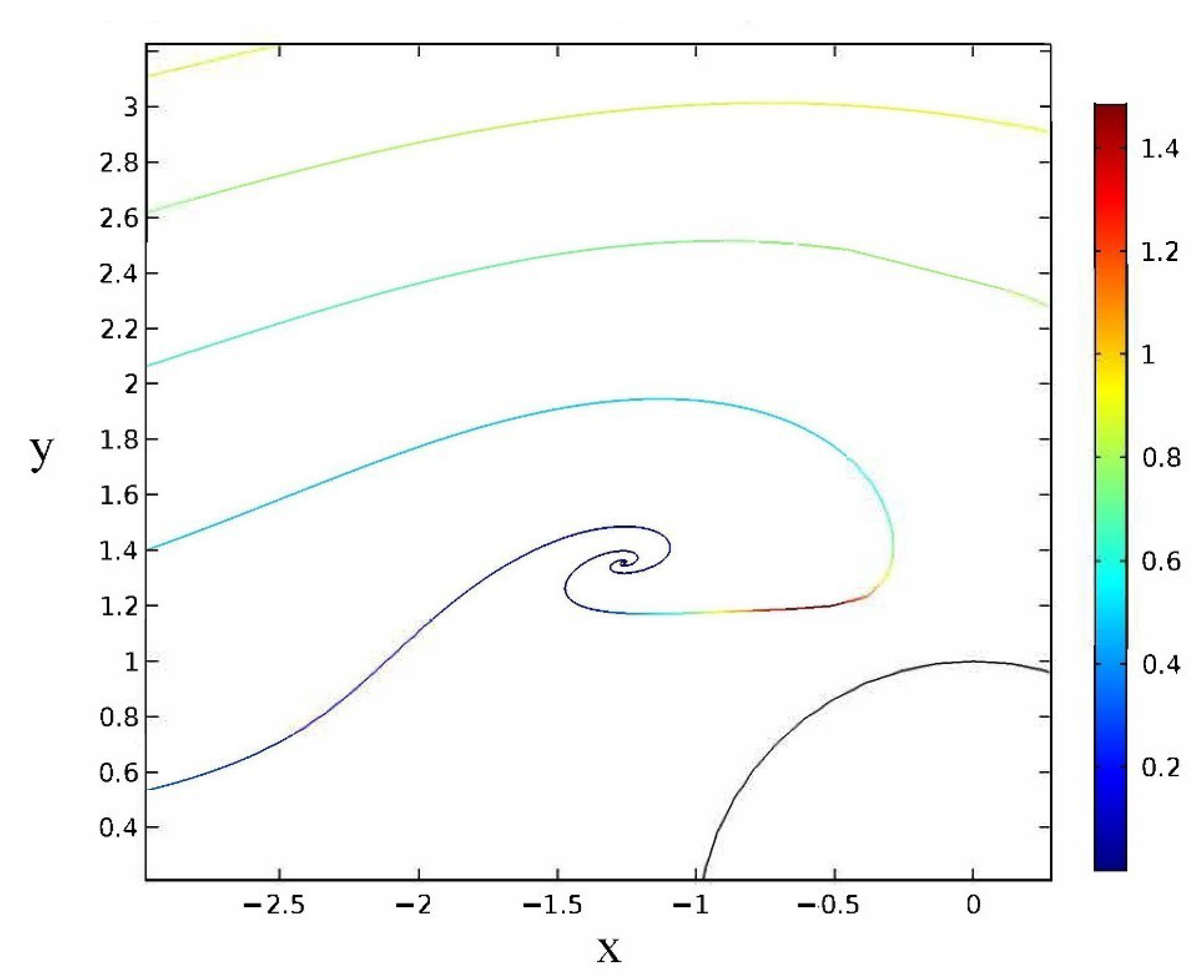
3. Numerical Simulations of the Trajectories
- (A)
- Electric field parallel to the fluid flow. We imposed boundary conditions of zero normal current density () at the cylinder surface and at upper and lower planes (see the geometry in Figure 1). Dirichlet boundary conditions were applied at the entrance and exit so that the applied electric field was equal to .
- (B)
- Electric field perpendicular to the fluid flow. We imposed boundary conditions of zero normal current density () at the cylinder surface and at the entrance and exit. Dirichlet boundary conditions were applied at upper and lower planes.
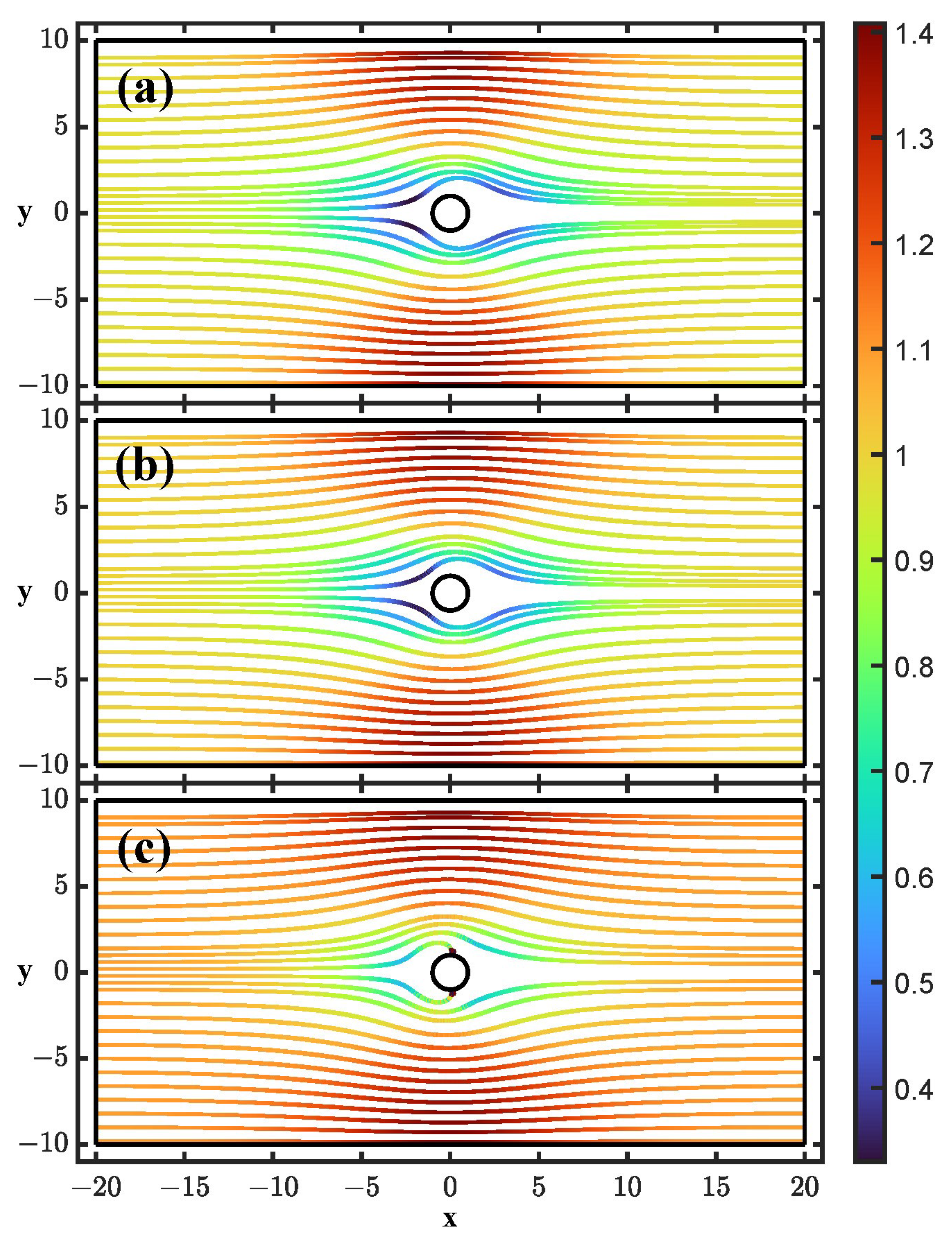
3.1. Electric Field Parallel to the Fluid Flow
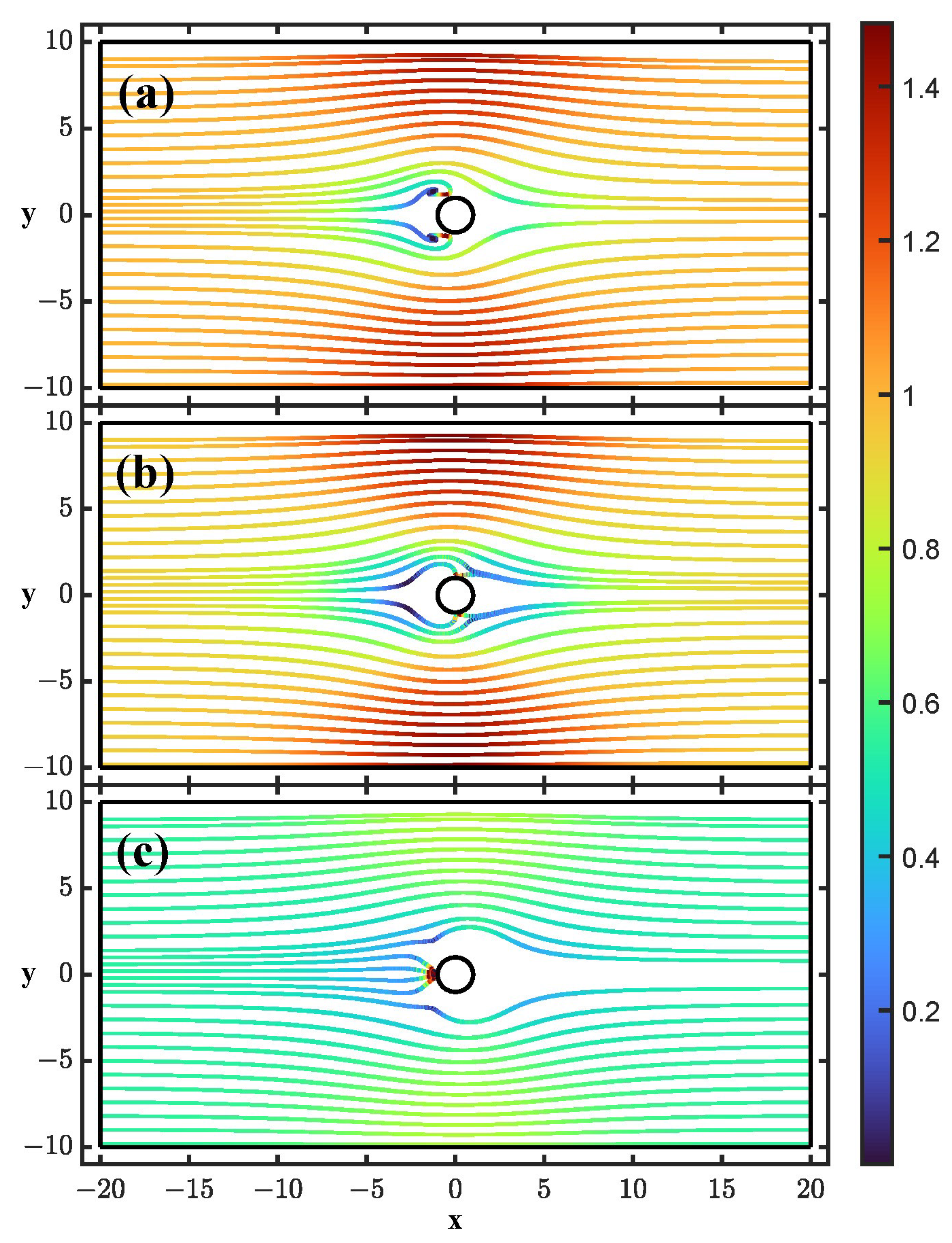
3.2. Electric Field Perpendicular to the Fluid Flow
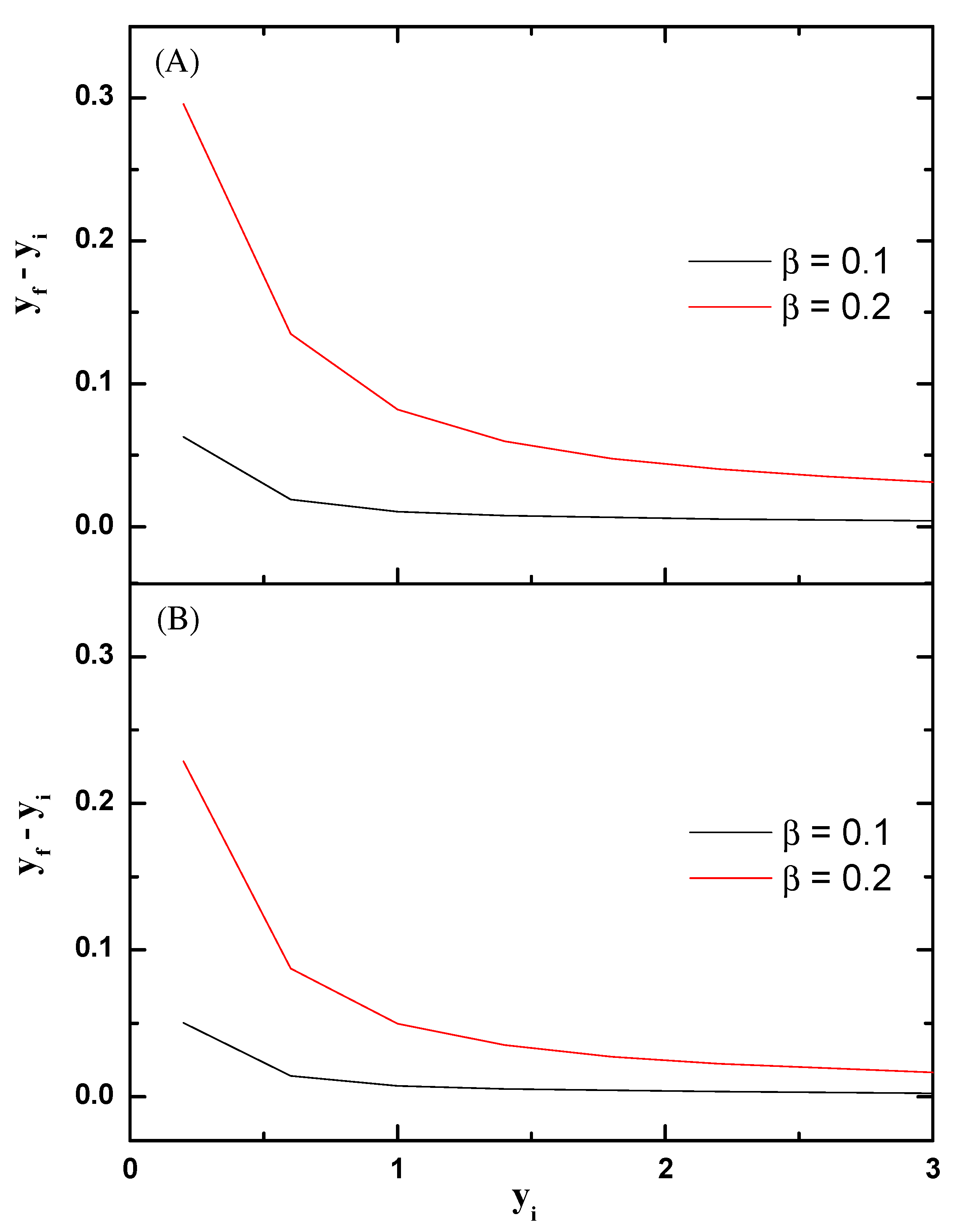
3.3. Particle Deviations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
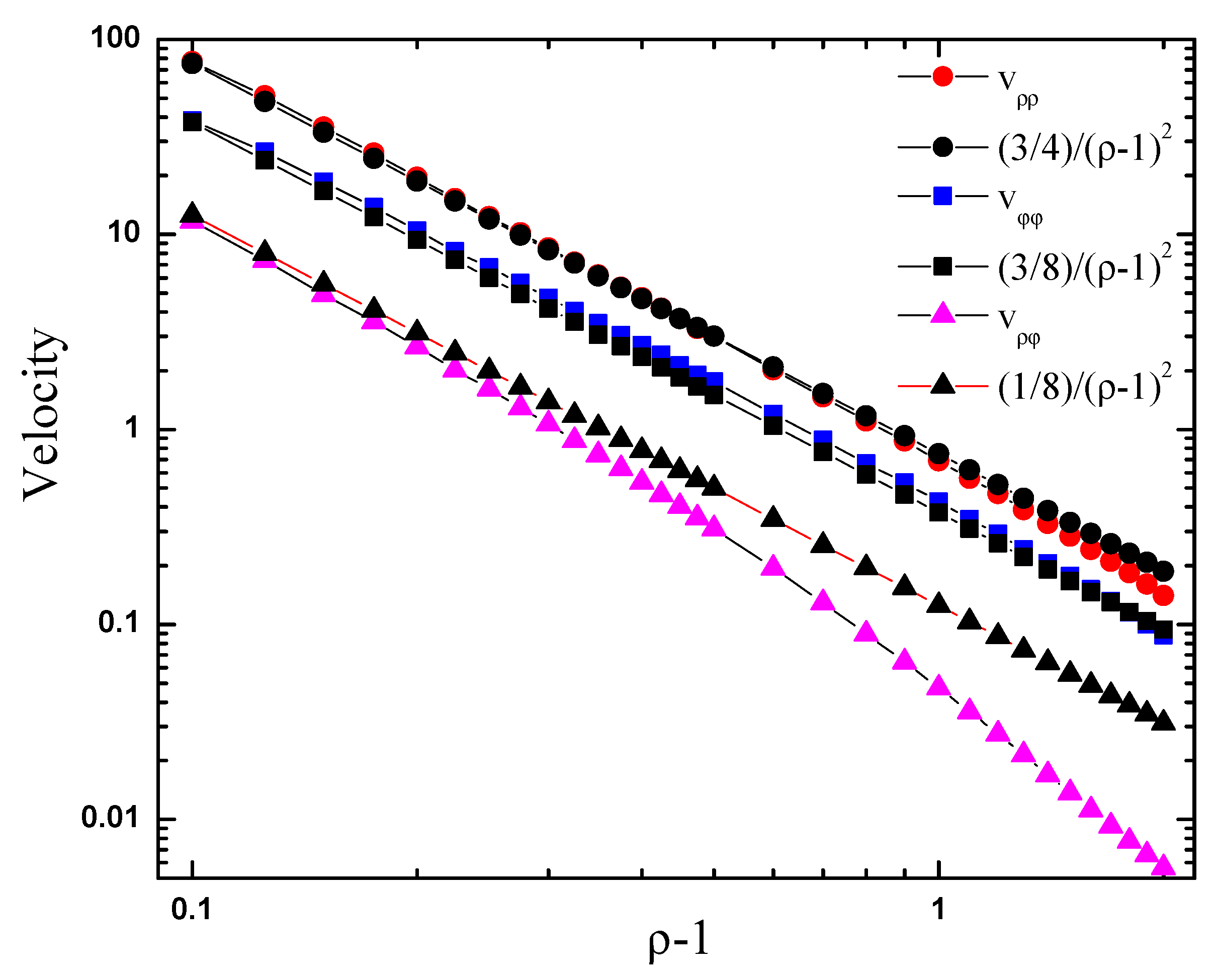
Appendix A. Dipole-Dipole Repulsion from a Cylinder

Appendix B. ICEO Interaction with a Cylinder
References
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. AC Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles; Research Studies Press Ltd.: Baldock, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Beech, J.P.; Jönsson, P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Tipping the balance of deterministic lateral displacement devices using dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2698–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, V.; Garcia-Sanchez, P.; Honrado, C.; Ramos, A.; Morgan, H. AC electrokinetic biased deterministic lateral displacement for tunable particle separation. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, B.D.; Beech, J.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Charge-Based Separation of Micro-and Nanoparticles. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, V.; Garcia-Sanchez, P.; Ramos, A.; Morgan, H. Combining DC and AC electric fields with deterministic lateral displacement for micro-and nano-particle separation. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 054110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frechette, J.; Drazer, G. Directional locking and deterministic separation in periodic arrays. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 627, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Ven, T.G.; Warszynski, P.; Wu, X.; Dabros, T. Colloidal particle scattering: A new method to measure surface forces. Langmuir 1994, 10, 3046–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Van de Ven, T. Characterization of hairy latex particles with colloidal particle scattering. Langmuir 1996, 12, 3859–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, M.; Murray, B.S.; Dickinson, E. Simulation of colloidal particle scattering: Sensitivity to attractive forces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 225, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H.; Simmons, B.A.; Cummings, E.B.; Fintschenko, Y. Insulator-based dielectrophoresis for the selective concentration and separation of live bacteria in water. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H.; Ozuna-Chacón, S.; Rito-Palomares, M. Protein manipulation with insulator-based dielectrophoresis and direct current electric fields. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1206, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H. On the recent developments of insulator-based dielectrophoresis: A review. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesch, G.R.; Du, F.; Schwientek, U.; Gehrmeyer, C.; Maurer, A.; Thöming, J.; Baune, M. Recovery of submicron particles using high-throughput dielectrophoretically switchable filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.; Malangré, D.; Du, F.; Baune, M.; Thöming, J.; Pesch, G.R. High-throughput dielectrophoretic filtration of sub-micron and micro particles in macroscopic porous materials. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 3903–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beech, J.P.; Keim, K.; Ho, B.D.; Guiducci, C.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Active posts in deterministic lateral displacement devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Mateo, R.; Calero, V.; Morgan, H.; García-Sánchez, P.; Ramos, A. Wall Repulsion of Charged Colloidal Particles during Electrophoresis in Microfluidic Channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 074501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.A.; Hoffman, B.; Saintillan, D.; Shaqfeh, E.S.; Santiago, J.G. Hydrodynamic interactions in metal rodlike-particle suspensions due to induced charge electroosmosis. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 011402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmeier, F.; Altaner, B.; List, J.; Gerland, U.; Simmel, F.C. Emergence of Colloidal Patterns in ac Electric Fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 058002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, E.B.; Singh, A.K. Dielectrophoresis in microchips containing arrays of insulating posts: Theoretical and experimental results. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4724–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.B. Electromechanics of Particles; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- García-Sánchez, P.; Ren, Y.; Arcenegui, J.J.; Morgan, H.; Ramos, A. Alternating Current Electrokinetic Properties of Gold-Coated Microspheres. Langmuir 2012, 28, 13861–13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; García-Sánchez, P.; Morgan, H. AC electrokinetics of conducting microparticles: A review. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 24, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Squires, T.M. Induced-charge electrokinetic phenomena: Theory and microfluidic applications. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 066101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamayunov, N.I.; Murtsovkin, V.A.; Dukhin, A.S. Pair interaction of particles in electric field. 1. Features of hydrodynamic interaction of polarized particles. Colloid J. USSR (Engl. Transl.) 1986, 48, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Oren, S.; Frankel, I. Induced-charge electrophoresis of ideally polarizable particle pairs. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2020, 5, 094201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saintillan, D. Nonlinear interactions in electrophoresis of ideally polarizable particles. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 067104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saintillan, D.; Darvel, E.; Shaqfeh, E. Hydrodynamic interactions in the induced-charge electrophoresis of colloidal rod dispersionss. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 563, 223–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, P.; Arcenegui, J.J.; Morgan, H.; Ramos, A. Self-assembly of metal nanowires induced by alternating current electric fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 023110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariv, E. Boundary-induced electrophoresis of uncharged conducting particles: Remote wall approximations. Proc. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 465, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, J.R.; Leighton, D.T., Jr. Measurement of the drift of a droplet due to the presence of a plane. Phys. Fluids Fluid Dyn. 1991, 3, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, J. A note on the image system for a stokeslet in a no-slip boundary. In Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1971; Volume 70, pp. 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Shilov, V.; Simonova, T. Polarization of electric double-layer of disperse particles and dipolophoresis in a steady (DC) field. Colloid J. USSR 1981, 43, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Miloh, T. A unified theory of dipolophoresis for nanoparticles. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 107105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloh, T. Dipolophoresis of nanoparticles. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 063303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Mena, J.E.; García-Sánchez, P.; Ramos, A. Dipolophoresis and Travelling-Wave Dipolophoresis of Metal Microparticles. Micromachines 2020, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.R.; Cox, E.C.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 2004, 304, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Wunsch, B.H.; Hu, H.; Smith, J.T.; Austin, R.H.; Stolovitzky, G. Broken flow symmetry explains the dynamics of small particles in deterministic lateral displacement arrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5034–E5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyklema, J. Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science; Academic Press Limited: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Calero, V.; Fernández-Mateo, R.; Morgan, H.; García-Sánchez, P.; Ramos, A. Stationary Electro-osmotic Flow Driven by ac Fields around Insulators. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 15, 014047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, V.; Garcia-Sanchez, P.; Ramos, A.; Morgan, H. Electrokinetic biased Deterministic Lateral Displacement: Scaling Analysis and Simulations. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1623, 461151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Mena, J.E.; García-Sánchez, P.; Ramos, A. Scattering of Metal Colloids by a Circular Post under Electric Fields. Micromachines 2023, 14, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010023
Flores-Mena JE, García-Sánchez P, Ramos A. Scattering of Metal Colloids by a Circular Post under Electric Fields. Micromachines. 2023; 14(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Mena, José Eladio, Pablo García-Sánchez, and Antonio Ramos. 2023. "Scattering of Metal Colloids by a Circular Post under Electric Fields" Micromachines 14, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010023
APA StyleFlores-Mena, J. E., García-Sánchez, P., & Ramos, A. (2023). Scattering of Metal Colloids by a Circular Post under Electric Fields. Micromachines, 14(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010023





