Novel Second-Order Fully Differential All-Pass Filter Using CNTFETs
Abstract
1. Introduction
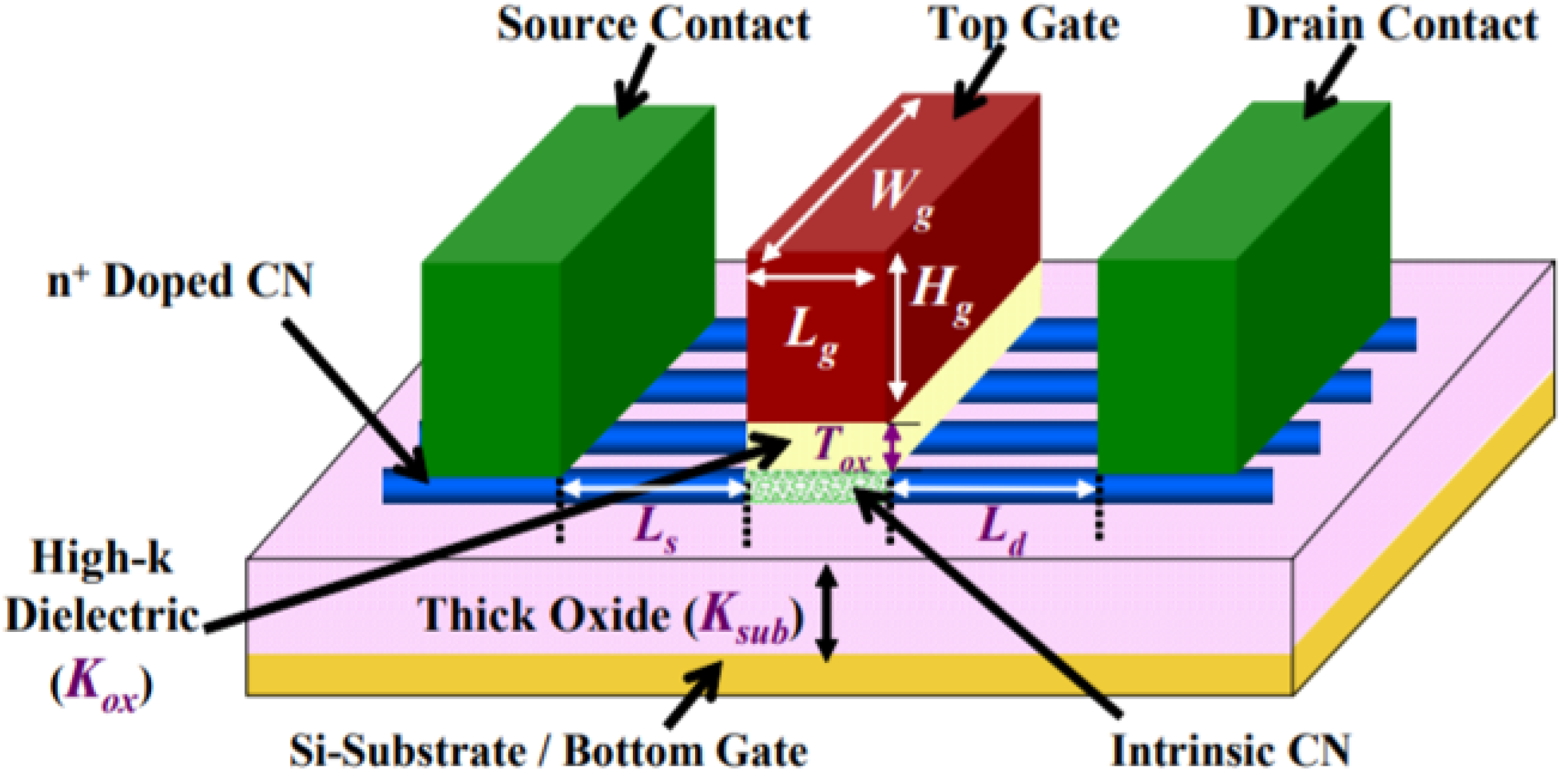
2. Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors
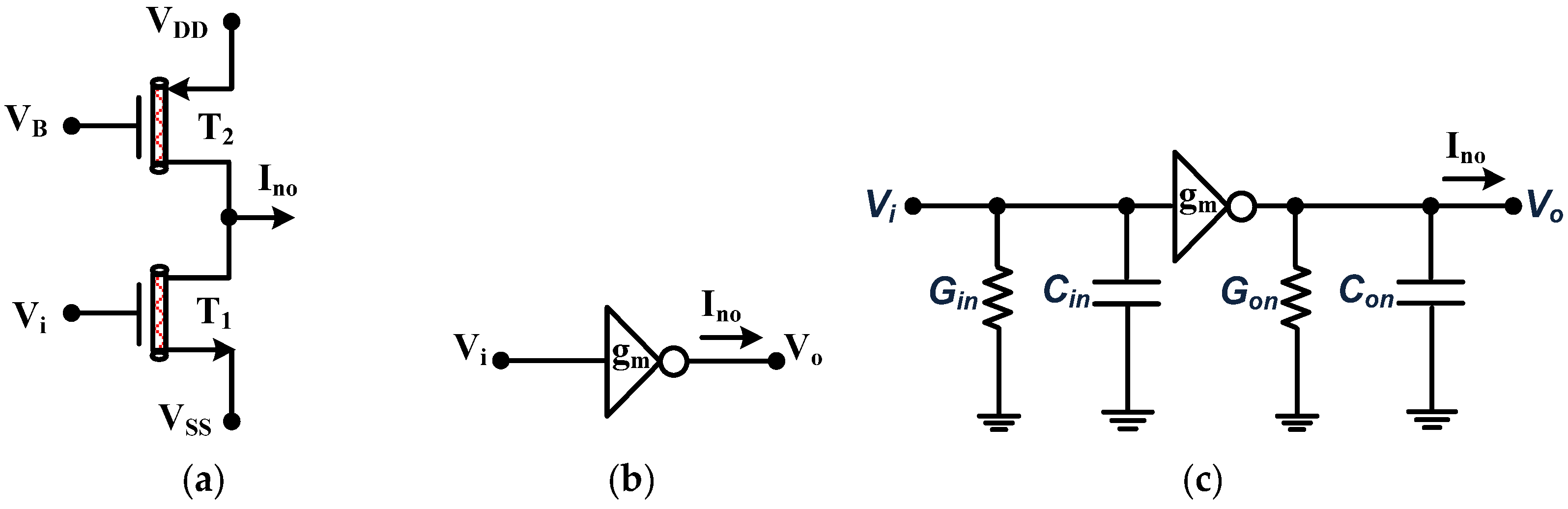
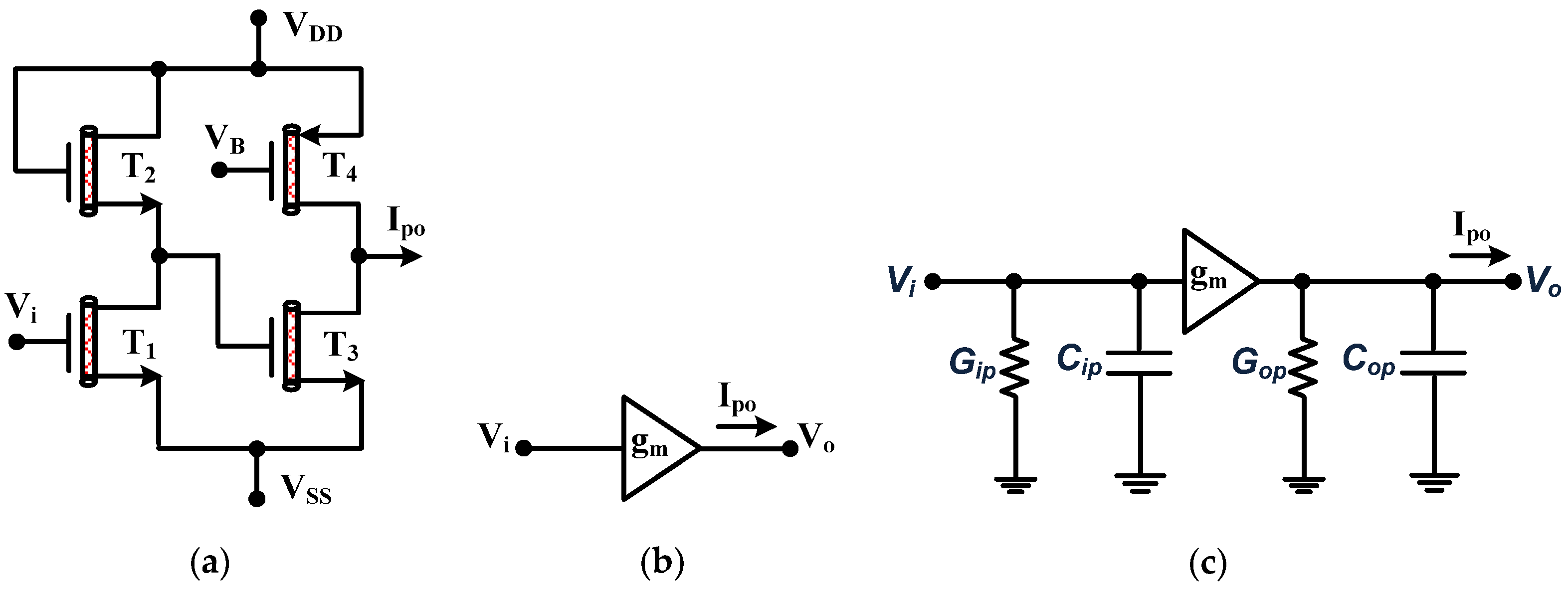
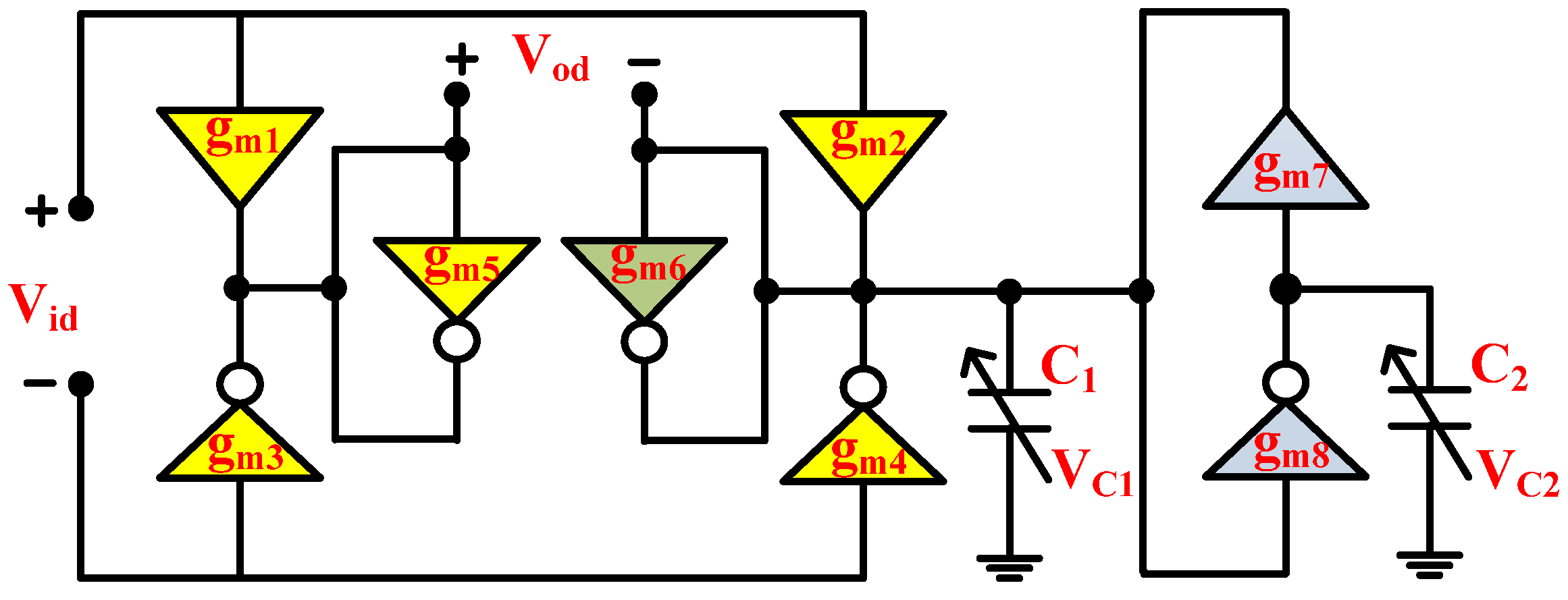
3. The Proposed Circuit
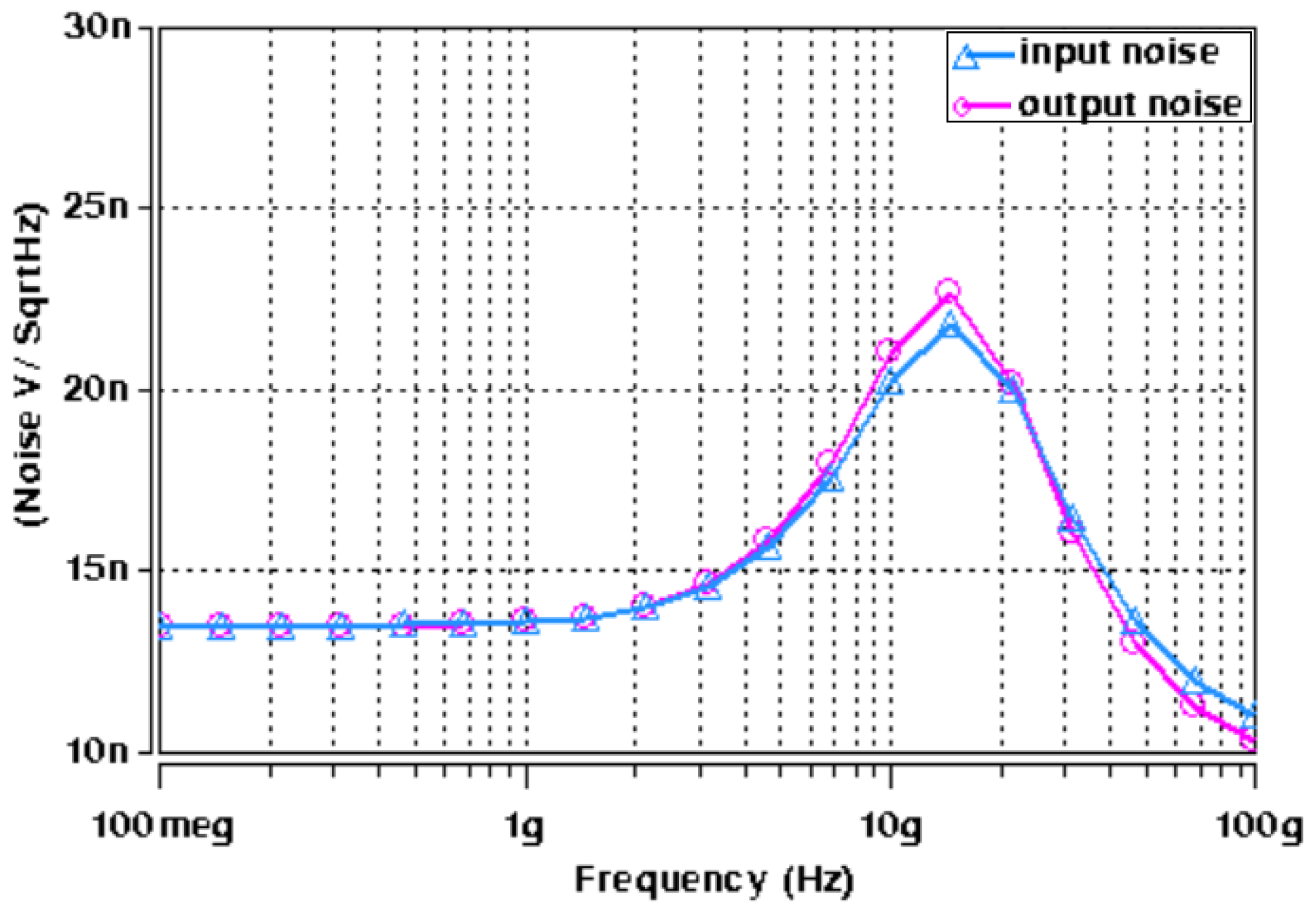
4. Proposed Filter Non-Ideal Analysis
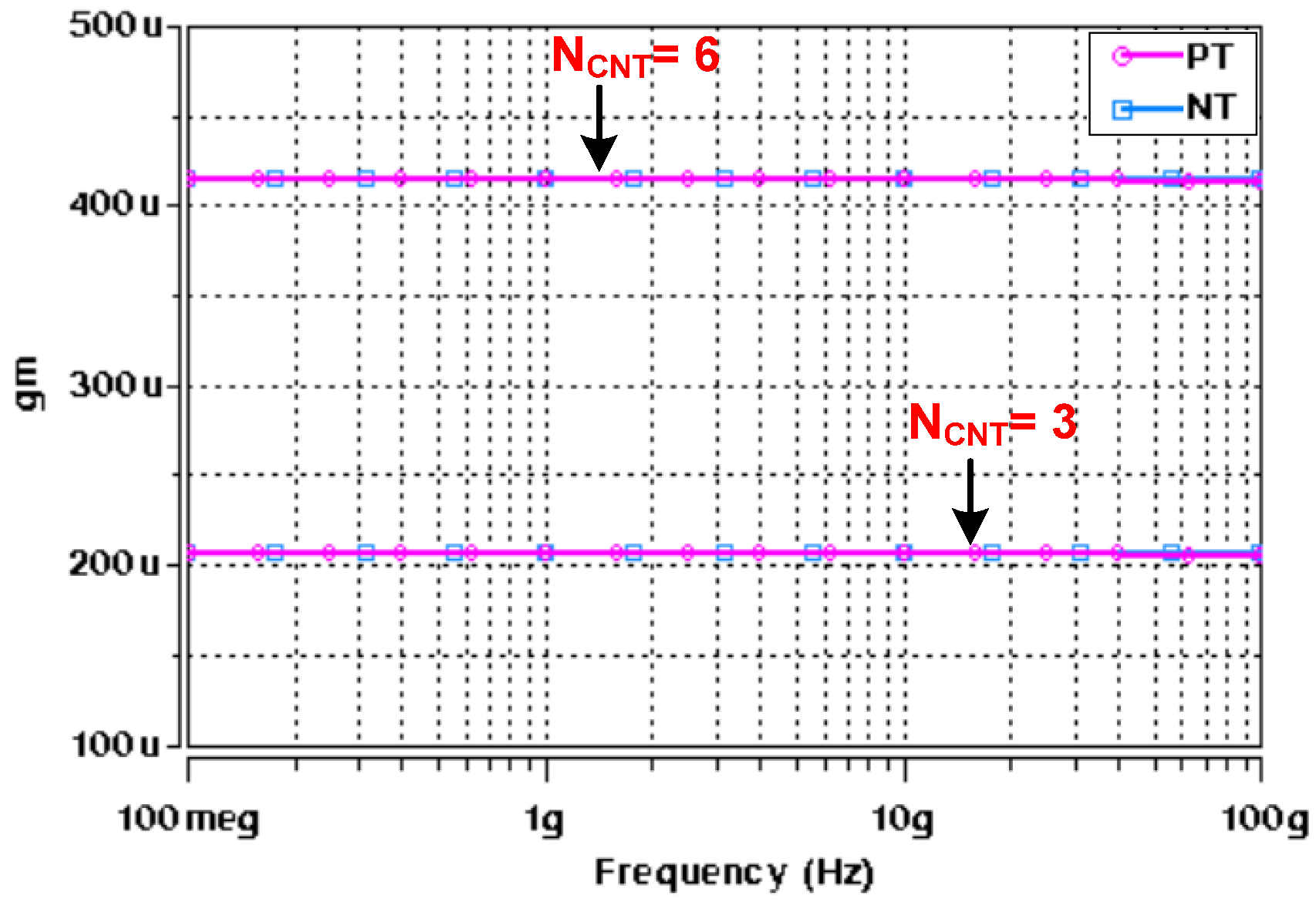
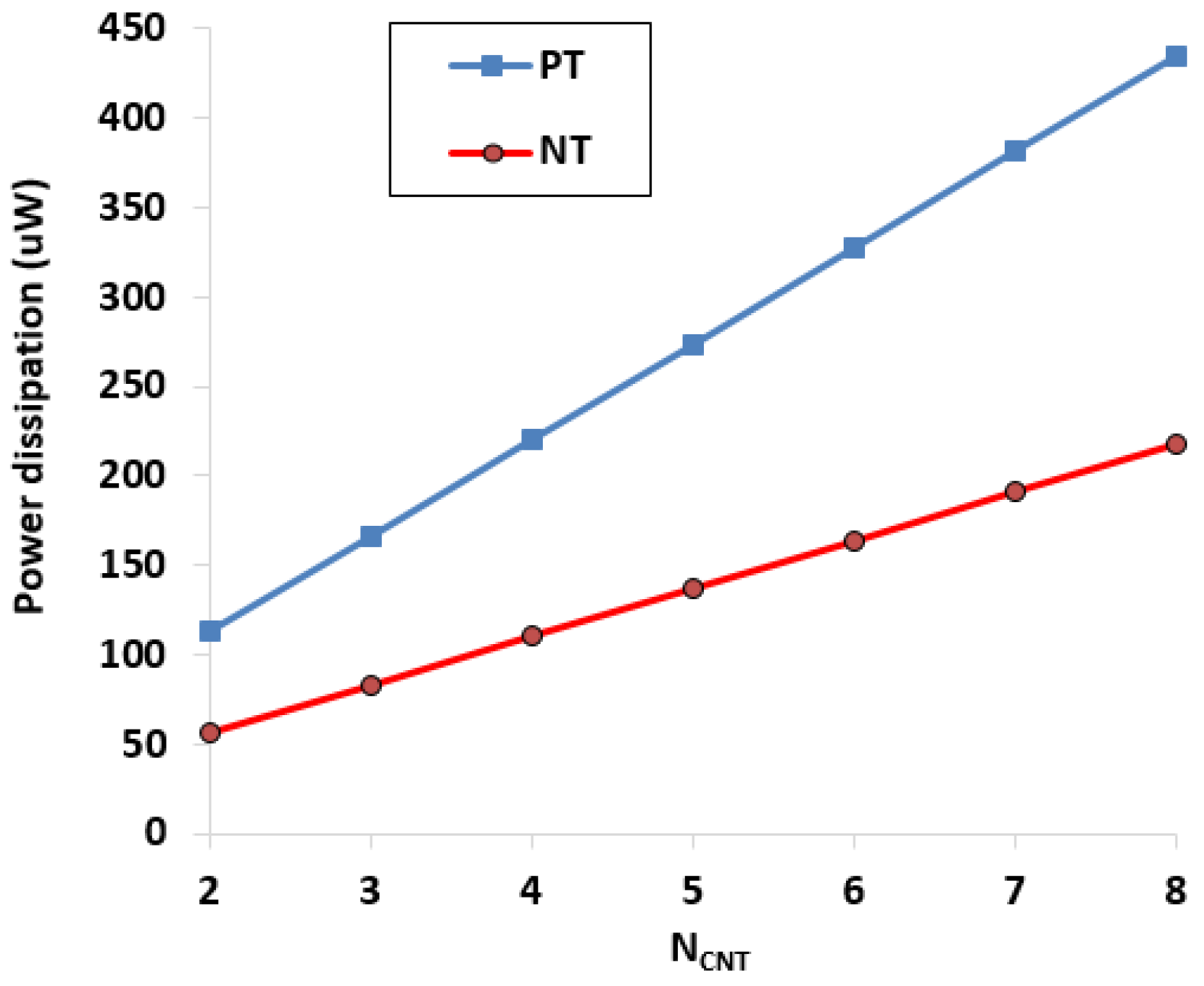
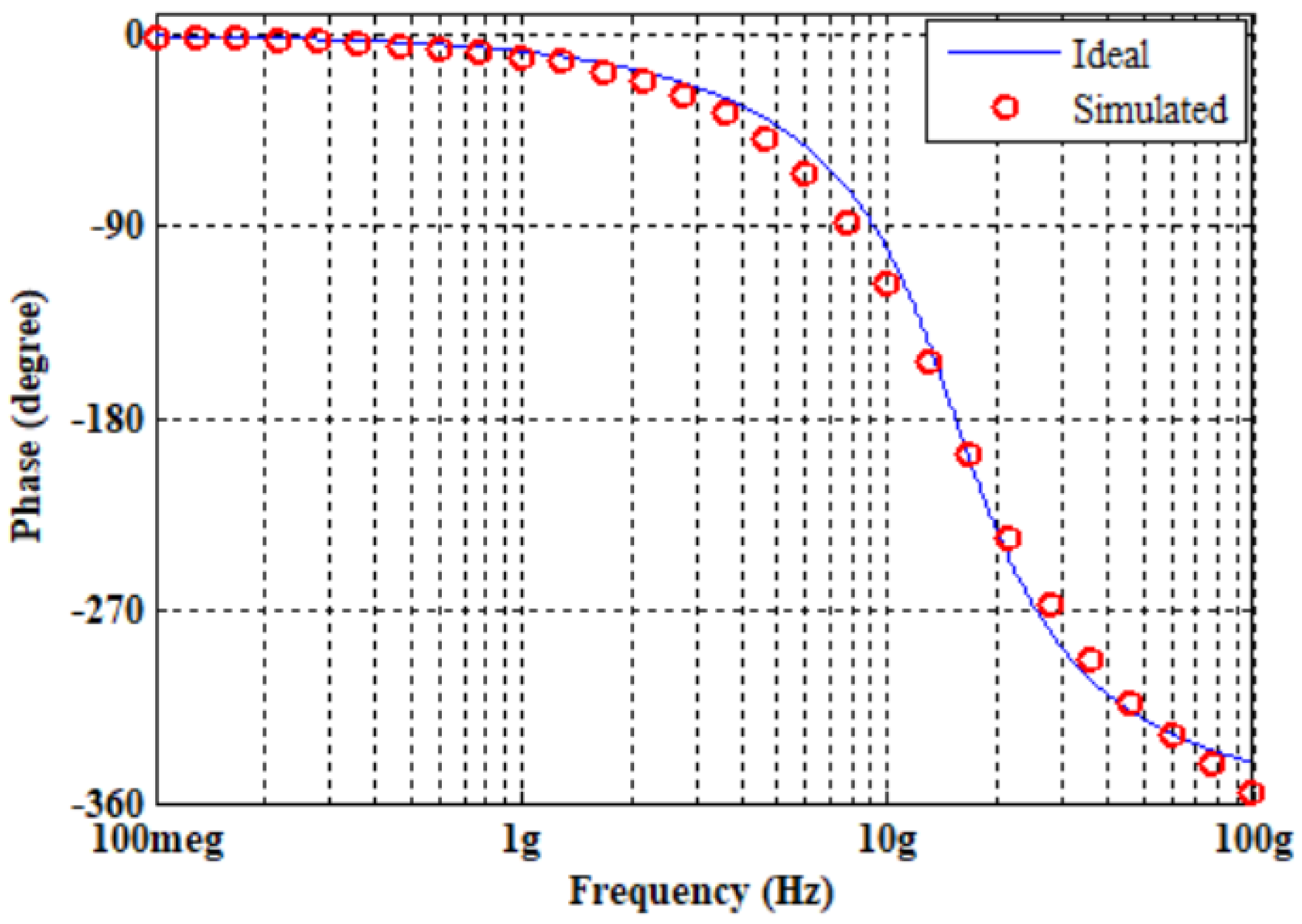
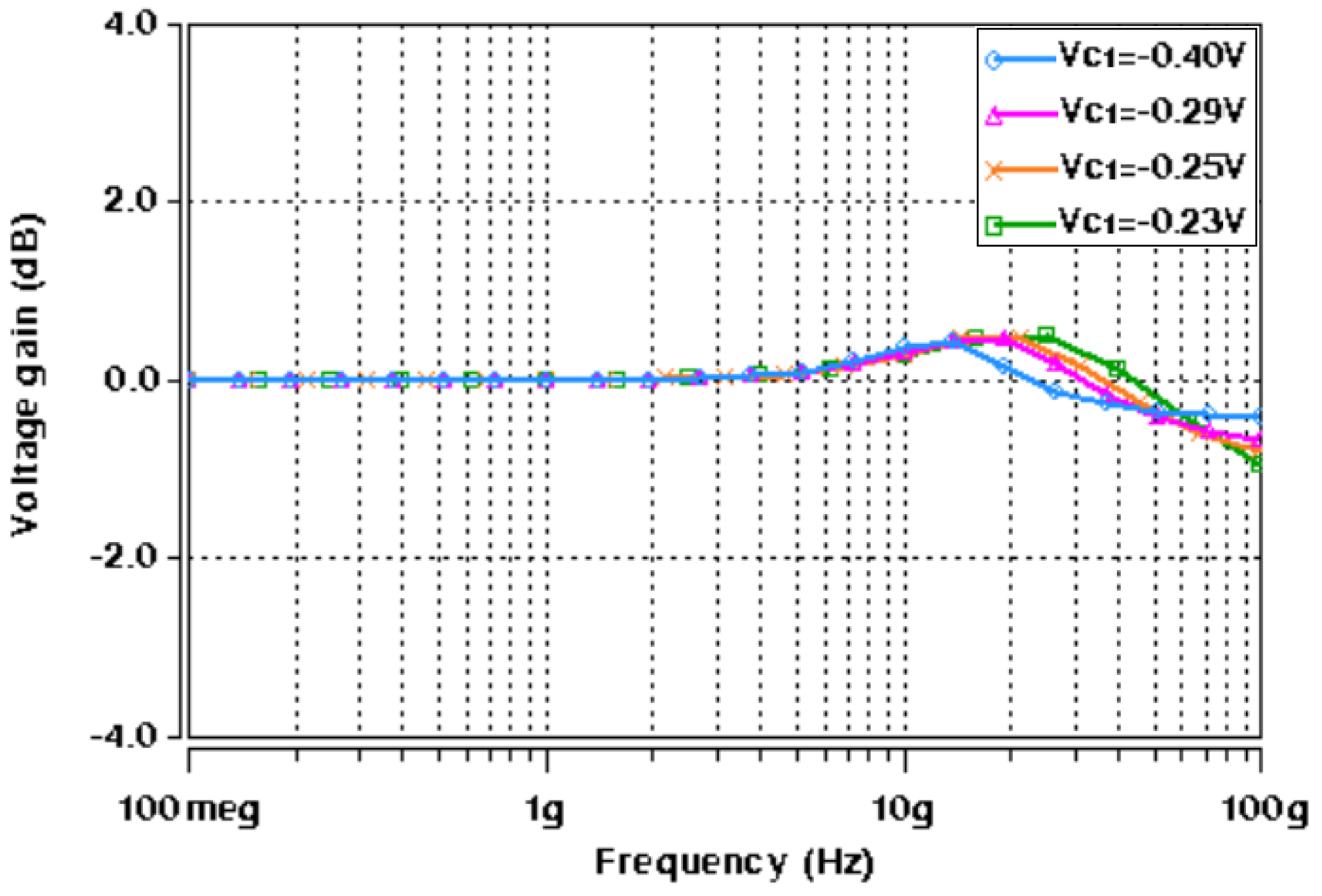
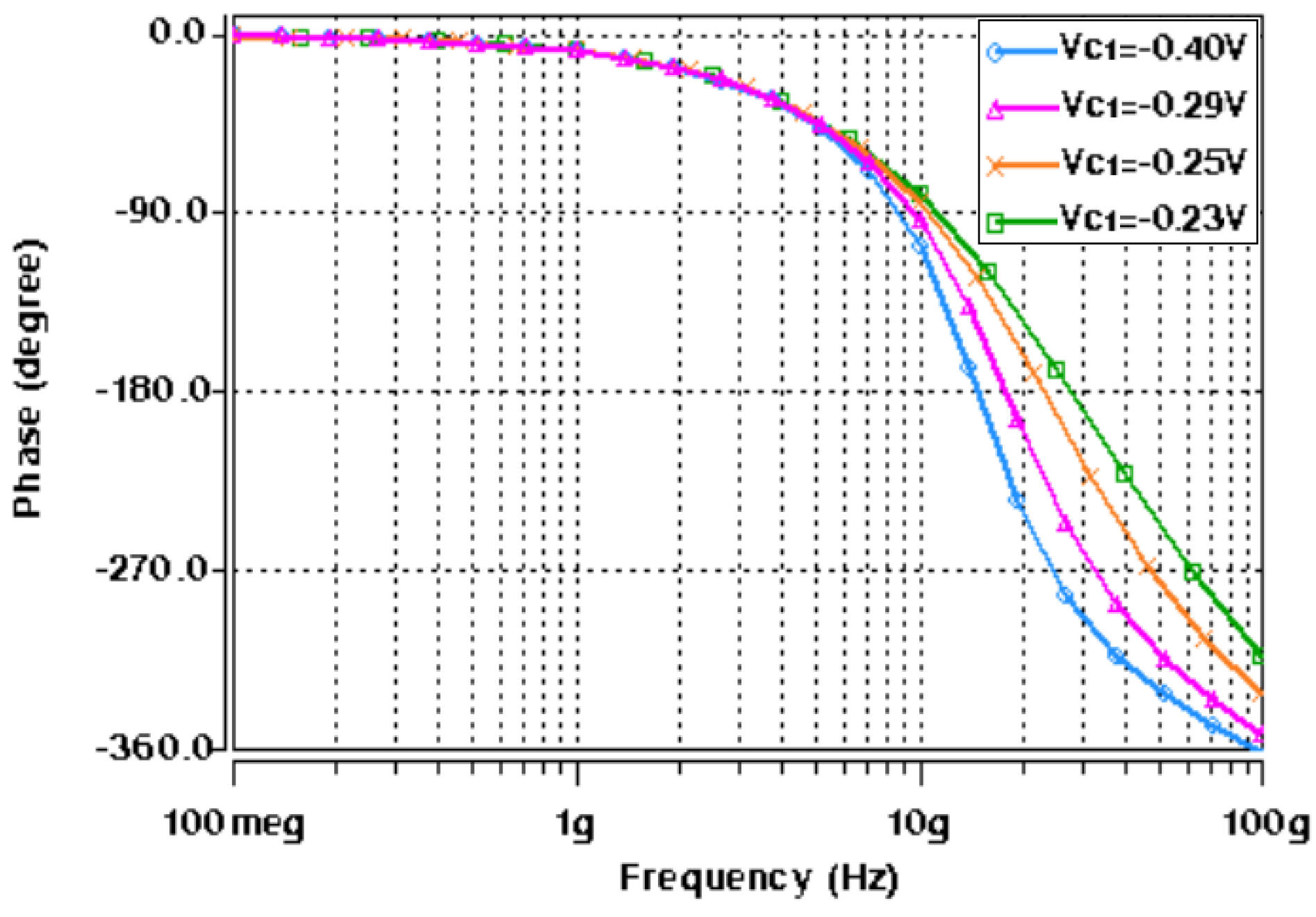
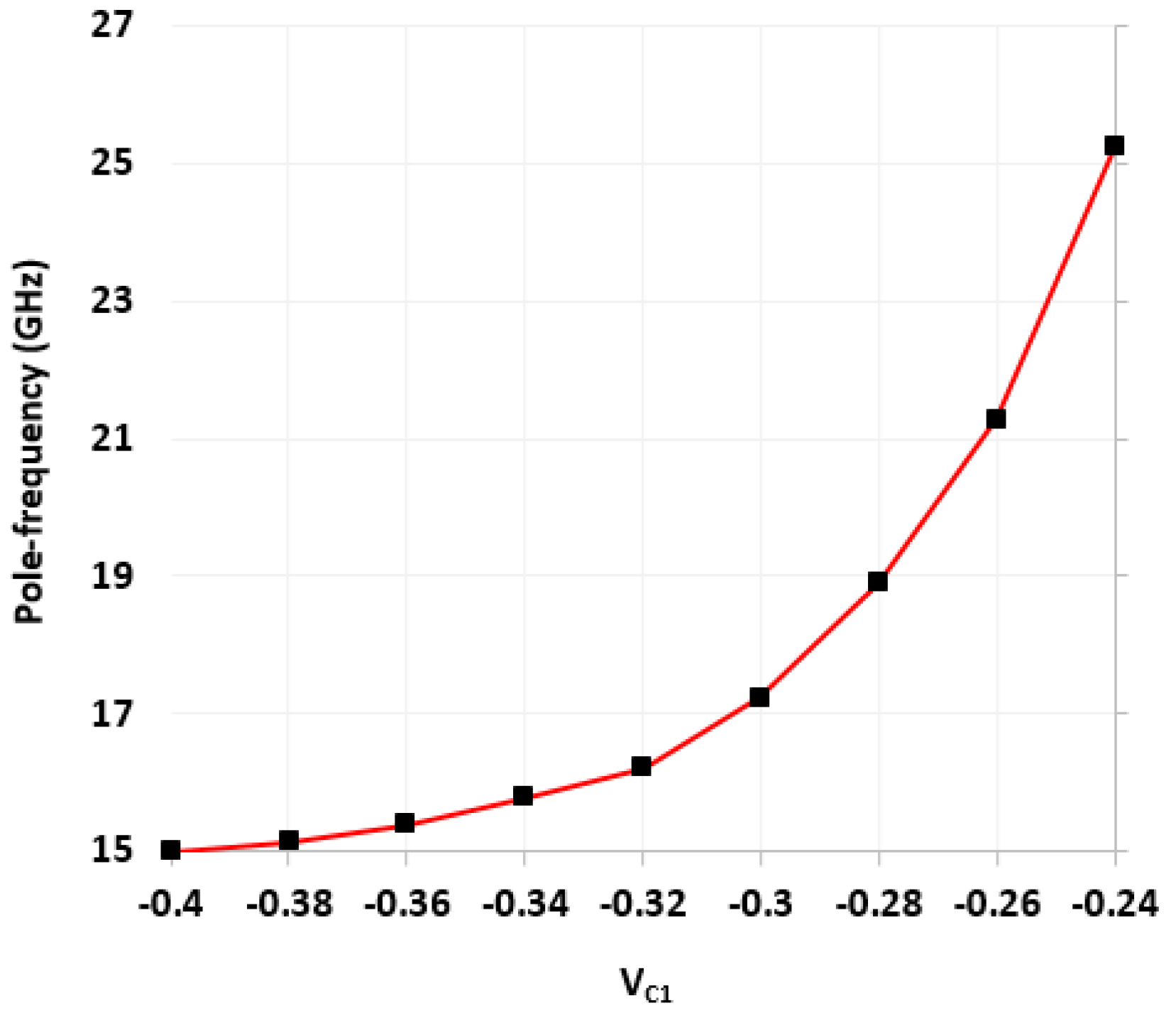
5. Design and Verifications
6. Comparison of the Proposed Filters with Other FDSOAPFs
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jerabek, J.; Sotner, R.; Koton, J.; Herencsar, N.; Vrba, K. Pseudo-differential electronically controllable second-order band-pass filter using modified current differencing/summing units. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Barcelona, Spain, 5–7 July 2017; pp. 320–324. [Google Scholar]
- Minaei, S.; Göknar, C.; Cicekoglu, O. A new differential configuration suitable for realization of high CMRR, all-pass/notch filters. Electr. Eng. 2006, 88, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mahmoud, S.A. New Fully-Differential CMOS Second-Generation Current Conveyer. ETRI J. 2006, 28, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerabek, J.; Dvorak, J.; Sotner, R.; Herencsar, N.; Koton, J. Experimental Verification of Pseudo-Differential Electronically Controllable Multifunction Filter Using Modified Current Differencing/Summing Units. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2019, 28, 1950098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koton, J.; Herencsar, N.; Sladok, O.; Horng, J.W. Pseudo-differential second-order band-reject filter using current conveyors. AEU–Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2016, 70, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaikla, W.; Khateb, F.; Kumngern, M.; Kulej, T.; Ranjan, R.K.; Suwanjan, P. 0.5 V fully differential universal filter based on multiple input OTAs. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 187832–187839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khateb, F.; Kumngern, M.; Kulej, T.; Psychalinos, C. 0.5 v universal filter based on multiple-input FDDAs. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 5896–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Vázquez-Leal, H.; Huerta-Chua, J.; Diaz-Sanchez, A. Fully Differential Miller Op-Amp with Enhanced Large-and Small-Signal Figures of Merit. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2022, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Elkamchouchi, D.H.; Urooj, S. Fully Differential Current-Mode Configuration for the Realization of First-Order Filters with Ease of Cascadability. Electronics 2022, 11, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, P.; Maheshwari, S.; Siddiqi, M.A. Digitally controlled fully differential voltage-and transadmittance-mode biquadratic filter. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2013, 7, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonk, A.; Afzal, N. Second generation fully differential current conveyor based analog circuits. J. Semicond. 2019, 40, 042401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.; A’ain, A.; Khan, I.; Husin, N. Design of voltage mode electronically tunable first order all pass filter in ±0.7 V 16 nm CNFET technology. Electronics 2019, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, P.; Ansari, M.S. Fully-differential first-order all-pass filters using CMOS DV-DXCCII. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia, Signal Processing and Communication Technologies (IMPACT), Aligarh, India, 24–26 November 2017; pp. 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Sotner, R.; Herencsar, N.; Jerabek, J.; Kartci, A.; Koton, J.; Dostal, T. Pseudo-differential filter design using novel adjustable floating inductance simulator with electronically controllable current conveyors. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2017, 23, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, J.W.; Wu, C.M.; Herencsar, N. Fully differential first-order all pass filters using a DDCC. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2014, 21, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Herencsar, N.; Sotner, R.; Kartci, A.; Vrba, K. A novel pseudo-differential integer/fractional-order voltage-mode all-pass filter. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Florence, Italy, 27–30 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, L.; Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Lopez-Martin, A.J.; Carvajal, R.G. Low-voltage first-order fully differential CMOS all-pass filter with programmable pole-zero. Electron. Lett. 2009, 45, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.A.; Masud, M.I.; Moiz, S.A. Reconfigurable fully differential first order all pass filter using digitally controlled CMOS DVCC. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 8th GCC Conference & Exhibition, Muscat, Oman, 1–4 February 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Masud, M.I.; A’ain, A.K.B.; Khan, I.A. Reconfigurable CNTFET based fully differential first order multifunctional filter. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Multimedia, Signal Processing and Communication Technologies (IMPACT), Aligarh, India, 24–26 November 2017; pp. 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Masud, M.; Khan, I.A. CNTFET Based Fully Differential First Order All Pass Filter. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 44, 2425–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herencsar, N.; Jerabek, J.; Koton, J.; Vrba, K.; Minaei, S.; Göknar, İ.C. Pole frequency and pass-band gain tunable novel fully-differential current-mode all-pass filter. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Lisbon, Portugal, 24–27 May 2017; pp. 2668–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, M.S.; Soni, G.S. Digitally-programmable fully-differential current-mode first-order LP, HP and AP filter sections. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Signal Propagation and Computer Technology (ICSPCT 2014), Ajmer, India, 12–13 July 2014; pp. 524–528. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Minaei, S.; Kuntman, H. DVCC based differential-mode all-pass and notch filters with high CMRR. Int. J. Electron. 2006, 93, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koton, J.; Herencsar, N.; Horng, J.W. Differential second-order voltage-mode all-pass filter using current conveyors. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2016, 22, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Masud, M.I.; A’ain, A.K.; Khan, I.A.; Shaikh-Husin, N. A CNTFET-C first order all pass filter. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2019, 100, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogad, S.; Alkhammash, H.I.; Afzal, N.; Loan, S.A. CNTFET-based active grounded inductor using positive and negative current conveyors and applications. Int. J. Numer. Model. Electron. Netw. Devices Fields 2021, 34, e2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogad, S.; Loan, S.A.; Afzal, N.; Alharbi, A.G. CNTFET based class AB current conveyor II: Design, analysis and waveform generator applications. Int. J. Numer. Model. Electron. Netw. Devices Fields 2021, 34, e2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.I.; A’ain, A.K.B.; Khan, I.A.; Shaikh-Husin, N. CNTFET based Voltage Mode MISO Active only Biquadratic Filter for Multi-GHz Frequency Applications. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 40, 4721–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, S.M.; Dousti, M.; Dolatshahi, M. A CNTFET universal mixed-mode biquad active filter in subthreshold region. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2018, 28, e21574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.I.; A’ain, A.K.B.; Khan, I.A. CNFET based reconfigurable first order filter. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE-GCC Conference and Exhibition (GCCCE), Manama, Bahrain, 8–11 May 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Che, Y.; Chen, H.; Gui, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, C. Review of carbon nanotube nanoelectronics and macroelectronics. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2014, 29, 073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydin, A.; Tay, F.; Fan, J.; Manjappa, M.; Gao, W.; Kono, J. Carbon Nanotube Devices for Quantum Technology. Materials 2022, 15, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, J.; Metternich, J.T.; Herbertz, S.; Kruss, S. Biosensing with fluorescent carbon nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoukat, R.; Khan, M.I. Carbon nanotubes: A review on properties, synthesis methods and applications in micro and nanotechnology. Microsyst. Technol. 2021, 27, 4183–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Gupta, S.M.; Sharma, S.K. Carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, properties and engineering applications. Carbon Lett. 2019, 29, 419–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.I.; Shaikh-Husin, N.; Khan, I.A.; A’Ain, A.K.B. CNTFET Based Grounded Active Inductor for Broadband Applications. Comput. Mater. Cintunua 2022, 73, 2135–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.; Kim, Y.B.; Lombardi, F.; Choi, M. Performance evaluation of CNFET-based logic gates. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Singapore, 5–7 May 2009; pp. 909–912. [Google Scholar]
- Almudever, C.G.; Rubio, A. Variability and reliability analysis of CNFET technology: Impact of manufacturing imperfections. Microelectron. Reliab. 2015, 55, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, I.; Liu, J.; Gaffiot, F.; Prégaldiny, F.; Lallement, C.; Maneux, C.; Leveugle, R. CNTFET modeling and reconfigurable logic-circuit design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2007, 54, 2365–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, M.; Loan, S.A.; Alamoud, A.R.; Abbassi, S.A. Design, simulation and comparative analysis of CNT based cascode operational transconductance amplifiers. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 395201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamatov, I.; Ozcelep, Y.; Kacar, F. CNTFET based voltage differencing current conveyor low power and universal filter. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2021, 110, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatov, I.; Ozcelep, Y.; Kacar, F. Voltage differencing buffered amplifier based low power, high frequency and universal filters using 32 nm CNTFET technology. Microelectron. J. 2021, 107, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wong, H.-S.P. A compact SPICE model for carbon-nanotube field-effect transistors including non idealities and its application—Part I: Model of the intrinsic channel region. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2007, 54, 3186–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wong, H.-S.P. A compact SPICE model for carbon-nanotube field-effect transistors including non idealities and its application—Part II: Full device model and circuit performance benchmarking. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2007, 54, 3195–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Naushad, A. Design of CNTFET-based CCII using gm/ID technique for low-voltage and low-power applications. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2020, 29, 2050143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, S.M.; Dousti, M.; Dolatshahi, M. Inverter-based, low-power and low-voltage, new mixed-mode Gm-C filter in subthreshold CNTFET technology. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2018, 12, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatov, I.; Ozcelep, Y.; Kacar, F. VDTA based Schmitt trigger using 32 nm CNTFET technology. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2022, 112, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
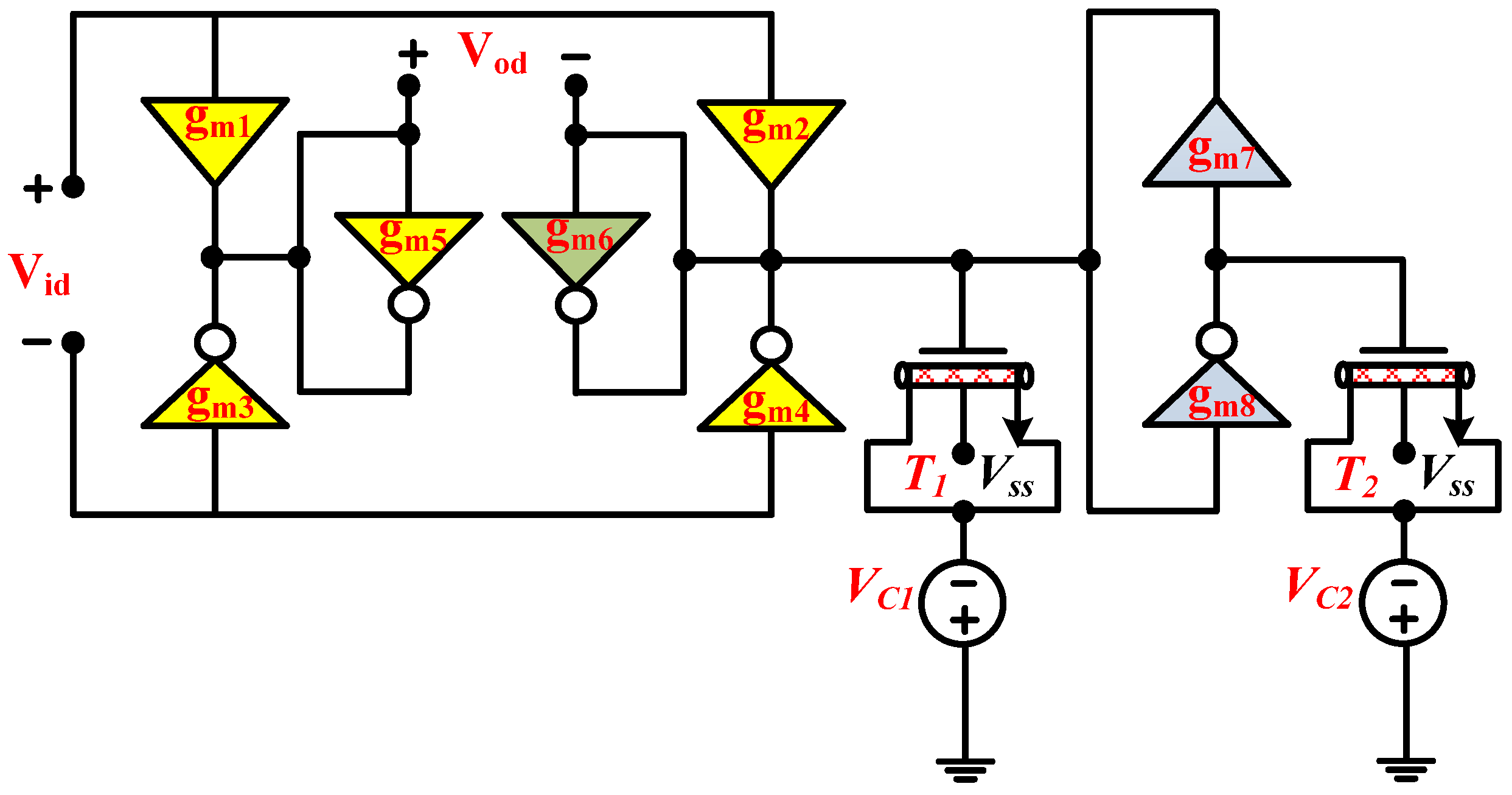




| CNTFET-Parameters | Parameter Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| V | Power supply | ±0.7 V |
| Lg | Channel length | 16 nm |
| Lceff | Mean free path | 200 nm |
| Kox | Dielectric constant | 25 |
| Ls/Ld | Source/drain side length of doped CNT | 16 nm |
| Tox | Oxide thickness | 3 nm |
| Ksub | Bottom gate dielectric constant | SiO2 (4) |
| SCNT | Inter-CNT Pitch | 10 nm |
| DCNT | CNT-Diameter | 1.5 nm |
| NCNT | Total CNTs utilized per CNTFET | - |
| Transconductance | NCNTs | |
|---|---|---|
| gm1 | 414.1 | 6 |
| gm2 | 414.1 | 6 |
| gm3 | 414.1 | 6 |
| gm4 | 414.1 | 6 |
| gm5 | 414.1 | 6 |
| gm6 | 207.1 | 3 |
| gm7 | 136.6 | 2 |
| gm8 | 136.6 | 2 |
| Reference | [2] | [23] | [24] | This Work Figure 4 | This Work Figure 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | CMOS | CMOS | CMOS | CNTFET | CNTFET |
| node | 0.35 μm | 0.5 μm | 0.35 μm | 16 nm | 16 nm |
| Voltage (V) | 2.5 V | 2.5 | 1.65 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| ABB utilized | CCII- | DVCC | (DDCC & CCII) | (PT & NT) | (PT & NT) |
| No. of R/C | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/2 | 0/2 | 0/0 |
| Tunability | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Pole frequency (Hz) | 195 K | 3.18 M | 100 K | 15.0 G | 15.0 G to 27.5 G |
| Power (mW) | - | - | - | 1.40 | 1.59 |
| (Grounded passive components) | No | No | Yes | Yes | ~ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masud, M.I.; Khan, I.A.; Moiz, S.A.; Younis, W.A. Novel Second-Order Fully Differential All-Pass Filter Using CNTFETs. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14101873
Masud MI, Khan IA, Moiz SA, Younis WA. Novel Second-Order Fully Differential All-Pass Filter Using CNTFETs. Micromachines. 2023; 14(10):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14101873
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasud, Muhammad I., Iqbal A. Khan, Syed Abdul Moiz, and Waheed A. Younis. 2023. "Novel Second-Order Fully Differential All-Pass Filter Using CNTFETs" Micromachines 14, no. 10: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14101873
APA StyleMasud, M. I., Khan, I. A., Moiz, S. A., & Younis, W. A. (2023). Novel Second-Order Fully Differential All-Pass Filter Using CNTFETs. Micromachines, 14(10), 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14101873







