Effects of Ambient Temperature on Nanosecond Laser Micro-Drilling of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Preparation of PDMS
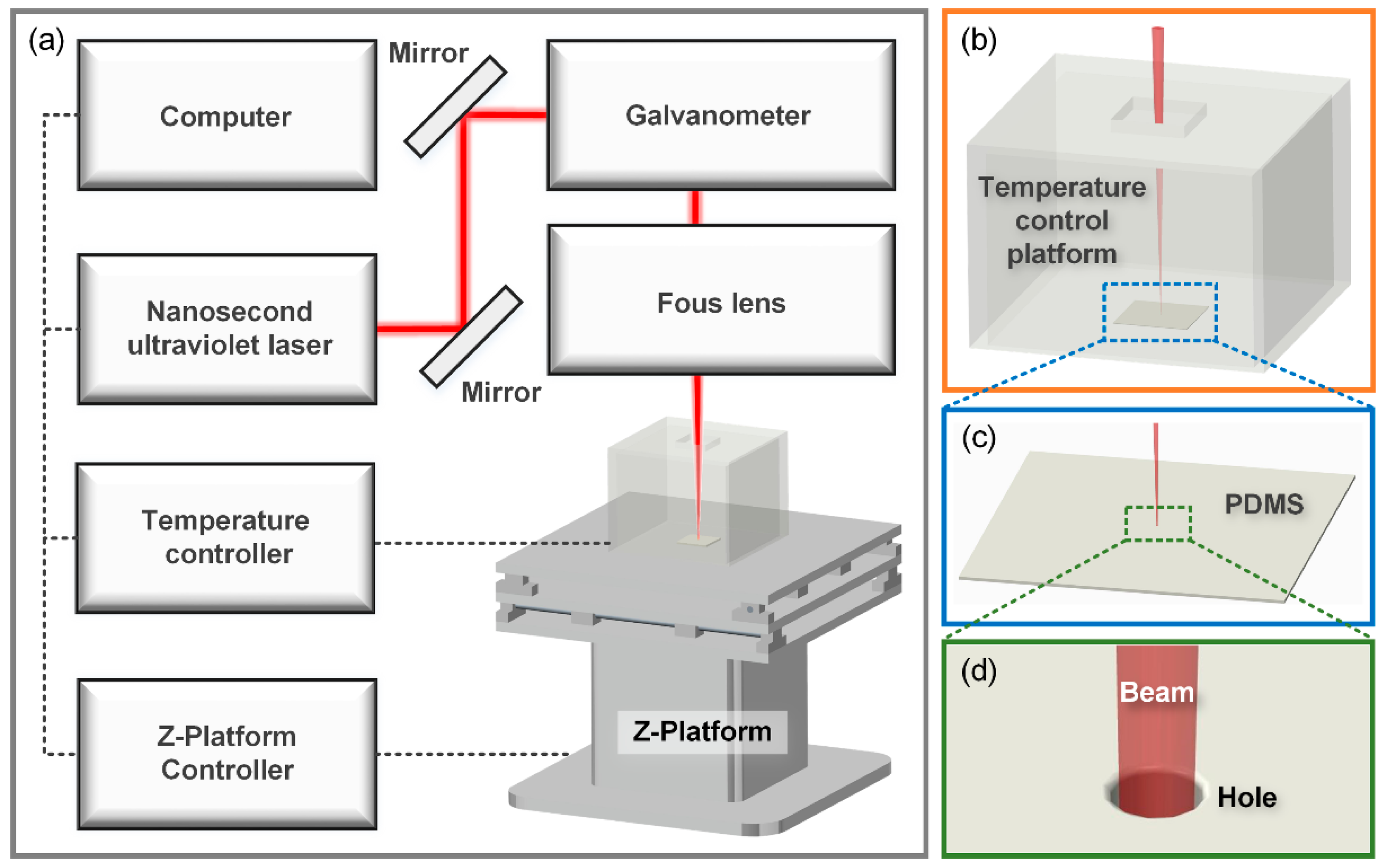
2.2. Laser Micro-Drilling System
2.3. Quality Evaluation Indexes of the Micro-Hole
2.4. Characterization
3. Thermo-Mechanical Modeling
- The laser energy distribution is assumed as a typical Gaussian distribution.
- When the temperature reaches the thermal decomposition temperature, the material is considered removed.
- Recoil pressure and the absorption of laser by the vapor and plasma are ignored.
- The solid-state phase transformation is ignored.
- The elastic model is used to calculate the thermal stress, ignoring the plastic effects.
3.1. Thermal Model
3.2. Thermal Stress Model
3.3. Computation Implementation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Temperature Distribution
4.2. The Effects of Ambient Temperature on Micro-Hole Geometry
4.3. The Effects of Ambient Temperature on HAZ
4.3.1. Composition and Diameter of HAZ
4.3.2. Evolution of Wrinkle Morphology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fürjes, P.; Holczer, E.G.; Tóth, E.; Iván, K.; Fekete, Z.; Bernier, D.; Dortu, F.; Giannone, D. PDMS microfluidics developed for polymer based photonic biosensors. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 21, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghir, R.; Arscott, S. Extended PDMS stiffness range for flexible systems. Sen. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 230, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, C.; Boretius, T.; Stieglitz, T. Polymers for neural implants. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Neyer, A.; Kuckuk, R.; Heise, H.M. Raman, mid-infrared, near-infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy of PDMS silicone rubber for characterization of polymer optical waveguide materials. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 976, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, A.K.; Guo, J.; Lee, E.-J.; Jeong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Leiknes, T. PDMS/PVDF hybrid electrospun membrane with superhydrophobic property and drop impact dynamics for dyeing wastewater treatment using membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Ge, M.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Deng, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, K.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Lai, Y. Robust fluorine-free superhydrophobic PDMS–ormosil@fabrics for highly effective self-cleaning and efficient oil–water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12179–12187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Lai, Y. Robust translucent superhydrophobic PDMS/PMMA film by facile one-step spray for self-cleaning and efficient emulsion separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.N.; Chen, Y.F.; Shu, Y.W.; Chen, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wu, H.K. Direct, one-step molding of 3D-printed structures for convenient fab-rication of truly 3D PDMS microfluidic chips. Microfluid Nanofluid 2015, 19, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Niu, Z.; Wang, H.; Leow, W.R.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wei, J.; Huo, F.; Chen, X. Microstructured Graphene Arrays for Highly Sensitive Flexible Tactile Sensors. Small 2014, 10, 3625–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, C. Combined pulse laser: Reliable tool for high-quality, high-efficiency material processing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 153, 108209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, C.; Dong, X.; Yin, K.; Zhang, F.; Xie, Z.; Chu, D.; Duan, J. Controllable superhydrophobic aluminum surfaces with tunable adhesion fabricated by femtosecond laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 102, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, N. Large-area cactus-like micro-/nanostructures with anti-reflection and su-perhydrophobicity fabricated by femtosecond laser and thermal treatment. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 33, 102292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.W.; Wang, C.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Lin, N.; Duan, J.A. Single-step femtosecond laser structuring of multifunctional colorful metal surface and its origin. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 34, 102386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Wen, L.; Men, D.; Hang, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, G.; Cai, W.; Lyu, X.; Li, Y. Bionic PDMS film with hybrid superhydrophilic/superhydrophobic arrays for water harvest. Surf. Innov. 2018, 6, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wu, S.-Z.; Chen, Q.-D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Jiao, J.; Piersol, J.A.; Wang, J.-N.; Sun, H.-B.; Jiang, L. Facile creation of hierarchical PDMS microstructures with extreme underwater superoleophobicity for anti-oil application in microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3873–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Shi, L.; Huang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Wu, D.; Chu, J. Microhole-Arrayed PDMS with Controllable Wettability Gradient by One-Step Femtosecond Laser Drilling for Ultrafast Underwater Bubble Unidirectional Self-Transport. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1900297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Huo, J.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X. Femtosecond laser induced underwater superaerophilic and su-peraerophobic PDMS sheets with through microholes for selective passage of air bubbles and further collection of underwater gas. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 3688–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Huo, J.; Hou, X. Remarkably simple achievement of superhydrophobicity, superhydrophilicity, underwater superoleophobicity, underwater superoleophilicity, underwater superaerophobicity, and underwater superaerophilicity on femtosecond laser ablated PDMS surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 25249–25257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Ruck, C.; Spychalski, G.; King, B.; Wu, B.; Zhao, Y. Writing Wrinkles on Poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) by Surface Oxidation with a CO2 Laser Engraver. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4295–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.-Q.; Xia, F.; Lv, R.-Q. Small in-fiber Fabry-Perot low-frequency acoustic pressure sensor with PDMS diaphragm embedded in hollow-core fiber. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 270, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Niu, L.; Gao, T.; Li, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, F.; et al. Biomimicking Topographic Elastomeric Petals (E-Petals) for Omnidi-rectional Stretchable and Printable Electronics. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1400021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Tang, X.; Gan, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Qin, Z.; Zhou, T.; Huang, J.; Xie, C.; et al. High-Adhesion Stretchable Electrode via Cross-Linking Intensified Electroless Deposition on a Biomimetic Elastomeric Micropore Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 20535–20544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankova, N.E.; Atanasov, P.A.; Nedyalkov, N.N.; Stoyanchov, T.R.; Kolev, K.N.; Valova, E.I.; Georgieva, J.S.; St A, A.; Amoruso, S.; Wang, X.; et al. fs- and ns-laser processing of poly-dimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer: Comparative study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 336, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criales, L.E.; Orozco, P.F.; Medrano, A.; Rodríguez, C.A.; Özel, T. Effect of Fluence and Pulse Overlapping on Fabrication of Micro-channels in PMMA/PDMS Via UV Laser Micromachining: Modeling and Experimentation. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankova, N.E.; Atanasov, P.A.; Nikov, R.G.; Nikov, R.G.; Nedyalkov, N.N.; Stoyanchov, T.R.; Fukata, N.; Kolev, K.N.; Valova, E.I.; Georgieva, J.S.; et al. Optical properties of polydime-thylsiloxane (PDMS) during nanosecond laser processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 374, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, P.; Stankova, N.; Nedyalkov, N.; Fukata, N.; Hirsch, D.; Rauschenbach, B.; Amoruso, S.; Wang, X.; Kolev, K.; Valova, E.; et al. Fs-laser processing of medical grade polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 374, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marla, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jabbari, M.; Sonne, M.R.; Spangenberg, J.; Hattel, J.H. Improvement in Surface Characterisitcs of Polymers for Subsequent Electroless Plating Using Liquid Assisted Laser Processing. Phys. Procedia 2016, 83, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Golnabi, H.; Bahar, M. Investigation of optimum condition in oxygen gas-assisted laser cutting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2009, 41, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi-Kumar, S.; Lies, B.; Zhang, X.; Lyu, H.; Qin, H. Laser ablation of polymers: A review. Polym. Int. 2019, 68, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenoweth, K.; Cheung, S.; van Duin, A.C.T.; Goddard, W.A.; Kober, E.M. Simulations on the Thermal Decomposition of a Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Polymer Using the ReaxFF Reactive Force Field. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7192–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilbas, B.S. Thermal Analysis of Laser Drilling Process; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.; Yang, S. Wrinkling instabilities in polymer films and their applications. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Srinivasan, K.; Subbarayan, G.; Siegmund, T. Buckling, Wrinkling and Debonding in Thin Film Systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Reliability Physics Symposium, Anaheim, CA, USA, 2–6 May 2010; IEEE: Anaheim, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 430–439. [Google Scholar]









| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Ambient temperature (°C) | −100, −125, −25, 25, 75, 125, 200 |
| Laser fluence (J/cm²) | 18.87 |
| Laser frequency (KHz) | 10 |
| Pulse duration (s) | 5 × 10−4 |
| Parameters | Symbol | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Output laser fluence (W) | Q0 | 0.8 |
| Laser spot radius (μm) | r | 40 |
| Pulse duration (s) | ts | 5 × 10−4 |
| Laser frequency (kHZ) | f | 10 |
| Density (kg/m2) | ρ | 980 |
| Specific heat J/(kg·K) | CP | 1465 |
| Ambient temperature (°C) | Tset | −100, −125, −25, 25, 75, 125, 200 |
| Thermal conductivity [W/(m·k)] | k | 0.17 |
| Surface emissivity | ε | 0.8 |
| Poisson’s ratio | ν | 0.49 |
| Young’s modulus (Mpa) | E | 2.3 |
| Linear expansion coefficient (W/k) | α | 9 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Lin, C.; Guo, M.; Rong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, C. Effects of Ambient Temperature on Nanosecond Laser Micro-Drilling of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Micromachines 2023, 14, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010090
Lu Y, Lin C, Guo M, Rong Y, Huang Y, Wu C. Effects of Ambient Temperature on Nanosecond Laser Micro-Drilling of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Micromachines. 2023; 14(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Ya, Chaoran Lin, Minghui Guo, Youmin Rong, Yu Huang, and Congyi Wu. 2023. "Effects of Ambient Temperature on Nanosecond Laser Micro-Drilling of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)" Micromachines 14, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010090
APA StyleLu, Y., Lin, C., Guo, M., Rong, Y., Huang, Y., & Wu, C. (2023). Effects of Ambient Temperature on Nanosecond Laser Micro-Drilling of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Micromachines, 14(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010090








