High-Contrast Marking of Stainless-Steel Using Bursts of Femtosecond Laser Pulses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup for Ablation of Metal Sheets
2.2. Theoretical Insights into the Formation of Lambertian Scattering White Surfaces
- Change in the height of the material due to manufactured irregularities should be larger than 150 nm, to induce scattering over the full angular spectrum;
- The distance between the formed dimples in the transverse coordinates (X and Y) should be smaller than 10 µm to manufacture a uniform scattering surface. The area between the dimples must have a low roughness <30 nm (Ra) to avoid a multiple reflection scenario which would increase light absorption on the surface.
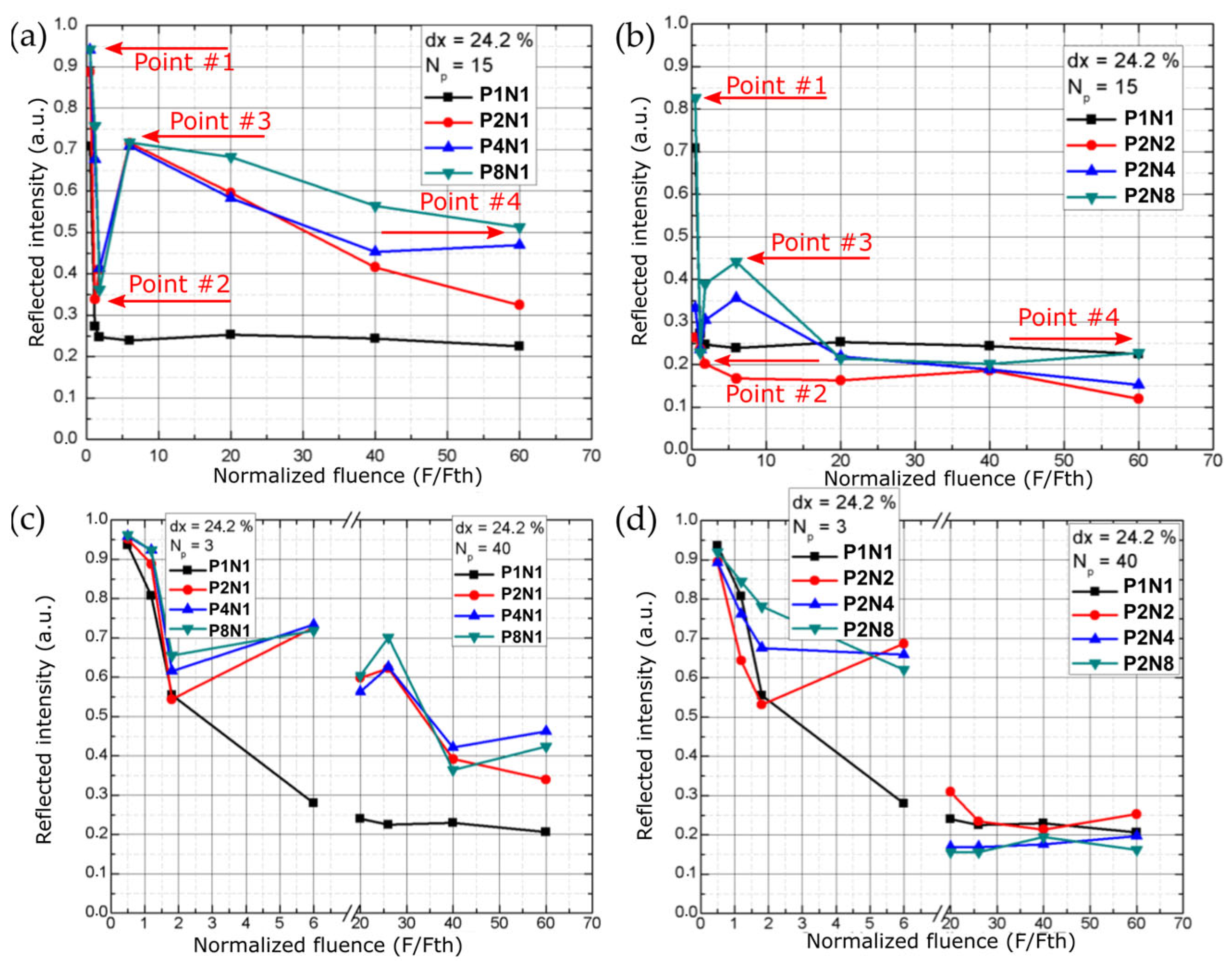
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, K.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, N.; Duan, J. Single-Step Femtosecond Laser Structuring of Multifunctional Colorful Metal Surface and Its Origin. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 34, 102386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazov, L.; Deneva, H.; Narica, P. Laser Marking Methods. Environ. Technol. Resour. Proc. Int. Sci. Pract. Conf. 2015, 1, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žemaitis, A.; Gaidys, M.; Gečys, P.; Barkauskas, M.; Gedvilas, M. Femtosecond Laser Ablation by Bibursts in the MHz and GHz Pulse Repetition Rates. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, T.M.; Yu, J.K.; Man, H.C. The Effect of Excimer Laser Surface Treatment on Pitting Corrosion Resistance of 316LS Stainless Steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 137, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courant, B.; Hantzpergue, J.J.; Avril, L.; Benayoun, S. Structure and Hardness of Titanium Surfaces Carburized by Pulsed Laser Melting with Graphite Addition. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 160, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.T. Laser Surface Alloying of Various Engineering Alloys for Sliding Wear and Corrosion Resistance. J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2010, 5, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiko, V.; Odintsova, G.; Vlasova, E.; Andreeva, Y.; Krivonosov, A.; Ageev, E.; Gorbunova, E. Laser Coloration of Titanium Films: New Development for Jewelry and Decoration. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 93, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwad, T.; Deng, S.; Butt, H.; Dimov, S. Laser Induced Single Spot Oxidation of Titanium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafaji, N.Y.; Demir, A.G.; Vitali, L.; Fustinoni, D.; Niro, A.; Previtali, B.; Taha, Z.A. Optical Characterization of Laser Coloured Titanium under Different Processing Atmospheres. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 321, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Fan, P.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Lin, C. Superhydrophobic and Colorful Copper Surfaces Fabricated by Picosecond Laser Induced Periodic Nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Niu, S.; Cao, X.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Bio-Inspired Micro-Nano Structured Surface with Structural Color and Anisotropic Wettability on Cu Substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 379, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräf, S.; Kunz, C.; Undisz, A.; Wonneberger, R.; Rettenmayr, M.; Müller, F.A. Mechano-Responsive Colour Change of Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 471, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, R.; Li, Z. Irregular LIPSS Produced on Metals by Single Linearly Polarized Femtosecond Laser. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2022, 4, 015102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Yao, Q.; Li, Z.; Sugioka, K. Liquid Vortexes and Flows Induced by Femtosecond Laser Ablation in Liquid Governing Formation of Circular and Crisscross LIPSS. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2022, 5, 210066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K.; Qiu, R. Uniformity Control of Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 932284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräf, S. Formation of Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Different Materials: Fundamentals, Properties and Applications. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2020, 9, 11–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenti, M.A.; Grande, M.; de Ceglia, D.; Stomeo, T.; Petruzzelli, V.; de Vittorio, M.; Scalora, M.; D’Orazio, A. Color Control through Plasmonic Metal Gratings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 201107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Huang, Z.; Laakso, M.J.; Niklaus, F.; Sliz, R.; Fabritius, T.; Somani, M.; Nyo, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Quantitative Assessment of Structural and Compositional Colors Induced by Femtosecond Laser: A Case Study on 301LN Stainless Steel Surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 484, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, J.-M.; Lesina, A.C.; Côté, G.; Charron, M.; Poitras, D.; Ramunno, L.; Berini, P.; Weck, A. Laser-Induced Plasmonic Colours on Metals. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageev, E.I.; Bychenkov, V.Y.; Ionin, A.A.; Kudryashov, S.I.; Petrov, A.A.; Samokhvalov, A.A.; Veiko, V.P. Double-Pulse Femtosecond Laser Peening of Aluminum Alloy AA5038: Effect of Inter-Pulse Delay on Transient Optical Plume Emission and Final Surface Micro-Hardness. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 211902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudiuso, C.; Kämmer, H.; Dreisow, F.; Ancona, A.; Tünnermann, A.; Nolte, S.; Gaudiuso, C.; Kämmer, H.; Dreisow, F.; Ancona, A.; et al. Ablation of Silicon with Bursts of Femtosecond Laser Pulses. Front. Ultrafast Opt. Biomed. Sci. Ind. Appl. 2016, 9740, 974017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, T.; Neuenschwander, B.; Jäggi, B.; Remund, S.; Hunziker, U.; Zürcher, J. Influence of Pulse Bursts on the Specific Removal Rate for Ultra-Fast Pulsed Laser Micromachining of Copper. Phys. Procedia 2016, 83, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US6552301B2- Burst-Ultrafast Laser Machining Method- Google Patents. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US6552301B2/en (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Chu, K.; Guo, B.; Jiang, L.; Hua, Y.; Gao, S.; Jia, J.; Zhan, N. Throughput Improvement in Femtosecond Laser Ablation of Nickel by Double Pulses. Materials 2021, 14, 6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrusyak, O.G.; Bubelnik, M.; Mares, J.; McGovern, T.; Siders, C.W.; Andrusyak, O.G.; Bubelnik, M.; Mares, J.; McGovern, T.; Siders, C.W. Single-Pulse and Burst-Mode Ablation of Gold Films Measured by Quartz Crystal Microbalance. SPIE 2005, 5647, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkus, S.; Jukna, V.; Paipulas, D.; Barkauskas, M.; Sirutkaitis, V. Micromachining of Invar Foils with GHz, MHz and KHz Femtosecond Burst Modes. Micromachines 2020, 11, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-W.; Chen, J.-K.; Kuo, C.-L.; Hsu, J.-C.; Ho, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-J. Drilling of Copper Using a Dual-Pulse Femtosecond Laser. Technologies 2016, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Cheng, C.W.; Chen, J.K.; Zhang, Y.; Tzou, D.Y. Thermal Ablation of Metal Films by Femtosecond Laser Bursts. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 70, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionin, A.A.; Kudryashov, S.I.; Makarov, S.v.; Seleznev, L.v.; Sinitsyn, D.v. Generation and Detection of Superstrong Shock Waves during Ablation of an Aluminum Surface by Intense Femtosecond Laser Pulses. JETP Lett. 2011, 94, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supersonic Flow and Shock Waves-Richard Courant, K.O. Friedrichs-Google. Available online: https://books.google.lt/books?hl=lt&lr=&id=Qsxec0QfYw8C&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&ots=aMMJB_pgdi&sig=4mgcni-pBg3wTs0bJfj1TD1-Lus&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 7 December 2022).
- Lin, Z.; Zhigilei, L.v.; Celli, V. Electron-Phonon Coupling and Electron Heat Capacity of Metals under Conditions of Strong Electron-Phonon Nonequilibrium. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter. Mater. Phys. 2008, 77, 075133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, A.S.; Dharmadhikari, A.K.; Kumar, G.R. Time Resolved Evolution of Structural, Electrical, and Thermal Properties of Copper Irradiated by an Intense Ultrashort Laser Pulse. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 97, 023526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.K.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.K. Superheating in Liquid and Solid Phases during Femtosecond-Laser Pulse Interaction with Thin Metal Film. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 103, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, H. Critical Data and Vapor Pressures for Aluminium and Copper. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 89, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.; Miotello, A. Comments on Explosive Mechanisms of Laser Sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1996, 96–98, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US11276985B2-Device and Method for Generation of High Repetition Rate Laser Pulse Bursts-Google Patents. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US11276985B2/en (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Lakowicz, J.R. (Ed.) Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-387-31278-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pinel, N.; Bourlier, C.; Saillard, J. Degree of Roughness of Rough Layers: Extensions of the Rayleigh Roughness Criterion and Some Applications. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2010, 19, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kažukauskas, E.; Butkus, S.; Tokarski, P.; Jukna, V.; Barkauskas, M.; Sirutkaitis, V. Micromachining of Transparent Biocompatible Polymers Applied in Medicine Using Bursts of Femtosecond Laser Pulses. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
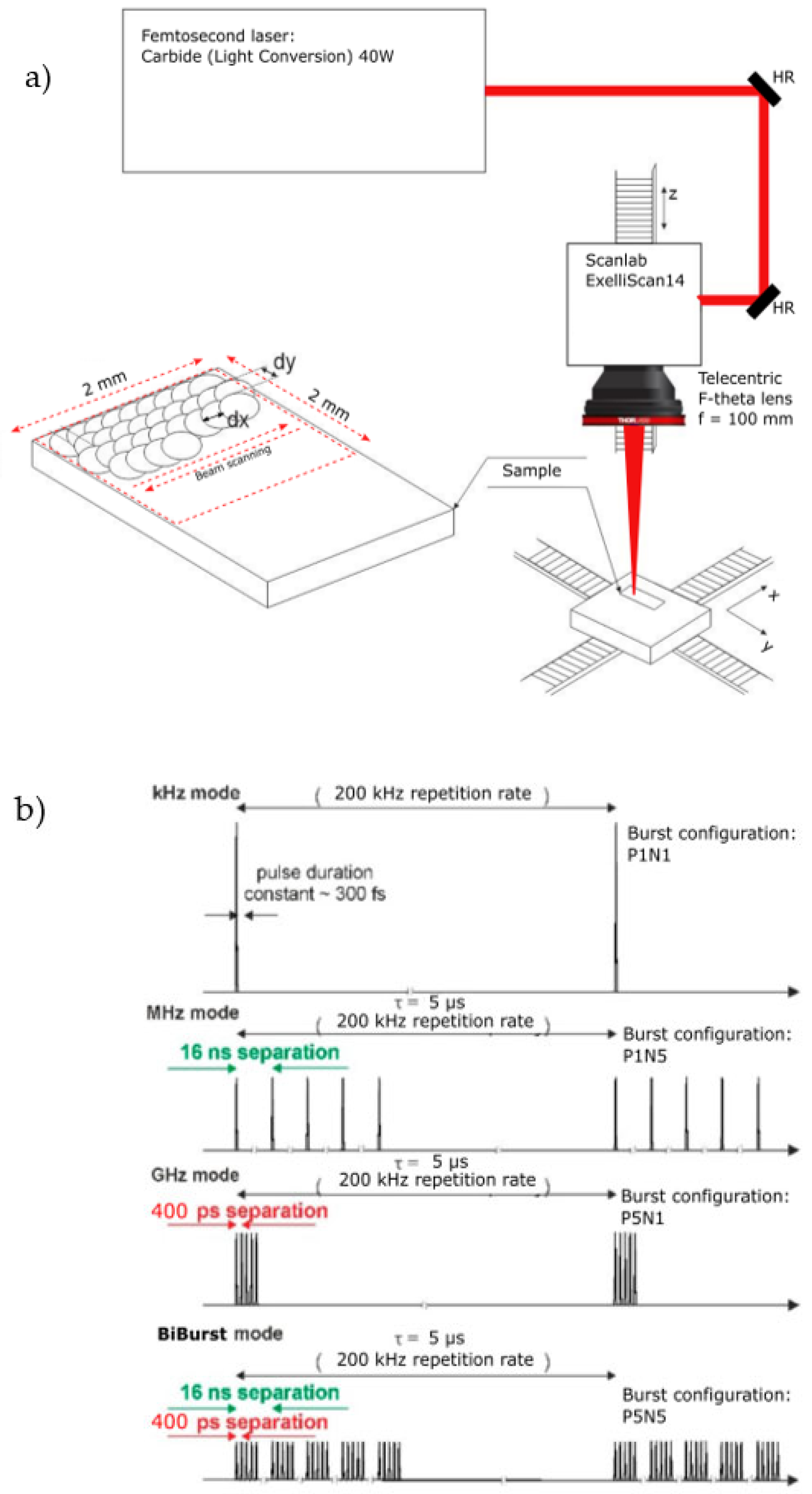



| Parameter | Setting, Value |
|---|---|
| F/Fth | 0.5, 0.7, 1.2, 1.8, 3, 4, 6, 14, 20, 26, 32, 40, 46, 53, 60 |
| Scanning overlap dx, dy (%) | 9, 24, 39, 54, 70 |
| # of repetitions (NP) | 1, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40 |
| Burst configuration | P2N1, P4N1, P8N1, P2N2, P2N4, P2N8, P1N2, P1N4, P1N8 |
| Wavelength (nm) | 1030 |
| Laser rep. rate (kHz) | 200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butkus, S.; Jukna, V.; Kažukauskas, E.; Svirksas, Ž.; Paipulas, D.; Sirutkaitis, V. High-Contrast Marking of Stainless-Steel Using Bursts of Femtosecond Laser Pulses. Micromachines 2023, 14, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010194
Butkus S, Jukna V, Kažukauskas E, Svirksas Ž, Paipulas D, Sirutkaitis V. High-Contrast Marking of Stainless-Steel Using Bursts of Femtosecond Laser Pulses. Micromachines. 2023; 14(1):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010194
Chicago/Turabian StyleButkus, Simas, Vytautas Jukna, Evaldas Kažukauskas, Žilvinas Svirksas, Domas Paipulas, and Valdas Sirutkaitis. 2023. "High-Contrast Marking of Stainless-Steel Using Bursts of Femtosecond Laser Pulses" Micromachines 14, no. 1: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010194
APA StyleButkus, S., Jukna, V., Kažukauskas, E., Svirksas, Ž., Paipulas, D., & Sirutkaitis, V. (2023). High-Contrast Marking of Stainless-Steel Using Bursts of Femtosecond Laser Pulses. Micromachines, 14(1), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010194










