Lightweight Fan-Beam Microstrip Grid Antenna for Airborne Microwave Interferometric Radiometer Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design and Simulation of Microstrip Grid Antenna
3. Simulation and Analysis of 1D Synthetic Aperture Non-Redundant Sparse Array Composed of Microstrip Grid Antenna
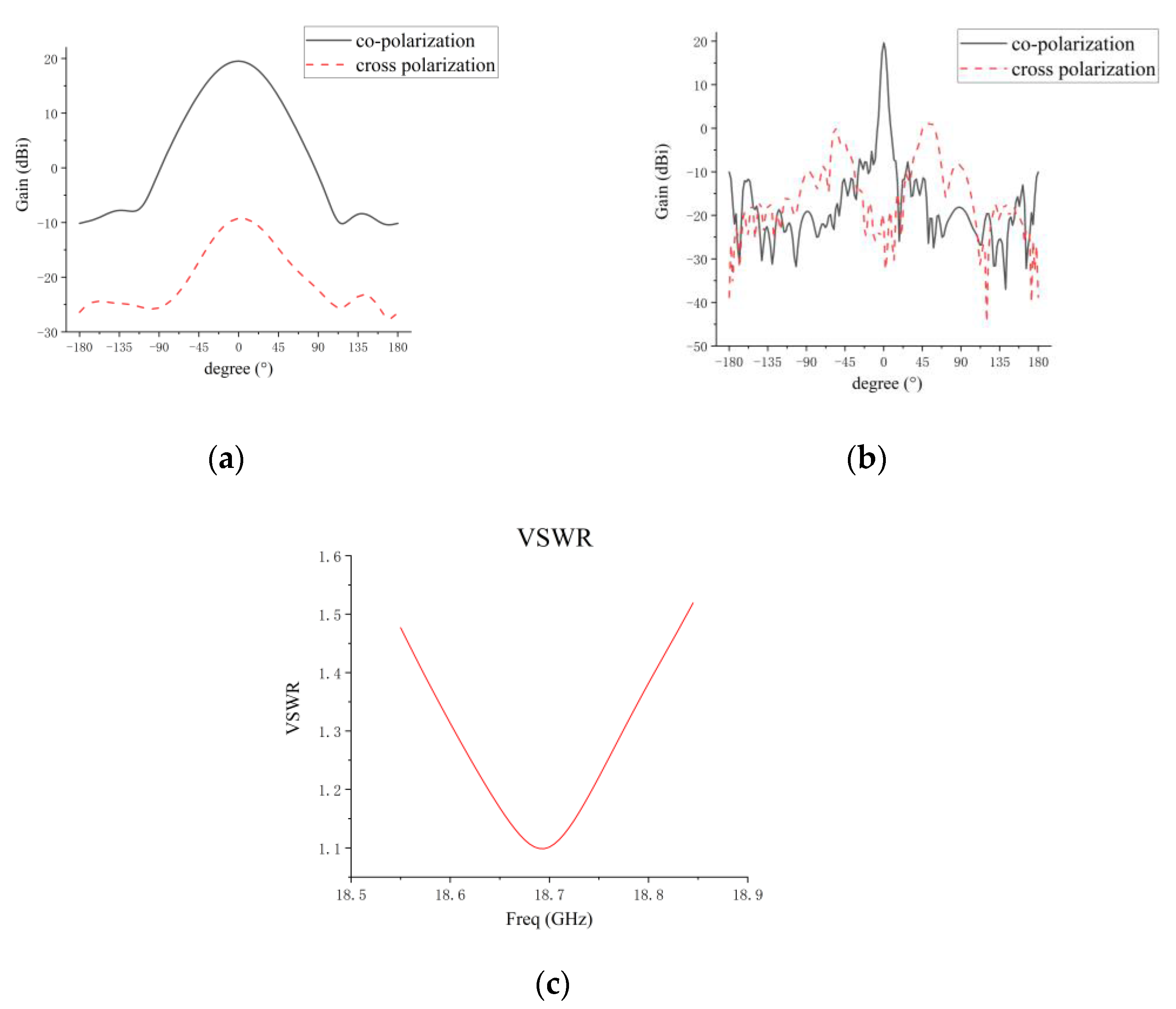
4. Measurement of the Designed Microstrip Grid Antenna
5. Measurement and Analysis of 1D Synthetic Aperture Non-Redundant Sparse Array Composed of Microstrip Grid Antenna
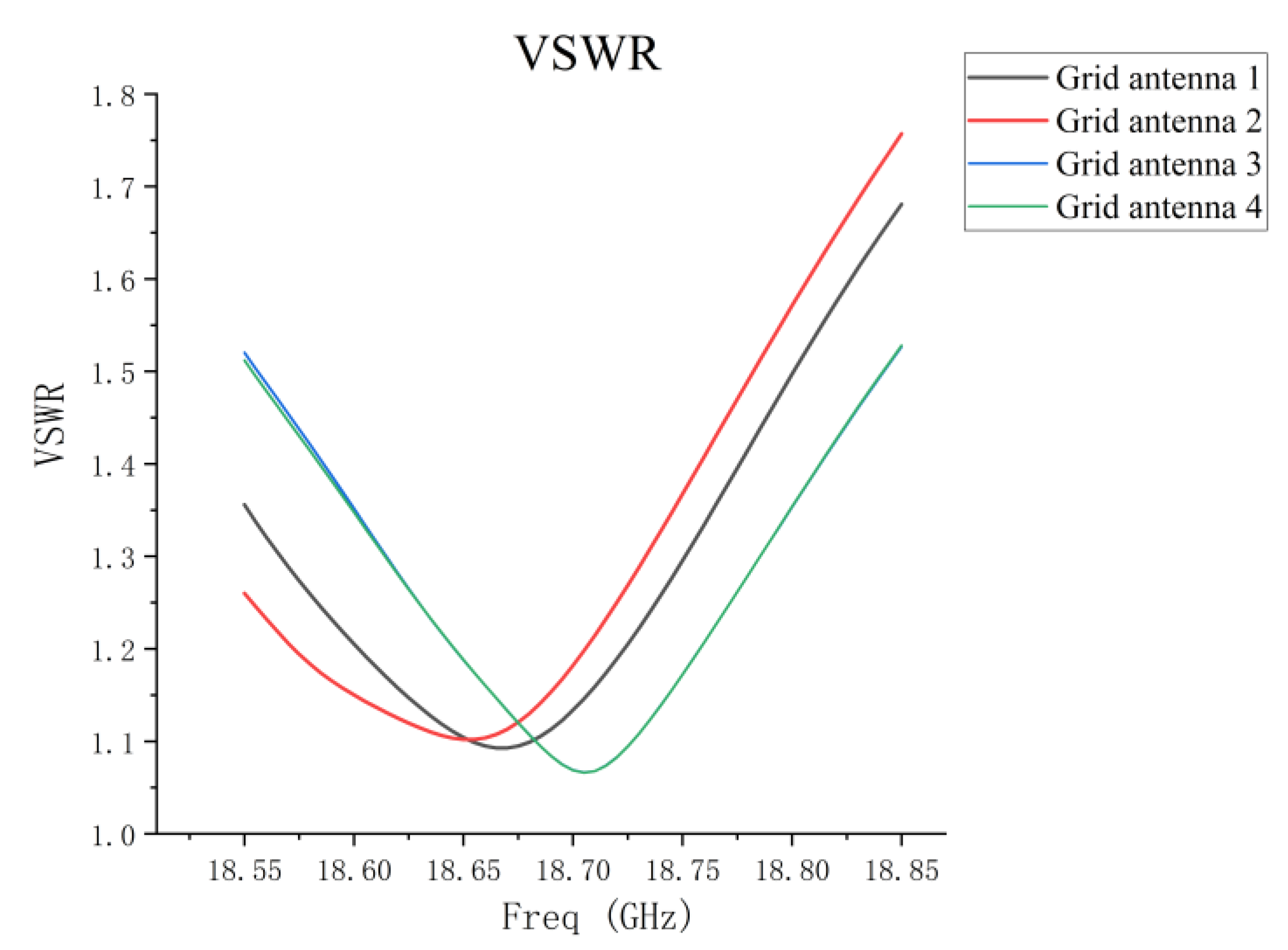
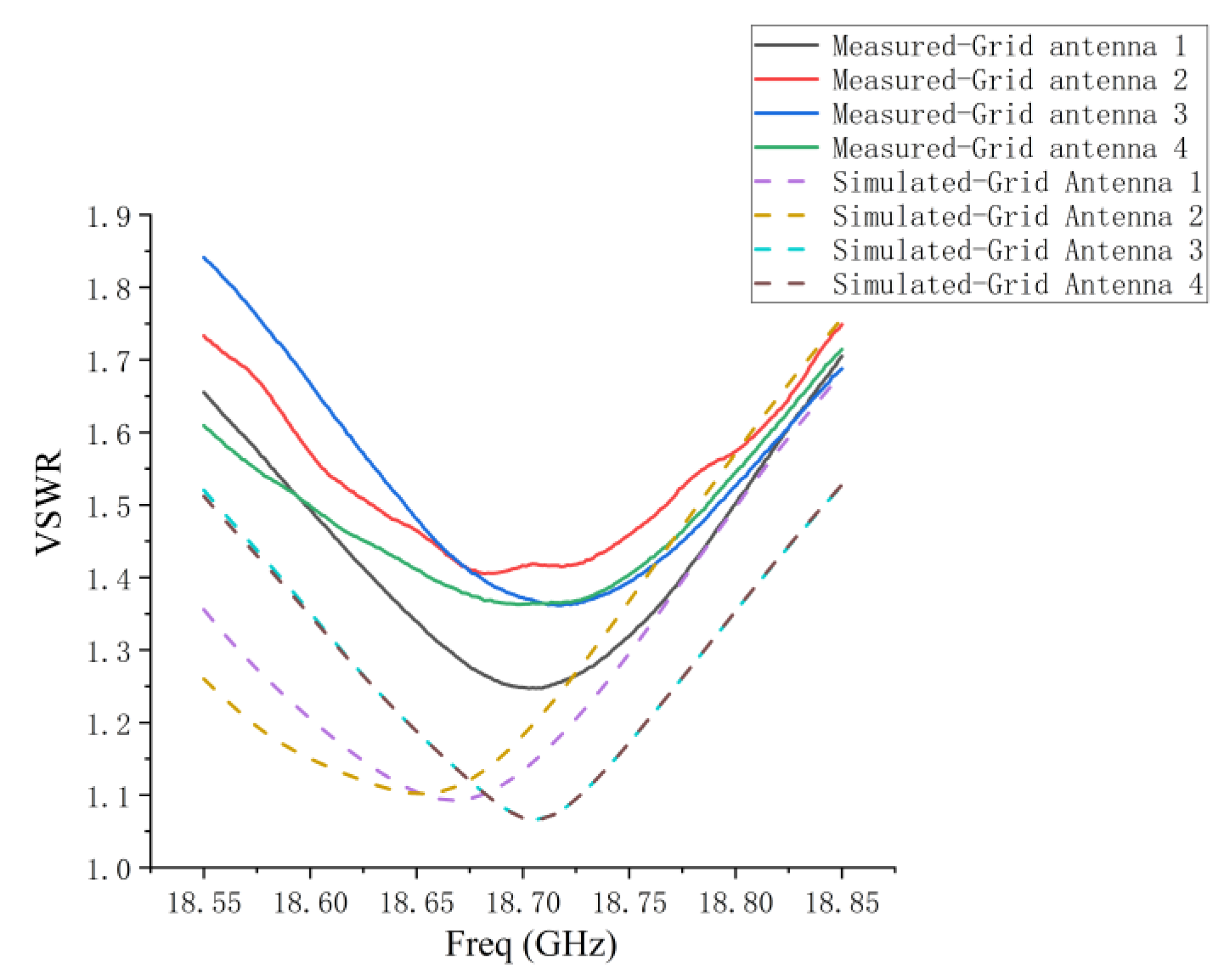
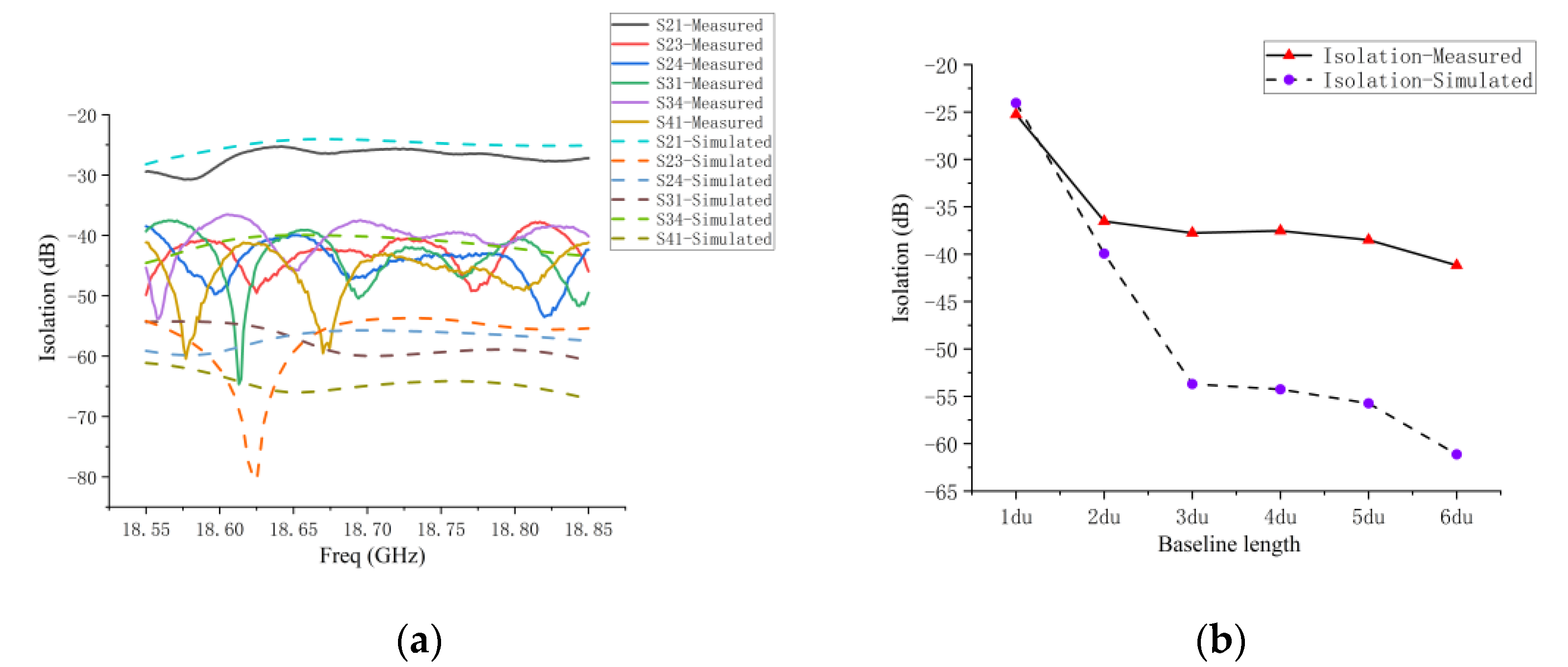
5.1. VSWR and Coupling of 1D Non-Redundant Sparse Array
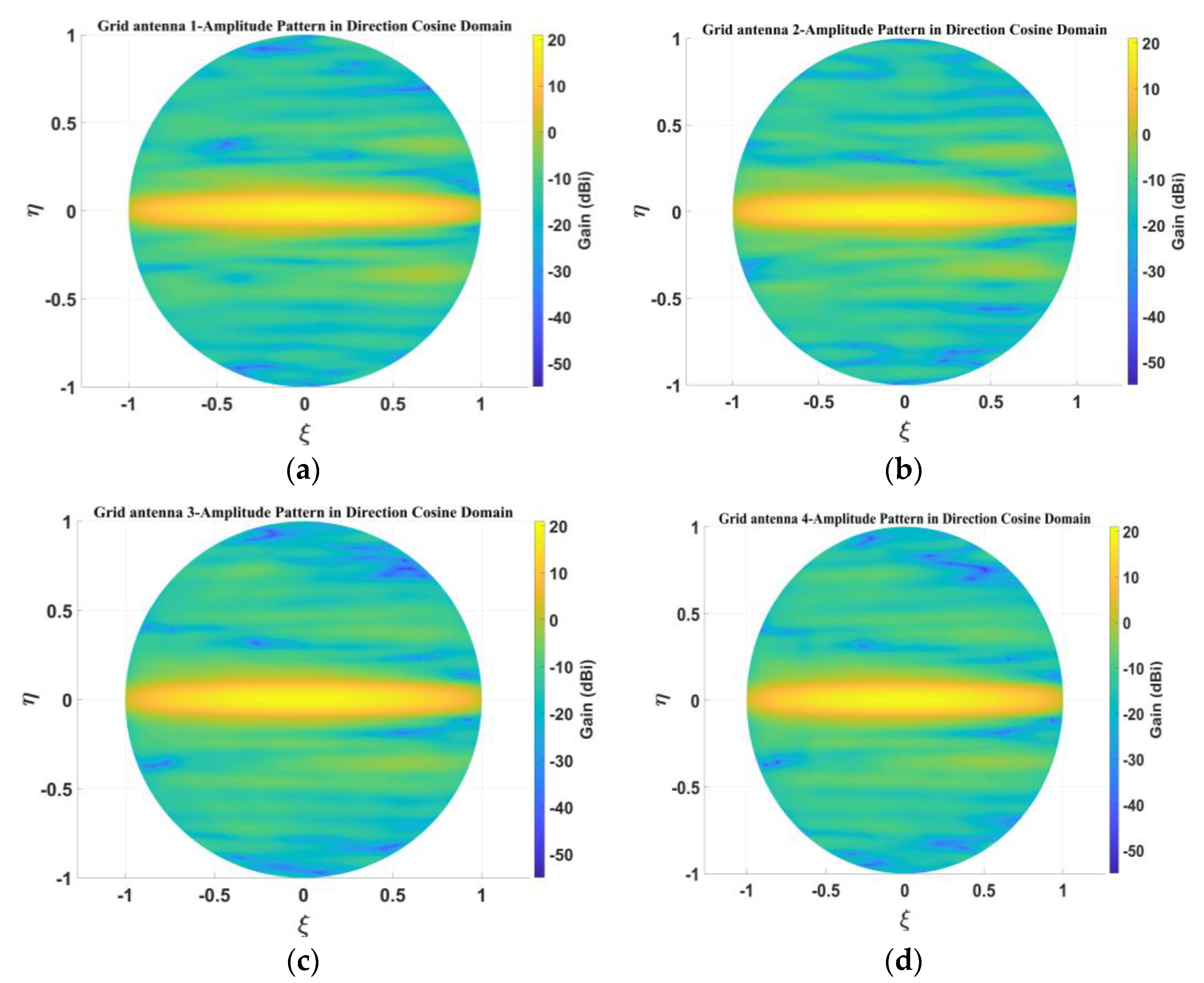
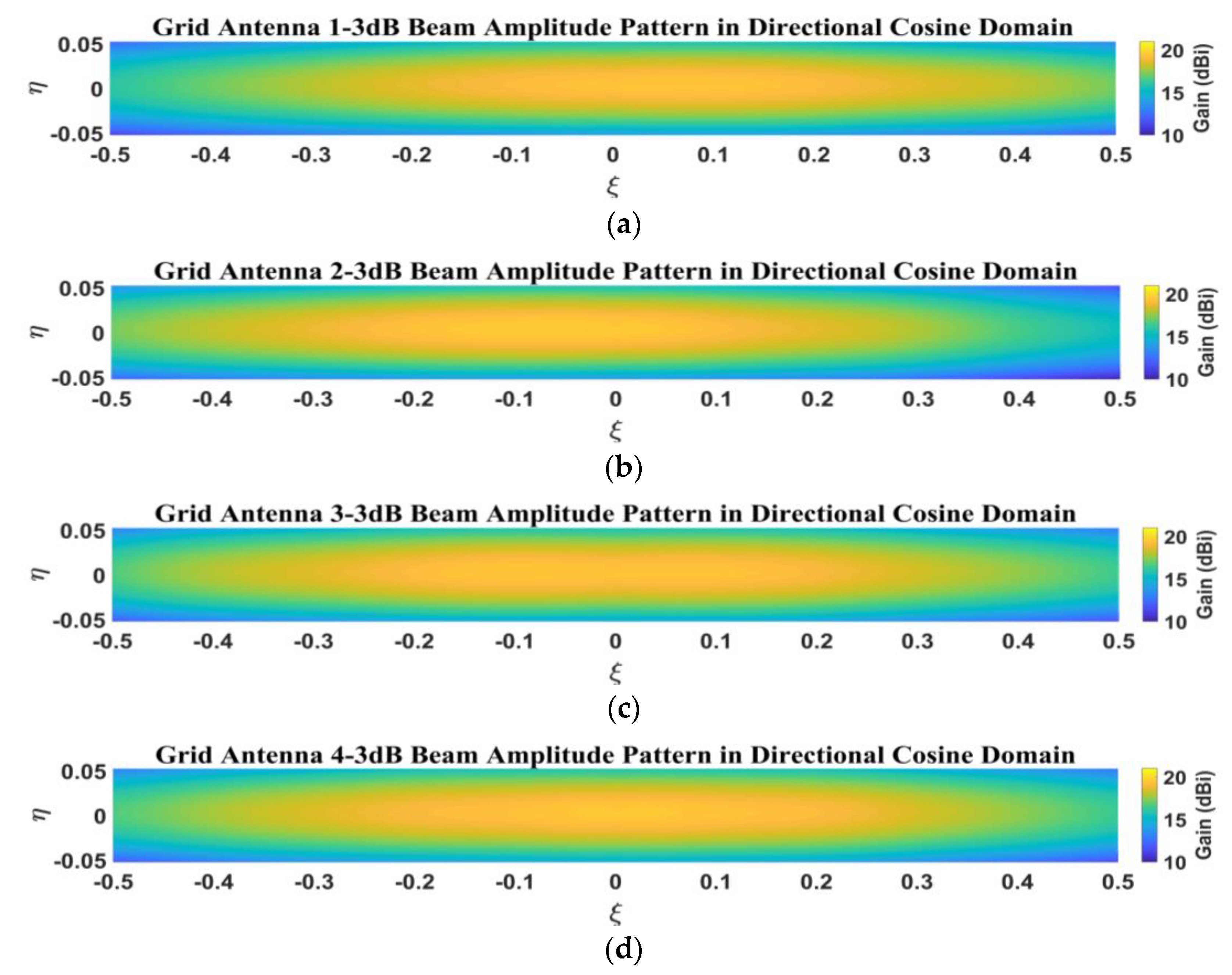
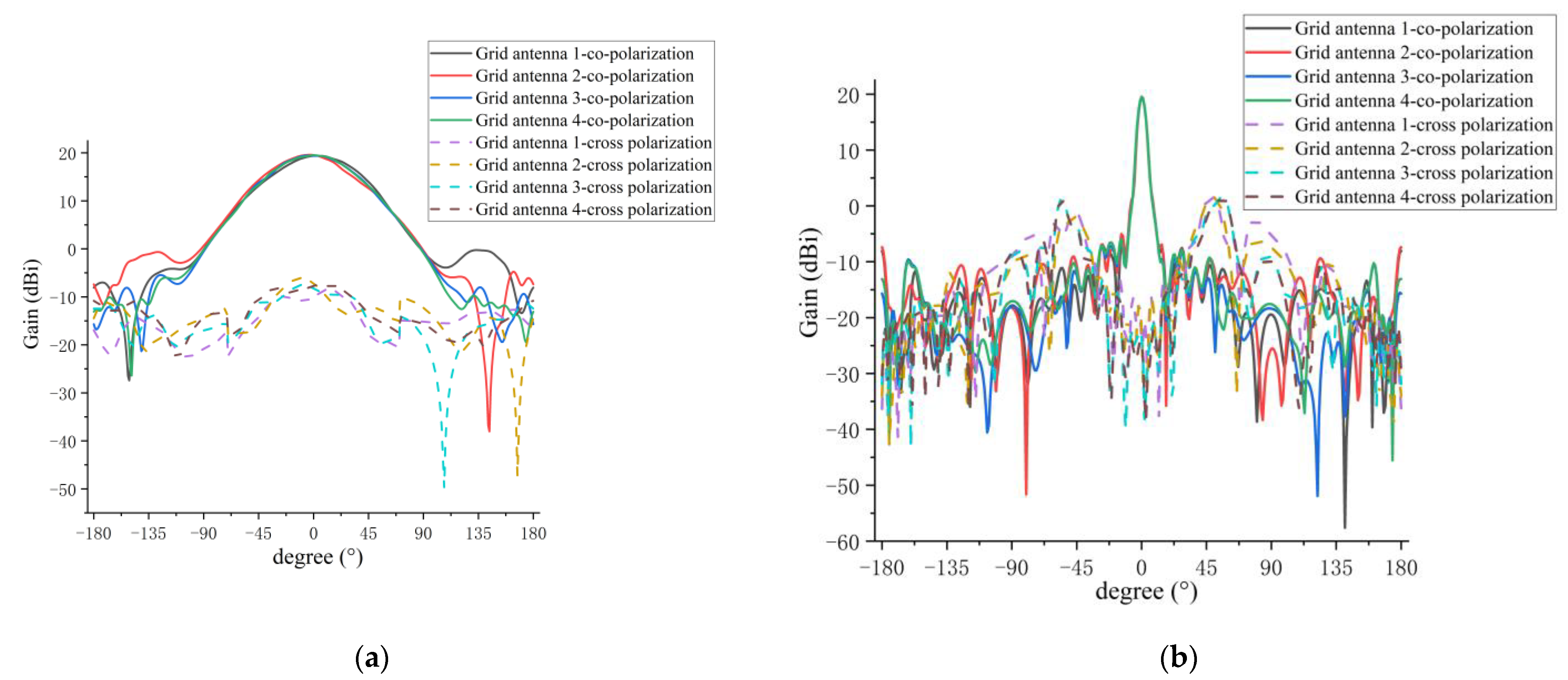
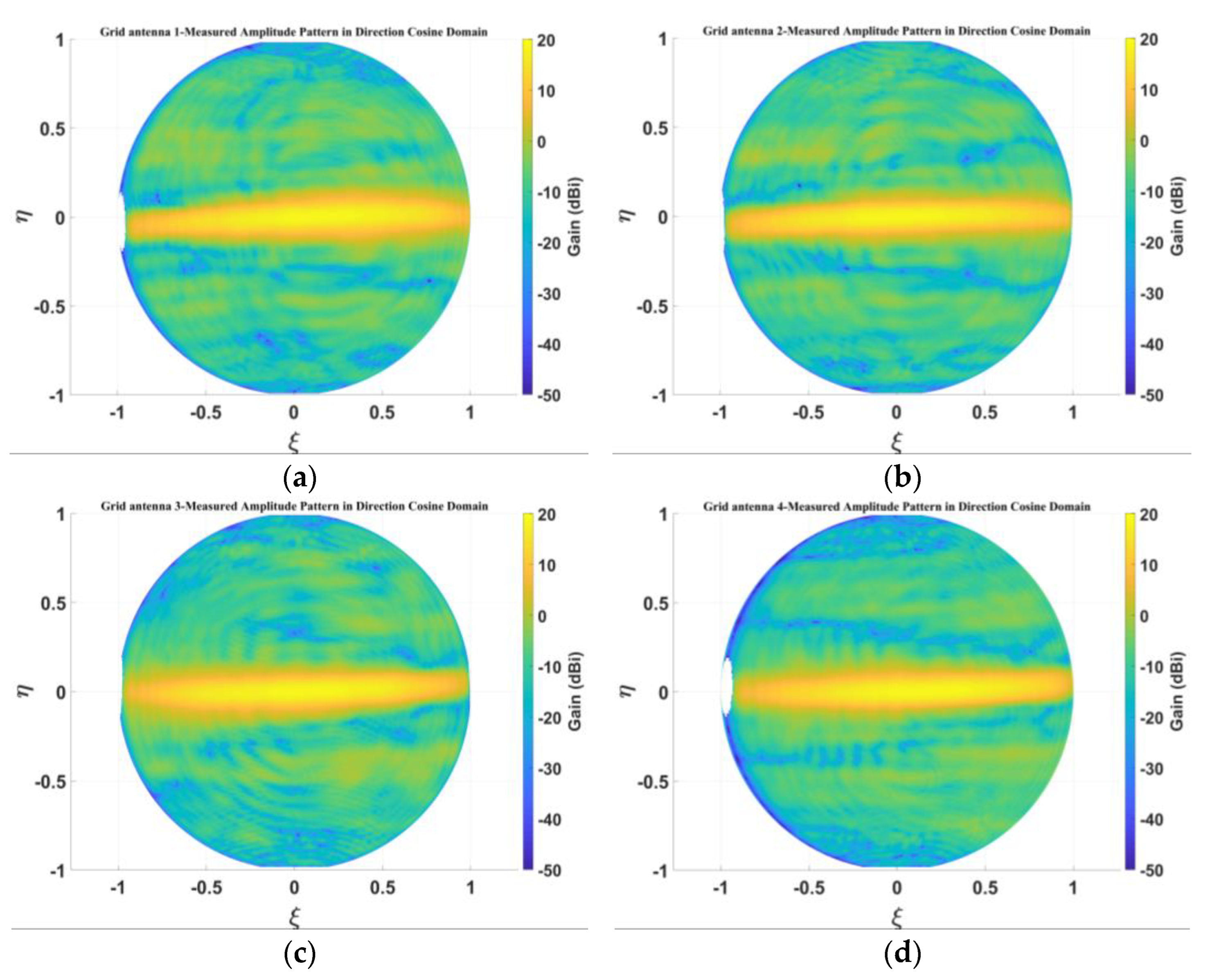
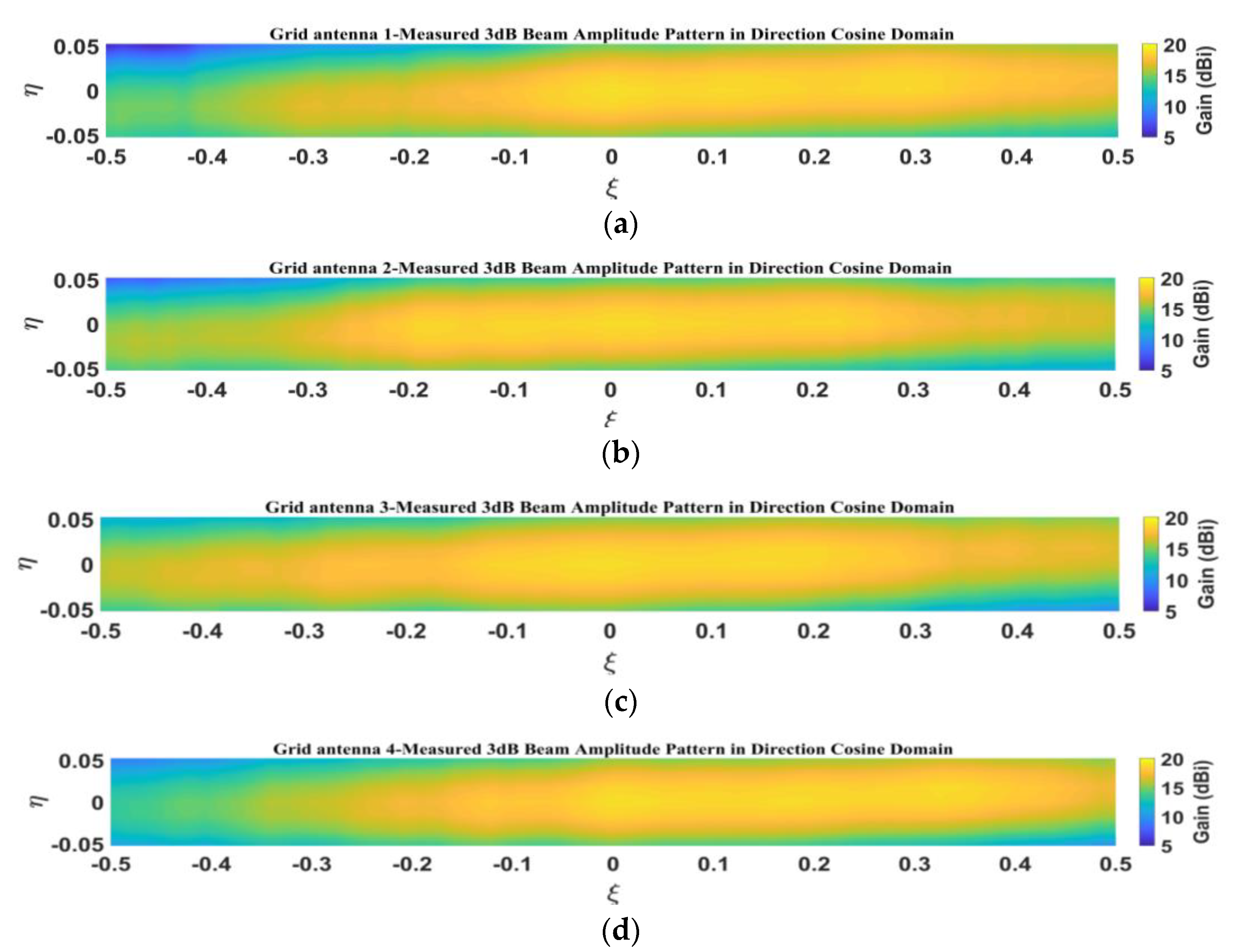
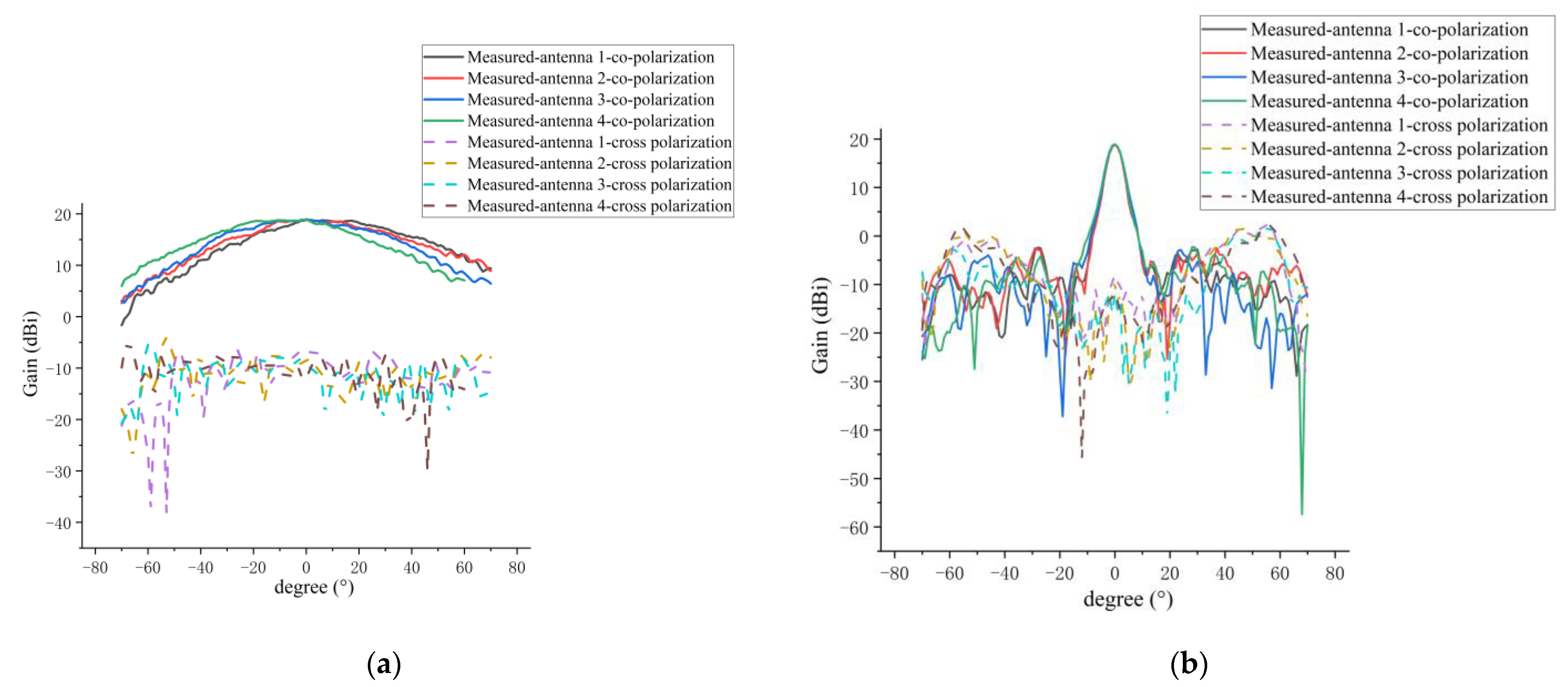
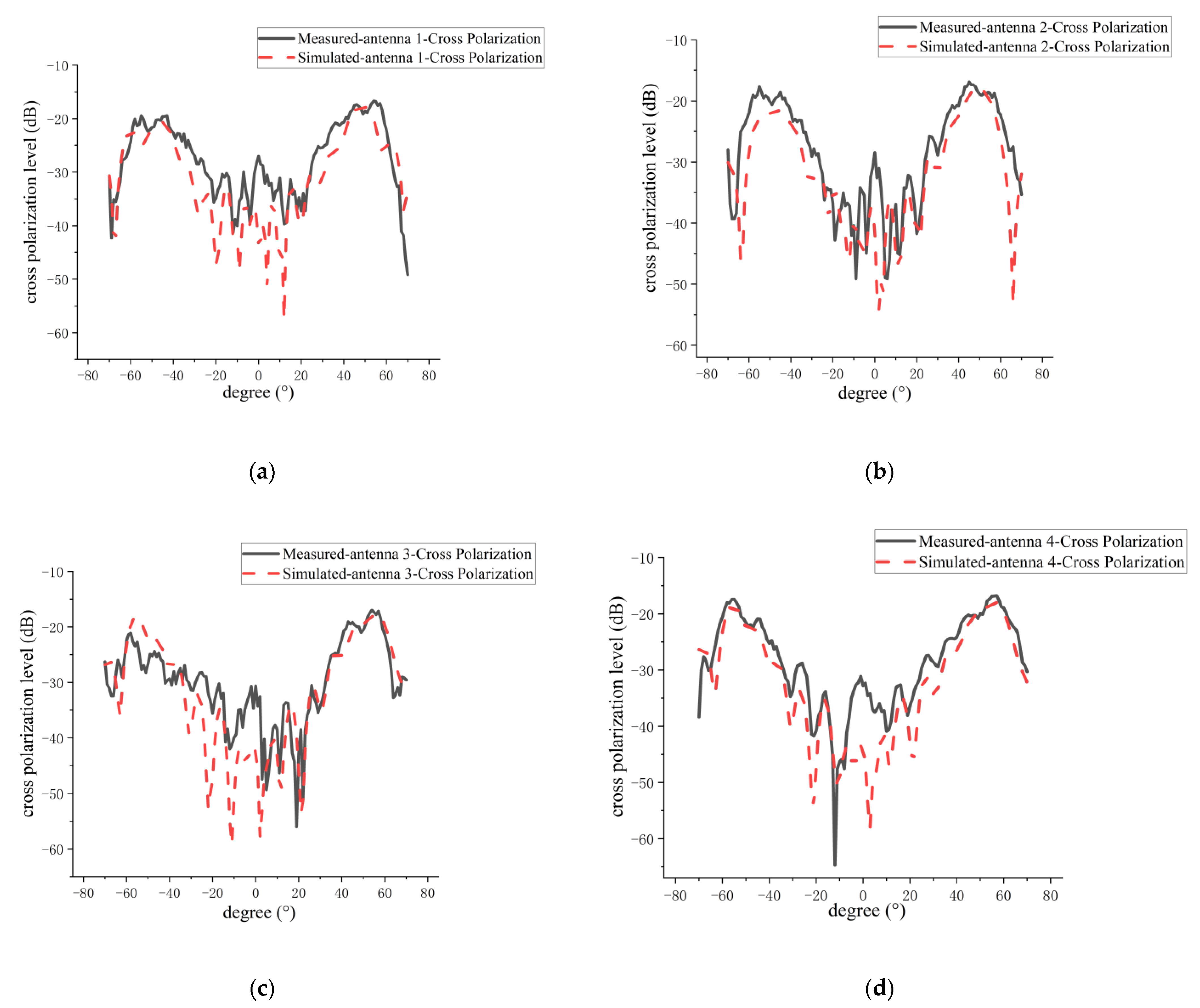
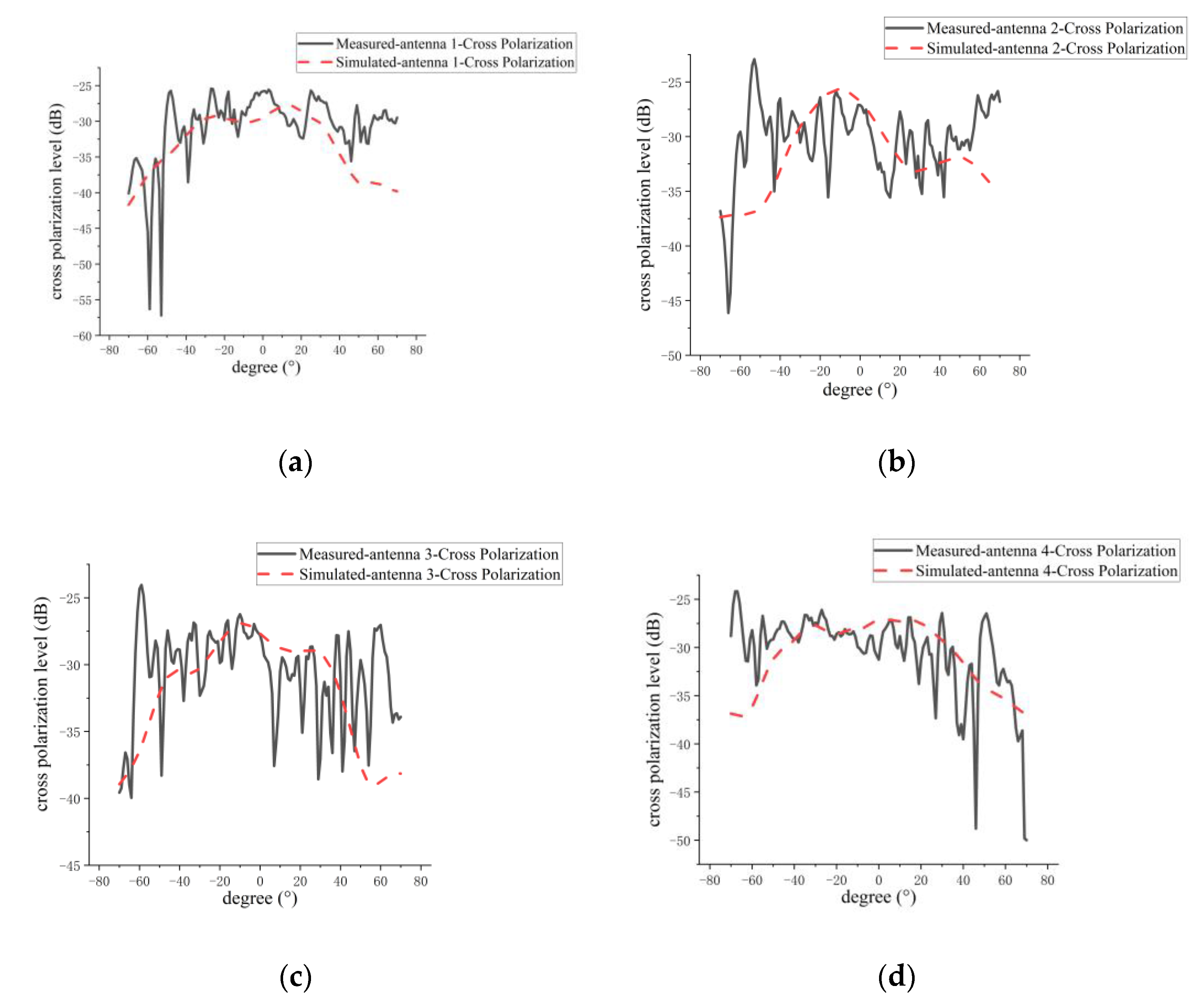
5.2. Measurement of Amplitude Patterns for 1D Non-Redundant Sparse Array
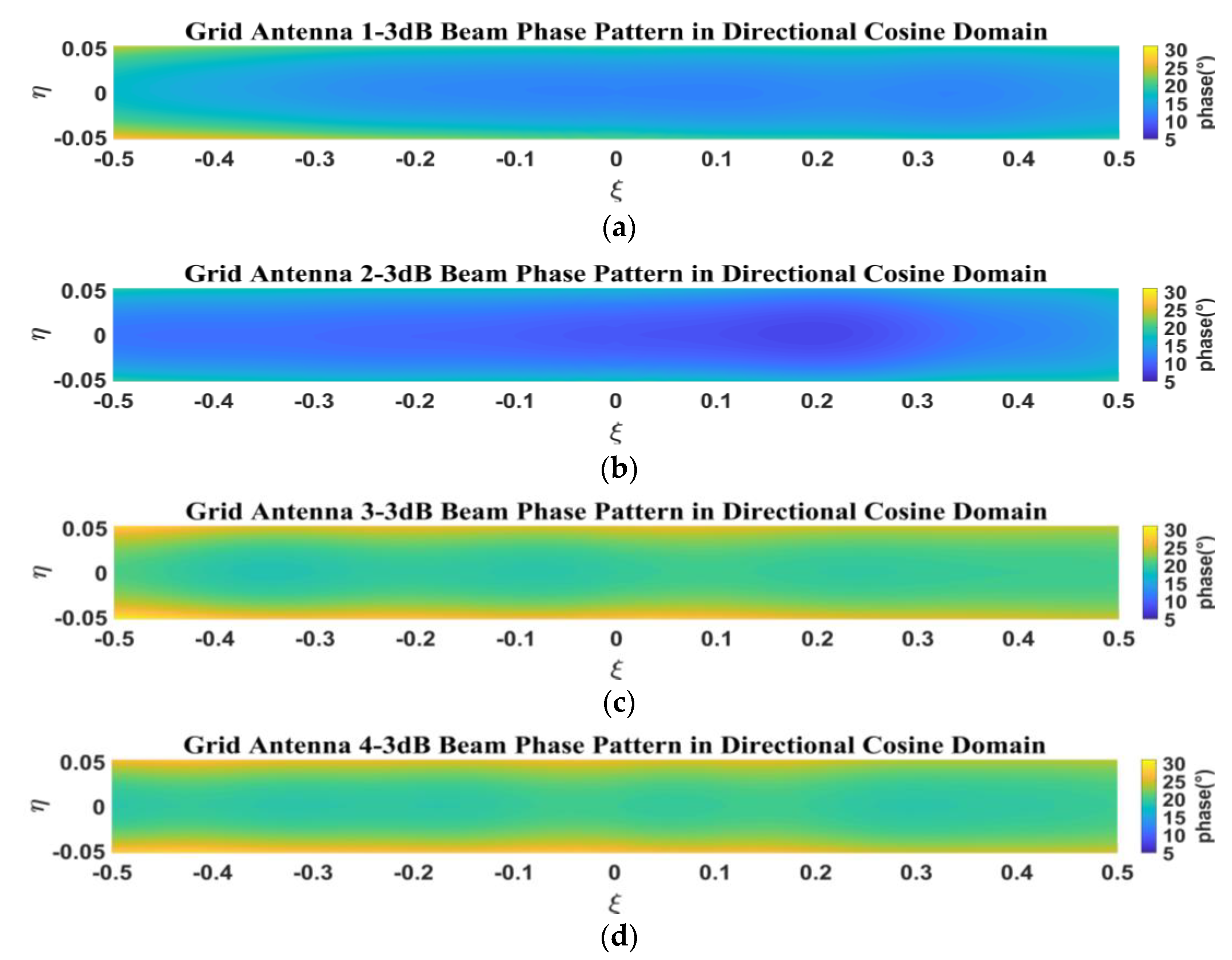
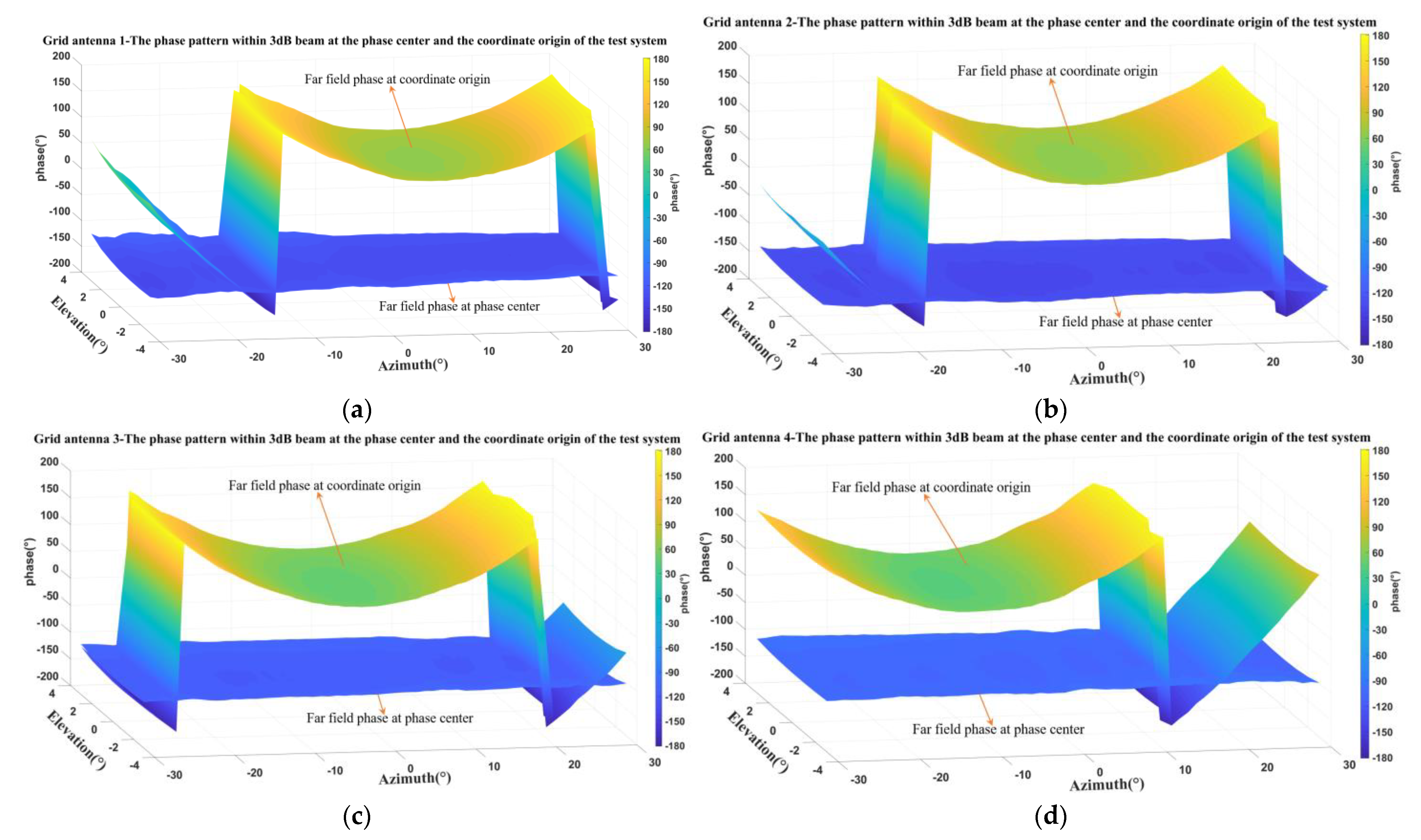
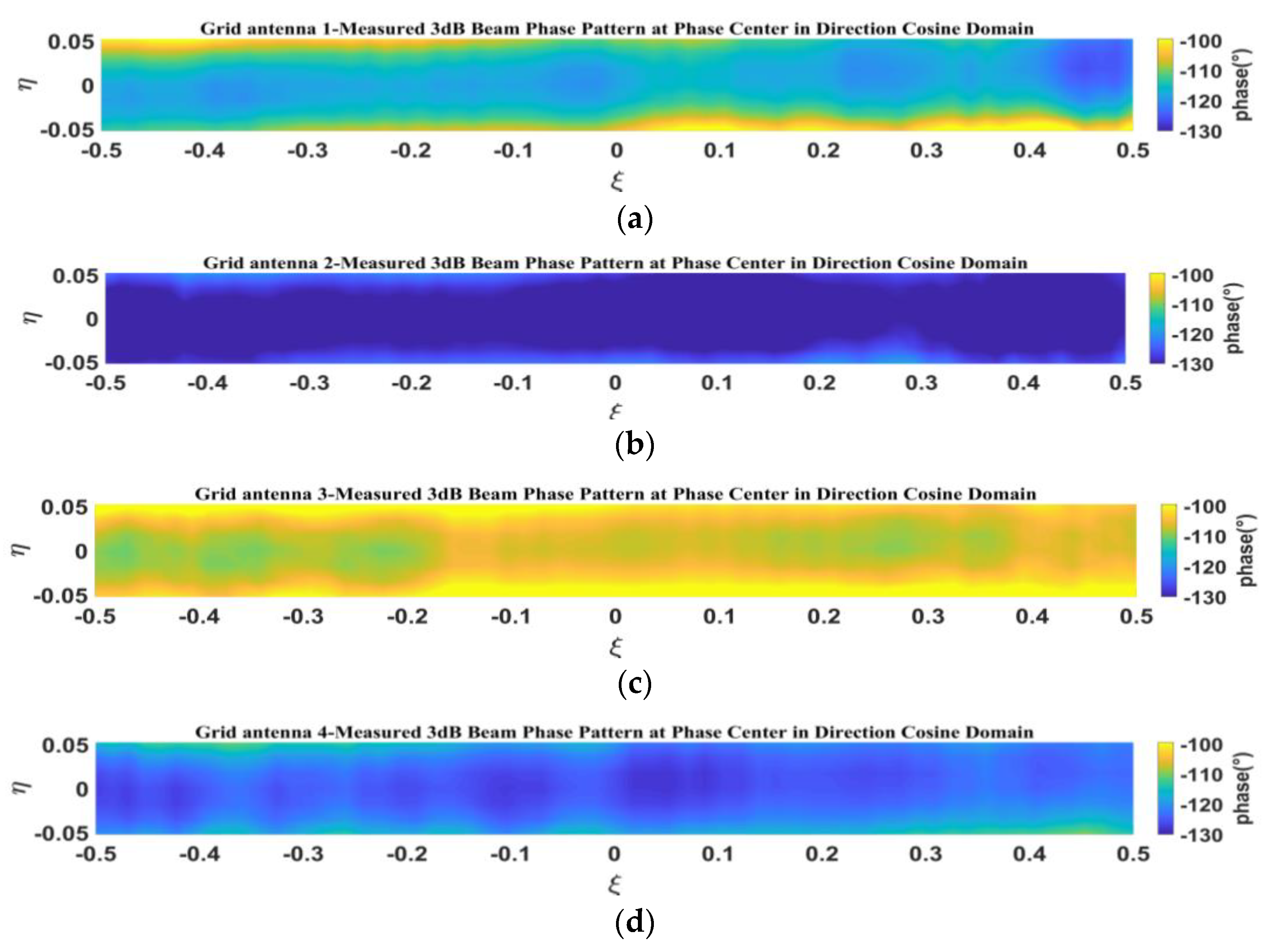
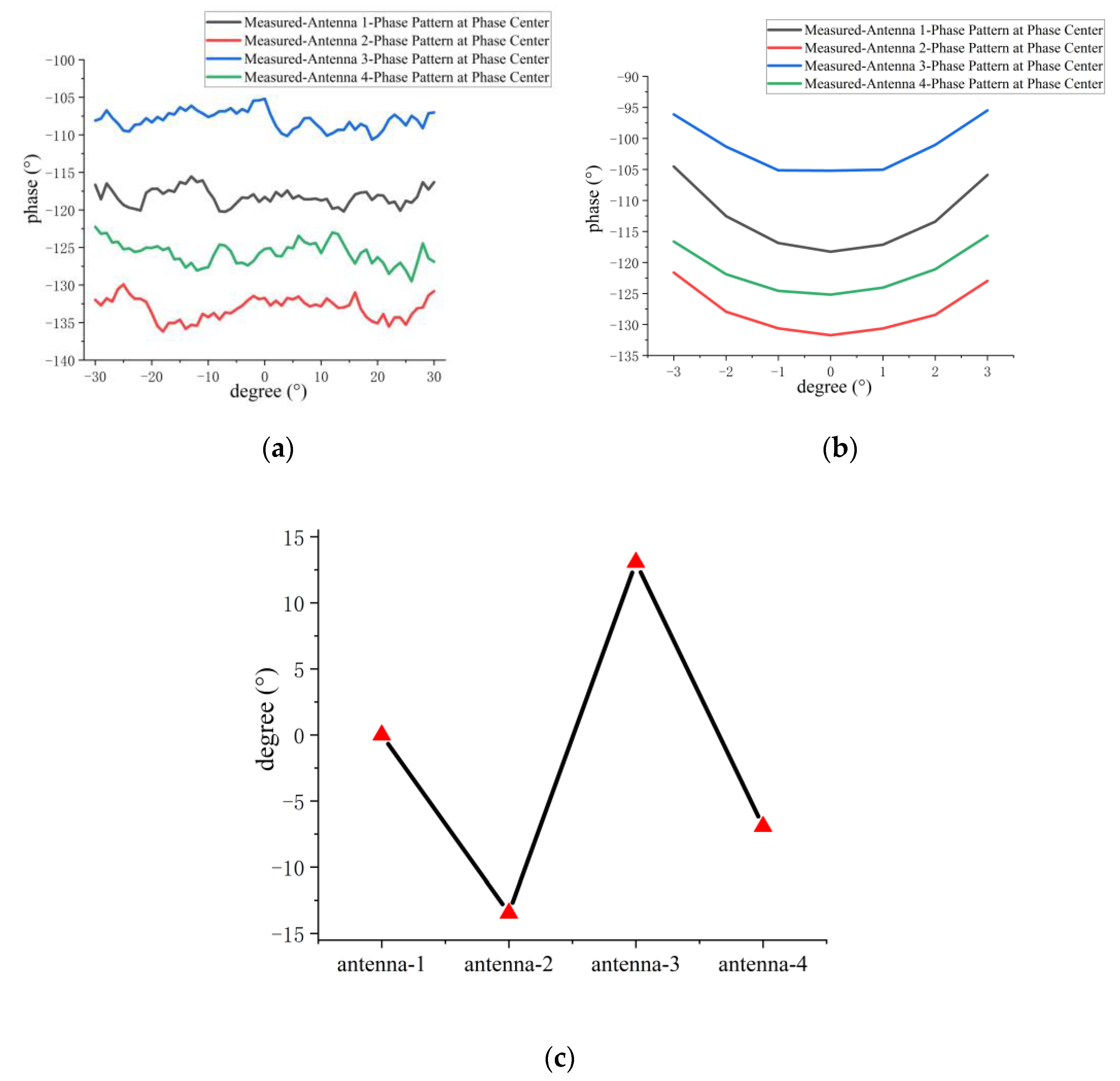
5.3. Measurement of Phase Patterns for 1D Non-Redundant Sparse Array
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martín-Neira, M.; LeVine, D.M.; Kerr, Y.; Skou, N.; Peichl, M.; Camps, A.; Corbella, I.; Hallikainen, M.; Font, J.; Wu, J.; et al. Microwave Interferometric Radiometry in Remote Sensing: An Invited Historical Review: MICROWAVE INTERFEROMETRIC RADIOMETRY. Radio Sci. 2014, 49, 415–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matey, J.M.A.; Palacios, H.; Vasal’lo, J.; Marti-Canales, J.; Martin-Neira, M. Large 2-D Thinned Array for the Microwave Imaging Radiometer with Synthetic Aperture (MIRAS). In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium. 1999 Digest. Held in Conjunction with: USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting (Cat. No.99CH37010), Orlando, FL, USA, 11–16 July 1999; IEEE: Orlando, FL, USA, 1999; Volume 3, pp. 1540–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Le Vine, D.M.; Haken, M.; Swift, C.T. Development of the Synthetic Aperture Radiometer ESTAR and the next Generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International IEEE International IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2004. IGARSS ’04, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; IEEE: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1260–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Rautiainen, K.; Kainulainen, J.; Auer, T.; Pihlflyckt, J.; Kettunen, J.; Hallikainen, M.T. Helsinki University of Technology L-Band Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radiometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.C.; Amarin, R.A.; Johnson, J.W.; Nelson, P.; James, M.W.; Simmons, D.E.; Ruf, C.S.; Jones, W.L.; Gong, X. Multi-Frequency Synthetic Thinned Array Antenna for the Hurricane Imaging Radiometer. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2010, 58, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Liu, H. FPIR: The Dual Polarization Antenna. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium-IGARSS, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; IEEE: Melbourne, Australia, 2013; pp. 374–377. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Wu, J.; Zhu, S.Y.; Sun, B.; Jiang, J. The Design and Implementation of CAS C-Band Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radiometer. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2000. IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Taking the Pulse of the Planet: The Role of Remote Sensing in Managing the Environment. Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37120), Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 July 2000; IEEE: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 866–868. [Google Scholar]
- Hao Liu, J.W. The CAS Airborne X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radiometer: System Configuration and Experimental Results. In Proceedings of the IEEE International IEEE International IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2004. IGARSS ’04, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; IEEE: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2004; Volume 3, pp. 2230–2233. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, K.; Guo, W.; Lang, L.; He, F.; Chen, L.; Xiong, Z. An Aperture Synthesis Radiometer at Millimeter Wave Band. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Nanjing, China, 21–24 April 2008; IEEE: Nanjing, China, 2008; pp. 1699–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, D.; Niu, L.; Wu, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yin, X.; et al. MICAP (Microwave Imager Combined Active and Passive): A New Instrument for Chinese Ocean Salinity Satellite. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; IEEE: Milan, Italy, 2015; pp. 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lambrigtsen, B.; Wilson, W.; Tanner, A.; Gaier, T.; Ruf, C.; Piepmeier, J. GeoSTAR-a Microwave Sounder for Geostationary Satellites. In Proceedings of the IEEE International IEEE International IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2004. IGARSS ’04, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; IEEE: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 777–780. [Google Scholar]
- Carlstrom, A.; Christensen, J.; Ingvarson, P.; Embretsen, J.; Emrich, A.; de Maagt, P. Geostationary Atmospheric Sounder (GAS) Demonstrator Development. In Proceedings of the 2009 3rd European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Berlin, Germany, 23–27 March 2009; pp. 2036–2040. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yan, J.; Niu, L.; Sun, W.; Li, H. Imaging Analysis and First Results of the Geostationary Interferometric Microwave Sounder Demonstrator. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J. A Backward Angle-Fire Array Antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1964, 12, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, R.; Toth, J.; Dowling, T.; Weiss, J. The Wire Grid Microstrip Antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1981, 29, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, L.T. The Analysis of Microstrip Wire-Grid Antenna Arrays. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Alsath, M.G.N.; Lawrance, L.; Kanagasabai, M. Bandwidth-Enhanced Grid Array Antenna for UWB Automotive Radar Sensors. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2015, 63, 5215–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ping, Z.Y. 24-GHz Microstrip Grid Array Antenna for Automotive Radars Application. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Singapore, 1–4 September 2015; IEEE: Singapore, September 2015; pp. 125–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z. A Dual-Feed Microstrip Grid Array Antenna for Balanced or Unbalanced Operation. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2017, 27, e21111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, O.; Meyer, J.; Baur, K.; Waldschmidt, C. Hybrid Thin Film Antenna for Automotive Radar at 79 GHz. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2017, 65, 5076–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosalanejad, M.; Ocket, I.; Soens, C.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E. Multilayer Compact Grid Antenna Array for 79 GHz Automotive Radar Applications. Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 1677–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.P. A Multiport Microstrip Grid Array Structure. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2016, 64, 4953–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Peng, H.-L.; Shao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, W.-Y. Dual-Band Differential Shifted-Feed Microstrip Grid Array Antenna with Two Parasitic Patches. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2020, 68, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Yang, L.X.; Huang, Z.X.; Wang, W.; Peng, H.L.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, W.Y. Microstrip Grid and Patch-Based Dual-Band Shared-Aperture Differentially Fed Array Antenna. Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2021, 20, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhou, W.; Lin, M.; Liu, H.; Li, Y. Performance Simulation of the Payload IMR and MICAP Onboard the Chinese Ocean Salinity Satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.D. Synthesis of the Microstrip Wire Grid Array. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Antennas and Propagation (ICAP), Edinburgh, UK, 14–17 April 1997; IEE: Edinburgh, UK, 1997; Volume 1997, pp. 1–114. [Google Scholar]

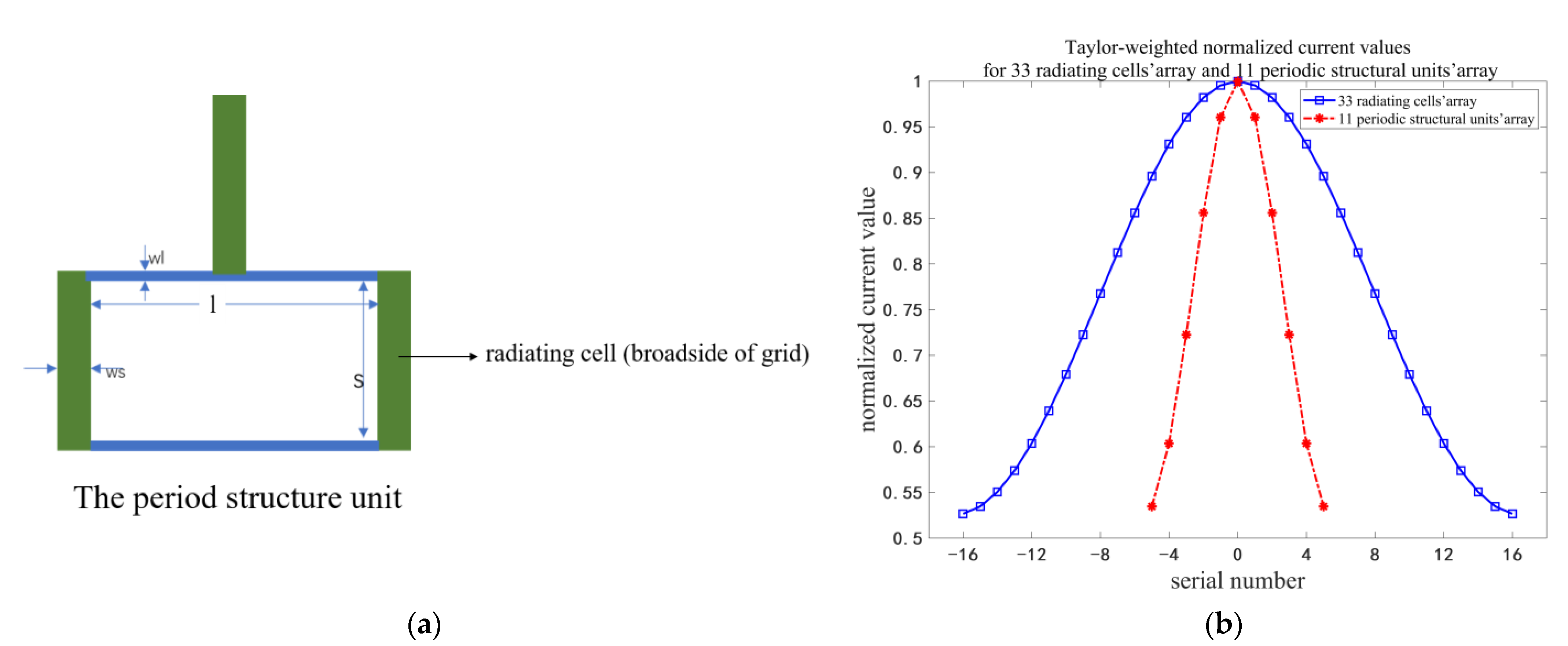
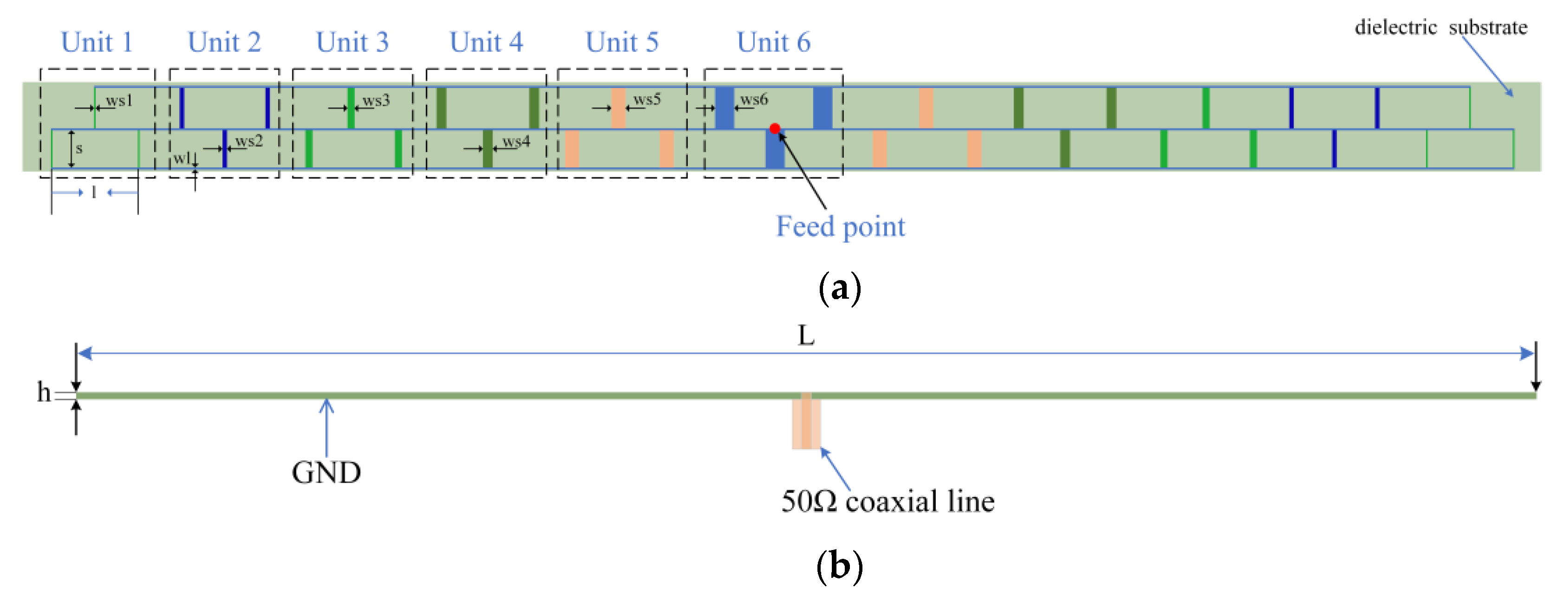





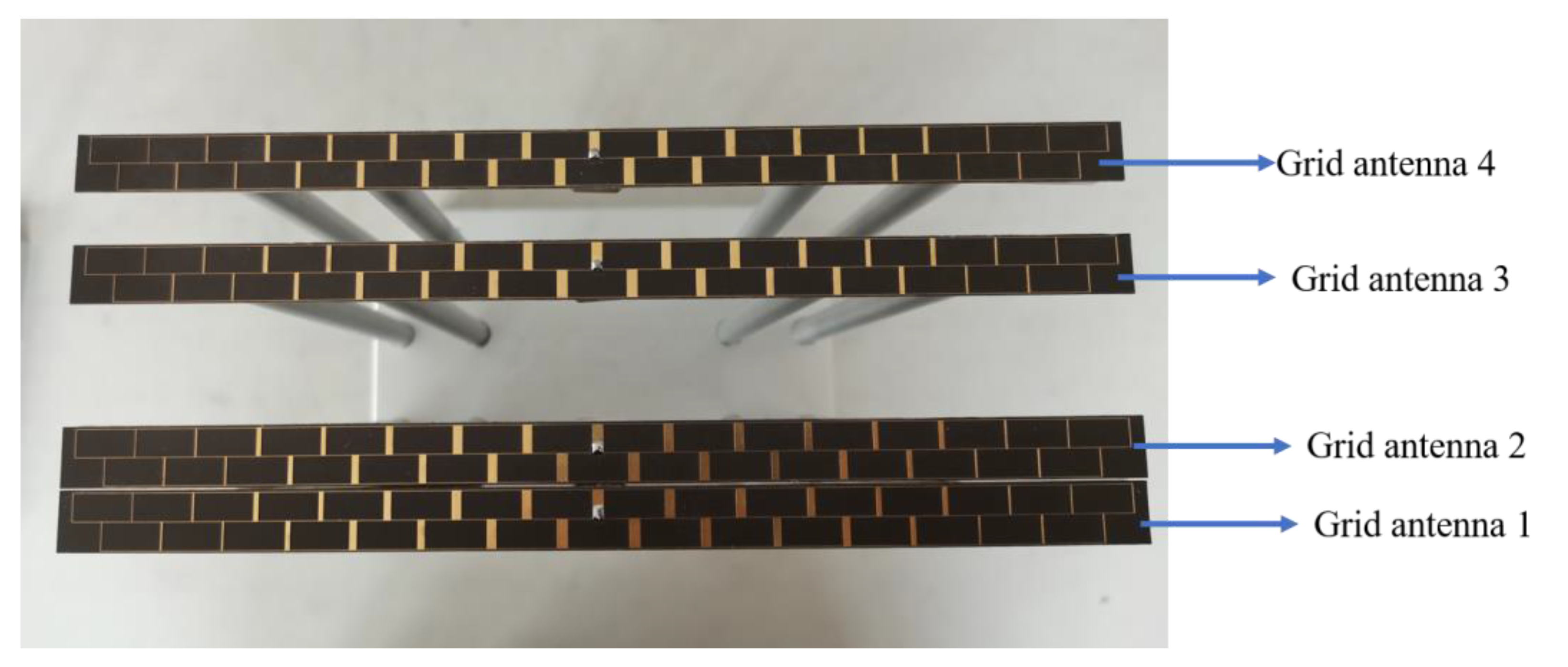



| Name | l | s | wl | ws1 | ws2 | ws3 | ws4 | ws5 | ws6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (mm) | 12.6 | 5.43 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
| Periodic Structural Unit | Theoretical Normalized Current Value | Simulated Normalized Current Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5234 | 0.1954 |
| 2 | 0.6013 | 0.2686 |
| 3 | 0.7231 | 0.5643 |
| 4 | 0.8401 | 0.8102 |
| 5 | 0.9605 | 0.9282 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 |
| E-Plane Phase Range within 3-dB Beamwidth | E-Plane Phase Fluctuation | H-Plane Phase Range within 3-dB Beamwidth | H-Plane Phase Fluctuation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid antenna 1 | 12.9–17.4° | 4.5° | 12.9–20.8° | 7.9° |
| Grid antenna 2 | 7.8–15.1° | 7.3° | 9.5–17.9° | 8.4° |
| Grid antenna 3 | 18.5–21° | 2.5° | 20.5–27.2° | 6.7° |
| Grid antenna 4 | 19–20.5° | 1.5° | 21–27.3° | 6.3° |
| Simulation Results | Measured Results | |
|---|---|---|
| Gain | 19.4 dBi | 19.1 dBi |
| Half-power beamwidth of E plane | 61° | 59.91° |
| Cross-polarization of E plane | <−28 dB | <−26 dB |
| Half-power beamwidth of H plane | 4.7° | 5.34° |
| H-plane sidelobe level | <−25 dB | <−21.4 dB |
| Cross-polarization of H plane | <−18.7 dB | <−17.37 dB |
| VSWR | frequency band < 1.53 center frequency: 1.12 | frequency band < 1.82 center frequency: 1.56 |
| Gain (dBi) | E-Plane Cross-Polarization (dB) | E-Plane 3-dB Beamwidth (°) | H-Plane Sidelobe Level (dB) | H-Plane Cross-Polarization (dB) | H-Plane 3-dB Beamwidth (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid antenna 1 | 18.93 | −25.2 | 54.6 | −21.17 | −16.71 | 5.25 |
| Grid antenna 2 | 18.83 | −23 | 53.85 | −20.1 | −16.93 | 4.97 |
| Grid antenna 3 | 18.87 | −24 | 57.69 | −21.45 | −17 | 5.24 |
| Grid antenna 4 | 18.9 | −24.17 | 56.55 | −21.22 | −16.76 | 5.25 |
| Measured Gain (dBi) | Simulated Gain (dBi) | Measured H-Plane Sidelobe Level (dB) | Simulated H-Plane Sidelobe Level (dB) | Measured H-Plane Cross-Polarization (dB) | Simulated H-Plane Cross-Polarization (dB) | Measured H-Plane 3-dB Beamwidth (°) | Simulated H-Plane 3-dB Beamwidth (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid antenna 1 | 18.93 | 19.34 | −21.17 | −26.35 | −16.71 | −17.78 | 5.25 | 4.84 |
| Grid antenna 2 | 18.83 | 19.55 | −20.1 | −24.58 | −16.93 | −18 | 4.97 | 4.73 |
| Grid antenna 3 | 18.87 | 19.38 | −21.45 | −25.4 | −17 | −17.69 | 5.24 | 4.95 |
| Grid antenna 4 | 18.9 | 19.53 | −21.22 | −25.52 | −16.76 | −17.9 | 5.25 | 4.95 |
| Measured E-Plane Cross-Polarization (dB) | Simulated E-Plane Cross-Polarization (dB) | Measured E-Plane 3-dB Beamwidth (°) | Simulated E-Plane 3-dB Beamwidth (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid antenna 1 | −25.2 | −27.77 | 54.6 | 62.07 |
| Grid antenna 2 | −23 | −25.67 | 53.85 | 56.92 |
| Grid antenna 3 | −24 | −26.9 | 57.69 | 61 |
| Grid antenna 4 | −24.17 | −27.1 | 56.55 | 60 |
| Measured E-Plane Phase Fluctuation within 3-dB Beam | Simulated E-Plane Phase Fluctuation within 3-dB Beam | Measured H-Plane Phase Fluctuation within 3-dB Beam | Simulated H-Plane Phase Fluctuation within 3-dB Beam | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid antenna 1 | 4.7° | 4.5° | 13.73° | 7.9° |
| Grid antenna 2 | 6.26° | 7.3° | 10.1° | 8.4° |
| Grid antenna 3 | 5.43° | 2.5° | 9.71° | 6.7° |
| Grid antenna 4 | 7.24° | 1.5° | 9.5° | 6.3° |
| References | Working Frequency (GHz) | Sidelobe Level (dB) | HPBW | Gain (dB) | Antenna Size | Coupling (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | 24 | −16 | 7° (narrow beam) 90° (wide beam) | 13.87 | 1.44λ × 11.68λ | — |
| [18] | 24 | −16 | 16° | 19.26 | 4.8λ × 4.8λ | — |
| [19] | 24 | −15 | 14° | 20.6 | 4.8λ × 4.8λ | −17.5 dB |
| [22] | 24 | −15 | — | 22.5 | 8λ × 8λ | −34 dB |
| This work | 18.7 | −21.4 | 5.34° (narrow beam) 55° (wide beam) | 19.1 | 0.77λ × 13.3λ | −25 dB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, C.; Liu, H.; Yi, M. Lightweight Fan-Beam Microstrip Grid Antenna for Airborne Microwave Interferometric Radiometer Applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010228
Gu C, Liu H, Yi M. Lightweight Fan-Beam Microstrip Grid Antenna for Airborne Microwave Interferometric Radiometer Applications. Micromachines. 2023; 14(1):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010228
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Chunwang, Hao Liu, and Min Yi. 2023. "Lightweight Fan-Beam Microstrip Grid Antenna for Airborne Microwave Interferometric Radiometer Applications" Micromachines 14, no. 1: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010228
APA StyleGu, C., Liu, H., & Yi, M. (2023). Lightweight Fan-Beam Microstrip Grid Antenna for Airborne Microwave Interferometric Radiometer Applications. Micromachines, 14(1), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010228







