The Dark Annulus of a Drop in a Hele-Shaw Cell Is Caused by the Refraction of Light through Its Meniscus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurement of Surface Tension Coefficient and Refractive Index
2.2. Fabrication of the Hele-Shaw Cell
2.3. Confocal Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging of a Drop
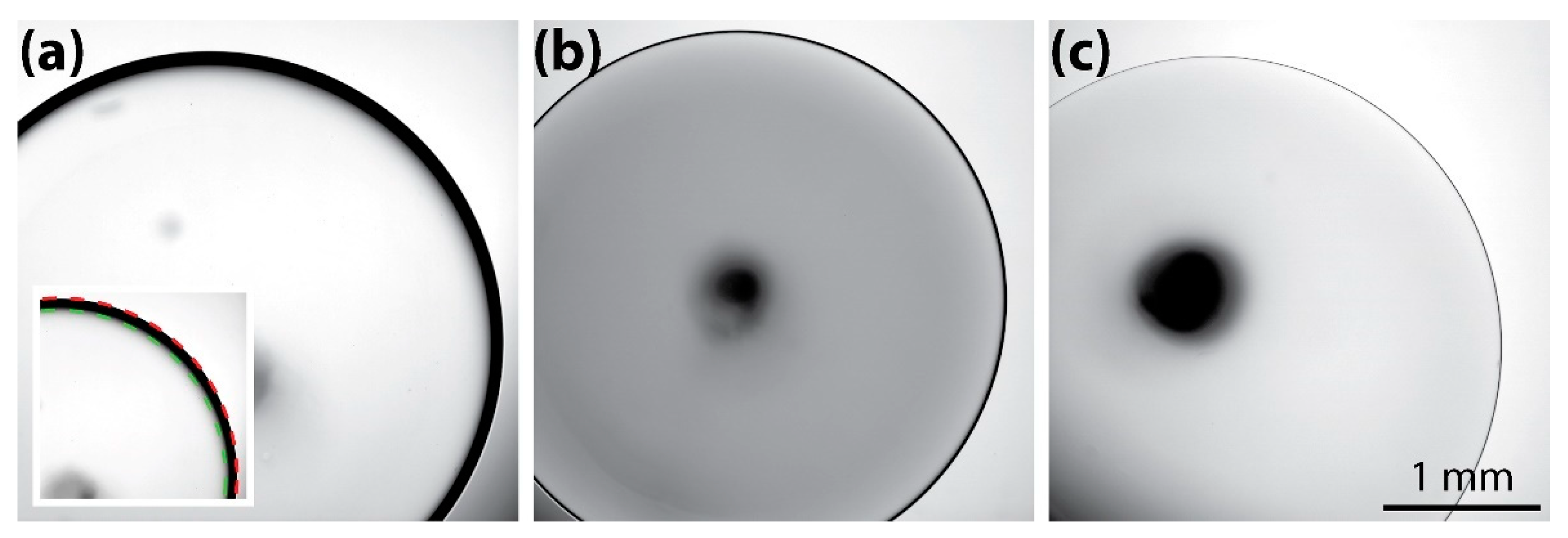
2.4. Image Processing
3. Results and Discussion
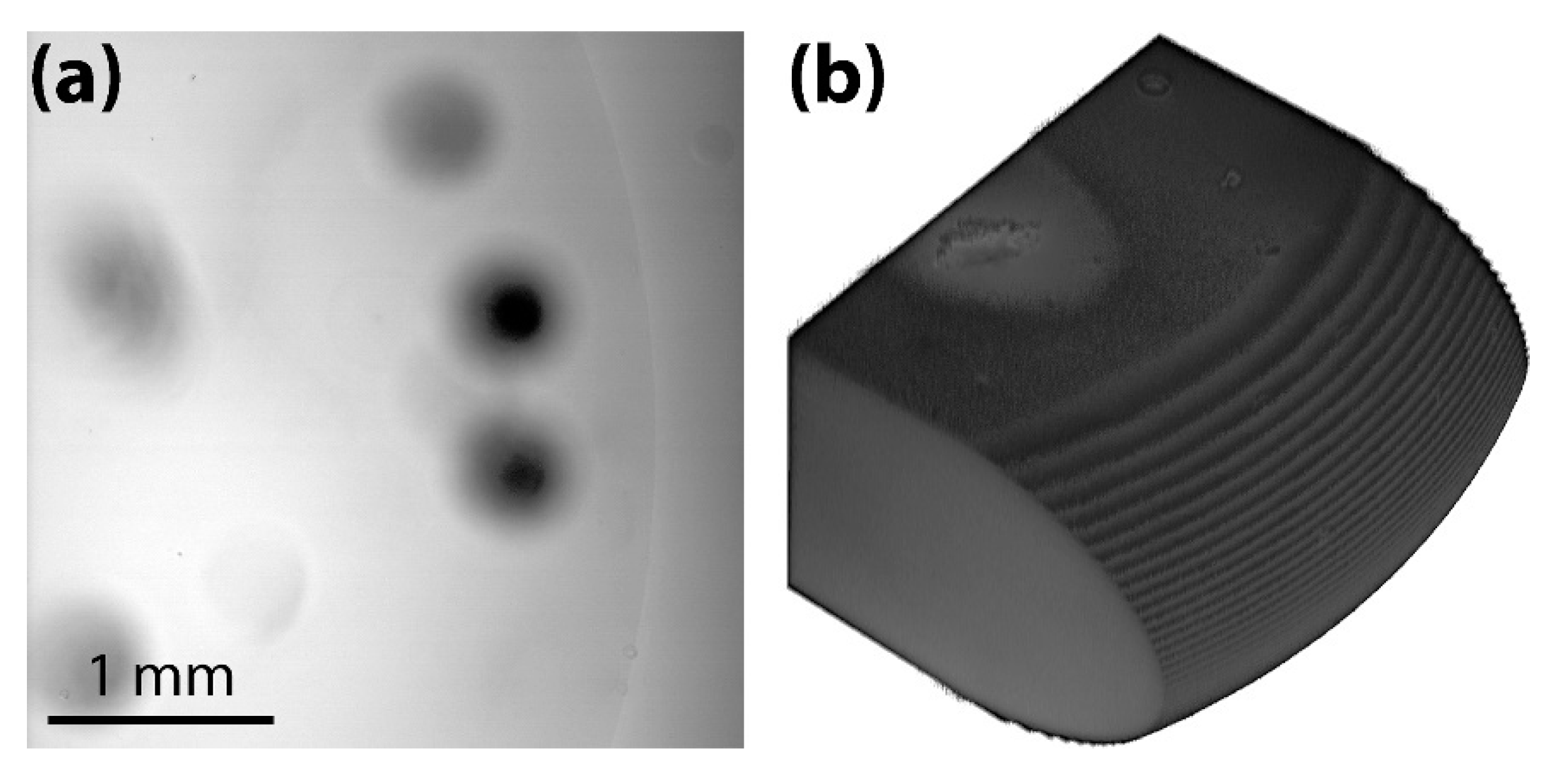
3.1. Brightfield Images: Dependence of the Dark Ring Width on Concentration
3.2. Confocal Images: The Thickness and Meniscus Profile of Drops
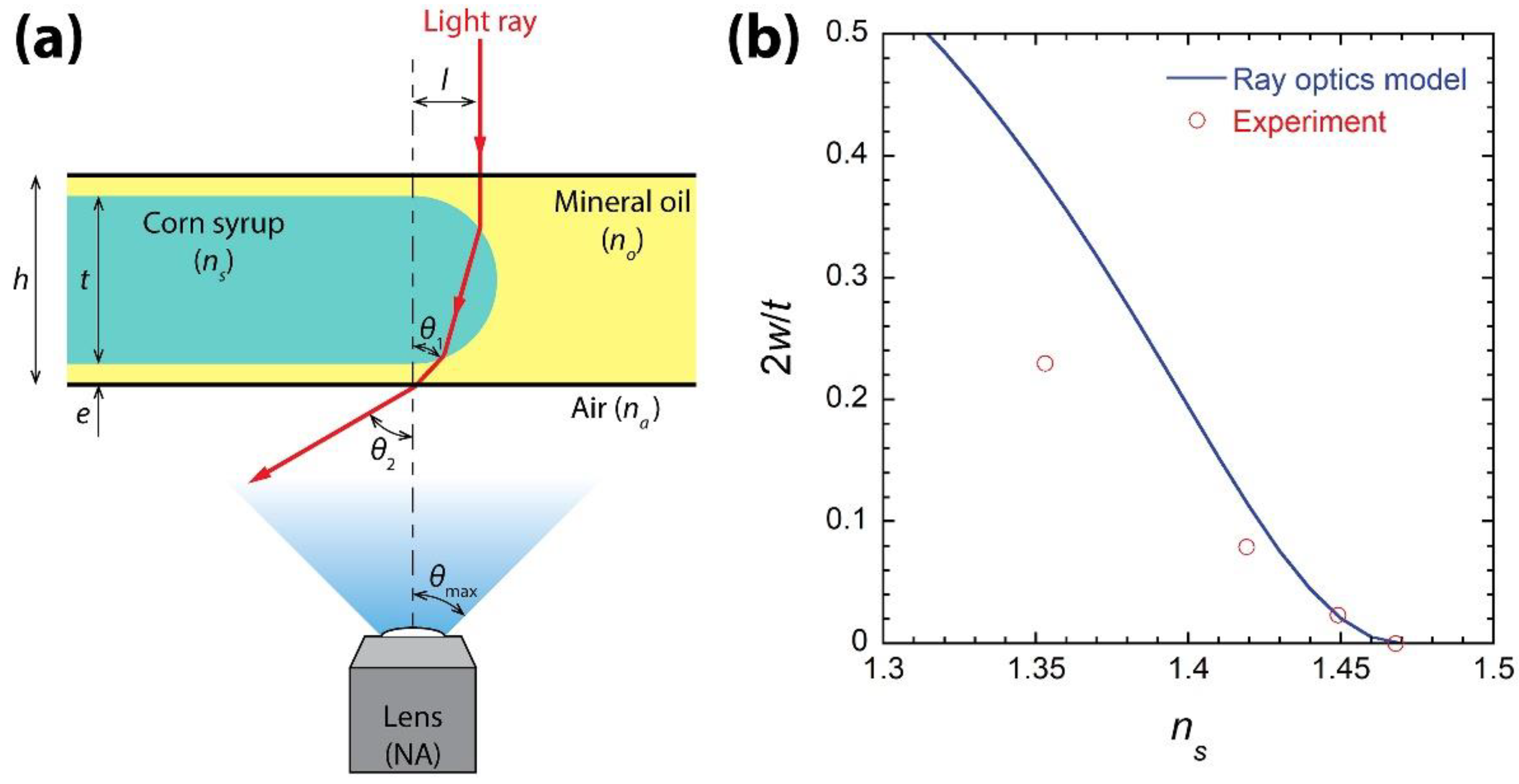
3.3. Ray Optics Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Gottberg, J.; Ryu, S. Contact angle measurement using a Hele-Shaw cell: A proof-of-concept study. Results Eng. 2021, 11, 100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, M.; Okumura, K. Dimensional crossover in the coalescence dynamics of viscous drops confined in between two plates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6395–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, M.; Okumura, K. Coalescence dynamics of a quasi two-dimensional viscous drop. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 81, SA015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Farinha, J.P.S.; Winnik, M.A.; Hahn, K.G. Characterization of oil droplets under a polymer film by laser scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy. Langmuir 2000, 16, 3391–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Amirfazli, A. Contact angle measurement for dispersed microspheres using scanning confocal microscopy. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2004, 25, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, K.K.; Gavriilidis, A.; Zapf, R.; Kost, H.-J.; Hessel, V.; Boyde, A. Characterisation of liquid film in a microstructured falling film reactor using laser scanning confocal microscopy. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2006, 30, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, M.; Månsson, A.; Tågerud, S. Contact angle measurements by confocal microscopy for non-destructive microscale surface characterization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 313, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, A.; Sausse, J.; Pironon, J.; Fourar, M.; De Veslud, C.L.C. 3D Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy to quantify contact angles in natural oil-water mixtures. Oil Gas Sci. Technol.-Rev. De L’ifp 2008, 63, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Xue, Y.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y.; Xi, P.; Lin, H.; Duan, H. Symmetric and asymmetric meniscus collapse in wetting transition on submerged structured surfaces. Langmuir 2015, 31, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmametov, A.; Gröger, R.; Hahn, H.; Schimmel, T.; Walheim, S. Bulk density measurements of small solid objects using laser confocal microscopy. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1600115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tress, M.; Karpitschka, S.; Papadopoulos, P.; Snoeijer, J.H.; Vollmer, D.; Butt, H., Jr. Shape of a sessile drop on a flat surface covered with a liquid flim. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 3760–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreder, M.J.; Daniel, D.; Tetreault, A.; Cao, Z.; Lemaire, B.; Timonen, J.V.I.; Aizenberg, J. Film dynamics and lubricant depletion by droplets moving on lubricated surfaces. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 031053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Srinivasan, V.; Wangaskar, B.; Khandekar, S. Dynamic evolution of an evaporating liquid meniscus from structured screen meshes. Transp. Porous Med. 2018, 121, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Pan, S.; Yi, B.; Ai, L.; Gao, J.; Mugele, F.; Yao, X. Wetting ridge assisted programmed magnetic actuation of droplets on ferrofluid-infused surface. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strombom, E.H.; Caicedo-Carvajal, C.E.; Thyagu, N.N.; Palumbo, D.; Shinbrot, T. Simple, simpler, simplest: Spontaneous pattern formation in a commonplace system. Am. J. Phys. 2012, 80, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, C.E. The measurement of surface tension by the pendant drop technique. J. Phys. Chem. 1965, 69, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- bin Mat Yunus, W.M.; bin Abdul Rahman, A. Refractive index of solutions at high concentrations. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 3341–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Segre, P.; Gammon, R.; Sengers, J.; Lamvik, M. Determination of the temperature and concentration dependence of the refractive index of a liquid mixture. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 5058–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-X. Dependence of refractive index on concentration and temperature in electrolyte solution, polar solution, nonpolar solution, and protein solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 2827–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Erickson, A.; You, T.; Dudley, A.T.; Ryu, S. Pneumatic microfluidic cell compression device for high-throughput study of chondrocyte mechanobiology. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Zhou, Y.; Ryu, S. Three-dimensional confocal microscopy indentation method for hydrogel elasticity measurement. Langmuir 2015, 31, 9684–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasa, I.A. Circle fitting procedure and its error analysis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1976, 25, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolganov, P.V.; Zverev, A.S.; Baklanova, K.D.; Dolganov, V.K. Dynamics of capillary coalescence and breakup: Quasi-two-dimensional nematic and isotropic droplets. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 104, 014702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolganov, P.V.; Zverev, A.S.; Baklanova, K.D.; Dolganov, V.K. Quasi-two-dimensional coalescence of nematic and isotropic droplets and Rayleigh–Plateau instability in flat optical cells. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohn, A.; Roth, N. Dynamics of Droplets; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht, E. Optics, 4th ed.; Addison Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]


| Liquid | Density (g/cm3) | Surface Tension Coefficient (mN/m) | Refractive Index (-) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral oil | 0.87 | - | 1.467 |
| Corn syrup (18% w/w) | 1.04 | 39.2 ± 0.7 | 1.353 |
| Corn syrup (67% w/w) | 1.26 | 41.1 ± 1.2 | 1.421 |
| Corn syrup (82% w/w) | 1.31 | 40.0 ± 0.3 | 1.445 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, S.; Zhang, H.; Emeigh, C. The Dark Annulus of a Drop in a Hele-Shaw Cell Is Caused by the Refraction of Light through Its Meniscus. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071021
Ryu S, Zhang H, Emeigh C. The Dark Annulus of a Drop in a Hele-Shaw Cell Is Caused by the Refraction of Light through Its Meniscus. Micromachines. 2022; 13(7):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071021
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Sangjin, Haipeng Zhang, and Carson Emeigh. 2022. "The Dark Annulus of a Drop in a Hele-Shaw Cell Is Caused by the Refraction of Light through Its Meniscus" Micromachines 13, no. 7: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071021
APA StyleRyu, S., Zhang, H., & Emeigh, C. (2022). The Dark Annulus of a Drop in a Hele-Shaw Cell Is Caused by the Refraction of Light through Its Meniscus. Micromachines, 13(7), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071021






