Thiourea-Isocyanate-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Tunable Surface Charge and Surface Area for Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange Removal from Aqueous Media
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
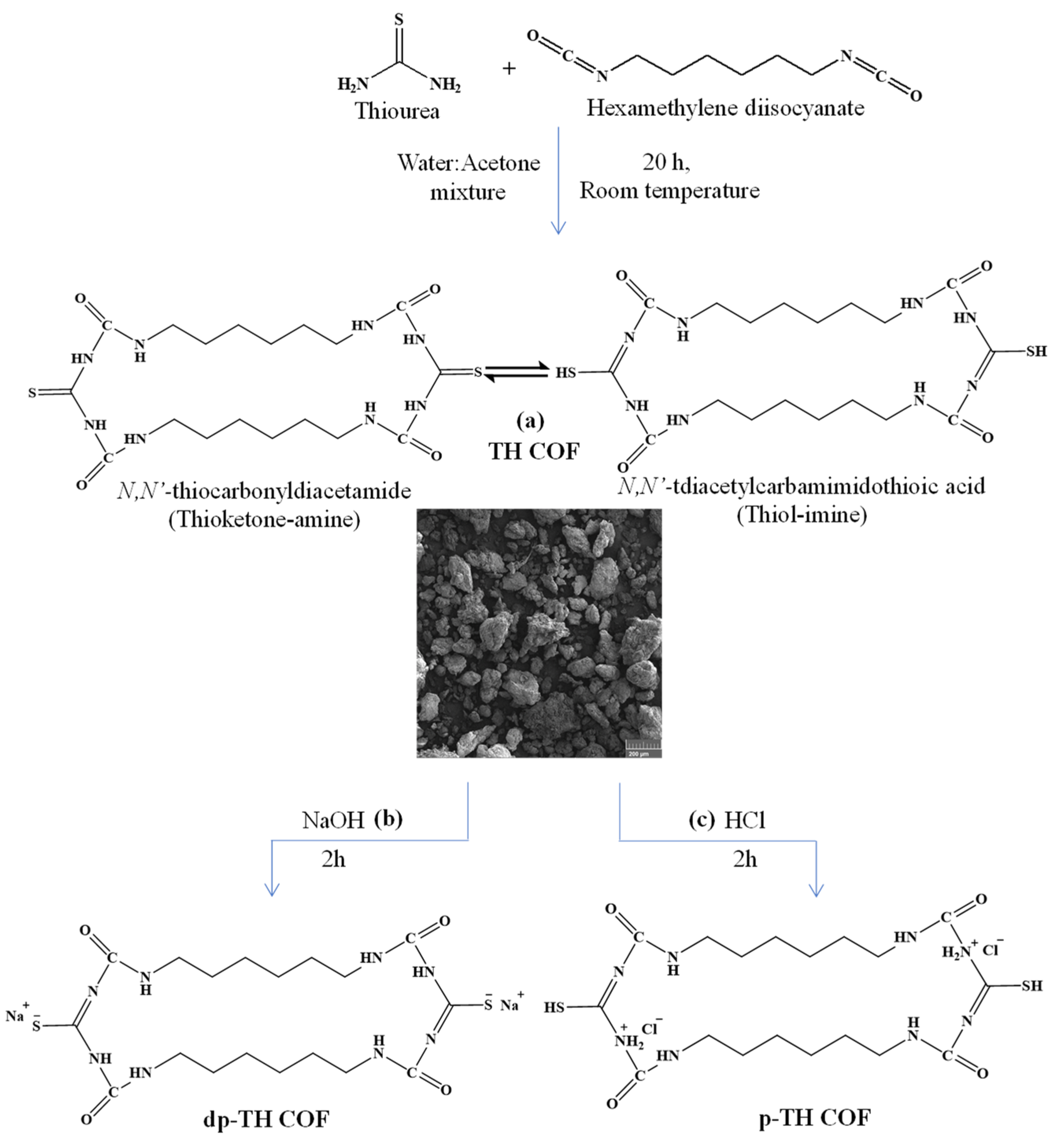
2.2. Synthesis of TH-Based COFs
2.3. Characterization of TH-Based COFs
2.4. Absorption Study
2.5. Absorption Isotherms and Kinetics
2.6. Distribution, Selectivity, and Relative Selectivity Coefficients
2.7. Reusability of dp-TH and p-TH COFs
3. Results and Discussion
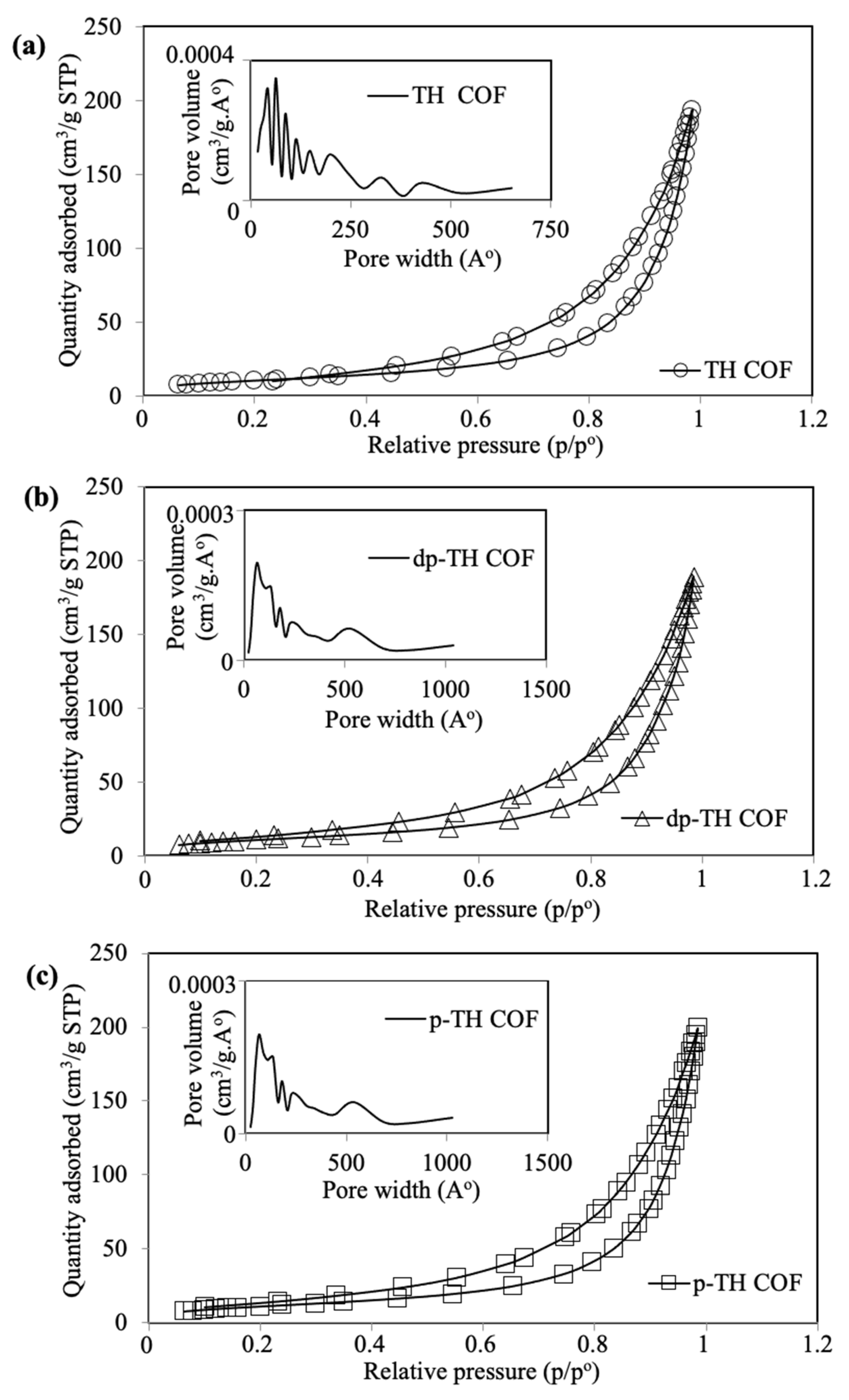
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of TH-Based COFs
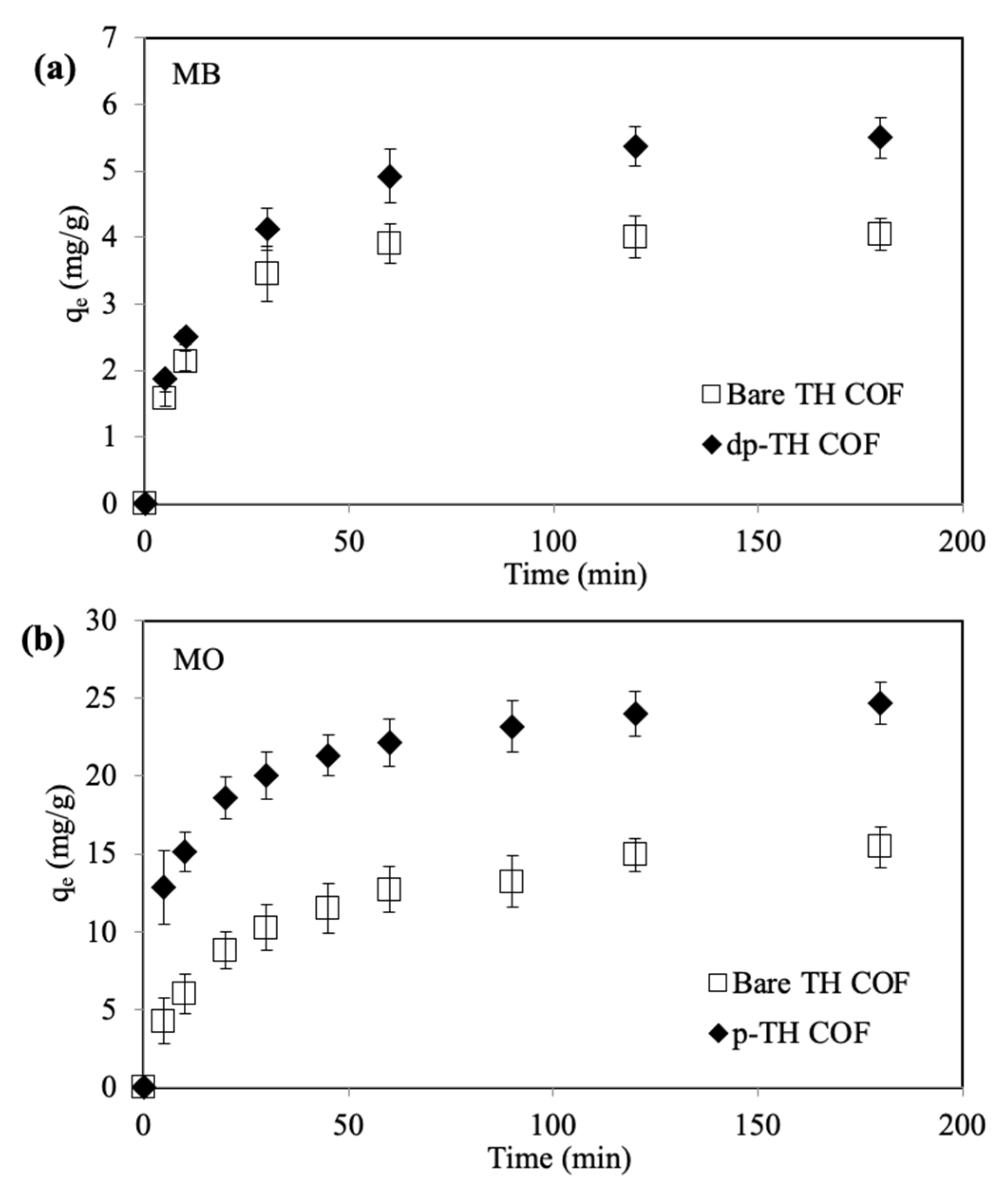
3.2. MB and MO Absorption
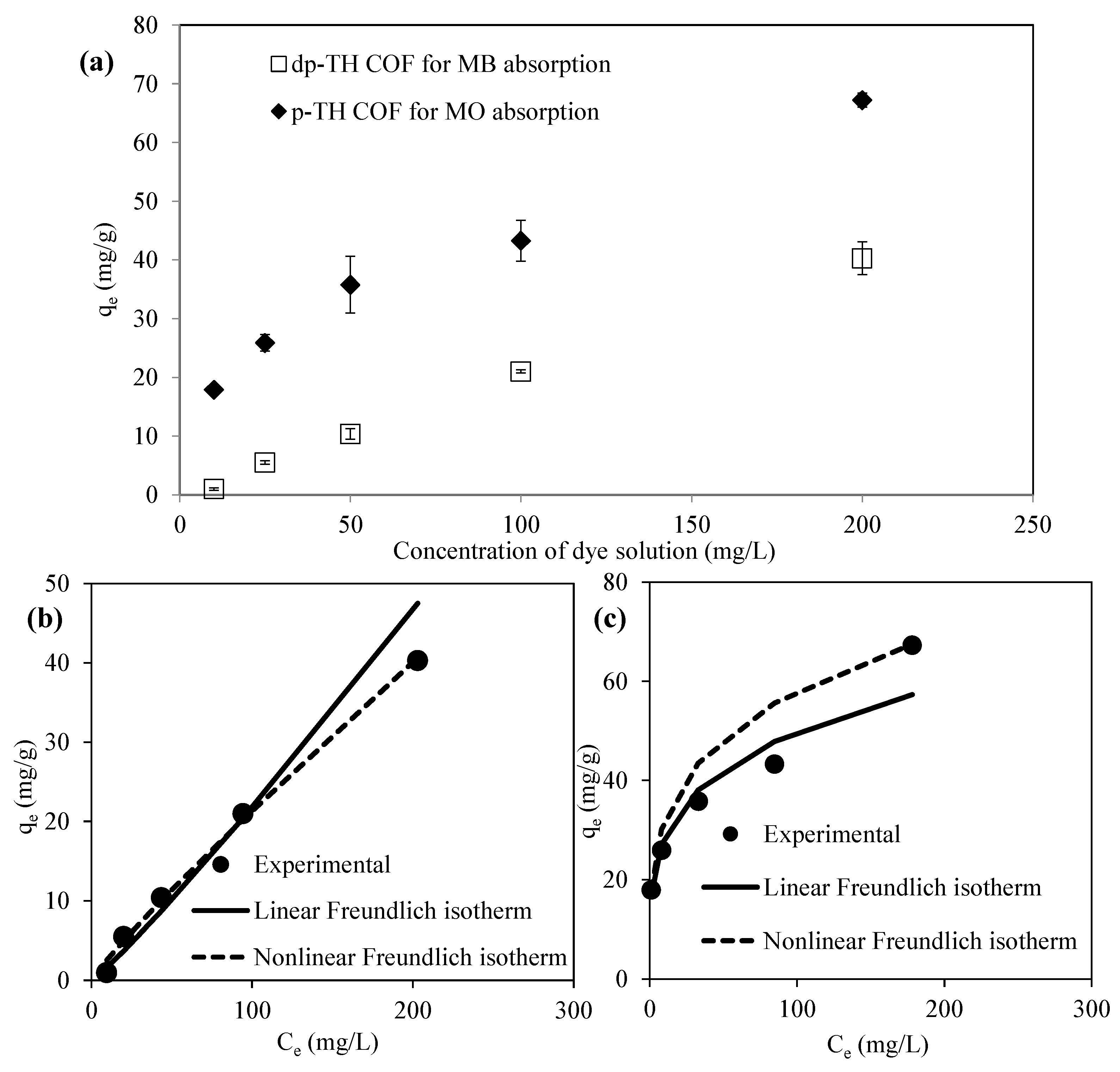
3.3. Absorption Isotherms
3.4. Absorption Kinetics
3.5. Determination of Absorption Coefficients
3.6. Reusabilities of dp-TH and p-TH COFs for MB and MO Absorption
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, V.K.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Ribeiro Carrott, M.M.L. Suhas Low-Cost Adsorbents: Growing Approach to Wastewater Treatment—A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 783–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Tanaka, M. Impacts of pollution on coastal and marine ecosystems including coastal and marine fisheries and approach for management: A review and synthesis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 624–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfahani, M.R.; Aktij, S.A.; Dabaghian, Z.; Firouzjaei, M.D.; Rahimpour, A.; Eke, J.; Escobar, I.C.; Abolhassani, M.; Greenlee, L.F.; Esfahani, A.R.; et al. Nanocomposite membranes for water separation and purification: Fabrication, modification, and applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 465–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, J.; Murthy, Z.V.P. Treatment of textile dyes containing wastewaters with PES/PVA thin film composite nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 183, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.B.; Vakili, M.; Horri, B.A.; Poh, P.E.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Salamatinia, B. Adsorption of dyes by nanomaterials: Recent developments and adsorption mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgariu, L.; Escudero, L.B.; Bello, O.S.; Iqbal, M.; Nisar, J.; Adegoke, K.A.; Alakhras, F.; Kornaros, M.; Anastopoulos, I. The utilization of leaf-based adsorbents for dyes removal: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 728–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reza, K.M.; Kurny, A.; Gulshan, F. Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karimifard, S.; Alavi Moghaddam, M.R. Application of response surface methodology in physicochemical removal of dyes from wastewater: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 772–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooto, N.D.; Thabede, P.M.; Bhila, B.; Moloto, H.; Naidoo, E.B. Lead ions and methylene blue dye removal from aqueous solution by mucuna beans (velvet beans) adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, K.; Raza, R.; Shezad, N.; Shabir, M.; Yang, W.; Ahmad, N.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Razzaq, A.; Hussain, M. Development of recoverable magnetic mesoporous carbon adsorbent for removal of methyl blue and methyl orange from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, A.M.; Vafaei, A. Applications of artificial neural networks for adsorption removal of dyes from aqueous solution: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 245, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Yahyaoui, S.; Hanafy, H.; Seliem, M.K.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Luiz Dotto, G.; Sellaoui, L.; Li, Q. Effective adsorption of dyes on an activated carbon prepared from carboxymethyl cellulose: Experiments, characterization and advanced modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Salomón, Y.L.O.; Georgin, J.; Franco, D.S.P.; Netto, M.S.; Foletto, E.L.; Allasia, D.; Dotto, G.L. Application of seed residues from Anadenanthera macrocarpa and Cedrela fissilis as alternative adsorbents for remarkable removal of methylene blue dye in aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2342–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, P.; Buckingham, P.; Holden, B.; Jefferson, B. Low energy ballasted flotation. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3427–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cote, A.P.; Côté, A.P.; Benin, A.I.; Ockwig, N.W.; O’Keeffe, M.; Matzger, A.J.; Yaghi, O.M. Porous, Crystalline, Covalent Organic Frameworks. Science 2005, 310, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.-Y.Y.; Wang, W. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs): From design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 548–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, P.J.; Gándara, F.; Yaghi, O.M. Chemistry of Covalent Organic Frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 3053–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.-B.B. Crystallization of Covalent Organic Frameworks for Gas Storage Applications. Molecules 2017, 22, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Gao, J.; Lin, J.; Addicoat, M.; Irle, S.; Jiang, D. Catalytic covalent organic frameworks via pore surface engineering. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1292–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Demirci, S.; Sel, K. Covalent organic framework based on melamine and dibromoalkanes for versatile use. J. Porous Mater. 2016, 23, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Tang, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xia, C.; Wang, C.; Hu, W. Constructing Universal Ionic Sieves via Alignment of Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs). Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 16304–16308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q. Recent progress in two-dimensional COFs for energy-related applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 14463–14479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Demirci, S. The use of covalent organic frameworks as template for conductive polymer synthesis and their sensor applications. J. Porous Mater. 2019, 26, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Phua, S.Z.F.; Lim, W.Q.; Jana, A.; Luo, Z.; Tham, H.P.; Zhao, L.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Nanoscale covalent organic frameworks as smart carriers for drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 4128–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdellah, A.R.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; El-Adasy, A.B.A.A.M.; Atalla, A.A.; Aly, K.I. One-pot synthesis of hierarchical porous covalent organic frameworks and two-dimensional nanomaterials for selective removal of anionic dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinari, M.; Hatami, M. Novel N-riched crystalline covalent organic framework as a highly porous adsorbent for effective cadmium removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.X.; Yang, Y.W. Applications of covalent organic frameworks (COFs): From gas storage and separation to drug delivery. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, H.; Mathe, S.D.R.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. Covalent organic frameworks: From materials design to biomedical application. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Xia, L.; Liu, X. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs): Perspectives of industrialization. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 1613–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.C.; Cheetham, A.K. Mechanical properties of hybrid inorganic–organic framework materials: Establishing fundamental structure–property relationships. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1059–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, P.; Antonietti, M.; Thomas, A. Porous, covalent triazine-based frameworks prepared by ionothermal synthesis. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3450–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdaoui, O.; Naffrechoux, E. Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chlorophenols onto granular activated carbonPart I. Two-parameter models and equations allowing determination of thermodynamic parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fil, B.A.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Bayar, S.; Elkoca, M.T. Investigation of adsorption of the dyestuff astrazon red violet 3rn (basic violet 16) on montmorillonite clay. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habeeb, O.A.; Ramesh, K.; Ali, G.A.M.; Yunus, R.M.; Olalere, O.A. Kinetic, Isotherm and Equilibrium Study of Adsorption Capacity of Hydrogen Sulfide-Wastewater System Using Modified Eggshells. IIUM Eng. J. 2017, 18, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Burleigh, M.C.; Ju, Y.H.; Gao, H.J.; Lin, J.S.; Pennycook, S.J.; Barnes, C.E.; Xue, Z.L. Hierarchically imprinted sorbents for the separation of metal ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 992–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Say, R.; Ersöz, A.; Türk, H.; Denizli, A. Selective separation and preconcentration of cyanide by a column packed with cyanide-imprinted polymeric microbeads. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 40, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenabeele-Trambouze, O.; Mion, L.; Garrelly, L.; Commeyras, A. Reactivity of organic isocyanates with nucleophilic compounds: Amines; alcohols; thiols; oximes; and phenols in dilute organic solutions. Adv. Environ. Res. 2001, 6, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent-Rocan, J.-F.; Ivanovich, R.A.; Clavette, C.; Leckett, K.; Bejjani, J.; Beauchemin, A.M. Cascade reactions of nitrogen-substituted isocyanates: A new tool in heterocyclic chemistry. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardini, J.; Licursi, D.; Anguillesi, I.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Antonetti, C.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M.; Lazzeri, A. Exploitation of Arundo donax L. Hydrolysis Residue for the Green Synthesis of Flexible Polyurethane Foams. BioResources 2017, 12, 3630–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otálora, A.; Lerma, T.A.; Palencia, M. Synthesis and characterization of polurea-based Hydrogels by Multicomponent Polycondensation of 1,6-Hexamethylenediisocyanate, sorbitol and cysteine. J. Sci. Technol. Appl. 2019, 7, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, J.S.; Cardoso, E.S.; Triboni, E.R.; Politi, M.J. Polyureas Versatile Polymers for New Academic and Technological Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharmin, E.; Zafar, F. Polyurethane: An Introduction. In Polyurethane, 1st ed.; Zafar, F., Sharmin, E., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristiani, F.; Devillanova, F.A.; Diaz, A.; Verani, G. Infrared vibrations of carbon—sulphur bonds in bis(benzoxazole-, benzoimidazole-benzothiazole-2-thiol)methane. Assignments by “selenation”. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Spectrosc. 1983, 39, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Fermin, D.J.; Chaudhuri, T.K.; Ray, A. Solution Processed Bismuth Ferrite Thin Films for All-Oxide Solar Photovoltaics. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 5872–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, M.; Madhurambal, G.; Ravindran, B.; Mojumdar, S.C. Thermal, FTIR and microhardness studies of bisthiourea-urea single crystal. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 104, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttersack, C. Modeling of type IV and v sigmoidal adsorption isotherms. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 5614–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halsey, G.D. The role of heterogeneity in adsorption and catalysis. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1950, 8, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.W.; Chakravorti, R.K. Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed‐bed adsorbers. AIChE J. 1974, 20, 228–238. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, M.; Mertens, S.F.; Ghorbani, M.; Arshadi, M.R. Asymmetrical Schiff bases as inhibitors of mild steel corrosion in sulphuric acid media. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 78, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günay, A.; Arslankaya, E.; Tosun, İ. Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dye | Materials | Exp. | Pseudo-First-Order-Model | Pseudo-Second-Order-Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mg/g) | k1 (1/min) | Qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (1/min) | Qe (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| MB | dp-TH COF | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 0.03 | 4.2 | 0.982 | 0.01 | 5.9 | 0.999 |
| MO | p-TH COF | 24 ± 1 | 0.03 | 13.3 | 0.935 | 0.005 | 25.5 | 0.999 |
| Dye | Kd (TH) | Kd (dp-TH) | Kd (p-TH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MB | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.003 ± 0.0006 |
| MO | 0.50 ± 0.09 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 1.32 ± 0.15 |
| k (TH) | k (dp-TH) | k (p-TH) | |
| MB | 0.19 ± 0.06 | 1.27 ± 0.64 | 0.002 ± 0.0005 |
| MO | 5.57 ± 2.06 | 0.93 ± 0.44 | 463 ± 98 |
| kı (dp-TH/TH) | kı (p-TH/TH) | kı (p-TH/dp-TH) | |
| MB | 6.45 ± 2.25 | 0.01 ± 0.003 | 0.002 ± 0.0009 |
| MO | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 87.9 ± 26 | 599 ± 385 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suner, S.S.; Demirci, S.; Sutekin, D.S.; Yilmaz, S.; Sahiner, N. Thiourea-Isocyanate-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Tunable Surface Charge and Surface Area for Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange Removal from Aqueous Media. Micromachines 2022, 13, 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13060938
Suner SS, Demirci S, Sutekin DS, Yilmaz S, Sahiner N. Thiourea-Isocyanate-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Tunable Surface Charge and Surface Area for Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange Removal from Aqueous Media. Micromachines. 2022; 13(6):938. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13060938
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuner, Selin S., Sahin Demirci, Duygu S. Sutekin, Selehattin Yilmaz, and Nurettin Sahiner. 2022. "Thiourea-Isocyanate-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Tunable Surface Charge and Surface Area for Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange Removal from Aqueous Media" Micromachines 13, no. 6: 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13060938
APA StyleSuner, S. S., Demirci, S., Sutekin, D. S., Yilmaz, S., & Sahiner, N. (2022). Thiourea-Isocyanate-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Tunable Surface Charge and Surface Area for Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange Removal from Aqueous Media. Micromachines, 13(6), 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13060938







