A Hydrogel-Based Self-Sensing Underwater Actuator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
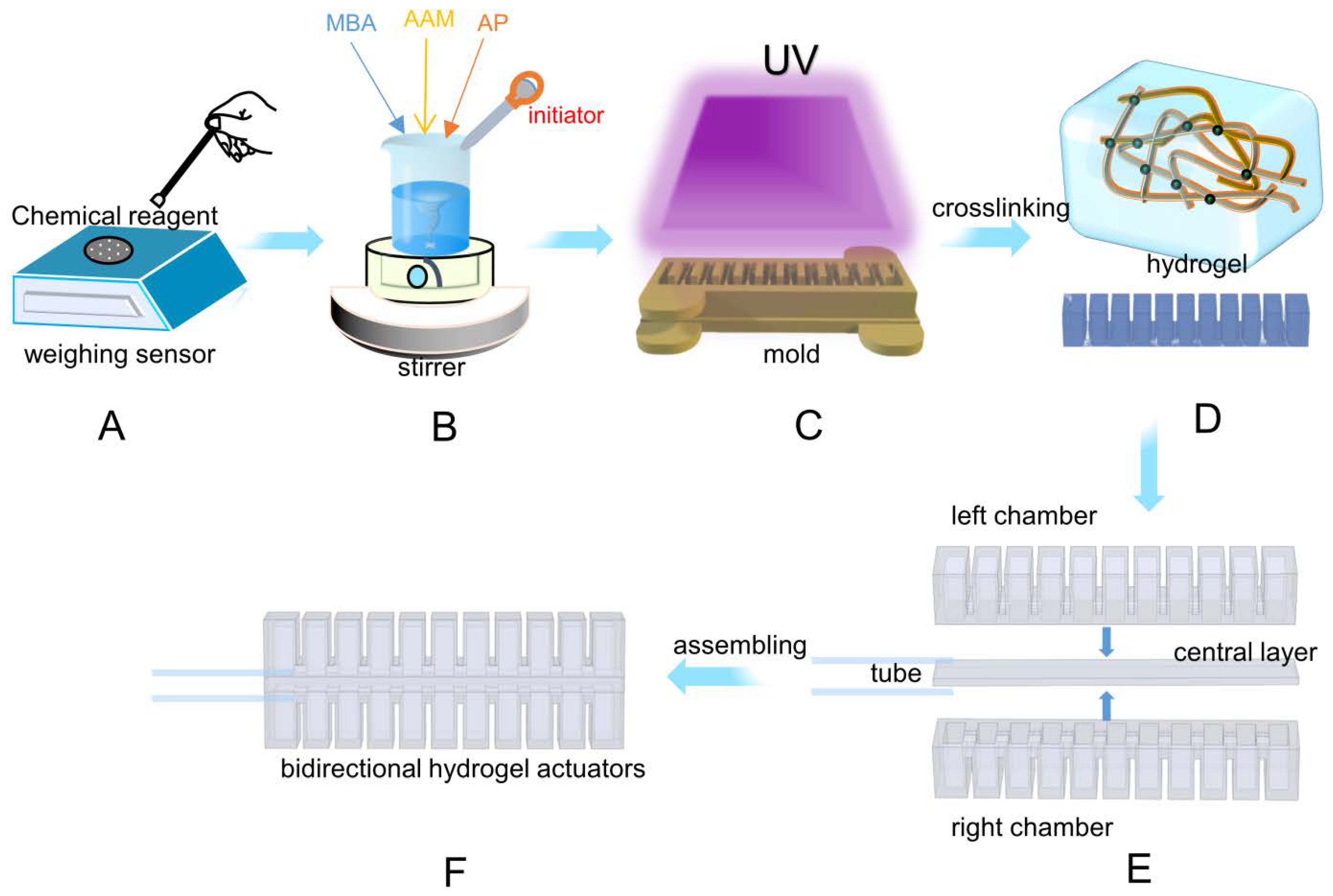
2.2. Fabrication of Hydraulic Hydrogel Actuators
2.3. Mechanical Properties and Test Methods of Hydrogels
2.4. Experimental Platform Setup
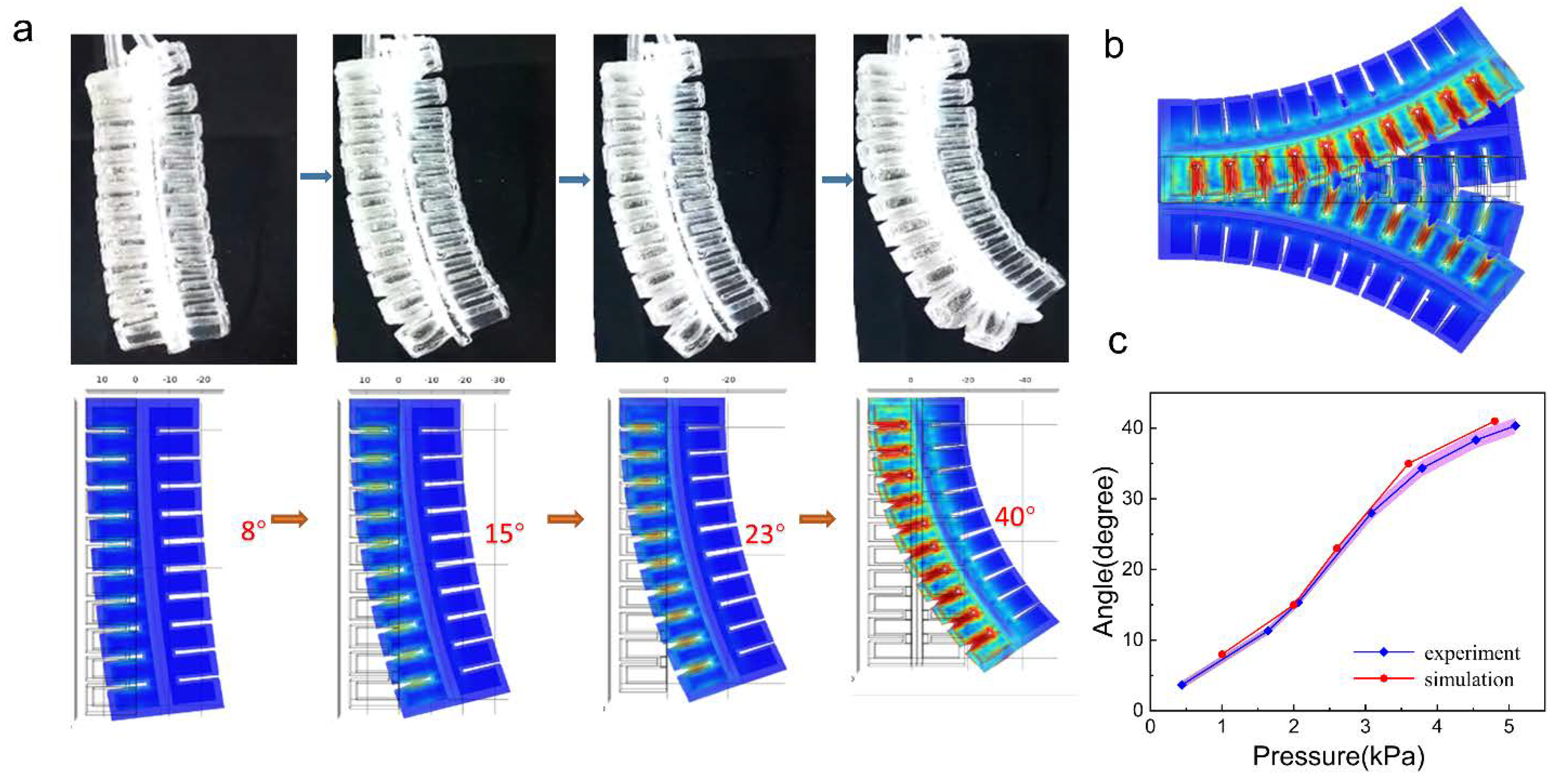
2.5. Finite-Element Analysis (FEA) Simulation
3. Results
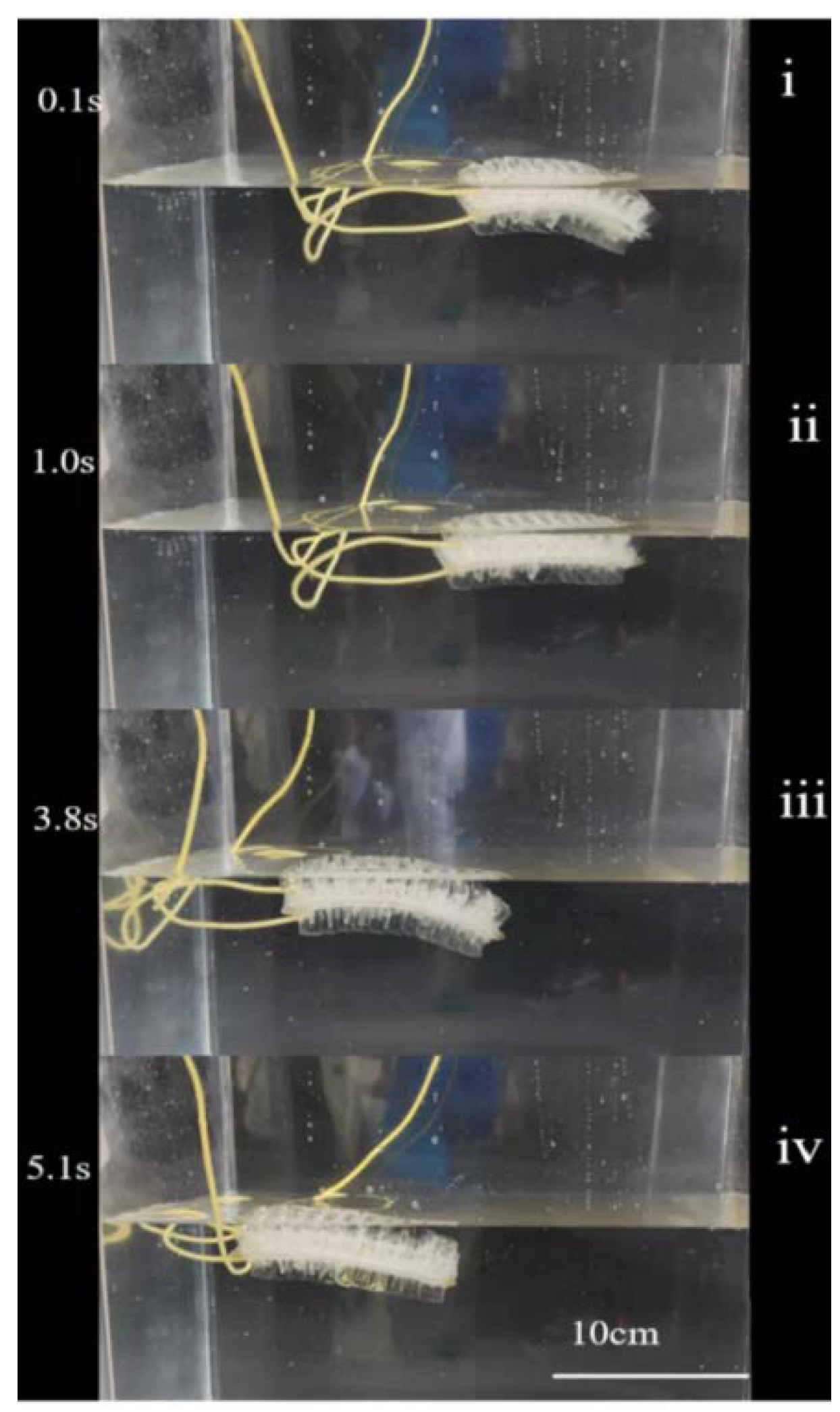
3.1. Characteristics of Actuation
3.2. Self-Sensing Characterization
3.3. Dynamic System Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katzschmann, R.K.; DelPreto, J.; MacCurdy, R.; Rus, D. Exploration of underwater life with an acoustically controlled soft robotic fish. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaar3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.S.X.; Lum, G.Z. Untethered Soft Robots for Future Planetary Explorations? Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 2100106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionov, L. Hydrogel-based actuators: Possibilities and limitations. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, B.; Yin, S.; et al. Self-powered soft robot in the Mariana Trench. Nature 2021, 591, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleau, E.; Morales, D.; Dickey, M.D.; Velev, O.D. Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuk, H.; Lin, S.; Ma, C.; Takaffoli, M.; Fang, N.X.; Zhao, X. Hydraulic hydrogel actuators and robots optically and sonically camouflaged in water. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Song, W.J.; Sun, J.Y. Hydrogel soft robotics. Mater. Today Phys. 2020, 15, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Liu, M.; Ishida, Y.; Ebina, Y.; Osada, M.; Sasaki, T.; Hikima, T.; Takata, M.; Aida, T. Thermoresponsive actuation ena-bled by permittivity switching in an electrostatically anisotropic hydrogel. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Le, X.; Tang, X.; He, J.; Xiao, P.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, H.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. A Multiresponsive Anisotropic Hydrogel with Macroscopic 3D Complex Deformations. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8670–8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ren, K.; Yang, D.; Wei, J. Bilayer-type fluorescence hydrogels with intelligent response serve as temperature/pH driven soft actuators. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 255, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaso, K.; Takashima, Y.; Harada, A. Fast response dry-type artificial molecular muscles with [c2]daisy chains. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Liao, L. Multi-responsive hydrogel actuator with photo-switchable color changing behaviors. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 174, 108042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xuan, C.; Qian, X.; Alsaid, Y.; Hua, M.; Jin, L.; He, X. Soft phototactic swimmer based on self-sustained hydrogel oscillator. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, aax7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Farino, C.; Yang, C.; Scott, T.; Browe, D.; Choi, W.; Freeman, J.W.; Lee, H. Soft Robotic Manipulation and Locomotion with a 3D Printed Electroactive Hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17512–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, L.; Santaniello, T.; Yan, Y.; Lenardi, C.; Milani, P. Low-voltage electrically driven homeostatic hydrogel-based actuators for underwater soft robotics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Suo, Z. Hydrogel ionotronics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 6, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Correll, N.; Morin, S.A.; Mosadegh, B.; Onal, C.D.; Petersen, K.; Cianchetti, M.; Tolley, M.T.; Shepherd, R.F. Soft Robotics: Review of Fluid-Driven Intrinsically Soft Devices; Manufacturing, Sensing, Control, and Applications in Human-Robot Interaction. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh, B.; Polygerinos, P.; Keplinger, C.; Wennstedt, S.; Shepherd, R.F.; Gupta, U.; Shim, J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Pneumatic Networks for Soft Robotics that Actuate Rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 15, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Siddall, R.; Schwab, F.; Fukushima, T.; Banerjee, H.; Baek, Y.; Vogt, D.; Park, Y.-L.; Jusufi, A. Modeling and Control of a Soft Robotic Fish with Integrated Soft Sensing. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 2000244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xiong, C.; Liu, C.; Li, P.; Chen, Y. Fabrication and Dynamic Modeling of Bidirectional Bending Soft Actuator Integrated with Optical Waveguide Curvature Sensor. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerboni, G.; Diodato, A.; Ciuti, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. Feedback Control of Soft Robot Actuators via Commercial Flex Bend Sensors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Du, X. Intelligent Polymer-Based Bioinspired Actuators: From Monofunction to Multifunction. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuruthel, T.G.; Shih, B.; Laschi, C.; Tolley, M.T. Soft robot perception using embedded soft sensors and recurrent neural networks. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaav1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassian, R.; Nguyen, V.H.; Umrao, S.; Mahato, M.; Kim, J.; Porfiri, M.; Oh, I. Graphene Mesh for Self-Sensing Ionic Soft Actuator Inspired from Mechanoreceptors in Human Body. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zuo, L. A highly stretchable hydrogel sensor for soft robot multi-modal perception. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 113006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Majidi, C.; Gu, G. Cutaneous Ionogel Mechanoreceptors for Soft Machines, Physiological Sensing, and Amputee Prostheses. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homberg, B.S.; Katzschmann, R.K.; Dogar, M.R.; Rus, D. Robust proprioceptive grasping with a soft robot hand. Auton. Robot. 2019, 43, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truby, R.L.; Wehner, M.; Grosskopf, A.K.; Vogt, D.M.; Uzel, S.G.M.; Wood, R.J.; Lewis, J.A. Soft Somatosensitive Actuators via Embedded 3D Printing. Adv. Mater. 2018, 15, 1706383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaasik, F.; Must, I.; Baranova, I.; Põldsalu, I.; Lust, E.; Johanson, U.; Punning, A.; Aabloo, A. Scalable fabrication of ionic and capacitive laminate actuators for soft robotics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kim, C.; Alsaid, Y.; Khodambashi, R.; Peet, M.; Fisher, R.; Marvi, H.; Berman, S.; Aukes, D.; et al. Highly stretchable self-sensing actuator based on conductive photothermally-responsive hydrogel. Mater. Today 2021, 50, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Tan, W.; Yang, J.; Lin, D.; Liu, L. Electroactive Polymer-Based Soft Actuator with Integrated Functions of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Motion and Perception. Soft Robot. 2022; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lo, C.-Y.; Ruan, L.; Pi, C.-H.; Kim, C.; Alsaid, Y.; Frenkel, I.; Rico, R.; Tsao, T.-C.; He, X. Somatosensory actuator based on stretchable conductive photothermally responsive hydrogel. Sci. Robot. 2021, 53, d5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruusamäe, K.; Punning, A.; Aabloo, A.; Asaka, K. Self-Sensing Ionic Polymer Actuators: A Review. Actuators 2015, 4, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punning, A.; Kruusmaa, M.; Aabloo, A. A self-sensing ion conducting polymer metal composite (IPMC) actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 136, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preechayasomboon, P.; Rombokas, E. Sensuator: A Hybrid Sensor–Actuator Approach to Soft Robotic Proprioception Using Recurrent Neural Networks. Actuators 2021, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.J., III; Jones, B.A. Design and Kinematic Modeling of Constant Curvature Continuum Robots: A Review. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 1661–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renda, F.; Giorelli, M.; Calisti, M.; Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C. Dynamic Model of a Multibending Soft Robot Arm Driven by Cables. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Thuruthel, T.; Falotico, E.; Manti, M.; Pratesi, A.; Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C. Learning Closed Loop Kinematic Controllers for Continuum Manipulators in Unstructured Environments. Soft Robot. 2017, 3, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yin, J. Leveraging Monostable and Bistable Pre-Curved Bilayer Actuators for High-Performance Multitask Soft Robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzoni, M.; Piccoli, E.; Migliorini, L.; Milana, E.; Iberite, F.; Vannozzi, L.; Ricotti, L.; Gerges, I.; Milani, P.; Marano, C.; et al. Monolithic Three-Dimensional Functionally Graded Hydrogels for Bioinspired Soft Robots Fabrication. Soft Robot. 2021, 9, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yao, Y.-C.; Gao, J.-Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, P.; Sheng, L.; Liu, J. LM-Jelly: Liquid Metal Enabled Biomimetic Robotic Jellyfish. Soft Robot. 2022; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, C.; Goldberg, N.N.; Deheyn, D.D.; Cai, S.; Tolley, M.T. Translucent soft robots driven by frameless fluid electrode dielectric elastomer actuators. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Actuator Shape | Materials | Actuation Method | Speed and Frequency | Feedback Sensing | Modeling | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | Hydrogel | Hydraulic | 0.19 BL/s (1 Hz) | No | FEA | [6] |
| Fish | Dielectric elastomer | Voltage induced stress | 0.24 BL/s (1 Hz) | No | FEA | [4] |
| Jelly-fish | Hydrogel | Pneumatic | 0.65 BL/s (0.67 Hz) | No | FEA and linear approximation | [39] |
| Fish | Hydrogel | Electroresponse | 0.006 BL/s (0.3 Hz) | No | NA | [40] |
| Jelly-fish | Liquid metal | Electromagnetic response | 0.2 BL/s (1 Hz) | Yes | NA | [41] |
| Leptocephali | Dielectric elastomer | Voltage induced stress | 0.009 BL/s (0.33–0.5 Hz) | No | Analytical bending model | [42] |
| Octopus | Hydrogel | Photothermal response | 34.6°/s | Yes | NA | [30] |
| Fish | Silicone, eGaIn | Pneumatic | 0.8–1.2 Hz | Yes | data-driven lumped parameter model | [19] |
| Fish | Hydrogel | Hydraulic | 0.18 BL/s (1 Hz) | Yes | Differential equation and FEA | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Sun, Z.; Duan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Sha, X.; Yu, S.; Zuo, L. A Hydrogel-Based Self-Sensing Underwater Actuator. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101779
Wang S, Sun Z, Duan S, Zhao Y, Sha X, Yu S, Zuo L. A Hydrogel-Based Self-Sensing Underwater Actuator. Micromachines. 2022; 13(10):1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101779
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuyu, Zhaojia Sun, Shuaiyang Duan, Yuliang Zhao, Xiaopeng Sha, Shifeng Yu, and Lei Zuo. 2022. "A Hydrogel-Based Self-Sensing Underwater Actuator" Micromachines 13, no. 10: 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101779
APA StyleWang, S., Sun, Z., Duan, S., Zhao, Y., Sha, X., Yu, S., & Zuo, L. (2022). A Hydrogel-Based Self-Sensing Underwater Actuator. Micromachines, 13(10), 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101779







