Au Wire Ball Welding and Its Reliability Test for High-Temperature Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
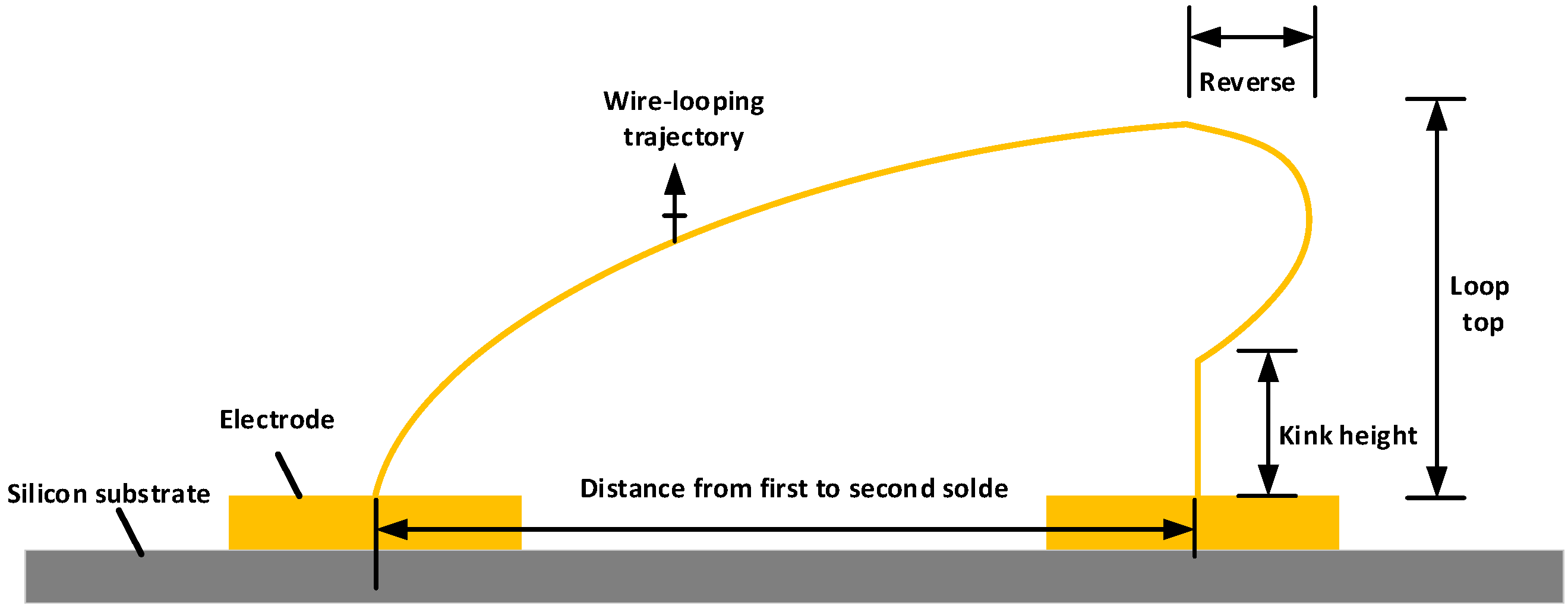
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
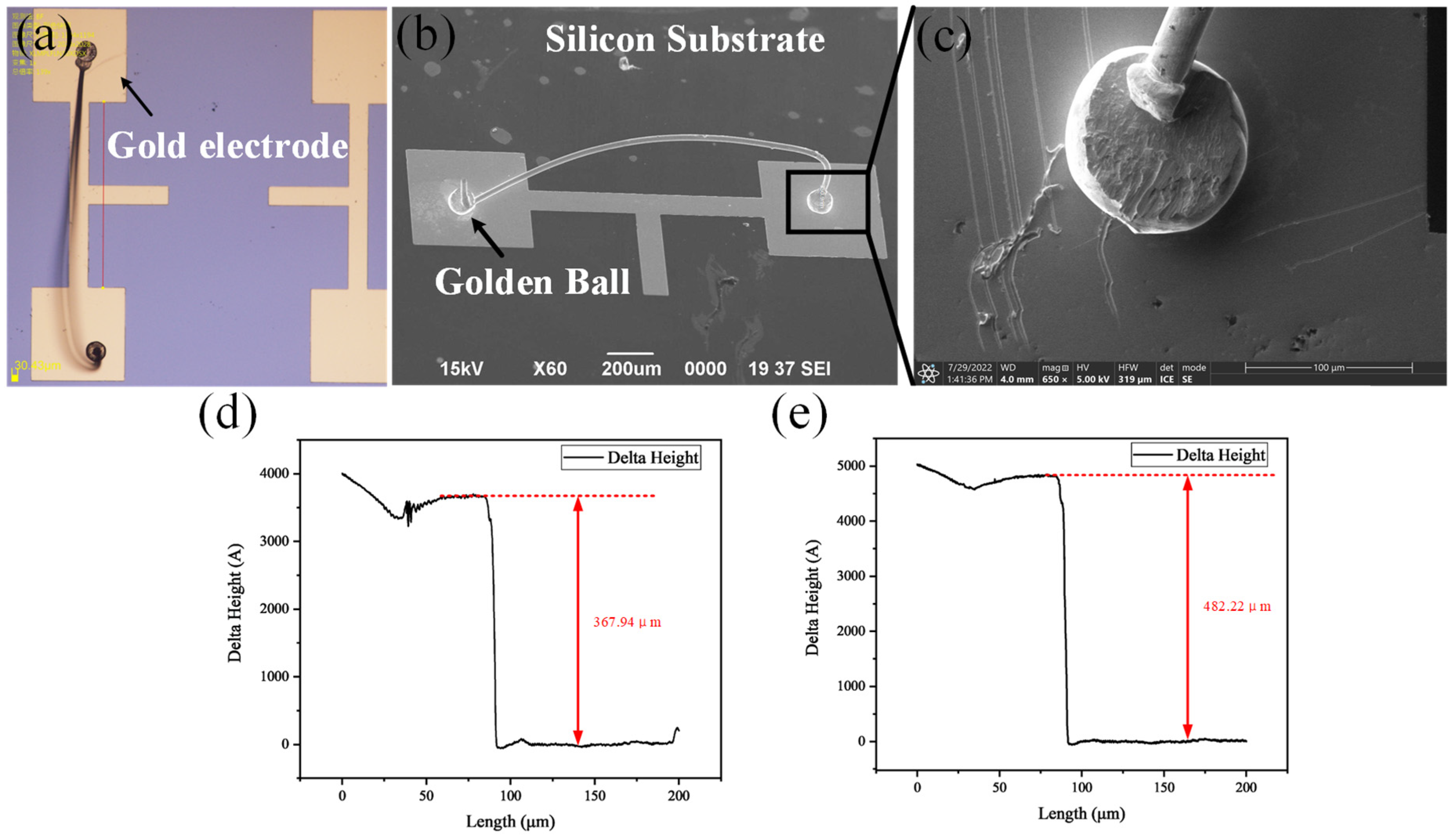
3.1. Bonding Result and Quality Test
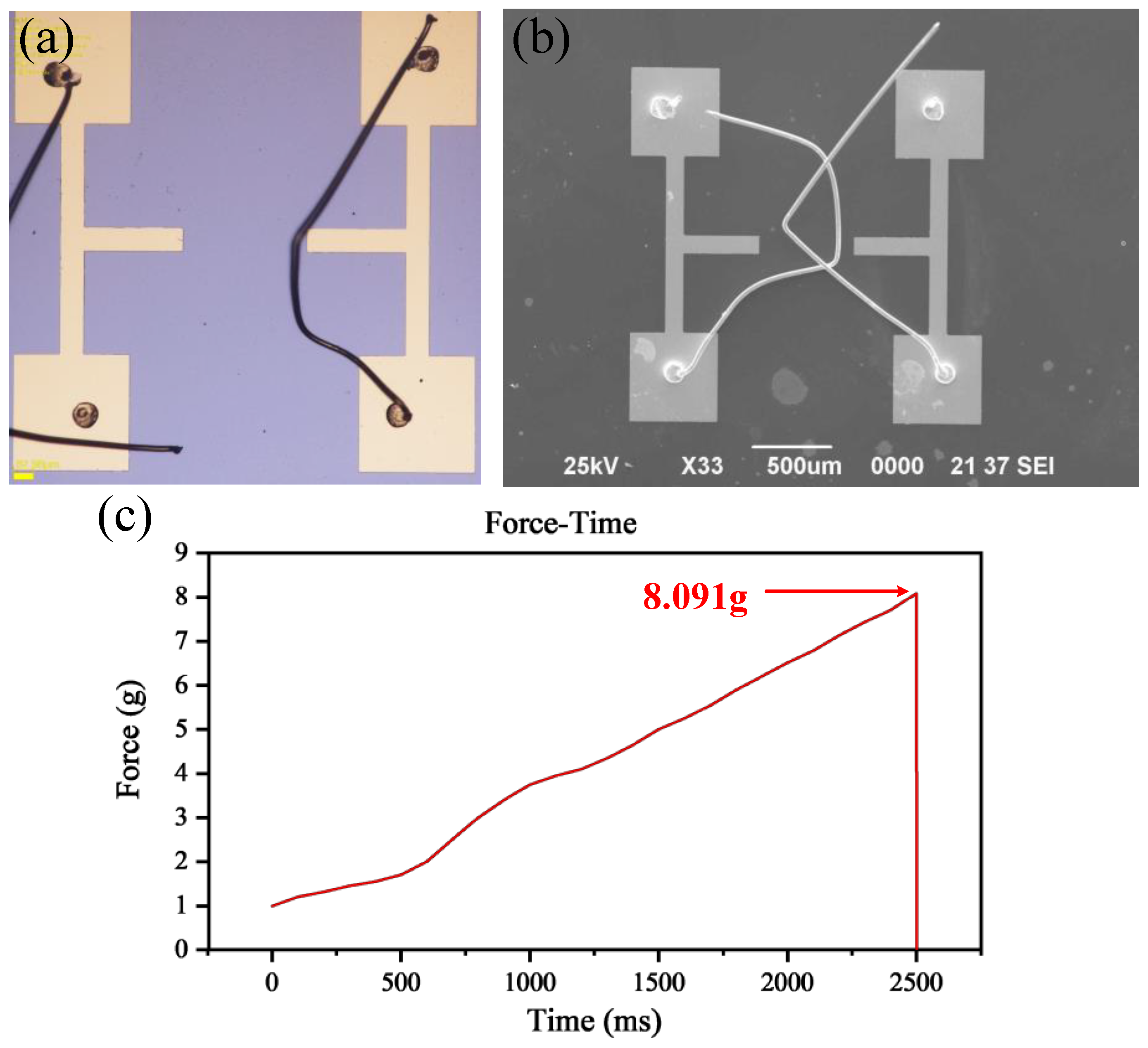
3.2. Testing of Mechanical Properties before High Temperature Annealing
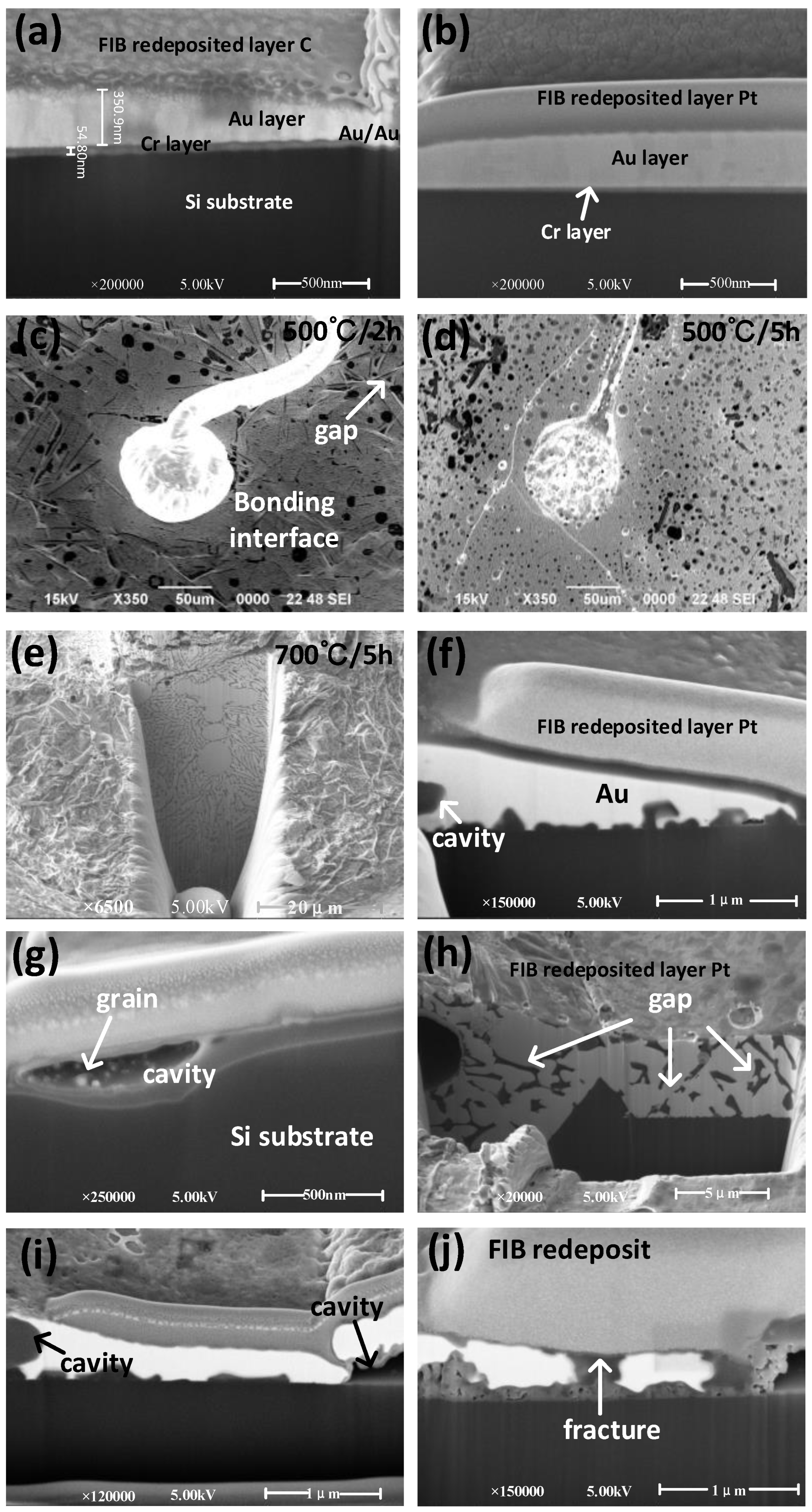
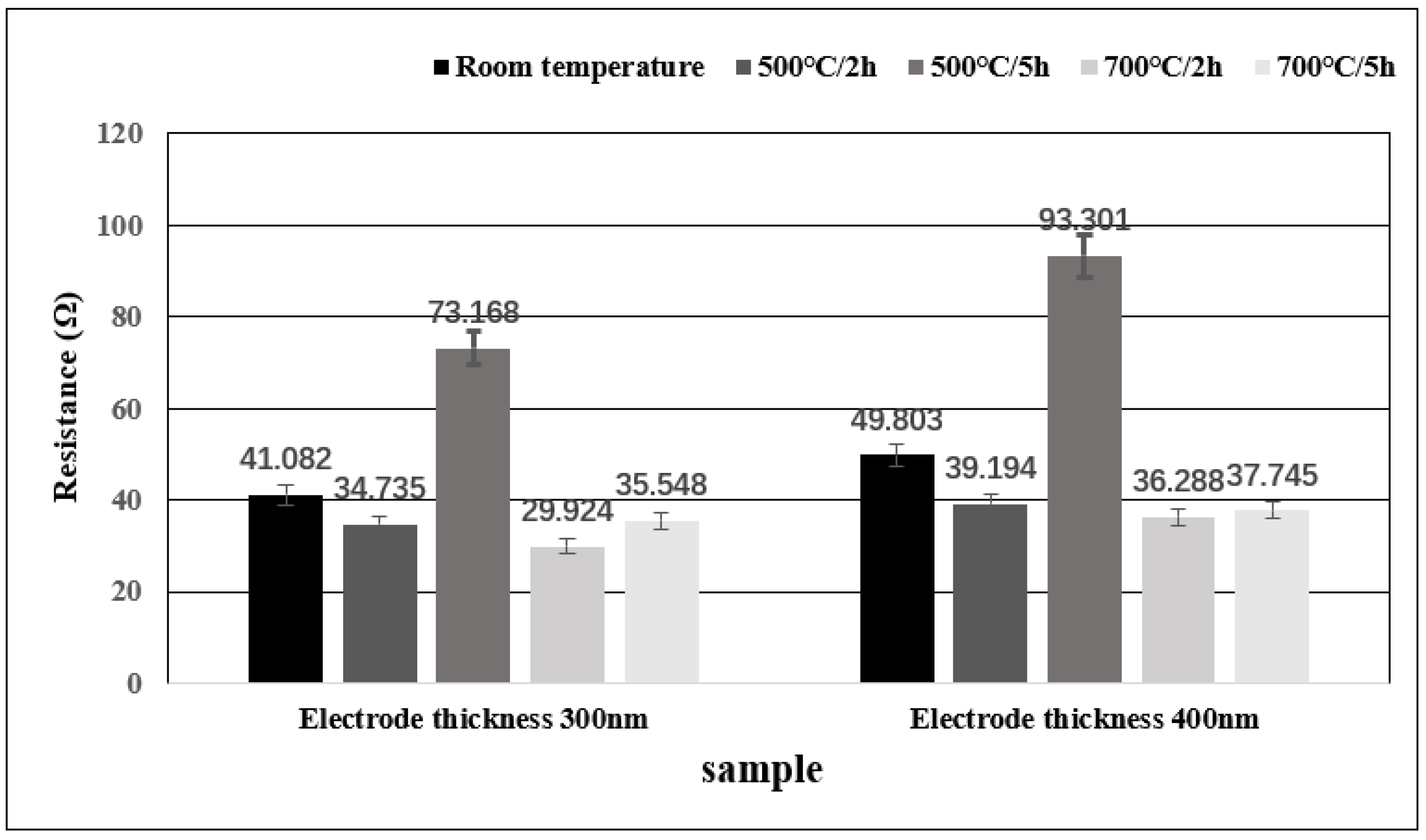
3.3. High-Temperature Reliability Test
3.4. Comparative Testing of Mechanical and Electrical Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, Y.; Xue, S.; Yang, Q.; Xiang, S.; He, H.; Zhu, R. A novel fiber Bragg grating high-temperature sensor. Opt.-Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2008, 119, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Z. A novel high temperature pressure sensor on the basis of SOI layers. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2003, 108, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yu, L.; Garcia, D.; Ren, R.X.; Zeng, X. Ionic liquid high-temperature gas sensor array. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6980–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.C.; Liao, K.H.; Udrea, F.; Covington, J.A.; Gardner, J.W. Multi-field simulations and characterization of CMOS-MEMS high-temperature smart gas sensors based on SOI technology. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 075010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Single-crystal sapphire-based optical high-temperature sensor for harsh environments. Opt. Eng. 2004, 43, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailov, S.J. Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors for Harsh Environments. Sensors 2012, 12, 1898–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, O.J.; You, T. Ceramic temperature sensors for harsh environments. IEEE Sens. J. 2005, 5, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, R.; Tang, X.; Burnett, A.; Lan, X.; Xiao, H.; Dong, J. Multilayer fiber optic sensors for in situ gas monitoring in harsh environments. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pufall, R. Automatic process control of wire bonding. In Proceedings of the IEEE 43rd Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC ’93), Orlando, FL, USA, 1–4 June 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, M.R.; Fahrner, W.R. Review on materials, microsensors, systems and devices for high-temperature and harsh-environment applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2001, 48, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikam, V.R.; Cheong, K.Y. Die Attach Materials for High Temperature Applications: A Review. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 1, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, D.; Chew, Y.H.; Goh, H.M.; Pasamanero, E.; Theint EP, P.; Calpito DR, M.; Ling, J. A Comparison Study of the Bondability and Reliability Performance of Au Bonding Wires with Different Dopant Levels. In Proceedings of the 2007 9th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference, Singapore, 10–12 December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- März, B.; Graff, A.; Klengel, R.; Petzold, M. Interface microstructure effects in Au thermosonic ball bonding contacts by high reliability wire materials. Microelectron. Reliab. 2014, 54, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, J.; Finot, E.; Thundat, T.; Fabre, A.; Nadal, M.H.; Eyraud, V.; Bourillot, E. Effects of temperature and pressure on microcantilever resonance response. Ultramicroscopy 2003, 97, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.F.; Guerreiro, A.; Baptista, J.M. Simultaneous Plasmonic Measurement of Refractive Index and Temperature Based on a D-Type Fiber Sensor with Gold Wires. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 2439–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, H.-W.; Hung, F.-Y.; Lui, T.-S.; Chen, L.-H. Microstructure, electric flame-off characteristics and tensile properties of silver bonding wires. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, N.; Murali, S.; Wong, Y.; Vath, C.J. Critical study of thermosonic copper ball bonding. Thin Solid Film. 2004, 462, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, B.; Knecht, S.; Handy, H.; Ramirez, J. The effect of ultrasonic frequency on fine pitch aluminum wedge wirebond. In Proceedings of the 1996 Proceedings 46th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 28–31 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zulkifli, M.N.; Harun, F.; Jalar, A. Effect of surface roughness and hardness of leadframe on the bondability of gold wedge bonds. Microelectron. Int. 2019, 36, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, I.; Mayer, M.; Zhou, Y. Footprint study of ultrasonic wedge-bonding with aluminum wire on copper substrate. J. Electron. Mater. 2006, 35, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, C.; Song, W.; Lum, I.; Mayer, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Moon, J.; Persic, J. Effect of electronic flame off parameters on copper bonding wire: Free-air ball deformability, heat affected zone length, heat affected zone breaking force. Microelectron. Eng. 2009, 86, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Mayer, M.; Zhou, N.; Persic, J. Microelectronic Wire Bonding with Insulated Au Wire: Effects of Process Parameters on Insulation Removal and Crescent Bonding. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 2347–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Du, L.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q. Annealing effect on the stability of platinum thin films covered by SiO2 or SiNx layer. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Suzhou, China, 7–10 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.-C.; Li, B.; Baumann, F.H.; Li, J.; Edelstein, D.; Rosenberg, R. Microstructure Modulation in Copper Interconnects. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2014, 35, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Li, B.; Edelstein, D.; Rosenberg, R. Effects of Metal Capping on Thermal Annealing of Copper Interconnects. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2012, 33, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupina, L.; Miclea, C.; Amarande, L.; Cioangher, M. Growth of highly oriented iridium oxide bottom electrode for Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 thin films using titanium oxide seed layer. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 6830–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffino, F.; Romano, L.; Pitruzzello, G.; Grimaldi, M.G. High-temperature annealing of thin Au films on Si: Growth of SiO2 nanowires or Au dendritic nanostructures? Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, X.X.; Shen, H. Preparation of Self-Assembled Au Nanoparticles Arrays for Silicon Solar Cell Applications. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 803, 257262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, E.; Riobóo, R.J.J.; Prieto, C.; Every, A. Surface acoustic wave velocity of gold films deposited on silicon substrates at different temperatures. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwidyantri, A.; El-Mekki, I.; Lai, C.-S. Tunable Plasmonic SERS “Hotspots” on Au-Film over Nanosphere by Rapid Thermal Annealing. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2017, 16, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakouz, T.; Tesler, A.B.; Sannomiya, T.; Feldman, Y.; Vaskevich, A.; Rubinstein, I. Mechanism of morphology transformation during annealing of nanostructured gold films on glass. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 4656–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachmann, E.; Seifert, M.; Ernst, D.; Menzel, S.B.; Gemming, T. Pt-wire bonding optimization for electroplated Pt films on γ-Al2O3 for high temperature and harsh environment applications. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 2018, 284, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovesey, S.W.; Balcar, E. A Guide to Electronic Multipoles in Photon Scattering and Absorption. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 82, 021008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Qiu, H.; Wu, P.; Chen, X. Effect of annealing on the characteristics of Au layers grown on the high-temperature deposited Ni50Fe50 layers. Vacuum 2006, 80, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Thickness of Thin Metal Layer Cr/Au (nm) | Sample | Temperature (°C) | Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50/300 | S-1 | No | 0 |
| 50/300 | S-2 | 500 | 2 |
| 50/300 | S-3 | 500 | 5 |
| 50/300 | S-4 | 700 | 2 |
| 50/300 | S-5 | 700 | 5 |
| 50/400 | S-6 | No | 0 |
| 50/400 | S-7 | 500 | 2 |
| 50/400 | S-8 | 500 | 5 |
| 50/400 | S-9 | 700 | 2 |
| 50/400 | S-10 | 700 | 5 |
| Sample and Sample Bonding Point | Thickness of Metal Layer Cr/Au (nm) | Breaking Critical Pull Value (g) | Standard Deviation (g) | Average Pull Value (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1–1 | 50/300 | 7.080 | -- | -- |
| S1–2 | 9.271 | 1.549 | 8.176 | |
| S1–3 | 7.566 | 1.150 | 7.973 | |
| S1–4 | 10.341 | 1.512 | 8.563 | |
| S1–5 | 14.486 | 3.115 | 9.829 | |
| S1–6 | 10.515 | 2.800 | 9.943 | |
| S2–1 | 50/400 | 16.171 | -- | -- |
| S2–2 | 15.506 | 0.470 | 15.839 | |
| S2–3 | 17.208 | 0.858 | 16.295 | |
| S3–1 | 50/400 | 12.497 | ||
| S3–2 | 13.357 | 0.607 | 12.927 | |
| S3–3 | 12.591 | 0.667 | 12.815 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, Y. Au Wire Ball Welding and Its Reliability Test for High-Temperature Environment. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101603
Wu C, Wang J, Liu X, Li M, Zhu Z, Qi Y. Au Wire Ball Welding and Its Reliability Test for High-Temperature Environment. Micromachines. 2022; 13(10):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101603
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chenyang, Junqiang Wang, Xiaofei Liu, Mengwei Li, Zehua Zhu, and Yue Qi. 2022. "Au Wire Ball Welding and Its Reliability Test for High-Temperature Environment" Micromachines 13, no. 10: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101603
APA StyleWu, C., Wang, J., Liu, X., Li, M., Zhu, Z., & Qi, Y. (2022). Au Wire Ball Welding and Its Reliability Test for High-Temperature Environment. Micromachines, 13(10), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13101603






