Experimental Study of the Deposition of Magnetic Particles on the Walls of Microchannels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
- PA or PE indicate the parallel or the perpendicular direction of the magnetization vector, respectively (see Figure 1).
- M3 or M5 indicate the size of the magnet (3 or 5 mm).
- P1 or P4, the size of the magnetic particles.
- C3 or C6 the hydraulic diameter of the microchannel (300 or 600 μm).
- QL, QM, and QH, the low, medium or high flow rate.
- PNM indicates the parts per ten thousands volume fraction of non-magnetic particles in the solution (09, 18, 36, or 55).
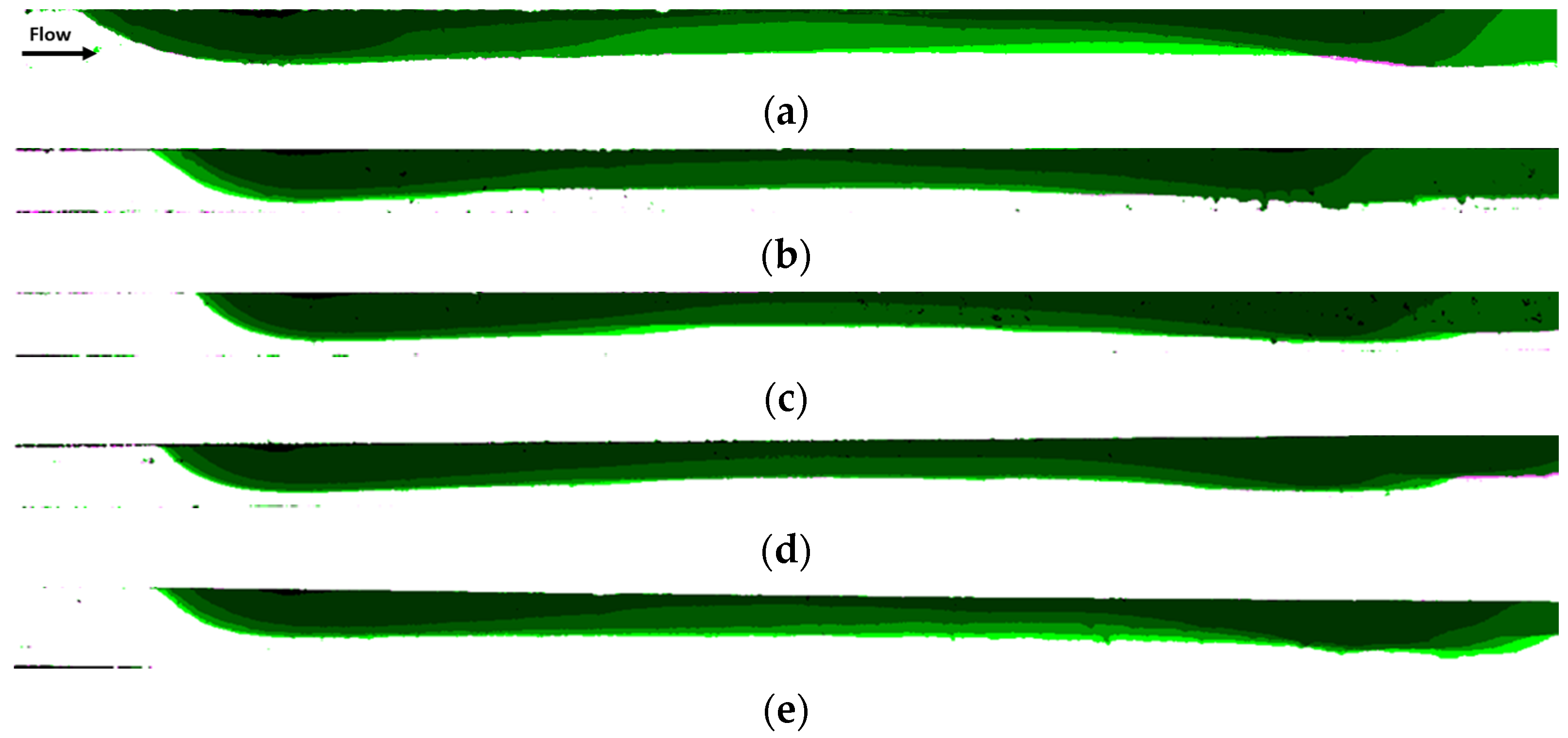
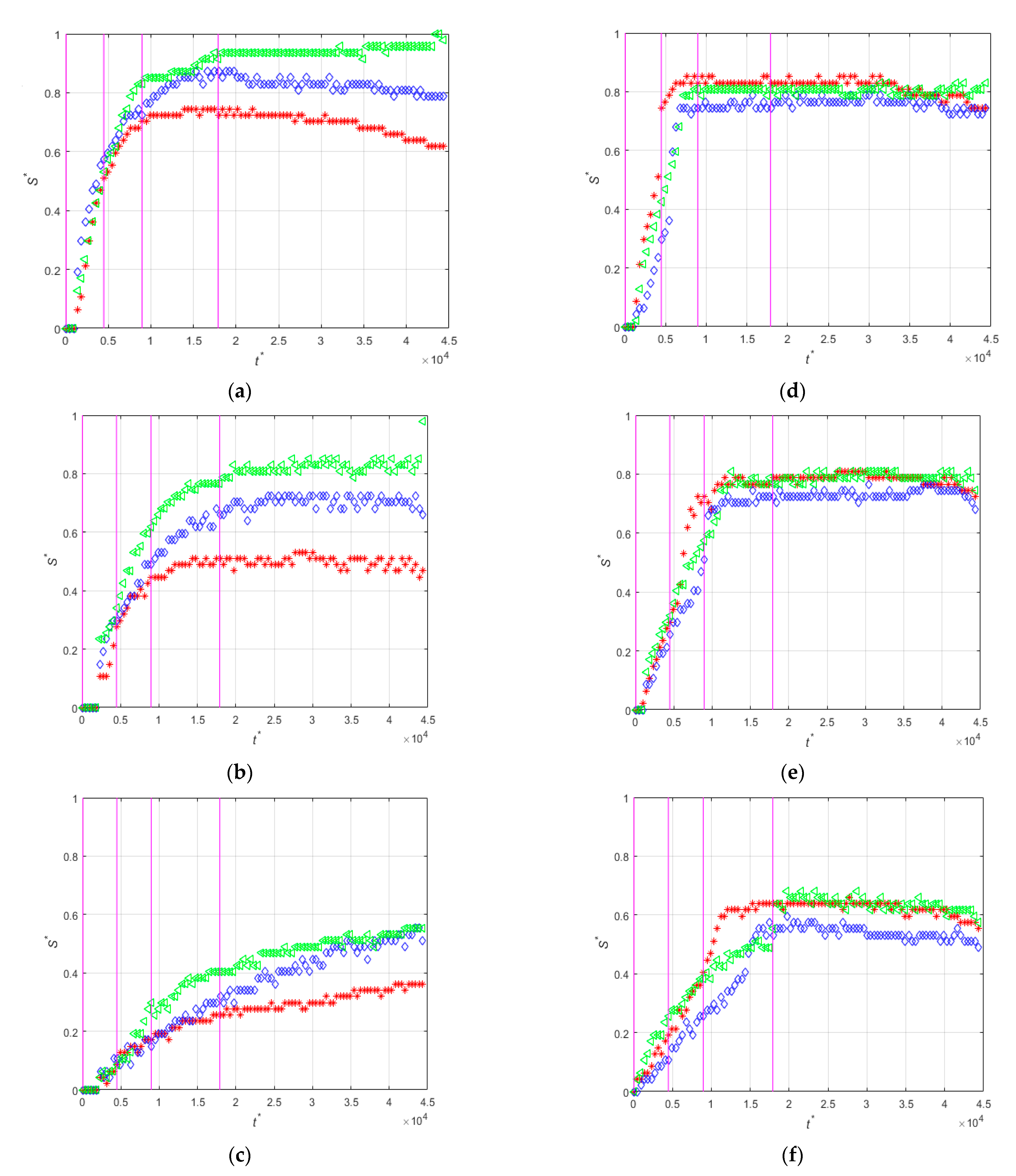
3.1. Effect the Orientation of the Magnetization Vector and of the Flow Rate
3.2. Effect of the Size of the Magnet
3.3. Effect of the Diameter of the Particles
3.3.1. Magnet Size of 5 mm
3.3.2. Magnet Size of 3 mm
3.4. Effect of the Hydraulic Diameter of the Microchannel
3.5. Effect of the Concentration of Non-Magnetic Particles on the Deposition of the Magnetic Beads
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| g | [m/s2] | Gravity acceleration |
| L | [m] | Length |
| S | [m] | Width of the accumulation |
| W | [m] | Width of the channel |
| A | [m2] | Area of the accumulation |
| Ms | [A/m] | Magnetization of the magnet |
| [m/s] | Mean Velocity | |
| x | [m] | Cartesian axis direction |
| y | [m] | Cartesian axis direction |
| z | [m] | Cartesian axis direction |
| [s] | Time between images | |
| nframes | [-] | Number of images |
| Non Dimensional Numbers | ||
| [-] | ||
| [-] | ||
| [-] | ||
| Subscripts | ||
| m | Magnet, magnetic | |
References
- Dreyfus, R.; Tabeling, P.; Willaime, H. Ordered and Disordered Patterns in Two-Phase Flows in Microchannels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 144505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.A.; Stroock, A.D.; Ajdari, A. Engineering Flows in Small Devices: Microfluidics toward a Lab-on-a-Chip. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2004, 36, 381–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, D.R.; Anna, S.L.; Weitz, D.A.; Stone, H.A. Geometrically Mediated Breakup of Drops in Microfluidic Devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 54503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatus, T.; Tlusty, T.; Bar-Ziv, R. Phonons in a one-dimensional microfluidic crystal. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatus, T.; Bar-Ziv, R.H.; Tlusty, T. The physics of 2D microfluidic droplet ensembles. Phys. Rep. 2012, 516, 103–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamme, N. Continuous flow separations in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1644–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, A.A.S.; Bow, H.; Hou, H.W.; Tan, S.J.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Microfluidics for cell separation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 48, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeesh, P.; Sen, A.K. Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: A review. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, A. Flow of complex suspensions. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Garg, A.; Campbell, A.I.; Howse, J.; Sen, A.; Velegol, D.; Golestanian, R.; Ebbens, S.J. Boundaries can steer active Janus spheres. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechinger, C.; Di Leonardo, R.; Löwen, H.; Reichhardt, C.; Volpe, G.; Volpe, G. Active particles in complex and crowded environments. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2016, 88, 45006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Bloom, M.; Bae, S.C.; Luijten, E.; Granick, S. Linking synchronization to self-assembly using magnetic Janus colloids. Nature 2012, 491, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazian, M.; Li, W.; Nguyen, N.-T. Lab on a chip for continuous-flow magnetic cell separation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Yang, F.; Zhu, L.; Qiao, R.; Zhao, Y. Manipulation of magnetic nanorod clusters in liquid by non-uniform alternating magnetic fields. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 3750–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyer, K.E.; Zhang, L.; Nelson, B.J. Bio-inspired magnetic swimming microrobots for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.K.; Petrov, P.G.; Winlove, C.P.; Gilbert, A.D.; Bryan, M.T.; Ogrin, F.Y. Magnetically controlled ferromagnetic swimmers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallares, J. A Criterion for the Complete Deposition of Magnetic Beads on the Walls of Microchannels. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Bai, F.; Wang, C. Magnetic separation of microparticles by shape. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, I.P.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Ong, H.C.; Leung, K.C.-F.; Ho, H.P.; Kong, S.K. In vitro effect of CTAB- and PEG-coated gold nanorods on the induction of eryptosis/erythroptosis in human erythrocytes. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R.; Lightbody, J.H.; Donaldson, K.; Sales, J.; Stone, V. Interactions between ultrafine particles and transition metals in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 184, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, P.E.; Øvrevik, J.; Hetland, R.B.; Becher, R.; Cassee, F.R.; Låg, M.; Løvik, M.; Dybing, E.; Refsnes, M. Importance of Size and Composition of Particles for Effects on Cells In Vitro. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijs, M.A.M.; Lacharme, F.; Lehmann, U. Microfluidic Applications of Magnetic Particles for Biological Analysis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1518–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, N.L.; Mirkin, C.A. Nanostructures in Biodiagnostics. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, A.M.; Ribeiro, T.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Ribeiro, B.; Frade, R.F.M.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Multifunctional Hybrid Silica Nanoparticles with a Fluorescent Core and Active Targeting Shell for Fluorescence Imaging Biodiagnostic Applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 4579–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pissuwan, D.; Valenzuela, S.M.; Cortie, M.B. Prospects for Gold Nanorod Particles in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2008, 25, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.; Singh, J.; Singh, A.; Srivastava, A.; Goyal, R.N.; Shim, Y.B. Gold Nanoparticles and Nanocomposites in Clinical Diagnostics Using Electrochemical Methods. J. Nanopart. 2013, 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almomani, T.; Udaykumar, H.S.; Marshall, J.S.; Chandran, K.B. Micro-scale Dynamic Simulation of Erythrocyte–Platelet Interaction in Blood Flow. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 36, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xi, T.; Bai, J. Biological effects induced by nanosilver particles: In vivo study. Biomed. Mater. 2007, 2, S126–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güunter, O. Toxicology of ultrafine particles: In vivo studies. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2000, 358, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.R.; Saunders, W.M.; Tobias, C.A.; Chen, G.T.Y.; Curtis, S.; Lyman, J.T.; Collier, J.M.; Pitluck, S.; Woodruff, K.A.; Blakely, E.A.; et al. Treatment of cancer with heavy charged particles. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1982, 8, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemmar, A.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Hoet, P.H.; Dinsdale, D.; Smith, T.; Xu, H.; Vermylen, J.; Nemery, B. Ultrafine particles affect experimental thrombosis in an in vivo hamster model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosendaal, F.R. Venous thrombosis: A multicausal disease. Lancet 1999, 353, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Deep vein thrombosis. Lancet 2005, 365, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.spherotech.com/ (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- Available online: https://www.dantecdynamics.com/ (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- Available online: https://www.supermagnete.es/eng/data_table.php (accessed on 19 April 2021).
- Available online: https://www.cmscientific.eu/ (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- Shevkoplyas, S.S.; Siegel, A.C.; Westervelt, R.M.; Prentiss, M.G.; Whitesides, G.M. The force acting on a superparamagnetic bead due to an applied magnetic field. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
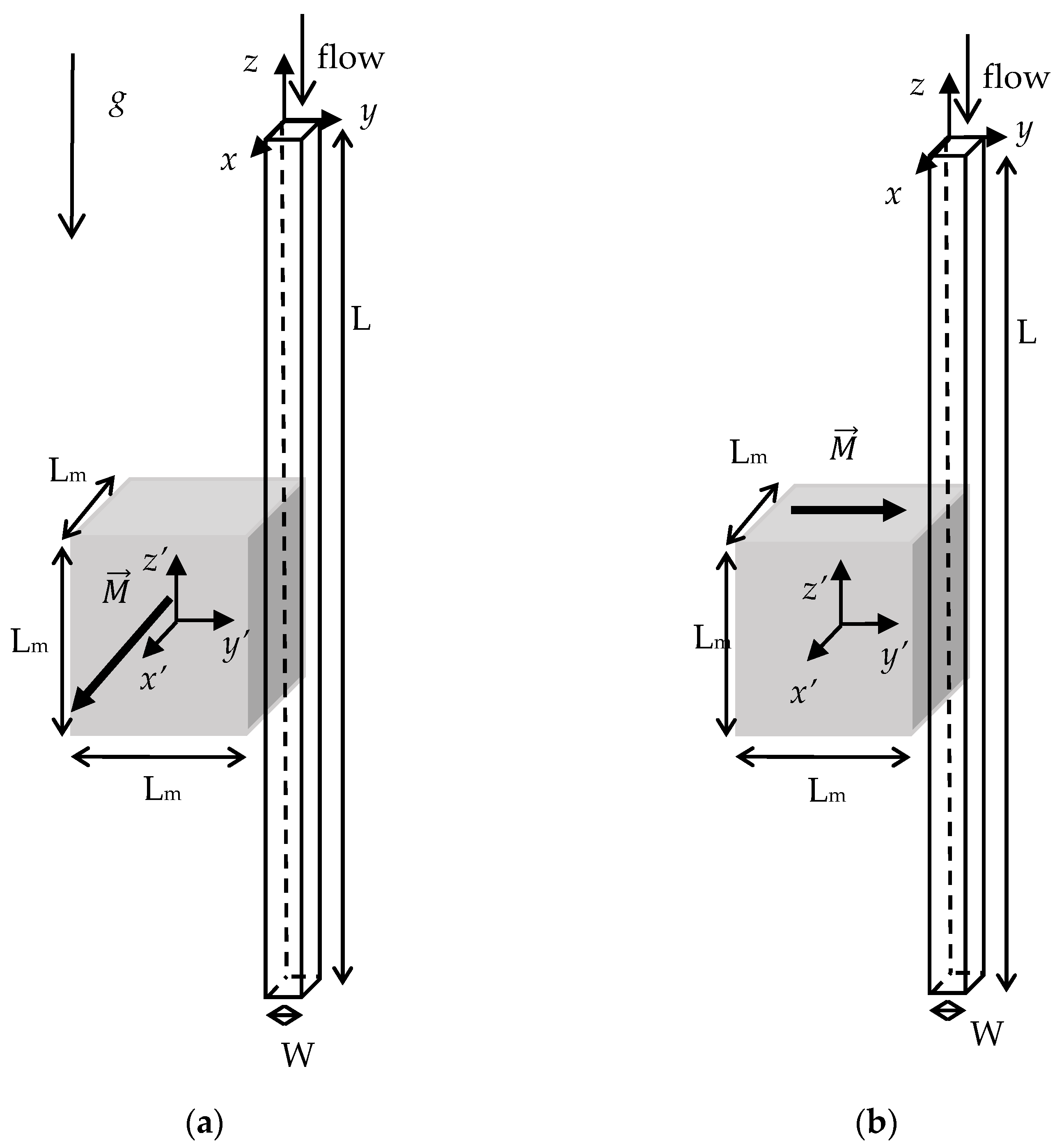
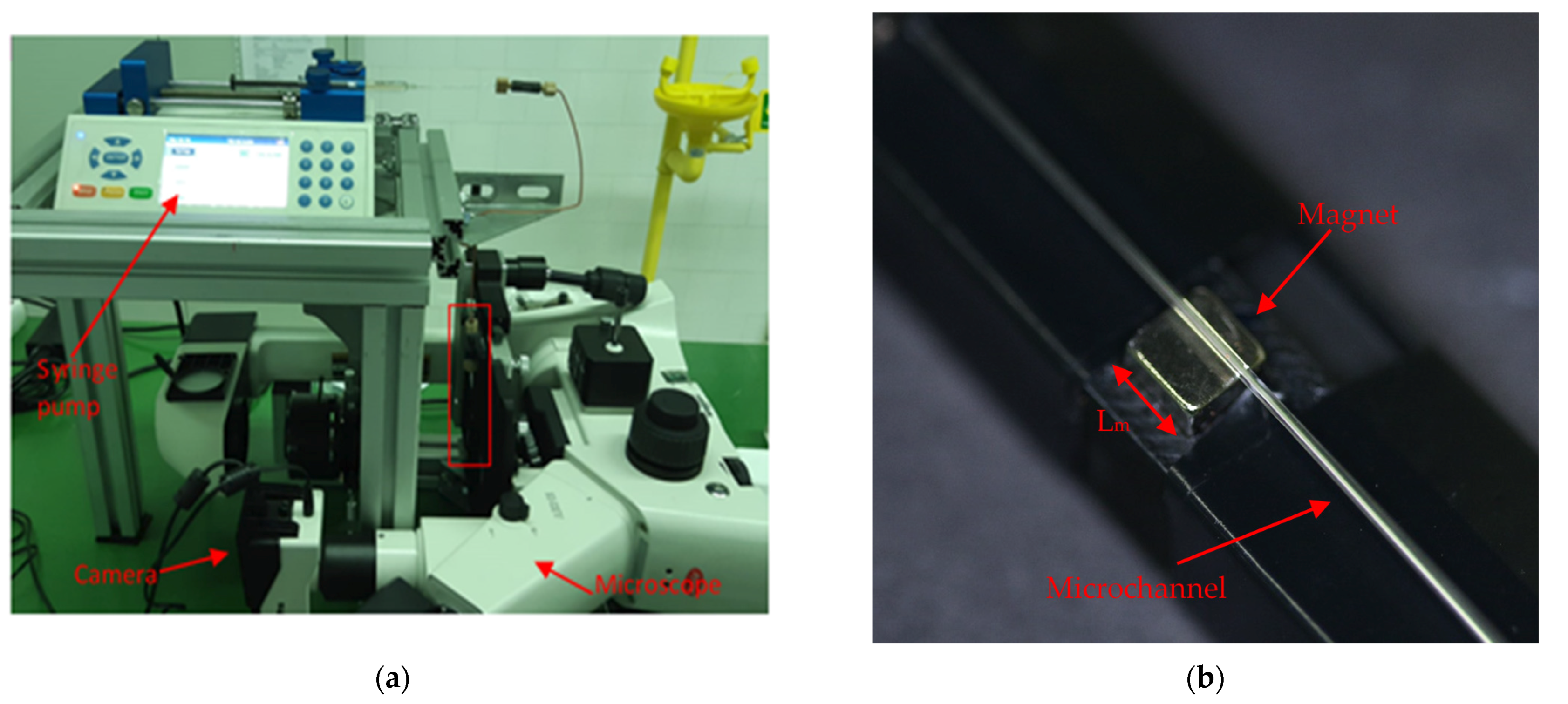

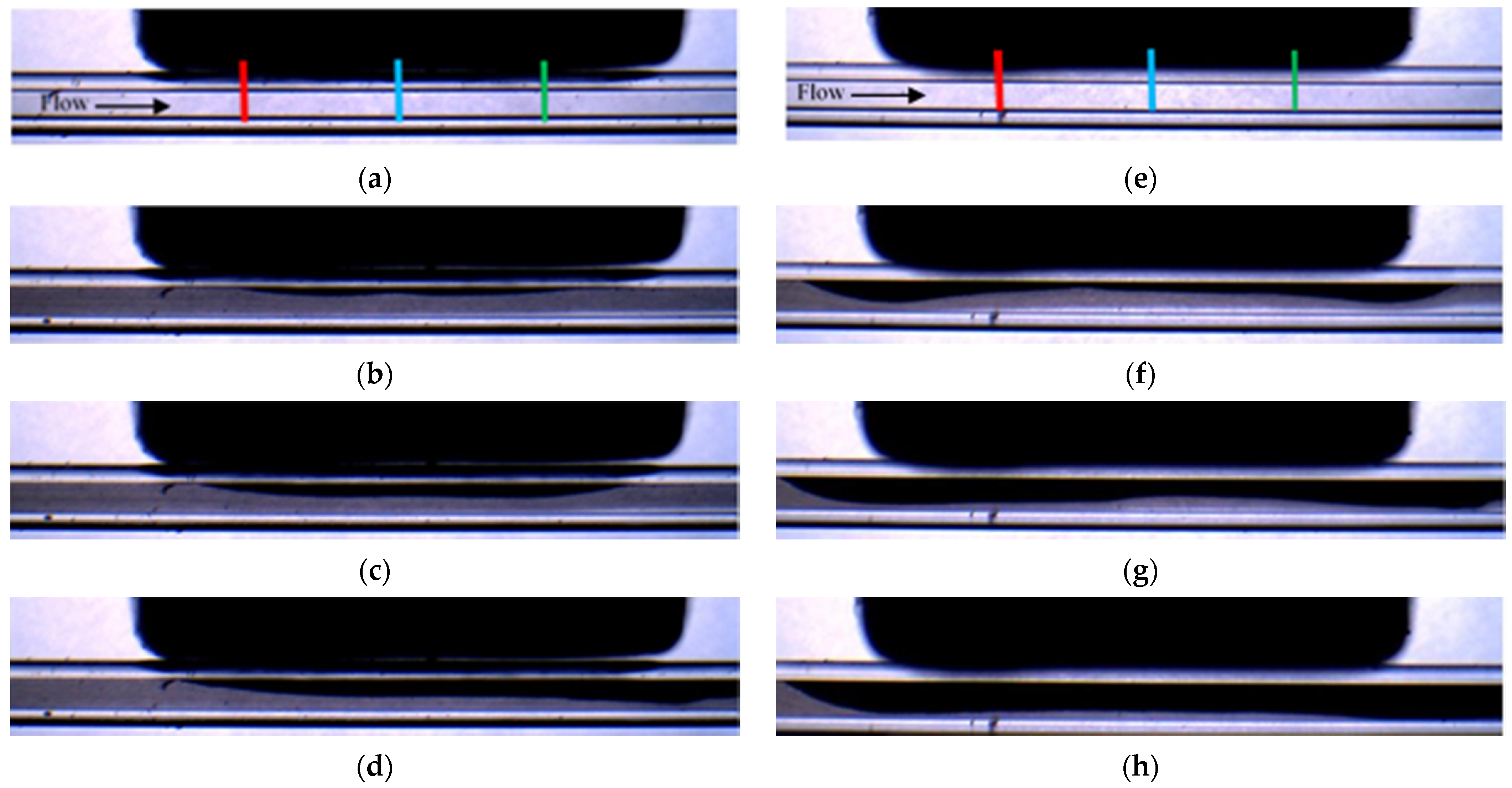


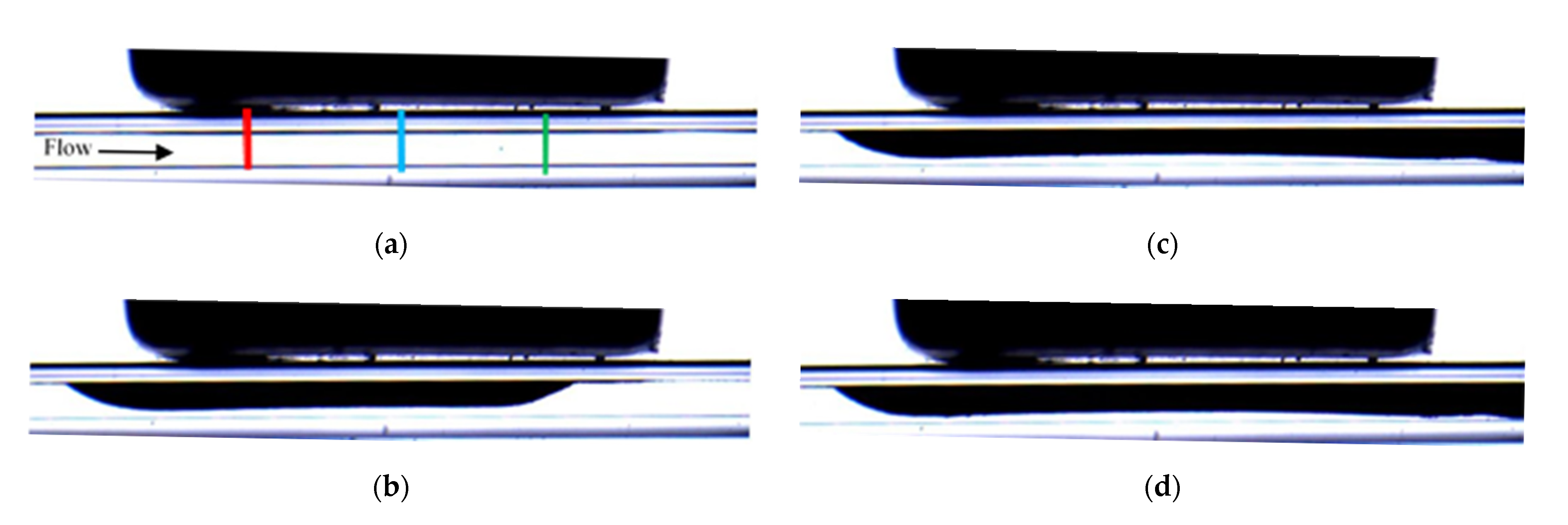
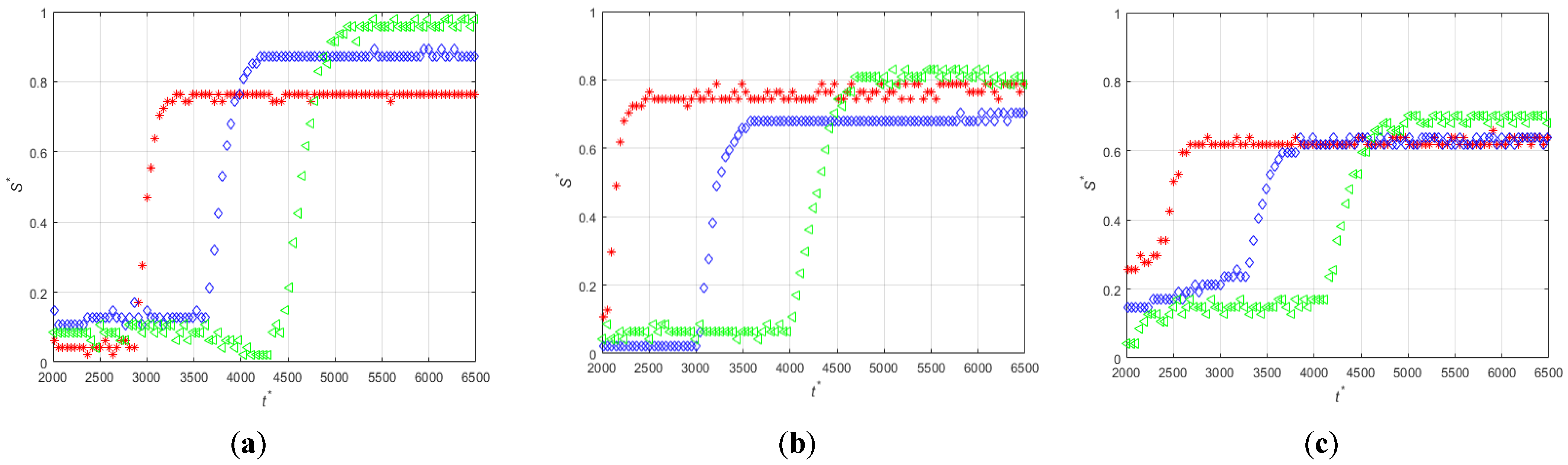
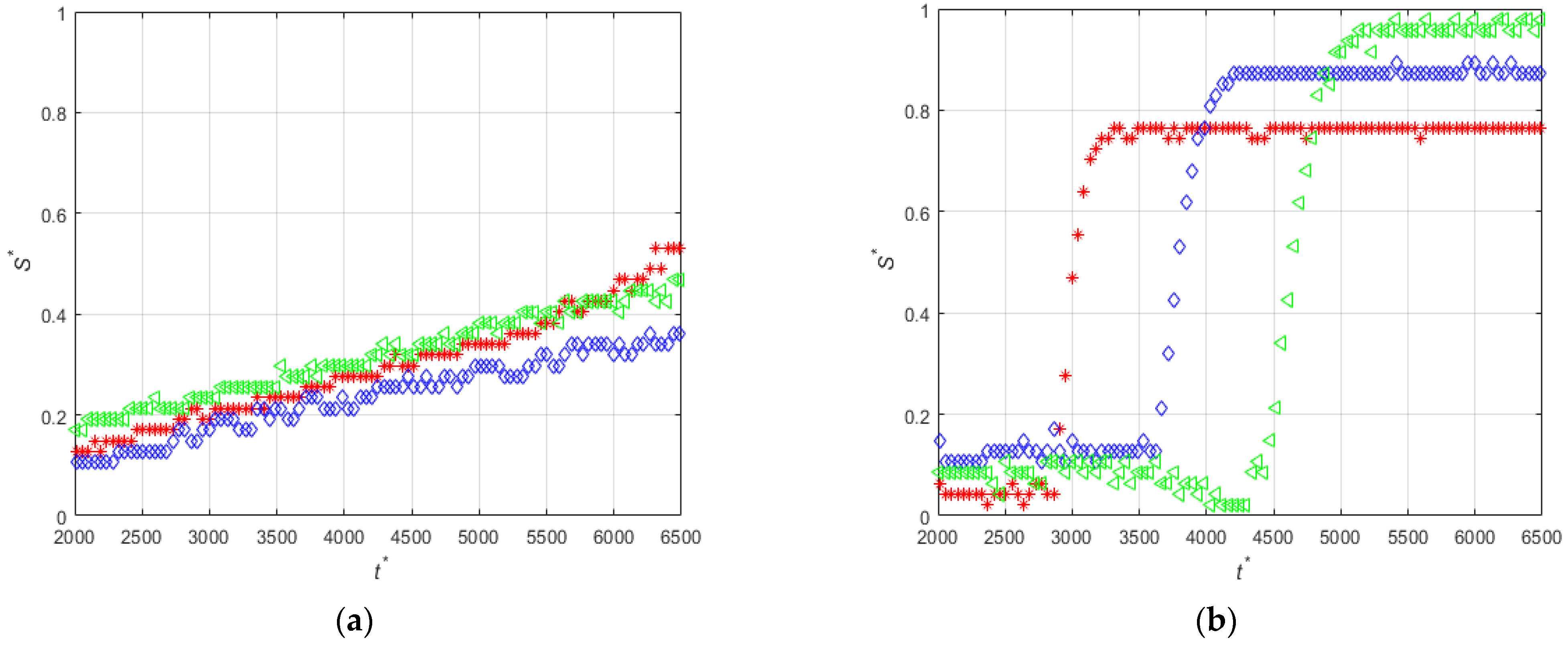

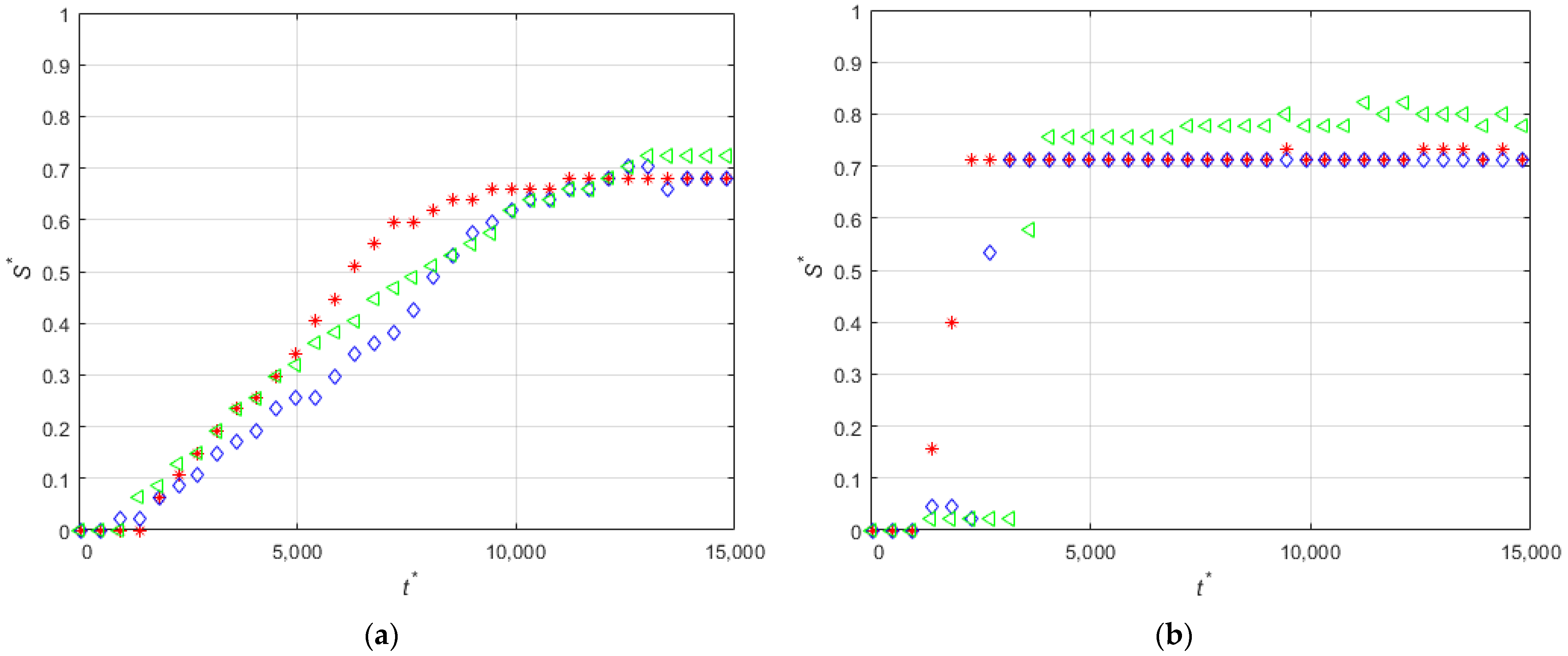
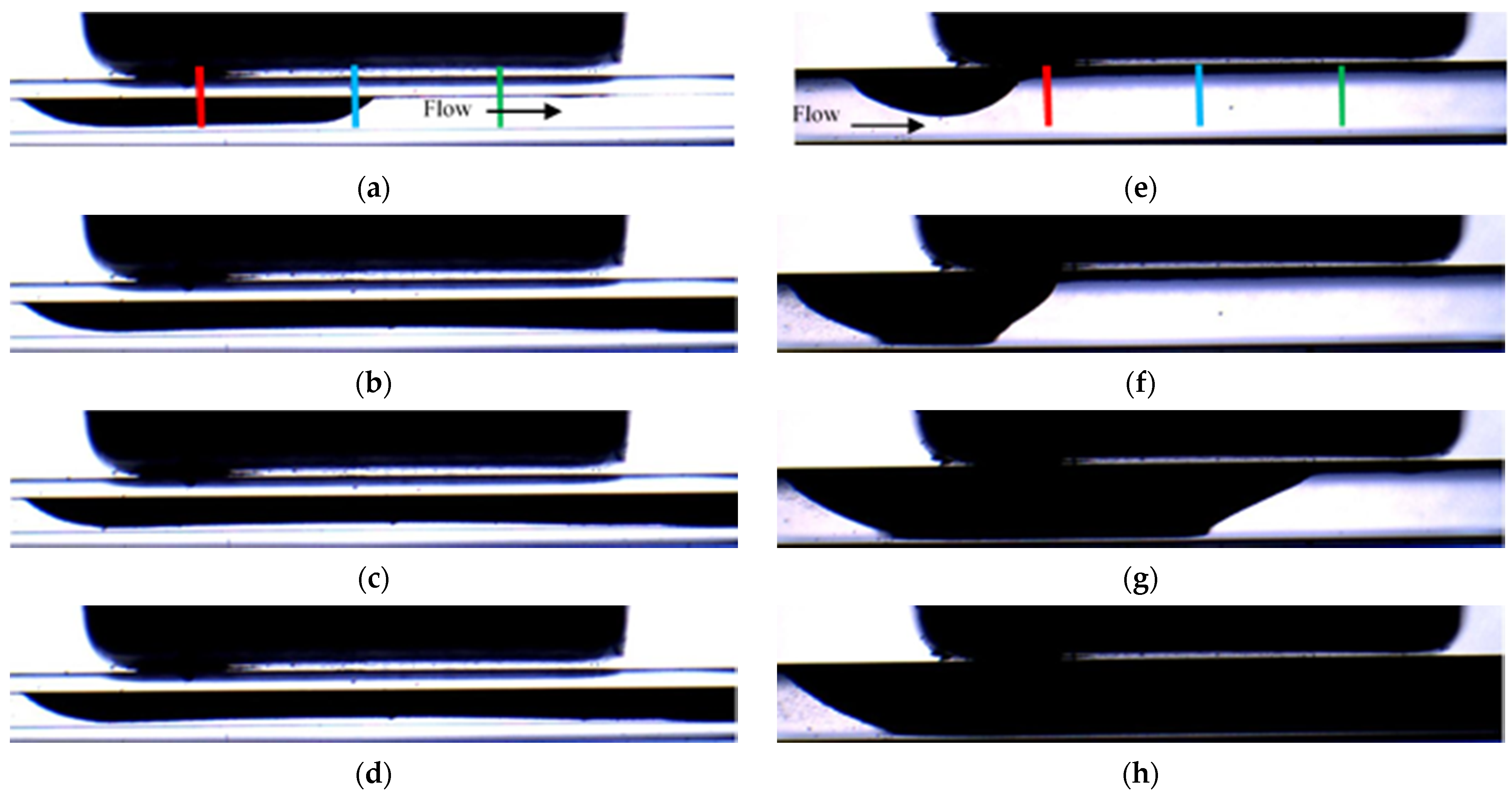
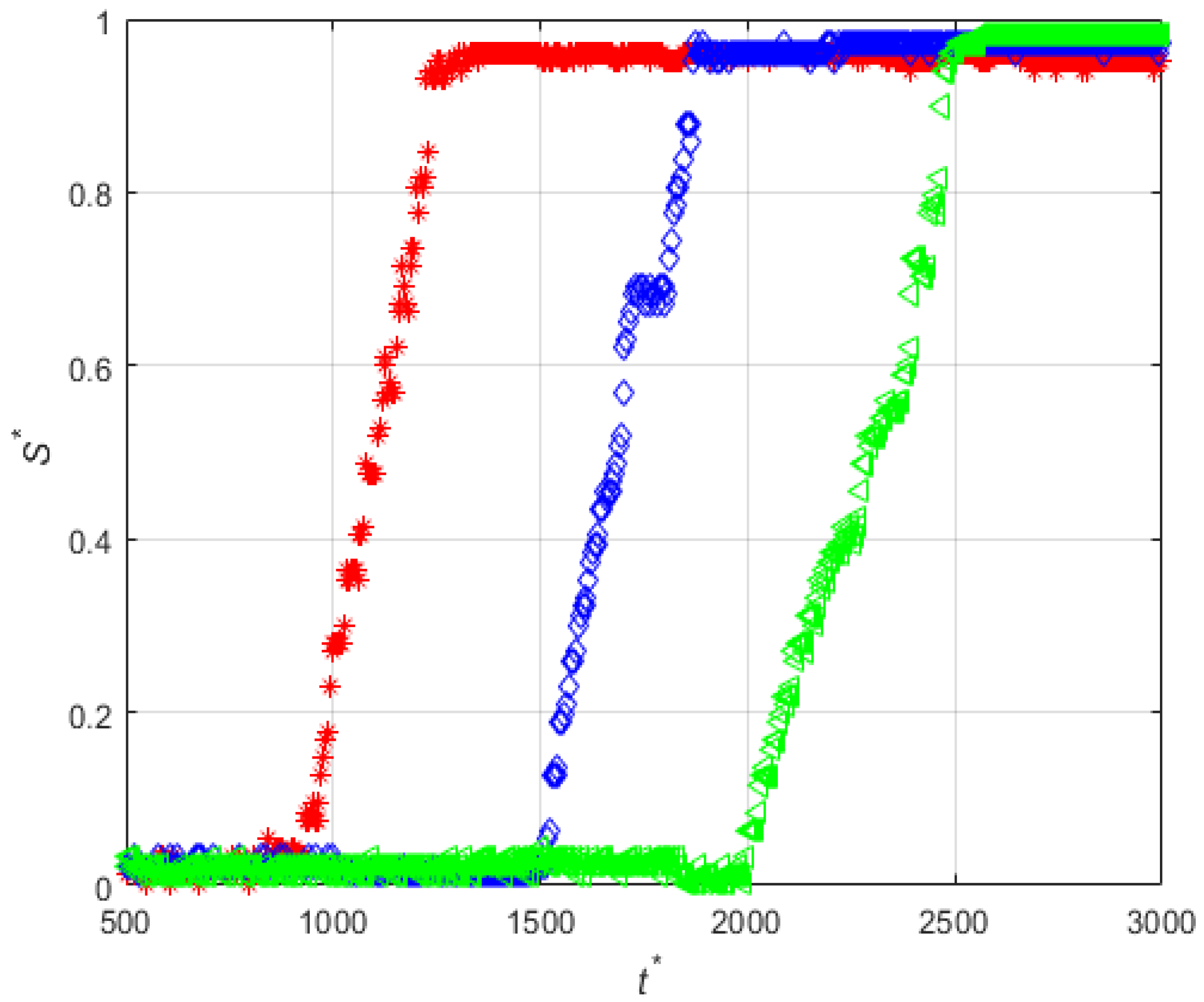
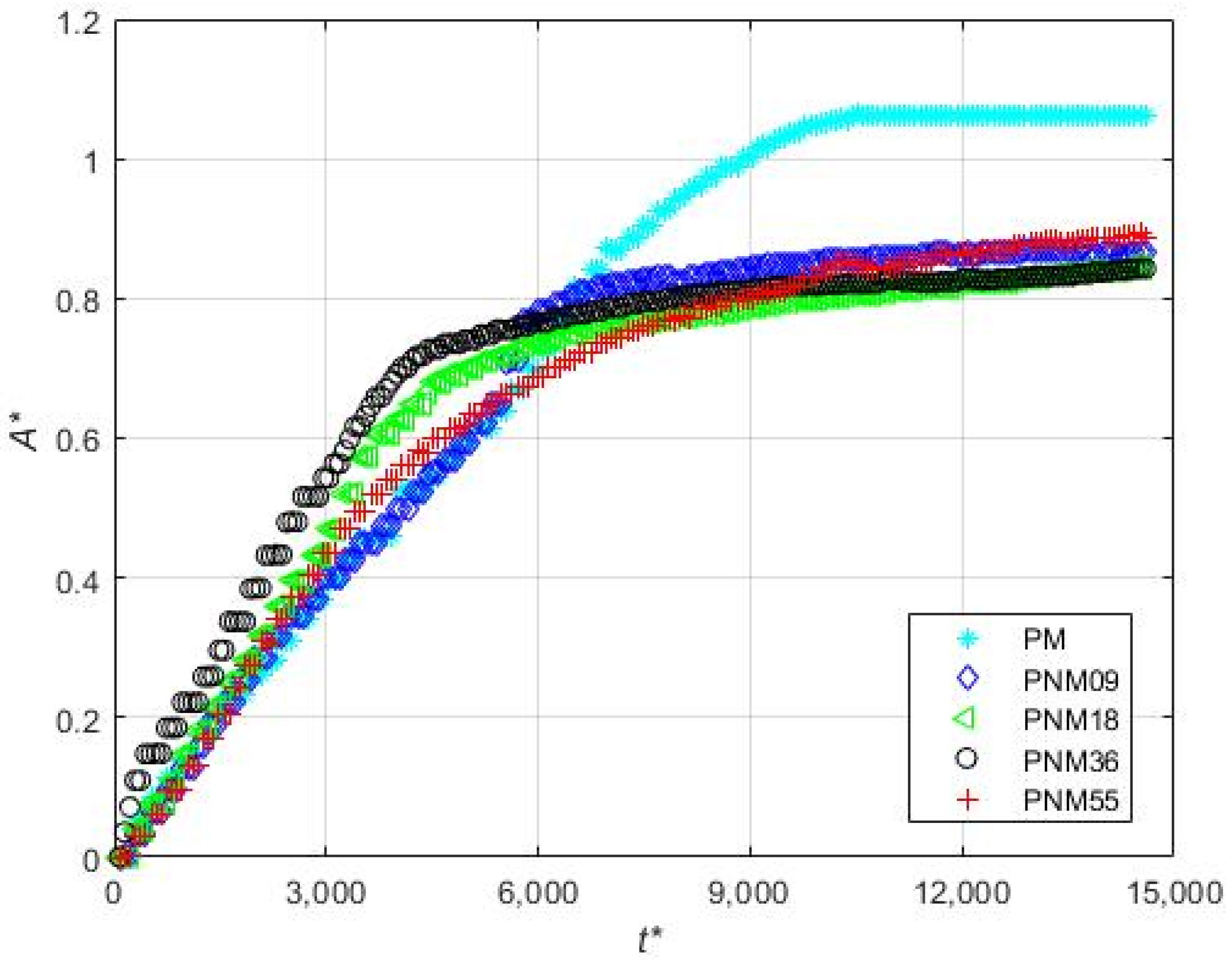


| Set | Experiment Label | Magnetization Vector Direction | MS (mm) | CD (μm) | PD (μm) | FR (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PA-M5-P1-C3-QL | 5 | 300 | 1.14 | 0.03 | |
| PA-M5-P1-C3-QM | 0.06 | |||||
| PA-M5-P1-C3-QH | 0.12 | |||||
| 2 | PE-M5-P1-C3-QL | 5 | 300 | 1.14 | 0.03 | |
| PE-M5-P1-C3-QM | 0.06 | |||||
| PE-M5-P1-C3-QH | 0.12 | |||||
| 3 | PE-M3-P1-C3-QM | 3 | 300 | 1.14 | 0.06 | |
| PE-M3-P4-C3-QM | 4.37 | |||||
| 4 | PE-M5-P4-C3-QL | 5 | 300 | 4.37 | 0.03 | |
| PE-M5-P4-C3-QM | 0.06 | |||||
| PE-M5-P4-C3-QH | 0.12 | |||||
| 5 | PE-M5-P4-C6-QL | 5 | 600 | 4.37 | 0.03 | |
| 6 | PE-M5-P1-C3-QM-PM | 5 | 300 | 1.14 | 0.06 | |
| PE-M5-P1-C3-QM-PNM09 | ||||||
| PE-M5-P1-C3-QM-PNM18 | ||||||
| PE-M5-P1-C3-QM-PNM36 | ||||||
| PE-M5-P1-C3-QM-PNM55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varela, S.; Rivas, A.; Vernet, A.; Pallarès, J. Experimental Study of the Deposition of Magnetic Particles on the Walls of Microchannels. Micromachines 2021, 12, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060712
Varela S, Rivas A, Vernet A, Pallarès J. Experimental Study of the Deposition of Magnetic Particles on the Walls of Microchannels. Micromachines. 2021; 12(6):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060712
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarela, Sylvana, Antonio Rivas, Anton Vernet, and Jordi Pallarès. 2021. "Experimental Study of the Deposition of Magnetic Particles on the Walls of Microchannels" Micromachines 12, no. 6: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060712
APA StyleVarela, S., Rivas, A., Vernet, A., & Pallarès, J. (2021). Experimental Study of the Deposition of Magnetic Particles on the Walls of Microchannels. Micromachines, 12(6), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060712








