Forced Convection in Wavy Microchannels Porous Media Using TiO2 and Al2O3–Cu Nanoparticles in Water Base Fluids: Numerical Results
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Description
3. Governing Equation and Boundary Conditions
Boundary Conditions and Solution Approach
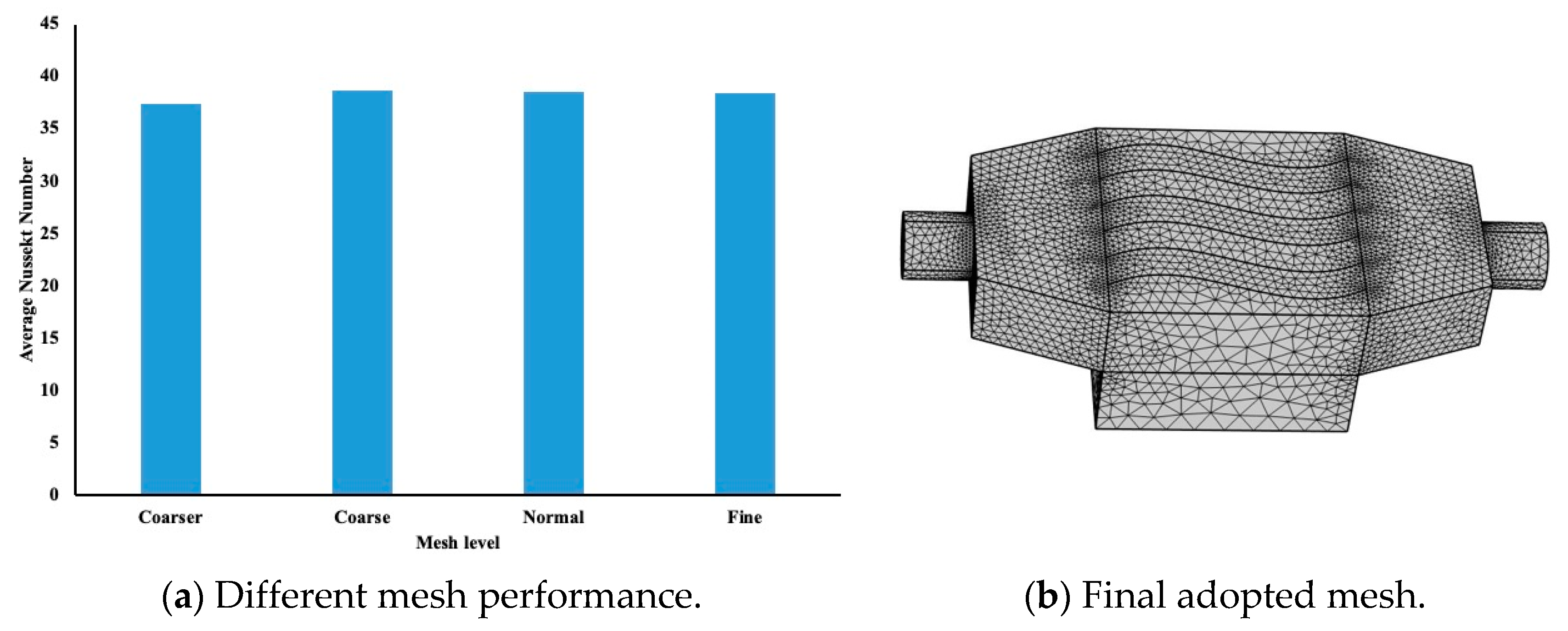
4. Mesh Sensitivity Analysis, Convergence Criteria and Model Verification
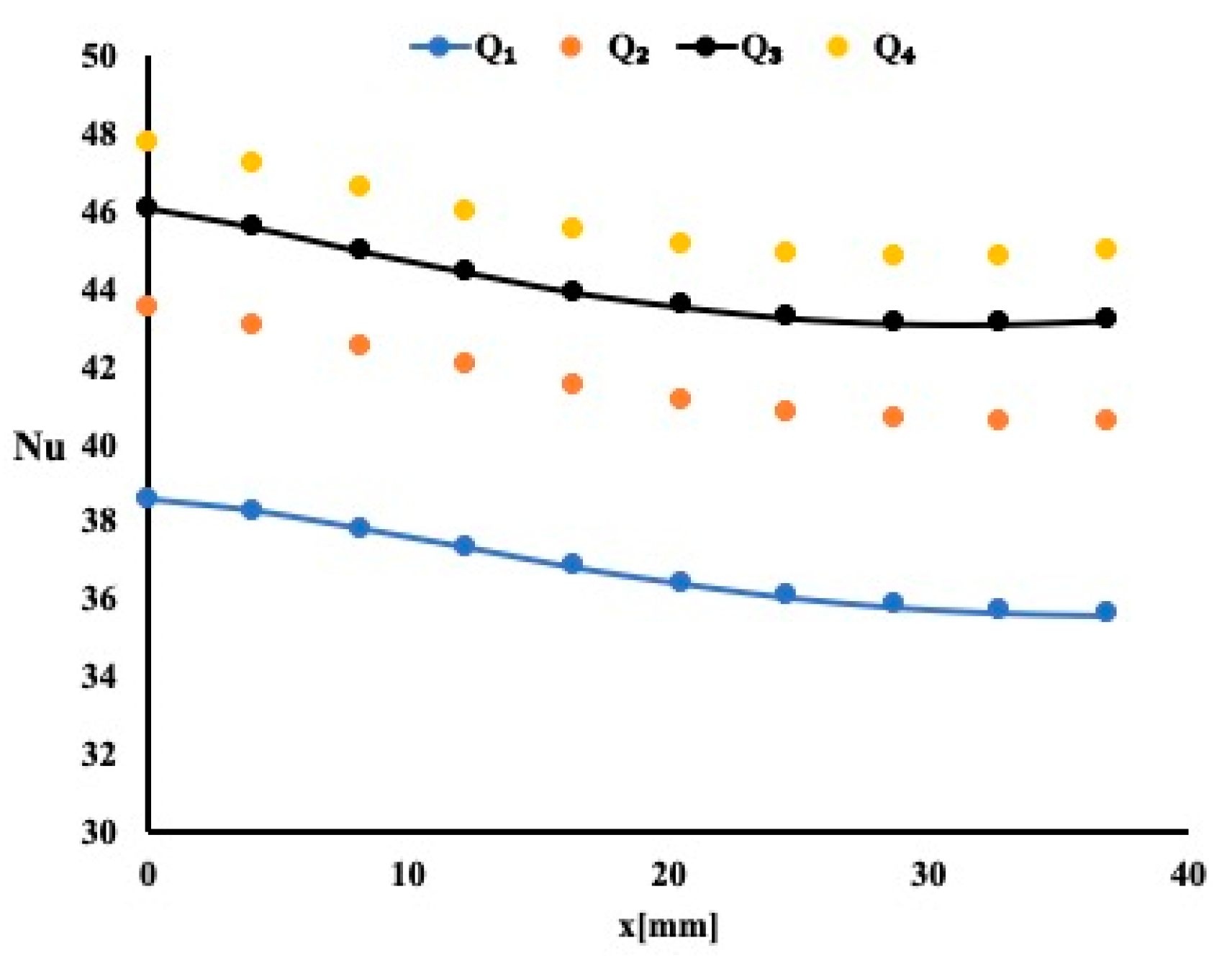
5. Results and Discussion
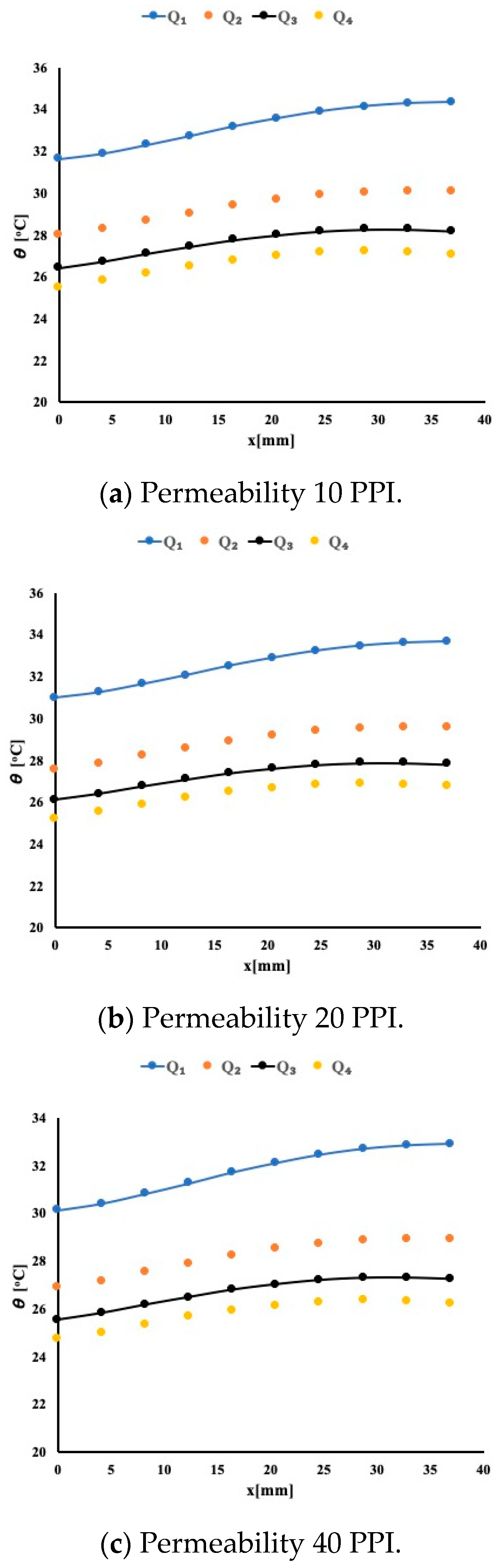
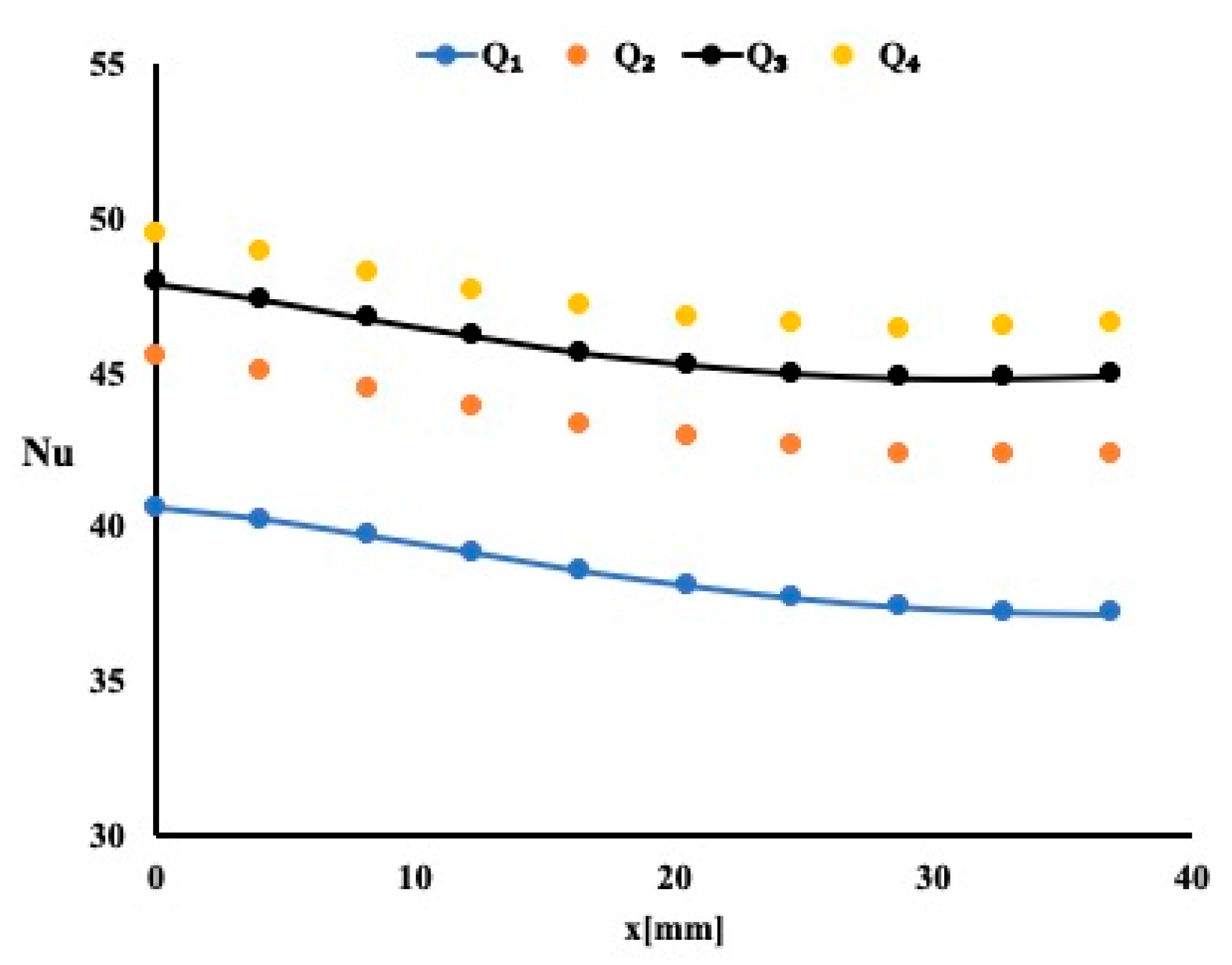
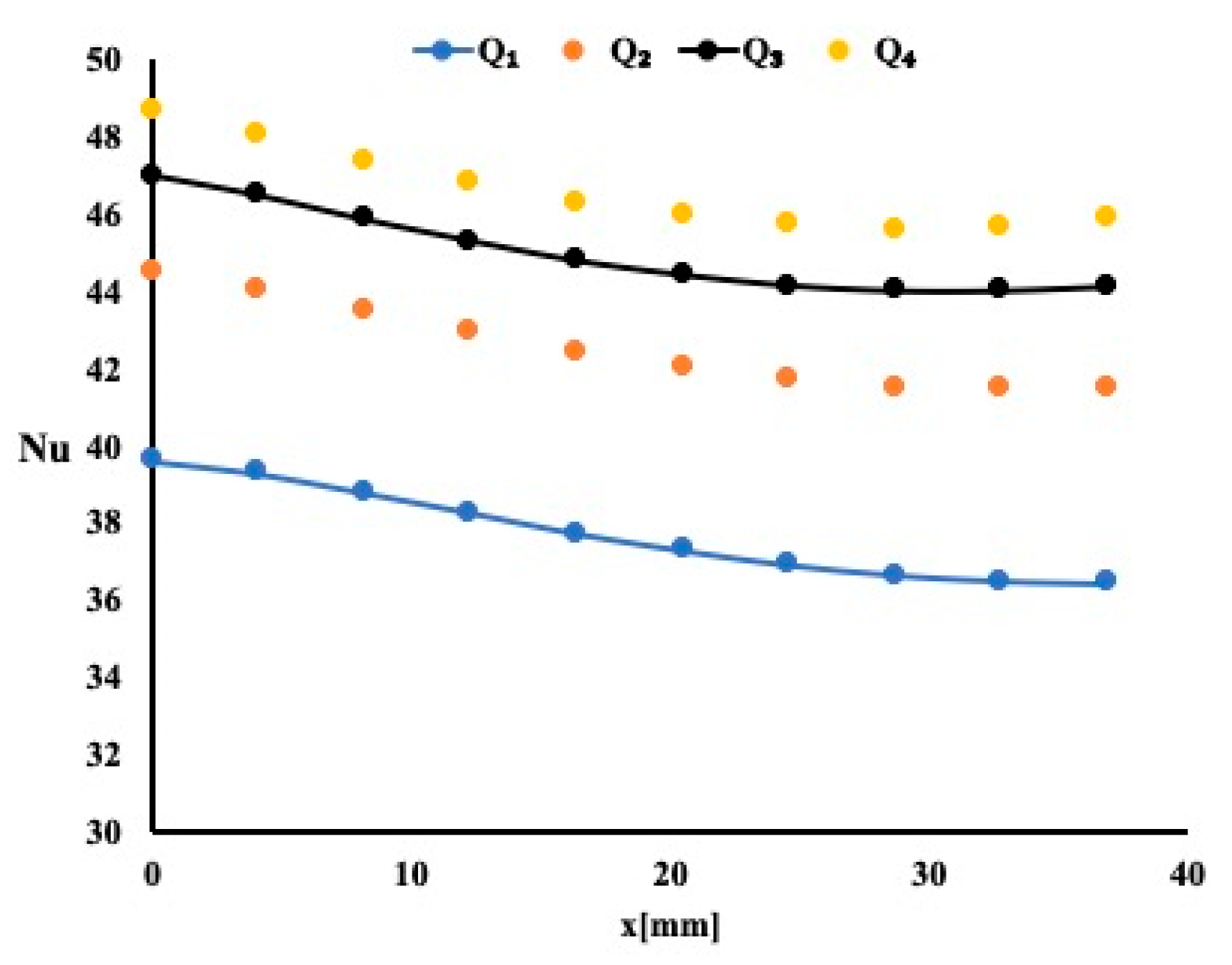
5.1. Heat Enhancement Using Water as Working Fluid
5.2. Heat Enhancement Using 1% TiO2 in Water as Working Fluid
5.3. Heat Enhancement Using 1% (Al2O3–Cu) in Water as Working Fluid
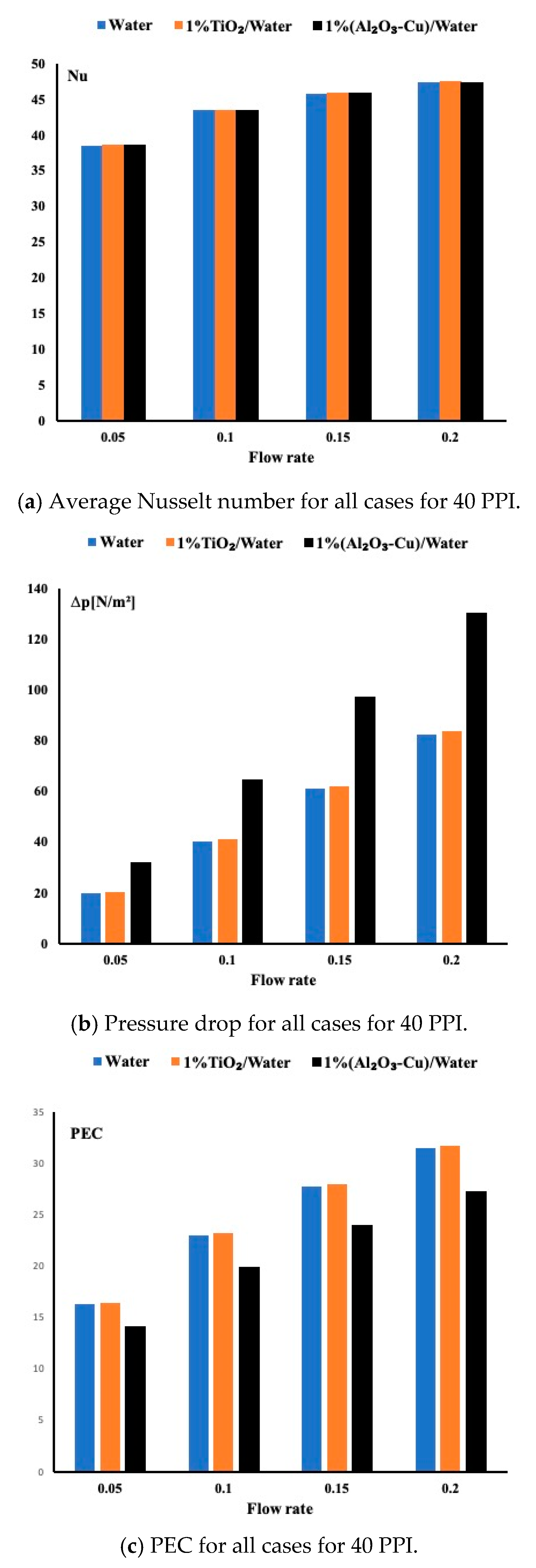
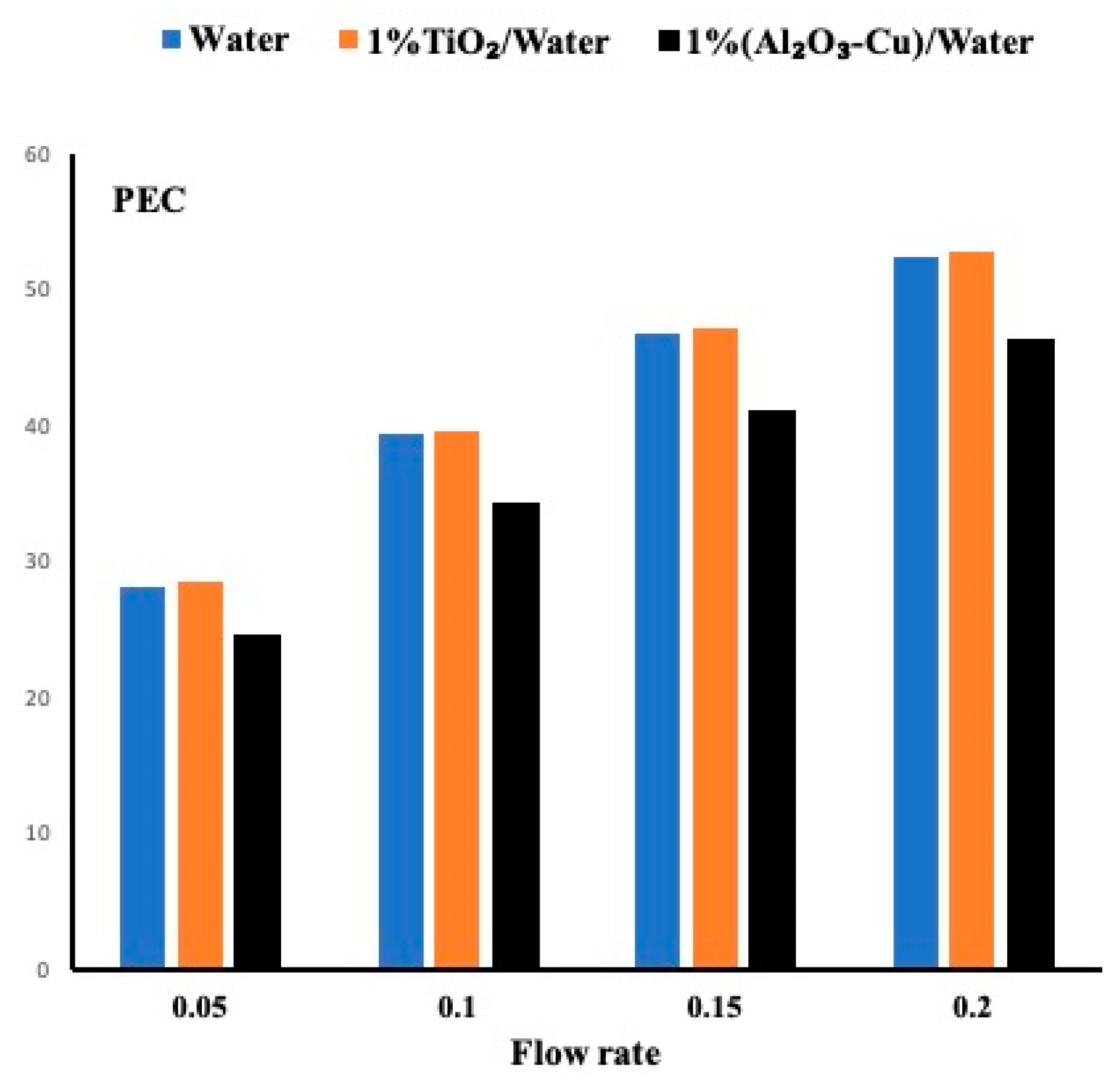
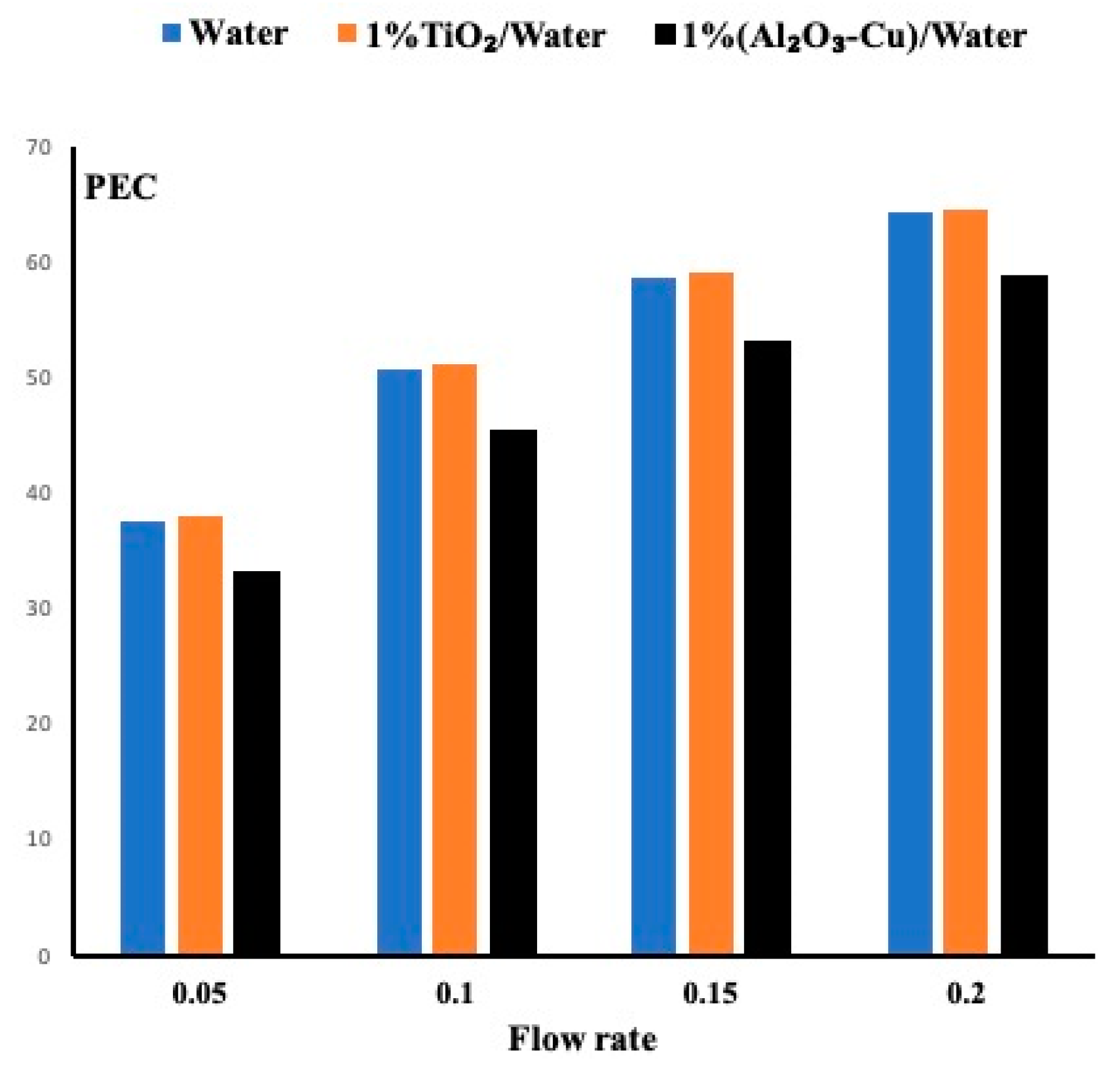
5.4. Performance Evaluation Criteria for All Fluids
6. Conclusions
- Channel waviness allows the flow to circulate longer than a straight channel, thus providing higher heat extraction.
- By increasing the flow rate, heat enhancement is improved.
- The presence of porous material helps in heat removal, and as the permeability increases, the pressure drop in the channel decreases accordingly.
- Amongst the three fluids, the TiO2 nanofluid exhibits slightly better performance than the water based on the Performance Evaluation Criteria coefficient. The hybrid fluid provided less performance due to the large pressure drop it exhibited.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Density | |
| μnf | Viscosity |
| Cpnf | Specific heat |
| knf | Conductivity |
| κ | Permeability |
| Effective heat capacity | |
| (knf)eff | Effective conductivity |
| Δp | Pressure difference |
| u,v,w | Velocity in x, y and z |
| p | Pressure |
| L | Block Length |
| Average Nusselt number | |
| Nu | Local Nusselt number |
| f | Fanning friction factor |
| PEC | Performance Evaluation Criterion |
| D | Hydraulic diameter |
| uin | Inlet velocity |
References
- Webb, R.L.; Kim, N.H. Principles of Enhanced Heat Transfer, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tuckerman, D.; Pease, R. High-performance heat sinking for VLSI. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1981, 2, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, B.; Li, K.; Wirtz, R. Heat transfer enhancement in a serpentine channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1993, 36, 2965–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, A.M.; Cárdenas, M.J.; Urzúa, F.A.; Araya, P.E. Heat transfer enhancement by flow bifurcations in asymmetric wavy wall channels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 3778–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Al-Azmi, B.; Marafie, A.; Pop, I. Non-Darcian effects on natural convection heat transfer in a wavy porous enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellões, F.V.; Quaresma, J.N.; Cotta, R.M. Convective heat transfer enhancement in low Reynolds number flows with wavy walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 2022–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yener, Y.; Kakaç, S.; Avelino, M.; Okutucu, T. Single-phase forced convection in micro-channels—A state-of-the-art review. In Microscale Heat Transfer—Fundamentals and Applications; NATO ASI Series; Kakaç, S., Vasiliev, L.L., Bayazitoglu, Y., Yener, Y., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Vanka, S.P. Convective heat transfer in periodic wavy passages. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1995, 38, 3219–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, G. Heat transfer optimization in corrugated wall channels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 43, 4299–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Chen, C.-K. Forced convection in a wavy-wall channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Chai, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, H. Effects of structural parameters on fluid flow and heat transfer in a microchannel with aligned fan-shaped re-entrant cavities. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 50, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In Development and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows; Siginer, D.A., Wang, H.P., Eds.; ASME FED-231/MD; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 66, pp. 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Chiam, Z.L.; Lee, P.S.; Singh, P.K.; Mou, N. Investigation of fluid flow and heat transfer in wavy micro-channels with alternating secondary branches. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 101, 1316–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Gunnasegaran, P.; Shuaib, N. Influence of channel shape on the thermal and hydraulic performance of microchannel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hatami, M.; Song, D.; Jing, D. Design of microchannel heat sink with wavy channel and its time-efficient optimization with combined RSM and FVM methods. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 103, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, S.U.-S.; Li, S.; Eastman, J. Measuring Thermal Conductivity of Fluids Containing Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Heat Transf. 1999, 121, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Roetzel, W. Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 43, 3701–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heris, S.Z.; Esfahany, M.N.; Etemad, G. Numerical investigation of nanofluid laminar convective heat transfer through a circular tube. Numer. Heat Transf. 2007, 52, 1043–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heris, S.Z.; Etemad, S.G.; Esfahany, M.N. Convective Heat Transfer of a Cu/Water Nanofluid Flowing Through a Circular Tube. Exp. Heat Transf. 2009, 22, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, A.K.; Sen, S.; Charaborty, N. Study of heat transfer due to laminar flow of copper-water nanofluid through two isothermally heated parallel plates. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2009, 48, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M. Forced convection of Al2O3, Fe3O4, ND-Fe3O4, and (MWCNT-Fe3O4) mixtures in rectangular channels: Experimental and numerical results. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M. Forced Convection of Al2O3-Cu, TiO2-SiO2, FWCNT-Fe3O4, and ND-Fe3O4 Hybrid Nanofluid in Porous Media. Energies 2020, 13, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, M.Z.; Welsford, C. Forced Convection in Porous Media Using Al2O3 and TiO2 Nanofluids in Differing Base Fluids. Energies 2020, 13, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, R.D.; Saghir, M.Z. Numerical and experimental investigation of high concentration aqueous alumina nanofluids in a two and three channel heat exchanger. Int. J. Thermofluids 2021, 9, 100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M. Toward the effectiveness of mono-nanofluid and hybrid nanofluid for heat enhancement: Experimental and numerical results. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Alhajaj, Z.; Bayomy, A.; Saghir, M. A comparative study on best configuration for heat enhancement using nanofluid. Int. J. Thermofluids 2020, 7–8, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, R.D.; Hodgson, G.K.; Impellizzeri, S.; Saghir, M.Z. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Heat Enhancement using a Hybrid Nanofluid of Copper Oxide/Alumina Nanoparticles in Water. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 141, 1951–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsford, C.; Thanapathy, P.; Bayomy, A.M.; Ren, M.; Saghir, M.Z. Heat Enhancement using Aluminum Metal Foam: Experimental and Numerical Approach. J. Porous Media 2020, 23, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayomy, A.M.; Saghir, M.Z. Thermal Performance of Finned Aluminum Heat Sink Filled with ERG Aluminum Foam: Experimental and Numerical Approach. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 4411–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhajaj, Z.; Bayomy, A.; Saghir, M.Z.; Rahman, M. Flow of nanofluid and hybrid fluid in porous channels: Experimental and numerical approach. Int. J. Thermofluids 2020, 1, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsford, C.; Delisle, C.; Plant, R.D.; Saghir, M.Z. Effects of Nanofluid Concentration and Channeling on the Thermal Effectiveness of Highly Porous Open-Cell Foam Metals: A Numerical and Experimental Study. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 140, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delisle, C.; Welsford, C.; Saghir, M.Z. Forced convection study with micro-porous channels and nanofluid: Experimental and numerical. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 140, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COMSOL User Manual, Version 5.6; COMSOL: Boston, MA, USA, 2021.

| Fluid | Pr (Prandtl Number) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 0.001002 | 998.2 | 4182 | 0.613 | 6.83 |
| 1% TiO2-0.99 Water | 0.001019 | 1030 | 4040 | 0.835 | 4.93 |
| 1% (Al2O3–Cu)-0.99 Water | 0.0016025 | 1024 | 4067 | 0.657 | 11.11 |
| COMSOL Mesh. | Details on Number of Elements at the Boundary and in the Domain |
|---|---|
| Coarser | 71,301 domain elements, 9686 boundary elements, 908 edge elements |
| Coarse | 157,028 domain elements, 17,902 boundary elements, 1276 edge elements |
| Normal | 320,985 domain elements, 29,642 boundary elements, 1674 edge elements |
| Fine | 643,293 domain elements, 47,756 boundary elements, 2140 edge elements |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elsafy, K.M.; Saghir, M.Z. Forced Convection in Wavy Microchannels Porous Media Using TiO2 and Al2O3–Cu Nanoparticles in Water Base Fluids: Numerical Results. Micromachines 2021, 12, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060654
Elsafy KM, Saghir MZ. Forced Convection in Wavy Microchannels Porous Media Using TiO2 and Al2O3–Cu Nanoparticles in Water Base Fluids: Numerical Results. Micromachines. 2021; 12(6):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060654
Chicago/Turabian StyleElsafy, Kholoud Maher, and Mohamad Ziad Saghir. 2021. "Forced Convection in Wavy Microchannels Porous Media Using TiO2 and Al2O3–Cu Nanoparticles in Water Base Fluids: Numerical Results" Micromachines 12, no. 6: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060654
APA StyleElsafy, K. M., & Saghir, M. Z. (2021). Forced Convection in Wavy Microchannels Porous Media Using TiO2 and Al2O3–Cu Nanoparticles in Water Base Fluids: Numerical Results. Micromachines, 12(6), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060654







