Highly Sensitive Hybrid Nanostructures for Dimethyl Methyl Phosphonate Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
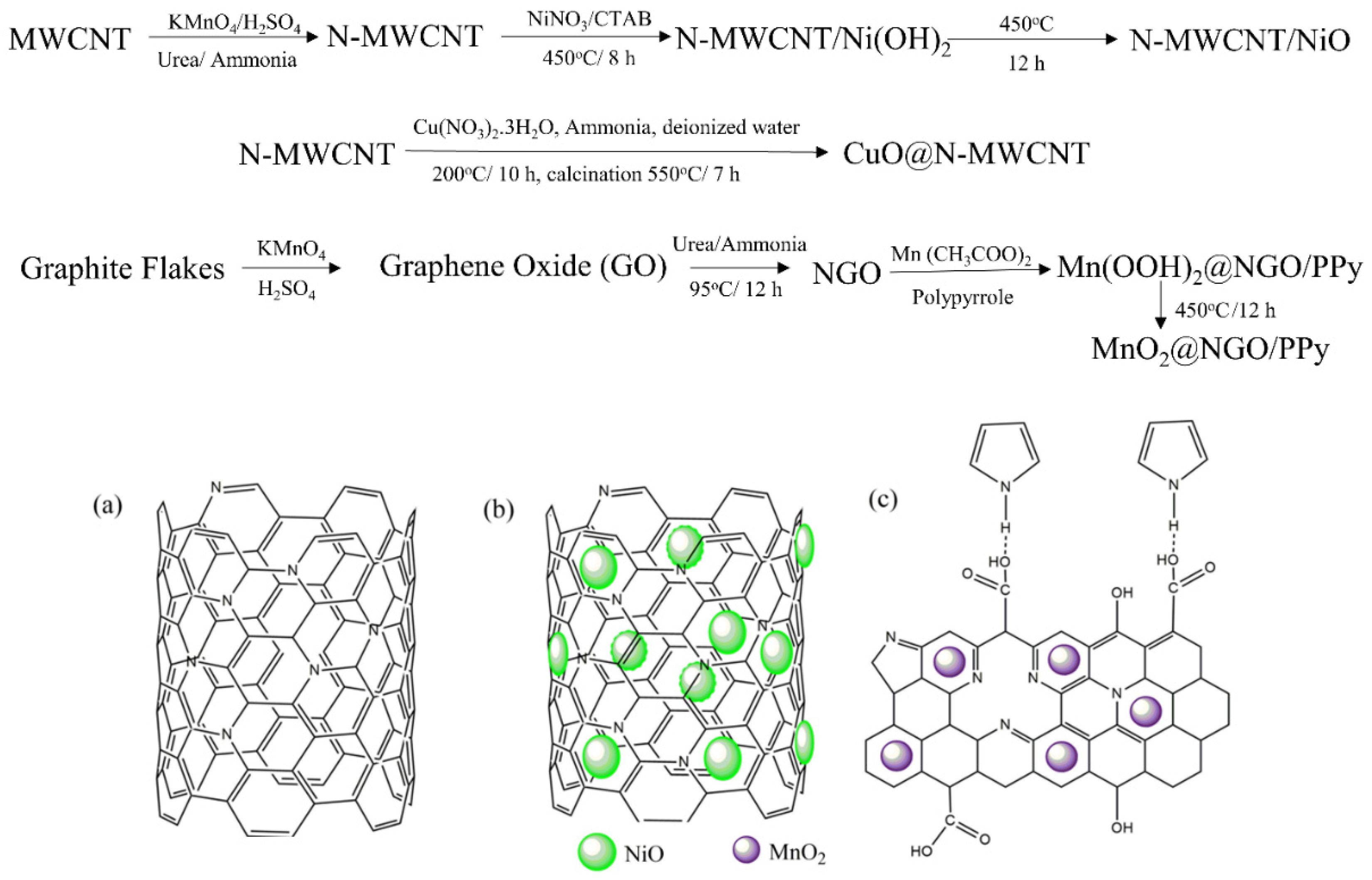
2.1. Fabrication of Composite Sensing Materials
2.2. Characterization Apparatus and Selectivity Conditions
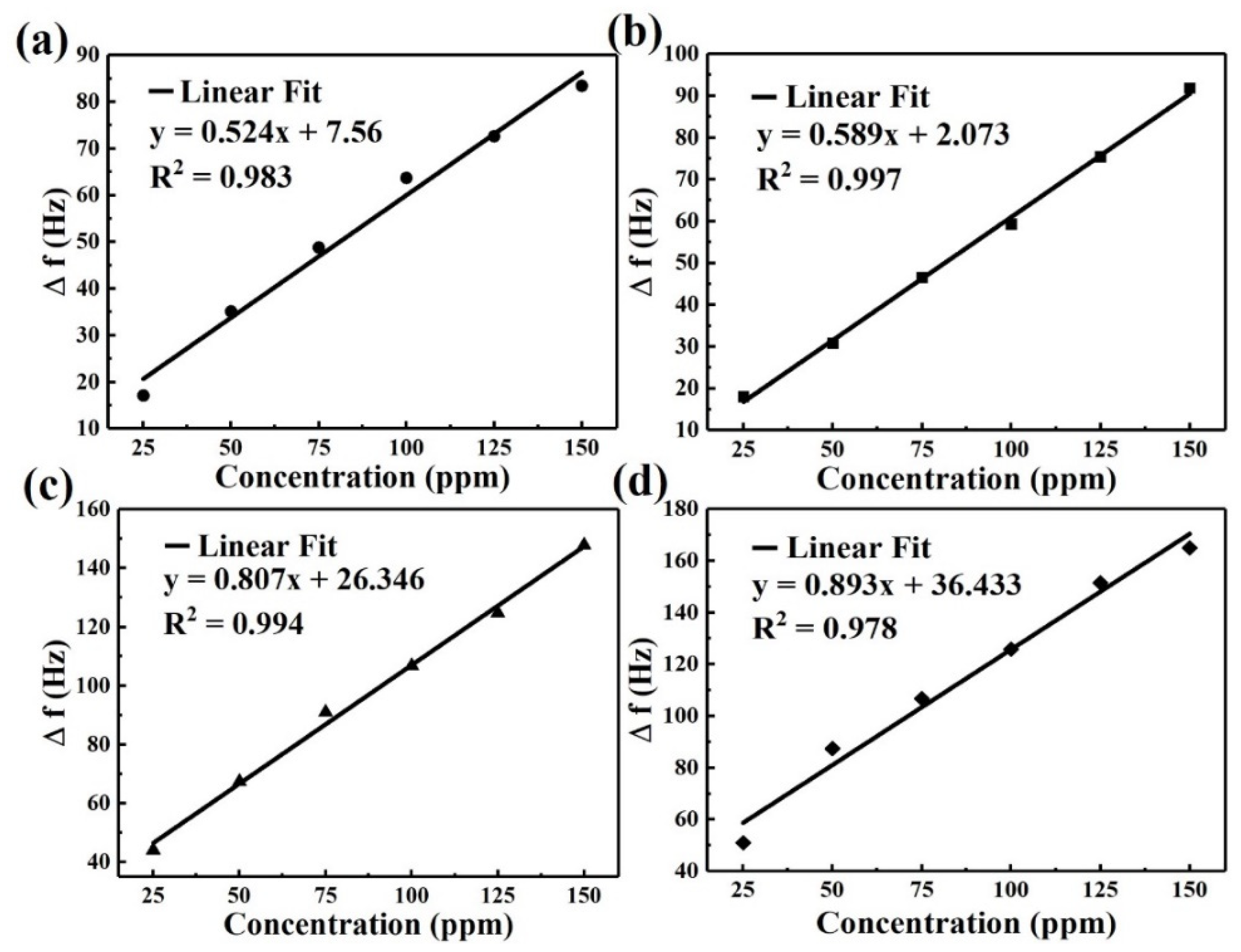
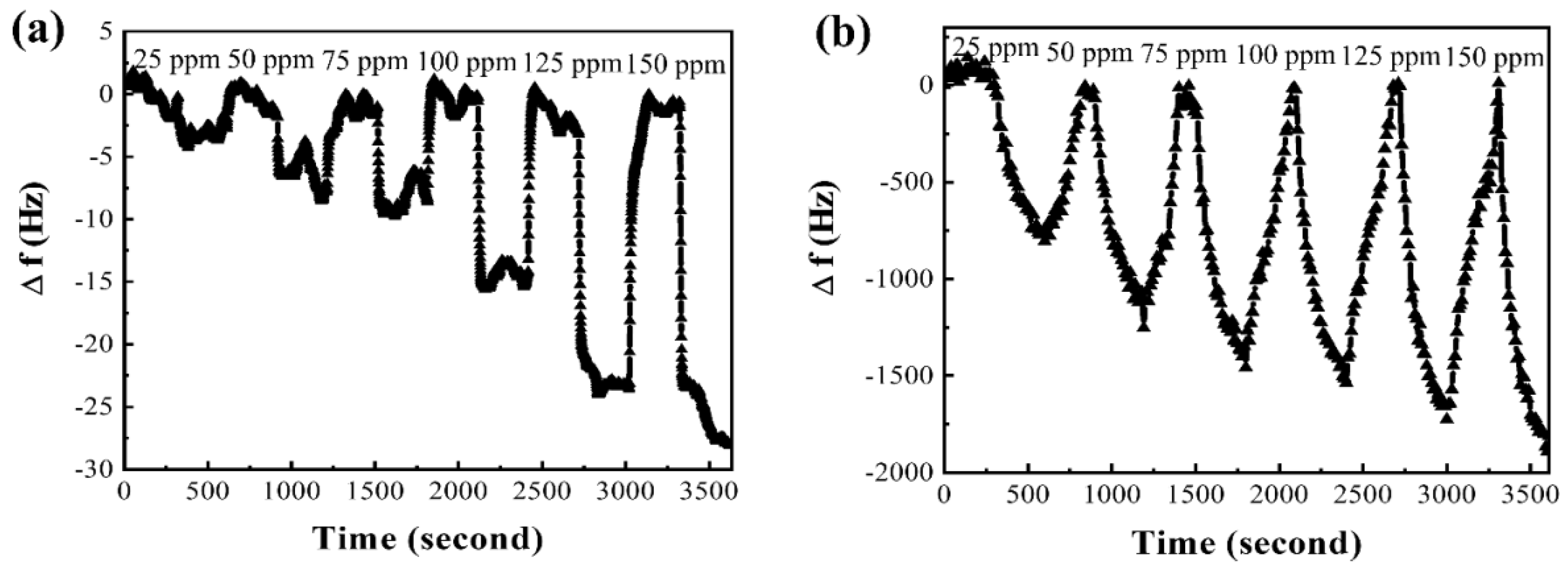
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chauhan, S.; D’Cruz, R.; Faruqi, S.; Singh, K.K.; Varma, S.; Singh, M.; Karthik, V. Chemical warfare agents. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 26, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, J.; Srinivasan, S.; Nagarajan, R. Using cheminformatics to find simulants for chemical warfare agents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 194, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.Y.; Loke, W.K.; Tan, Y.T.; Nguyen, N.T. A lab-on-a-chip for detection of nerve agent sarin in blood. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hou, Z.; Xu, D.; Wei, L.; Kong, E.S.W.; Zhang, Y. Flexible gas sensors with assembled carbon nanotube thin films for DMMP vapor detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Gas sensors based on deposited single-walled carbon nanotube networks for DMMP detection. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 345502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Ying, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T.; Xie, G. Synthesis and evaluation of a new polysiloxane as SAW sensor coatings for DMMP detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 134, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Shitang, H.; Shunzhou, L.; Minghua, L.; Yong, P. Enhanced sensitivity of SAW gas sensor coated molecularly imprinted polymer incorporating high frequency stability oscillator. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-G.; Kim, J.-H.; Yun, J.; Jang, W.J. Detection of dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP) using polyhedral poligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS). J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 6565–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Du, X.; Xie, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, H. PVDF coated quartz crystal microbalance sensor for DMMP vapor detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.P.; Snow, E.S.; Houser, E.J.; Park, D.; Stepnowski, J.L.; McGill, R.A. Nerve agent detection using networks of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 4026–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gu, H.; Swager, T.M. Carbon nanotube/polythiophene chemiresistive sensors for chemical warfare agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5392–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ji, H.F.; Thundat, T. Nerve agents detection using a Cu2+/L-cysteine bilayer-coated microcantilever. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1124–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Feng, W.; Wang, C.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Sun, P.; Shimanoe, K.; Yamazoe, N.; Lu, G. Porous ZnO/ZnCo2O4 hollow spheres: Synthesis, characterization, and applications in gas sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17683–17690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Ma, X.; Ding, P.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Z.; Li, G. Study of a QCM dimethyl methylphosphonate sensor based on a zno-modified nanowire-structured manganese dioxide film. Sensors 2010, 10, 8275–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, J.M.; Pariente, F.; Hernandez, L.; Abruna, H.D.; Lorenzo, E. Determination of organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides using a piezoelectric biosensor. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2848–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivens, D.E.; Palmer, R.J., Jr.; White, D.C. Continuous nondestructive monitoring of microbial biofilms: A review of analytical techniques. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 15, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Bai, Q.; Hu, J.; Hou, D. A practical model of quartz crystal microbalance in actual applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirri, F.; Palomba, E.; Longobardo, A.; Zampetti, E.; Saggin, B.; Scaccabarozzi, D. A review of quartz crystal microbalances for space applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 287, 48–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Ha, S.; Song, C.; Jang, W.J.; Yun, J. Four-channel Monitoring System with Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors for Detection of Chemical Warfare Agents. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 7151–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannov, A.G.; Popov, M.V.; Brester, A.E.; Kurmashov, P.B. Recent advances in ammonia gas sensors based on carbon nanomaterials. Micromachines 2021, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Park, S.; Cho, H.J. A carbon nanotube-metal oxide hybrid material for visible-blind flexible UV-Sensor. Micromachines 2020, 11, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Multiple-walled nanotubes made of metals. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, T.; Nitze, F.; Barzegar, H.R.; Tai, C.W.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Malolepszy, A.; Stobinski, L.; Wågberg, T. Nitrogen doped multi walled carbon nanotubes produced by CVD-correlating XPS and Raman spectroscopy for the study of nitrogen inclusion. Carbon 2012, 50, 3535–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, I.; Matatagui, D.; Fernández, M.J.; Fontecha, J.L.; Jurewicz, I.; Garriga, R.; Muñoz, E. Graphene oxide as sensitive layer in Love-wave surface acoustic wave sensors for the detection of chemical warfare agent simulants. Talanta 2016, 148, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.C.; Sharma, R.; Vyas, K.D.; Boopathi, M.; Singh, V.V.; Pandey, P. Electrochemical incorporation of copper phthalocyanine in conducting polypyrrole for the sensing of DMMP. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 151, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.; Kim, J.; Song, M.J.; Lee, W.; Noh, J.S. Nano-composite sensors composed of single-walled carbon nanotubes and polyaniline for the detection of a nerve agent simulant gas. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, S.R.; Suib, S.L.; Tang, X.; Satyapal, S. Photoassisted decomposition of dimethyl methylphosphonate over amorphous manganese oxide catalysts. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Yadav, H.M.; Karuppasamy, K.; Vikraman, D.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Fabrication of manganese oxide@nitrogen doped graphene oxide/polypyrrole (MnO2@NGO/PPy) hybrid composite electrodes for energy storage devices. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4227–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Karuppasamy, K.; Yadav, H.M.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H. Ni(OH)2-decorated nitrogen doped MWCNT nanosheets as an efficient electrode for high performance supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.; Kathalingam, A.; Karuppasamy, K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.S. Nanostructured CuO/Co2O4@ nitrogen doped MWCNT hybrid composite electrode for high-performance supercapacitors. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 166, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QCM200 Quartz Crystal Microbalance Digital Controller. Available online: https://www.thinksrs.com/downloads/pdfs/manuals/QCM200m.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- Hersee, S.D.; Ballingall, J.M. The operation of metalorganic bubblers at reduced pressure. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. Vac. Surf. Film 1990, 8, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butrow, A.B.; Buchanan, J.H.; Tevault, D.E. Vapor pressure of organophosphorus nerve agent simulant compounds. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, D.; Sprake, C.H.S. Thermodynamic properties of organic oxygen compounds XXV. Vapour pressures and normal boiling temperatures of aliphatic alcohols. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1970, 2, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamham, C.B.; Taylor, W.J.; Pignocco, J.M.; Rossini, F.D. Vapor pressures and boiling points of some paraffin, alkylcyclopentane, alkylcyclohexane, and alkylbenzene hydrocarbons. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1945, 35, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaws, C.L.; Yang, H.C. To estimate vapor pressure easily. Hydrocarb. Process. 1989, 49, 795–802. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ha, S.C.; Yang, H.; Kim, Y.T. Gas sensor measurement system capable of sampling volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in wide concentration range. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 122, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dou, H.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, T. Encapsuled nanoreactors (Au@SnO2): A new sensing material for chemical sensors. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2686–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Shi, D.; Ye, P.; Dai, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, D.; Wang, Z. Hole doping and surface functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotube chemiresistive sensors for ultrasensitive and highly selective organophosphor vapor detection. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 425501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, E.; Zeinali, S. Nanoporous MIL-101(Cr) as a sensing layer coated on a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) nanosensor to detect volatile organic compounds (VOCs). RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 24460–24470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.; Rao, V.K.; Ramana, G.V.; Halder, M.; Gutch, P.K.; Pandey, P.; Jain, R. p-Hexafluoroisopropanol phenyl functionalized graphene for QCM based detection of dimethyl methylphosphonate, a simulant of the nerve agent sarin. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 8240–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kösemen, A.; Öztürk, S.; Şen, Z.; Kösemen, Z.A.; Harbeck, M.; Öztürk, Z.Z. Volatile organic compounds and dimethyl methyl phosphonate (DMMP) sensing properties of the metal oxide functionalized QCM transducers at room temperature. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, B657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Msolli, S.; Kim, J.-G.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.-H. Synthesis of a Co3O4@ gold/MWCNT/polypyrrole hybrid composite for DMMP detection in chemical sensors. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50912–50919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, H.; Fan, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Hu, R. A wireless-electrodeless quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation DMMP sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Yao, W.; Hu, Y.; Ren, N.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of nanozeolites as adsorbent for Dimethyl Methylphosphonate. Sens. Mater. 2011, 23, 303–313. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Yang, M.; Gao, S.; Zuo, G.; Yan, C.; Cheng, Z. Single crystal WO3 nanoflakes as quartz crystal microbalance sensing layer for ultrafast detection of trace sarin simulant. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 654, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, G.-H.; Jung, D.; Kim, J.-H. Dimethyl Methylphosphonate detection using a quartz crystal microbalance as chemical warfare sensor. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2015, 7, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procek, M.; Stolarczyk, A.; Pustelny, T.; Maciak, E. A Study of a QCM Sensor Based on TiO2 Nanostructures for the Detection of NO2 and Explosives Vapours in Air. Sensors 2015, 15, 9563–9581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Vapors | Equation | Unit | A | B | C | Temp. Range [K] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMMP | (2) | T (K), P (Pa) | 22.31900 | 4340.00 | −51.700 | 263.2–453.8 |
| Ethanol | (3) | T (K), P (kPa) | 7.24739 | 1599.04 | −46.391 | 292.8–366.6 |
| N-hexane | (3) | T (°C), P (mmHg) | 6.87776 | 1171.53 | 224.366 | 286.18–342.7 |
| Water | (3) | T (°C), P (mmHg) | 8.07131 | 1730.63 | 233.426 | 274.0–373.0 |
| Toluene | (3) | T (°C), P (mmHg) | 6.95464 | 1344.80 | 219.482 | 279.0–409.0 |
| Methanol | (3) | T (°C), P (mmHg) | 8.07240 | 1574.99 | 238.870 | 257.0–364.0 |
| Sensing Nanocomposite Film | Response (Hz) | Standard Deviation (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| CuO@N-MWCNT | 12.6 | 1.71 |
| N-MWCNT | 19.02 | 1.21 |
| N-MWCNT@NiO | 47.40 | 2.38 |
| MnO2@NGO/PPy | 47.29 | 2.69 |
| Sensor Characteristics | DMMP Concentration (ppm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanocomposites | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | |
| Response time (s) τ90% | CuO@N-MWCNT | ~121 | ~115 | ~108 | ~104 | ~102 |
| N-MWCNT | ~130 | ~100 | ~100 | ~101 | ~100 | |
| N-MWCNT@NiO | ~117 | ~104 | ~106 | ~103 | ~96 | |
| MnO2@NGO/PPy | ~136 | ~101 | ~103 | ~99 | ~123 | |
| Recovery time (s) τ90% | CuO@N-MWCNT | ~155 | ~195 | ~113 | ~139 | ~143 |
| N-MWCNT | ~193 | ~142 | ~135 | ~132 | ~170 | |
| N-MWCNT@NiO | ~206 | ~142 | ~150 | ~139 | ~144 | |
| MnO2@NGO/PPy | ~142 | ~123 | ~117 | ~118 | ~113 | |
| Ref. | Materials | Concentration (ppm) | Response (Hz) | Response Time (s) | Recovery Times (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [41] | HFIPP-GR | 5 | 71 ± 4 | T80 < 108 | T80 = 600 |
| [42] | V2O5 coated ZnO nanorods | 15 | ~40 | T80 < 300 | T80 > 900 |
| [43] | Co3O4@gold/MWCNT/polypyrrole | 60 | 90 | T98 = 60 | T98 = 493 |
| [44] | In2O3-Au | 50 | <80 | <100 | ~200 |
| [45] | Zeolite Socony Mobil-5 | 20 | ~55 | T80 < 100 | - |
| [46] | WO3 nanoflake | 3.91 | <160 | 30 | 73 |
| [47] | Polyvinylidene fluoride | 150 | ~50 | ~60 | ~60 |
| This work | MnO2@NGO/PPy | 50 | 87 | T90 = 101 | T90 = 123 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lama, S.; Kim, J.; Ramesh, S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.-H. Highly Sensitive Hybrid Nanostructures for Dimethyl Methyl Phosphonate Detection. Micromachines 2021, 12, 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060648
Lama S, Kim J, Ramesh S, Lee Y-J, Kim J, Kim J-H. Highly Sensitive Hybrid Nanostructures for Dimethyl Methyl Phosphonate Detection. Micromachines. 2021; 12(6):648. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060648
Chicago/Turabian StyleLama, Sanjeeb, Jinuk Kim, Sivalingam Ramesh, Young-Jun Lee, Jihyun Kim, and Joo-Hyung Kim. 2021. "Highly Sensitive Hybrid Nanostructures for Dimethyl Methyl Phosphonate Detection" Micromachines 12, no. 6: 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060648
APA StyleLama, S., Kim, J., Ramesh, S., Lee, Y.-J., Kim, J., & Kim, J.-H. (2021). Highly Sensitive Hybrid Nanostructures for Dimethyl Methyl Phosphonate Detection. Micromachines, 12(6), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060648





