Capacitance Effects of a Hydrophobic-Coated Ion Gel Dielectric on AC Electrowetting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals of an Ion Gel Dielectric for AC Electrowetting
3. Experimental Setup
4. Results and Discussion
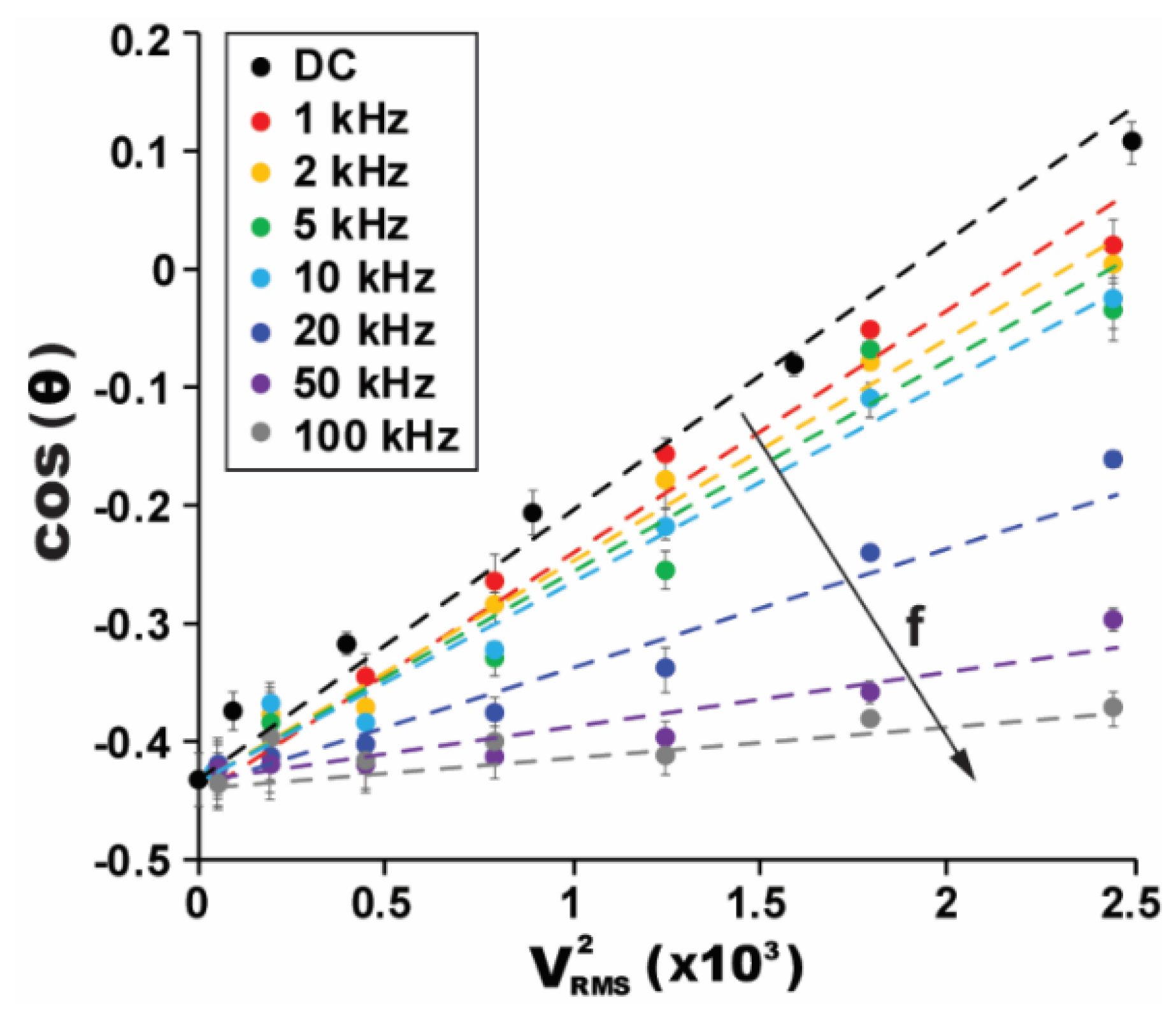
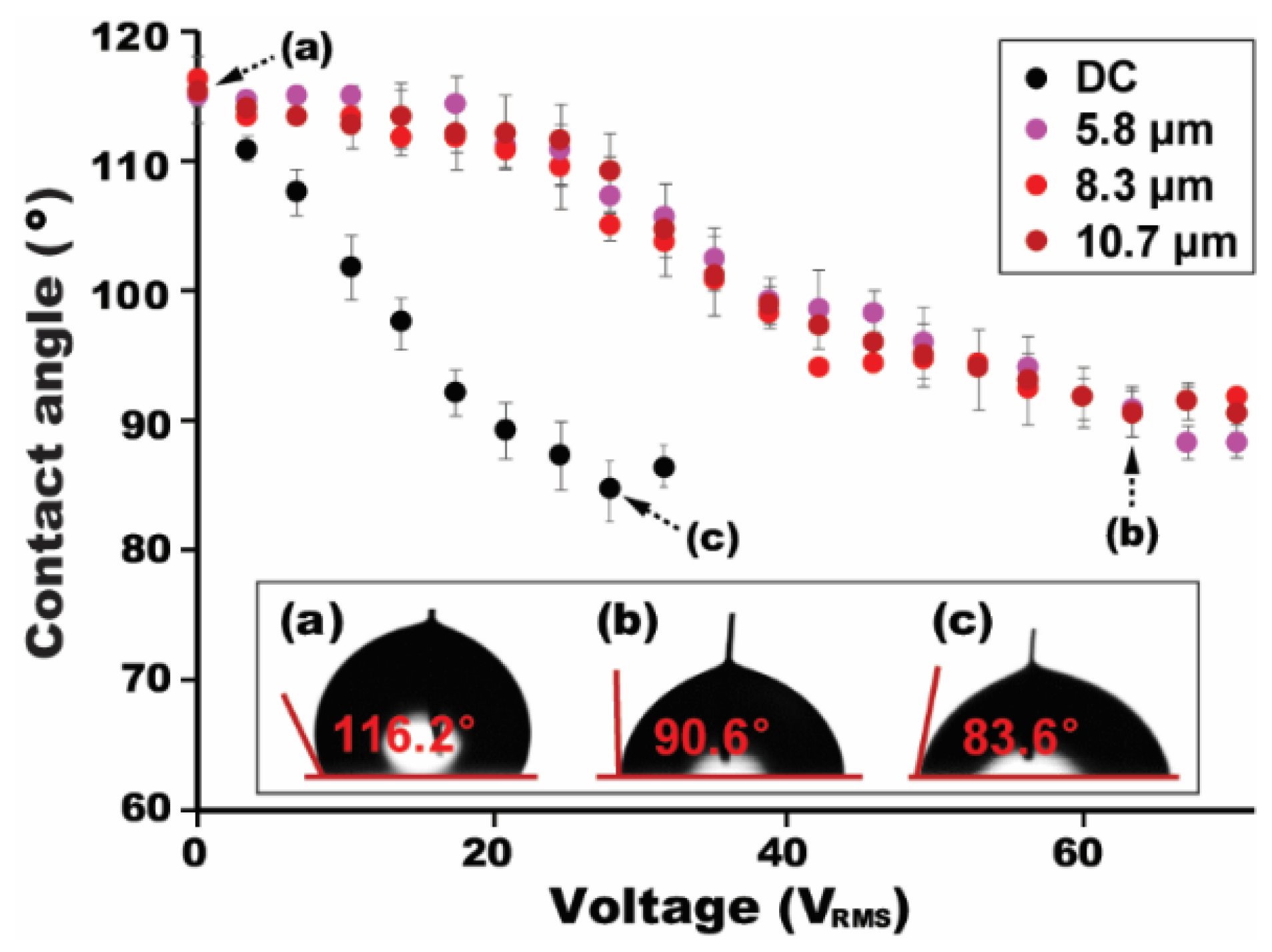
4.1. High-Frequency AC Electrowetting with the Ion Gel
4.2. Low-Frequency AC Electrowetting with the Ion Gel
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wheeler, A.R. Putting Electrowetting to Work. Science 2008, 322, 539–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, M.G.; Richard, B.F.; Shenderov, A.D. Electrowetting-based actuation of liquid droplets for microfluidic applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 1725–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Teitell, M.A.; Chiou, E.P.Y. Single-sided continuous optoelectrowetting (SCOEW) for droplet manipulation with light patterns. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugele, F.; Baret, J.-C. Electrowetting: From basics to applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, 705–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Cho, S.K.; Garrell, R.L.; Kim, C.-J. Low voltage electrowetting-on-dielectric. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 4080–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, M.G. Relations entre les phénomènes electriques et capillaires. Ann. Chim. Phys. 1875, 5, 494–549. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, H.; Wheeler, A.R.; Garrell, R.L.; Loo, J.A.; Kim, C.-J. An integrated digital microfluidic chip for multiplexed proteomic sample preparation and analysis by MALDI-MS. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Lee, S.; Bae, S.W.; Park, S.-Y. Smartphone integrated optoelectrowetting (SiOEW) for on-chip sample processing and microscopic detection of water quality. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-W.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Fan, S.-K. Constructing 3D heterogeneous hydrogels from electrically manipulated prepolymer droplets and crosslinked microgels. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, C.; Thio, S.K.; Park, S.-Y. An optofluidic tunable Fresnel lens for spatial focal control based on electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD). Sens. Actuators B 2017, 240, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J. Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 2003, 425, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, C.E.; Park, S.-Y. High-performance beam steering using electrowetting-driven liquid prism fabricated by a simple dip-coating method. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 191601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, S.K.; Jiang, D.; Park, S.-Y. Electrowetting-driven solar indoor lighting (e-SIL): An optofluidic approach towards sustainable buildings. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupenkin, T.; Taylor, J.A. Reverse electrowetting as a new approach to high-power energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, V.; Jiang, D.; Park, S.-Y. Design and optical analyses of an arrayed microfluidic tunable prism panel for enhancing solar energy collection. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Nam, Y. Single-sided Digital Microfluidic (SDMF) Devices for Effective Coolant Delivery and Enhanced Two-Phase Cooling. Micromachines 2017, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, K.; Baird, E. Digitized Heat Transfer Using Electrowetting on Dielectric. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 2007, 11, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, V.; Park, S.-Y. An ion gel as a low-cost, spin-coatable, high-capacitance dielectric for electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD). Langmuir 2015, 31, 8512–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Zhang, S.; Lodge, T.P.; Frisbie, C.D. Electrical impedance of spin-coatable ion gel films. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.; Xia, Y.; Kim, B.; He, Y.; Renn, M.J.; Lodge, T.P.; Frisbie, C.D. Printable ion-gel gate dielectrics for low-voltage polymer thin-film transistors on plastic. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, M.V.; Kornyshev, A.A. Ionic liquids at electrified interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 2978–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.; He, Y.; Kim, B.; Lodge, T.P.; Frisbie, C.D. High-capacitance ion gel gate dielectrics with faster polarization response times for organic thin film transistors. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.B. More about the electromechanics of electrowetting. Mech. Res. Commun. 2009, 36, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.S.; Ko, S.H.; Kang, K.H.; Kang, I.S. A numerical investigation on AC electrowetting of a droplet. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2008, 5, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.M.; Ko, S.H.; Kang, K.H. Shape Oscillation of a Drop in ac Electrowetting. Langmuir 2008, 24, 8379–8386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baret, J.-C.; Decre, M.M.J. Self-Excited Drop Oscillations in Electrowetting. Langmuir 2007, 23, 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.H.; Lee, H.; Kang, K.H. Hydrodynamic Flows in Electrowetting. Langmuir 2008, 24, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugele, F.; Baret, J.-C.; Steinhauser, D. Microfluidic mixing through electrowetting-induced droplet oscillations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 204106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-L.; Jones, T.B. Saturation effects in dynamic electrowetting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 054104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, B.; Peseux, J. Variable Focal Lens Controlled by an External Voltage: An Application of Electrowetting. Eur. Phys. J. E 2000, 3, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiński, M.; Lewandowski, A.; Stępniak, I. Ionic liquids as electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5567–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, A.; Bardi, U.; Caporali, S.; Mastragostino, M.; Soavia, F. Ionic liquids for hybrid supercapacitors. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yuan, C.; Guo, J.; Qiu, L.; Yan, F. Supramolecular ionic liquid gels for quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 8723–8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.T.; Jeong, S.S.; Xue, M.Z.; Balducci, A.; Winter, M.; Passerini, S.; Alessandrini, F.; Appetecchi, G.B. Development of ionic liquid-based lithium battery prototypes. J. Power Sources 2012, 199, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Ionic liquid lubricants: Designed chemistry for engineering applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kang, M.S.; Zhang, S.; Gu, Y.; Lodge, T.P.; Frisbie, C.D. “Cut and stick” rubbery ion gels as high capacitance gate dielectrics. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4457–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lee, K.H.; Frisbie, D.; Lodge, T.P. Ionic conductivity, capacitance, and viscoelastic properties of block copolymer-based ion gels. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornyshev, A.A. Double-Layer in Ionic Liquids: Paradigm Change? J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 5545–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugele, F.; Duits, M.; van den Ende, D. Electrowetting: A versatile tool for drop manipulation, generation, and characterization. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 161, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.B.; Wang, K.L.; Yao, D.J. Frequency-dependent electromechanics of aqueous liquids: Electrowetting and dielectrophoresis. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2813–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sur, A.; Pascente, C.; Ravi Annapragada, S.; Ruchhoeft, P.; Liu, D. Dynamics of droplet motion induced by Electrowetting. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 2017, 106, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, T.; Park, S.-Y. Capacitance Effects of a Hydrophobic-Coated Ion Gel Dielectric on AC Electrowetting. Micromachines 2021, 12, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12030320
Lee T, Park S-Y. Capacitance Effects of a Hydrophobic-Coated Ion Gel Dielectric on AC Electrowetting. Micromachines. 2021; 12(3):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12030320
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Taewoo, and Sung-Yong Park. 2021. "Capacitance Effects of a Hydrophobic-Coated Ion Gel Dielectric on AC Electrowetting" Micromachines 12, no. 3: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12030320
APA StyleLee, T., & Park, S.-Y. (2021). Capacitance Effects of a Hydrophobic-Coated Ion Gel Dielectric on AC Electrowetting. Micromachines, 12(3), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12030320






