A Rapid Digital PCR System with a Pressurized Thermal Cycler
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
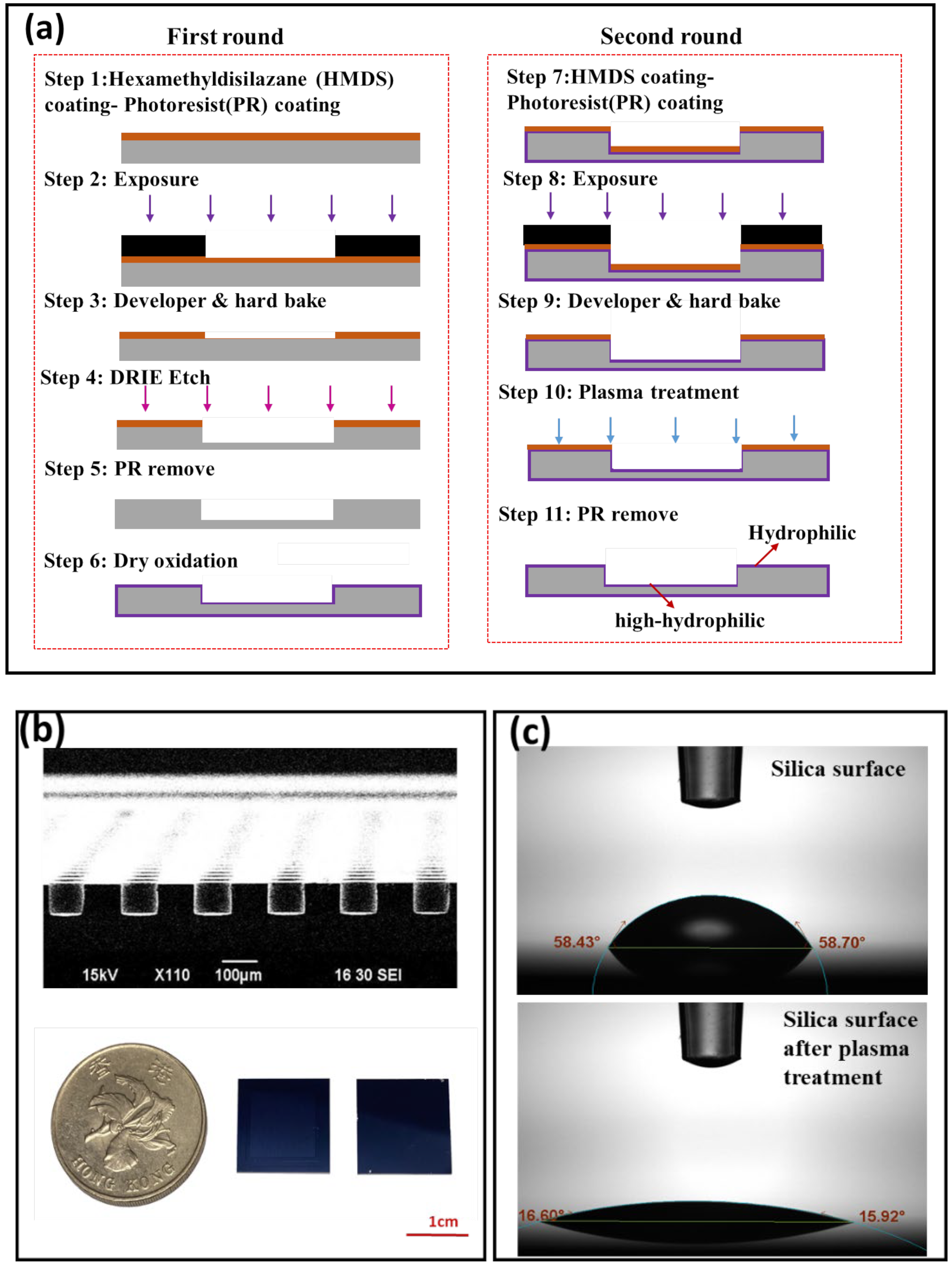
2.1. Open Well SDA Chip
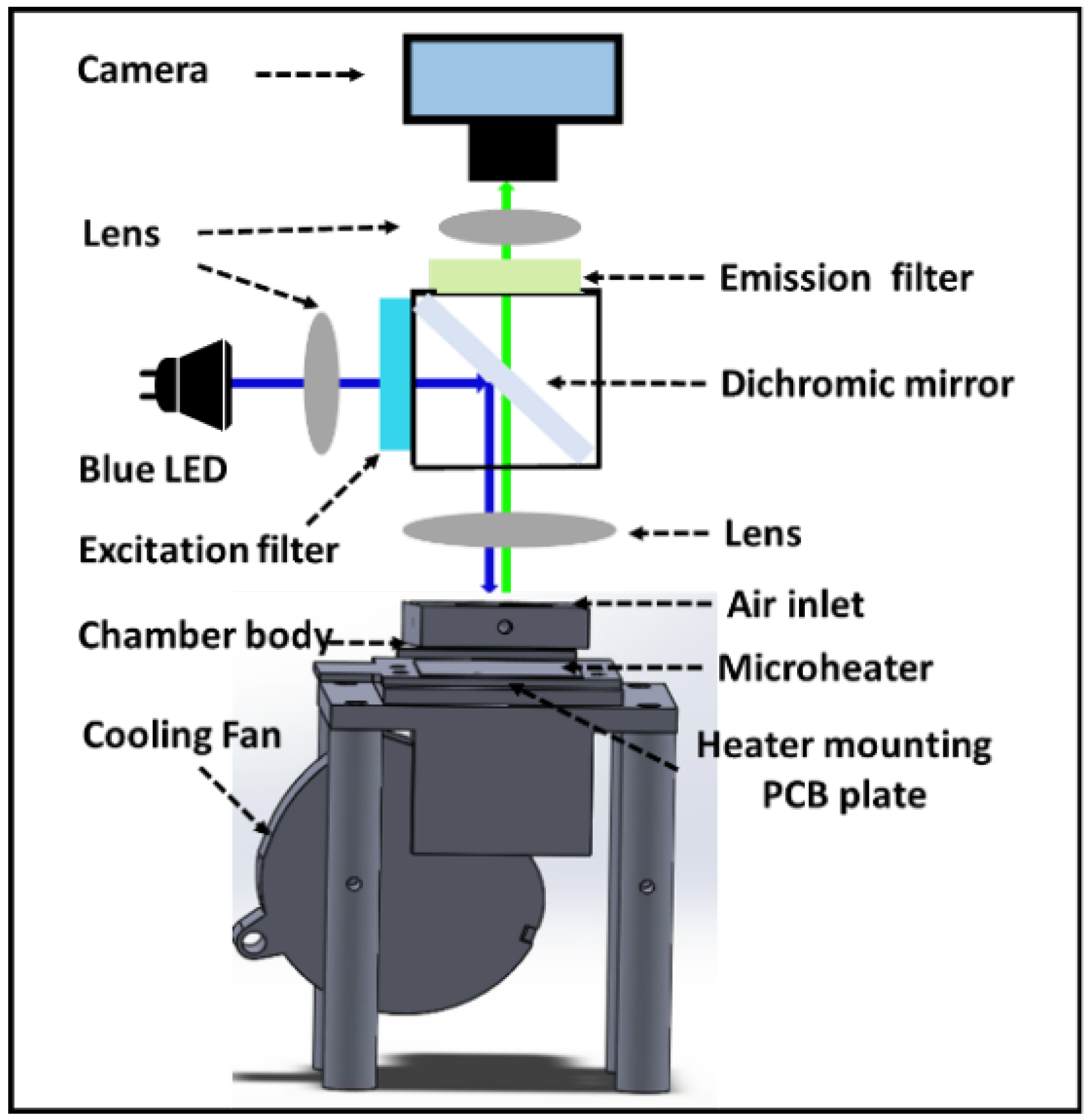
2.2. Real-Time Fluorescence Monitoring System
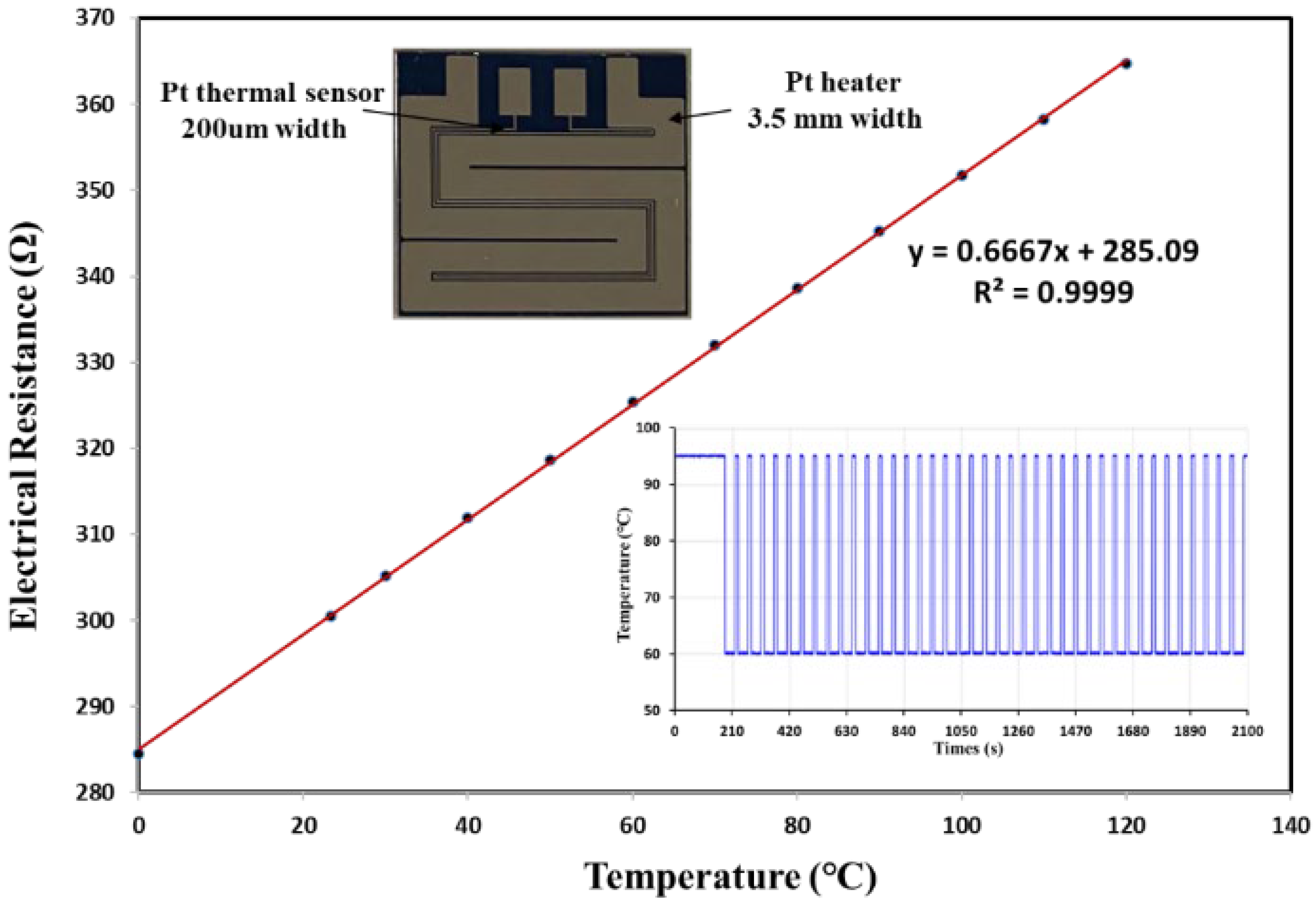
2.3. Design and Configuration of the Pressurized Thermal Cycler (PTC)
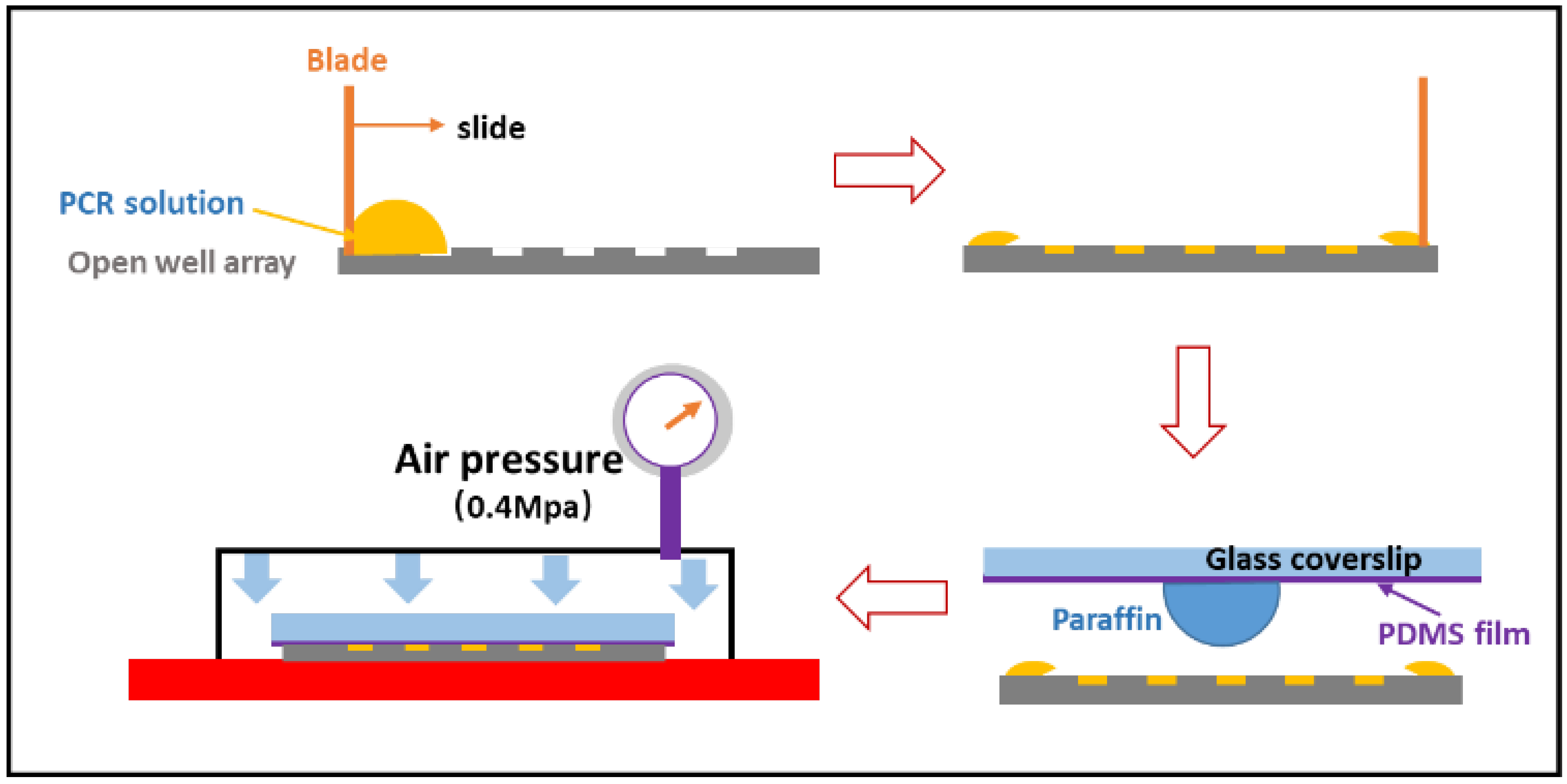
2.4. Sample Loading and Sealing
2.5. Digital PCR
3. Results and Discussion
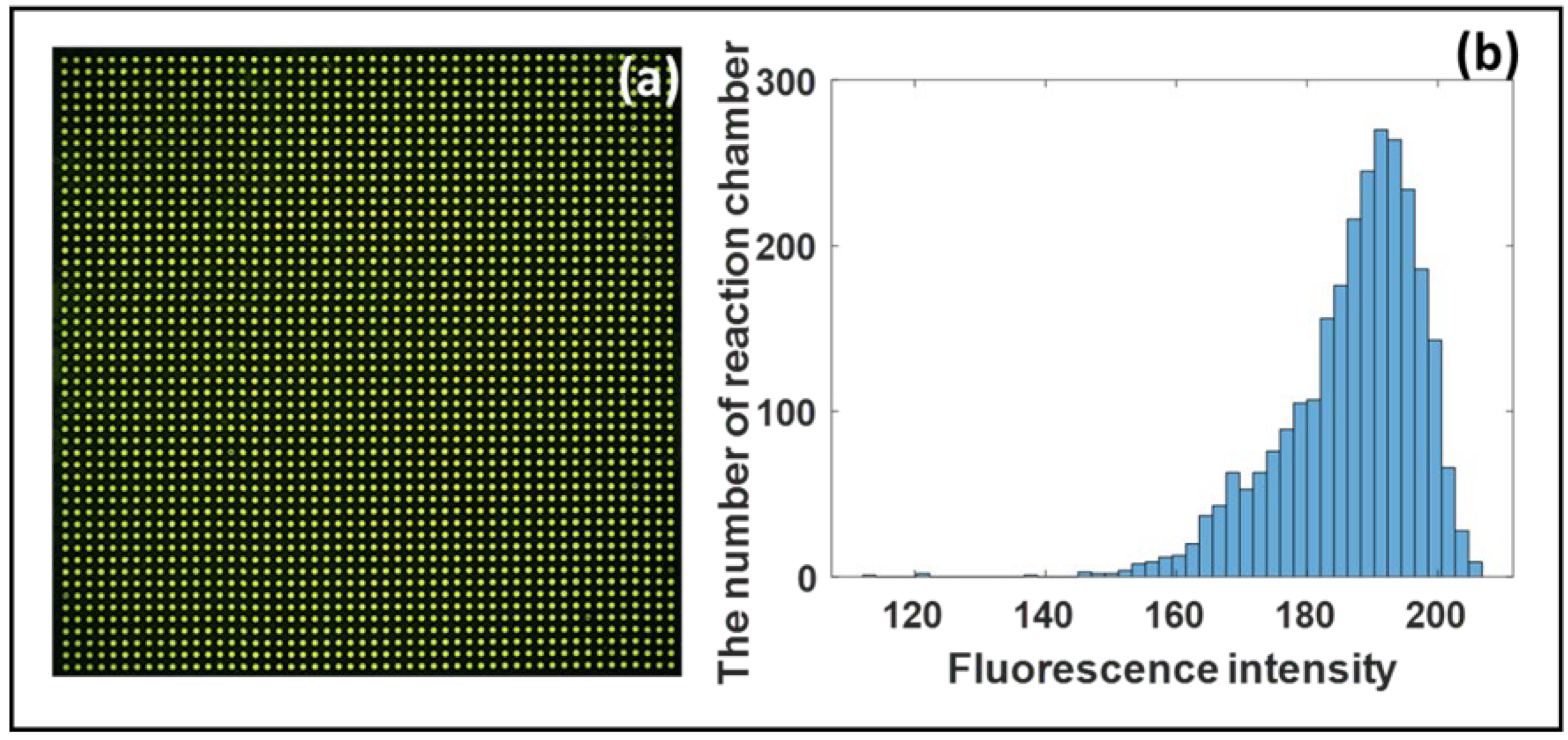
3.1. The Uniformity of Test Solution
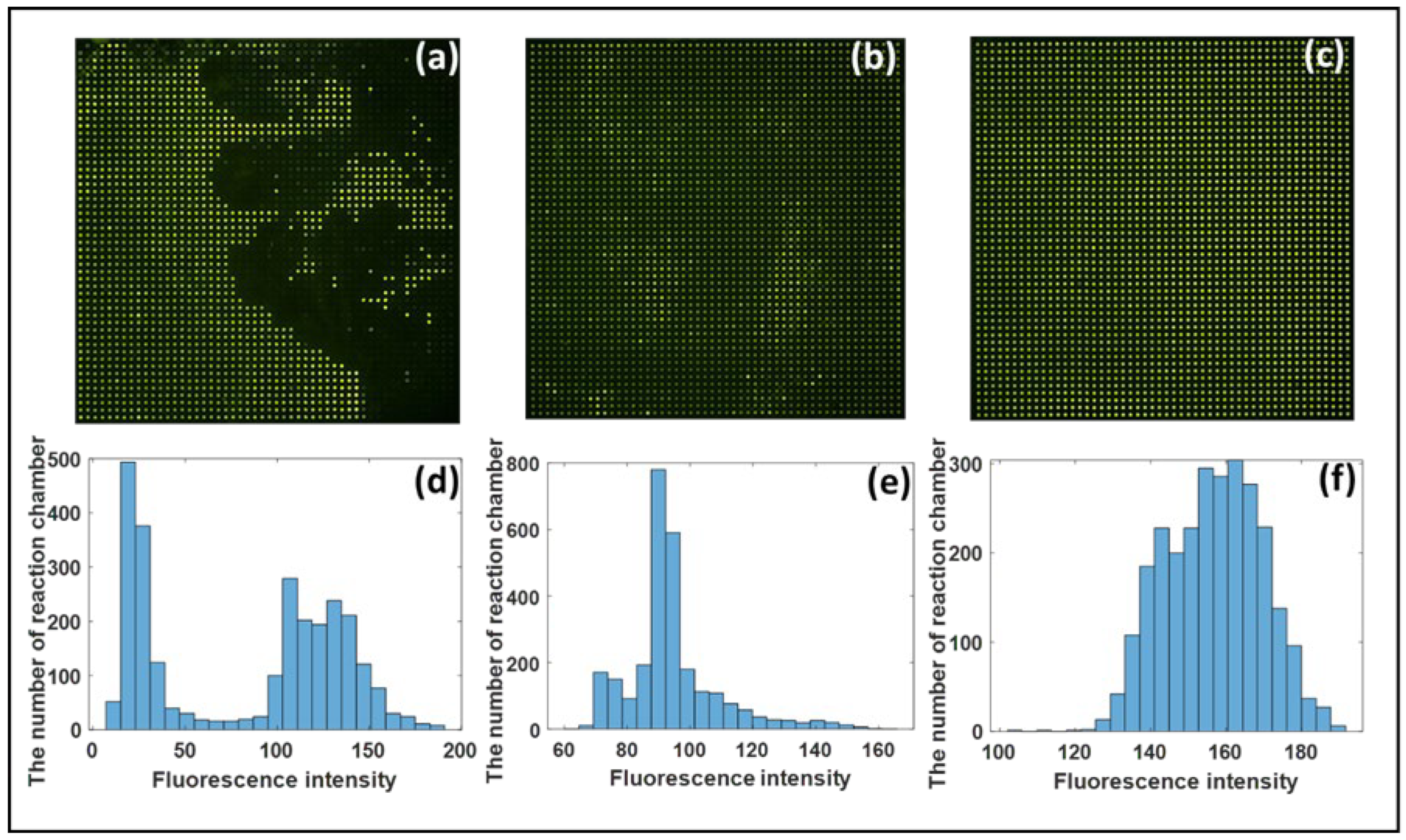
3.2. Analysis of Chip Anti-Evaporation Effect
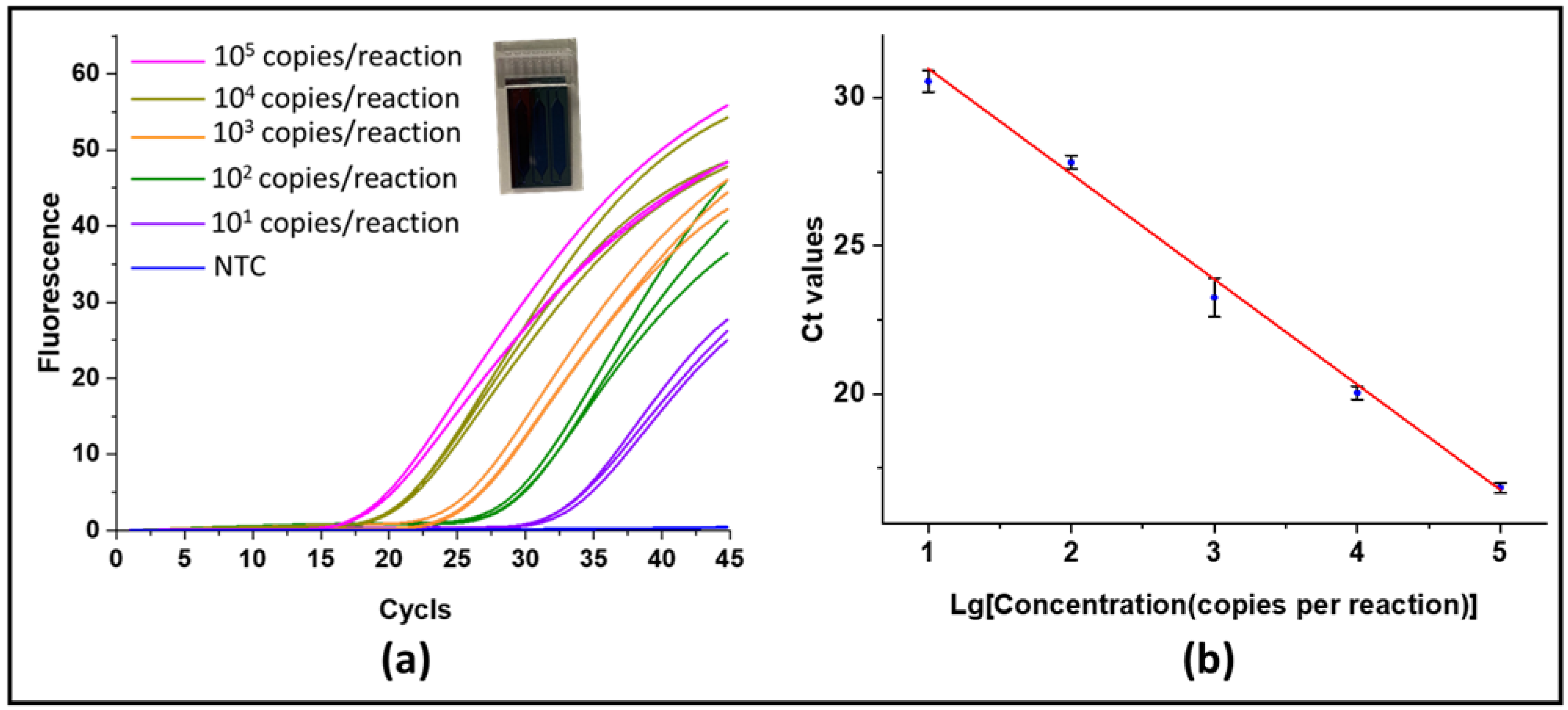
3.3. Digital PCR Analysis
3.4. Real-Time PCR Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Digital PCR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9236–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pohl, G.; Shih, I. Principle and applications of digital PCR. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2004, 4, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekin, D.; Skhiri, Y.; Baret, J.; Le Corre, D.; Mazutis, L.; Salem, C.B.; Millot, F.; El Harrak, A.; Hutchison, J.B.; Larson, J.W. Quantitative and sensitive detection of rare mutations using droplet-based microfluidics. Lab. Chip. 2011, 11, 2156–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggett, J.F.; Cowen, S.; Foy, C.A. Considerations for digital PCR as an accurate molecular diagnostic tool. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dube, S.; Qin, J.; Ramakrishnan, R. Mathematical analysis of copy number variation in a DNA sample using digital PCR on a nanofluidic device. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettger, L.M.; Handsaker, R.E.; Zody, M.C.; McCarroll, S.A. Structural haplotypes and recent evolution of the human 17q21.31 region. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alikian, M.; Ellery, P.; Forbes, M.; Gerrard, G.; Kasperaviciute, D.; Sosinsky, A.; Mueller, M.; Whale, A.S.; Milojkovic, D.; Apperley, J. Next-generation sequencing-assisted DNA-based digital PCR for a personalized approach to the detection and quantification of residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia patients. J. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 18, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; Cao, L.; Huang, Y.; Bai, D.; Huang, S.; Lin, M.; Yang, Q.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F.; Li, F. In vitro diagnosis of DNA methylation biomarkers with digital PCR in breast tumors. Analyst 2018, 143, 3011–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Isa, S.; Ando, M.; Tamiya, A.; Kubo, A.; Saka, H.; Takeo, S.; Adachi, H.; Tagawa, T. Ultra-sensitive detection of the pretreatment EGFR T790M mutation in non–small cell lung cancer patients with an EGFR-activating mutation using droplet digital PCR. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3552–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbisier, P.; Bhat, S.; Partis, L.; Xie, V.R.D.; Emslie, K.R. Absolute quantification of genetically modified MON810 Maize (Zea mays L.) by digital polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Jeong, S.; Cho, K. Comparison of droplet digital PCR and quantitative real-time PCR for examining population dynamics of bacteria in soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6105–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, N.R.; Hindson, B.J.; Wheeler, E.K.; Hall, S.B.; Rose, K.A.; Kennedy, I.M.; Colston, B.W. On-chip, real-time, single-copy polymerase chain reaction in picoliter droplets. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8471–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hindson, B.J.; Ness, K.D.; Masquelier, D.A.; Belgrader, P.; Heredia, N.J.; Makarewicz, A.J.; Bright, I.J.; Lucero, M.Y.; Hiddessen, A.L.; Legler, T.C. High-throughput droplet digital PCR system for absolute quantitation of DNA copy number. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8604–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, L.; He, J.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Wu, P.; He, L. Capillary-based integrated digital PCR in picoliter droplets. Lab. Chip. 2018, 18, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, N.; Koga, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Nakajima, H.; Lin, J.; Uchiyama, K. Inkjet printing based droplet generation for integrated online digital polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5329–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, Y.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sims, P.A.; Greenleaf, W.J.; Huang, Y. Digital polymerase chain reaction in an array of femtoliter polydimethylsiloxane microreactors. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4262–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottesen, E.A.; Hong, J.W.; Quake, S.R.; Leadbetter, J.R. Microfluidic digital PCR enables multigene analysis of individual environmental bacteria. Science 2006, 314, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundberg, S.O.; Wittwer, C.T.; Gao, C.; Gale, B.K. Spinning disk platform for microfluidic digital polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Li, L.; Nichols, K.P.; Ismagilov, R.F. SlipChip. Lab. Chip. 2009, 9, 2286–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Sun, J.; Mu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Jin, Q. A new method for polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microfluidic chips to maintain vacuum-driven power using parylene C. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Zhang, L.; Song, Q.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Lou, K.; Gong, X.; Gao, Y.; Wen, W. A fully portable microchip real-time polymerase chain reaction for rapid detection of pathogen. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Wen, W. High-throughput generation of durable droplet arrays for single-cell encapsulation, culture, and monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4303–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarsi, P. Digital PCR—Methods and protocols. Eur. J. Histochem. EJH 2019, 63, 3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Song, Q.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Lou, K.; Liu, Y.; Wen, W. A Rapid Digital PCR System with a Pressurized Thermal Cycler. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121562
Chen X, Song Q, Zhang B, Gao Y, Lou K, Liu Y, Wen W. A Rapid Digital PCR System with a Pressurized Thermal Cycler. Micromachines. 2021; 12(12):1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121562
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xuee, Qi Song, Beini Zhang, Yibo Gao, Kai Lou, Yiteng Liu, and Weijia Wen. 2021. "A Rapid Digital PCR System with a Pressurized Thermal Cycler" Micromachines 12, no. 12: 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121562
APA StyleChen, X., Song, Q., Zhang, B., Gao, Y., Lou, K., Liu, Y., & Wen, W. (2021). A Rapid Digital PCR System with a Pressurized Thermal Cycler. Micromachines, 12(12), 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121562




