Design and Fabrication of a Microfluidic Chip for Particle Size-Exclusion and Enrichment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Working Principle and Experimental Equipment
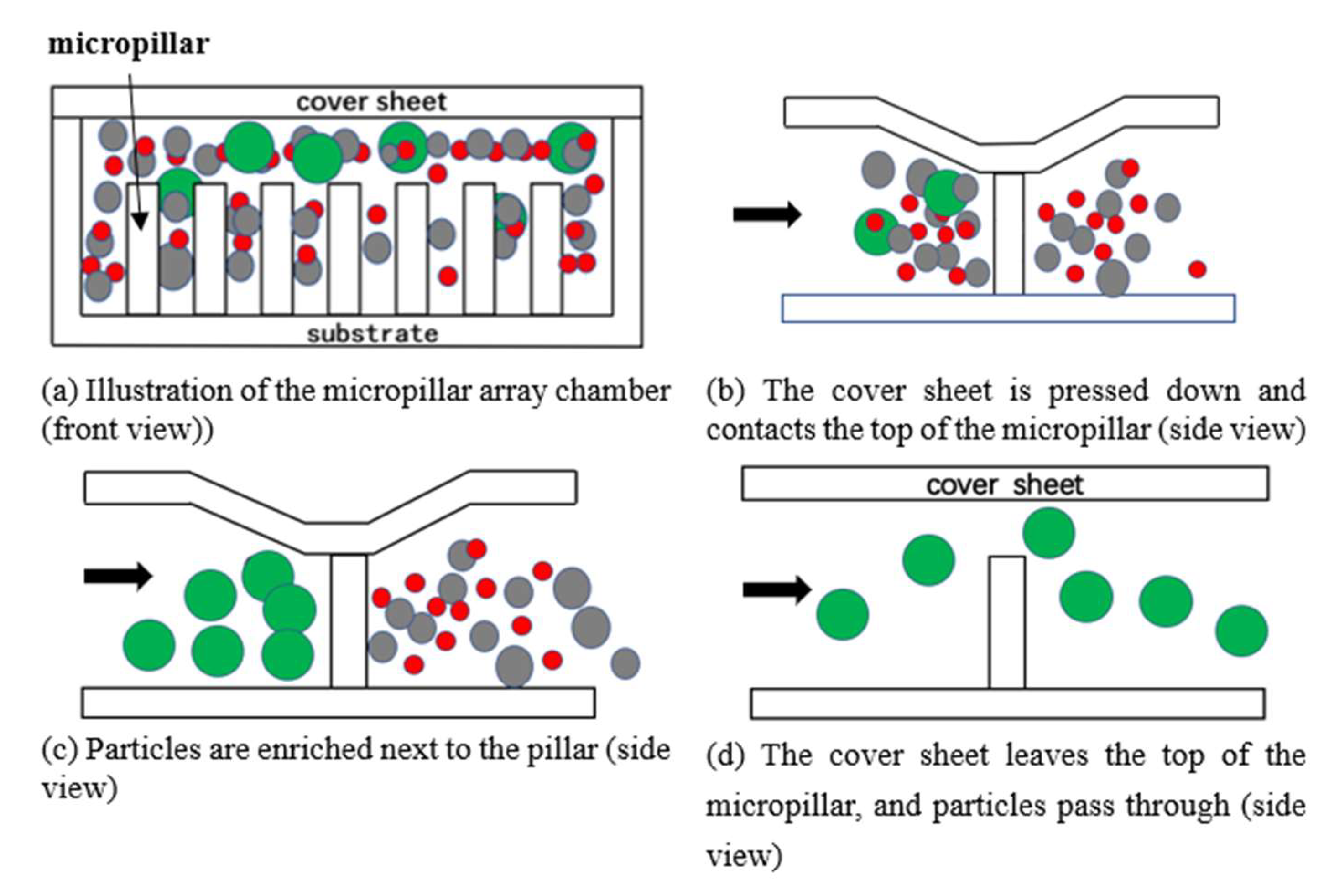
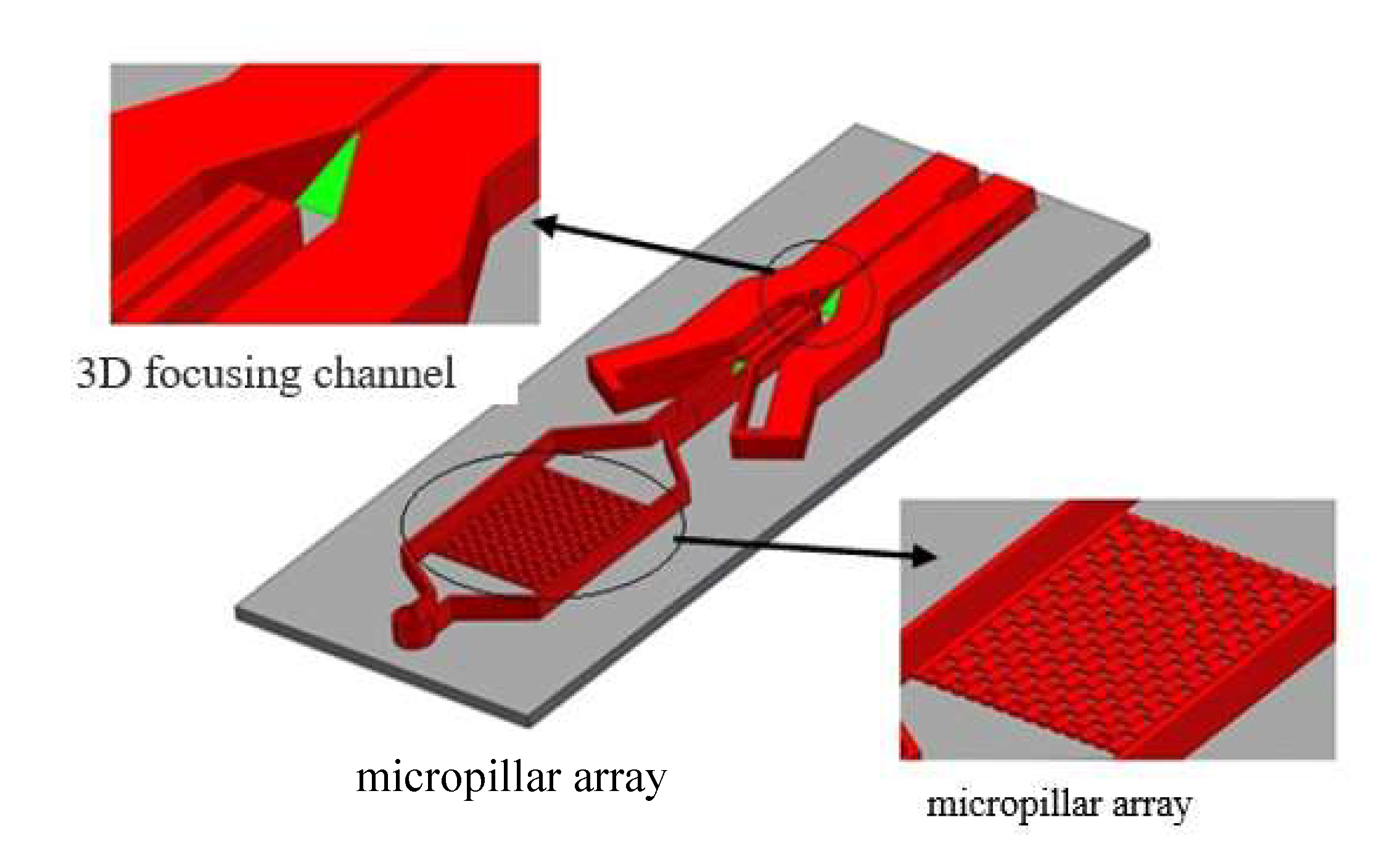
2.1. Enrichment and Sorting Principle of Specific Size Micro Particles by Microfluidic Chip
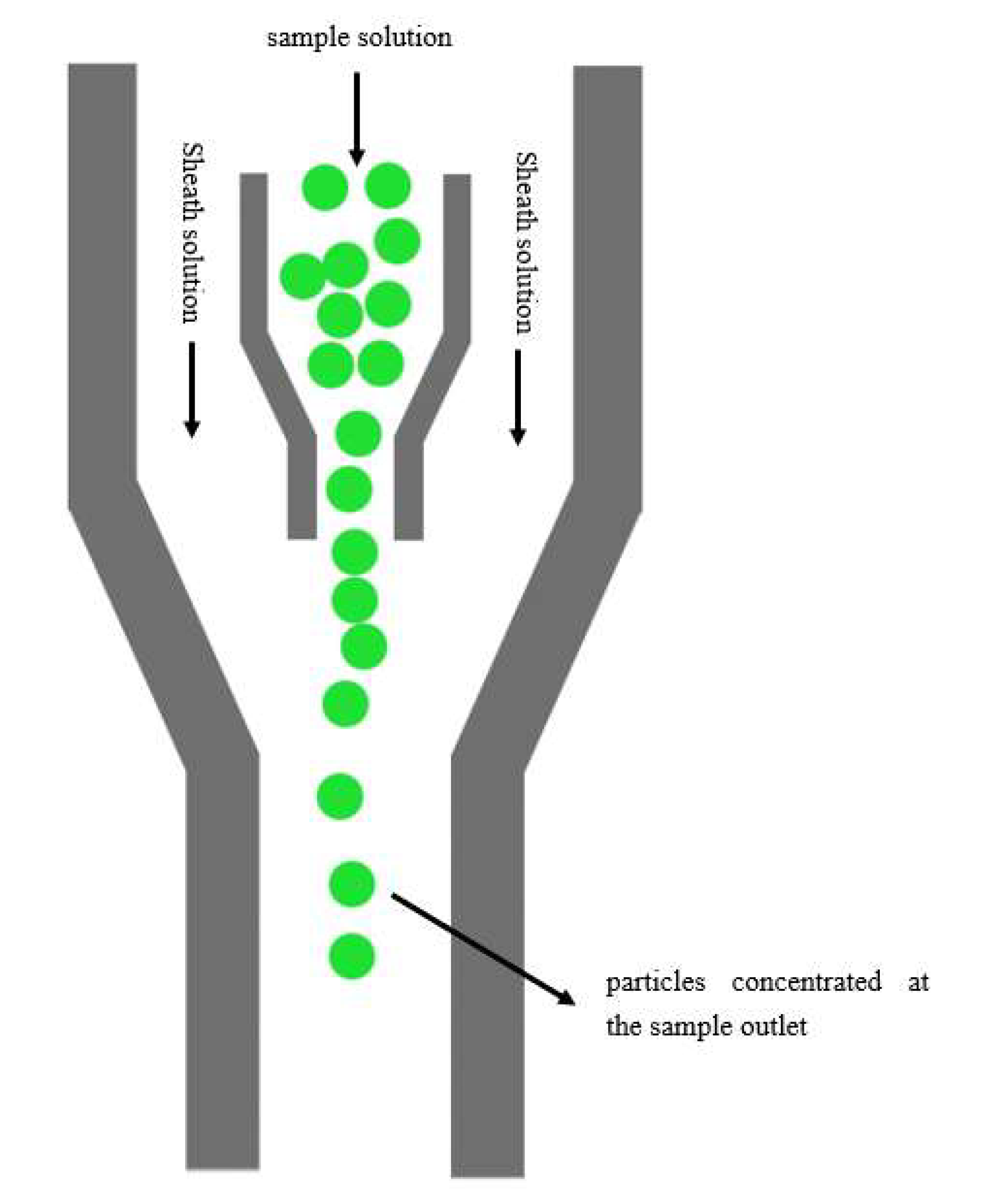
2.2. Principal of the Micro Particles Counting
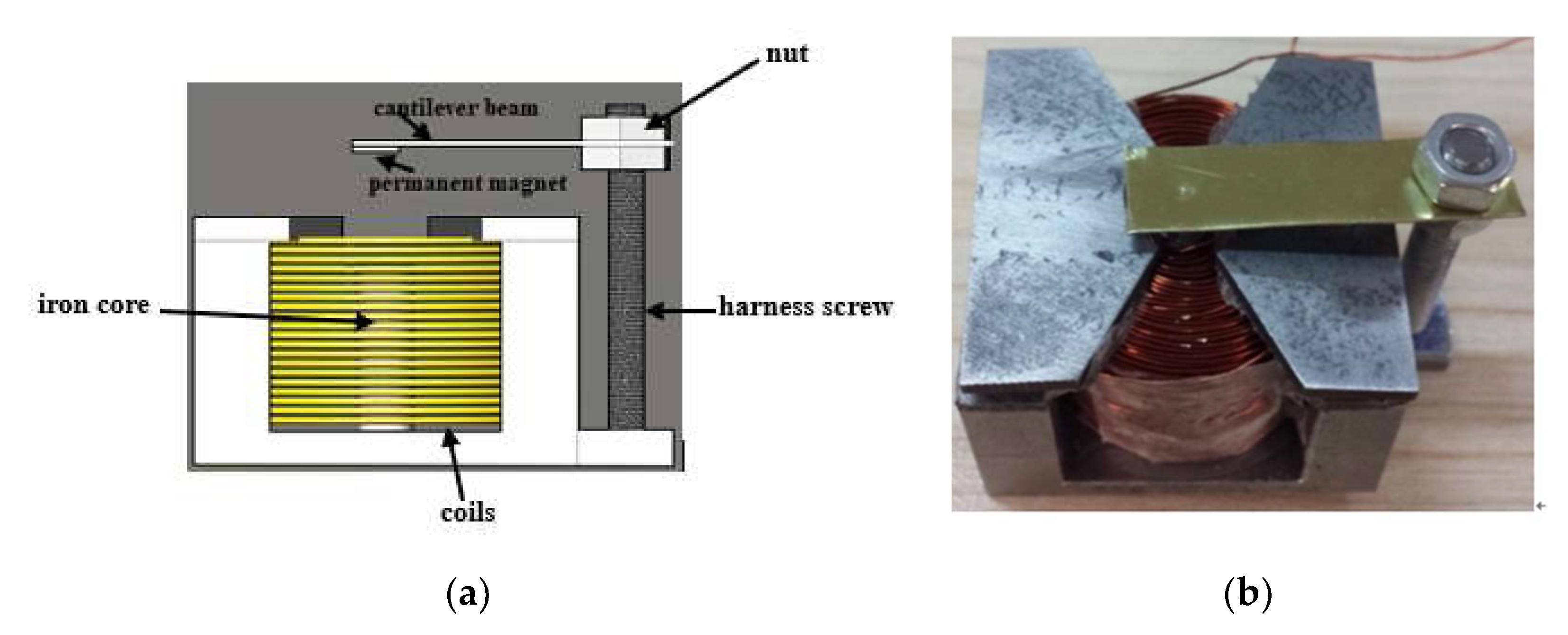
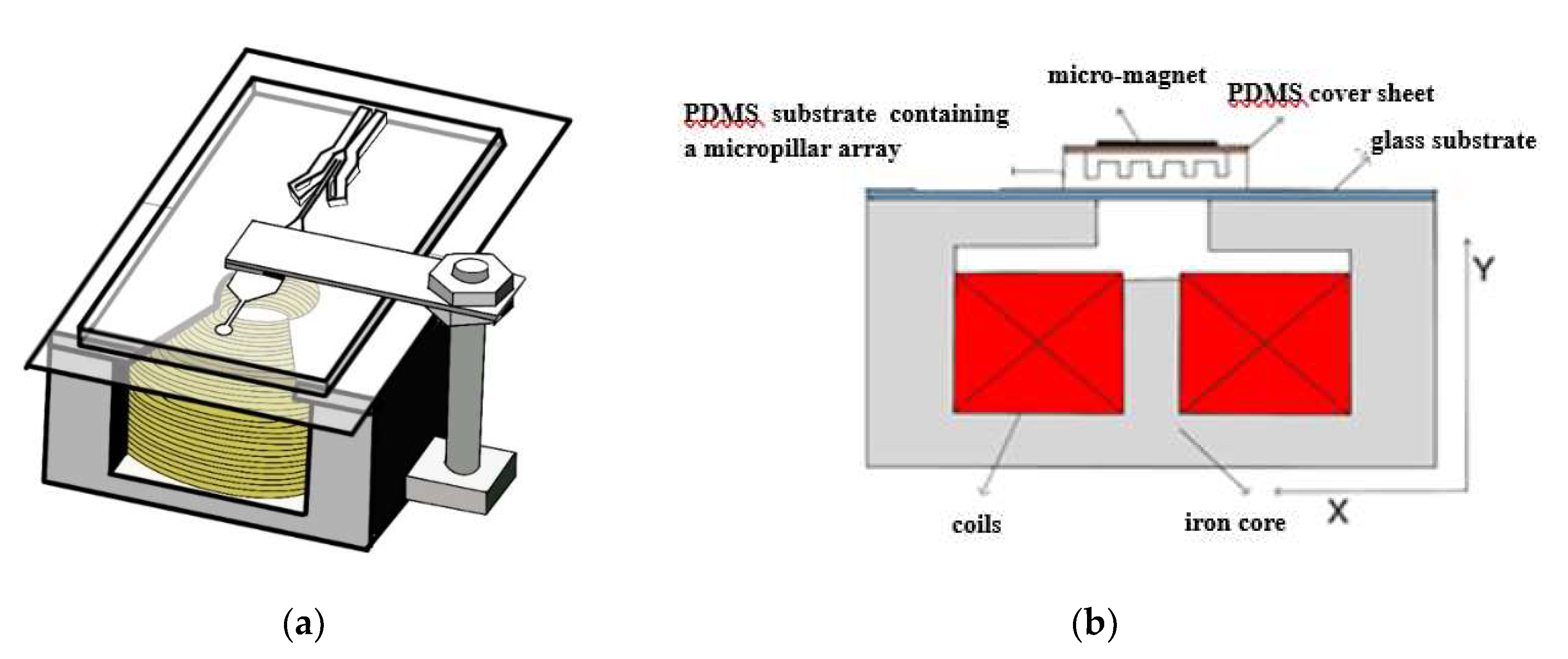
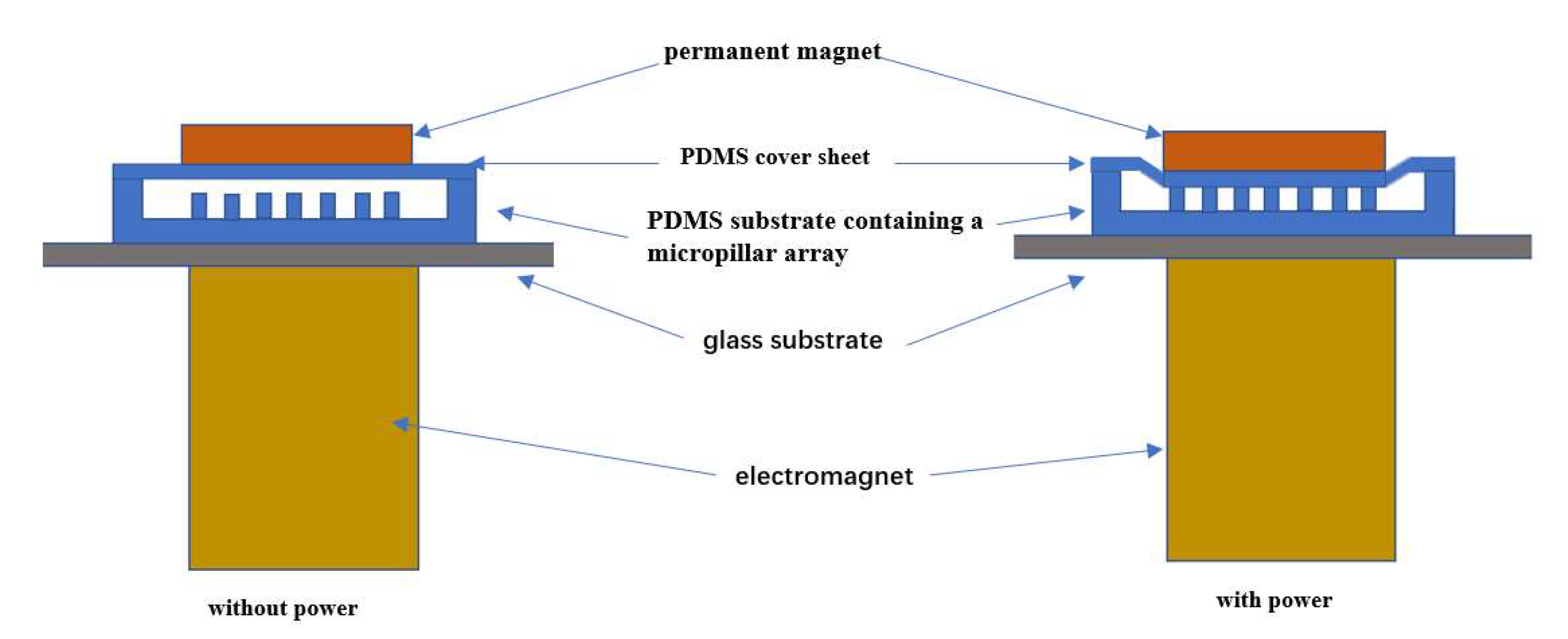
2.3. Electromagnetic Drive Device Design
3. Design and Fabrication of the Microfluidic Chip
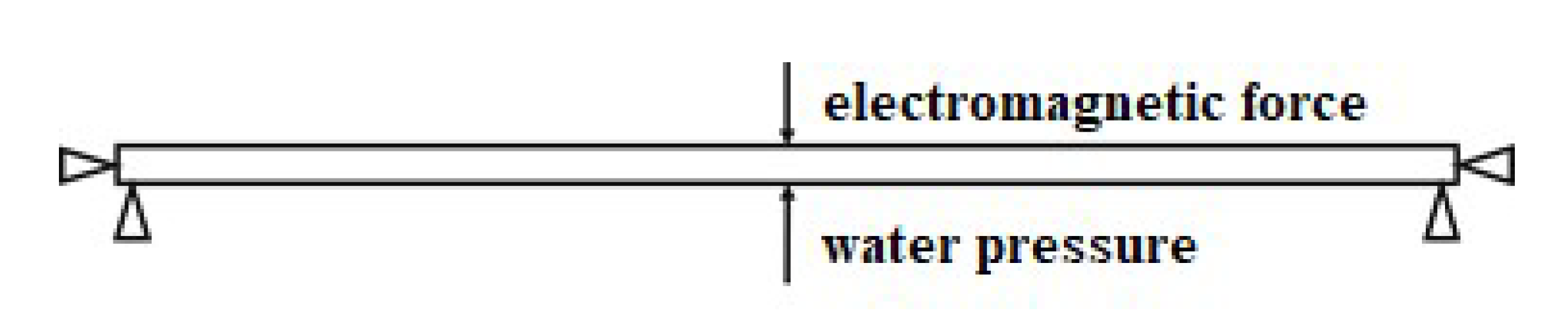
3.1. Force Analysis of the Microfluidic Chip
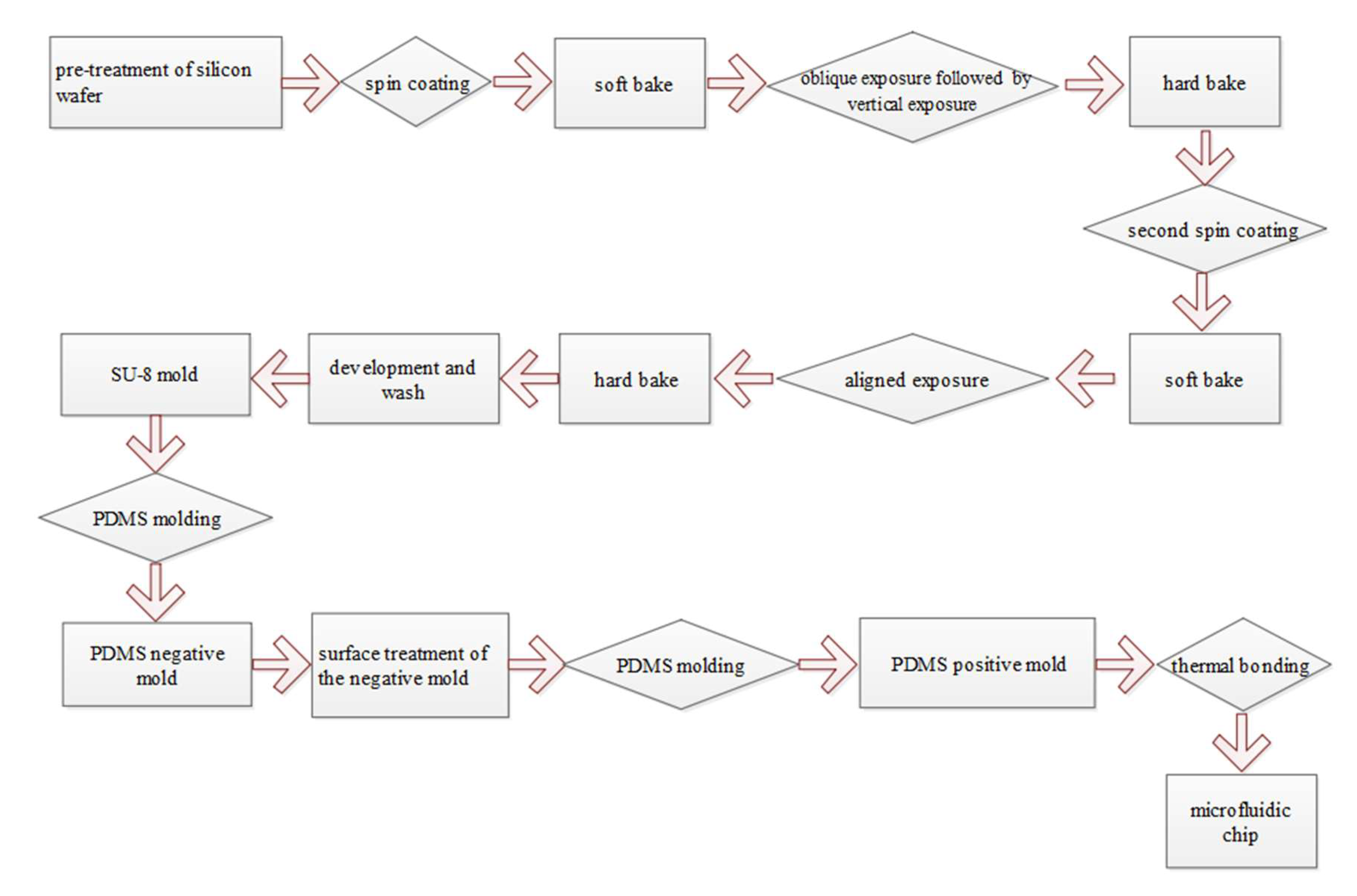
3.2. Fabrication of the Microfluidic Chip
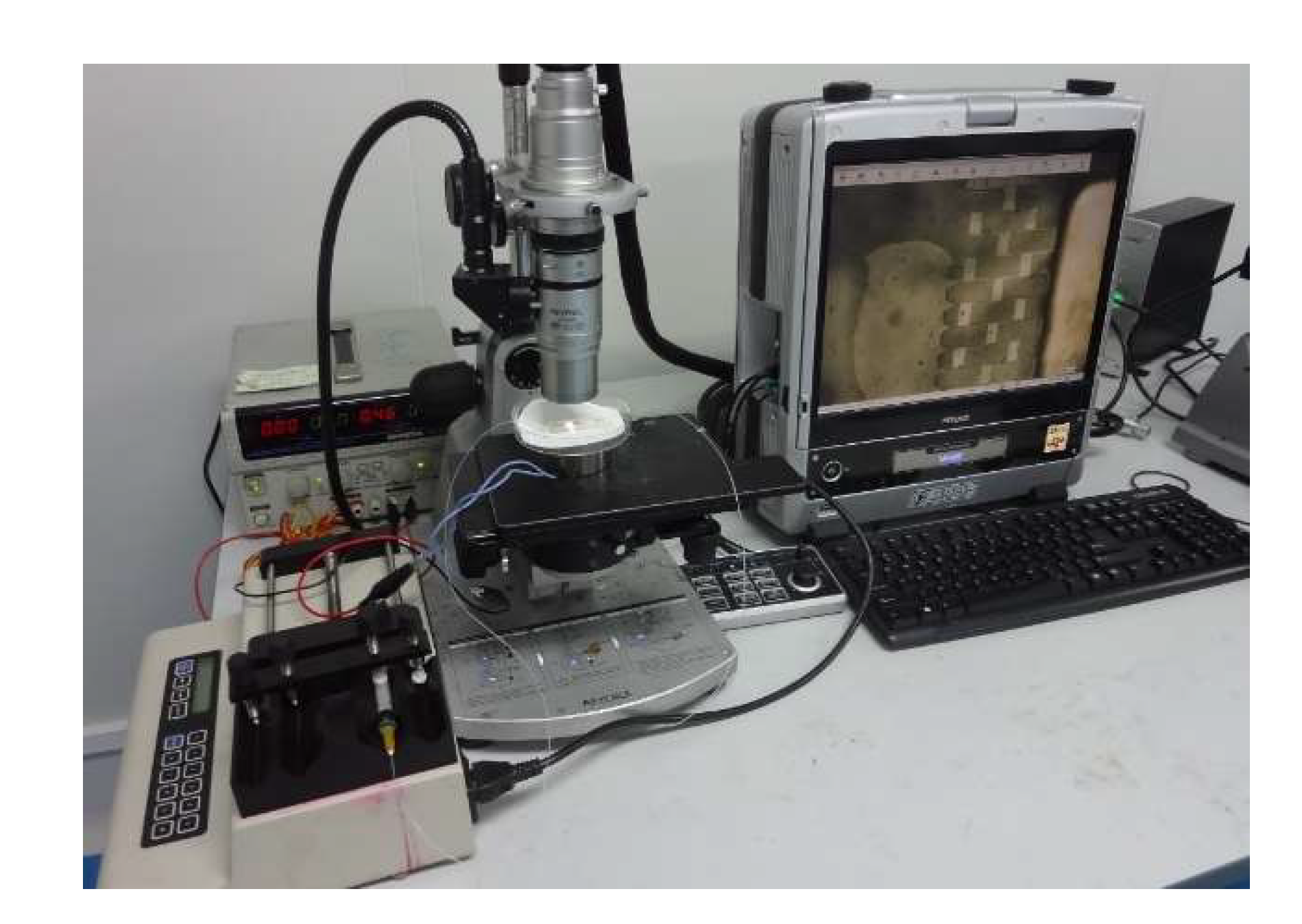
4. Experiments and Testing Results
4.1. Chip Fabrication Results
4.2. Experimental Test Results
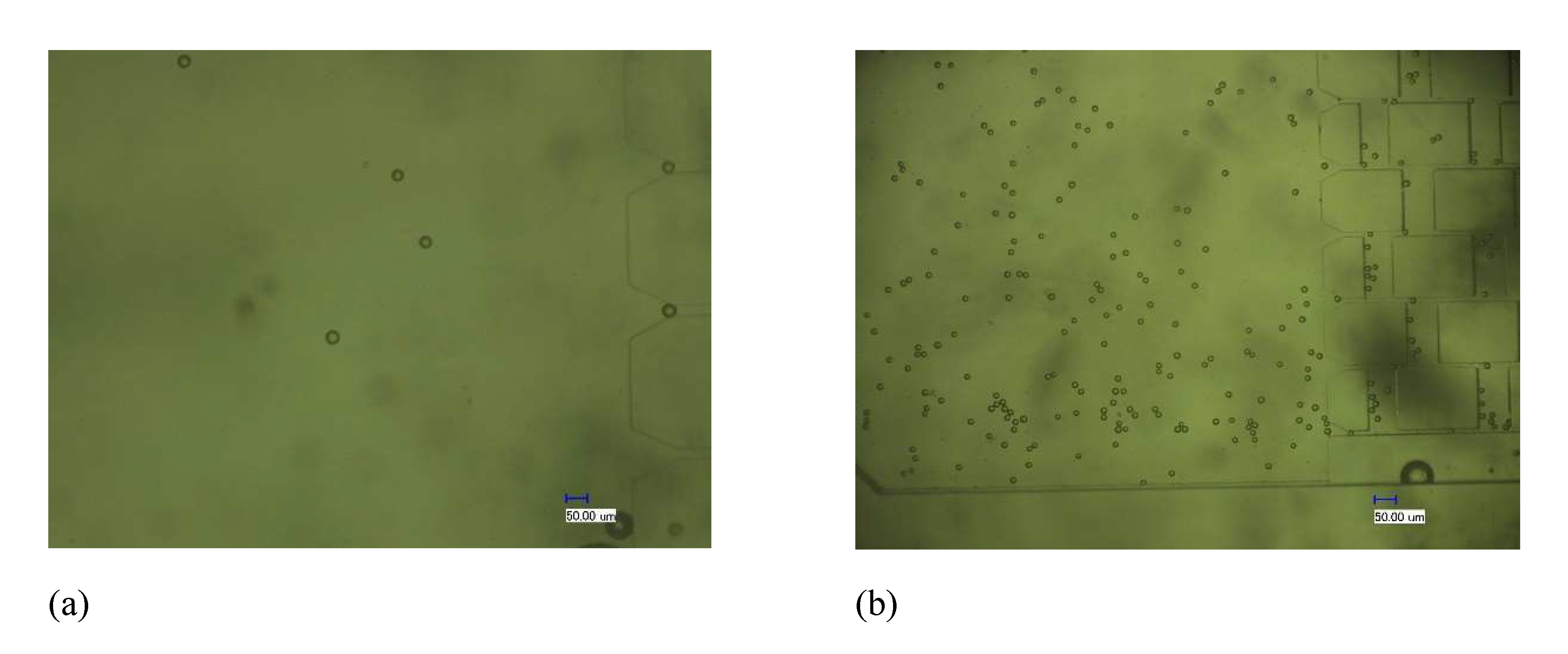
4.2.1. Enrichment Test Results of the Chip
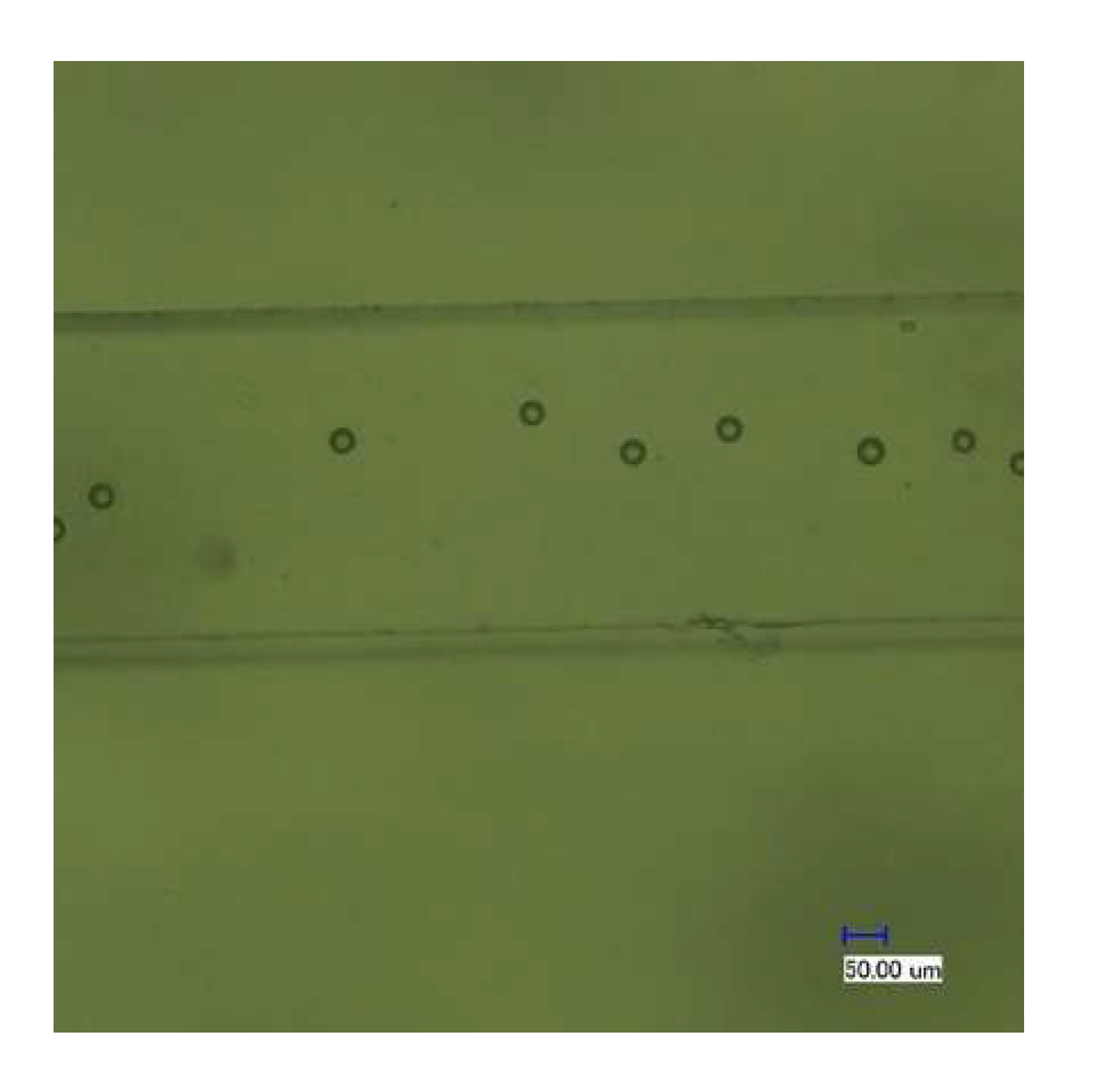
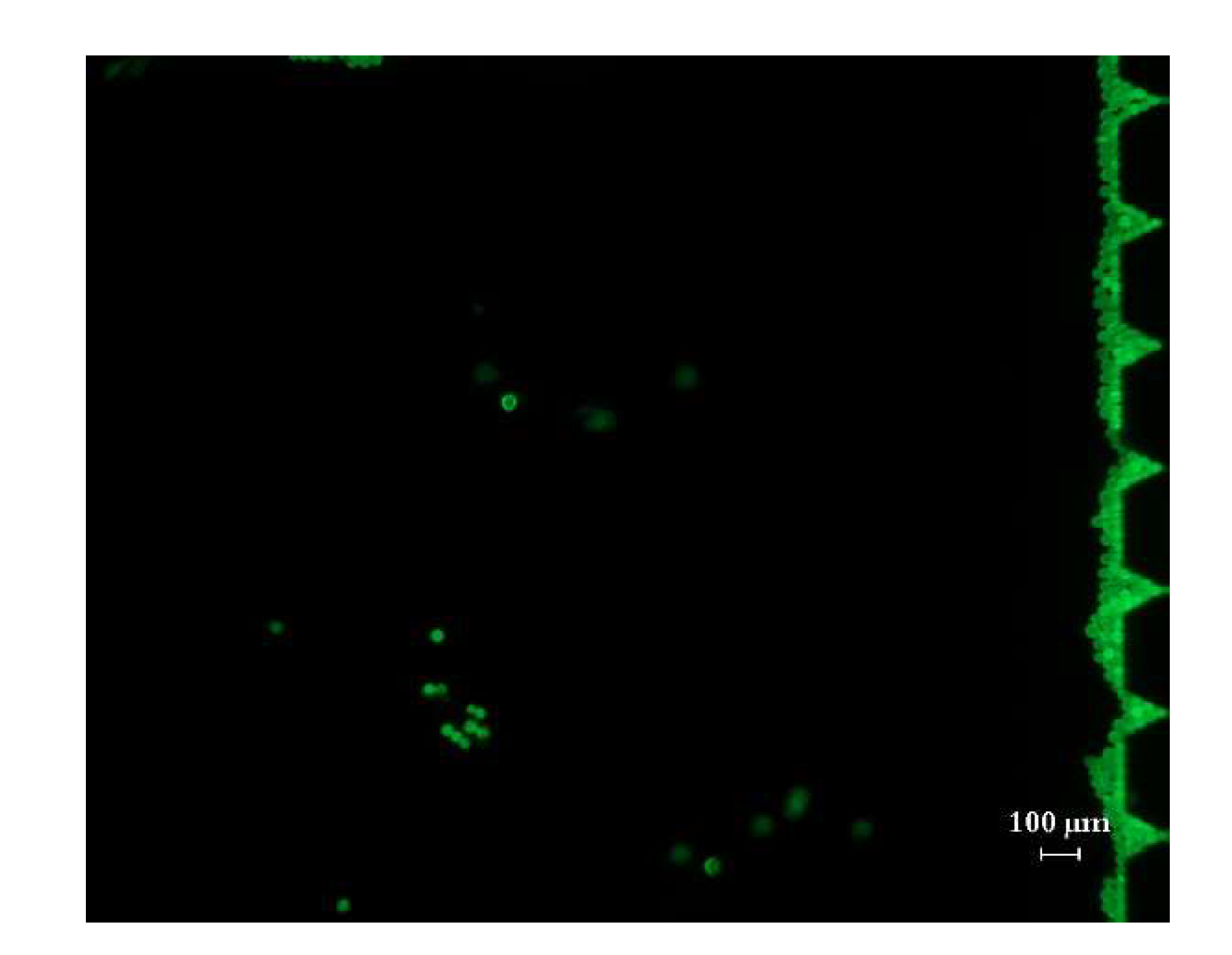
4.2.2. The Focusing and Counting Effect of the Chip
5. Discussion
5.1. Optimization of the Chip Structure
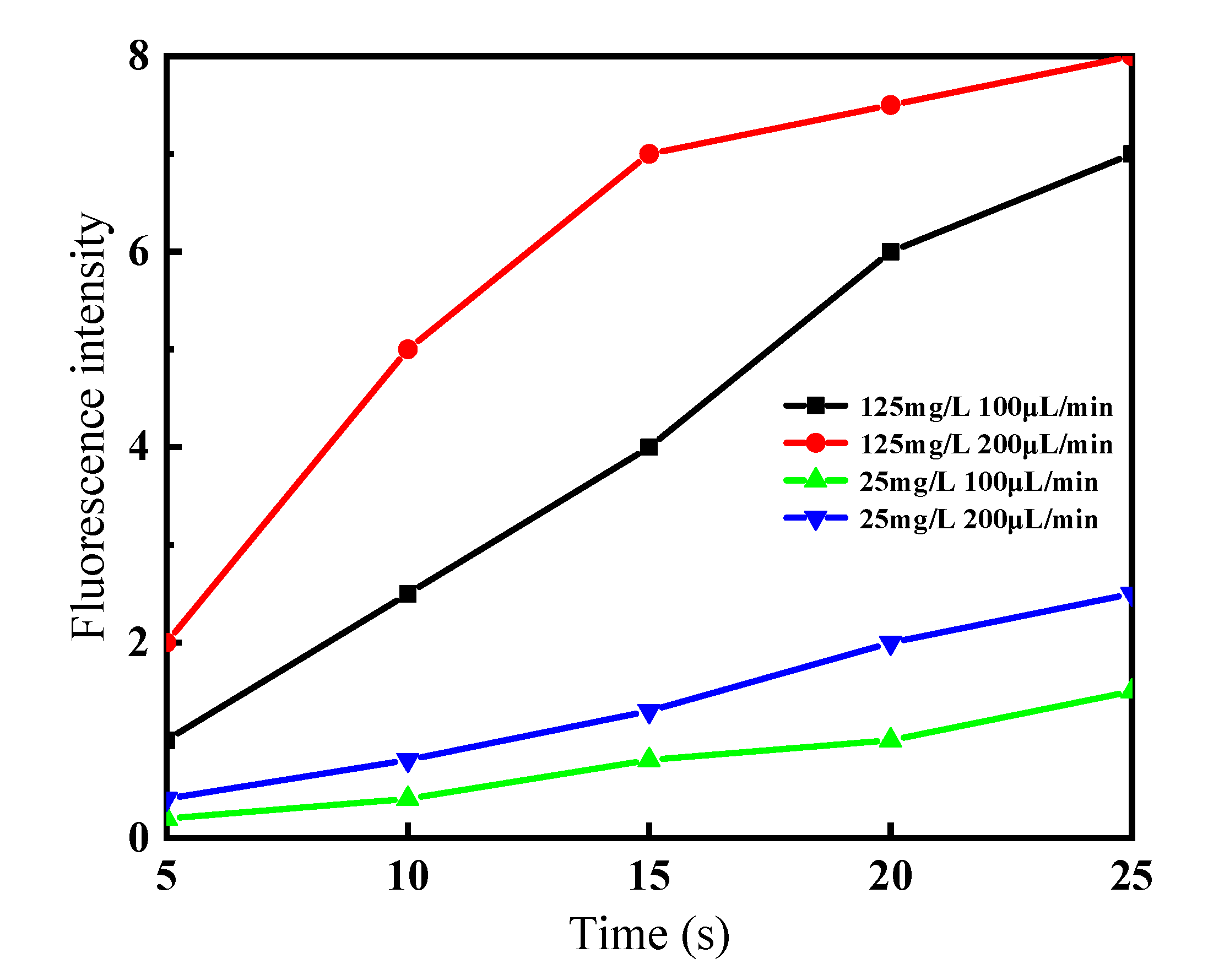
5.2. The Effects of Flow Rate and Concentration on the Enrichment Efficiency of the Chip
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.M. Cell Analysis on Microfluidics; The Science Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.X.; Fan, C.; Pan, J.Z.; Fang, Q. Research advances in clinical biochemical analysis systems based on microfluidic driving and control technique. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2020, 38, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.F.; Gao, W.L.; Yin, J.W.; Fan, W.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Hu, K.K.; Mai, Y.L.; Luan, A.B.; Xu, B.J.; Jin, Q.H. A high-precision thermometry microfluidic chip for real-time monitoring of the physiological process of live tumour cells. Talanta 2021, 226, 122101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunipe, P.K.; Das, A.K. Development of microfluidic chip for dilation of slurry. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2020, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.K.; Xu, R.; Liang, C.; Liu, D.Y.; Ma, W.; Wibool, P.; Vitshak, Z. Isolation of circulating tumor cells under hydrodynamic loading using microfluidic technology. Adv. Mech. 2014, 44, 447–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorges, T.M.; Tinhofer, I.; Drosch, M.; Röse, L.; Zollner, T.M.; Krahn, T.; Von Ahsen, O. Circulating tumour cells escape from EpCAM-based detection due to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.X.; Liu, W.W.; Zou, K.; Wei, S.; Zhang, X.R.; Li, E.C.; Wang, Q. Design and clinical application of an integrated microfluidic device for circulating tumor cells isolation and single-cell analysis. Micromachines 2021, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshchi, F.; Hasanzadeh, M. Microfluidic biosensing of circulating tumor cells (CTCs): Recent progress and challenges in efficient diagnosis of cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, K.-A.; Kwon, K.; Han, H.; Kim, S.-I.; Jung, H.-I. Microfluidic flow fractionation device for label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from breast cancer patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cordero, J.L.; Maerkl, S.J. Microfluidic systems for cancer diagnostics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 65, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, J.H.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.P. Advances in isolation and enrichment of circulating tumor cells in microfluidic chips. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2014, 32, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Wang, Y. Microfluidic technology-based method for sorting circulating tumor cells. Chin. J. Med Phys. 2019, 36, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earhart, C.M.; Hughes, C.E.; Gaster, R.S.; Ooi, C.C.; Wilson, R.J.; Zhou, L.Y.; Humke, E.W.; Xu, L.; Wong, D.J.; Willingham, S.B.; et al. Isolation and mutational analysis of circulating tumor cells from lung cancer patients with magnetic sifters and biochips. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.B.; Huang, F.; Du, J.H.; Shu, W.L.; Feng, H.T.; Xu, X.P.; Chen, Y. Rapid isolation of cancer cells using microfluidic deterministic lateral displacement structure. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.Q.; Li, L.; Chen, H.M.; Chen, P.; Liu, J. Advances in isolating circulating tumor cells with microfluidic chips. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 42, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.X.; Hao, X.J.; Wang, C.S.; Zhang, B.Z.; Wang, W.J. Rapid and low cost replication of complex microfluidic structures with PDMS double casting technology. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 20, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.X.; Hao, X.J.; Wang, C.S.; Zhang, B.Z.; Wang, W.J. Three-dimensional focusing microfluidic chip. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2013, 21, 2309–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Ye, T.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Wei, Y. Design and Fabrication of a Microfluidic Chip for Particle Size-Exclusion and Enrichment. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12101218
Yang L, Ye T, Zhao X, Hu T, Wei Y. Design and Fabrication of a Microfluidic Chip for Particle Size-Exclusion and Enrichment. Micromachines. 2021; 12(10):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12101218
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Luxia, Tian Ye, Xiufeng Zhao, Taotao Hu, and Yanlong Wei. 2021. "Design and Fabrication of a Microfluidic Chip for Particle Size-Exclusion and Enrichment" Micromachines 12, no. 10: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12101218
APA StyleYang, L., Ye, T., Zhao, X., Hu, T., & Wei, Y. (2021). Design and Fabrication of a Microfluidic Chip for Particle Size-Exclusion and Enrichment. Micromachines, 12(10), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12101218




