Preliminary Study on Polishing SLA 3D-Printed ABS-Like Resins for Surface Roughness and Glossiness Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Specimens 3D Printing Methodology
2.2. Polishihng Methodology
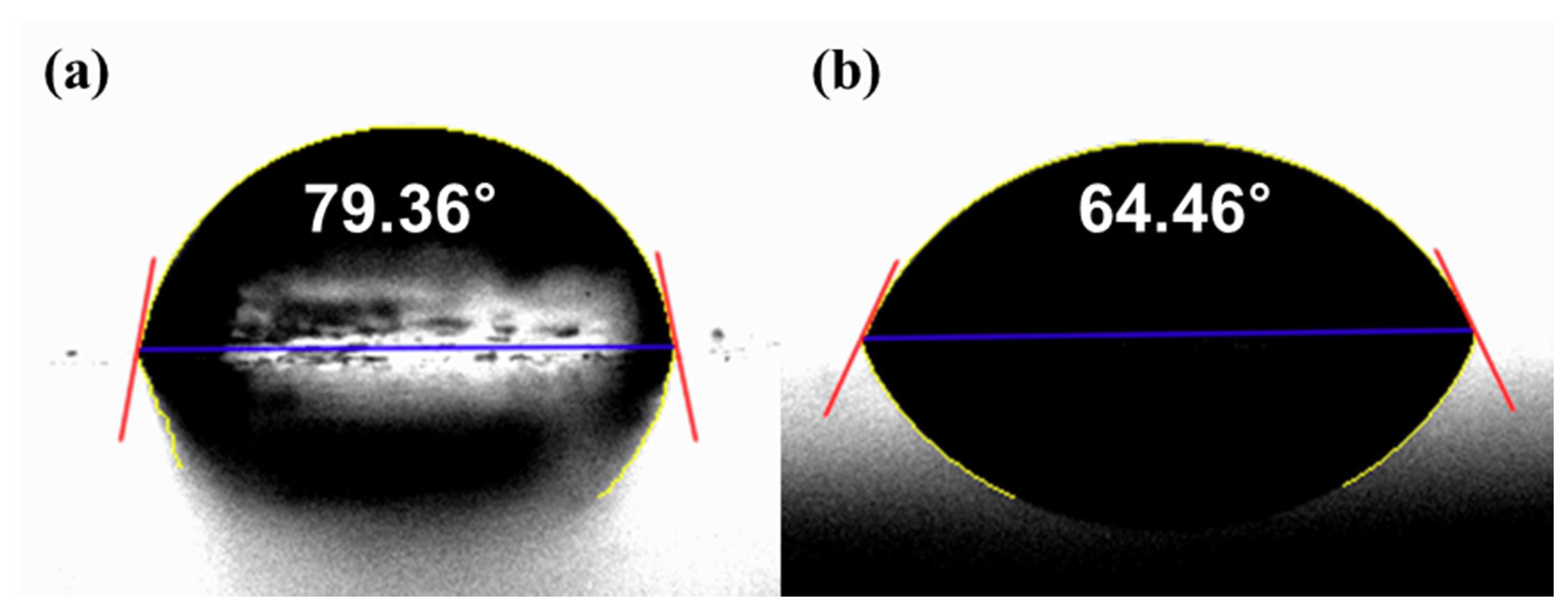
2.3. Measurement of Surface Roughness and Glossiness
3. Results and Discussion
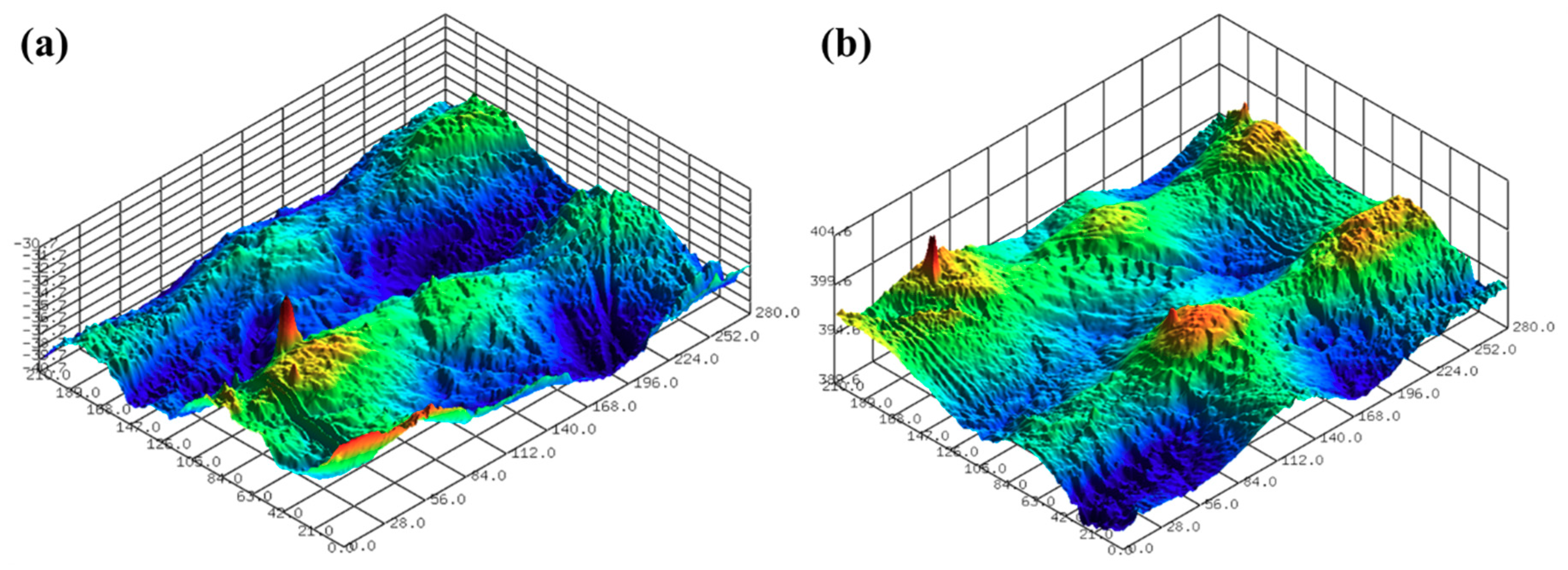
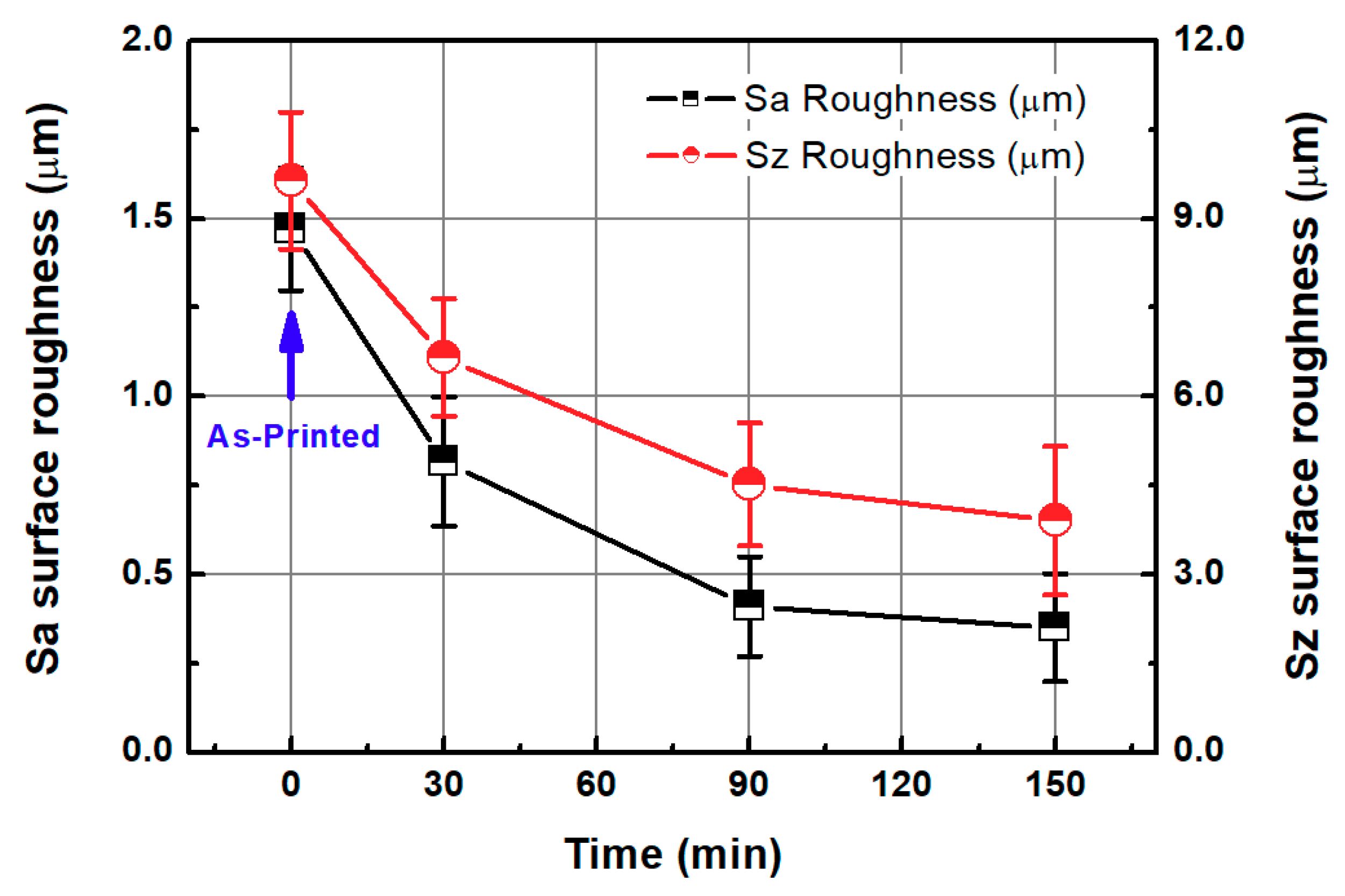
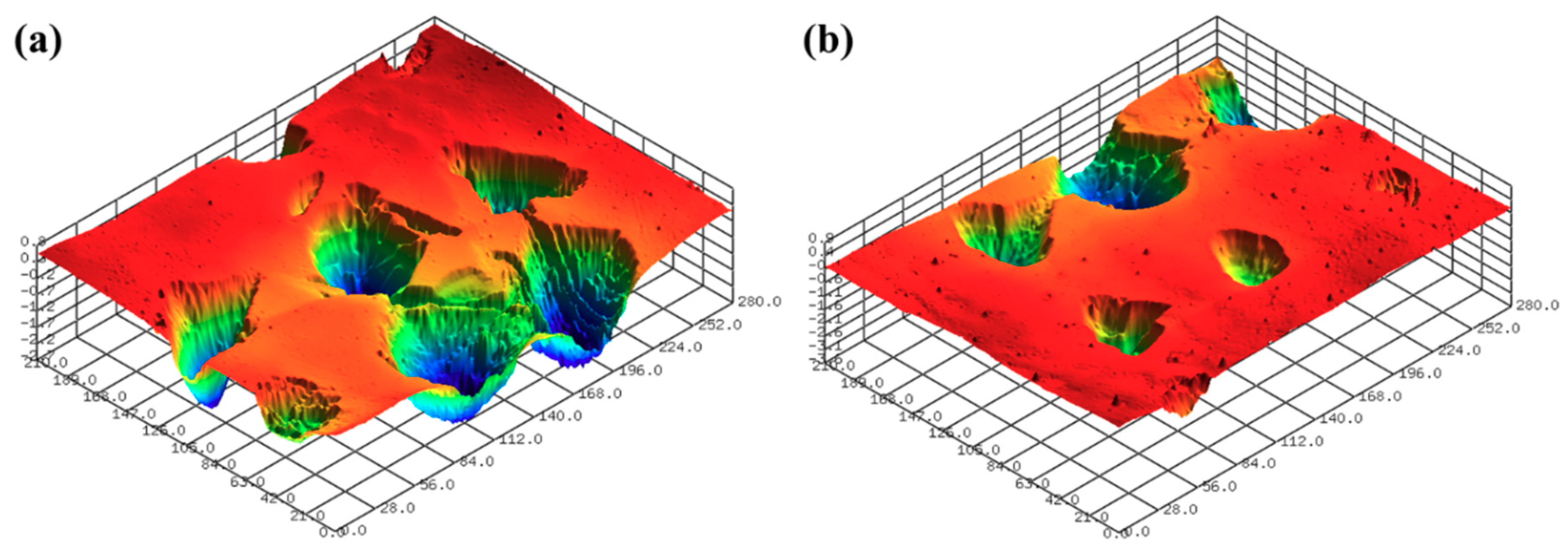
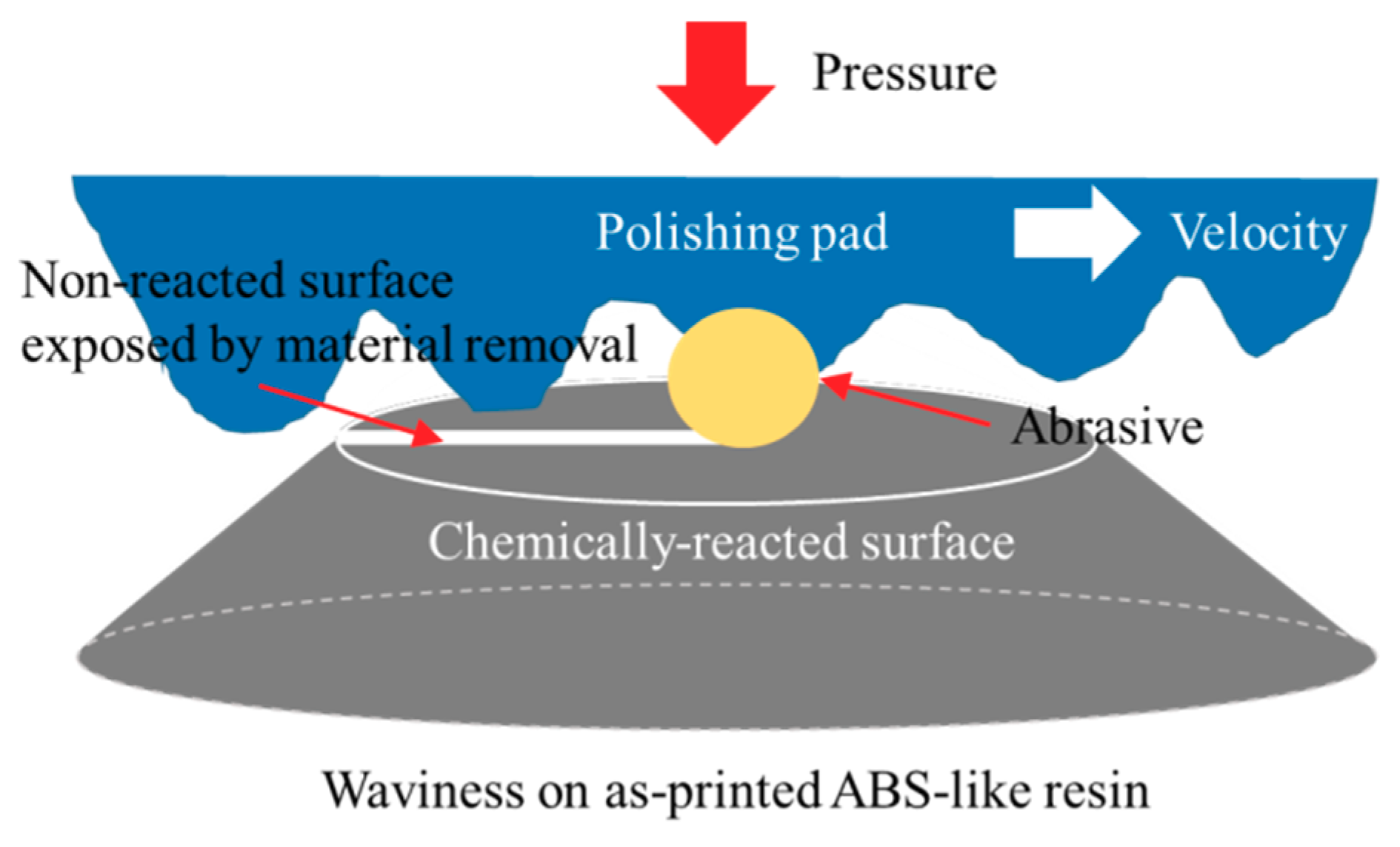
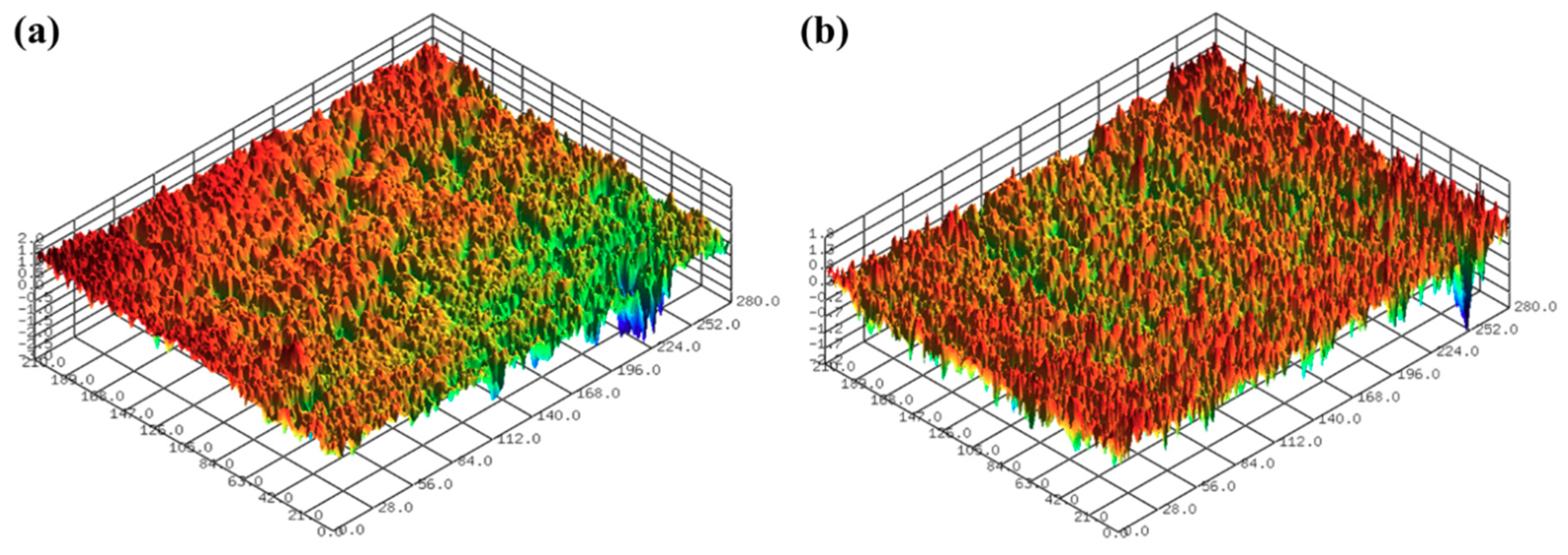
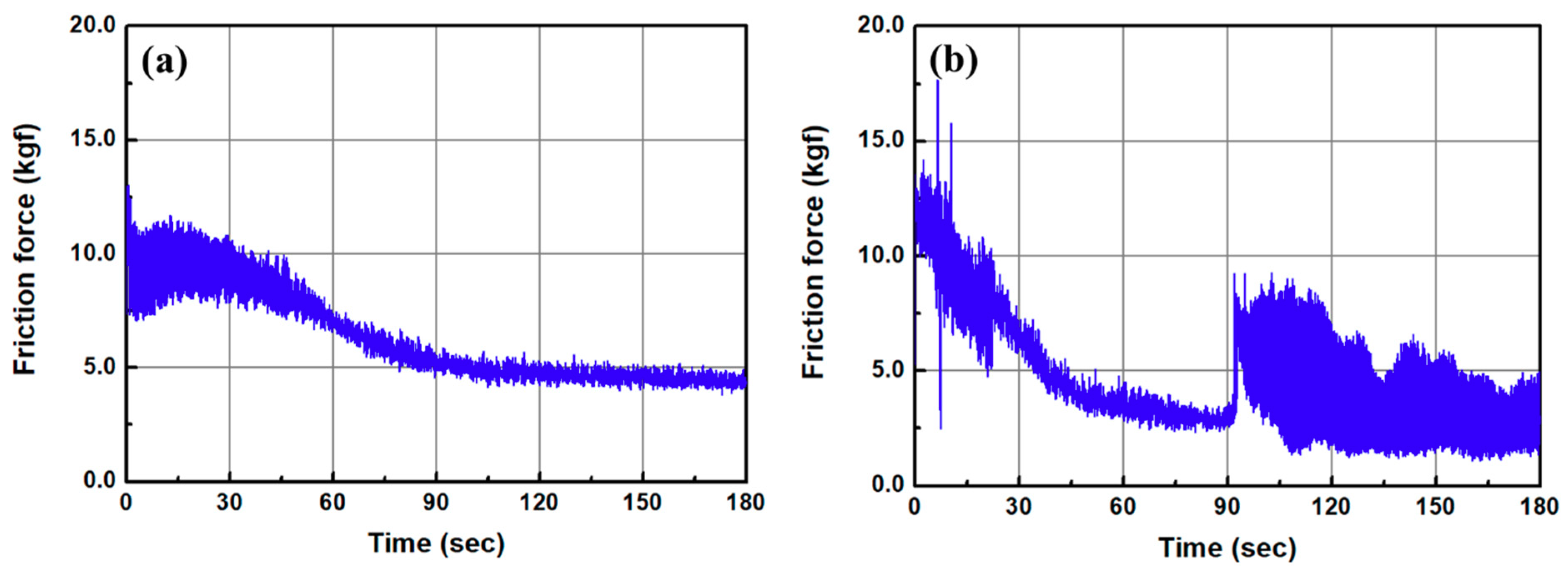
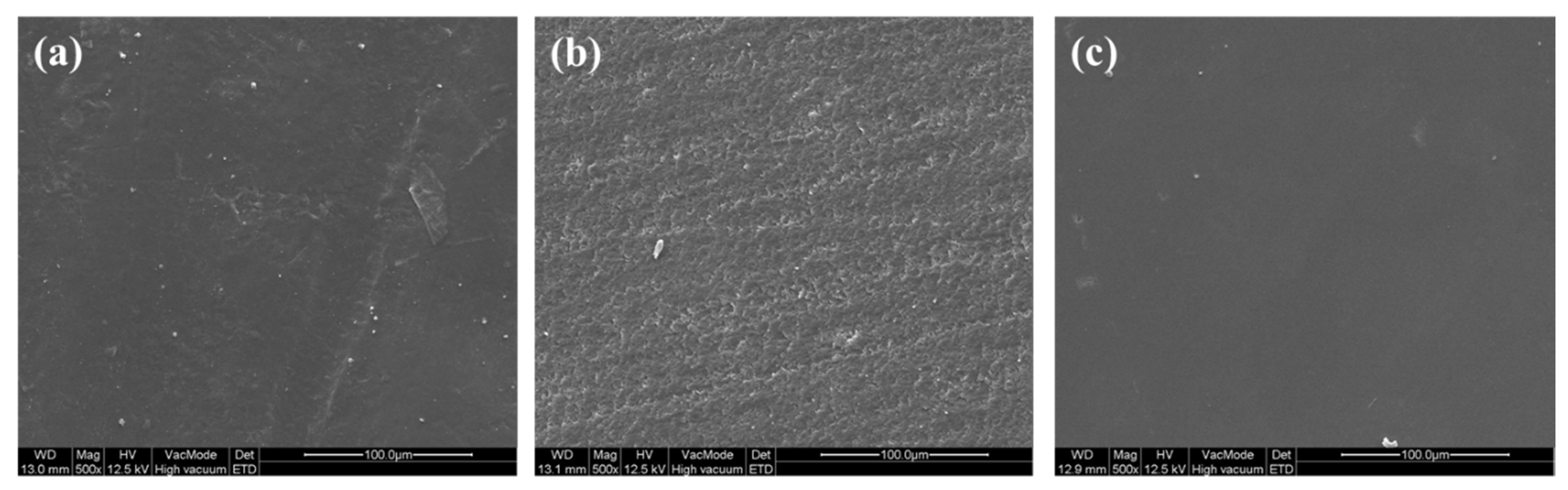
3.1. One-Step Polishing
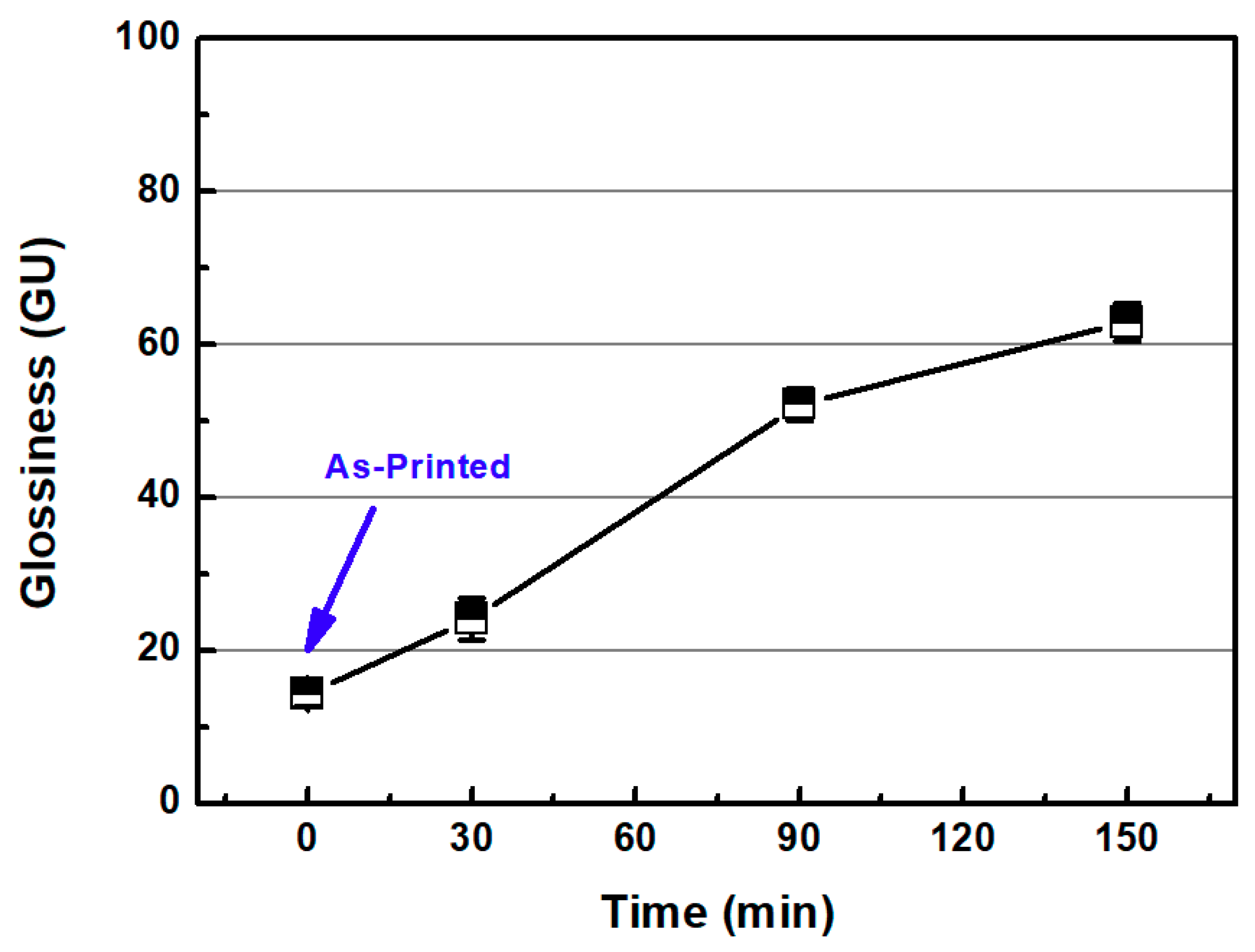
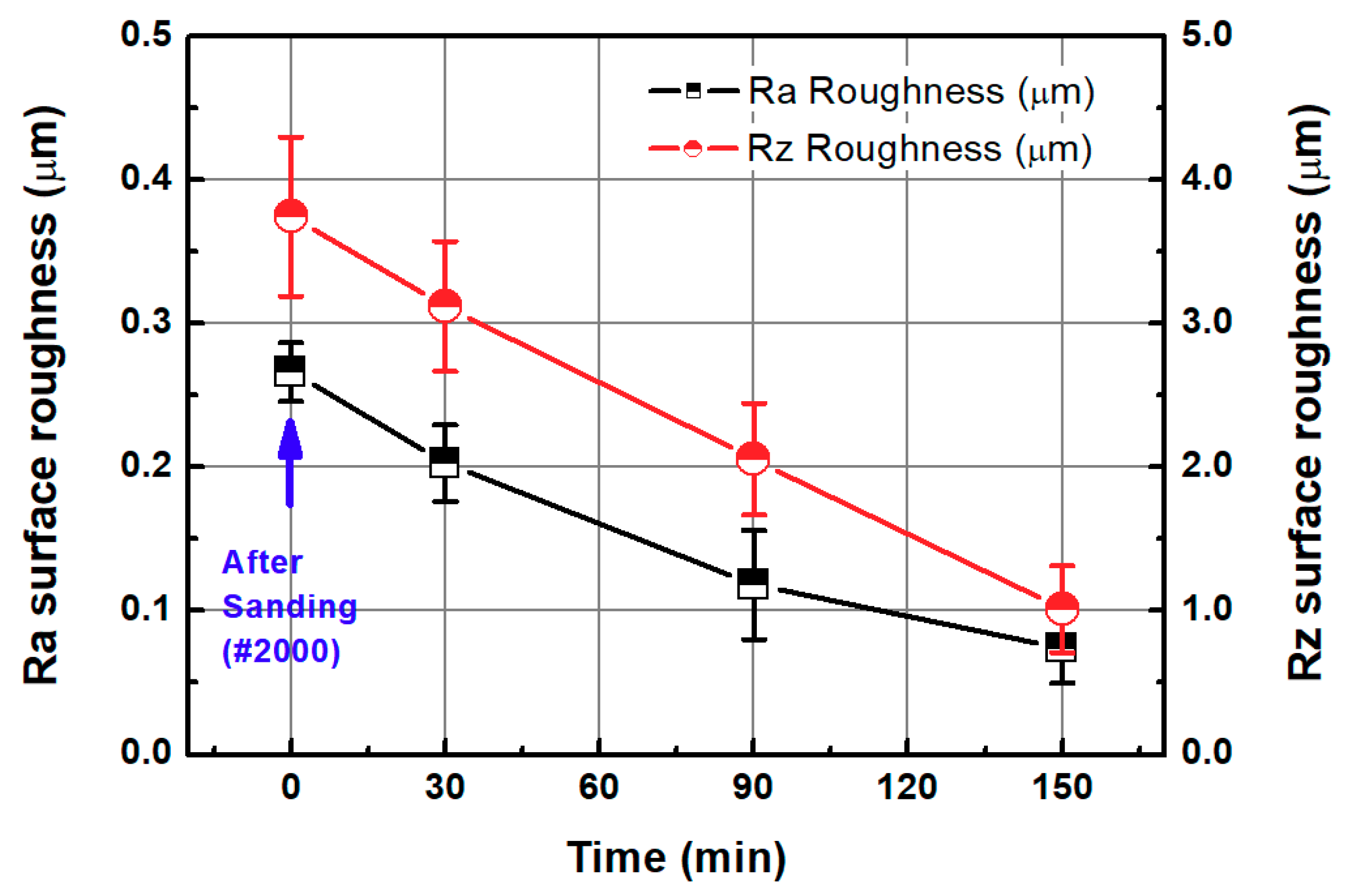
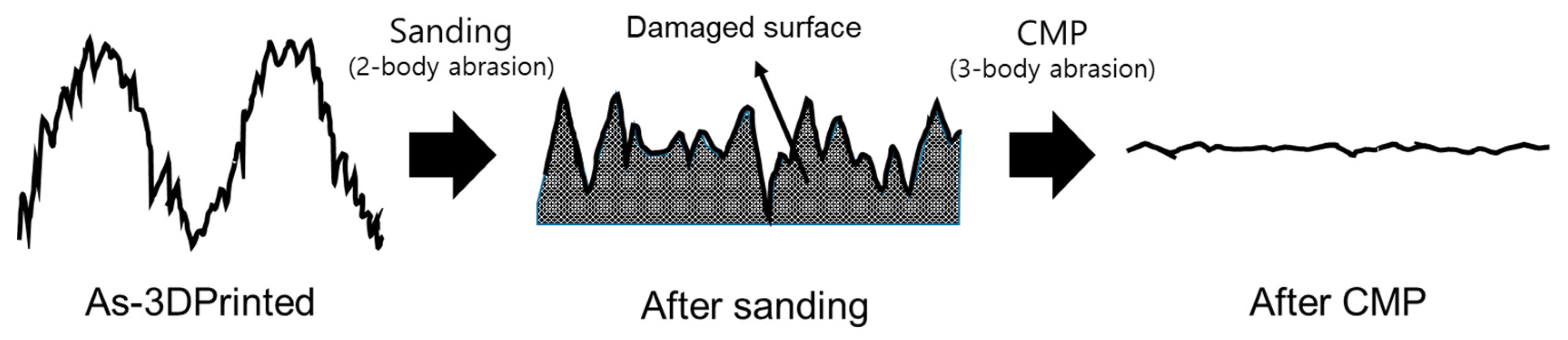
3.2. Two-Step Polishing
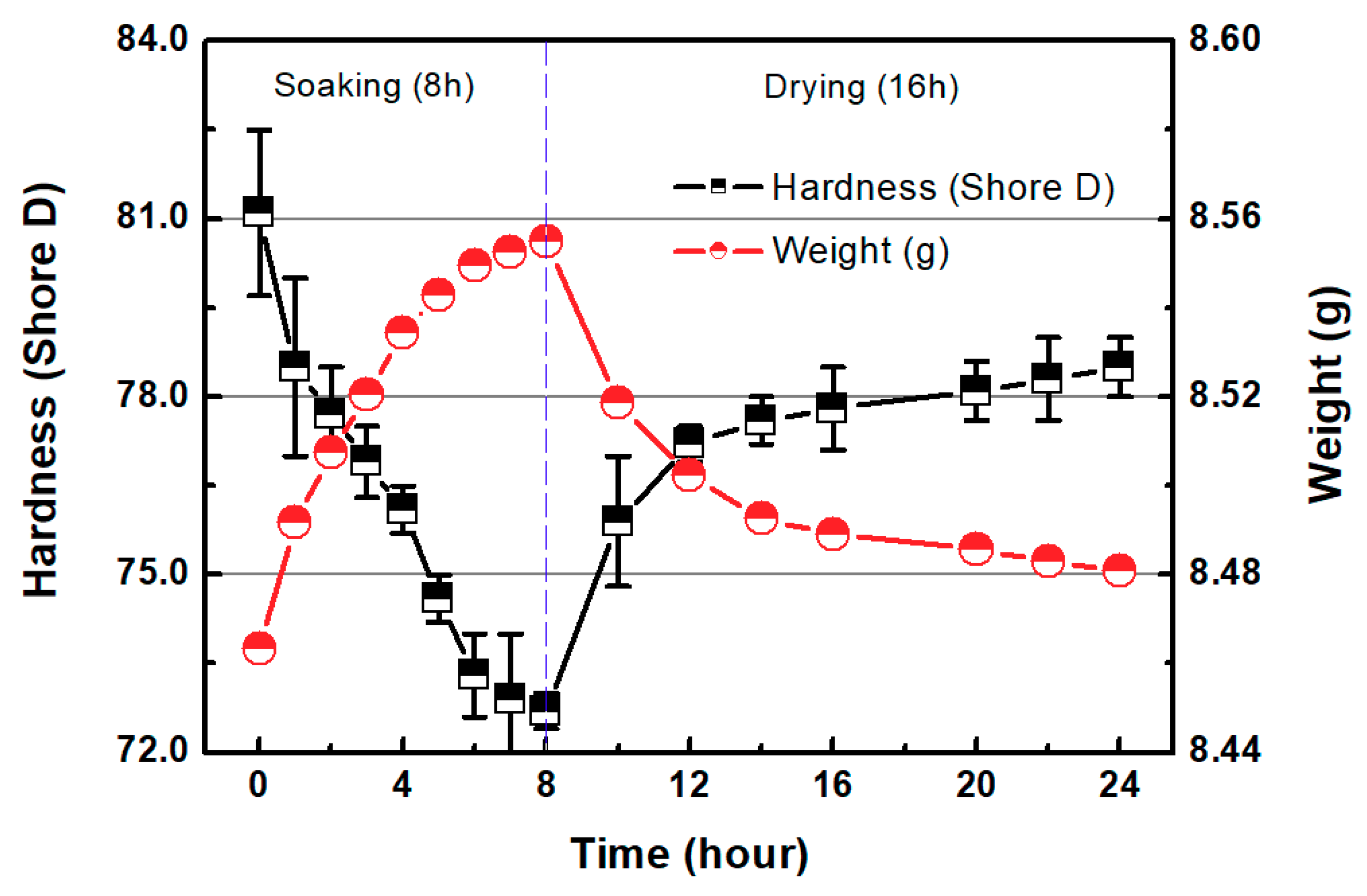
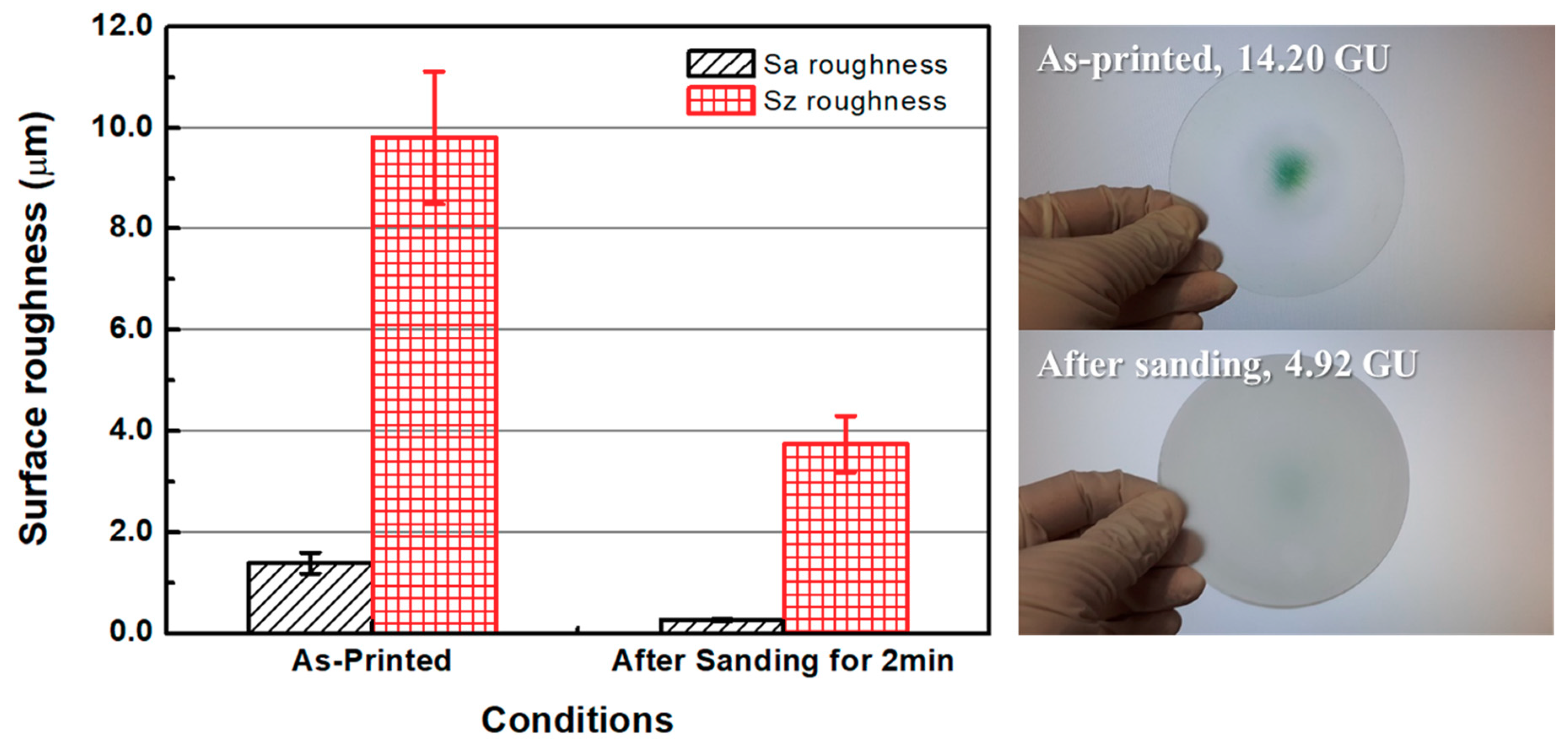
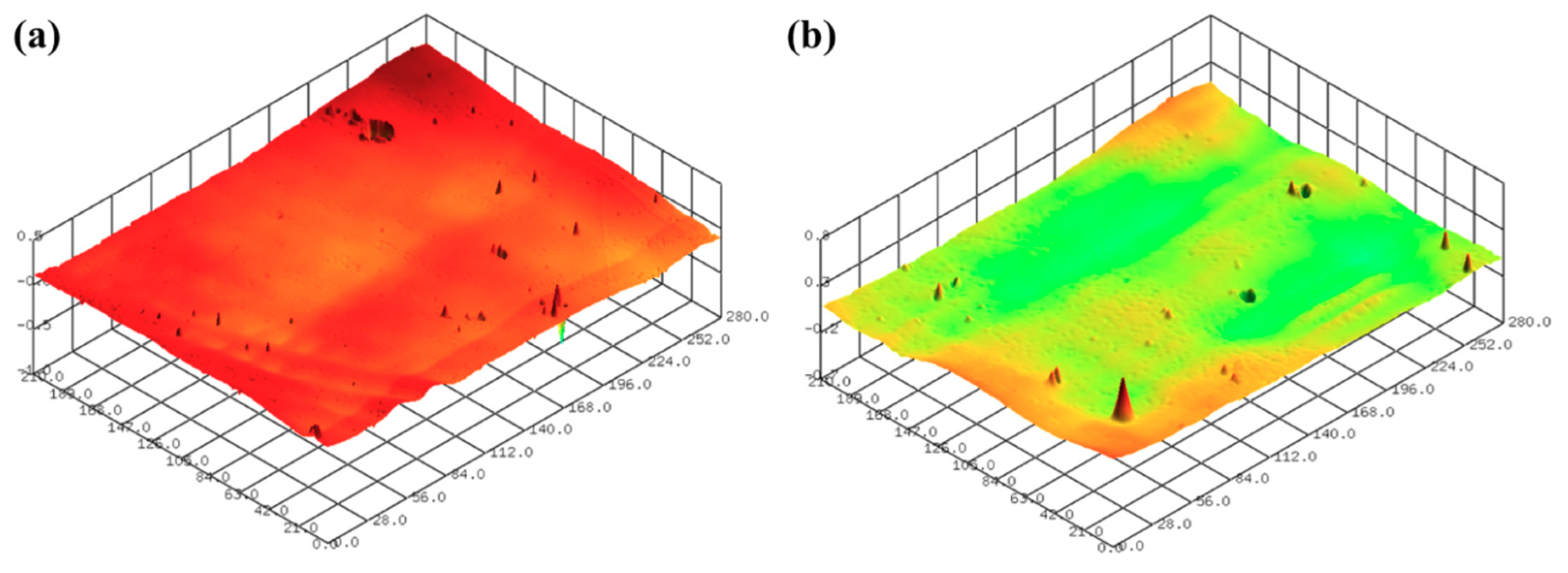
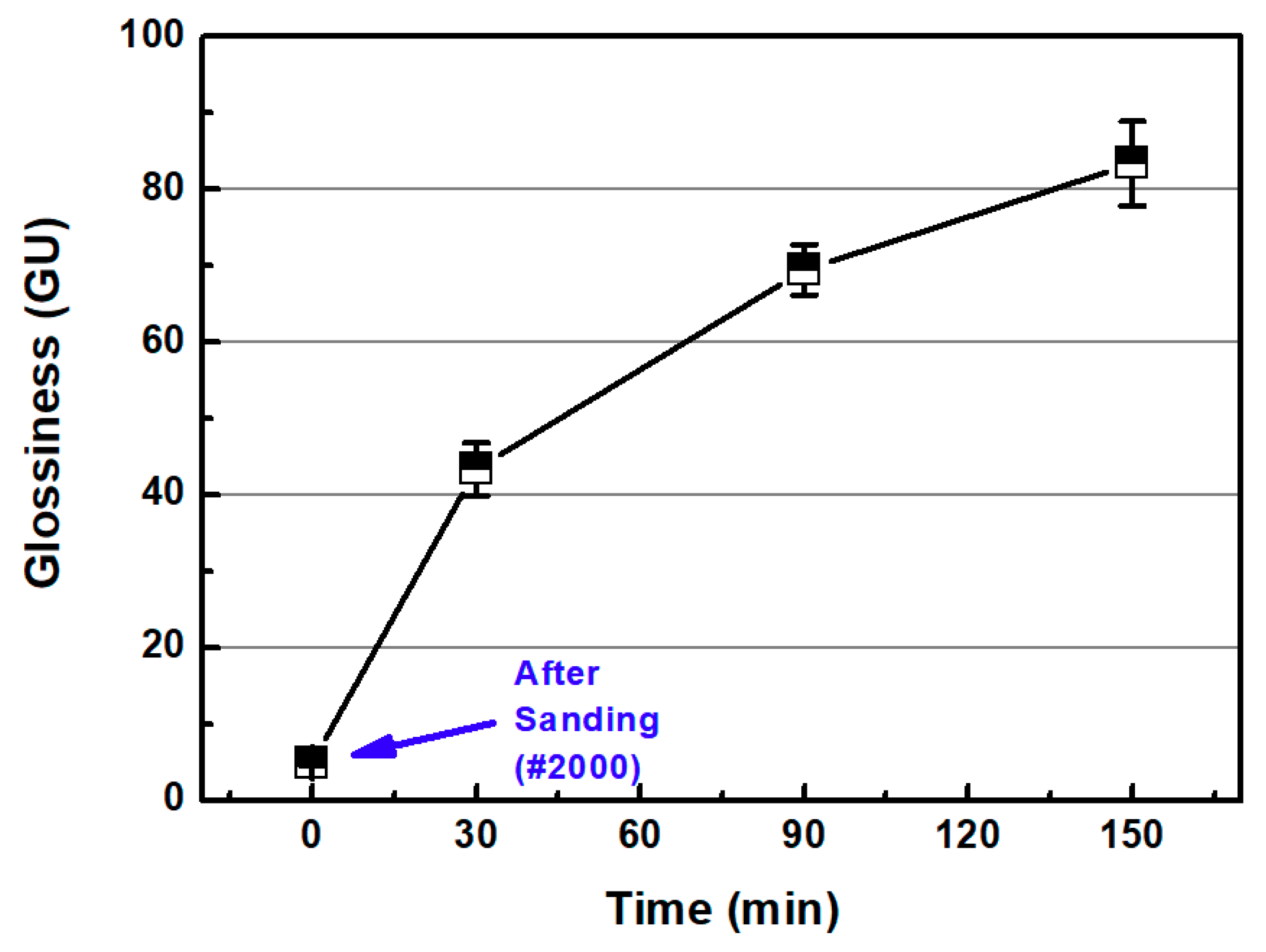
3.2.1. Sanding
3.2.2. Chemical-Mechanical Polishing (CMP) after Sanding
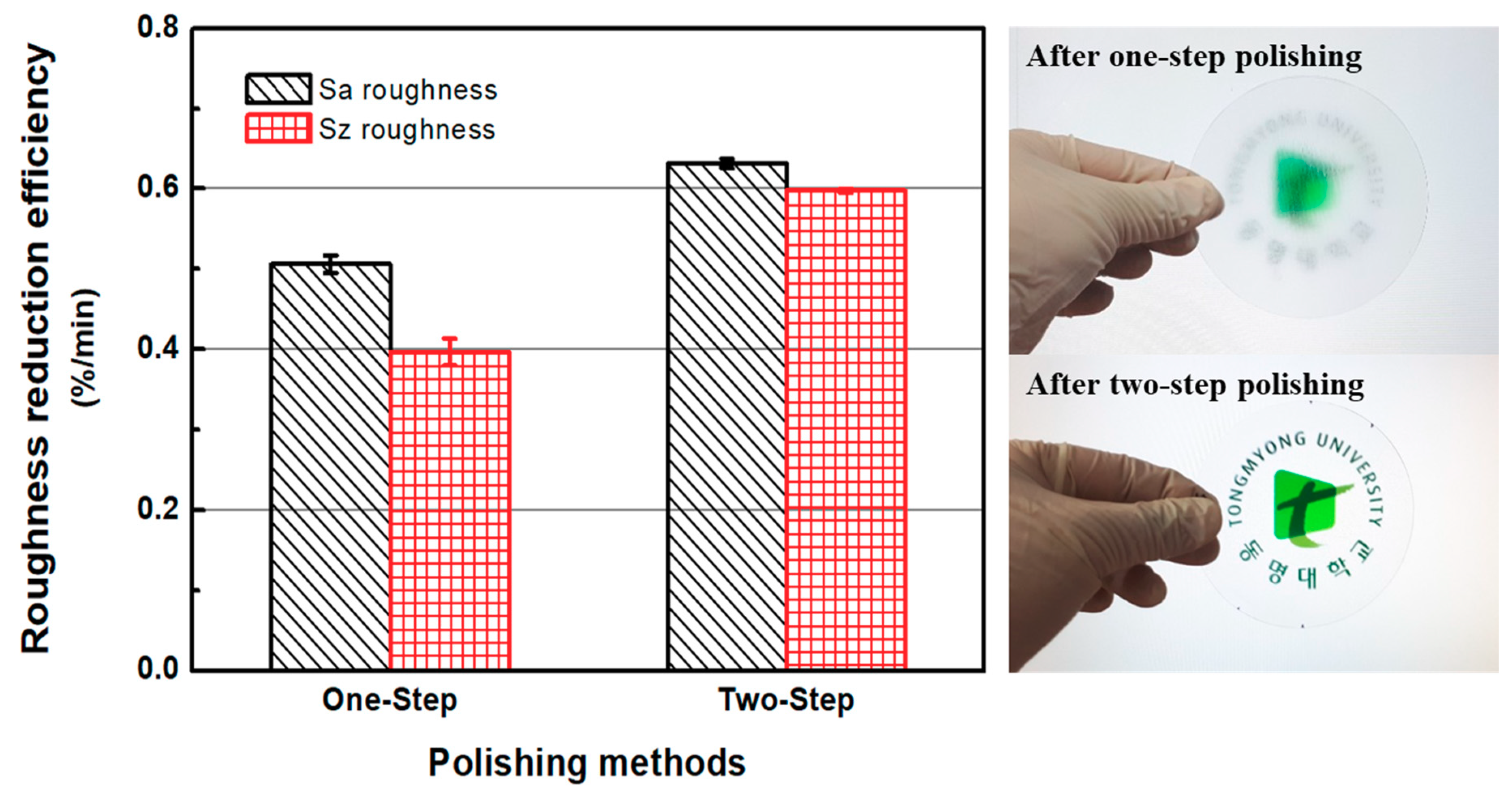
3.3. Comparison of One-Step and Two-Step Polishing Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, G.; Wei, Z.; Wang, W.; Feng, D.; Xu, A.; Liu, W.; Song, Z. Review on modeling and application of chemical mechanical polishing. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, D.; Jeong, H. Mechanical aspects of the chemical mechanical polishing process: A review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 17, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, H.; Jeong, H. Slurry components in metal chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) process: A review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 17, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. Tribology Research Trends in Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) Process. Tribol. Lubr. 2018, 34, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kuan, W.-H.; Hu, C.-Y. Chemical evidences for the optimal coagulant dosage and pH adjustment of silica removal from chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) wastewater. Colloid. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 342, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnels, S.R.; Eyman, L.M. Tribology Analysis of Chemical-Mechanical Polishing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. Semi-empirical Material Removal Model with Modified Real Contact Area for CMP. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 20, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.R. Chemical-Mechanical Planarization of Semiconductor Materials, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, H. Effect of pad groove geometry on material removal characteristics in chemical mechanical polishing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 13, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, S. Investigation of pad wear in CMP with swing-arm conditioning and uniformity of material removal. Precis. Eng. 2017, 49, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, H. Estimating the mechanical properties of polyurethane-impregnated felt pads. J. Mech. Sci. Tech. 2017, 31, 5705–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shin, D.W.; Tomozawa, M.; Murarka, S.P. The effect of the polishing pad treatments on the chemical-mechanical polishing of SiO2 films. Thin Solid Films 1995, 270, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Sung, I.-H. Chemical Mechanical Polishing: A Selective Review of R&D Trends in Abrasive Particle Behaviors and Wafer Materials. Tribol. Lubr. 2019, 35, 274–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ein-Eli, Y.; Starosvetsky, D. Review on copper chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) and post-CMP cleaning in ultra large system integrated (ULSI)-An electrochemical perspective. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 1825–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, M.; Nalaskowski, J.W.; Cook, L.M. Chemical Mechanical Planarization: Slurry Chemistry, Materials, and Mechanisms. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 178–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizon, J.R.C.; Espera, A.H., Jr.; Chen, Q.; Advincula, R.C. Mechanical characterization of 3D-printed polymers. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 20, 44–67. [Google Scholar]
- Paolini, A.; Kollmannsberger, S.; Rank, E. Additive manufacturing in construction: A review on processes, applications, and digital planning methods. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.V.; Hernandez, A. A Review of Additive Manufacturing. ISRN Mech. Eng. 2012, 2012, 208760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Werken, N.; Tekinalp, H.; Khanbolouki, P.; Ozcan, S.; Williams, A.; Tehrani, M. Additively manufactured carbon fiber-reinforced composites: State of the art and perspective. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 31, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchels, F.P.W.; Feijen, J.; Grijpma, D.W. A review on stereolithography and its applications in biomedical engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6121–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somos® WaterClear Ultra 10122 User Guide. Available online: https://www.dsm.com/solutions/additive-manufacturing/en_US/resource-center/user-guide/somos-waterclear.html (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Yang, C.-M.; Hrnjak, P. Visualization of two-phase flow of R410A in horizontal smooth and axial micro-finned tubes. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 2019, 138, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Im, D.J. Comparison of Surface Characteristics According to 3D Printing Methods and Materials for the Fabrication of Microfluidic Systems. Korean Chem. Eng. Res. 2019, 57, 706–713. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Miao, K.; Li, D. A novel method for improving surface finish of streolithography apparatus. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, P.E.; Cobb, R.C. Reducing the surface deviation of streolithography using in-process technique. Rapid Prototyp. J. 1997, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.G.; Herscovici, D.; Chen, D.C. Parametric process optimization to improve the accuracy of rapid prototyped streolithography parts. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf. 2000, 40, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.; Monsees, D.; Hey, J.; Schweyen, R. Surface Quality of 3D-Printed Models as a Function of Various Printing Parameters. Materials 2019, 12, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.E.; Melton, V.L. Abrasive flow finishing of streolithography prototypes. Rapid Prototyp. J. 1998, 4, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.K.; Lee, S.H. Improving the surface roughness of SL parts using a coating and grinding process. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2007, 8, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Neirynck, J.M.; Yang, G.-R.; Murarka, S.P.; Gutmann, R.J. The addition of surfactant to slurry for polymer CMP: Effect on polymer surface, removal rate and underlying Cu. Thin Solid Films 1996, 290–291, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.W.; Wang, Z.F.; Zirajutheen, B.M.P. Chemical mechanical polishing of polycarbonate and poly methyl methacrylate substrates. Microelectron. Eng. 2005, 81, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.W.; Wang, Z.F.; Tan, Y.H. Chemical mechanical polishing of polymeric materials for MEMS applications. Microelectron. J. 2006, 37, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towery, D.; Fury, M.A. Chemical Mechanical Polishing of Polymer Films. J. Electron. Mater. 1998, 27, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Joo, S.; Kim, H.; Jeong, H. Chemical Mechanical Planarization Method for Thick Copper Films of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems and Integrated Circuits. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 5708–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagoubi, J.E.; Lubineau, G.; Roger, F.; Verdu, J. A fully coupled diffusion-reaction scheme for moisture sorption-desorption in an anhydride-cured epoxy resin. Polymer 2012, 53, 5582–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neve, B.D.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Water absorption by an epoxy resin and its effect on the mechanical properties and infra-red spectra. Polymer 1993, 34, 5099–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.S. Water Absorption and Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Insulation, Science in Energy and Environment. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, Z.; Basim, G.B. Effect of chemical mechanical polishing on surface nature of titanium implants FT-IR and wettability data of titanium implants surface after chemical mechanical polishing implementation. Data Brief 2017, 10, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, Z.; Ozdemir, A.; Basim, G.B. Application of chemical mechanical polishing process on titanium based implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Polishing Case. | Method. |
|---|---|
| One-step polishing | Chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) |
| Two-step polishing | Sanding (#2000) + CMP |
| Process. | Parameter | Value or Consumable |
|---|---|---|
| Sanding | Sandpaper | #2000 |
| Applied pressure | 9.81 kPa | |
| Rotating speed | 80 rpm | |
| CMP | Applied pressure | 41.2 kPa |
| Rotating speed | Head 150 rpm/Platen 150 rpm | |
| Slurry flow rate | 150 mL/min | |
| Slurry | Colloidal silica slurry (diluted with deionized water) | |
| Polishing pad | KONI pad (KPX Chemical, Seoul, Korea) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, J.; Lee, H. Preliminary Study on Polishing SLA 3D-Printed ABS-Like Resins for Surface Roughness and Glossiness Reduction. Micromachines 2020, 11, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11090843
Son J, Lee H. Preliminary Study on Polishing SLA 3D-Printed ABS-Like Resins for Surface Roughness and Glossiness Reduction. Micromachines. 2020; 11(9):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11090843
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Jungyu, and Hyunseop Lee. 2020. "Preliminary Study on Polishing SLA 3D-Printed ABS-Like Resins for Surface Roughness and Glossiness Reduction" Micromachines 11, no. 9: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11090843
APA StyleSon, J., & Lee, H. (2020). Preliminary Study on Polishing SLA 3D-Printed ABS-Like Resins for Surface Roughness and Glossiness Reduction. Micromachines, 11(9), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11090843






