Fabrication of Hard–Soft Microfluidic Devices Using Hybrid 3D Printing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Hard–Soft Microfluidic Devices Using Hybrid 3D Printing
2.3. Hybrid 3D-Printed LAMP Reactor Assay Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
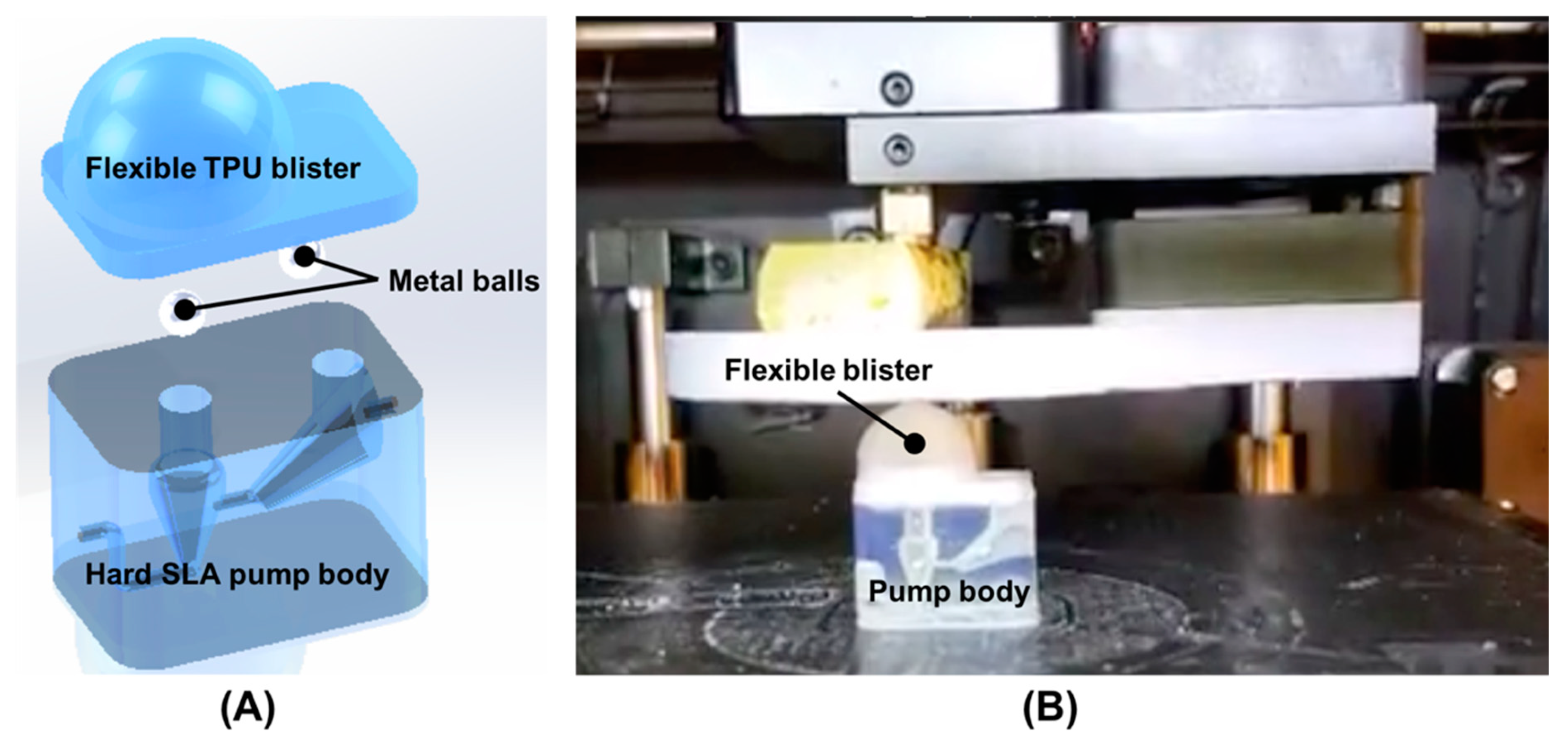
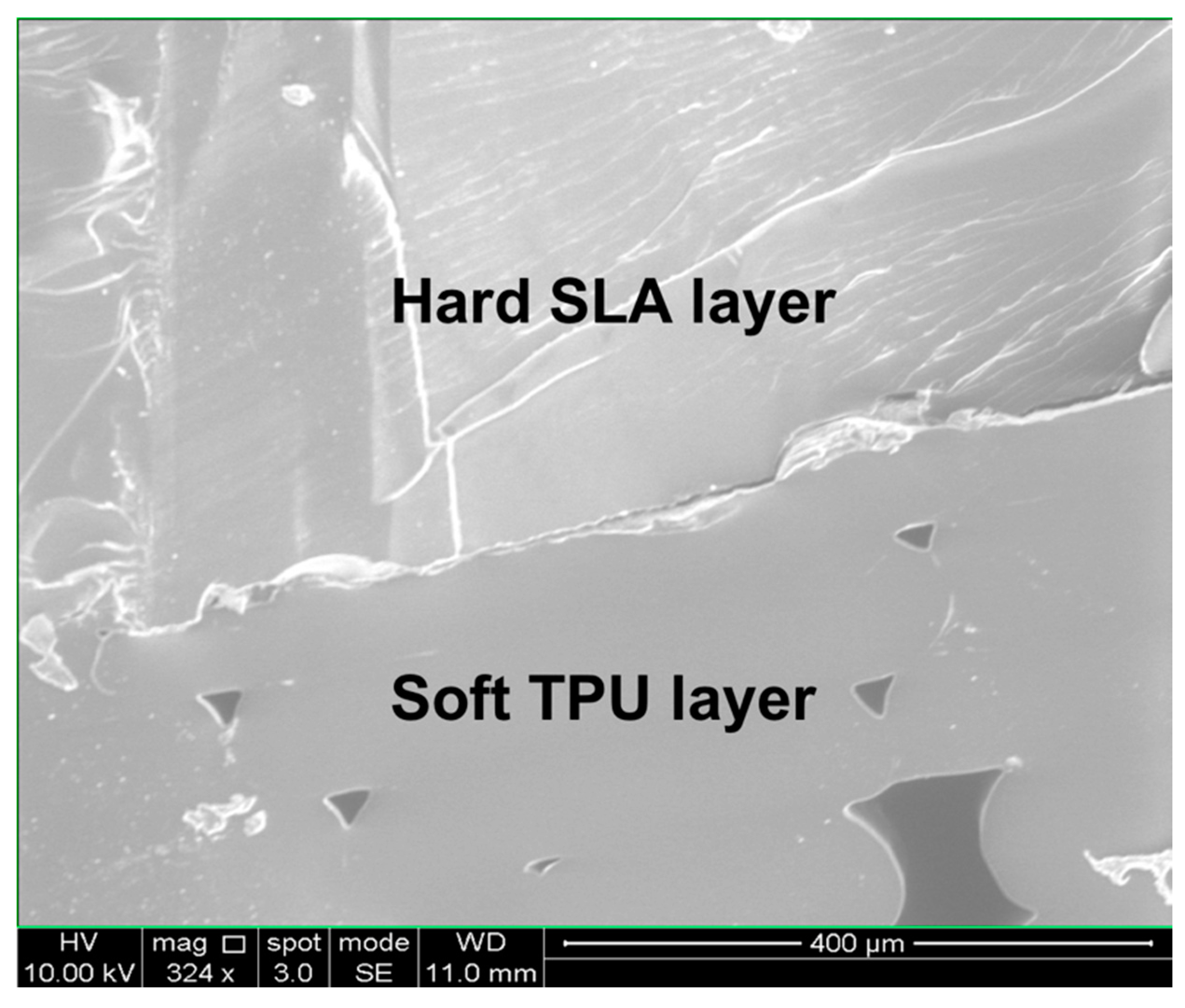
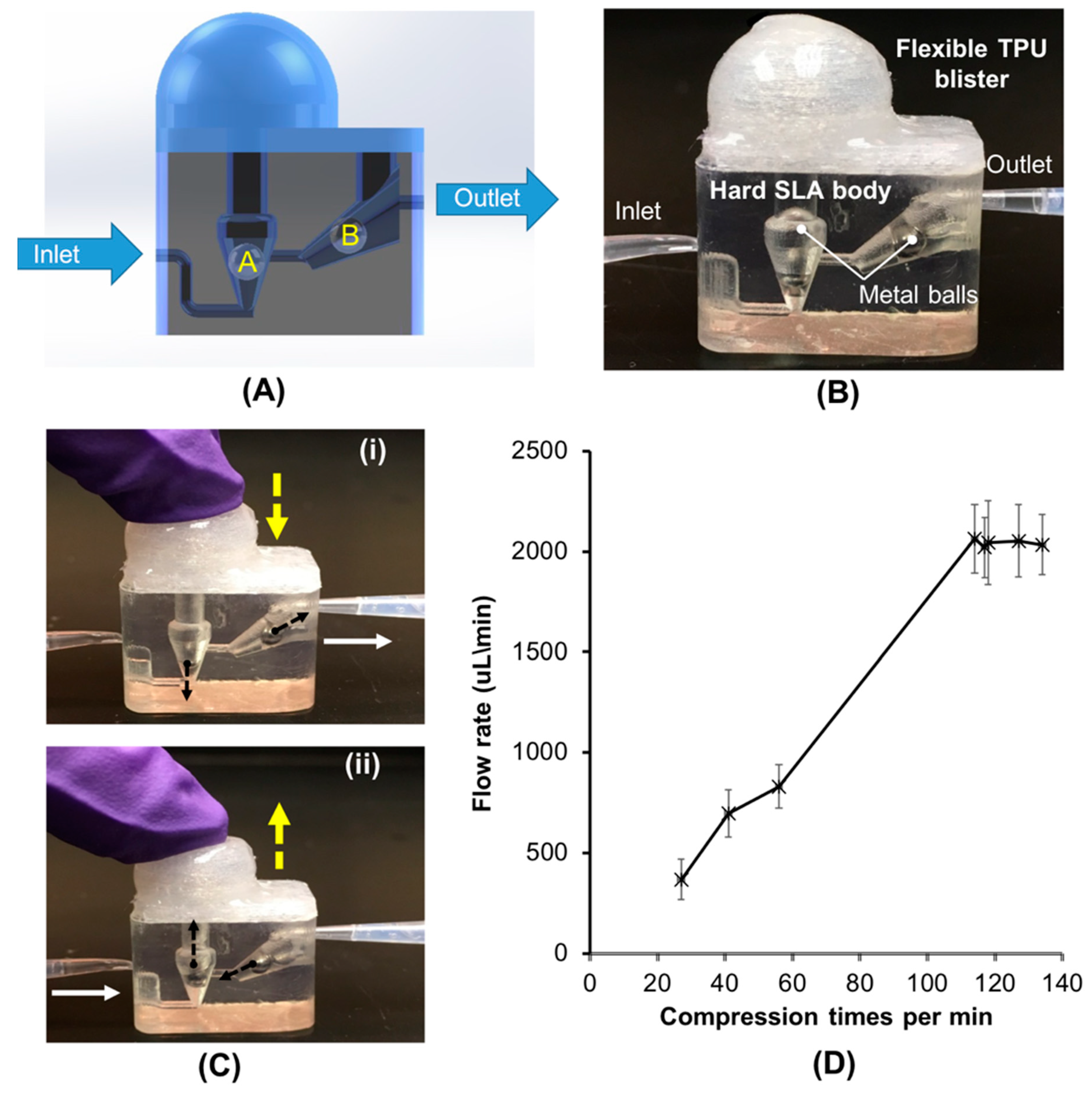
3.1. Finger-Powered, Hard–Soft 3D-Printed Micropump
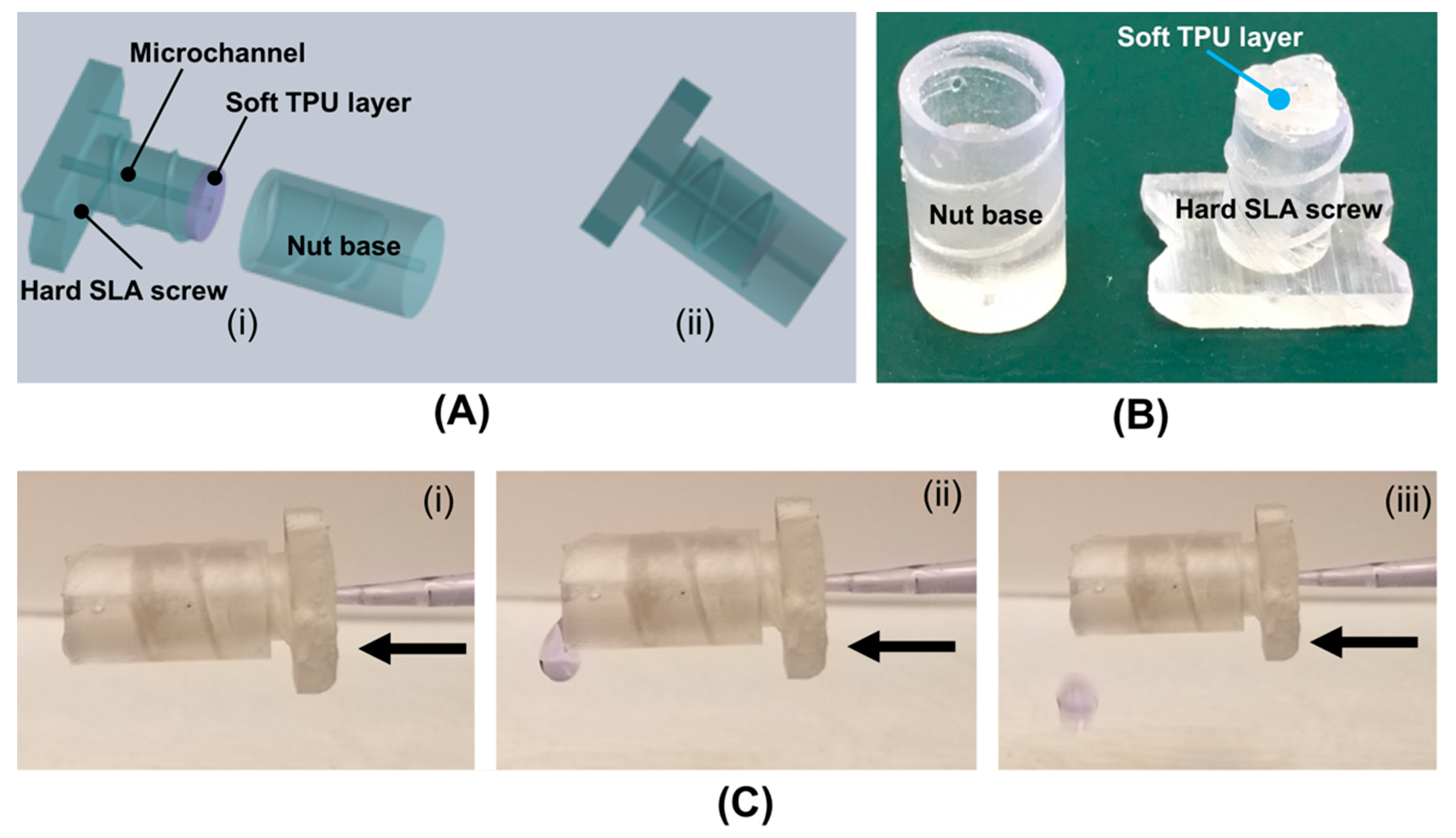
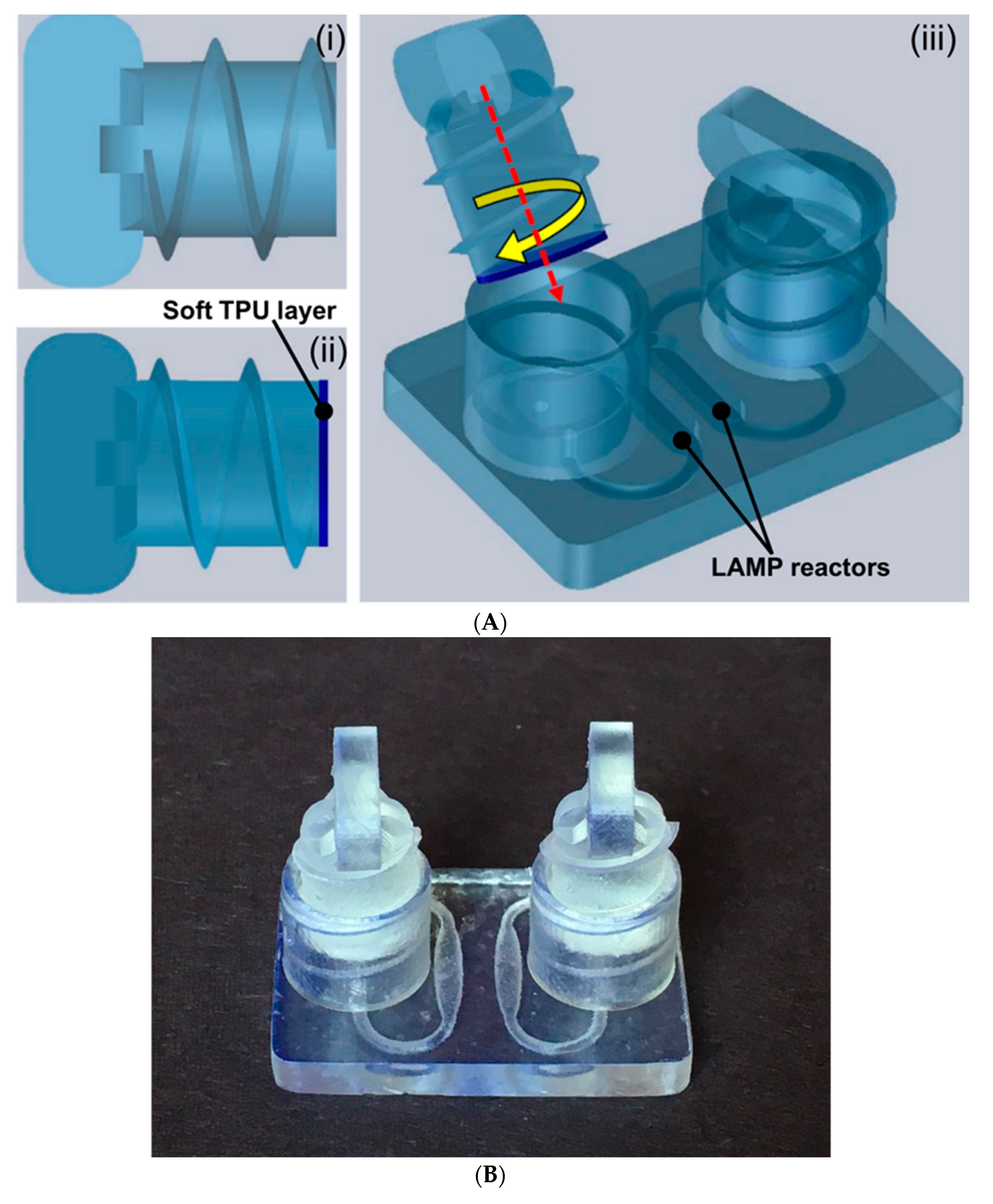
3.2. Hard–Soft Hybrid Microfluidic Connector
3.3. Molecular Detection on 3D-Printed Microfluidic Reactor Chip with the Hard–Soft Threaded Screw Sealer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, W.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L.; Qin, J. Microfluidic platforms towards point-of-care diagnostics in infectious diseases. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1377, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K.; Luppa, P.B.; Yeo, L.Y.; Ozcan, A.; Luong, J.H.T. Emerging technologies for next-generation point-of-care testing. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasseri, B.; Soleimani, N.; Rabiee, N.; Kalbasi, N.; Kalbasi, A.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Point-of-care microfluidic devices for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandley, C.M.; Augustine, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Nara, S.; Srivastavo, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Microfluidics based point-of-care diagnostics. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cui, D.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Chen, J. Continuous flow microfluidic device for cell separation, cell lysis and DNA purification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Geva, E.; Mauk, M.; Qiu, X.; Abrams, W.R.; Malamud, D.; Curtis, K.; Owen, S.M.; Bau, H.H. An isothermal amplification reactor with an integrated isolation membrane for point-of-care detection of infectious diseases. Analyst 2011, 136, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mauk, M.; Qiu, X.; Liu, C.; Kim, J.; Ramprasad, S.; Ongagna, S.; Abrams, W.R.; Malamud, D.; Corstjens, P.L.; et al. An integrated, self-contained microfluidic cassette for isolation, amplification, and detection of nucleic acids. Biomed. Microdevices 2010, 12, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L.; Qin, J.; Lin, B. Rapid prototyping of paper-based microfluidics with wax for low-cost, portable bioassay. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qiu, X.; Ongagna, S.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z.; Abrams, W.R.; Malamud, D.; Corstjens, P.L.; Bau, H.H. A timer-actuated immunoassay cassette for detecting molecular markers in oral fluids. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Hejazian, M.; Ooi, C.H.; Kashaninejad, N. Recent advances and future perspectives on microfluidic liquid handling. Micromachines 2017, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W. Polymer microfluidics: Simple, low-cost fabrication process bridging academic lab research to commercialized production. Micromachines 2016, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadimisetty, K.; Song, J.; Doto, A.M.; Hwang, Y.; Peng, J.; Mauk, M.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Gross, R.; Jarvis, J.N.; Liu, C. Fully 3D printed integrated reactor array for point-of-care molecular diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 109, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.B.; Lockwood, S.Y.; Martin, R.S.; Spence, D.M. A 3D printed fluidic device that enables integrated features. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5622–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alapan, Y.; Hasan, M.N.; Shen, R.; Gurkan, U.A. Three-dimensional printing based hybrid manufacturing of microfluidic devices. J. Nanotechnol. Eng. Med. 2015, 6, 021007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaal, G.; Mendes, M.; de Almeida, T.P.; Piazzetta, M.H.; Gobbi, Â.L.; Riul, A., Jr.; Rodrigues, V. Simplified fabrication of integrated microfluidic devices using fused deposition modeling 3D printing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, L.H.; Chen, P.C. Simple and low-cost production of hybrid 3D-printed microfluidic devices. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 024108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Macdonald, N.P.; Guijt, R.M.; Breadmore, M.C. Increasing the functionalities of 3D printed microchemical devices by single material, multimaterial, and print-pause-print 3D printing. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Woolley, A.T.; Nordin, G.P. High density 3D printed microfluidic valves, pumps, and multiplexers. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2450–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, D.; Li, H. A hard–soft microfluidic-based biosensor flow cell for SPR imaging application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, G.; Lee, J.; Cha, W.; Tung, Y.C.; Linderman, J.J.; Takayama, S. Hard top soft bottom microfluidic devices for cell culture and chemical analysis. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3714–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, W.C.; Kuan, Y.K.; Li, M.-H.; Ying, J.Y. Rapid prototyping of multi-level polydimethylsiloxane-based microfluidic devices. Proc. SPIE 2008, 7269, 72690B. [Google Scholar]
- Sochol, R.D.; Sweet, E.; Glick, C.C.; Venkatesh, S.; Avetisyan, A.; Ekman, K.F.; Raulinaitis, A.; Tsai, A.; Wienkers, A.; Korner, K.; et al. 3D printed microfluidic circuitry via multijet-based additive manufacturing. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Smejkal, P.; Macdonald, N.P.; Guijit, R.M.; Breadmore, M.C. One-step fabrication of a microfluidic device with an integrated membrane and embedded reagents by multimaterial 3D printing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4701–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiaux, A.D.; Pinger, C.W.; Hayter, E.A.; Bunn, M.E.; Martin, R.S.; Spence, D.M. PolyJet 3D-printed enclosed microfluidic channels without photocurable supports. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6910–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara-Kudo, Y.; Yoshino, M.; Kojima, T.; Ikedo, M. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the rapid detection of Salmonella. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 253, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Mauk, M.G.; Hackett, B.A.; Cherry, S.; Bau, H.H.; Liu, C. Instrument-free point-of-care molecular detection of Zika virus. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7289–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.C.; Fu, C.C.; Hu, L.; Thakur, R.; Feng, J.; Lee, L.P. Self-powered integrated microfluidic point-of-care low-cost enabling (SIMPLE) chip. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1501645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Xu, Z.; Yin, K.; Sfeir, M.; Liu, C. Dual-Priming Isothermal Amplification (DAMP) for Highly Sensitive and Specific Molecular Detection with Ultralow Nonspecific Signals. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12852–12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Pandian, V.; Kadimisetty, K.; Ruiz, C.; Cooper, K.; You, J.; Liu, C. Synergistically enhanced colorimetric molecular detection using smart cup: A case for instrument-free HPV-associated cancer screening. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauk, M.; Song, J.; Bau, H.H.; Gross, R.; Bushman, F.D.; Collman, R.G.; Liu, C. Miniaturized devices for point of care molecular detection of HIV. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, P. Point of care testing for infectious diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 493, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Fohlerova, Z.; Chang, H.; Iliescu, C.; Neuzil, P. LAMP on a chip: Revising microfluidic platforms for loop-mediated DNA amplification. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz, C.; Kadimisetty, K.; Yin, K.; Mauk, M.G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, C. Fabrication of Hard–Soft Microfluidic Devices Using Hybrid 3D Printing. Micromachines 2020, 11, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11060567
Ruiz C, Kadimisetty K, Yin K, Mauk MG, Zhao H, Liu C. Fabrication of Hard–Soft Microfluidic Devices Using Hybrid 3D Printing. Micromachines. 2020; 11(6):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11060567
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz, Carlos, Karteek Kadimisetty, Kun Yin, Michael G. Mauk, Hui Zhao, and Changchun Liu. 2020. "Fabrication of Hard–Soft Microfluidic Devices Using Hybrid 3D Printing" Micromachines 11, no. 6: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11060567
APA StyleRuiz, C., Kadimisetty, K., Yin, K., Mauk, M. G., Zhao, H., & Liu, C. (2020). Fabrication of Hard–Soft Microfluidic Devices Using Hybrid 3D Printing. Micromachines, 11(6), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11060567




