The Potential of Pandanus amaryllifolius Leaves Extract in Fabrication of Dense and Uniform ZnO Microrods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
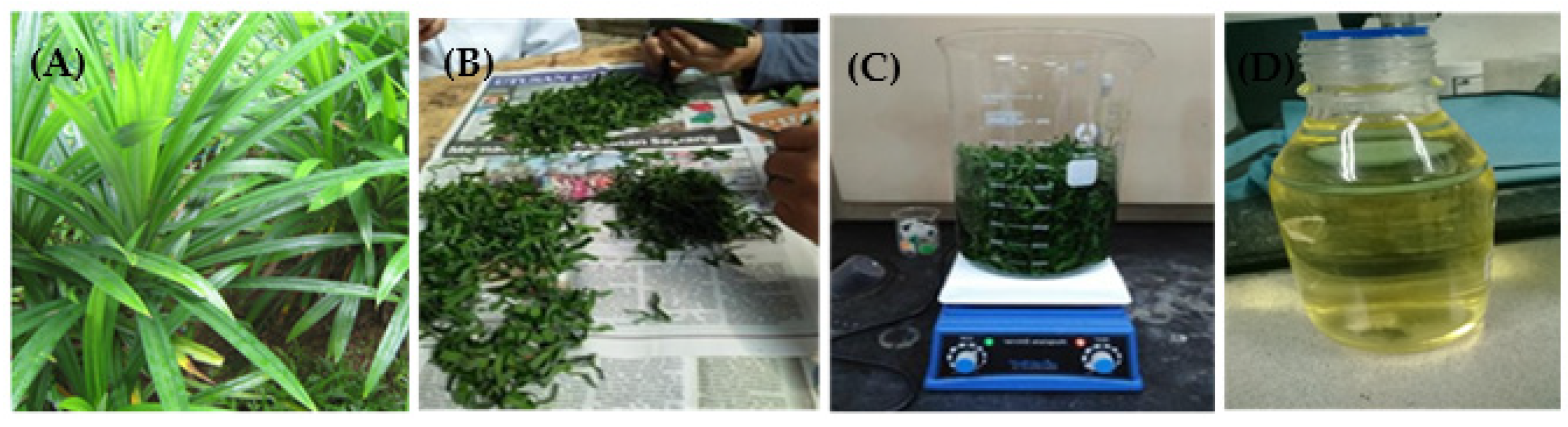
2.1. Preparation of Pandanus amaryllifolius Leaves Extract
2.2. Preparation of ZnO Seed Layers
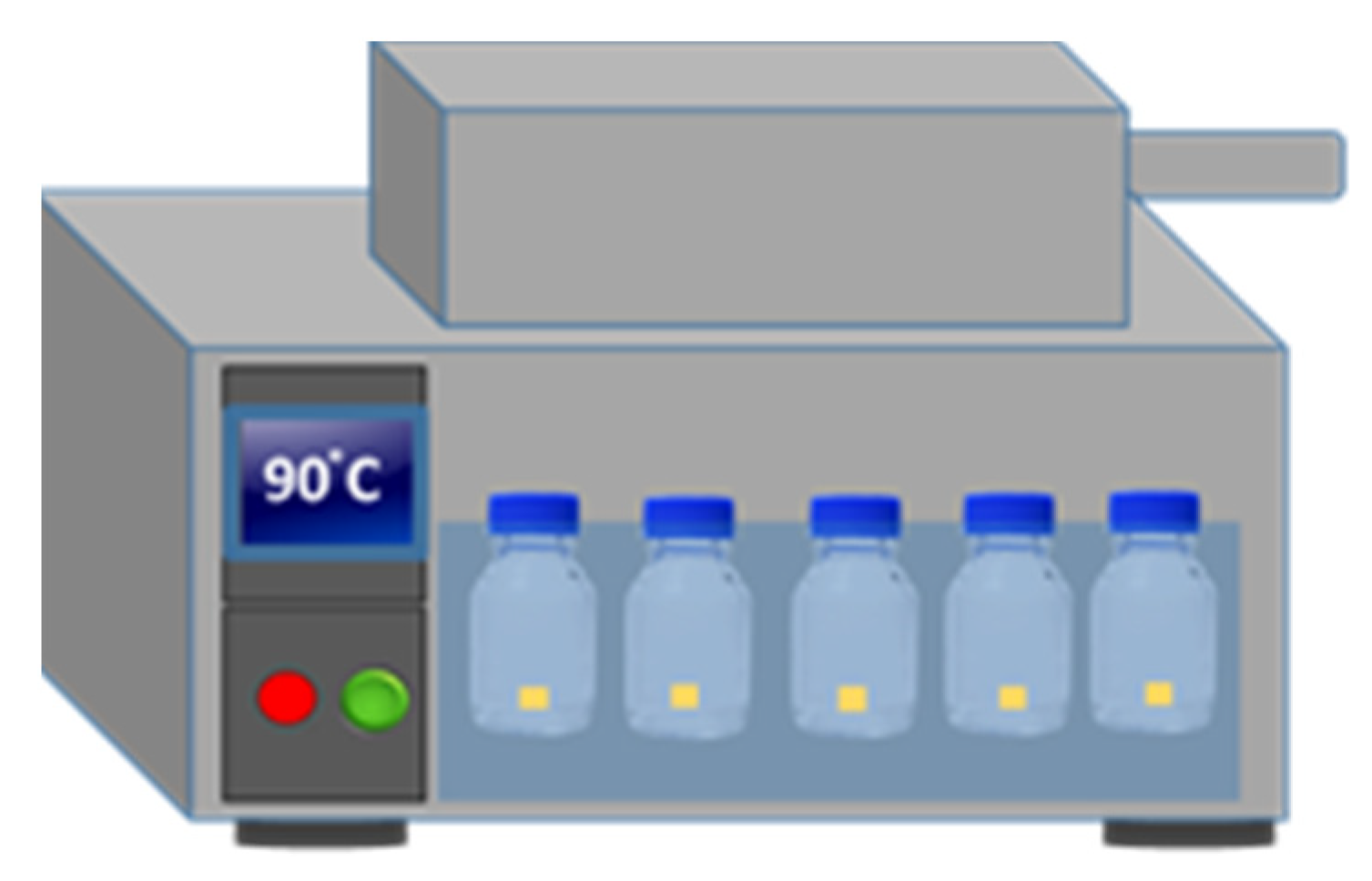
2.3. Preparation of ZnO Nanostructures
2.4. Characterization
- D = the crystal size;
- λ = the wavelength of the X-ray radiation (λ = 0.15406 nm);
- K = usually taken as 0.94;
- β = the full width at half maximum height;
- θ = highest diffraction angle.
3. Results
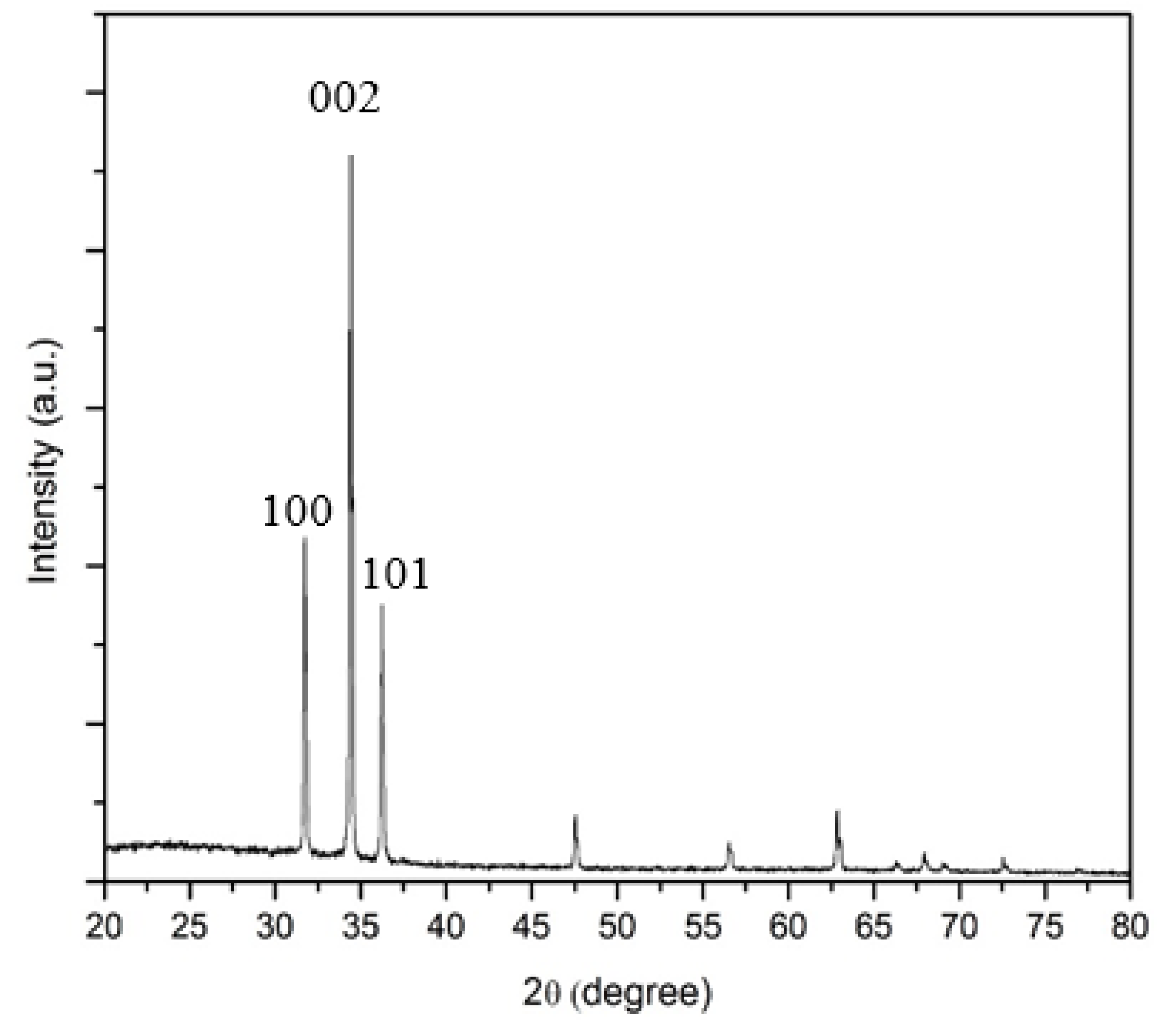
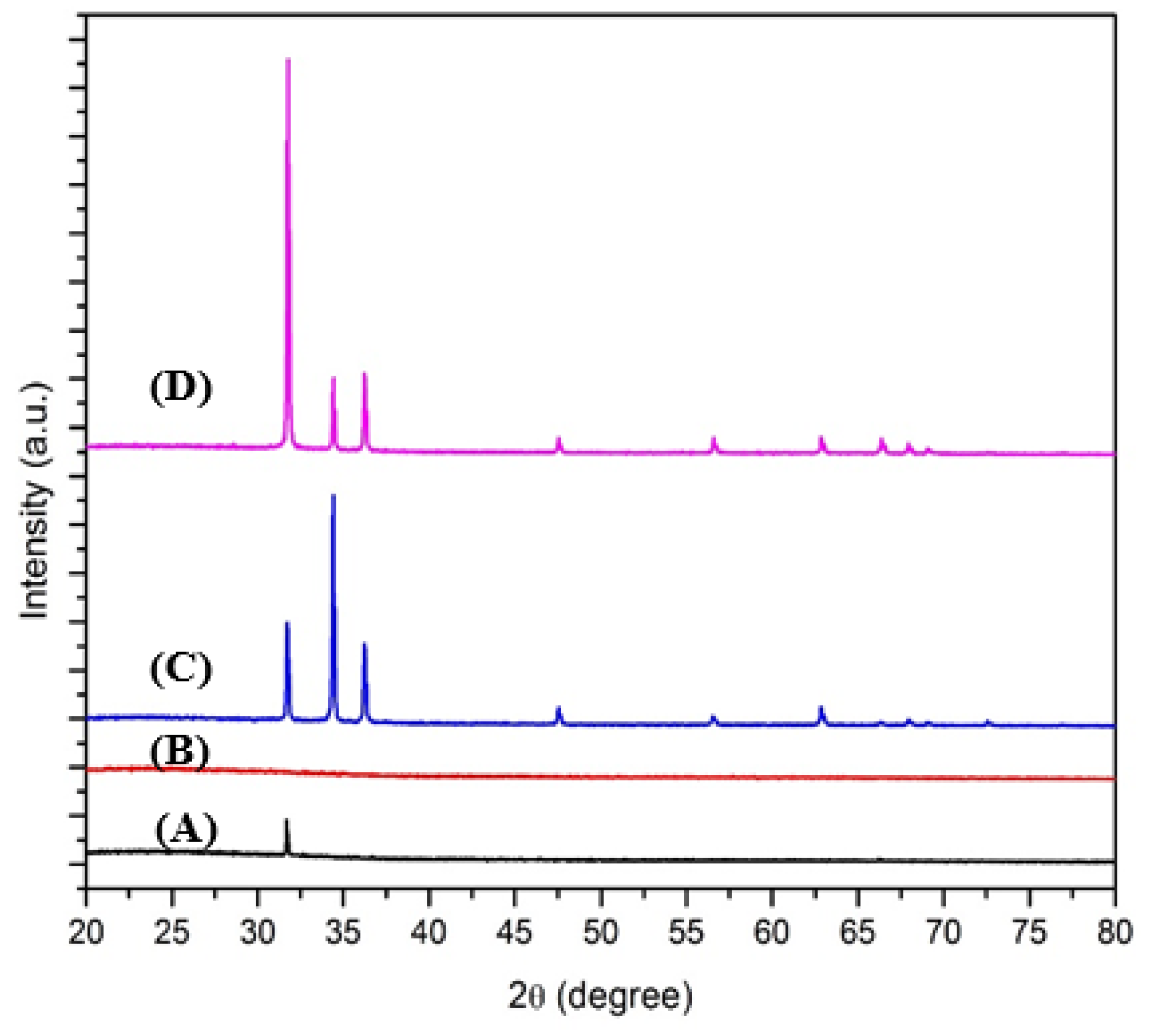
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
- Ihkl = hkl peak intensity;
- ∑Ihkl = sum of the intensities of all the diffraction peaks.
3.2. Phytochemical Analysis
3.3. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV–Vis) Analysis
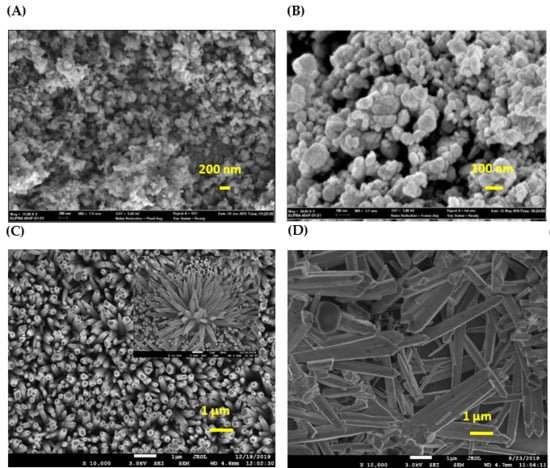
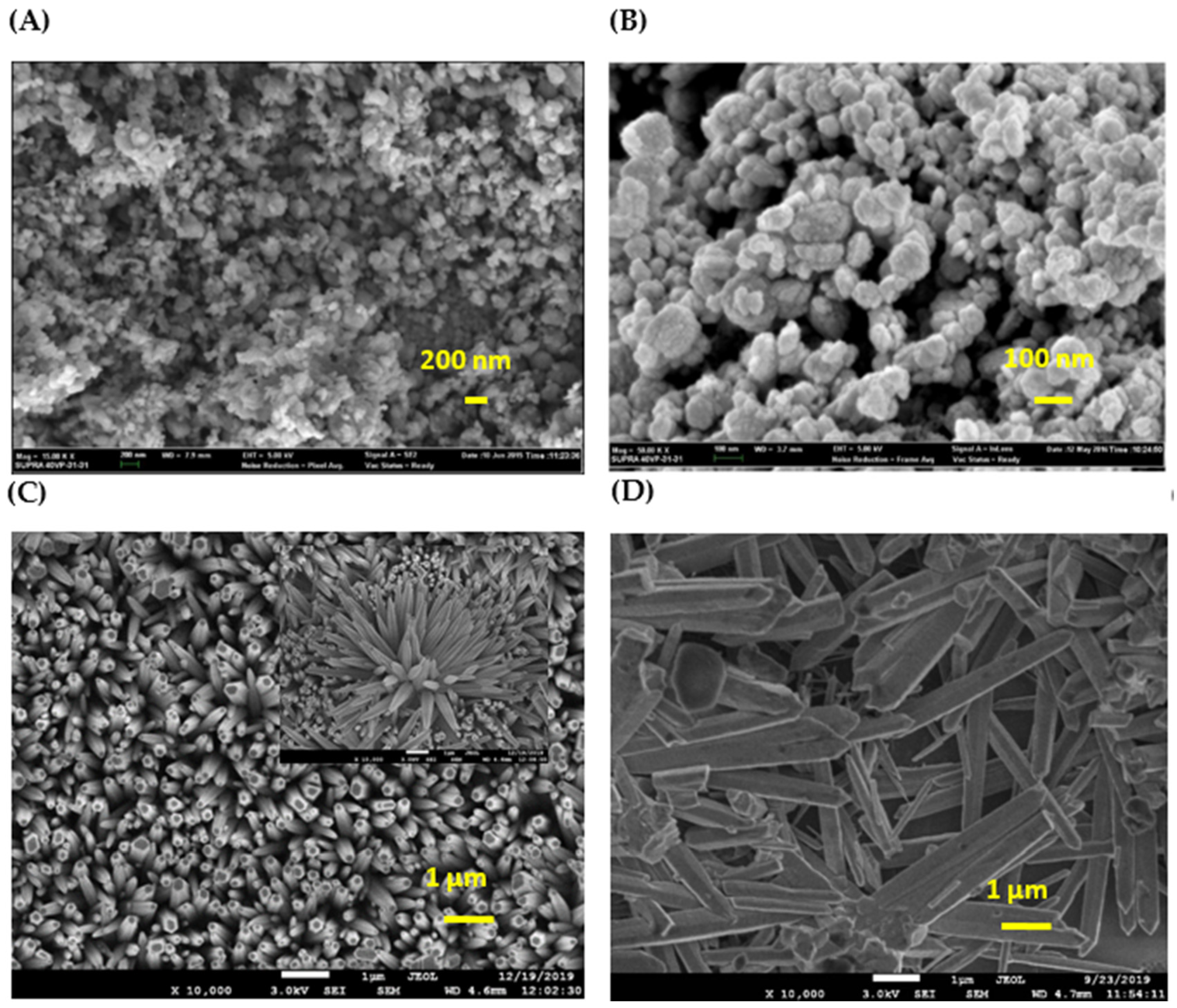
3.4. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, R.; Xia, Z.; Ge, S. Flash synthesis of flower-like ZnO nanostructures by microwave-induced combustion process. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehru, L.C.; Swaminathan, V.; Sanjeeviraja, C. Rapid synthesis of nanocrystalline ZnO by a microwave-assisted combustion method. Powder Technol. 2012, 226, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.U.; Kim, J.A.; Pawar, S.M.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Creation of nanoscale two-dimensional patterns of ZnO nanorods using laser interference lithography followed by hydrothermal synthesis at 90 °C. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 4256–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Lee, J.; Yang, J.; Lim, S. Hydrothermal synthesis of Al-doped ZnO nanorod arrays on Si substrate. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2010, 405, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshhesab, Z.M.; Sarfaraz, M.; Asadabad, M.A. Preparation of ZnO nanostructures by chemical precipitation method. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Chem. 2011, 41, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udom, I.; Ram, M.K.; Stefanakos, E.K.; Hepp, A.F.; Goswami, D.Y. One dimensional-ZnO nanostructures: Synthesis, properties and environmental applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2013, 16, 2070–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samat, N.A.; Nor, R.M. Sol–gel synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Citrus aurantifolia extracts. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, S545–S548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, M.H.; Khusaimi, Z.; Musa, M.Z.; Sahdan, M.Z.; Rusop, M. Novel synthesis of aligned Zinc oxide nanorods on a glass substrate by sonicated sol–gel immersion. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1211–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badnore, A.U.; Pandit, A.B. Effect of pH on sonication assisted synthesis of ZnO nanostructures: Process details. Chem. Eng. Process. 2017, 122, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.; Ramesh, V.; Thivaharan, V. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Calliandra haematocephala leaf extract, their antibacterial activity and hydrogen peroxide sensing capability. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Mehata, M.S. Medicinal plant leaf extract and pure flavonoid mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial property. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.U.H.; Khan, A.; Shah, A.; Wan, P.; Chen, Y.; Khan, G.M.; Khan, A.U.; Tahir, K.; Muhammad, N.; Khan, H.U. Enhanced photocatalytic and electrocatalytic applications of green synthesized silver nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemike, E.E.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Ekennia, A.C.; Ehiri, R.C.; Nnaji, N.J. Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extracts of Lippia citriodora: Antimicrobial, larvicidal and photocatalytic evaluations. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhoshkumar, J.; Kumar, S.V.; Rajeshkumar, S. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant leaf extract against urinary tract infection pathogen. Resour. Effic. Technol. 2017, 3, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Noreen, F.; Kanwal, S.; Iqbal, A.; Hussain, G. Green synthesis of ZnO and Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles from leaf extracts of Abutilon indicum, Clerodendrum infortunatum, Clerodendrum inerme and investigation of their biological and photocatalytic activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 82, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundrarajan, M.; Ambika, S.; Bharathi, K. Plant-extract mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pongamia pinnata and their activity against pathogenic bacteria. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, T.T. Tribulus terrestris leaf extract assisted green synthesis and gas sensing properties of Ag-coated ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2015, 158, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutham, S.; Kaur, S.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Bal, J.K.; Jayarambabu, N.; Kumar, D.S.; Rao, K.V. Nanostructured ZnO gas sensors obtained by green method and combustion technique. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 57, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Joshi, M.; Panthari, P.; Malhotra, B.; Kharkwal, A.C.; Kharkwal, H. Citrulline rich structurally stable zinc oxide nanostructures for superior photo catalytic and optoelectronic applications: A green synthesis approach. Nano Struct. Nano Objects 2017, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, H.; Karaköse, E.; Duman, F. High optoelectronic and antimicrobial performances of green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles using Aesculus hippocastanum. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevanandam, J.; San Chan, Y.; Ku, Y.H. Aqueous Eucalyptus globulus leaf extract-mediated biosynthesis of MgO nanorods. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2018, 61, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnukumar, P.; Vivekanandhan, S.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Recent advances and emerging opportunities in phytochemical synthesis of ZnO nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 80, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulianova, V.; Zazerin, A.; Pashkevich, G.; Bogdan, O.; Orlov, A. High-performance ultraviolet radiation sensors based on zinc oxide nanorods. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 234, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.Q.; Trung, T.Q.; Duy, L.T.; Kim, B.Y.; Siddiqui, S.; Lee, W.; Lee, N.E. High-performance flexible ultraviolet (UV) phototransistor using hybrid channel of vertical ZnO nanorods and graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11032–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, M.H.; Malek, M.F.; Hafizah, N.N.; Khusaimi, Z.; Musa, M.Z.; Rusop, M. Fabrication of an ultraviolet photoconductive sensor using novel nanostructured, nanohole-enhanced, aligned aluminium-doped zinc oxide nanorod arrays at low immersion times. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 195, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, J.P.; Das, S.N.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, Y.A.; Lee, T.Y.; Myoung, J.M. Fabrication of UV detectors based on ZnO nanowires using silicon microchannel. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 3305–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.C.; Jung, B.O.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, H.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.H. Dramatically enhanced ultraviolet photosensing mechanism in a n-ZnO nanowires/i-MgO/n-Si structure with highly dense nanowires and ultrathin MgO layers. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 265506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Khusaimi, Z.; Afaah, A.N.; Aziz, A.; Mamat, M.H.; Rusop, M. Effect of annealing temperature of magnesium doped zinc oxide nanorods growth on silicon substrate. J. Nano Res. 2014, 26, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.Y.; Bae, K.H.; Kim, H.S.; Park, N.G. Effects of seed layer on growth of ZnO nanorod and performance of perovskite solar cell. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 10321–10328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Mohamed, R.; Afaah, A.N.; Asib, N.A.M.; Rusop, M.; Khusaimi, Z. Morphological and Optical Properties of Different Mg Percentage of ZnO/Mg Thin Films Prepared by Sol-gel Spin-coating and Immersion Method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1107, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Rouhi, J.; Malek, M.F.; Ismail, A.S.; Alrokayan, S.A.; Khan, H.A.; Khusaimi, Z.; Mamat, M.H.; Mahmood, M.R. Sol gel synthesized zinc oxide nanorods on single and Co-doped ZnO seed layer templates: Morphological, optical and electrical properties. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, M.B.; Sharma, A.; Malaidurai, M.; Thangavel, R. Effect of Sn doping on structural, mechanical, optical and electrical properties of ZnO nanoarrays prepared by sol-gel and hydrothermal process. Superlattices Microstruct. 2018, 117, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asib, N.A.M.; Husairi, F.S.; Eswar, K.A.; Afaah, A.N.; Mamat, M.H.; Rusop, M.; Khusaimi, Z. Developing high-sensitivity UV sensors based on ZnO nanorods grown on TiO2 seed layer films using solution immersion method. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 302, 111827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennimalai, M.; Do, J.Y.; Kang, M.; Senthil, T.S. A facile green approach of ZnO NRs synthesized via Ricinus communis L. leaf extract for Biological activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Utashiro, K.; Abe, Y.; Kawwamura, M. Growth of zinc oxide nanorods using various seed layer annealing temperatures and substrate materials. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar]
- Malek, M.F.; Mamat, M.H.; Soga, T.; Rahman, S.A.; Bakar, S.A.; Ismail, A.S.; Mohamed, R.; Alrokayan, S.A.; Khan, H.A.; Mahmood, M.R. Thickness-controlled synthesis of vertically aligned c-axis oriented ZnO nanorod arrays: Effect of growth time via novel dual sonication sol–gel process. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 55, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, M.; Ye, Z.; Lu, J.; He, H.; Huang, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, B. Growth and properties of ZnO nanorod and nanonails by thermal evaporation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3972–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Suriani, A.B.; Jabur, A.R. The enhancement Of UV sensor response by zinc oxide nanorods/reduced graphene oxide bilayer nanocomposites film. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1003, 012070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkari, R.; Jaber, B.; Labrim, H.; Ouafi, M.; Zayyoun, N.; Laânab, L. Effect of Solvents and Stabilizer Molar Ratio on the Growth Orientation of Sol-Gel-Derived ZnO Thin Films. Int. J. Photoenergy 2019, 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhir, R.M.; Norashikin, M.H.; Mahat, M.M.; Bonnia, N.N. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Corrosion Protection Application. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 4, 488–492. [Google Scholar]
- Momeni, S.S.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Rustaiyan, A. Green synthesis of the Cu/ZnO nanoparticles mediated by Euphorbia prolifera leaf extract and investigation of their catalytic activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 472, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Ikram, S. A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and microbes: A prospect towards green chemistry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 166, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zikalala, N.; Matshetshe, K.; Parani, S.; Oluwafemi, O.S. Biosynthesis protocols for colloidal metal oxide nanoparticles. Nano Struct. Nano Objects 2018, 16, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingale, A.G.; Chaudhari, A.N. Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles and potential applications: An eco-friendly approach. J. Nanomed. Nanotechol. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, V.V.; Love, A.J.; Sinitsyna, O.V.; Makarova, S.S.; Yaminsky, I.V.; Taliansky, M.E.; Kalinina, N.O. “Green” nanotechnologies: Synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat. 2014, 6, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Ahmad, M.B.; Namvar, F.; Mohamad, R. Green biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using brown marine macroalga Sargassum muticum aqueous extract. Mater. Lett. 2014, 116, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, P.; Chanu, T.I.; Samanta, D.; Chatterjee, S. A review on bio-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant extracts as reductants and stabilizing agents. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 183, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, N.; Saha, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Maiti, M.; Das, S.; Basu, R.; Nandy, P. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract: Effect of temperature on synthesis, anti-bacterial activity and anti-diabetic activity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 4993–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed Ul Haq, A.; Nadhman, A.; Ullah, I.; Mustafa, G.; Yasinzai, M.; Khan, I. Synthesis approaches of zinc oxide nanoparticles: The dilemma of ecotoxicity. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, P.; Xiang, L. Effects of NaOH on formation of ZnO nanorods from ε-Zn(OH)2. Mater. Lett. 2015, 141, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.L.; Hashim, U.; Muhammad, K.; Voon, C.H. Sol–gel synthesized zinc oxide nanorods and their structural and optical investigation for optoelectronic application. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Sun, M.; Li, L.; Xu, N.; Wu, J.; Sun, J. High visible photoelectrochemical activity of Ag nanoparticle-sandwiched CdS/Ag/ZnO nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Yi, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, Y.; Yi, Y. Fabriction of ZnO nanorods with strong UV absorption and different hydrophobicity on foamed nickel under different hydrothermal conditions. Micromachines 2019, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Test | Observation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Lead acetate | Pale yellow precipitate | + |
| Sodium hydroxide | Deep yellow precipitate | + |
| Ferric chloride | Black precipitate | + |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Md Akhir, R.; Umbaidilah, S.Z.; Abdullah, N.A.; Alrokayan, S.A.H.; Khan, H.A.; Soga, T.; Rusop, M.; Khusaimi, Z. The Potential of Pandanus amaryllifolius Leaves Extract in Fabrication of Dense and Uniform ZnO Microrods. Micromachines 2020, 11, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030299
Md Akhir R, Umbaidilah SZ, Abdullah NA, Alrokayan SAH, Khan HA, Soga T, Rusop M, Khusaimi Z. The Potential of Pandanus amaryllifolius Leaves Extract in Fabrication of Dense and Uniform ZnO Microrods. Micromachines. 2020; 11(3):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030299
Chicago/Turabian StyleMd Akhir, Rabiatuladawiyah, Siti Zulaikha Umbaidilah, Nurul Afaah Abdullah, Salman A.H. Alrokayan, Haseeb A. Khan, Tetsuo Soga, M. Rusop, and Zuraida Khusaimi. 2020. "The Potential of Pandanus amaryllifolius Leaves Extract in Fabrication of Dense and Uniform ZnO Microrods" Micromachines 11, no. 3: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030299
APA StyleMd Akhir, R., Umbaidilah, S. Z., Abdullah, N. A., Alrokayan, S. A. H., Khan, H. A., Soga, T., Rusop, M., & Khusaimi, Z. (2020). The Potential of Pandanus amaryllifolius Leaves Extract in Fabrication of Dense and Uniform ZnO Microrods. Micromachines, 11(3), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030299