Microfluidic Device for Microinjection of Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
1. Introduction
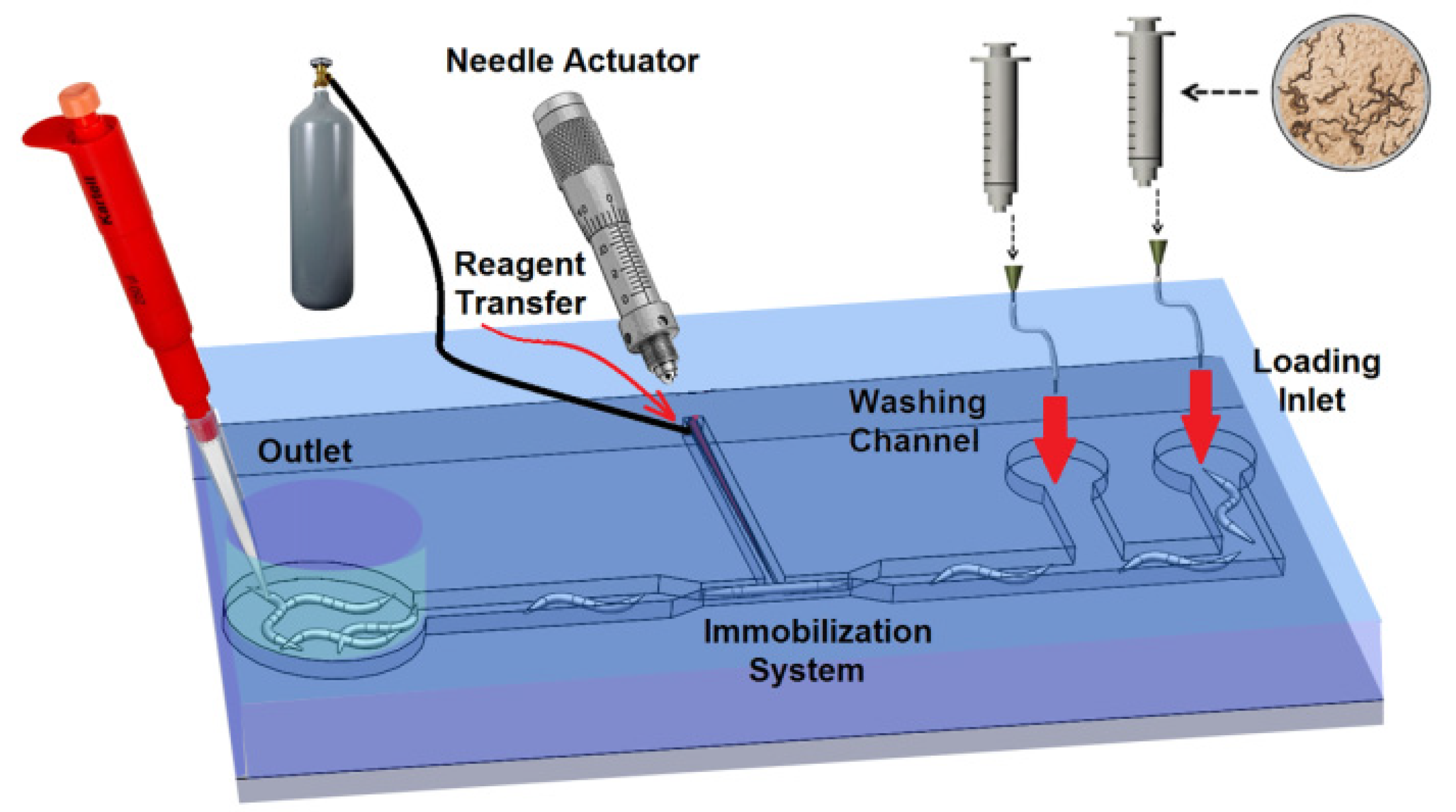
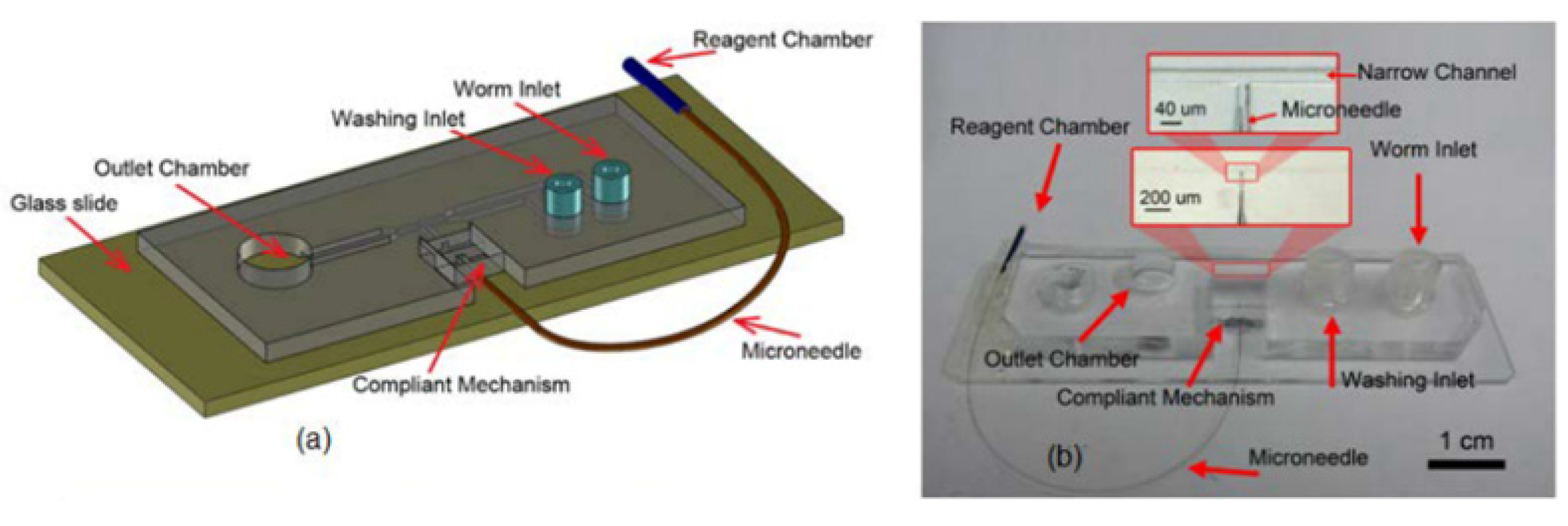
2. Device Design
2.1. Loading System
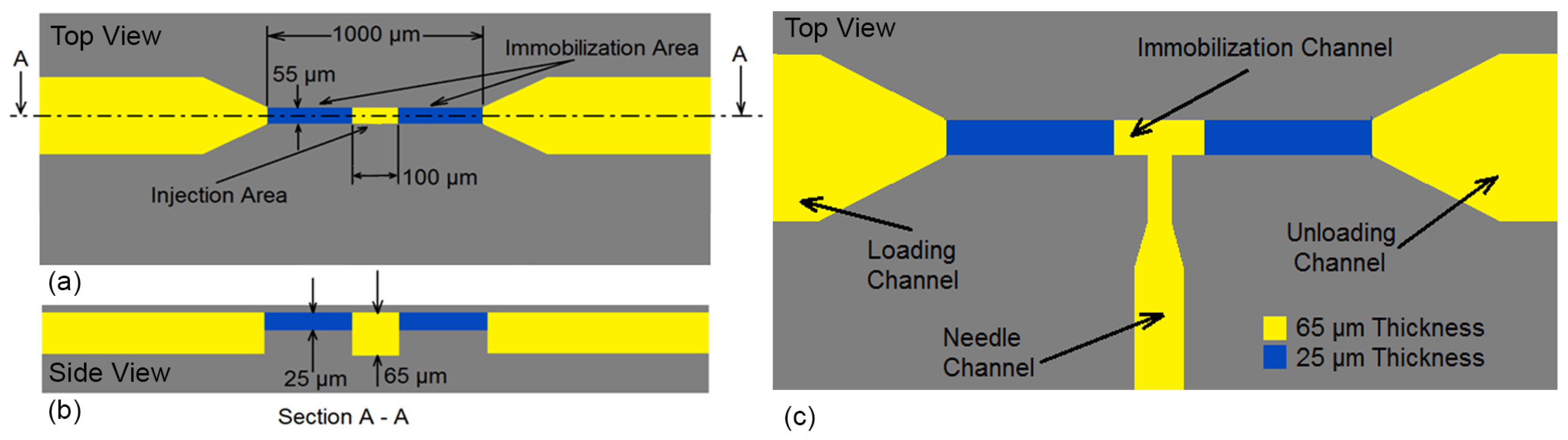
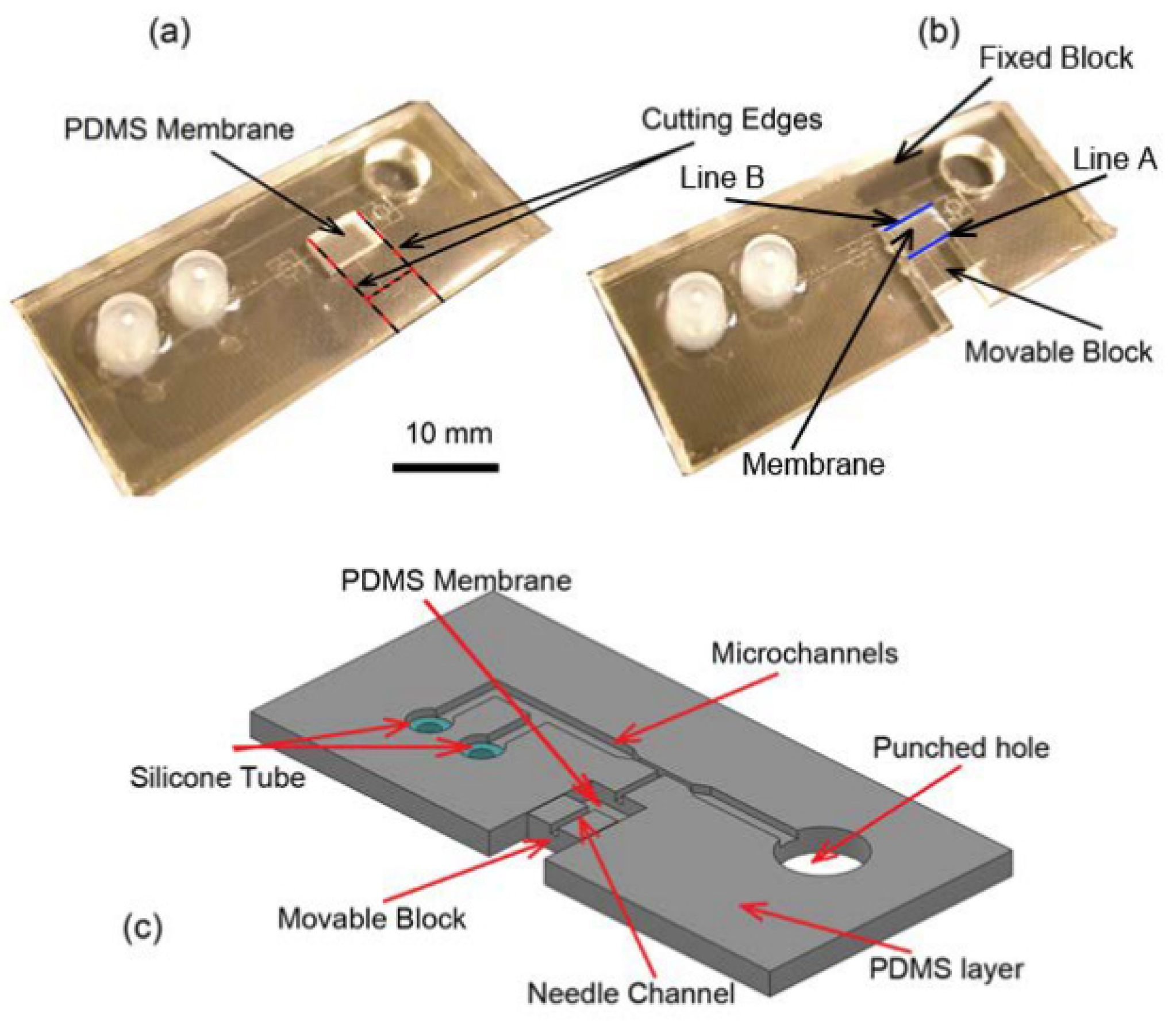
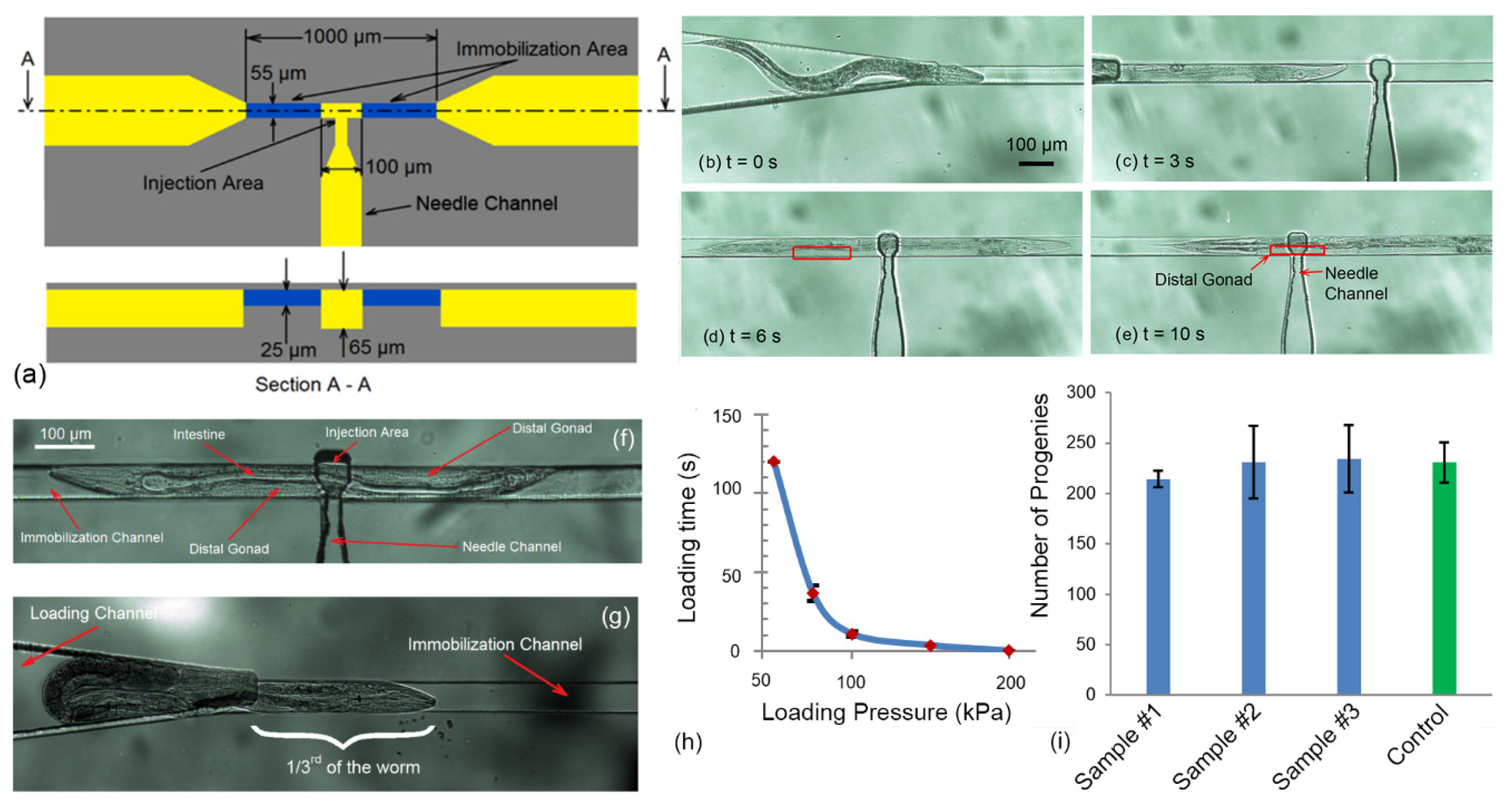
2.2. Immobilization Channel
2.3. Needle Size
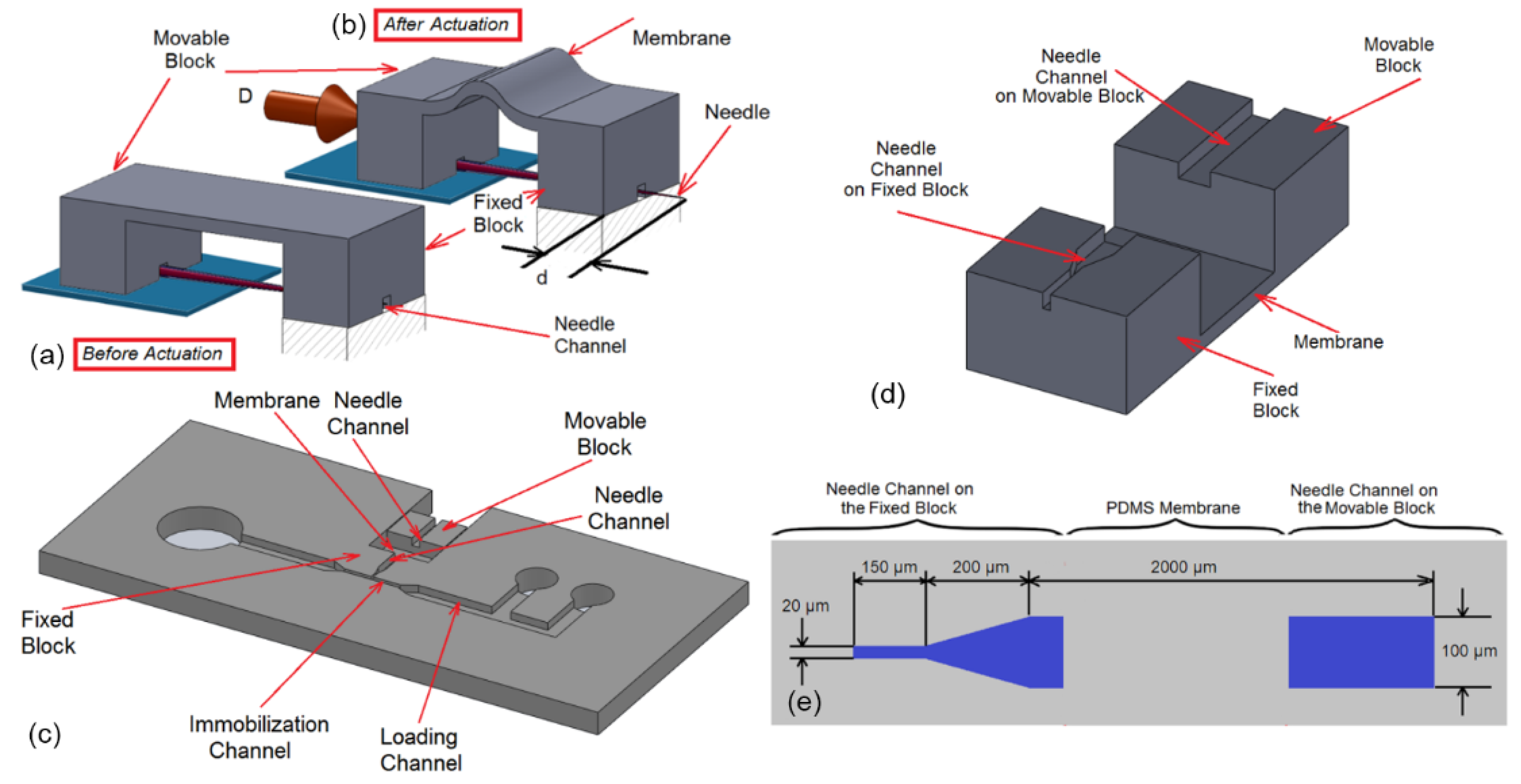
2.4. Needle Actuation
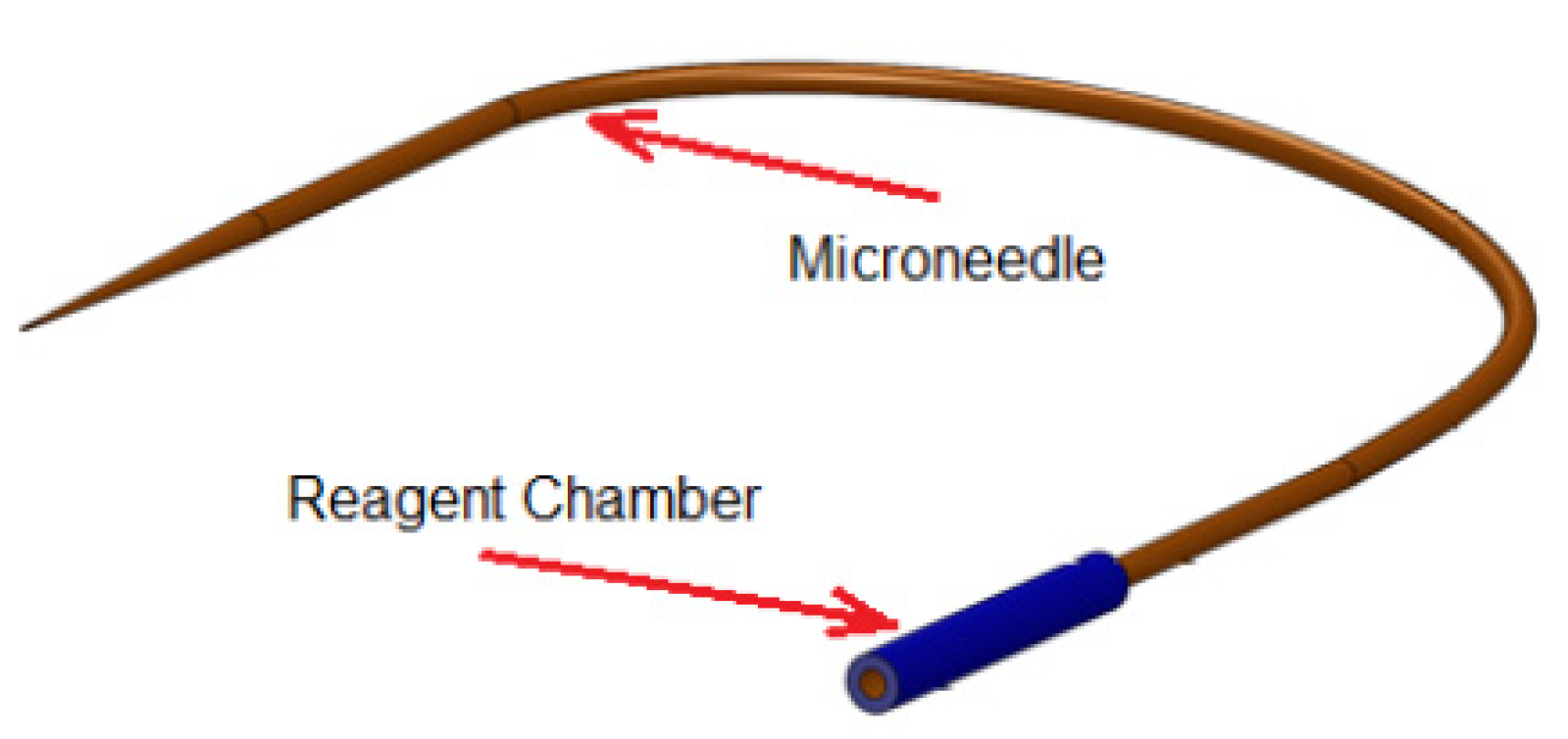
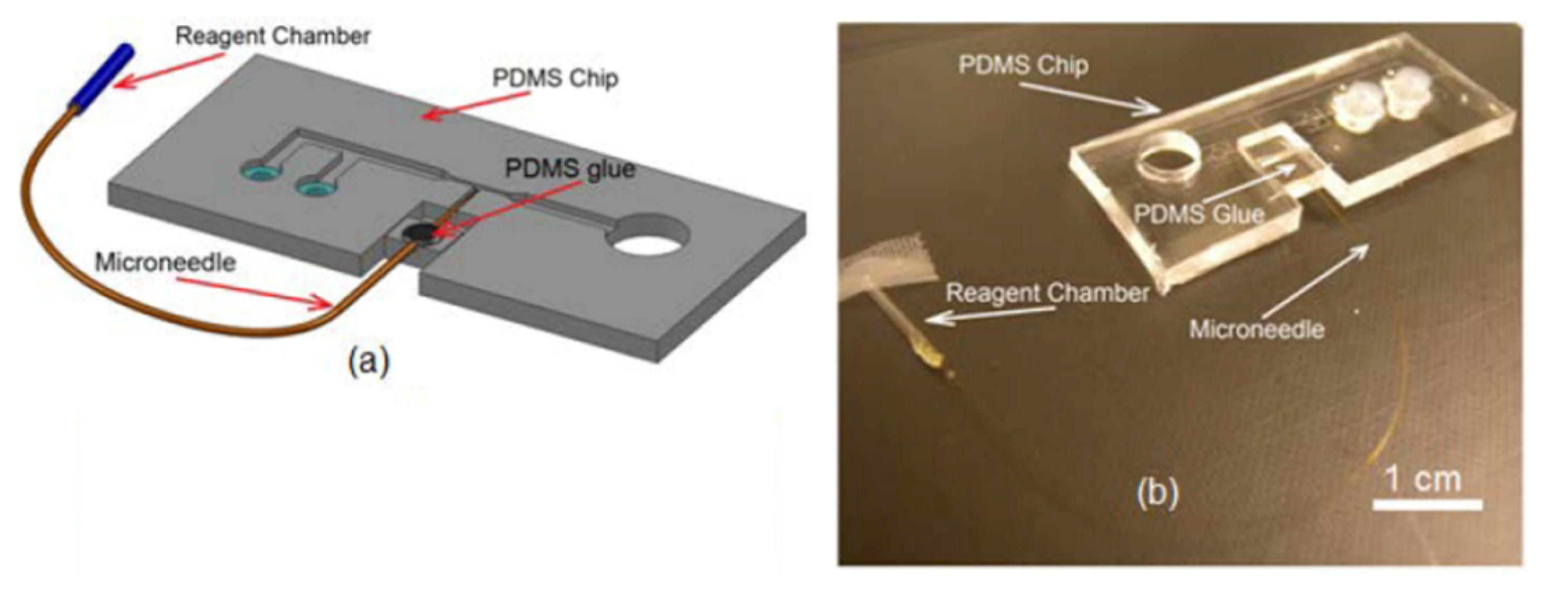
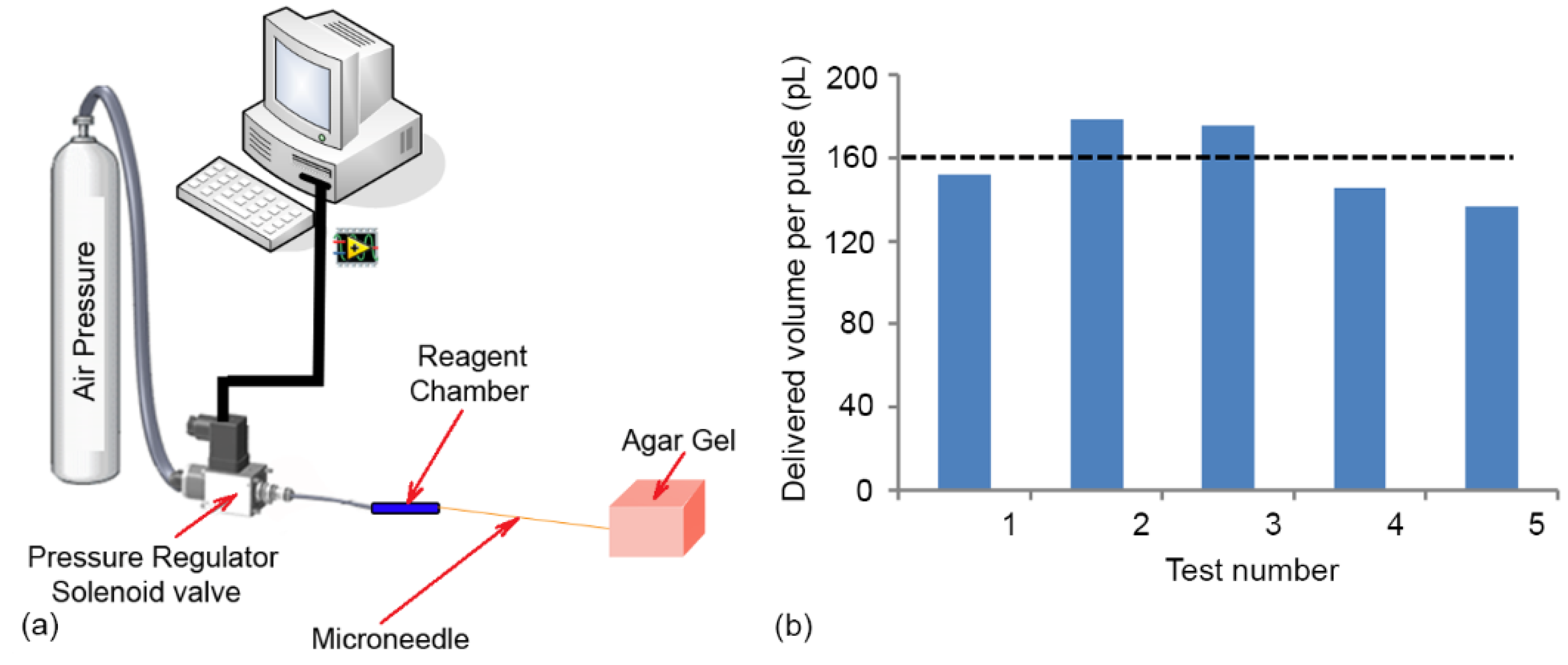
2.5. Reagent Chamber
2.6. Worm Unloading and Plating
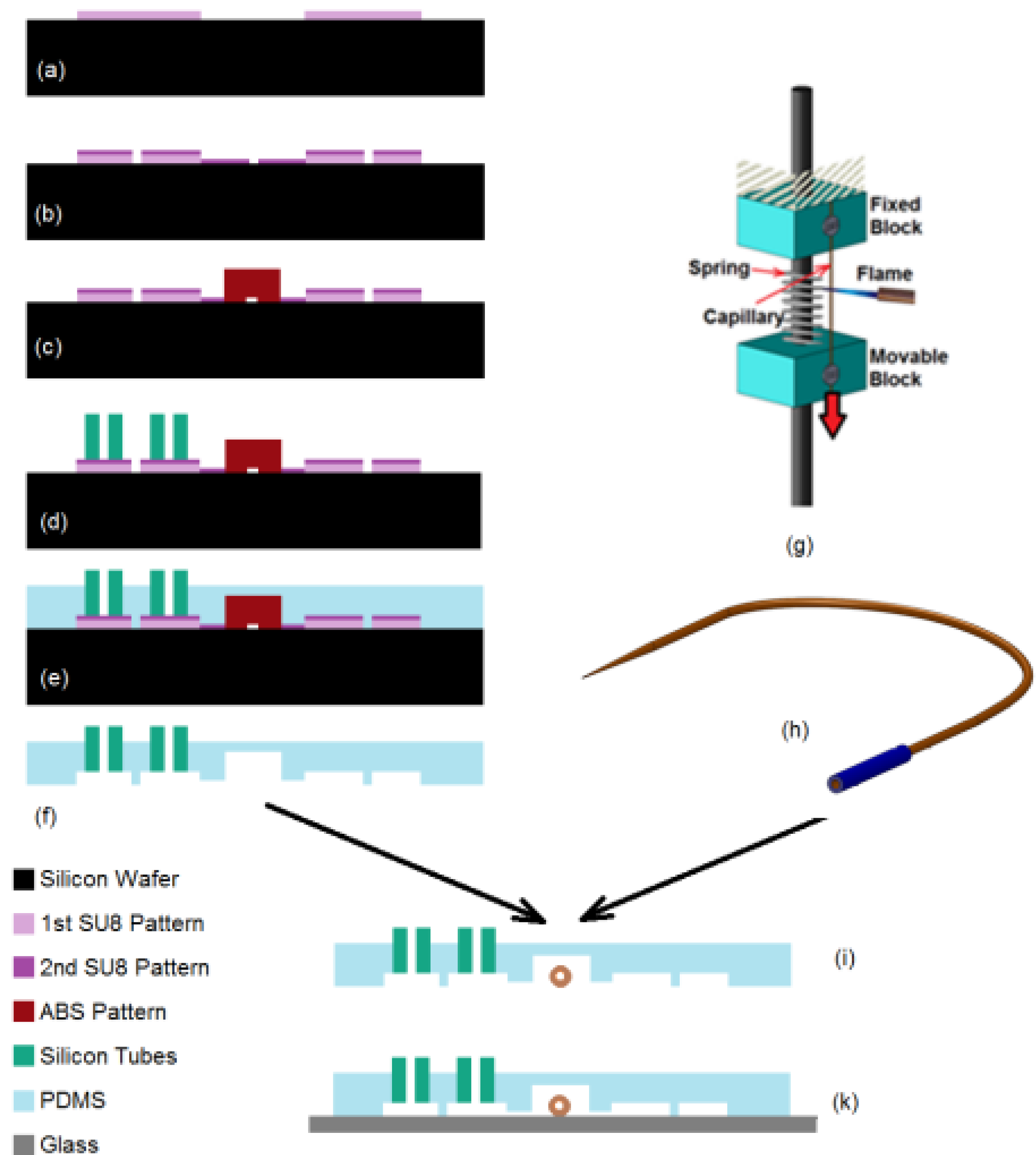
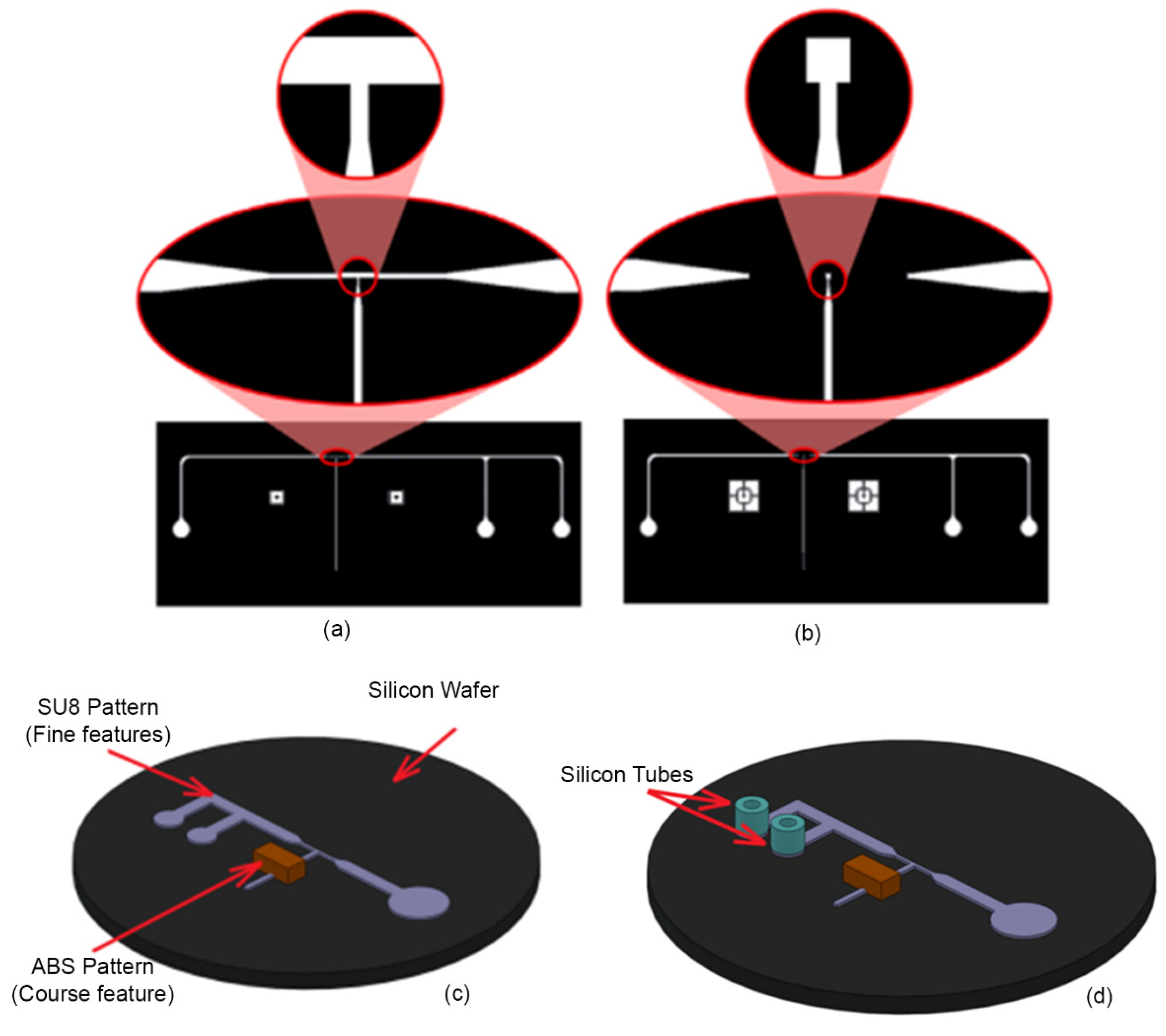
3. Device Fabrication
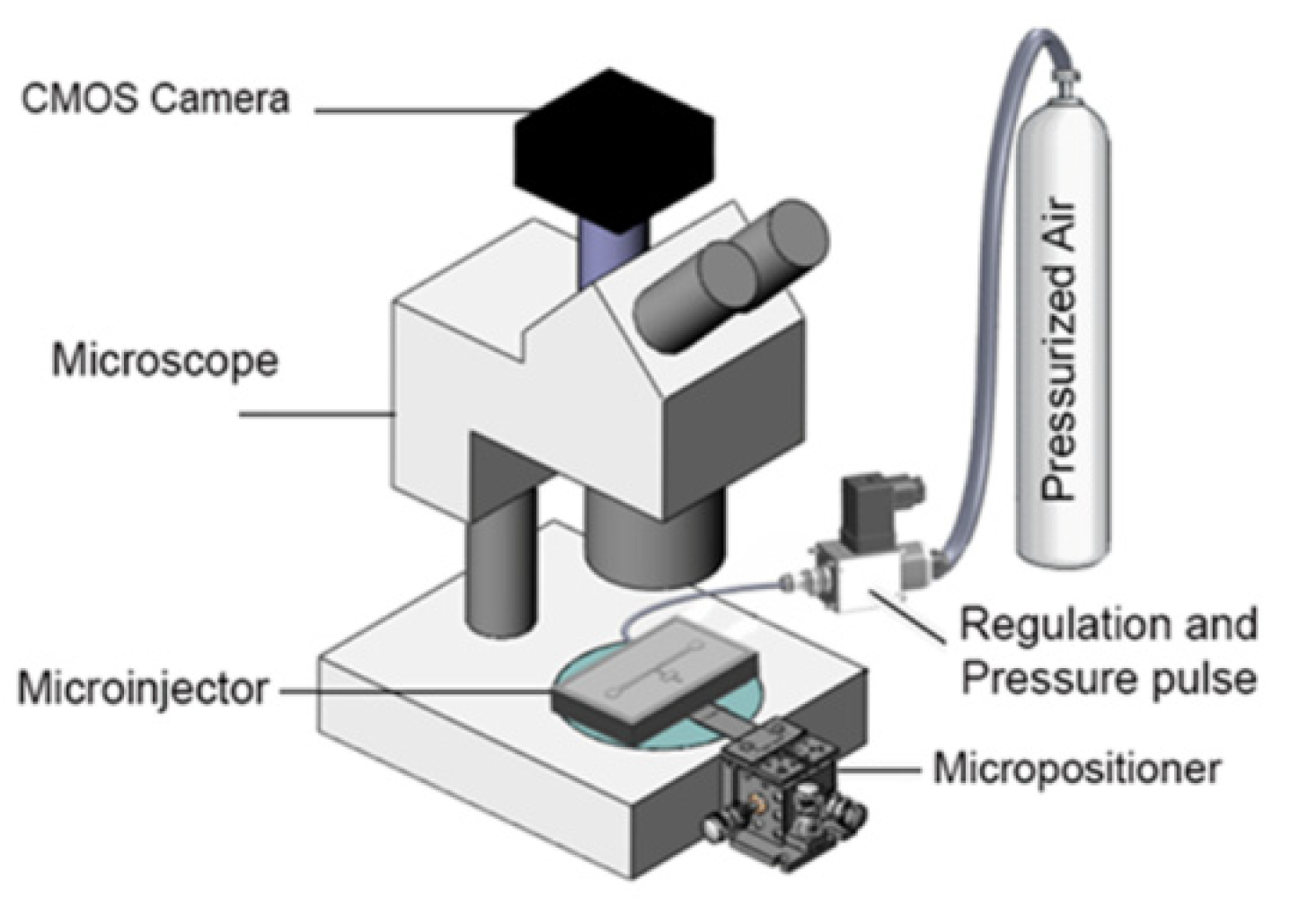
4. Experimental Setup
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Characterization of the Immobilization System
5.2. Characterization of Compliant Mechanism
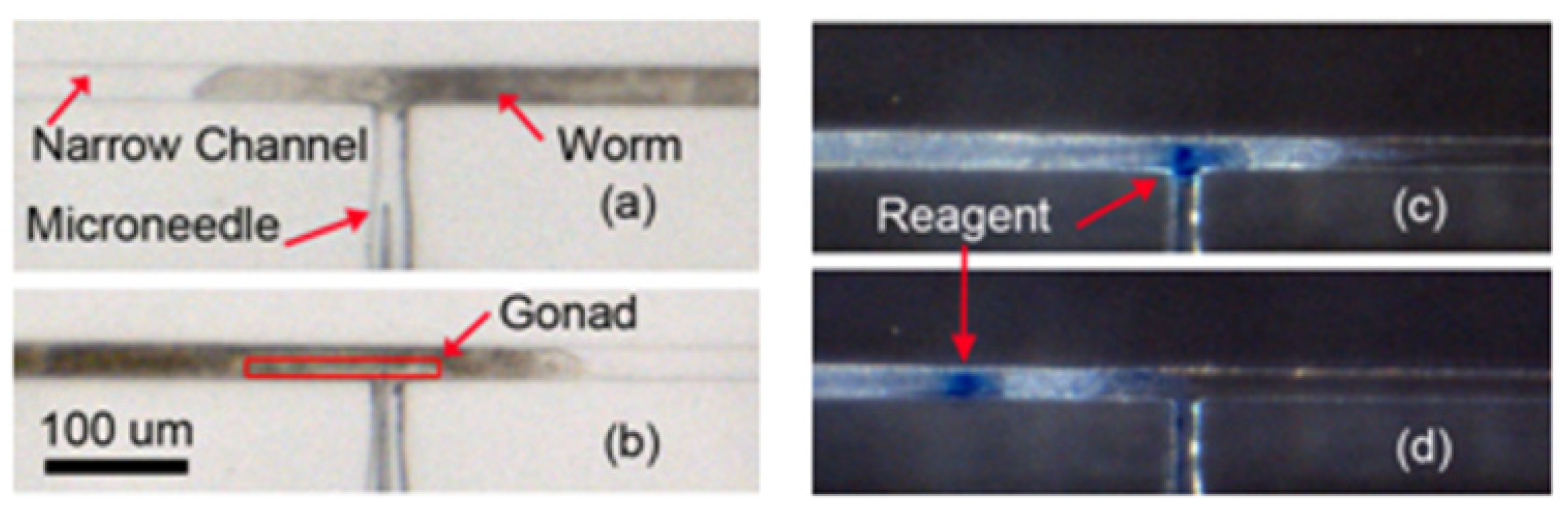
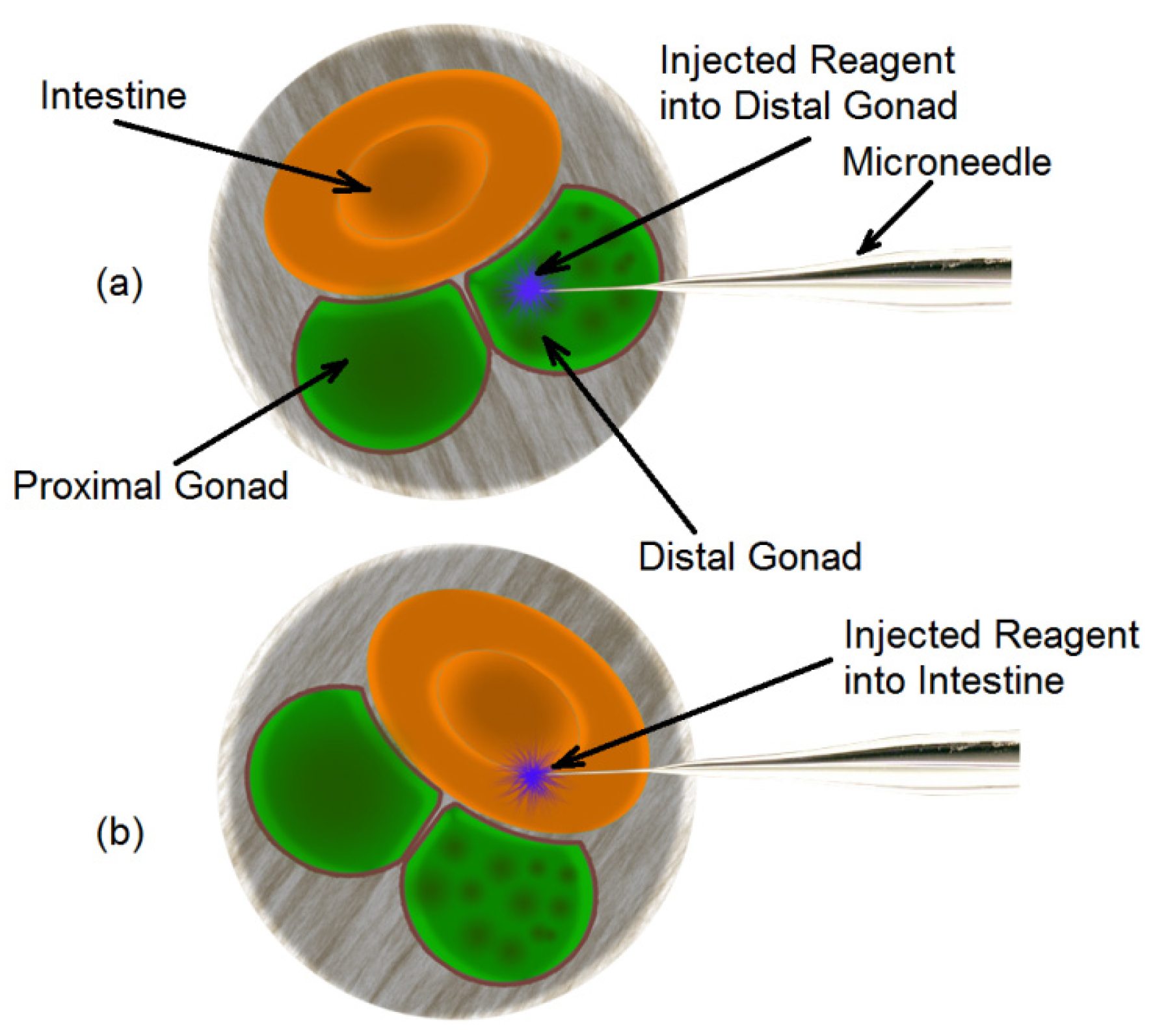
5.3. Characterization of Reagent Delivery
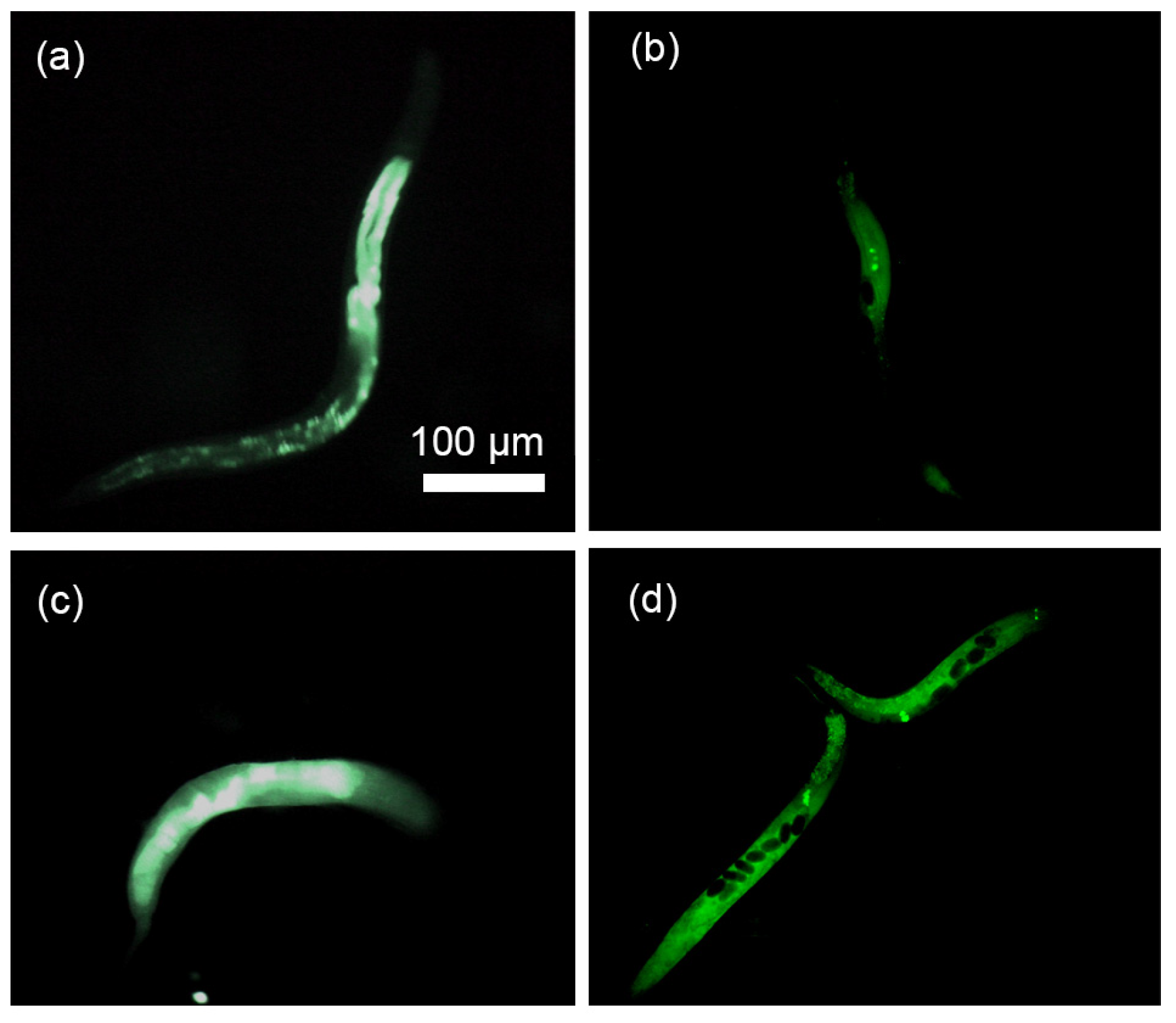
5.4. Microinjection of the Worm and Its Visualization
5.5. DNA Injection
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, A.G.; Marfil, V.; Li, C. Use of Caenorhabditis elegans as a model to study Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeski, A.E.; Dice, J.F. Mechanisms of chaperone-mediated autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, N.; Chen, C.S.; Hsieh, H.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Chang, H.C. In vivo imaging and toxicity assessments of fluorescent nanodiamonds in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3692–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, C.C.; Kramer, J.M.; Stinchcomb, D.; Ambros, V. Efficient gene transfer in C. elegans: Extrachromosomal maintenance and integration of transforming sequences. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 3959–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaletta, T.; Hengartner, M.O. Finding function in novel targets: C. elegans as a model organism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanik, M.F.; Rohde, C.B.; Pardo-Martin, C. Technologies for micromanipulating, imaging, and phenotyping small invertebrates and vertebrates. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 13, 185–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, S.E.; Whitesides, G.M. Chemistry and the worm: Caenorhabditis elegans as a platform for integrating chemical and biological research. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4774–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, P.; Siddiqui, A.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Gupta, B. Electrotaxis of C. elegans in a microfluidic environment. Lab A Chip 2010, 10, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, P.; Salam, S.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Gupta, B. Pulse DC Electrotaxis of Nematodes Caenorhabditis elegans and Caenorhabditis briggsae. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 44116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, P.; Salam, S.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Gupta, B.P. Electrical sorting of Caenorhabditis elegans. Lab A Chip 2012, 12, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Ahlawat, S.; Rau, K.; Venkataraman, V.; Koushika, S.P. Imaging in vivo neuronal transport in genetic model organisms using microfluidic devices. Traffic 2011, 12, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghannad-Rezaie, M.; Wang, X.; Mishra, B.; Collins, C.; Chronis, N. Microfluidic chips for in vivo imaging of cellular responses to neural injury in Drosophila larvae. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaemi, R.; Rezai, P.; Nejad, F.R.; Selvaganapathy, P.R. Characterization of microfluidic clamps for immobilizing and imaging of Drosophila Melanogaster larva’s central nervous system. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 34113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckscher, E.S.; Lockery, S.R.; Doe, C.Q. Characterization of Drosophila larval crawling at the level of organism, segment, and somatic body wall musculature. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12460–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Zappe, S.; Sahin, O.; Zhang, X.J.; Fish, M.; Scott, M.; Solgaard, O. Design and operation of a microfluidic sorter for Drosophila embryos. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 102, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, R.W.; Zhang, X.; Zappe, S.; Fish, M.; Scott, M.; Solgaard, O. Characterization of fluidic microassembly for immobilization and positioning of Drosophila embryos in 2-D arrays. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2004, 114, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.; Kim, Y.; Kanodia, J.S.; Gong, E.; Shvartsman, S.Y.; Lu, H. A microfluidic array for large-scale ordering and orientation of embryos. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Gupta, B.; Selvaganapathy, P.R. An Automated Microfluidic System for Screening Caenorhabditis elegans Behaviors using Electrotaxis. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 14117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Scott, M.P.; Quate, C.F.; Solgaard, O. Microoptical characterization of piezoelectric vibratory microinjections in Drosophila embryos for genome-wide RNAi screen. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, R.; Rezai, P.; Iyengar, B.G.; Selvaganapathy, P.R. Microfluidic devices for imaging neurological response of Drosophila melanogaster larva to auditory stimulus. Lab A Chip 2015, 15, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chun, K.; Hashiguchi, G.; Hiroyuki Fujita, H.T. Fabrication of array of hollow microcapillaries used for injection of genetic materials into animal/plant cells. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 38, L279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jeong, W.; Beebe, D.J. Microfluidic valve with cored glass microneedle for microinjection. Lab A Chip 2003, 3, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaume-Gentil, O.; Potthoff, E.; Ossola, D.; Dörig, P.; Zambelli, T.; Vorholt, J.A. Force-Controlled Fluidic Injection into Single Cell Nuclei. Small 2013, 9, 1904–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, A.; Jensen, K.F. Microfluidic based single cell microinjection. Lab A Chip 2008, 8, 1258–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delubac, D.; Highley, C.B.; Witzberger-Krajcovic, M.; Ayoob, J.C.; Furbee, E.C.; Minden, J.S.; Zappe, S. Microfluidic system with integrated microinjector for automated Drosophila embryo injection. Lab A Chip 2012, 12, 4911–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, A.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Wilson, J. Microinjection in a microfluidic format using flexible and compliant channels and electroosmotic dosage control. Lab A Chip 2009, 9, 3202–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, F.; Tang, L.; Du, W.; Feng, X.; Liu, B.F. Microfluidic chip-based C. elegans microinjection system for investigating cell–cell communication in vivo. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilleland, C.L.; Falls, A.T.; Noraky, J.; Heiman, M.G.; Yanik, M.F. Computer-assisted transgenesis of Caenorhabditis elegans for deep phenotyping. Genetics 2015, 201, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Krajniak, J.; Matsunaga, Y.; Benian, G.M.; Lu, H. On-demand optical immobilization of Caenorhabditis elegans for high-resolution imaging and microinjection. Lab A Chip 2014, 14, 3498–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.C. Transformation and Microinjection. In WormBook (online text companion to WormBase); 2006; Available online: http://www.wormbook.org/ (accessed on 2 March 2020).

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghaemi, R.; Tong, J.; Gupta, B.P.; Selvaganapathy, P.R. Microfluidic Device for Microinjection of Caenorhabditis elegans. Micromachines 2020, 11, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030295
Ghaemi R, Tong J, Gupta BP, Selvaganapathy PR. Microfluidic Device for Microinjection of Caenorhabditis elegans. Micromachines. 2020; 11(3):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030295
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhaemi, Reza, Justin Tong, Bhagwati P. Gupta, and P. Ravi Selvaganapathy. 2020. "Microfluidic Device for Microinjection of Caenorhabditis elegans" Micromachines 11, no. 3: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030295
APA StyleGhaemi, R., Tong, J., Gupta, B. P., & Selvaganapathy, P. R. (2020). Microfluidic Device for Microinjection of Caenorhabditis elegans. Micromachines, 11(3), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030295





